Pinfire on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

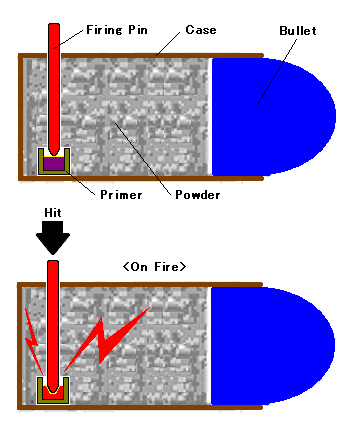 The pin-fire (or pinfire) is an obsolete type of metallic cartridge used in
The pin-fire (or pinfire) is an obsolete type of metallic cartridge used in
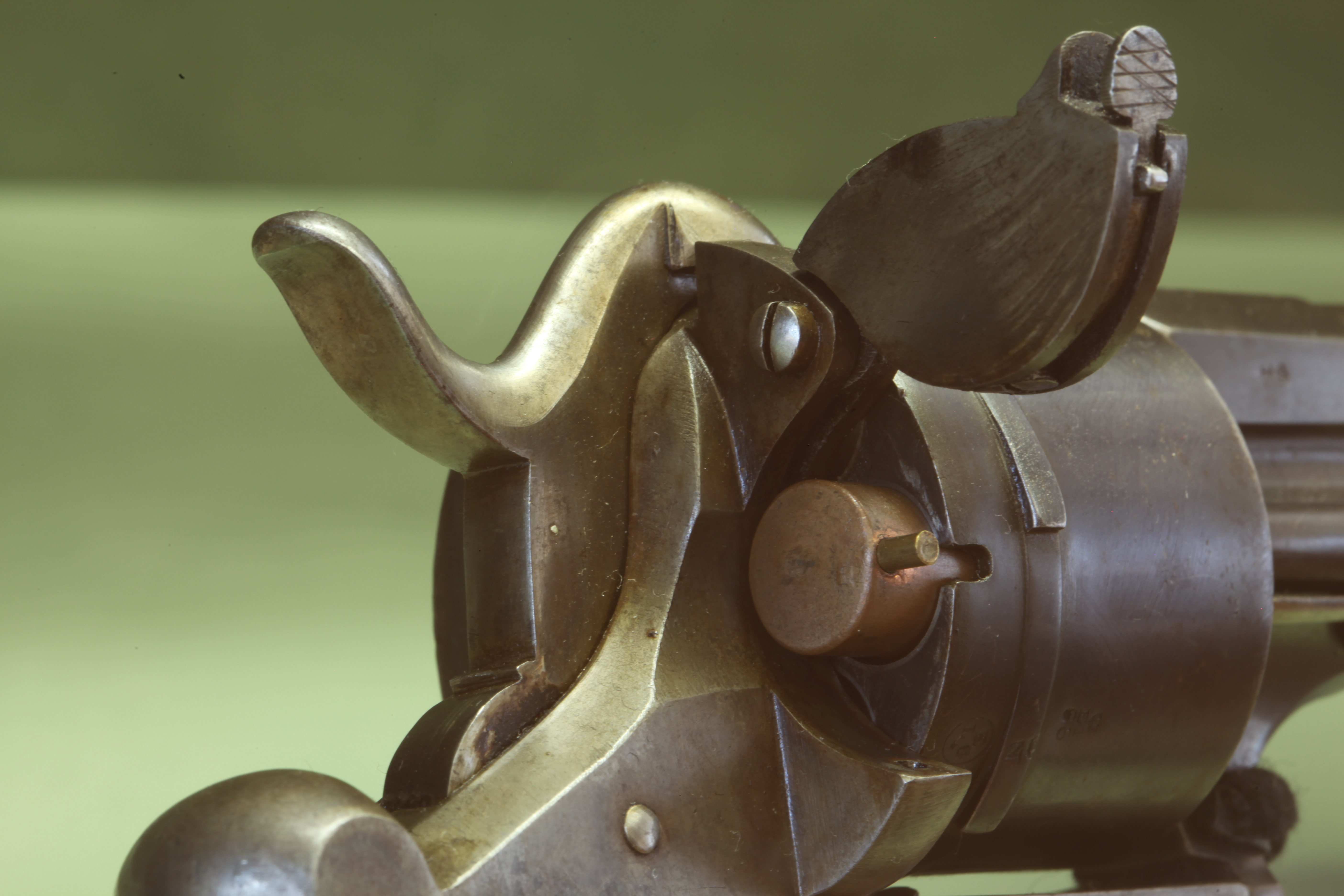 The Swiss gun maker Samuel Joannes Pauly patented the first breechloading cartridge in 1812. This was for use in a shotgun with fixed barrels which was loaded by lifting a breech block on the top. French gun maker Henri Roux attempted to improve this cartridge in the 1820s but a constantly primed cartridge was felt by many to be too dangerous and many breechloading guns reverted to using an unprimed cartridge. This was fired by a separate percussion cap which was used on the still dominant muzzle-loading guns.
