Physical Hazard on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Machines are commonplace in many industries, including
Machines are commonplace in many industries, including
 In the United States, noise is recognized as a hazard in the workplace by the
In the United States, noise is recognized as a hazard in the workplace by the
occupational hazard
An occupational hazard is a hazard experienced in the workplace. This encompasses many types of hazards, including chemical hazards, biological hazards (biohazards), psychosocial hazards, and physical hazards. In the United States, the Nation ...
or environmental hazard
Environmental hazards are hazards that affect biomes or ecosystems. Well known examples include oil spills, water pollution, slash and burn deforestation, air pollution, ground fissures, and Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, build-up of atmosp ...
. Physical hazards include ergonomic hazard
Ergonomic hazards are physical conditions that may pose a risk of injury to the musculoskeletal system due to poor ergonomics. These hazards include awkward or static postures, high forces, Repetitive strain injury, repetitive motion, or insuffici ...
s, radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
, heat and cold stress, vibration
Vibration () is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. Vibration may be deterministic if the oscillations can be characterised precisely (e.g. the periodic motion of a pendulum), or random if the os ...
hazards, and noise
Noise is sound, chiefly unwanted, unintentional, or harmful sound considered unpleasant, loud, or disruptive to mental or hearing faculties. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrat ...
hazards. Engineering controls
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve systems. Modern engineering comprises many subfi ...
are often used to mitigate physical hazards.
Physical hazards are a common source of injuries in many industries. They are perhaps unavoidable in certain industries, such as construction
Construction are processes involved in delivering buildings, infrastructure, industrial facilities, and associated activities through to the end of their life. It typically starts with planning, financing, and design that continues until the a ...
and mining
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasib ...
, but over time people have developed safety methods and procedures to manage the risks of physical danger in the workplace. Employment of children may pose special problems.
A physical hazard is also a naturally occurring process that has the potential to create loss or damage. Physical hazards include earthquakes
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they c ...
, floods
A flood is an overflow of water (list of non-water floods, or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant con ...
, fires, and tornadoes
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with the surface of Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, although the ...
. Physical hazards often have both human and natural elements. For example, flood problems can be affected by the natural elements of climate fluctuations and storm frequency, and by land drainage and building in a flood plain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river. Floodplains stretch from the banks of a river channel to the base of the enclosing valley, and experience flooding during periods of high Discharge (hydrolog ...
, human elements. Geomagnetic storms
A geomagnetic storm, also known as a magnetic storm, is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere that is driven by interactions between the magnetosphere and large-scale transient plasma and magnetic field structures that originate ...
can disrupt or damage technological infrastructure, and disorient species with magnetoception
Magnetoreception is a sense which allows an organism to detect the Earth's magnetic field. Animals with this sense include some arthropods, molluscs, and vertebrates (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals). The sense is mainly used ...
. Another physical hazard, X-rays
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
, naturally occur from solar radiation
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrared (typically p ...
, but have also been utilized by humans for medical purposes; however, overexposure
In photography, exposure is the amount of light per unit area reaching a frame of photographic film or the surface of an electronic image sensor. It is determined by shutter speed, lens f-number, and scene luminance. Exposure is measured in units ...
can lead to cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, skin burns, and tissue damage.
Falls
Falls are a common cause of occupational injuries and fatalities, especially in construction, extraction, transportation,healthcare
Health care, or healthcare, is the improvement or maintenance of health via the preventive healthcare, prevention, diagnosis, therapy, treatment, wikt:amelioration, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other disability, physic ...
, and building cleaning and maintenance. Circumstances like floor holes and wall opening, misused fall protection, slippery, cluttered, or unstable walking surfaces, unprotected edges and unsafely situated ladders are associated with occupational fall injuries.
According to 2014 published data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the government of the United States, U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics, labor economics and ...
