Perseverance (rover) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Perseverance'', nicknamed ''Percy'', is a car-sized Mars rover designed to explore the Jezero crater on Mars as part of
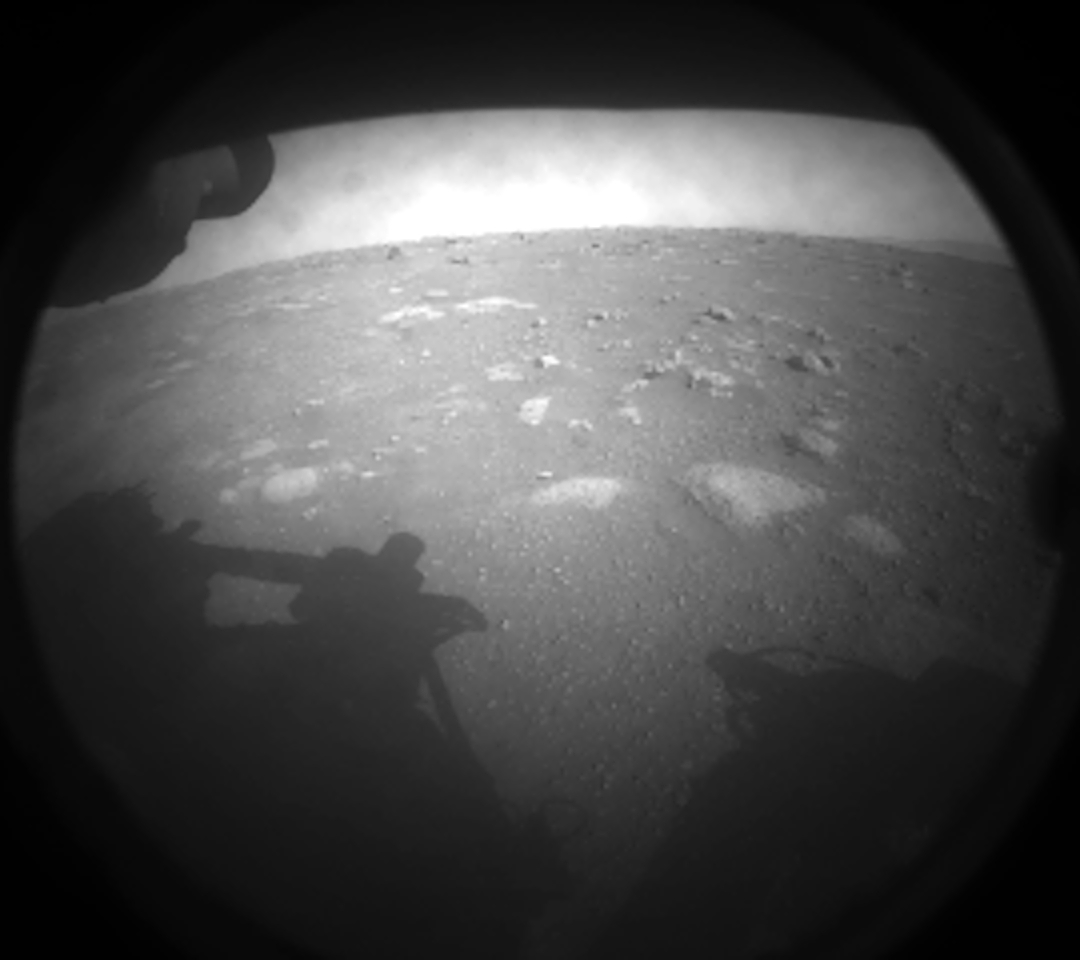 Despite the high-profile success of the ''Curiosity'' rover landing in August 2012, NASA's Mars Exploration Program was in a state of uncertainty in the early 2010s. Budget cuts forced NASA to pull out of a planned collaboration with the European Space Agency which included a rover mission. By the summer of 2012, a program that had been launching a mission to Mars every two years suddenly found itself with no missions approved after 2013.
In 2011, the Planetary Science Decadal Survey, a report from the
Despite the high-profile success of the ''Curiosity'' rover landing in August 2012, NASA's Mars Exploration Program was in a state of uncertainty in the early 2010s. Budget cuts forced NASA to pull out of a planned collaboration with the European Space Agency which included a rover mission. By the summer of 2012, a program that had been launching a mission to Mars every two years suddenly found itself with no missions approved after 2013.
In 2011, the Planetary Science Decadal Survey, a report from the
 The ''Perseverance'' design evolved from its predecessor, the ''Curiosity'' rover. The two rovers share a similar body plan, landing system, cruise stage, and power system, but the design was improved in several ways for ''Perseverance''. Engineers designed the rover wheels to be more robust than ''Curiosity'' wheels, which have sustained some damage. ''Perseverance'' has thicker, more durable
The ''Perseverance'' design evolved from its predecessor, the ''Curiosity'' rover. The two rovers share a similar body plan, landing system, cruise stage, and power system, but the design was improved in several ways for ''Perseverance''. Engineers designed the rover wheels to be more robust than ''Curiosity'' wheels, which have sustained some damage. ''Perseverance'' has thicker, more durable  The combination of larger instruments, new sampling and caching system, and modified wheels makes ''Perseverance'' heavier, weighing compared to ''Curiosity'' at —a 14% increase.