Casimir Lefaucheux of Paris decided in 1832 to patent a breechloader where the barrel hinged downwards to reveal the breech ends. These still used a separate percussion cap. Though used before this, (as seen in surviving pinfire shotshells that lists the names of early gun makers he signed contracts with in 1833 and 1834,)
in 1835FR patent 6348, Casimir Lefaucheux, "fusil se chargeant par la culasse, au moyen d'un mécanisme qui fait basculer le canon", filed 1835-01-08, issued 1835-03-31 he was granted an addition to the 1832 patent for a new type of cartridge in which the cartridge's priming compound is ignited by striking a small pin which protrudes radially from just above the base of the cartridge. These pins fitted into a small groove cut in the top of each barrel-end and made it easy to see if the gun was loaded. The interior side of the chamber served as an anvil so that the cap won't move, which was a problem in some early cartridge designs at the time. The cartridge used metal bases (often brass) with paper tubes which were usually loaded by the shooter or his staff but were not entirely gas-tight. This reduced the force of the charge and allowed powder residue and gas to escape.
The pinfire cartridge was greatly improved by the 1846 patent (number 1963) by Benjamin Houllier of Paris which introduced a base wad and effectively made the cartridge gas-tight which greatly improved the performance. They were cheap and clean shooting. These improved pinfire guns grew in popularity in France and some were imported by British gun makers to overwhelming indifference on the part of the gun users there. They were prejudiced technically against a gun that 'broke' in the middle, despite the much vaunted benefits of breechloading. They owned muzzle-loaders of exquisite perfection, considered themselves the best engineers in the world (inventing the Industrial Revolution), and had a poor view of the French - the old enemy and an unreliable ally.
It was not until the Great Exhibition of 1851 was held in London that breechloading guns were taken more seriously by British and American gun makers in particular. The display of a Lefaucheux breechloading gun inspired English apprentice gunmaker Edwin Charles Hodges (1831–1925) to make an improved copy and persuade leading London gun maker Joseph Lang that this was the gun of the future. Lang was universally credited to be the first established British gunmaker to produce pinfires in any numbers. His first weapon of this new type was produced in 1853. Other British gun makers including Lancaster, Blanch and Reilly were similarly inspired by French originals and improved pinfire breechloaders became the new type of gun which by 1857–1858 every fashionable British prince and titled gentleman wanted to have. EC Hodges continued to make a good living as a specialist independent maker of breechloading actions commissioned by leading gunmakers such as Boss, Lancaster, Egg, Grant, Atkin, Rigby, Dickson, Purdey, Woodward, Army and Navy, and many others.
After Casimir's death in 1852, his son Eugene continued to market the pinfire design with great success. It became increasingly popular in Europe and large numbers of
The Swiss gun maker Samuel Joannes Pauly patented the first breechloading cartridge in 1812. This was for use in a shotgun with fixed barrels which was loaded by lifting a breech block on the top. French gun maker Henri Roux attempted to improve this cartridge in the 1820s but a constantly primed cartridge was felt by many to be too dangerous and many breechloading guns reverted to using an unprimed cartridge. This was fired by a separate percussion cap which was used on the still dominant muzzle-loading guns.
Casimir Lefaucheux of Paris decided in 1832 to patent a breechloader where the barrel hinged downwards to reveal the breech ends. These still used a separate percussion cap. Though used before this, (as seen in surviving pinfire shotshells that lists the names of early gun makers he signed contracts with in 1833 and 1834,)
in 1835FR patent 6348, Casimir Lefaucheux, "fusil se chargeant par la culasse, au moyen d'un mécanisme qui fait basculer le canon", filed 1835-01-08, issued 1835-03-31 he was granted an addition to the 1832 patent for a new type of cartridge in which the cartridge's priming compound is ignited by striking a small pin which protrudes radially from just above the base of the cartridge. These pins fitted into a small groove cut in the top of each barrel-end and made it easy to see if the gun was loaded. The interior side of the chamber served as an anvil so that the cap won't move, which was a problem in some early cartridge designs at the time. The cartridge used metal bases (often brass) with paper tubes which were usually loaded by the shooter or his staff but were not entirely gas-tight. This reduced the force of the charge and allowed powder residue and gas to escape.
