Pictor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pictor is a constellation in the
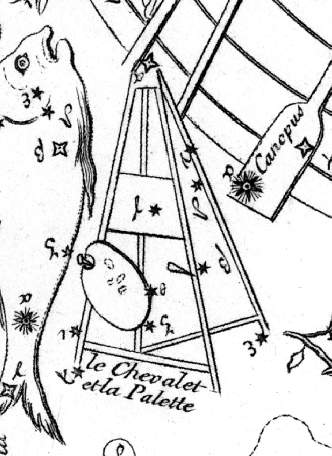 The French astronomer Abbé
The French astronomer Abbé
 Pictor is a faint constellation; its three brightest stars can be seen near the prominent
Pictor is a faint constellation; its three brightest stars can be seen near the prominent  Located about 1298 light-years from Earth,
Located about 1298 light-years from Earth,
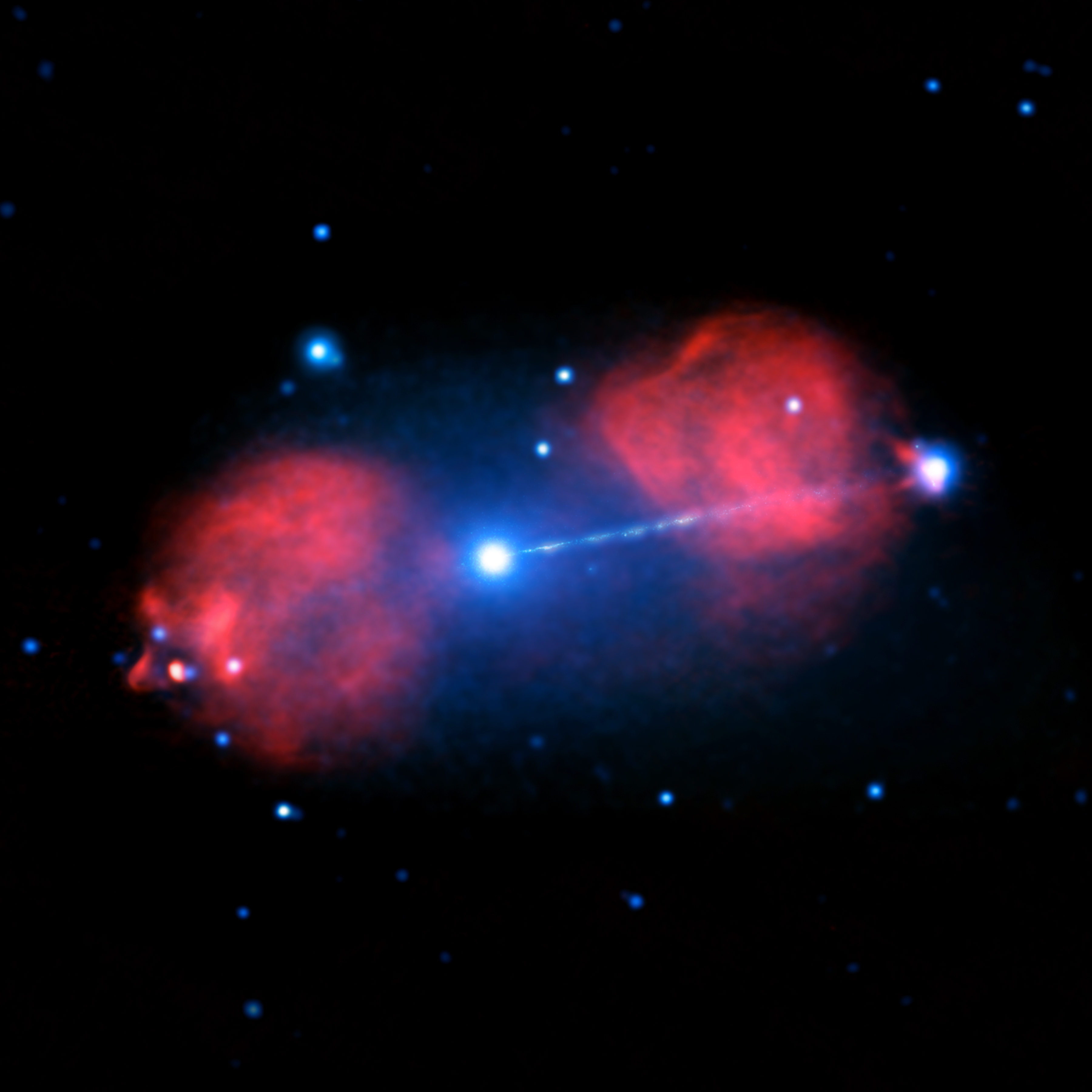 NGC 1705 is an irregular dwarf galaxy 17 million light-years from Earth. It is one of the most active star forming galaxies in the nearby universe, despite the fact that its rate of star formation peaked around 30 million years ago. Pictor A, around 485 million light-years away, is a double-lobed
NGC 1705 is an irregular dwarf galaxy 17 million light-years from Earth. It is one of the most active star forming galaxies in the nearby universe, despite the fact that its rate of star formation peaked around 30 million years ago. Pictor A, around 485 million light-years away, is a double-lobed
The clickable Pictor
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Pictor Southern constellations Constellations listed by Lacaille
Southern Celestial Hemisphere
The southern celestial hemisphere, also called the Southern Sky, is the southern half of the celestial sphere; that is, it lies south of the celestial equator. This arbitrary sphere, on which seemingly fixed stars form constellations, appear ...
, located between the star Canopus
Canopus is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Carina and the second-brightest star in the night sky. It is also designated α Carinae, which is Latinised to Alpha Carinae. With a visual apparent magnitude of ...
and the Large Magellanic Cloud
The Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), or Nubecula Major, is a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. At a distance of around 50 kiloparsecs (≈160,000 light-years), the LMC is the second- or third-closest galaxy to the Milky Way, after the ...
. Its name is Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
for painter
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called the "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and ...
, and is an abbreviation of the older name Equuleus Pictoris (the "painter's easel