The rover's radioisotope thermoelectric power generator (
The combination of larger instruments, new sampling and caching system, and modified wheels makes ''Perseverance'' heavier, weighing compared to ''Curiosity'' at —a 14% increase.
The rover's radioisotope thermoelectric power generator (
 Associate Administrator of
Associate Administrator of
"Astrobiologist Kennda Lynch Uses Analogs on Earth to Find Life on Mars"
. ''NASA''. Retrieved 2021-03-02.Daines, Gary (August 14, 2020)
"Season 4, Episode 15 Looking For Life in Ancient Lakes".
''Gravity Assist.'' NASA. Podcast. Retrieved 2021-03-02. It was selected as the landing site for this mission in part because paleolake basins tend to contain perchlorates. Astrobiologist Dr. Kennda Lynch's work in analog environments on Earth suggests that the composition of the crater, including the bottomset deposits accumulated from three different sources in the area, is a likely place to discover evidence of perchlorates-reducing microbes, if such bacteria are living or were formerly living on Mars. A few days after landing, ''Perseverance'' released the first audio recorded on the surface of Mars, capturing the sound of Martian wind During its travels on Mars, NASA scientists had observed around Sol 341 (February 4, 2022) that a small rock had dropped into one of its wheels while the rover was studying the Máaz rock formation. The rock was visible from one of the hazard avoidance cameras, and was determined not to be harmful to the rover's mission. The rock has since stayed on ''Perseverance''s wheels for at least 123 sols (126 days) as the rover traveled over on the surface. NASA deemed that ''Perseverance'' had adopted a pet rock for its journey.
NASA photogallery
(Including Raw) * Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman and Luminescence for Organics and Chemicals (SHERLOC), an ultraviolet
Learn About the Rover
 It is planned for ''Perseverance'' to visit the bottom and upper parts of the 3.4 to 3.8 billion-year-old Neretva Vallis delta, the smooth and etched parts of the Jezero Crater floor deposits interpreted as volcanic ash or aeolian airfall deposits, emplaced before the formation of the delta; the ancient shoreline covered with Transverse Aeolian Ridges (dunes) and mass wasting deposits, and finally, it is planned to climb onto the Jezero Crater rim.
In its progressive commissioning and tests, ''Perseverance'' made its first test drive on Mars on March 4, 2021. NASA released photographs of the rover's first wheel tracks on the Martian soil.
It is planned for ''Perseverance'' to visit the bottom and upper parts of the 3.4 to 3.8 billion-year-old Neretva Vallis delta, the smooth and etched parts of the Jezero Crater floor deposits interpreted as volcanic ash or aeolian airfall deposits, emplaced before the formation of the delta; the ancient shoreline covered with Transverse Aeolian Ridges (dunes) and mass wasting deposits, and finally, it is planned to climb onto the Jezero Crater rim.
In its progressive commissioning and tests, ''Perseverance'' made its first test drive on Mars on March 4, 2021. NASA released photographs of the rover's first wheel tracks on the Martian soil.

 In support of the Mars sample-return mission, rock, regolith ( Martian 'soil'), and atmosphere samples are being cached by ''Perseverance''. Currently, out of 43 sample tubes, rock sample tubes cached: 15, rock sample tubes cached: 2, atmosphere sample tubes cached: 1, witness tubes cached: 3, tubes due to be cached: 22. Before launch, 5 of the 43 tubes were designated “witness tubes” and filled with materials that would capture particulates in the ambient environment of Mars.
In support of the Mars sample-return mission, rock, regolith ( Martian 'soil'), and atmosphere samples are being cached by ''Perseverance''. Currently, out of 43 sample tubes, rock sample tubes cached: 15, rock sample tubes cached: 2, atmosphere sample tubes cached: 1, witness tubes cached: 3, tubes due to be cached: 22. Before launch, 5 of the 43 tubes were designated “witness tubes” and filled with materials that would capture particulates in the ambient environment of Mars.
 Part of ''Perseverance''s cargo is a geocaching trackable item viewable with the SHERLOC's WATSON camera.
In 2016, NASA SHERLOC co-investigator Dr. Marc Fries — with help from his son Wyatt — was inspired by Geocaching's 2008 placement of a cache on the International Space Station to set out and try something similar with the rover mission. After floating the idea around mission management, it eventually reached NASA scientist Francis McCubbin, who would join the SHERLOC instrument team as a collaborator to move the project forward. The Geocaching inclusion was scaled-down to a trackable item that players could search for from NASA camera views and then log on to the site. In a manner similar to the "Send Your Name to Mars" campaign, the geocaching trackable code was carefully printed on a one-inch, polycarbonate glass disk serving as part of the rover's calibration target. It will serve as an optical target for the WATSON imager and a spectroscopic standard for the SHERLOC instrument. The disk is made of a prototype astronaut helmet visor material that will be tested for its potential use in crewed missions to Mars. Designs were approved by the mission leads at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), NASA Public Affairs, and NASA HQ, in addition to Groundspeak Geocaching HQ.
