Phonotypic Alphabet on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


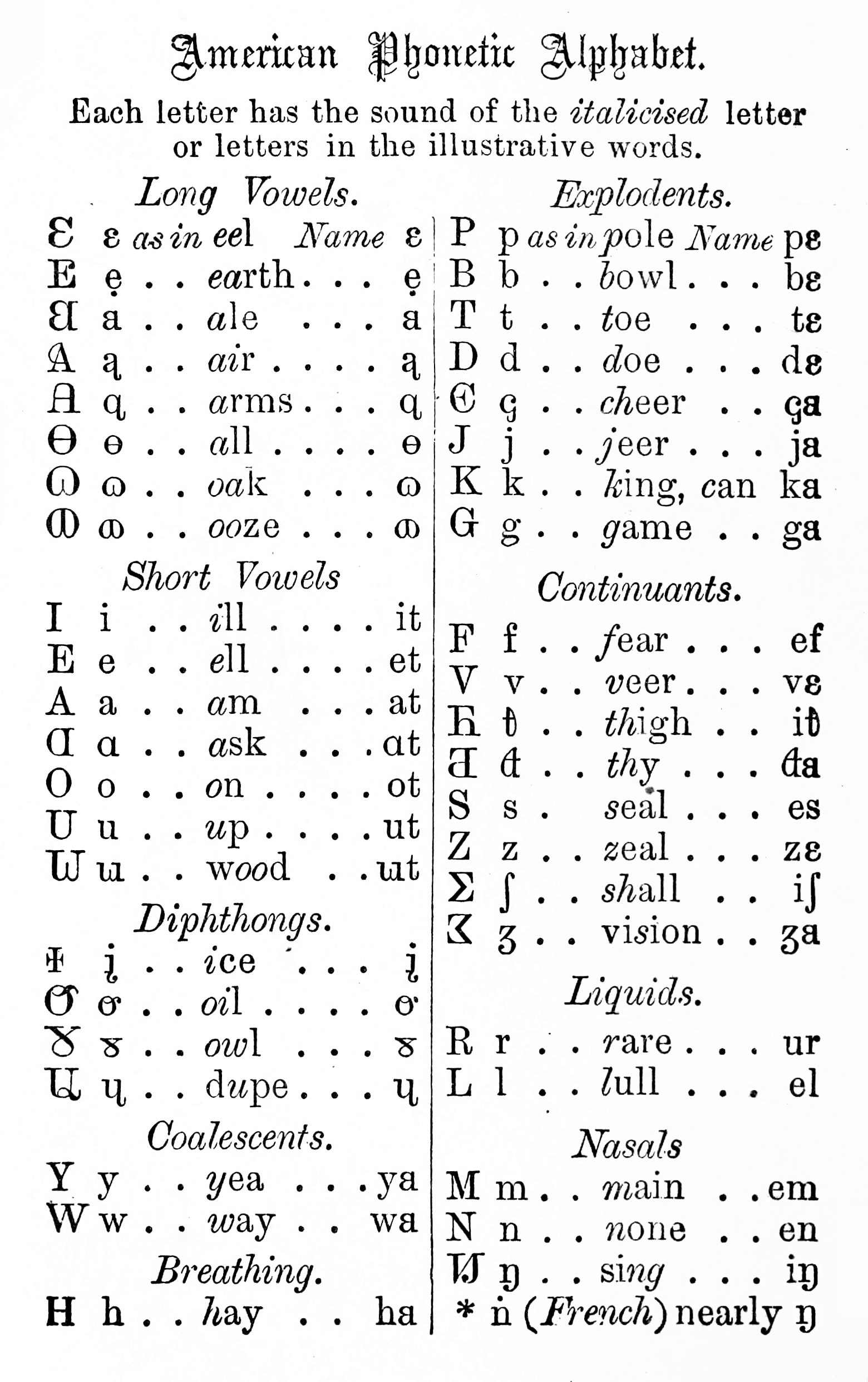
 The English Phonotypic Alphabet is a phonetic alphabet developed by Sir Isaac Pitman and
The English Phonotypic Alphabet is a phonetic alphabet developed by Sir Isaac Pitman and
Third Revised Proposal to encode characters for the English Phonotypic Alphabet (EPA) in the UCS, October 18th 2011">Third Revised Proposal to encode characters for the English Phonotypic Alphabet (EPA) in the UCS, October 18th 2011
Completion of the Phonotypic Alphabet
Extension of the Phonotypic Alphabet
1845 introductions Writing systems introduced in the 19th century Phonics Phonetic alphabets English spelling reform Reading (process)



 The English Phonotypic Alphabet is a phonetic alphabet developed by Sir Isaac Pitman and
The English Phonotypic Alphabet is a phonetic alphabet developed by Sir Isaac Pitman and Alexander John Ellis
Alexander John Ellis, (14 June 1814 – 28 October 1890), was an English mathematician, philologist and early phonetician who also influenced the field of musicology. He changed his name from his father's name, Sharpe, to his mother's maiden na ...
