Peripheral Head-Mounted Display (PHMD) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A Peripheral Head-Mounted Display (PHMD) describes a visual display ( monocular or
A Peripheral Head-Mounted Display (PHMD) describes a visual display ( monocular or
 The most important uniqueness is that the user's FOV is not being fully covered, allowing the user to perform real world tasks without limitations, while not having the pretension to raise or create immersion, such as HMDs often aim for. For current display technologies, while projecting image onto the eye, the screen needs to be focused by the pupil to enable a clear reading of the screen, thus the environment becomes blurred and out-of-focus. So a PHMD such as
The most important uniqueness is that the user's FOV is not being fully covered, allowing the user to perform real world tasks without limitations, while not having the pretension to raise or create immersion, such as HMDs often aim for. For current display technologies, while projecting image onto the eye, the screen needs to be focused by the pupil to enable a clear reading of the screen, thus the environment becomes blurred and out-of-focus. So a PHMD such as
 While most of these factors mentioned above become problematic when both eyes are covered with displays, a single display resting in the peripheral vision can be considered to be unproblematic, since it does not permanently influence the perceived picture of the real world.
As mentioned earlier, there are two types of information being perceivable with a peripheral head mounted display: (1) detailed information: when consciously focusing on the display and (2) peripheral information: through the human's visual perception, when focusing at the 'real world'. (see also picture above)
Most obvious changes are “
While most of these factors mentioned above become problematic when both eyes are covered with displays, a single display resting in the peripheral vision can be considered to be unproblematic, since it does not permanently influence the perceived picture of the real world.
As mentioned earlier, there are two types of information being perceivable with a peripheral head mounted display: (1) detailed information: when consciously focusing on the display and (2) peripheral information: through the human's visual perception, when focusing at the 'real world'. (see also picture above)
Most obvious changes are “

 A Peripheral Head-Mounted Display (PHMD) describes a visual display ( monocular or
A Peripheral Head-Mounted Display (PHMD) describes a visual display ( monocular or binocular
Binocular may refer to:
Science and technology
* Binocular vision, seeing with two eyes
* Binoculars, a telescopic tool
* Binocular microscope, binocular viewing of objects through a single objective lens
Other uses
* Binocular (horse), a thoroug ...
) mounted to the user's head that is in the peripheral of the user's field of view (FOV) / Peripheral Vision. Whereby the actual position of the mounting (as the display technology) is considered to be irrelevant as long as it does not cover the entire FOV. While a PHMD provide an additional, always-available visual output channel, it does not limit the user performing real world tasks.Matthies, D.J.C., Haescher, M., Alm, R., & Urban, B. (2015). Properties of a peripheral head-mounted display (phmd). In International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction (pp. 208-213). Springer.
The term PHMD includes devices such as Google Glass
Google Glass, or simply Glass, is a brand of smart glasses developed and sold by Google. It was developed by X (previously Google X), with the mission of producing an ubiquitous computer. Google Glass displays information to the wearer using ...
, which are often misclassified as a Head-up display (HUD)Starner, T. (2013). Project glass: An extension of the self. In Pervasive Computing, IEEE, 12(2), 14-16. if following the original definition by NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding t ...
.Prinzel, L., & Risser, M. Head-up displays and attention capture. In ''NASA TechnicalMemorandum'', 213000. 2004. While NASA defined this term over centuries of space flight research, it actually describes a display that addresses the eyes-free problem, by absolving the user from the need to angle down their head. Furthermore, it provides augmented information in the user's forward field of view (FOV), which is commonly projected on a windshield. In contrast, the Head-Down Display (HDD) is located at the instrument control panel. Also, a HUD is mainly used to augment additional information into reality, which is technically not feasible yet for products such as Google Glass
Google Glass, or simply Glass, is a brand of smart glasses developed and sold by Google. It was developed by X (previously Google X), with the mission of producing an ubiquitous computer. Google Glass displays information to the wearer using ...
(lens focus on the display causes a blurred environment – see figure below).
This taxonomy for head-mounted displays is based on the property of its functionality and the ability of the human eye
The human eye is a sensory organ, part of the sensory nervous system, that reacts to visible light and allows humans to use visual information for various purposes including seeing things, keeping balance, and maintaining circadian rhythm.
...
to perceive peripheral information, instead of being technology-dependent. In this article Human Factors for visual perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous system ...
are being summarized, which are important to be taken into consideration when designing visual interfaces for PHMDs.