Part of ''Perseverance''s cargo is a geocaching trackable item viewable with the SHERLOC's WATSON camera.
In 2016, NASA SHERLOC co-investigator Dr. Marc Fries — with help from his son Wyatt — was inspired by Geocaching's 2008 placement of a cache on the International Space Station to set out and try something similar with the rover mission. After floating the idea around mission management, it eventually reached NASA scientist Francis McCubbin, who would join the SHERLOC instrument team as a collaborator to move the project forward. The Geocaching inclusion was scaled-down to a trackable item that players could search for from NASA camera views and then log on to the site. In a manner similar to the "Send Your Name to Mars" campaign, the geocaching trackable code was carefully printed on a one-inch, polycarbonate glass disk serving as part of the rover's calibration target. It will serve as an optical target for the WATSON imager and a spectroscopic standard for the SHERLOC instrument. The disk is made of a prototype astronaut helmet visor material that will be tested for its potential use in crewed missions to Mars. Designs were approved by the mission leads at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), NASA Public Affairs, and NASA HQ, in addition to Groundspeak Geocaching HQ.
 ''Perseverance'' launched during the
''Perseverance'' launched during the
 The orange-and-white parachute used to land the rover on Mars contained a coded message that was deciphered by Twitter users. NASA's systems engineer Ian Clark used binary code to hide the message "dare mighty things" in the parachute color pattern. The parachute consisted of 80 strips of fabric that form a hemisphere-shape canopy, and each strip consisted of four pieces. Dr. Clark thus had 320 pieces with which to encode the message. He also included the
The orange-and-white parachute used to land the rover on Mars contained a coded message that was deciphered by Twitter users. NASA's systems engineer Ian Clark used binary code to hide the message "dare mighty things" in the parachute color pattern. The parachute consisted of 80 strips of fabric that form a hemisphere-shape canopy, and each strip consisted of four pieces. Dr. Clark thus had 320 pieces with which to encode the message. He also included the
Mars 2020 and ''Perseverance'' rover
official site at
Mars 2020: Landing of rover (3:55pm/et/usa, 18 February 2021
Mars 2020 ''Perseverance'' Launch Press Kit
Video: Mars ''Perseverance'' rover/''Ingenuity'' helicopter report(9 May 2021; CBS-TV, ''60 Minutes''; 13:33)
Official archive of all raw images taken by the rover's and helicopter's cameras
Official archive of all Mastcam-Z images in two different calibrations
Nonofficial archive of daily color-calibrated images taken by the rover's Navcam, Hazcam, Watson cam and the helicopter's RTE camera
{{Portal bar, Astronomy, Outer space, Spaceflight Individual space vehicles Jet Propulsion Laboratory Mars rovers * NASA space probes Robots of the United States Six-wheeled robots Space probes launched in 2020 2020 in the United States 2020 robots 2021 on Mars Articles containing video clips Mars robots
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedi ...
's Mars 2020 mission. It was manufactured by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and launched on July 30, 2020, at 11:50 UTC. Confirmation that the rover successfully landed on Mars was received on February 18, 2021, at 20:55 UTC. As of , ''Perseverance'' has been active on Mars for sols ( Earth days, or ) since its landing. Following the rover's arrival, NASA named the landing site Octavia E. Butler Landing
Octavia E. Butler Landing is the February 18, 2021, landing site of the Mars 2020 Perseverance (rover), ''Perseverance'' rover within Jezero (crater), Jezero crater on planet Mars. On March 5, 2021, NASA named the site for the renowned America ...
.
''Perseverance'' has a similar design to its predecessor rover, '' Curiosity'', although it was moderately upgraded. It carries seven primary payload instruments, nineteen cameras, and two microphones.
The rover also carried the mini-helicopter '' Ingenuity'' to Mars, an experimental aircraft and technology testbed that made the first powered flight on another planet on April 19, 2021. As of December 22, 2022, it has made 37 successful flights. ''Ingenuitys 25th successful flight, which occurred on April 8, 2022, saw the helicopter set new records for highest speed and distance traveled during a single flight.
The rover's goals include identifying ancient Martian environments capable of supporting life, seeking out evidence of former microbial life existing in those environments, collecting rock and soil samples to store on the Martian surface, and testing oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
production from the Martian atmosphere to prepare for future crewed missions.
Mission
Science objectives
The ''Perseverance'' rover has four main science objectives that support the Mars Exploration Program's science goals: * Looking for habitability: identify past environments that were capable of supporting microbial life. * Seeking biosignatures: seek signs of possible past microbial life in those habitable environments, particularly in specific rock types known to preserve signs over time. * Caching samples: collect core rock and regolith ("soil") samples and store them on the Martian surface. * Preparing for humans: testoxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
production from the Martian atmosphere.
In the first science campaign ''Perseverance'' performs an arching drive southward from its landing site to the Séítah unit to perform a "toe dip" into the unit to collect remote-sensing measurements of geologic targets. After that it will return to the Crater Floor Fractured Rough to collect the first core sample there. Passing by the Octavia E. Butler landing site concludes the first science campaign.
