Persian scale on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
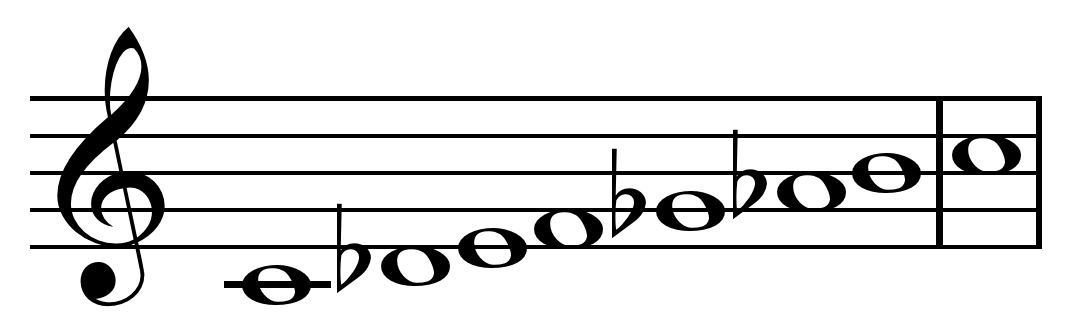 The Persian scale is a
The Persian scale is a
Persian Scale demonstrated for a Guitar
{{scales Heptatonic scales Hemitonic scales Tritonic scales Musical scales with augmented seconds
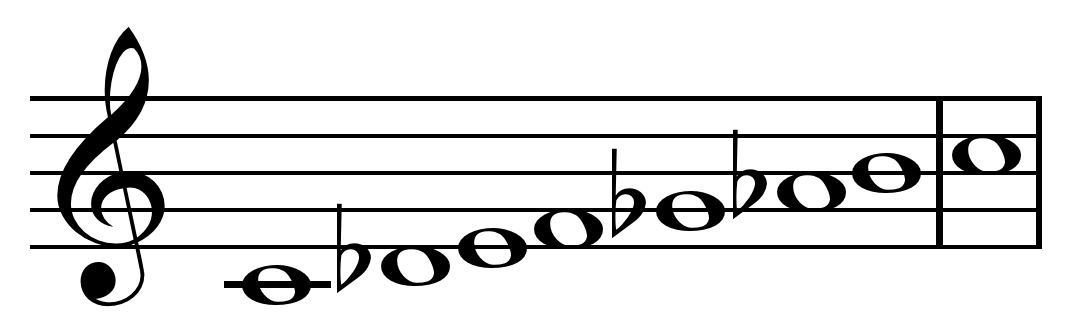 The Persian scale is a
The Persian scale is a musical scale
In music theory, a scale is any set of musical notes ordered by fundamental frequency or pitch. A scale ordered by increasing pitch is an ascending scale, and a scale ordered by decreasing pitch is a descending scale.
Often, especially in the ...
occasionally found in guitar scale books, along with other scales inspired by Middle Eastern music. It is characterized by the liberal use of half steps (4), augmented seconds (2), and frequent use of chromaticism
Chromaticism is a compositional technique interspersing the primary diatonic scale, diatonic pitch (music), pitches and chord (music), chords with other pitches of the chromatic scale. In simple terms, within each octave, diatonic music uses o ...
. Compare this to the one augmented second of the harmonic minor or the use of only two half-steps in all diatonic scales. This is also the Locrian mode The Locrian mode is the seventh mode of the major scale. It is either a musical mode or simply a diatonic scale. On the piano, it is the scale that starts with B and only uses the white keys from there. Its ascending form consists of the key note, ...
with a major third
In classical music, a third is a musical interval encompassing three staff positions (see Interval number for more details), and the major third () is a third spanning four semitones. Forte, Allen (1979). ''Tonal Harmony in Concept and P ...
and major seventh
In music from Western culture, a seventh is a musical interval encompassing seven staff positions (see Interval number for more details), and the major seventh is one of two commonly occurring sevenths. It is qualified as ''major'' because it i ...
degree.
In Hindustani Classical Music
Hindustani classical music is the classical music of northern regions of the Indian subcontinent. It may also be called North Indian classical music or, in Hindustani, ''shastriya sangeet'' (). It is played in instruments like the violin, sita ...
, this corresponds to the raga
A ''raga'' or ''raag'' (; also ''raaga'' or ''ragam''; ) is a melodic framework for improvisation in Indian classical music akin to a musical mode, melodic mode. The ''rāga'' is a unique and central feature of the classical Indian music tradit ...
Lalit.
The sequence of steps is as follows:
*H, WH, H, H, W, WH, H
*(W = Whole step - H = Half step)
Beginning on C:
*C, D♭, E, F, G♭, A♭, B, C
Modes
This rather unusual scale contains the followingmodes
Mode ( la, modus meaning "manner, tune, measure, due measure, rhythm, melody") may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* '' MO''D''E (magazine)'', a defunct U.S. women's fashion magazine
* ''Mode'' magazine, a fictional fashion magazine which is ...
, with rather debatable names: '
:
See also
*It is most closely related to thePhrygian dominant scale
In music, the Phrygian dominant scale is the fifth musical mode, mode of the minor scale#Harmonic and melodic minor, harmonic minor scale, the fifth being the dominant (music), dominant.Dave Hunter (2005). ''Play Acoustic'', San Francisco: Backbe ...
as their bottom tetrachords are identical.Stetina, Troy (1999). ''The Ultimate Scale Book'', p.61. . It can also be obtained by flattening the fifth degree of the double harmonic scale
In music, the double harmonic major scaleStetina, Troy (1999). ''The Ultimate Scale Book'', p. 59. . is a scale whose gaps may sound unfamiliar to Western listeners. This is also known as Mayamalavagowla, Bhairav Raga, Byzantine scale, Arabic (Hi ...
.
Sources
Further reading
*Hewitt, Michael. ''Musical Scales of the World''. The Note Tree. 2013. .External links
Persian Scale demonstrated for a Guitar
{{scales Heptatonic scales Hemitonic scales Tritonic scales Musical scales with augmented seconds