, 261,930 private industry and government workers lost one or more days of work and around 798 workers died as a result of fall injuries in the workplace. There was a general upward trend in fatal fall injuries which increased 25 percent overall from 2011 to 2016. For carpenters, heavy and tractor-trailer truck drivers, tree trimmers and pruners, and roofers, fall injuries increased by more than 25 percent in 2016. The highest rate of nonfatal fall injuries experienced in the health services, and the wholesale and retail industries, while the highest counts for fall-related deaths associated with the construction industry
Construction are processes involved in delivering buildings, infrastructure, industrial facilities, and associated activities through to the end of their life. It typically starts with planning, financing, and design that continues until the ...
. According to Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the government of the United States, U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics, labor economics and ...
, there were total 991 construction-related fall incidents in 2016. In the United States, fall-related fatalities result in a significant financial burden of estimated $70 billion annually in the form of worker's compensation and occupational fall incident related medical costs. The international public health community works to reduce fall injuries at work settings by developing strategies because many other countries face similar problems in the workplace as in the United States.
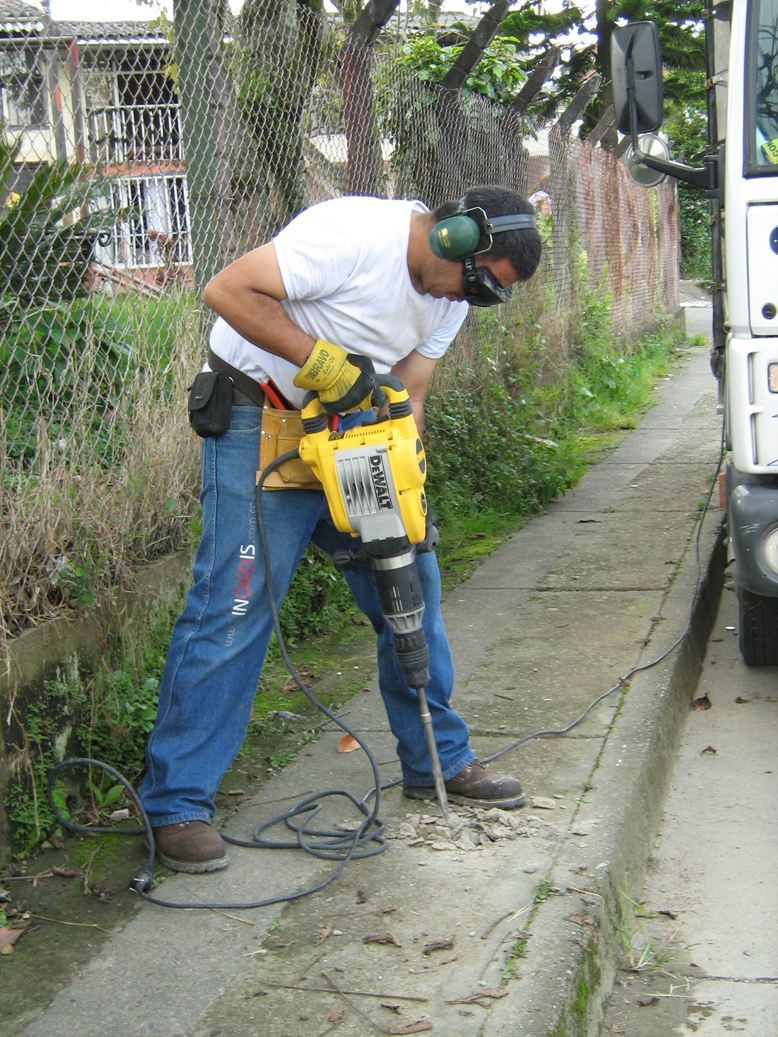
Machines
 Machines are commonplace in many industries, including
Machines are commonplace in many industries, including manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer ...
, mining
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasib ...
, construction
Construction are processes involved in delivering buildings, infrastructure, industrial facilities, and associated activities through to the end of their life. It typically starts with planning, financing, and design that continues until the a ...
and agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
, and can be dangerous to workers. Many machines involve moving parts, sharp edges, hot surfaces and other hazards with the potential to crush, burn
A burn is an injury to skin, or other tissues, caused by heat, electricity, chemicals, friction, or ionizing radiation (such as sunburn, caused by ultraviolet radiation). Most burns are due to heat from hot fluids (called scalding), soli ...
