Percophidae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Percophidae, duckbills, are a family of percomorph fishes, from the
 * Subfamily Bembropinae
** ''
* Subfamily Bembropinae
** ''
ImageSize = width:1000px height:auto barincrement:15px
PlotArea = left:10px bottom:50px top:10px right:10px
Period = from:-65.5 till:10
TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal
ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:5 start:-65.5
ScaleMinor = unit:year increment:1 start:-65.5
TimeAxis = orientation:hor
AlignBars = justify
Colors =
#legends
id:CAR value:claret
id:ANK value:rgb(0.4,0.3,0.196)
id:HER value:teal
id:HAD value:green
id:OMN value:blue
id:black value:black
id:white value:white
id:cenozoic value:rgb(0.54,0.54,0.258)
id:paleogene value:rgb(0.99,0.6,0.32)
id:paleocene value:rgb(0.99,0.65,0.37)
id:eocene value:rgb(0.99,0.71,0.42)
id:oligocene value:rgb(0.99,0.75,0.48)
id:neogene value:rgb(0.999999,0.9,0.1)
id:miocene value:rgb(0.999999,0.999999,0)
id:pliocene value:rgb(0.97,0.98,0.68)
id:quaternary value:rgb(0.98,0.98,0.5)
id:pleistocene value:rgb(0.999999,0.95,0.68)
id:holocene value:rgb(0.999,0.95,0.88)
BarData=
bar:eratop
bar:space
bar:periodtop
bar:space
bar:NAM1
bar:NAM2
bar:space
bar:period
bar:space
bar:era
PlotData=
align:center textcolor:black fontsize:M mark:(line,black) width:25
shift:(7,-4)
bar:periodtop
from: -65.5 till: -55.8 color:paleocene text:
order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of d ...
Trachiniformes
Trachiniformes is an order of percomorph bony fish which is traditionally the suborder Trachinoidei of the Perciformes.
However, the classification is also considered as a polyphyly by molecular phylogenies. Trachinidae itself is eventually ...
, found in tropical and subtropical waters of the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
and Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
s and in the southwestern and southeastern Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
.
They are small fishes: the largest species, the Brazilian flathead
The Brazilian flathead (''Percophis brasiliensis'') is a species of duckbill which is the only species in the genus ''Percophis'', the type genus of the monotypic subfamily Percophinae of the duckbill family Percophidae
The Percophidae, duckbill ...
, ''Percophis brasiliensis'', grows up to about , but to is more typical. A few species are fished commercially, including the Brazilian flathead.
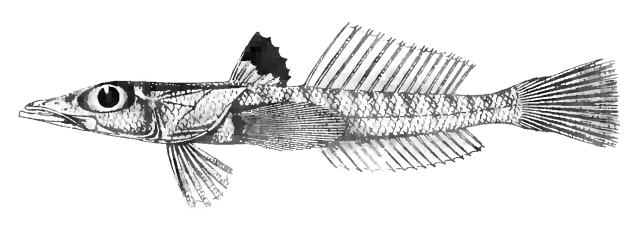
Characteristics
The species in the family Percophidae are elongated,benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "t ...
fishes with an anteriorly depressed head, a broad flat snout which gives rise to the common name
In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of everyday life; and is often contrast ...
duckbills. The mouth is large with a prognathous
Prognathism, also called Habsburg jaw or Habsburgs' jaw primarily in the context of its prevalence amongst members of the House of Habsburg, is a positional relationship of the Human mandible, mandible or maxilla to the skeletal base where eithe ...
lower jaw and exposed maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The t ...
. They have large closely placed eyes. There are two spines on the opercula and one on subopercula. They have tiny conical teeth on the mandibles and on the vomer
The vomer (; lat, vomer, lit=ploughshare) is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxill ...
and palatine
A palatine or palatinus (in Latin; plural ''palatini''; cf. derivative spellings below) is a high-level official attached to imperial or royal courts in Europe since Roman times.
bones. There are two dorsal fins
A dorsal fin is a fin located on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates within various taxa of the animal kingdom. Many species of animals possessing dorsal fins are not particularly closely related to each other, though through conv ...
an anterior dorsal fin with 6 slender spines and a posterior dorsal fin with 13 to 18 soft rays, the pelvic fin
Pelvic fins or ventral fins are paired fins located on the ventral surface of fish. The paired pelvic fins are homologous to the hindlimbs of tetrapods.
