Phugoid on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In 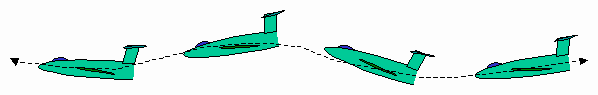
Analysis of phugoid motion
Aerodynamics Flight control systems
aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air ...
, a phugoid or fugoid is an aircraft motion in which the vehicle pitches up and climbs, and then pitches down and descends, accompanied by speeding up and slowing down as it goes "downhill" and "uphill". This is one of the basic flight dynamics modes of an aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines ...
(others include short period
The dynamic stability of an aircraft refers to how the aircraft behaves after it has been disturbed following steady non-oscillating flight.
Longitudinal modes
Oscillating motions can be described by two parameters, the period of time required ...
, roll subsidence, dutch roll, and spiral divergence
The dynamic stability of an aircraft refers to how the aircraft behaves after it has been disturbed following steady non-oscillating flight.
Longitudinal modes
Oscillating motions can be described by two parameters, the period of time require ...
), and is a classic example of a positive feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in the ...
system.

Detailed description
The phugoid has a nearly constantangle of attack
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or \alpha) is the angle between a reference line on a body (often the chord line of an airfoil) and the vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is m ...
but varying pitch, caused by a repeated exchange of airspeed
In aviation, airspeed is the speed of an aircraft relative to the air. Among the common conventions for qualifying airspeed are:
* Indicated airspeed ("IAS"), what is read on an airspeed gauge connected to a Pitot-static system;
* Calibrated a ...
and altitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context ...
. It can be excited by an elevator
An elevator or lift is a wire rope, cable-assisted, hydraulic cylinder-assisted, or roller-track assisted machine that vertically transports people or freight between floors, levels, or deck (building), decks of a building, watercraft, ...
singlet (a short, sharp deflection followed by a return to the centered position) resulting in a pitch increase with no change in trim
Trim or TRIM may refer to:
Cutting
* Cutting or trimming small pieces off something to remove them
** Book trimming, a stage of the publishing process
** Pruning, trimming as a form of pruning often used on trees
Decoration
* Trim (sewing), or ...
from the cruise condition. As speed decays, the nose drops below the horizon. Speed increases, and the nose climbs above the horizon. Periods can vary from under 30 seconds for light aircraft
A light aircraft is an aircraft that has a maximum gross takeoff weight of or less.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 308. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997.
Light aircraft are used as utility aircraft c ...
to minutes for larger aircraft. Microlight aircraft
Ultralight aviation (called microlight aviation in some countries) is the flying of lightweight, 1- or 2-seat fixed-wing aircraft. Some countries differentiate between weight-shift control and Aircraft flight control system, conventional three-a ...
typically show a phugoid period of 15–25 seconds, and it has been suggested that birds and model airplanes show convergence between the phugoid and short period modes. A classical model for the phugoid period can be simplified to about (0.85 × speed in knots
A knot is a fastening in rope or interwoven lines.
Knot may also refer to:
Places
* Knot, Nancowry, a village in India
Archaeology
* Knot of Isis (tyet), symbol of welfare/life.
* Minoan snake goddess figurines#Sacral knot
Arts, entertainme ...
) seconds, but this only really works for larger aircraft.
Phugoids are often demonstrated to student pilot
An aircraft pilot or aviator is a person who controls the flight of an aircraft by operating its directional flight controls. Some other aircrew members, such as navigators or flight engineers, are also considered aviators, because they a ...
s as an example of the speed stability of the aircraft and the importance of proper trimming. When it occurs, it is considered a nuisance, and in lighter airplanes (typically showing a shorter period) it can be a cause of pilot-induced oscillation
Pilot-induced oscillations (PIOs), as defined by MIL-HDBK-1797A, are ''sustained or uncontrollable oscillations resulting from efforts of the pilot to control the aircraft''. They occur when the pilot of an aircraft inadvertently commands an oft ...
.
The phugoid, for moderate amplitude, occurs at an effectively constant angle of attack, although in practice the angle of attack actually varies by a few tenths of a degree. This means that the stalling angle of attack is never exceeded, and it is possible (in the <1g section of the cycle) to fly at speeds below the known stalling speed. Free flight models with badly unstable phugoid typically stall or loop, depending on thrust.
An unstable or divergent phugoid is caused, mainly, by a large difference between the incidence angles of the wing and tail. A stable, decreasing phugoid can be attained by building a smaller stabilizer on a longer tail, or, at the expense of pitch and yaw "static" stability, by shifting the center of gravity to the rear.
Aerodynamically efficient aircraft typically have low phugoid damping.
The term "phugoid" was coined by Frederick W. Lanchester, the British aerodynamicist who first characterized the phenomenon. He derived the word from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
words and to mean "flight-like" but recognized the diminished appropriateness of the derivation given that meant flight in the sense of "escape" (as in the word "fugitive") rather than vehicle flight.
Aviation accidents
In 1972, an Aero Transporti ItalianiFokker F-27 Friendship
The Fokker F27 Friendship is a turboprop airliner developed and manufactured by the Dutch aircraft manufacturer Fokker. It is the most numerous post-war aircraft manufactured in the Netherlands; the F27 was also one of the most successful Euro ...