The second campaign will include several months of travel towards the "Three Forks" where ''Perseverance'' can access geologic locations at the base of the ancient delta of Neretva river, as well as ascend the delta by driving up a valley wall to the northwest.
History
 Despite the high-profile success of the ''Curiosity'' rover landing in August 2012, NASA's Mars Exploration Program was in a state of uncertainty in the early 2010s. Budget cuts forced NASA to pull out of a planned collaboration with the European Space Agency which included a rover mission. By the summer of 2012, a program that had been launching a mission to Mars every two years suddenly found itself with no missions approved after 2013.
In 2011, the Planetary Science Decadal Survey, a report from the
Despite the high-profile success of the ''Curiosity'' rover landing in August 2012, NASA's Mars Exploration Program was in a state of uncertainty in the early 2010s. Budget cuts forced NASA to pull out of a planned collaboration with the European Space Agency which included a rover mission. By the summer of 2012, a program that had been launching a mission to Mars every two years suddenly found itself with no missions approved after 2013.
In 2011, the Planetary Science Decadal Survey, a report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine
The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (also known as NASEM or the National Academies) are the collective scientific national academy of the United States. The name is used interchangeably in two senses: (1) as an umbrell ...
containing an influential set of recommendations made by the planetary science community, stated that the top priority of NASA's planetary exploration program in the decade between 2013 and 2022 should be to begin a Mars Sample Return campaign, a four-mission project to cache, retrieve, launch, and safely return samples of the Martian surface to Earth. The report stated that NASA should invest in a sample-caching rover as the first step in this effort, with the goal of keeping costs under US$2.5 billion.
After the success of the ''Curiosity'' rover and in response to the recommendations of the decadal survey, NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedi ...
announced its intent to launch a new Mars rover mission by 2020 at the American Geophysical Union
The American Geophysical Union (AGU) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization of Earth, atmospheric, ocean, hydrologic, space, and planetary scientists and enthusiasts that according to their website includes 130,000 people (not members). AGU's ...
conference in December 2012.
Though initially hesitant to commit to an ambitious sample-caching capability (and subsequent follow-on missions), a NASA-convened science definition team for the Mars 2020 project released a report in July 2013 that the mission should "select and store a compelling suite of samples in a returnable cache."
Design
 The ''Perseverance'' design evolved from its predecessor, the ''Curiosity'' rover. The two rovers share a similar body plan, landing system, cruise stage, and power system, but the design was improved in several ways for ''Perseverance''. Engineers designed the rover wheels to be more robust than ''Curiosity'' wheels, which have sustained some damage. ''Perseverance'' has thicker, more durable
The ''Perseverance'' design evolved from its predecessor, the ''Curiosity'' rover. The two rovers share a similar body plan, landing system, cruise stage, and power system, but the design was improved in several ways for ''Perseverance''. Engineers designed the rover wheels to be more robust than ''Curiosity'' wheels, which have sustained some damage. ''Perseverance'' has thicker, more durable aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It h ...
wheels, with reduced width and a greater diameter, , than ''Curiosity'' wheels. The aluminum wheels are covered with cleats for traction and curved titanium spokes for springy support. The heat shield
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is al ...
for the rover was made out of phenolic-impregnated carbon ablator
Atmospheric entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: ''uncontrolled entry'', such as the entr ...
(PICA), to allow it to withstand up to of heat. Like ''Curiosity'', the rover includes a robotic arm, although ''Perseverance''s arm is longer and stronger, measuring . The arm hosts an elaborate rock-coring and sampling mechanism to store geologic samples from the Martian surface in sterile
Sterile or sterility may refer to:
*Asepsis, a state of being free from biological contaminants
* Sterile (archaeology), a sediment deposit which contains no evidence of human activity
*Sterilization (microbiology), any process that eliminates or ...
caching tubes. There is also a secondary arm hidden below the rover that helps store the chalk-sized samples. This arm is known as the Sample Handling Assembly (SHA), and is responsible for moving the soil samples to various stations within the Adaptive Caching Assembly (ACA) on the underside of the rover. These stations include volume assessment (measuring the length of sample), imaging, seal dispensing, and hermetic seal station, among others. Owing to the small space in which the SHA must operate, as well as load requirements during sealing activities, the Sample Caching System "is the most complicated, most sophisticated mechanism that we have ever built, tested and readied for spaceflight."
 The combination of larger instruments, new sampling and caching system, and modified wheels makes ''Perseverance'' heavier, weighing compared to ''Curiosity'' at —a 14% increase.
The rover's radioisotope thermoelectric power generator (
The combination of larger instruments, new sampling and caching system, and modified wheels makes ''Perseverance'' heavier, weighing compared to ''Curiosity'' at —a 14% increase.
The rover's radioisotope thermoelectric power generator (MMRTG
The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) is a type of radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) developed for NASA space missions such as the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL), under the jurisdiction of the United States Depar ...
) has a mass of and uses of Plutonium-238 oxide as its power source. The natural decay of plutonium-238, which has a half-life of 87.7 years, gives off heat which is converted to electricity—approximately 110 watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Wa ...
s at launch. This will decrease over time as its power source decays. The MMRTG charges two lithium-ion rechargeable batteries which power the rover's activities, and must be recharged periodically. Unlike solar panels, the MMRTG provides engineers with significant flexibility in operating the rover's instruments even at night, during dust storms, and through winter.