Characteristics
 The most important uniqueness is that the user's FOV is not being fully covered, allowing the user to perform real world tasks without limitations, while not having the pretension to raise or create immersion, such as HMDs often aim for. For current display technologies, while projecting image onto the eye, the screen needs to be focused by the pupil to enable a clear reading of the screen, thus the environment becomes blurred and out-of-focus. So a PHMD such as
The most important uniqueness is that the user's FOV is not being fully covered, allowing the user to perform real world tasks without limitations, while not having the pretension to raise or create immersion, such as HMDs often aim for. For current display technologies, while projecting image onto the eye, the screen needs to be focused by the pupil to enable a clear reading of the screen, thus the environment becomes blurred and out-of-focus. So a PHMD such as Google Glass
Google Glass, or simply Glass, is a brand of smart glasses developed and sold by Google. It was developed by X (previously Google X), with the mission of producing an ubiquitous computer. Google Glass displays information to the wearer using ...
is capable of displaying detailed information, when the pupil is focusing the display itself, as it also allows for peripheral information when the eye focuses on the real world. Still, simple information
Information is an abstract concept that refers to that which has the power to inform. At the most fundamental level information pertains to the interpretation of that which may be sensed. Any natural process that is not completely random ...
such as notifications are perceivable when focusing on the real world instead of the display.
Physiological Factors: Visual Perception
Research shows that designing an optimal visual output for Head-Mounted Displays is a complex issue, since there are several physiological factors that significantly impact users’perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous system ...
.Laramee, R. S., & Ware, C. (2002). Rivalry and interference with a head-mounted display. In ACM Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction, 9(3), 238-251 The following effects are known in research:
Depth of Focus / Field
Switches permanently by refocusing on objects, which is different in distances to the user. A display mounted somehow to user's eye has fixed focal distance. Focusing information such as presented on a screen leads to a change in the depth of focus. This causes blurring of information presented at other layers, which especially degrades the perception of high spatial frequency information such as text.Eye-Movements
Are actually done at a specific angle of 10°. To focus an object out of this angle, head movements are used automatically for support. However, when wearing an HMD with eye-movements that exceed this angle, since head movements do not have any effect on the interface, a drop in comfort might occur due to tiredeye muscle
The extraocular muscles (extrinsic ocular muscles), are the seven extrinsic muscles of the human eye. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior and inferior oblique muscles, control movement of the eye and the o ...
.
Field-Of-View
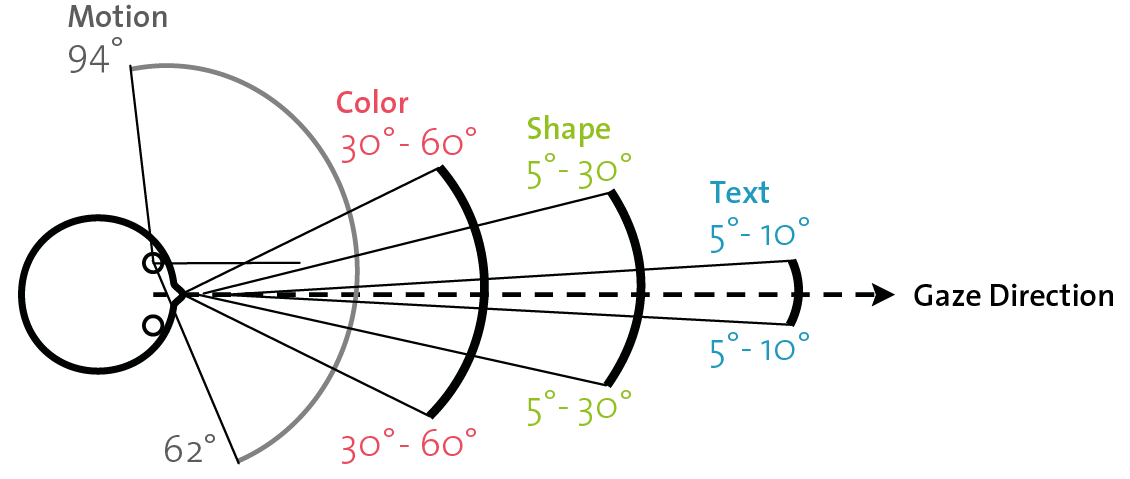
Describes the FOV. The User's eye has a viewing angle of 94° from the center and 62° on the nose side.Ishiguro, Y., & Rekimoto, J. (2011). Peripheral vision annotation: noninterference information presentation method for mobile augmented reality. In Proceedings of the 2nd Augmented Human International Conference. ACM, 8-11. The vertical angle is about 60° upwards and 75° downwards. HMDs often do not cover the whole FOV, which is also a reason for increased cybersickness.Binocular Rivalry
Describes the phenomenon, which occurs when dissimilar images are presented to the human eye.Alais, D., & Blake, R. (1999). Grouping visual features during binocular rivalry. In Vision research, 39(26), 4341-4353.Collins, J. F., & Blackwell, L. K. (1974). Effects of eye dominance and retinal distance on binocular rivalry. In Perceptual and Motor Skills, 39(2), 747-754. As the two images captured by each eye is incompatible for stereo processing, they fight for visual dominance over the other eye's side view, resulting in alternating views from the two eyes, where the non-dominant view is almost unseen. This effect often occurs when wearing a monocular HMD. In this setup, researchers Peli, E. (1999). Optometric and perceptual issues with head-mounted displays. In Visual instrumentation: Optical design and engineering principles, 205-276. also observed objects that completely vanish for several seconds from user'sattention