The pinfire cartridge was greatly improved by the 1846 patent (number 1963) by Benjamin Houllier of Paris which introduced a base wad and effectively made the cartridge gas-tight which greatly improved the performance. They were cheap and clean shooting. These improved pinfire guns grew in popularity in France and some were imported by British gun makers to overwhelming indifference on the part of the gun users there. They were prejudiced technically against a gun that 'broke' in the middle, despite the much vaunted benefits of breechloading. They owned muzzle-loaders of exquisite perfection, considered themselves the best engineers in the world (inventing the Industrial Revolution), and had a poor view of the French - the old enemy and an unreliable ally.
It was not until the Great Exhibition of 1851 was held in London that breechloading guns were taken more seriously by British and American gun makers in particular. The display of a Lefaucheux breechloading gun inspired English apprentice gunmaker Edwin Charles Hodges (1831–1925) to make an improved copy and persuade leading London gun maker Joseph Lang that this was the gun of the future. Lang was universally credited to be the first established British gunmaker to produce pinfires in any numbers. His first weapon of this new type was produced in 1853. Other British gun makers including Lancaster, Blanch and Reilly were similarly inspired by French originals and improved pinfire breechloaders became the new type of gun which by 1857–1858 every fashionable British prince and titled gentleman wanted to have. EC Hodges continued to make a good living as a specialist independent maker of breechloading actions commissioned by leading gunmakers such as Boss, Lancaster, Egg, Grant, Atkin, Rigby, Dickson, Purdey, Woodward, Army and Navy, and many others.
After Casimir's death in 1852, his son Eugene continued to market the pinfire design with great success. It became increasingly popular in Europe and large numbers of
File:Ethan Allen Pinfire Cartridge Box.jpg, Pinfire Cartridge Box by Ethan Allen & Co.
File:Pinfire Cartridge Box by Allen & Wheelock & Co..jpg, Pinfire Cartridge Box by Allen & Wheelock & Co.
File:Pinfire Cartridge Box by C.D. Leet & Co. .jpg, Pinfire Cartridge Box by C.D. Leet & Co.
File:Pinfire Cartridge Boxes by Union Metallic Cartridge Company.jpg, Pinfire Cartridge Boxes by Union Metallic Cartridge Company
File:Eley Brothers Pinfire Cartridge Box.jpg, Pinfire Cartridge Box by Eley Brothers
File:Kynoch & Co. Pinfire Cartridge Box.jpg, Pinfire Cartridge Box by Kynoch & Co.

firearm
A firearm is any type of gun that uses an explosive charge and is designed to be readily carried and operated by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see legal definitions).
The first firearms originate ...
s, where the priming compound is ignited by striking a small pin that protrudes radially from above the base of the cartridge. Invented by Frenchman Casimir Lefaucheux in 1832, but not patented until 1835, it was one of the earliest practical designs of a metallic cartridge to hasten the loading and firing process of a firearm. Its history is closely associated with the development of the breechloader
A breechloader is a firearm in which the user loads the ammunition from the breech end of the barrel (i.e., from the rearward, open end of the gun's barrel), as opposed to a muzzleloader, in which the user loads the ammunition from the ( muzz ...
, which would eventually replace all muzzle-loading
A muzzleloader is any firearm in which the user loads the projectile and the propellant charge into the muzzle end of the gun (i.e., from the forward, open end of the gun's barrel). This is distinct from the modern designs of breech-loading fire ...
firearms.
The cartridge featured a small pin that, when struck, would ignite the priming compound and initiate the firing process. Despite initial resistance, especially from British gun users, the pinfire cartridge gained popularity following the Great Exhibition
The Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations, also known as the Great Exhibition or the Crystal Palace Exhibition (in reference to the temporary structure in which it was held), was an international exhibition that took ...
of 1851. Its advantages included easier and faster loading than percussion
A percussion instrument is a musical instrument that is sounded by being struck or scraped by a percussion mallet, beater including attached or enclosed beaters or Rattle (percussion beater), rattles struck, scraped or rubbed by hand or ...
weapons, and it was more likely to fire reliably when wet. However, with the introduction of reliable rimfire and centerfire
Two rounds of .357 Magnum, a centerfire cartridge; notice the circular primer in the center
A center-fire (or centerfire) is a type of metallic cartridge used in firearms, where the primer is located at the center of the base of its casing (i. ...
cartridges, which were quicker to load and safer, the pinfire cartridge became obsolete. Today, enthusiasts of vintage weaponry often create pinfire cartridges from modern materials for use in antique firearms.