, cut
Cut or CUT may refer to:
Common uses
* The act of cutting, the separation of an object into two through acutely directed force
** A type of wound
** Cut (archaeology), a hole dug in the past
** Cut (clothing), the style or shape of a garment
** ...
, shear, stab or otherwise strike
Strike may refer to:
People
*Strike (surname)
* Hobart Huson, author of several drug related books
Physical confrontation or removal
*Strike (attack), attack with an inanimate object or a part of the human body intended to cause harm
* Airstrike, ...
or wound
A wound is any disruption of or damage to living tissue, such as skin, mucous membranes, or organs. Wounds can either be the sudden result of direct trauma (mechanical, thermal, chemical), or can develop slowly over time due to underlying diseas ...
workers if used unsafely. Various safety measures exist to minimize these hazards, including lockout-tagout procedures for machine maintenance and roll over protection systems for vehicles. According to the United States Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the government of the United States, U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics, labor economics and ...
, machine-related injuries were responsible for 64,170 cases that required days away from work in 2008. More than a quarter of these cases required more than 31 days spent away from work. That same year, machines were the primary or secondary source of over 600 work-related fatalities. Machines are also often involved indirectly in worker deaths and injuries, such as in cases in which a worker slips and falls, possibly upon a sharp or pointed object. Power tools
A power tool is a tool that is actuated by an additional power source and mechanism other than the solely manual labor used with hand tools. The most common types of power tools use electric motors. Internal combustion engines and compressed air ...
, used in many industries, present a number of hazards due to sharp moving parts, vibrations, or noise. The transportation sector bears many risks for the health of commercial drivers, for example from vibration, long periods of sitting, work stress and exhaustion. These problems occur in Europe but in other parts of the world the situation is even worse. More drivers die in accidents due to security defects in vehicles. Long waiting times at borders cause that drivers are away from home and family much longer and even increase the risk of HIV infections.
Confined spaces
Confined spaces also present a work hazard. TheNational Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the List of United States federal agencies, United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related occ ...
(NIOSH) defines "confined space" as having limited openings for entry and exit and unfavorable natural ventilation, and which is not intended for continuous employee occupancy. Spaces of this kind can include storage tanks, ship compartments, sewers, and pipelines. Confined spaces can pose a hazard not just to workers, but also to people who try to rescue them. In 2015, around 136 U.S. workers died in fatalities related to confined spaces according to the data collected in response to the annual Census of Fatal Occupational Injuries (CFOI) program of the Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the government of the United States, U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics, labor economics and ...
. Hazards like entrapment and drowning to asphyxia
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen to the body which arises from abnormal breathing. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which affects all the tissues and organs, some more rapidly than others. There are m ...
tion and toxic chemical exposure results in the deaths and injuries that occur in these confined spaces. Physical and atmospheric hazards due to confined spaces can be avoided by addressing and recognizing these hazards before entering in the confined spaces to perform work.
Noise
Noise presents a fairly common workplace hazard:occupational hearing loss
Occupational hearing loss (OHL) is hearing loss that occurs as a result of occupational hazards, such as excessive noise and ototoxic chemicals. Noise is a common workplace hazard, and recognized as the risk factor for noise-induced hearing loss a ...
is the most common work-related injury in the United States, with 22 million workers exposed to hazardous noise levels at work and an estimated $242 million spent annually on worker's compensation for hearing loss disability. Noise is not the only source of occupational hearing loss
Occupational hearing loss (OHL) is hearing loss that occurs as a result of occupational hazards, such as excessive noise and ototoxic chemicals. Noise is a common workplace hazard, and recognized as the risk factor for noise-induced hearing loss a ...