Structure and function Structure
In actinopterygians, the pelvic fin consists of two en ...
s have 1 weak spine and 5 branched rays and these are positioned anteriorly to the pectoral fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as ...
s with their bases widely separated. The anal fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as se ...
has only 15 to 25 soft rays and the pectoral fins have between 20 and 28 rays. They body is covered in ctenoid
A fish scale is a small rigid plate that grows out of the skin of a fish. The skin of most jawed fishes is covered with these protective scales, which can also provide effective camouflage through the use of reflection and colouration, as ...
scales and the lateral line
The lateral line, also called the lateral line organ (LLO), is a system of sensory organs found in fish, used to detect movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the surrounding water. The sensory ability is achieved via modified epithelial ...
curves underneath the anterior dorsal fin to below the middle of the flank with the 2 or 3 scales nearest the head being keeled. They are generally brownish in colour with indistinct dark blotches along the body. They are benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "t ...
, carnivorous fish which are found at depths of . They are relatively small and uncommon and are of no interest to fisheries.
Subfamilies and genera
The family Percophidae is divided into threesubfamilies
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end subfamily botanical names with "-oideae", and zoologi ...
 * Subfamily Bembropinae
** ''
* Subfamily Bembropinae
** ''Bembrops
''Bembrops'' is a genus of fish, it is the type genus of the subfamily Bembropinae of the family Percophidae.
Species
The following species are classified as members of the genus ''Bembrops'':
* '' Bembrops anatirostris'' Ginsburg, 1955
* ' ...
''
** ''Chrionema
''Chrionema'' is a genus of fish from the duckbill family Percophidae
The Percophidae, duckbills, are a family of percomorph fishes, from the order Trachiniformes, found in tropical and subtropical waters of the Atlantic and Indian Oceans and i ...
''
*Subfamily Hemerocoetinae
** '' Acanthaphritis''
** '' Dactylopsaron''
** '' Enigmapercis''
** ''Hemerocoetes
''Hemerocoetes'' is a genus of duckbill fishes.
References
Percophidae
Extant Rupelian first appearances
Marine fish genera
Taxa named by Achille Valenciennes
Rupelian genus first appearances
{{Perciformes-stub ...
''
** '' Matsubaraea''
** '' Osopsaron''
** '' Pteropsaron''
** '' Squamicreedia''
* Subfamily Percophinae
** '' Percophis''
Timeline of genera
Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), E ...
from: -55.8 till: -33.9 color:eocene text:Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
from: -33.9 till: -23.03 color:oligocene text:Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the ...
from: -23.03 till: -5.332 color:miocene text:Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
from: -5.332 till: -2.588 color:pliocene text: Plio.
from: -2.588 till: -0.0117 color:pleistocene text:Pleist.
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
from: -0.0117 till: 0 color:holocene text: H.
bar:eratop
from: -65.5 till: -23.03 color:paleogene text:Paleogene
The Paleogene ( ; British English, also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene; informally Lower Tertiary or Early Tertiary) is a geologic period, geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period million yea ...
from: -23.03 till: -2.588 color:neogene text:Neogene
The Neogene ( ), informally Upper Tertiary or Late Tertiary, is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period Mya. ...
from: -2.588 till: 0 color:quaternary text: Q.
PlotData=
align:left fontsize:M mark:(line,white) width:5 anchor:till align:left
color:eocene bar:NAM1 from: -37.2 till: 0 text: Bembrops
''Bembrops'' is a genus of fish, it is the type genus of the subfamily Bembropinae of the family Percophidae.
Species
The following species are classified as members of the genus ''Bembrops'':
* '' Bembrops anatirostris'' Ginsburg, 1955
* ' ...
color:oligocene bar:NAM2 from: -33.9 till: 0 text: Hemerocoetes
''Hemerocoetes'' is a genus of duckbill fishes.
References
Percophidae
Extant Rupelian first appearances
Marine fish genera
Taxa named by Achille Valenciennes
Rupelian genus first appearances
{{Perciformes-stub ...
PlotData=
align:center textcolor:black fontsize:M mark:(line,black) width:25
bar:period
from: -65.5 till: -55.8 color:paleocene text:Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), E ...
from: -55.8 till: -33.9 color:eocene text:Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
from: -33.9 till: -23.03 color:oligocene text:Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the ...
from: -23.03 till: -5.332 color:miocene text:Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
from: -5.332 till: -2.588 color:pliocene text: Plio.
from: -2.588 till: -0.0117 color:pleistocene text:Pleist.
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
from: -0.0117 till: 0 color:holocene text: H.
bar:era
from: -65.5 till: -23.03 color:paleogene text:Paleogene
The Paleogene ( ; British English, also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene; informally Lower Tertiary or Early Tertiary) is a geologic period, geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period million yea ...
from: -23.03 till: -2.588 color:neogene text:Neogene
The Neogene ( ), informally Upper Tertiary or Late Tertiary, is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period Mya. ...
from: -2.588 till: 0 color:quaternary text: Q.
References
* * {{Taxonbar, from=Q1651138 Trachiniformes Marine fish families