The rover's computer uses the BAE Systems RAD750 radiation-hardened single board computer based on a ruggedized PowerPC G3 microprocessor (PowerPC 750). The computer contains 128 megabytes of volatile DRAM, and runs at 133 MHz. The flight software runs on the VxWorks Operating System, is written in C and is able to access 4 gigabytes of NAND non-volatile memory on a separate card. ''Perseverance'' relies on three antennas for telemetry, all of which are relayed through craft currently in orbit around Mars. The primary UHF
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter (on ...
antenna can send data from the rover at a maximum rate of two megabits per second. Two slower X-band antennas provide communications redundancy.
Twin rover
JPL built a copy of the ''Perseverance''; a twin rover used for testing and problem solving, ''OPTIMISM'' (Operational Perseverance Twin for Integration of Mechanisms and Instruments Sent to Mars), a vehicle system test bed (VSTB). It is housed at the JPLMars Yard
''Sojourner'' is a robotic Mars rover that landed in the Ares Vallis channel in the Chryse Planitia region of the Oxia Palus quadrangle on July 4, 1997. ''Sojourner'' was operational on Mars for 92 sols (95 Earth days). It was the first whee ...
and is used to test operational procedures and to aid in problem solving should any issues arise with ''Perseverance''.
Mars ''Ingenuity'' helicopter experiment
The ''Ingenuity'' helicopter, powered by solar-charged batteries, was sent to Mars in the same bundle with ''Perseverance''. With a mass of , it demonstrated the reality of flight in the rarefied Martian atmosphere and the potential usefulness of aerial scouting for rover missions. Its pre-launch experimental test plan was 3 flights in 45 days. As of August 31, 2022, it has made 30 successful flights. ''Ingenuitys 25th successful flight, which occurred on April 8, 2022, saw the helicopter set new records for highest speed and distance traveled during a single flight. It carries two cameras but no scientific instruments and communicates with Earth via a base station onboard ''Perseverance''. The first takeoff was attempted on April 19, 2021, at 07:15 UTC, withlivestreaming
Livestreaming is streaming media simultaneously recorded and broadcast in real-time over the internet. It is often referred to simply as streaming. Non-live media such as video-on-demand, vlogs, and YouTube videos are technically streamed, but no ...
three hours later at 10:15 UTC confirming the flight. It was the first powered flight by an aircraft on another planet. ''Ingenuity'' made additional incrementally more ambitious flights, several of which were recorded by ''Perseverance''s cameras.
Name
 Associate Administrator of
Associate Administrator of NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedi ...
's Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen selected the name ''Perseverance'' following a nationwide K-12
K-1 is a professional kickboxing promotion established in 1993, well known worldwide mainly for its heavyweight division fights and Grand Prix tournaments. In January 2012, K-1 Global Holdings Limited, a company registered in Hong Kong, acquired ...
student "name the rover" contest that attracted more than 28,000 proposals. A seventh-grade student, Alexander Mather from Lake Braddock Secondary School in Burke, Virginia, submitted the winning entry at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. In addition to the honor of naming the rover, Mather and his family were invited to NASA's Kennedy Space Center to watch the rover's July 2020 launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, a ...
.
Mather wrote in his winning essay:Curiosity. InSight. Spirit. Opportunity. If you think about it, all of these names of past Mars rovers are qualities we possess as humans. We are always curious, and seek opportunity. We have the spirit and insight to explore the Moon, Mars, and beyond. But, if rovers are to be the qualities of us as a race, we missed the most important thing. Perseverance. We as humans evolved as creatures who could learn to adapt to any situation, no matter how harsh. We are a species of explorers, and we will meet many setbacks on the way to Mars. However, we can persevere. We, not as a nation but as humans, will not give up. The human race will always persevere into the future.
Mars transit
The ''Perseverance'' rover lifted off successfully on July 30, 2020, at 11:50:00 UTC aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V launch vehicle fromSpace Launch Complex 41
Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41), previously Launch Complex 41 (LC-41), is an active launch site at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. As of 2020, the site is used by United Launch Alliance (ULA) for Atlas V launches. Previously, it had been use ...
, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, a ...
.
The rover took about seven months to travel to Mars and made its landing in Jezero Crater on February 18, 2021, to begin its science phase.
After May 17, 2022, the rover will roll uphill, stopping every so often to examine rocks that look to have the best chance of retaining evidence of past life on the planet Mars. On its way back down, ''Perseverance'' will collect some of these rocks, placing the samples at the base of the delta to be retrieved by later missions. The goal is to bring this material back to Earth in the 2030s for detailed inspection.