originally as an English language spelling reform. Although never gaining wide acceptance, elements of it were incorporated into the modern International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic transcription, phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standa ...
.
It was originally published in June 1845. Subsequently, adaptations were published which extended the alphabet to the German, Arabic, Spanish, Tuscan, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
, Italian, Dutch, Polish, Portuguese and Sanskrit languages.''Extension of the Phonotypic Alphabet'', The Phonotypic Journal, 5 Nelson Place, Bath, Phonographic Institution, vol. 4, no 43, June 1845, p. 121–123
Letters
The letters are as follows (with some approximations to accommodate Unicode)Late 1843 (English)
At this stage, long vowels had a cross-bar, and short vowels did not ;Long vowels Ɨ /iː/, E /eɪ/, A /ɑː/, Ɵ /ɔː/, Ʉ /oʊ/?, ꭐ-bar /uː/ ;Short vowels I /ɪ/, ⵎ /ɛ/, Ʌ /æ/, O /ɒ/, U /ʌ/, ꭐ /ʊ/ (a proper was taller and without the dot, like but with the middle stem not so tall as the others, and did not have a serif at the bottom right) ;Diphthongs Ɯ /juː/, ⅄ /aɪ/, Ȣ /aʊ/? ;Reduced ('obscure') vowels Ǝ /ə/, ⵎ /ᵊ/ ;Consonants P B, T D, Є J /tʃ dʒ/, K G F V, Θ Δ /θ ð/, S Z, Σ Σ /ʃ ʒ/, L R, M N, И /ŋ/, Y W H. :_a /eɪ/ :(Ā)ᶐ /ɑː/ :Ɵɵ /ɔː/ :_ɷ /oʊ/ :Ɯɯ /uː/ :Ii /ɪ/ :Ee /ɛ/ :Aɑ /æ/ :Oo /ɒ/ :Uu /ʌ/ :_(ꭐ) :_ᶙ /juː/ :Yy /j/ :Ww /w/ :Hh /h/ :Pp /p/ :Bb /b/ :Tt /t/ :Dd /d/ :Єꞔ /tʃ/ :Jj /dʒ/ :Cc /k/ :Gg /ɡ/ :Ff /f/ :Vv /v/ :Ꞁ(ⱦ) /θ/ :Ƌ(đ) /ð/ :Ss /s/ :Zz /z/ :Σʃ /ʃ/ :(Ʒ)ʒ /ʒ/ :Rr /r/ :Ll /l/ :Mm /m/ :Nn /n/ :(Ŋ)ŋ /ŋ/References
{{reflistSee also
* The Phonetic JournalExternal links
Third Revised Proposal to encode characters for the English Phonotypic Alphabet (EPA) in the UCS, October 18th 2011">Third Revised Proposal to encode characters for the English Phonotypic Alphabet (EPA) in the UCS, October 18th 2011
Completion of the Phonotypic Alphabet
Extension of the Phonotypic Alphabet
1845 introductions Writing systems introduced in the 19th century Phonics Phonetic alphabets English spelling reform Reading (process)