, en route from Rome Fiumicino to Foggia, climbing through 13,500 feet, entered an area of poor weather with local thunderstorm activity. At almost 15,000 feet the aircraft suddenly lost 1200 feet of altitude and its speed dropped. It developed phugoid oscillations from which the pilots could not recover. The aircraft struck the ground at a speed of 340 knots. Three crew and fifteen passengers on board were all killed.
In the 1975 Tan Son Nhut C-5 accident
It was also declared the ''International Women's Year'' by the United Nations and the European Architectural Heritage Year by the Council of Europe.
Events
January
* January 1 - Watergate scandal (United States): John N. Mitchell, H. R. H ...
, USAF C-5 68-0218 with flight controls damaged by failure of the rear cargo/pressure door, encountered phugoid oscillations while the crew was attempting a return to base, and crash-landed in a rice paddy adjacent to the airport. Of the 328 people on board, 153 died, making it the deadliest accident involving a US military aircraft.
In 1985, Japan Airlines Flight 123
Japan Air Lines Flight 123 (JAL123) () was a scheduled domestic Japan Air Lines passenger flight from Haneda Airport in Tokyo to Itami International Airport in Osaka. On August 12, 1985, the Boeing 747SR operating this flight suffered a sudden ...
lost all hydraulic controls after its vertical stabiliser blew off due to an aft pressure bulkhead
The aft pressure bulkhead or rear pressure bulkhead is the rear component of the pressure seal in all aircraft that cruise in a tropopause zone in the earth's atmosphere. It helps maintain pressure when stratocruising and protects the aircraft from ...
failure, and went into phugoid motion. While the crew were able to maintain near-level flight through the use of engine power, the plane lost height over a mountain range northwest of Tokyo before crashing into Mount Takamagahara
Mount Takamagahara (高天原山, ''Takamagahara-yama'') is a mountain in the Gunma Prefecture of Japan, near Ueno village. Its measurement is tall. Takamagahara is the world of heaven in Japanese mythology.
The crash of Japan Airlines Flight ...
. With 520 deaths, it remains the deadliest single-aircraft disaster in history.
In 1989, United Airlines Flight 232
United Airlines Flight 232 was a regularly scheduled United Airlines flight from Stapleton International Airport in Denver to O'Hare International Airport in Chicago, continuing to Philadelphia International Airport. On July 19, 1989, the DC ...
suffered an uncontained engine failure
A turbine engine failure occurs when a turbine engine unexpectedly stops producing power due to a malfunction other than fuel exhaustion. It often applies for aircraft, but other turbine engines can fail, like ground-based turbines used in power ...
in the #2 (tail) engine, which caused total hydraulic system
Hydraulics (from Greek language, Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is th ...
failure. The crew flew the aircraft with throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle'' ...
only. Suppressing the phugoid tendency was particularly difficult. The pilots reached Sioux Gateway Airport
Sioux Gateway Airport , also known as Colonel Bud Day Field, is a public and military use airport in Woodbury County, Iowa, United States. It is located six nautical miles (7 mi, 11 km) south of the central business district of Sioux ...
but crashed during the landing attempt. All four cockpit crewmembers (one an assisting DC-10 captain on the flight as a passenger) and a majority of the passengers survived.
Another aircraft that lost all hydraulics and experienced phugoid was a DHL operated Airbus A300B4
The Airbus A300 is a wide-body airliner developed and manufactured by Airbus.
In September 1967, aircraft manufacturers in the United Kingdom, France, and West Germany signed a memorandum of understanding to develop a large airliner.
West G ...
that was hit by a surface-to-air missile
A surface-to-air missile (SAM), also known as a ground-to-air missile (GTAM) or surface-to-air guided weapon (SAGW), is a missile designed to be launched from the ground to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-aircraft syst ...
fired by the Iraqi resistance in the 2003 Baghdad DHL attempted shootdown incident. This was the first time that a crew landed an air transport aircraft safely by only adjusting engine thrust.
The 2003 crash of the Helios solar-powered aircraft was precipitated by reacting to an inappropriately diagnosed phugoid oscillation that ultimately made the aircraft structure exceed design loads.
Chesley "Sully" Sullenberger, Captain of US Airways Flight 1549
US Airways Flight 1549 was a regularly scheduled US Airways flight from New York City (LaGuardia Airport), to Charlotte, North Carolina, Charlotte and Seattle, in the United States. On January 15, 2009, the Airbus A320 serving the flight bir ...
that ditched
In aviation, a water landing is, in the broadest sense, an Landing, aircraft landing on a body of water. Seaplanes, such as floatplanes and flying boats, land on water as a normal operation. Ditching is a controlled emergency landing on the ...
in the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between N ...
on January 15, 2009, said in a Google talk that the landing could have been less violent had the anti-phugoid software installed on the Airbus A320-214
The Airbus A320 family is a series of narrow-body airliners developed and produced by Airbus.
The A320 was launched in March 1984, first flew on 22 February 1987, and was introduced in April 1988 by Air France.
The first member of the famil ...
not prevented him from manually getting maximum lift during the four seconds before water impact.Sully Sullenberger: "Making a Difference" Talks at Google, 2012, (40:23) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cKuw49KBywA
See also
*Maneuvering Characteristics Augmentation System
The Maneuvering Characteristics Augmentation System (MCAS) is a flight stabilizing feature developed by Boeing that became notorious for its role in two fatal accidents of the 737 MAX, which killed all 346 passengers and crew among both flights ...
References
{{ReflistExternal links
Analysis of phugoid motion
Aerodynamics Flight control systems