An easel is an upright support used for displaying and/or fixing something resting upon it, at an angle of about 20° to the vertical. In particular, easels are traditionally used by painters to support a painting while they work on it, normally ...
"). Normally represented as an easel, Pictor was named by Abbé Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille
Abbé Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille (; 15 March 171321 March 1762), formerly sometimes spelled de la Caille, was a French astronomer and geodesist who named 14 out of the 88 constellations. From 1750 to 1754, he studied the sky at the Cape of Good ...
in the 18th century. The constellation's brightest star is Alpha Pictoris, a white main-sequence star around 97 light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 101 ...
s away from Earth. Pictor also hosts RR Pictoris, a cataclysmic variable star system
In astronomy, cataclysmic variable stars (CVs) are stars which irregularly increase in brightness by a large factor, then drop back down to a quiescent state. They were initially called novae (), since ones with an outburst brightness visible to ...
that flared up as a nova
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramati ...
, reaching apparent (visual) magnitude 1.2 in 1925 before fading into obscurity.
Pictor has attracted attention because of its second-brightest star Beta Pictoris
Beta Pictoris (abbreviated β Pictoris or β Pic) is the second brightest star in the constellation Pictor. It is located from the Solar System, and is 1.75 times as massive and 8.7 times as luminous as the Sun. The Beta Pictoris sy ...
, 63.4 light-years distant from Earth, which is surrounded by an unusual dust disk rich in carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes ...
, as well as an exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
(extrasolar planet). Another five stars in the constellation have been observed to have planets. Among them is HD 40307, an orange dwarf
A K-type main-sequence star, also referred to as a K-type dwarf or an orange dwarf, is a main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type K and luminosity class V. These stars are intermediate in size between red M-type main-sequence stars ...
that has six planets orbiting it, one of which— HD 40307 g—is a potential super-Earth
A super-Earth is an extrasolar planet with a mass higher than Earth's, but substantially below those of the Solar System's ice giants, Uranus and Neptune, which are 14.5 and 17 times Earth's, respectively.