Landing
The successful landing of ''Perseverance'' in Jezero Crater was announced at 20:55 UTC on February 18, 2021, the signal from Mars taking 11 minutes to arrive at Earth. The rover touched down at , roughly southeast of the center of its 7.7 × 6.6 km (4.8 × 4.1 mi) wide landing ellipse. It came down pointed almost directly to the southeast, with the RTG on the back of the vehicle pointing northwest. The descent stage ("sky crane"), parachute and heat shield all came to rest within 1.5 km of the rover (see satellite image). The landing was more accurate than any previous Mars landing; a feat enabled by the experience gained from '' Curiosity''s landing and the use of new steering technology. One such new technology is Terrain Relative Navigation (TRN), a technique in which the rover compares images of the surface taken during its descent with reference maps, allowing it to make last minute adjustments to its course. The rover also uses the images to select a safe landing site at the last minute, allowing it to land in relatively unhazardous terrain. This enables it to land much closer to its science objectives than previous missions, which all had to use a landing ellipse devoid of hazards. The landing occurred in the late afternoon, with the first images taken at 15:53:58 on the mission clock (local mean solar time). The landing took place shortly after Mars passed through its northern vernal equinox ( Ls = 5.2°), at the start of the astronomical spring, the equivalent of the end of March on Earth. The parachute descent of the ''Perseverance'' rover was photographed by the HiRISE high-resolution camera on the '' Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (MRO). Jezero Crater is a paleolake basin.Smith, Yvette (February 2, 2021)"Astrobiologist Kennda Lynch Uses Analogs on Earth to Find Life on Mars"
. ''NASA''. Retrieved 2021-03-02.Daines, Gary (August 14, 2020)
"Season 4, Episode 15 Looking For Life in Ancient Lakes".
''Gravity Assist.'' NASA. Podcast. Retrieved 2021-03-02. It was selected as the landing site for this mission in part because paleolake basins tend to contain perchlorates. Astrobiologist Dr. Kennda Lynch's work in analog environments on Earth suggests that the composition of the crater, including the bottomset deposits accumulated from three different sources in the area, is a likely place to discover evidence of perchlorates-reducing microbes, if such bacteria are living or were formerly living on Mars. A few days after landing, ''Perseverance'' released the first audio recorded on the surface of Mars, capturing the sound of Martian wind During its travels on Mars, NASA scientists had observed around Sol 341 (February 4, 2022) that a small rock had dropped into one of its wheels while the rover was studying the Máaz rock formation. The rock was visible from one of the hazard avoidance cameras, and was determined not to be harmful to the rover's mission. The rock has since stayed on ''Perseverance''s wheels for at least 123 sols (126 days) as the rover traveled over on the surface. NASA deemed that ''Perseverance'' had adopted a pet rock for its journey.
Instruments
NASA considered nearly 60 proposals for rover instrumentation. On July 31, 2014, NASA announced the seven instruments that would make up the payload for the rover: * Mars Oxygen ISRU Experiment (MOXIE), an exploration technology investigation to produce a small amount ofoxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
() from Martian atmospheric carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
(). On April 20, 2021, 5.37 grams of oxygen were produced in an hour, with nine more extractions planned over the course of two Earth years to further investigate the instrument. This technology could be scaled up in the future for human life support or to make the rocket fuel for return missions.
* Planetary Instrument for X-Ray Lithochemistry
Planetary Instrument for X-Ray Lithochemistry (PIXL) is an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer to determine the fine scale elemental composition of Martian surface materials designed for the ''Perseverance'' rover as part of the Mars 2020 mission. ...
(PIXL), an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer
A spectrometer () is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the ...
to determine the fine scale elemental composition of Martian surface materials.
* Radar Imager for Mars' subsurface experiment (RIMFAX), a ground-penetrating radar to image different ground densities, structural layers, buried rocks, meteorites, and detect underground water ice and salty brine
Brine is a high-concentration Solution (chemistry), solution of salt (NaCl) in water (H2O). In diverse contexts, ''brine'' may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawater, on the lower end of that of ...
at depth. The RIMFAX is being provided by the Norwegian Defence Research Establishment
The Norwegian Defence Research Establishment (''Forsvarets forskningsinstitutt'' – ''FFI'') is a research institute that conducts research and development on behalf of the Norwegian Armed Forces and provides expert advice to political and mi ...
(FFI).
* Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer
The Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer (MEDA) is an instrument on board the Mars 2020 ''Perseverance (rover), Perseverance'' rover that will characterize the dust size and morphology, as well as surface weather.Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
's Centro de Astrobiología.
* SuperCam
SuperCam is a suite of remote-sensing instruments for the Mars 2020 ''Perseverance'' rover mission that performs remote analyses of rocks and soils with a camera, two lasers and four spectrometers to seek organic compounds that could hold biosigna ...
, an instrument suite that can provide imaging, chemical composition analysis, and mineralogy in rocks and regolith from a distance. It is an upgraded version of the ChemCam on the ''Curiosity'' rover but with two lasers and four spectrometers that will allow it to remotely identify biosignatures and assess the past habitability. SuperCam is used in conjucntion with the AEGIS targeting system. Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory (often shortened as Los Alamos and LANL) is one of the sixteen research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy (DOE), located a short distance northwest of Santa Fe, New Mexico, i ...
, the Research Institute in Astrophysics and Planetology ( IRAP) in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, the French Space Agency ( CNES), the University of Hawaii, and the University of Valladolid in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
cooperated in the SuperCam's development and manufacture.