Attention is the behavioral and cognitive process of selectively concentrating on a discrete aspect of information, whether considered subjective or objective, while ignoring other perceivable information. William James (1890) wrote that "Atte ...
.
Visual Interference
Describes the phenomenon when both eyes perceive different images that are overlapping, but thebrain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
is not able to distinguish between those. This phenomenon is also known as the inability for visual separation.
Phoria
Describes a muscle state of the eye, when the eyes are not focusing on a specific point. There are three different states, which can be distinguished: Esophoria,Exophoria
Exophoria is a form of heterophoria in which there is a tendency of the eyes to deviate outward. During examination, when the eyes are dissociated, the visual axes will appear to diverge away from one another.
The axis deviation in exophoria is u ...
, Orthophoria
Orthophoria is a condition of binocular fixation in which the lines of vision meet at the object toward which they are directed, and considered as a normal condition of balance of the ocular muscles of the two eyes. The condition opposite of Orth ...
. While one eye is closed or being obstructed by a display, phoria can occur, which has the potential to cause Vertigo and Nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the ...
as well.Z-Health Performance Solutions (2011). http://www.zhealth.net/articles/the-eyes-have-it
Eye-Dominance
Although the user has two eyes, one eye is predominantly used. The other eye is used to make corrections and provide additional spatial information. It is recommended to wear a monocular HMD over the dominant eye.Peripheral Perception
 While most of these factors mentioned above become problematic when both eyes are covered with displays, a single display resting in the peripheral vision can be considered to be unproblematic, since it does not permanently influence the perceived picture of the real world.
As mentioned earlier, there are two types of information being perceivable with a peripheral head mounted display: (1) detailed information: when consciously focusing on the display and (2) peripheral information: through the human's visual perception, when focusing at the 'real world'. (see also picture above)
Most obvious changes are “
While most of these factors mentioned above become problematic when both eyes are covered with displays, a single display resting in the peripheral vision can be considered to be unproblematic, since it does not permanently influence the perceived picture of the real world.
As mentioned earlier, there are two types of information being perceivable with a peripheral head mounted display: (1) detailed information: when consciously focusing on the display and (2) peripheral information: through the human's visual perception, when focusing at the 'real world'. (see also picture above)
Most obvious changes are “motion
In physics, motion is the phenomenon in which an object changes its position with respect to time. Motion is mathematically described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed and frame of reference to an observer and mea ...
”, which can be perceived over the whole spectrum of the FOV. In a smaller angle, change in color is also quite well perceivable (see figure). In contrast, perceiving shapes and reading text requires very dedicated attention of the pupil. However, when being very focused on a dedicated task, rough changes in shapes are still perceivable in a peripheral way.Hau Chua, S., Perrault, S., Matthies, D., Zhao, S. (2015). Positioning Glass: Investigating Display Positions of monocular Optical See-Through Head-Mounted Display. Even in the field of Human-Computer Interaction, there have been investigations on this visual “peripheral channel”, such as peripheral color perception with eyeglasses. Furthermore, researchers proposed to additionally utilize an eye tracker for a peripheral head-mounted display, in order to improve user experience. There has also been investigations on which display positions are most suitable. It has been found out that notifications presented at the middle and bottom areas of our human vision
Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment through photopic vision (daytime vision), color vision, scotopic vision (night vision), and mesopic vision (twilight vision), using light in the visible spectrum reflecte ...
is more noticeable. However, top and middle positions are less distracting and more comfortable and preferred by the users. Among all the positions, the middle right position was found to strike the best balance between noticeability, comfort, and distraction.
