Pharr Mounds on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pharr Mounds is a
Pharr Mounds on Flickr
Archaeology of prehistoric native America: an encyclopedia
{{Protected Areas of Mississippi Archaeological sites on the National Register of Historic Places in Mississippi Miller culture Mounds in Mississippi National Register of Historic Places in Itawamba County, Mississippi National Register of Historic Places in Prentiss County, Mississippi Protected areas of Itawamba County, Mississippi Protected areas of Mississippi Protected areas of Prentiss County, Mississippi
Middle Woodland period
In the classification of archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 BCE to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeolog ...
archaeological site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology an ...
located near Tupelo
Tupelo , genus ''Nyssa'' , is a small genus of deciduous trees with alternate, simple leaves. It is sometimes included in the subfamily Nyssoideae of the dogwood family, Cornaceae, but is placed by other authorities in the family Nyssaceae. In ...
in parts of Itawamba
Levi Colbert (1759–1834), also known as ''Itawamba'' in Chickasaw, was a leader and chief of the Chickasaw nation. Colbert was called ''Itte-wamba Mingo'', meaning ''bench chief''. He and his brother George Colbert were prominent interpreters ...
and Prentiss counties in northern Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
. This complex was made of earthwork mounds.
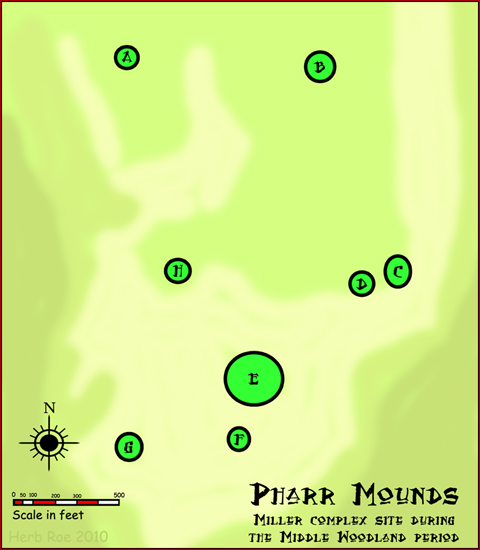
The complex of eight dome-shaped, tumulus burial mounds
A tumulus (plural tumuli) is a mound of Soil, earth and Rock (geology), stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a ...
was in use during the Miller 1 phase of the Miller culture. These were constructed as earthwork mounds between 1 and 200 CE. The complex is considered to be one of the largest and most important sites from this era. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978 as part of the Natchez Trace Parkway
The Natchez Trace Parkway is a national parkway in the southeastern United States that commemorates the historic Natchez Trace and preserves sections of that original trail. Its central feature is a two-lane road that extends 444 miles (715 ...
at milepost 286.7.
Site description
The site is located at the headwaters of theTombigbee River
The Tombigbee River is a tributary of the Mobile River, approximately 200 mi (325 km) long, in the U.S. states of Mississippi and Alabama. Together with the Alabama, it merges to form the short Mobile River before the latter empties int ...
, a rugged, hilly area with many broad, swampy streams. It is named for "Pharr Flats", a wide, gently rolling terrace overlooking the confluence of Little Brown and Mackeys creeks. The site features eight dome-shaped mounds of differing sizes, several of which have been nearly flattened by plowing and cultivation during European-American farming. The mounds in the Pharr Mounds site are found over an area of 90 acres of land.

Archaeology
In 1966 Charles Bohannon, an archaeologist for theNational Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational propertie ...
, supervisedExcavation at the Pharr Mounds, US Department of Interior. July, 1972 an excavation of four of the mounds. The excavators found fire pits and low clay platforms at the base of the mounds. They also found human remains, some cremated, as well as various ceremonial artifacts.
Many of the artifacts were made from non-local materials, such as Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
copper and greenstone, galena
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver.
Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It cryst ...
, and mica
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into extremely thin elastic plates. This characteristic is described as perfect basal cleavage. Mica is ...
, demonstrating the reach of trading through the Hopewell exchange system
The Hopewell tradition, also called the Hopewell culture and Hopewellian exchange, describes a network of precontact Native American cultures that flourished in settlements along rivers in the northeastern and midwestern Eastern Woodlands from ...
. These artifacts, which include copper ear-spool
A plug (sometimes earplug or earspool), in the context of body modification, is a short, cylindrical piece of jewelry commonly worn in larger-gauge body piercings. Modern western plugs are also called flesh tunnels. Because of their size—which ...
s and a greenstone platform pipe, show the connection of the local peoples with the larger Middle Woodland period world of the time, reaching to the Great Lakes.
See also
* Bynum Mound and Village Site *Grand Gulf Mound
The Grand Gulf Mound (22CB522) is an Early Marksville culture archaeological site located near Port Gibson in Claiborne County, Mississippi, on a bluff east of the Mississippi River, north of the mouth of the Big Black River. The site has an e ...
* Woodland period
In the classification of :category:Archaeological cultures of North America, archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 Common Era, BCE to European con ...
References
External links
Pharr Mounds on Flickr
Archaeology of prehistoric native America: an encyclopedia
{{Protected Areas of Mississippi Archaeological sites on the National Register of Historic Places in Mississippi Miller culture Mounds in Mississippi National Register of Historic Places in Itawamba County, Mississippi National Register of Historic Places in Prentiss County, Mississippi Protected areas of Itawamba County, Mississippi Protected areas of Mississippi Protected areas of Prentiss County, Mississippi