* Mastcam-Z, a stereoscopic imaging system with the ability to zoom. Many photos were included in the publisheNASA photogallery
(Including Raw) * Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman and Luminescence for Organics and Chemicals (SHERLOC), an ultraviolet
Raman spectrometer
Raman spectroscopy () (named after Indian physicist C. V. Raman) is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman s ...
that uses fine-scale imaging and an ultraviolet (UV) laser to determine fine-scale mineralogy and detect organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon- hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. Th ...
s.
There are additional cameras and two audio microphones (the first working microphones on Mars), that will be used for engineering support during landing, driving, and collecting samples. For a full look at ''Perseverance''s components seLearn About the Rover
Traverse
 It is planned for ''Perseverance'' to visit the bottom and upper parts of the 3.4 to 3.8 billion-year-old Neretva Vallis delta, the smooth and etched parts of the Jezero Crater floor deposits interpreted as volcanic ash or aeolian airfall deposits, emplaced before the formation of the delta; the ancient shoreline covered with Transverse Aeolian Ridges (dunes) and mass wasting deposits, and finally, it is planned to climb onto the Jezero Crater rim.
In its progressive commissioning and tests, ''Perseverance'' made its first test drive on Mars on March 4, 2021. NASA released photographs of the rover's first wheel tracks on the Martian soil.
It is planned for ''Perseverance'' to visit the bottom and upper parts of the 3.4 to 3.8 billion-year-old Neretva Vallis delta, the smooth and etched parts of the Jezero Crater floor deposits interpreted as volcanic ash or aeolian airfall deposits, emplaced before the formation of the delta; the ancient shoreline covered with Transverse Aeolian Ridges (dunes) and mass wasting deposits, and finally, it is planned to climb onto the Jezero Crater rim.
In its progressive commissioning and tests, ''Perseverance'' made its first test drive on Mars on March 4, 2021. NASA released photographs of the rover's first wheel tracks on the Martian soil.

Samples cached for the Mars sample-return mission
 In support of the Mars sample-return mission, rock, regolith ( Martian 'soil'), and atmosphere samples are being cached by ''Perseverance''. Currently, out of 43 sample tubes, rock sample tubes cached: 15, rock sample tubes cached: 2, atmosphere sample tubes cached: 1, witness tubes cached: 3, tubes due to be cached: 22. Before launch, 5 of the 43 tubes were designated “witness tubes” and filled with materials that would capture particulates in the ambient environment of Mars.
In support of the Mars sample-return mission, rock, regolith ( Martian 'soil'), and atmosphere samples are being cached by ''Perseverance''. Currently, out of 43 sample tubes, rock sample tubes cached: 15, rock sample tubes cached: 2, atmosphere sample tubes cached: 1, witness tubes cached: 3, tubes due to be cached: 22. Before launch, 5 of the 43 tubes were designated “witness tubes” and filled with materials that would capture particulates in the ambient environment of Mars.
Cost
NASA plans to invest roughly US$2.75 billion in the project over 11 years, including US$2.2 billion for the development and building of the hardware, US$243 million for launch services, and US$291 million for 2.5 years of mission operations. Adjusted for inflation, ''Perseverance'' is NASA's sixth-most expensive robotic planetary mission, though it is cheaper than its predecessor, ''Curiosity''. ''Perseverance'' benefited from spare hardware and "build-to print" designs from the ''Curiosity'' mission, which helped reduce development costs and saved "probably tens of millions, if not 100 million dollars" according to Mars 2020 Deputy Chief Engineer Keith Comeaux.Commemorative artifacts
"Send Your Name to Mars"
NASA's "Send Your Name to Mars" campaign invited people from around the world to submit their names to travel aboard the agency's next rover to Mars. 10,932,295 names were submitted. The names were etched by an electron beam onto three fingernail-sized silicon chips, along with the essays of the 155 finalists in NASA's "Name the Rover" contest. The three chips share space on an anodized plate with a laser engraved graphic representing Earth, Mars, and the Sun. The rays emanating from the Sun contain the phrase "Explore As One" written inMorse code
Morse code is a method used in telecommunication to encode text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations, called ''dots'' and ''dashes'', or ''dits'' and ''dahs''. Morse code is named after Samuel Morse, one of ...
. The plate was then mounted on the rover on March 26, 2020.
Geocaching in Space Trackable
 Part of ''Perseverance''s cargo is a geocaching trackable item viewable with the SHERLOC's WATSON camera.
In 2016, NASA SHERLOC co-investigator Dr. Marc Fries — with help from his son Wyatt — was inspired by Geocaching's 2008 placement of a cache on the International Space Station to set out and try something similar with the rover mission. After floating the idea around mission management, it eventually reached NASA scientist Francis McCubbin, who would join the SHERLOC instrument team as a collaborator to move the project forward. The Geocaching inclusion was scaled-down to a trackable item that players could search for from NASA camera views and then log on to the site. In a manner similar to the "Send Your Name to Mars" campaign, the geocaching trackable code was carefully printed on a one-inch, polycarbonate glass disk serving as part of the rover's calibration target. It will serve as an optical target for the WATSON imager and a spectroscopic standard for the SHERLOC instrument. The disk is made of a prototype astronaut helmet visor material that will be tested for its potential use in crewed missions to Mars. Designs were approved by the mission leads at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), NASA Public Affairs, and NASA HQ, in addition to Groundspeak Geocaching HQ.