The term "super-Earth" refers only to ...
in the circumstellar habitable zone
In astronomy and astrobiology, the circumstellar habitable zone (CHZ), or simply the habitable zone, is the range of orbits around a star within which a planetary surface can support liquid water given sufficient atmospheric pressure.J. F. Kast ...
. Kapteyn's Star, the nearest star in Pictor to Earth, is a red dwarf
''Red Dwarf'' is a British science fiction comedy franchise created by Rob Grant and Doug Naylor, which primarily consists of a television sitcom that aired on BBC Two between 1988 and 1999, and on Dave (TV channel), Dave since 2009, gaining a ...
located 12.76 light-years away that was found to have two super-Earths in orbit in 2014. Pictor A is a radio galaxy
A radio galaxy is a galaxy with giant regions of radio emission extending well beyond its visible structure. These energetic radio lobes are powered by jets from its active galactic nucleus. They have luminosities up to 1039 W at radio wa ...
that is shooting an 800,000 light-year long jet of plasma from a supermassive black hole
A supermassive black hole (SMBH or sometimes SBH) is the largest type of black hole, with its mass being on the order of hundreds of thousands, or millions to billions of times the mass of the Sun (). Black holes are a class of astronomical obj ...
at its centre. In 2006, a gamma-ray burst
In gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are immensely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the most energetic and luminous electromagnetic events since the Big Bang. Bursts can last from ten milli ...
—GRB 060729
GRB 060729 was a gamma-ray burst that was first observed on 29 July 2006. It is likely the signal of a type Ic supernova—the core collapse of a massive star. It was also notable for its extraordinarily long X-ray afterglow, detectable 642 days ...
—was observed in Pictor, its extremely long X-ray afterglow
An afterglow in meteorology consists of several atmospheric optical phenomena, with a general definition as a broad arch of whitish or pinkish sunlight in the twilight sky, consisting of the bright segment and the purple light. Purple light ma ...
detectable for nearly two years.
History
Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille
Abbé Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille (; 15 March 171321 March 1762), formerly sometimes spelled de la Caille, was a French astronomer and geodesist who named 14 out of the 88 constellations. From 1750 to 1754, he studied the sky at the Cape of Good ...
first described Pictor as '' le Chevalet et la Palette'' (the easel and palette) in 1756, after observing and cataloguing 10,000 southern stars during a two-year stay at the Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( af, Kaap die Goeie Hoop ) ;''Kaap'' in isolation: pt, Cabo da Boa Esperança is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is ...
. He devised 14 new constellations in uncharted regions of the Southern Celestial Hemisphere
The southern celestial hemisphere, also called the Southern Sky, is the southern half of the celestial sphere; that is, it lies south of the celestial equator. This arbitrary sphere, on which seemingly fixed stars form constellations, appear ...
not visible from Europe. All but one honored instruments that symbolised the Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intel ...
. He gave these constellations Bayer designation
A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek or Latin letter followed by the genitive form of its parent constellation's Latin name. The original list of Bayer designations contained 1,564 stars. T ...
s, including ten stars in Pictor now named Alpha to Nu Pictoris. He labelled the constellation Equuleus Pictorius on his 1763 chart, the word "Equuleus" meaning small horse, or easel—perhaps from an old custom among artists of carrying a canvas on a donkey. The German astronomer Johann Bode
Johann Elert Bode (; 19 January 1747 – 23 November 1826) was a German astronomer known for his reformulation and popularisation of the Titius–Bode law. Bode determined the orbit of Uranus and suggested the planet's name.