While most HMDs suffer badly of the effects of binocular rivalry, Depth of Field
The depth of field (DOF) is the distance between the nearest and the furthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus in an image captured with a camera.
Factors affecting depth of field
For cameras that can only focus on one object dist ...
and Phoria it is different for the PHMD. Since the PHMD is not totally covering the FOV and also not augmenting information on real objects, it is not affected by known problems monocular HMDs usually suffer from, such as the effect of attention switching between reality and projection. Such problems have been figured out over centuries of airspace research and usually occur when trying to augment reality.Rash, C. E., Verona, R. W., & Crowley, J. S. (1990). Human factors and safety considerations of night-vision systems flight using thermal imaging systems. In International Society for Optics and Photonics, Orlando, 16-20, 142-164. These potential dangers, when operating in critical situations, such as taking part in traffic, are less pronounced for PHMDs.
Peripheral Interaction
Since the PHMD is resting in the peripheral of the user's FOV, it has a high availability and can be quickly demanded by focusing it. Furthermore, significant changes - depending on the stimuli - of the screen content is still perceivable without focusing thedisplay
Display may refer to:
Technology
* Display device, output device for presenting information, including:
** Cathode ray tube, video display that provides a quality picture, but can be very heavy and deep
** Electronic visual display, output devi ...
.Costanza, E., Inverso, S. A., Pavlov, E., Allen, R., & Maes, P. (2006). eye-q: Eyeglass peripheral display for subtle intimate notifications. In Proceedings of the 8th conference on Human-computer interaction with mobile devices and services. ACM, 211-218. This effect can be used to design peripheral information (e.g. such as visual notifications for incoming emails, approaching appointments, warnings). An efficient response to such perceived information
Information is an abstract concept that refers to that which has the power to inform. At the most fundamental level information pertains to the interpretation of that which may be sensed. Any natural process that is not completely random ...
could be accomplished in quick peripheral input, such as a quick hand movement. This way, the user is not being greatly interrupted while completing real world tasks. In Human-Computer Interaction research this is also denoted as Peripheral Interaction Hausen, D. (2013). Peripheral Interaction - Exploring the Design Space, PhD Thesis, Faculty of Mathematics, Computer Science and Statistics, University of Munich.
Notwithstanding, suitable input modalities for PHMDs that are not socially awkward remain to be discovered. Negative or positive social effects by wearing a PHMD and devoting attention on the screen while taking part in a conversation might be present, but are not proven yet. In addition, taking part in traffic while focusing on a visual input modality can lead to a considerable decrease of attention to the road (see also Semantic memory
Semantic memory refers to general world knowledge that humans have accumulated throughout their lives. This general knowledge (word meanings, concepts, facts, and ideas) is intertwined in experience and dependent on culture. We can learn about n ...
& Multimodal Interaction). However, compared to smartphone
A smartphone is a portable computer device that combines mobile telephone and computing functions into one unit. They are distinguished from feature phones by their stronger hardware capabilities and extensive mobile operating systems, whic ...
interaction
Interaction is action that occurs between two or more objects, with broad use in philosophy and the sciences. It may refer to:
Science
* Interaction hypothesis, a theory of second language acquisition
* Interaction (statistics)
* Interactions o ...
, a quick switch to real world tasks is attainable, because there is no need for getting the device out of a pocket or bag. Furthermore, a PHMD does not need to be held by the user's hands, which offers a fully hands-free interaction. Since it is always available, it can provide peripheral visual information at any time, whereas peripheral information on smartphone
A smartphone is a portable computer device that combines mobile telephone and computing functions into one unit. They are distinguished from feature phones by their stronger hardware capabilities and extensive mobile operating systems, whic ...
in a pocket is not at all or barely perceivable (e.g. in a club/discothèque, while walking).
References
{{reflist Wearable devices Wearable computers