Part of ''Perseverance''s cargo is a geocaching trackable item viewable with the SHERLOC's WATSON camera.
In 2016, NASA SHERLOC co-investigator Dr. Marc Fries — with help from his son Wyatt — was inspired by Geocaching's 2008 placement of a cache on the International Space Station to set out and try something similar with the rover mission. After floating the idea around mission management, it eventually reached NASA scientist Francis McCubbin, who would join the SHERLOC instrument team as a collaborator to move the project forward. The Geocaching inclusion was scaled-down to a trackable item that players could search for from NASA camera views and then log on to the site. In a manner similar to the "Send Your Name to Mars" campaign, the geocaching trackable code was carefully printed on a one-inch, polycarbonate glass disk serving as part of the rover's calibration target. It will serve as an optical target for the WATSON imager and a spectroscopic standard for the SHERLOC instrument. The disk is made of a prototype astronaut helmet visor material that will be tested for its potential use in crewed missions to Mars. Designs were approved by the mission leads at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), NASA Public Affairs, and NASA HQ, in addition to Groundspeak Geocaching HQ.
Tribute to healthcare workers
 ''Perseverance'' launched during the
''Perseverance'' launched during the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identified ...
, which began to affect the mission planning in March 2020. To show appreciation for healthcare workers who helped during the pandemic, an plate with a staff-and-serpent symbol (a Greek symbol of medicine) was placed on the rover. The project manager, Matt Wallace, said he hoped that future generations going to Mars would be able to appreciate healthcare workers during 2020.
Family portrait of NASA Mars rovers
One of the external plates of ''Perseverance'' includes a simplified representation of all previous NASA Martian rovers, ''Sojourner'', ''Spirit'', ''Opportunity'', ''Curiosity'', as well as ''Perseverance'' and ''Ingenuity'', similar to the trend of automobile window decals used to show a family's makeup.NASA outreach to students
In December 2021, the NASA team announced a program to students who have ''persevered'' with academic challenges. Those nominated will be rewarded with a personal message beamed back from Mars by the ''Perseverance'' rover.
Media, cultural impact, and legacy
Parachute with coded message
 The orange-and-white parachute used to land the rover on Mars contained a coded message that was deciphered by Twitter users. NASA's systems engineer Ian Clark used binary code to hide the message "dare mighty things" in the parachute color pattern. The parachute consisted of 80 strips of fabric that form a hemisphere-shape canopy, and each strip consisted of four pieces. Dr. Clark thus had 320 pieces with which to encode the message. He also included the
The orange-and-white parachute used to land the rover on Mars contained a coded message that was deciphered by Twitter users. NASA's systems engineer Ian Clark used binary code to hide the message "dare mighty things" in the parachute color pattern. The parachute consisted of 80 strips of fabric that form a hemisphere-shape canopy, and each strip consisted of four pieces. Dr. Clark thus had 320 pieces with which to encode the message. He also included the GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of t ...
coordinates for the Jet Propulsion Laboratory's headquarters in Pasadena, California
Pasadena ( ) is a city in Los Angeles County, California, northeast of downtown Los Angeles. It is the most populous city and the primary cultural center of the San Gabriel Valley. Old Pasadena is the city's original commercial district.
Its ...
(34°11’58” N 118°10’31” W). Clark said that only six people knew about the message before landing. The code was deciphered a few hours after the image was presented by ''Perseverance''s team.
"Dare mighty things" is a quote attributed to U.S. president Theodore Roosevelt and is the unofficial motto of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. It adorns many of the JPL center's walls.
Gallery
Notes
See also
* Exploration of Mars * ''Viking 1'' (lander) * ''Viking 2'' (lander) * ''Sojourner'' (rover) * ''Spirit'' (rover) * ''Opportunity'' (rover) * ''Curiosity'' (rover) * ''Zhurong'' (rover) * ''Rosalind Franklin'' (rover) (planned mission) * List of rovers on extraterrestrial bodiesReferences
External links
Mars 2020 and ''Perseverance'' rover
official site at
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedi ...
*
*
*
*
Mars 2020: Landing of rover (3:55pm/et/usa, 18 February 2021
Mars 2020 ''Perseverance'' Launch Press Kit
Video: Mars ''Perseverance'' rover/''Ingenuity'' helicopter report
Official archive of all raw images taken by the rover's and helicopter's cameras
Official archive of all Mastcam-Z images in two different calibrations
Nonofficial archive of daily color-calibrated images taken by the rover's Navcam, Hazcam, Watson cam and the helicopter's RTE camera
{{Portal bar, Astronomy, Outer space, Spaceflight Individual space vehicles Jet Propulsion Laboratory Mars rovers * NASA space probes Robots of the United States Six-wheeled robots Space probes launched in 2020 2020 in the United States 2020 robots 2021 on Mars Articles containing video clips Mars robots