Life and career
Bo ...
called it Pluteum Pictoris. The name was shortened to its current form in 1845 by the English astronomer Francis Baily on the suggestion of his countryman Sir John Herschel
Sir John Frederick William Herschel, 1st Baronet (; 7 March 1792 – 11 May 1871) was an English polymath active as a mathematician, astronomer, chemist, inventor, experimental photographer who invented the blueprint and did botanic ...
.
Characteristics
Pictor is a small constellation bordered byColumba
Columba or Colmcille; gd, Calum Cille; gv, Colum Keeilley; non, Kolban or at least partly reinterpreted as (7 December 521 – 9 June 597 AD) was an Irish abbot and missionary evangelist credited with spreading Christianity in what is tod ...
to the north, Puppis
Puppis is a constellation in the southern sky. Puppis, the Latin translation of " poop deck", was originally part of an over-large constellation Argo Navis (the ship of Jason and the Argonauts), which centuries after its initial description, w ...
and Carina to the east, Caelum
Caelum is a faint constellation in the southern sky, introduced in the 1750s by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille and counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name means “''chisel''” in Latin, and it was formerly known as Caelum Sculptorium ...
to the northwest, Dorado
Dorado () is a constellation in the southern sky. It was named in the late 16th century and is now one of the 88 modern constellations. Its name refers to the dolphinfish (''Coryphaena hippurus''), which is known as ''dorado'' in Spanish, alt ...
to the southwest and Volans
Volans is a constellation in the southern sky. It represents a flying fish; its name is a shortened form of its original name, Piscis Volans. Volans was one of twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Di ...
to the south. The three-letter abbreviation for the constellation, as adopted by the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach ...
in 1922, is "Pic". The official constellation boundaries, as set by Belgian astronomer Eugène Delporte in 1930, are defined by a polygon of 18 segments (''illustrated in infobox''). In the equatorial coordinate system
The equatorial coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system widely used to specify the positions of celestial objects. It may be implemented in spherical or rectangular coordinates, both defined by an origin at the centre of Earth, a fun ...
, the right ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the March equinox to the ( hour circle of the) point in question above the earth.
When pai ...
coordinates of these borders lie between and , while the declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. Declination's angle is measured north or south of t ...
coordinates are between −42.79° and −64.15°. Pictor culminates each year at 9 p.m. on 17 March. Its position in the far Southern Celestial Hemisphere means that the whole constellation is visible to observers south of latitude 26°N, and parts become circumpolar south of latitude 35°S.
Features
Stars
 Pictor is a faint constellation; its three brightest stars can be seen near the prominent
Pictor is a faint constellation; its three brightest stars can be seen near the prominent Canopus
Canopus is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Carina and the second-brightest star in the night sky. It is also designated α Carinae, which is Latinised to Alpha Carinae. With a visual apparent magnitude of ...
. Within the constellation's borders, there are 49 stars brighter than or equal to apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's li ...
6.5. Located about 97 light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 101 ...
s away from Earth, Alpha Pictoris is the brightest star in the constellation; it is a white main-sequence star with an apparent magnitude of 3.3, and spectral type
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting th ...
A8VnkA6. A rapidly spinning star with a projected rotational velocity
Stellar rotation is the angular motion of a star about its axis. The rate of rotation can be measured from the spectrum of the star, or by timing the movements of active features on the surface.
The rotation of a star produces an equatorial bulge ...
estimated at 206 km/s, it has a shell of circumstellar gas. Beta Pictoris
Beta Pictoris (abbreviated β Pictoris or β Pic) is the second brightest star in the constellation Pictor. It is located from the Solar System, and is 1.75 times as massive and 8.7 times as luminous as the Sun. The Beta Pictoris sy ...
is another white main sequence star of spectral type A6V and apparent magnitude 3.86. Located around 63.4 light-years distant from Earth, it is a member of the Beta Pictoris moving group
The Beta Pictoris Moving Group is a young moving group of stars located relatively near Earth. A moving group, in astronomy, is a group of stars that share a common motion through space as well as a common origin. This moving group is named for B ...