History
rifle
A rifle is a long gun, long-barreled firearm designed for accurate shooting and higher stopping power, with a gun barrel, barrel that has a helical or spiralling pattern of grooves (rifling) cut into the bore wall. In keeping with their focus o ...
s, shotgun
A shotgun (also known as a scattergun, peppergun, or historically as a fowling piece) is a long gun, long-barreled firearm designed to shoot a straight-walled cartridge (firearms), cartridge known as a shotshell, which discharges numerous small ...
s, and revolver
A revolver is a repeating handgun with at least one barrel and a revolving cylinder containing multiple chambers (each holding a single cartridge) for firing. Because most revolver models hold six cartridges before needing to be reloaded, ...
s (often called Lefaucheux guns after their inventor whoever the maker was), were manufactured from the mid-1850s until the late 1890s. They were quicker and easier to load than percussion weapons with loose black powder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, charcoal (which is mostly carbon), and potassium nitrate, potassium ni ...
, percussion caps and bullet
A bullet is a kinetic projectile, a component of firearm ammunition that is shot from a gun barrel. They are made of a variety of materials, such as copper, lead, steel, polymer, rubber and even wax; and are made in various shapes and constru ...
; and they were also much more likely to fire reliably when wet. Pinfire cartridges were available in a large number of sizes for various types of weapon.
While pinfire rifles and shotguns began to decline in use from the early 1860s onward, after the introduction of mass-produced centerfire rifle and shotgun cartridges, pinfire revolvers in particular became very successful and widespread, being adopted by the armies of France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
, and others. They were also widely used during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
, although sometimes despised because of their low-power compared to more common percussion revolvers made by gun manufacturers such as Colt and Smith & Wesson
Smith & Wesson Brands, Inc. (S&W) is an American Firearms manufacturer, firearm manufacturer headquartered in Maryville, Tennessee, United States.
Smith & Wesson was founded by Horace Smith (inventor), Horace Smith and Daniel B. Wesson as the ...
. Some navies also adopted them for "sea service", these examples were often being made out of brass
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, in proportions which can be varied to achieve different colours and mechanical, electrical, acoustic and chemical properties, but copper typically has the larger proportion, generally copper and zinc. I ...
which is largely unaffected by the corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
, caused by the salt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as r ...
in a maritime environment.
Pinfire became obsolete once reliable rimfire and centerfire
Two rounds of .357 Magnum, a centerfire cartridge; notice the circular primer in the center
A center-fire (or centerfire) is a type of metallic cartridge used in firearms, where the primer is located at the center of the base of its casing (i. ...
cartridges became available because without a pin which needed aligning in the slot in the chamber wall they were quicker to load. They were also safer because they had no protruding pin which could cause the ammunition to accidentally detonate during rough handling, particularly of loose ammunition.
American manufacturers
* Ethan Allen & Co. of Worcester, Massachusetts * Allen & Wheelock of Worcester, Massachusetts * C.D. Leet & Co. of Springfield, Massachusetts * C. Sharps & Co. of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania * Union Metallic Cartridge Company of Bridgeport, Connecticut *William Tibbals of South Coventry, ConnecticutBritish manufacturers
* Eley Brothers of London * Kynoch & Co. of BirminghamCurrent status
Although pinfire revolver, rifle, and shotgun cartridges are technically obsolete, as pinfire guns have not been made in large numbers since the early 20th century, enthusiasts of vintage weaponry often make pinfire cartridges from modern materials and shoot their old guns. Some modern novelty miniature pinfire pistols are manufactured in calibers as small as 2 to 3 millimeters (.0787 to .118 inches) in diameter. Although not practical weapons, they use pinfire ammunition because the caliber is too small for centerfire or rimfire. Antique pinfire firearms and cartridges are available on the collector market and modern reloading kits exist which contain specialized cartridges which can be hand loaded, though the process is far more complex than loading rimfire or centerfire cartridges."To Shoot My Pinfire" by Darrel G Dennis inSee also
* Teat-fire cartridge * List of firearms before the 20th century * Antique firearmsNotes
{{reflist Ammunition French inventions