; exposure to chemicals such as aromatic solvents and metals including lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
, arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
, and mercury can also cause hearing loss. Naturally, noise is more of concern for certain occupations than others; musician
A musician is someone who Composer, composes, Conducting, conducts, or Performing arts#Performers, performs music. According to the United States Employment Service, "musician" is a general Terminology, term used to designate a person who fol ...
s, mine workers, and construction
Construction are processes involved in delivering buildings, infrastructure, industrial facilities, and associated activities through to the end of their life. It typically starts with planning, financing, and design that continues until the a ...
workers are exposed to higher and more constant levels of noise and therefore are at a higher risk of developing hearing loss. Since noise-induced hearing loss
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is a Hearing loss, hearing impairment resulting from exposure to loud sound. People may have a loss of perception of a narrow range of Frequency, frequencies or impaired perception of sound including hyperacusi ...
, while entirely preventable, is permanent and irreversible, it is vital that companies and their employees are aware of limits and prevention methods available.
 In the United States, noise is recognized as a hazard in the workplace by the
In the United States, noise is recognized as a hazard in the workplace by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the List of United States federal agencies, United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related occ ...
(NIOSH) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA; ) is a regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. The United States Congress established ...
(OSHA). Both organizations work to set and enforce standards for occupational noise exposure and ultimately prevent hearing loss. Examples of initiatives made by NIOSH to prevent the negative effects of noise exposure include the Buy Quiet
Buy Quiet is an American health and safety initiative to select and purchase the lowest noise emitting power tools and machinery in order to reduce occupational and community noise exposure. Buy Quiet Programs are examples of noise control strategi ...
program, which encourages employers to purchase machinery that produces lower noise levels, and the Safe-In-Sound Award, which was created to recognize organizations that excel in noise control.
Temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
extremes can cause a danger to workers.
Cold stress
Overexposure to freezing conditions or extreme cold can result in a risk to many workers. Employees who work outdoors in the winter months such as fishers, hunters, divers, hydro and telecommunications linemen, construction workers, transportation workers, military personnel, emergency response workers, and those work in the refrigerated warehouse are especially vulnerable to cold. Effects of extreme cold working conditions include: * Nonfreezing injuries –chilblains
Chilblains, also known as pernio, is a medical condition in which damage occurs to capillary beds in the skin, most often in the hands or feet, when blood perfuses into the nearby tissue, resulting in redness, itching, inflammation, and possibly ...
, trench foot
Trench foot, also known by #Names, other names, is a type of immersion foot syndromes, foot damage due to moisture. Initial symptoms often include tingling or itching which can progress to numbness. The feet may become erythema, red or cyanosis, ...
* Freezing injuries – frostbite
Frostbite is a skin injury that occurs when someone is exposed to extremely low temperatures, causing the freezing of the skin or other tissues, commonly affecting the fingers, toes, nose, ears, cheeks and chin areas. Most often, frostbite occ ...
and frostnip
Frostbite is a skin injury that occurs when someone is exposed to extremely low temperatures, causing the freezing of the skin or other tissues, commonly affecting the fingers, toes, nose, ears, cheeks and chin areas. Most often, frostbite occ ...
* Hypothermia
Hypothermia is defined as a body core temperature below in humans. Symptoms depend on the temperature. In mild hypothermia, there is shivering and mental confusion. In moderate hypothermia, shivering stops and confusion increases. In severe ...
* Lower work efficiency
* Higher accident rates
* Impaired performance of complex mental tasks
* Reduced muscular strength and stiffened joints
* Reduced mental alertness
* Impaired manual tasks because of sensitivity and dexterity
Fine motor skill (or dexterity) is the coordination of small muscles in movement with the eyes, hands and fingers. The complex levels of manual dexterity that humans exhibit can be related to the nervous system. Fine motor skills aid in the growt ...
of fingers
Use of personal protective equipment such as insulating clothes, gloves, boots, and masks, engineering controls
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve systems. Modern engineering comprises many subfi ...
such as radiant heaters, and safe work practices are used to minimize the risk of cold injuries.
Heat stress
Workers who are working in laundries, bakeries, restaurant kitchens, steel foundries, glass factories, brick-firing and ceramic plants, electrical utilities,smelters
Smelting is a process of applying heat and a chemical reducing agent to an ore to extract a desired base metal product. It is a form of extractive metallurgy that is used to obtain many metals such as iron, copper, silver, tin, lead and zinc. Sm ...