—a group of 17 star systems around 12 million years old moving through space together. In 1984 Beta Pictoris was the first star discovered to have a debris disk
A debris disk (American English), or debris disc (Commonwealth English), is a circumstellar disk of dust and debris in orbit around a star. Sometimes these disks contain prominent rings, as seen in the image of Fomalhaut on the right. Debris di ...
. Since then, an exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
about eight times the mass of Jupiter has been discovered orbiting approximately 8 astronomical unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au, or or AU) is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and approximately equal to or 8.3 light-minutes. The actual distance from Earth to the Sun varies by about 3% as Earth orbi ...
s (AU) away from the star—a similar distance as that between our Sun and Saturn. The European Southern Observatory
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere, commonly referred to as the European Southern Observatory (ESO), is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental research organisation made up of 16 mem ...
(ESO) confirmed its presence through the use of direct imagery with the Very Large Telescope
The Very Large Telescope (VLT) is a telescope facility operated by the European Southern Observatory on Cerro Paranal in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile. It consists of four individual telescopes, each with a primary mirror 8.2 m across, ...
in late 2009.; .
Gamma Pictoris
Gamma Pictoris, Latinised from γ Pictoris, is a single, orange-hued star in the southern constellation of Pictor. It is a faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.50. Based upon an annual parallax shif ...
is an orange giant of spectral type K1III that has swollen to 1.4 times the diameter of the Sun. Shining with an apparent magnitude of 4.5, it lies 174 light-years distant from Earth. HD 42540, called 47 Pictoris by American astronomer Benjamin Apthorp Gould, is a slightly cooler orange giant, with a spectral type of K2.5III and average magnitude 5.04. It has also been suspected of being a variable star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as e ...
. Lacaille mistakenly named this star Mu Doradus, but had recorded its Right Ascension one hour too low. Lacaille named two neighbouring stars Eta Pictoris. Eta2 Pictoris, also known as HR 1663, is an orange giant of spectral type K5III and apparent magnitude 5.05. 474 light-years distant, it has a diameter 5.6 times that of the Sun. Eta1 Pictoris, also known as HR 1649, is 85 light-years distant and is a main sequence star of spectral type F5V and visual magnitude 5.38. A double star, it has a companion of magnitude 13; the two are separated by 11 arcseconds.
 Located about 1298 light-years from Earth,
Located about 1298 light-years from Earth, Delta Pictoris
Delta Pictoris, Latinized from δ Pictoris, is a binary star system in the southern constellation Pictor. It is visible to the naked with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.72. The system is located at a distance of approximate ...
is an eclipsing binary
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in ...
of the Beta Lyrae type. Composed of two blue stars of spectral types B3III and O9V, the system has a period of 1.67 days, and is observed to dip from apparent magnitude 4.65 to 4.9. The stars are oval-shaped as they are gravitationally distorted by each other. TV Pictoris
TV Pictoris is a rotating ellipsoidal variable star in the constellation Pictor. It ranges between apparent magnitude 7.37 - 7.53 over a period of 0.85 days. It was first discovered to be variable in 1987. The system is inclined at an angl ...
is a spectroscopic binary system composed of an A-type star and an F-type star which rotate around each other in a very close orbit. The latter star is elliptical in shape and itself varies in brightness. The visual magnitude ranges between 7.37 and 7.53 every 20 hours.
Aside from Beta, five other stars in Pictor are known to host planetary systems. AB Pictoris is a BY Draconis variable star with a substellar companion that is either a large planet or a brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs (also called failed stars) are substellar objects that are not massive enough to sustain nuclear fusion of ordinary hydrogen (hydrogen-1, 1H) into helium in their cores, unlike a main sequence, main-sequence star. Instead, they have ...
, which was discovered by direct imaging in 2005. HD 40307 is an orange main sequence star of spectral type K2.5V and apparent magnitude 7.17 located about 42 light-years away. Doppler spectroscopy
Doppler spectroscopy (also known as the radial-velocity method, or colloquially, the wobble method) is an indirect method for finding extrasolar planets and brown dwarfs from radial-velocity measurements via observation of Doppler shifts in t ...
with the High Accuracy Radial Velocity Planet Searcher (HARPS) indicates that HD 40307 is host to six super-Earth
A super-Earth is an extrasolar planet with a mass higher than Earth's, but substantially below those of the Solar System's ice giants, Uranus and Neptune, which are 14.5 and 17 times Earth's, respectively.
The term "super-Earth" refers only to ...
planets, one of which, HD 40307 g, lies in the circumstellar habitable zone
In astronomy and astrobiology, the circumstellar habitable zone (CHZ), or simply the habitable zone, is the range of orbits around a star within which a planetary surface can support liquid water given sufficient atmospheric pressure.J. F. Kast ...
of the star, and is not close enough to be tidally locked
Tidal locking between a pair of co-orbiting astronomical bodies occurs when one of the objects reaches a state where there is no longer any net change in its rotation rate over the course of a complete orbit. In the case where a tidally locked b ...
(i.e. with the same face always facing the star), unlike the other planets in the same system, and many other planets which orbit close to their parent stars. HD 41004 is a complex binary system about 139 light-years distant. The primary is an orange dwarf of spectral type K1V orbited by a planet roughly 2.65 times the mass of Jupiter every 963 days, while the secondary is a red dwarf of spectral type M2V and orbited by a brown dwarf that is at least 19 times as massive as Jupiter. Both substellar components were discovered by doppler spectroscopy using the CORALIE spectrograph
Leonhard Euler Telescope, or the Swiss EULER Telescope, is a national, fully automatic reflecting telescope, built and operated by the Geneva Observatory. It is located at an altitude of at ESO's La Silla Observatory site in the Chilean Nor ...
in 2004 and 2002 respectively. Kapteyn's Star, a nearby red dwarf
''Red Dwarf'' is a British science fiction comedy franchise created by Rob Grant and Doug Naylor, which primarily consists of a television sitcom that aired on BBC Two between 1988 and 1999, and on Dave (TV channel), Dave since 2009, gaining a ...
at the distance of 12.78 light-years, has a magnitude of 8.8. It has the largest proper motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of the observed changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects in the sky, as seen from the center of mass of the Solar System, compared to the abstract background of the more dista ...
of any star in the sky after Barnard's Star
Barnard's Star is a red dwarf about six light-years from Earth in the constellation of Ophiuchus. It is the fourth-nearest-known individual star to the Sun after the three components of the Alpha Centauri system, and the closest star in the ...
. Moving around the Milky Way in the opposite direction to most other stars, it may have originated in a dwarf galaxy that was merged into the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked ey ...
, with the main remnant being the Omega Centauri
Omega Centauri (ω Cen, NGC 5139, or Caldwell 80) is a globular cluster in the constellation of Centaurus that was first identified as a non-stellar object by Edmond Halley in 1677. Located at a distance of , it is the largest-known globular clus ...
globular cluster. In 2014 analysis of the doppler variations of Kapteyn's Star with the HARPS spectrograph showed that it hosts two super-Earths—Kapteyn b
Kapteyn b is an exoplanet that orbits within the habitable zone of the red subdwarf Kapteyn's Star, located approximately from Earth. Kapteyn b is within the estimated habitable zone of its star. It was the closest-suspected potentially habitab ...
and Kapteyn c. Kapteyn b is the oldest-known potentially habitable planet, estimated to be possibly 11 billion years old.
Located 1.5 degrees west southwest of Alpha, RR Pictoris is a cataclysmic variable that flared up as a nova
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramati ...