, and outdoor workers such as construction workers, firefighters, farmers, and mining workers are more vulnerable to exposure to extreme heat. Effects of heat stress include:
* Increased irritability
* Dehydration
* Heat stroke
Heat stroke or heatstroke, also known as sun-stroke, is a severe heat illness that results in a body temperature greater than , along with red skin, headache, dizziness, and confusion. Sweating is generally present in exertional heatstro ...
* Chronic heat exhaustion
Heat exhaustion is a heat-related illness characterized by the body's inability to effectively cool itself, typically occurring in high ambient temperatures or during intense physical exertion. In heat exhaustion, core body temperature ranges from ...
* Cramps, rashes, and burns
* Sweaty palms and dizziness
Dizziness is an imprecise term that can refer to a sense of disorientation in space, vertigo, or lightheadedness. It can also refer to Balance disorder, disequilibrium or a non-specific feeling, such as giddiness or foolishness.
Dizziness is a ...
* Increased risk of other accidents
* Loss of concentration and ability to do mental tasks and heavy manual work
* Sleep disturbances, sickness, and susceptibility to minor injuries
Engineering controls such as air conditioning and ventilation, training to build up a level of tolerance to work in extreme heat conditions and use of cooled protective clothing can help to reduce heat-related illnesses.
Electricity
Electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
poses a danger to many workers. Electrical injuries can be divided into four types: fatal electrocution, electric shock
An electrical injury (electric injury) or electrical shock (electric shock) is damage sustained to the skin or internal organs on direct contact with an electric current.
The injury depends on the Current density, density of the current, tissu ...
, burns, and falls caused by contact with electric energy. Electrocution
Electrocution is death or severe injury caused by electric shock from electric current passing through the body. The word is derived from "electro" and "execution", but it is also used for accidental death.
The term "electrocution" was coined ...
is one of the major hazards on construction sites. It can be fatal and can result in serious and permanent burn injuries to the skin, internal tissues and damage to the heart depending on the length and severity of the shock. When electric current
An electric current is a flow of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is defined as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface. The moving particles are called charge c ...
flows through tissues or bone, it produces heat that causes electrical burns. Electrical burns cause tissue damage and need immediate medical attention. Electric shocks can result in injuries such as muscle spasms
A spasm is a sudden involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ, such as the bladder.
A spasmodic muscle contraction may be caused by many medical conditions, including dystonia. Most commonly, it is a musc ...
, palpitations
Palpitations occur when a person becomes aware of their heartbeat. The heartbeat may feel hard, fast, or uneven in their chest.
Symptoms include a very fast or irregular heartbeat. Palpitations are a sensory symptom. They are often described as ...
, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
, collapse, and unconsciousness
Unconsciousness is a state in which a living individual exhibits a complete, or near-complete, inability to maintain an awareness of self and environment or to respond to any human or environmental stimulus. Unconsciousness may occur as the r ...
. Faulty electrical connections and damaged electrical equipment can lead to an electric shock to workers and to others at or near the workplace.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the government of the United States, U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics, labor economics and ...
, a total 1,738 accidents occurred due to contact with electric current between 2003 and 2010, and out of that, the highest number of electrical fatalities, 849, occurred in the construction industry. Five occupations from the construction industry—electrician
An electrician is a tradesman, tradesperson specializing in electrical wiring of buildings, transmission lines, stationary machines, and related equipment. Electricians may be employed in the installation of new electrical components or the ...
s, roofer
A roofer, roof mechanic, or roofing contractor is a tradesman who specializes in roof construction. Roofers replace, repair, and install the roofs of buildings, using a variety of materials, including shingles, single-ply, bitumen, and met ...
s, painters, carpenters, and construction laborers—account for more than 32% of all electrical fatalities. Improper grounding, wet conditions, damaged tools and equipment, inadequate wiring, exposed electrical parts, overhead power lines and overloaded circuits are the common electrical hazards which are found on construction sites.
Electrical injuries are preventable through safe work practices like keeping electrical tools properly maintained, de-energizing electrical appliances before inspection or repair, and exercising caution when working near energized lines. Personal protective equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is protective clothing, helmets, goggles, or other garments or equipment designed to protect the wearer's body from injury or infection. The hazards addressed by protective equipment include physical, elect ...
such as hard hats, hoods, sleeves, rubber or insulating gloves and insulating clothing can be useful to reduce any electrical accidents.
Sunlight
Sunlight
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible spectrum, visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrare ...
is the most commonly known physical hazard which affects people who work outside. Outdoor workers get highest sunlight exposure during high-intensity hours between 10:00 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. and during the summertime. The risk of getting sunburn
Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and other animals include red or reddish skin tha ...
ed is higher throughout these times. Some commonly used medicines such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a Indication (medicine), therapeutic drug class which Analgesic, reduces pain, Anti-inflammatory, decreases inflammation, Antipyretic, decreases fever, and Antithrombotic, prevents bl ...
s (NSAIDs), antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides ...
s, tetracyclines
Tetracyclines are a group of broad-spectrum antibiotic compounds that have a common basic structure and are either isolated directly from several species of ''Streptomyces'' bacteria or produced semi-synthetically from those isolated compounds. ...
, thiazide
Thiazide () refers to both a class of sulfur-containing organic molecules and a class of diuretics based on the chemical structure of benzothiadiazine. The thiazide drug class was discovered and developed at Merck and Co. in the 1950s. The firs ...
s, sulfa antibiotics, and diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics ...
s increase sensitivity to sunlight and result in skin rash
A rash is a change of the skin that affects its color, appearance, or texture.
A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, cracke ...
es and sunburn. Moreover, sunlight is a source of ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
(UV) rays which are a form of non-ionizing radiation
Non-ionizing (or non-ionising) radiation refers to any type of electromagnetic radiation that does not carry enough energy per quantum ( photon energy) to ionize atoms or molecules—that is, to completely remove an electron from an atom or mol ...
. UV rays directly from sunlight and indirect sun exposure, such as light reflected by snow and light-shaded sand can penetrate workers' uncovered skin. Long time, continuous exposure to ultraviolet radiation results in suppression of the immune system, eye damage, skin aging, and skin cancer
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the Human skin, skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells (biology), cells that have the ability to invade or metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. It occurs when skin cells grow ...
. Some non-solar sources of UV radiation
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of t ...
, for example, projection lamps, the curing of paints and inks, germicidal lamps used in hospitals, fluorescent tubes, sunlamps, and welding arcs, can also cause adverse health effects in other workers.
Personal protective equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is protective clothing, helmets, goggles, or other garments or equipment designed to protect the wearer's body from injury or infection. The hazards addressed by protective equipment include physical, elect ...
, engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
, and administrative controls
Administrative controls are training, procedure, policy, or shift designs that lessen the threat of a hazard to an individual. Administrative controls typically change the behavior of people (e.g., factory workers) rather than removing the act ...
such as the provision of shade cover, and rotating job shifts can minimize the risk of sun exposure for outdoor workers. In case of non-solar sources of UV radiation, suitable engineering controls and administrative controls such as safety sign
A safety sign is a sign designed to warn of hazards, indicate mandatory actions or required use of personal protective equipment, prohibit actions or objects, identify the location of firefighting or First aid kit, safety equipment, or marking ...
s and training of employees can be useful.
Vibration
Vibration
Vibration () is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. Vibration may be deterministic if the oscillations can be characterised precisely (e.g. the periodic motion of a pendulum), or random if the os ...
has long been recognized as a serious occupational hazard. Continuously repeated exposure to high levels of vibration results in injuries or illnesses. Vibration exposure is classified into two general types: hand-arm and whole-body vibration. Hand arm vibration causes direct injury to the fingers and hand and affects feeling, dexterity, and grip of the hand. It is a known causative factor for other ergonomic
Ergonomics, also known as human factors or human factors engineering (HFE), is the application of psychological and physiological principles to the engineering and design of products, processes, and systems. Primary goals of human factors engi ...