, reaching magnitude 1.2 on 9 June 1925. Six months after its peak brightness, it had faded to be invisible to the unaided eye, and was magnitude 12.5 by 1975. RR Pictoris is a close binary system composed of a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
and secondary star that orbit each other every 3.48 hours—so close that the secondary is filling up its Roche lobe
In astronomy, the Roche lobe is the region around a star in a binary system within which orbiting material is gravitationally bound to that star. It is an approximately teardrop-shaped region bounded by a critical gravitational equipotential, ...
with stellar material, which is then transferred onto the first star's accretion disk
An accretion disk is a structure (often a circumstellar disk) formed by diffuse material in orbital motion around a massive central body. The central body is typically a star. Friction, uneven irradiance, magnetohydrodynamic effects, and other ...
. Once this material reaches a critical mass, it ignites and the system brightens tremendously. Calculations from the orbital speed suggest the secondary star is not dense enough for its size to still be on the main sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Her ...
, so it also must have begun expanding and cooling already after its core ran out of hydrogen fuel. The RR Pictoris system is estimated to lie around 1300 light-years distant from Earth.
Deep-sky objects
 NGC 1705 is an irregular dwarf galaxy 17 million light-years from Earth. It is one of the most active star forming galaxies in the nearby universe, despite the fact that its rate of star formation peaked around 30 million years ago. Pictor A, around 485 million light-years away, is a double-lobed
NGC 1705 is an irregular dwarf galaxy 17 million light-years from Earth. It is one of the most active star forming galaxies in the nearby universe, despite the fact that its rate of star formation peaked around 30 million years ago. Pictor A, around 485 million light-years away, is a double-lobed radio galaxy
A radio galaxy is a galaxy with giant regions of radio emission extending well beyond its visible structure. These energetic radio lobes are powered by jets from its active galactic nucleus. They have luminosities up to 1039 W at radio wa ...
and a powerful source of radio wave
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies of 300 gigahertz ( GHz) and below. At 300 GHz, the corresponding wavelength is 1 mm (sho ...
s in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. From a supermassive black hole
A supermassive black hole (SMBH or sometimes SBH) is the largest type of black hole, with its mass being on the order of hundreds of thousands, or millions to billions of times the mass of the Sun (). Black holes are a class of astronomical obj ...
at its centre, a relativistic jet shoots out to an X-ray hot spot 800,000 light years away. SPT-CL J0546-5345 SPT-CL J0546-5345
is one of the most massive galaxy clusters ever found in the early universe. It is thought to be 7 billion light years away. It was discovered at the South Pole Telescope in 2008 by the Sunyaev-Zel'dovich-Effect. The cl ...
is a massive galaxy cluster
A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. They are the second-la ...
located around 7 billion light-years away with a mass equivalent to approximately 800 trillion suns.
GRB 060729
GRB 060729 was a gamma-ray burst that was first observed on 29 July 2006. It is likely the signal of a type Ic supernova—the core collapse of a massive star. It was also notable for its extraordinarily long X-ray afterglow, detectable 642 days ...
was a gamma-ray burst
In gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are immensely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the most energetic and luminous electromagnetic events since the Big Bang. Bursts can last from ten milli ...
that was first observed on 29 July 2006. It is likely the signal of a type Ic supernova—the core collapse of a massive star. It was also notable for its extraordinarily long X-ray afterglow
An afterglow in meteorology consists of several atmospheric optical phenomena, with a general definition as a broad arch of whitish or pinkish sunlight in the twilight sky, consisting of the bright segment and the purple light. Purple light ma ...
, detectable 642 days (nearly two years) after the original event. The event was remote, with a redshift
In physics, a redshift is an increase in the wavelength, and corresponding decrease in the frequency and photon energy, of electromagnetic radiation (such as light). The opposite change, a decrease in wavelength and simultaneous increase in f ...
of 0.54.
See also
* Pictor (Chinese astronomy)Notes
References
Citations Sources * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Online sources * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
The clickable Pictor
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Pictor Southern constellations Constellations listed by Lacaille