-related fatalities. Hand-arm vibration injury associated with use of appliances or equipment with vibration such as grinders
Grinder may refer to:
Machinery
*Various types of grinding machine, used in a machining operation to refine the surface of materials
*Food grinders
**Blade grinder, includes food processors, blenders, electric coffee and spice grinders, etc.
**Co ...
, impact drills, chipping hammers, pavement breakers, dental tools, sander
A sander is a power tool used to smooth surfaces by abrasion with sandpaper. Sanders have a means to attach the sandpaper and a mechanism to move it rapidly contained within a housing with means to handhold it or fix it to a workbench. Woodw ...
s, air-powered wrenches, and saws of all types. Repeated long time use of vibrating machinery results in long-term effects—independent vascular Vascular can refer to:
* blood vessels, the vascular system in animals
* vascular tissue
Vascular tissue is a complex transporting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. The primary components of vascular tissue ...
, neurosensory and musculoskeletal disorder
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are injuries or pain in the human musculoskeletal system, including the joints, ligaments, muscles, nerves, tendons, and structures that support limbs, neck and back. MSDs can arise from a sudden exertion (e.g. ...
s of the hand and arm which is known as hand-arm vibration syndrome (HAVS). Whole-body vibration is one of the most common causes of lost time and production output and causes low back pain
Low back pain or wiktionary:lumbago#Etymology, lumbago is a common musculoskeletal disorders, disorder involving the muscles, nerves, and bones of the back, in between the lower edge of the ribs and the lower fold of the buttocks. Pain can var ...
and injury due to higher than expected levels of vibration. Whole-body vibration injuries associated with off-road vehicles in industries such as agriculture, forestry
Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests and woodlands for associated resources for human and Natural environment, environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and ...
, mining
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasib ...
, quarry
A quarry is a type of open-pit mining, open-pit mine in which dimension stone, rock (geology), rock, construction aggregate, riprap, sand, gravel, or slate is excavated from the ground. The operation of quarries is regulated in some juri ...
ing and with small-fast boats used off-shore.
A combination of control measures such as redesigning the appliances to reduce vibration exposure, using machines that are designed to decrease the vibration transmitted to the operator, implementing speed limits, scheduling regular work breaks, posture changes or job rotation to reduce exposure time, providing training, information and supervision on adjusting and operating equipment can be used for successful vibration exposure reduction.
Other hazards
Lighting
Lighting or illumination is the deliberate use of light to achieve practical or aesthetic effects. Lighting includes the use of both artificial light sources like lamps and light fixtures, as well as natural illumination by capturing daylight. ...
, and air pressure (high or low) can also cause work-related illness and injury. Asphyxiation
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen to the body which arises from abnormal breathing. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which affects all the tissues and organs, some more rapidly than others. There are ...
is a potential work hazard in certain situations. Musculoskeletal disorders
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are injuries or pain in the human musculoskeletal system, including the joints, ligaments, muscles, nerves, tendons, and structures that support limbs, neck and back. MSDs can arise from a sudden exertion (e.g., l ...
are avoided by the employment of good ergonomic design and the reduction of repeated strenuous movements or lifts. Ionizing (alpha
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter ''aleph'' , whose name comes from the West Semitic word for ' ...
, beta
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; or ) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive . In Modern Greek, it represe ...
, gamma
Gamma (; uppercase , lowercase ; ) is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. In Ancient Greek, the letter gamma represented a voiced velar stop . In Modern Greek, this letter normally repr ...
, X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
, neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nucle ...
), and non-ionizing radiation
Non-ionizing (or non-ionising) radiation refers to any type of electromagnetic radiation that does not carry enough energy per quantum ( photon energy) to ionize atoms or molecules—that is, to completely remove an electron from an atom or mol ...
(microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
, intense infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
, radio frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the u ...
, ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
, laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
at visible and non-visible wavelengths), can also be a potent hazard.
See also
* * s * *References
{{Occupational safety and health Occupational hazards