Per Martin-Löf on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Per Erik Rutger Martin-Löf (; ; born 8 May 1942) is a Swedish logician,
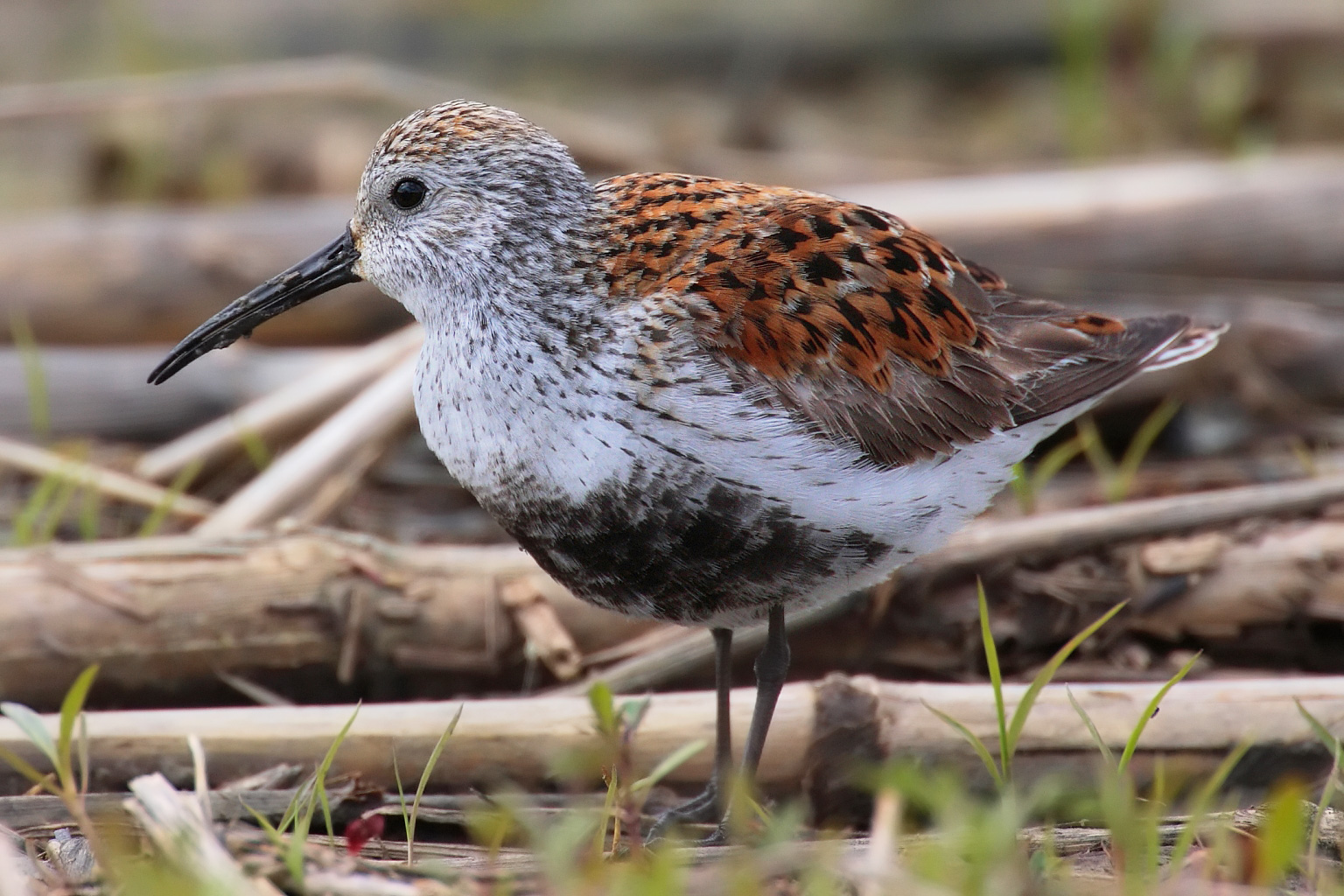 Per Martin-Löf began bird watching in his youth and remains an enthusiastic bird-watcher. As a teenager, he published an article on estimating the
Per Martin-Löf began bird watching in his youth and remains an enthusiastic bird-watcher. As a teenager, he published an article on estimating the
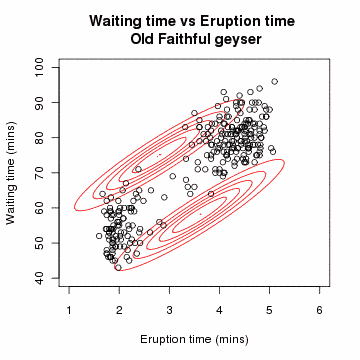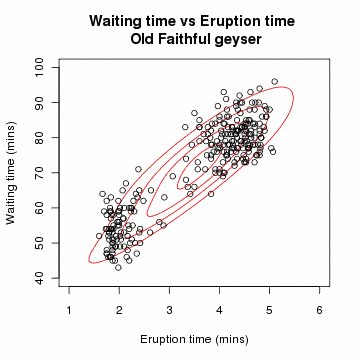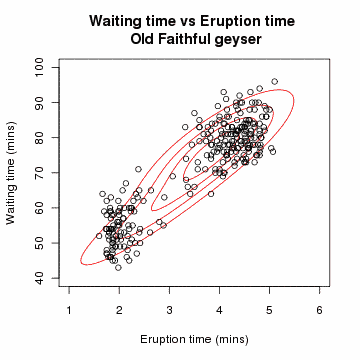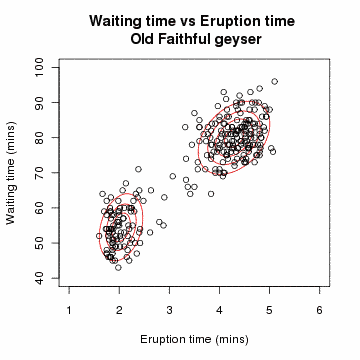 In the 1970s, Per Martin-Löf made important contributions to statistical theory and inspired further research, especially by Scandinavian statisticians including Rolf Sundberg, Thomas Höglund, and Steffan Lauritzen. In this work, Martin-Löf's previous research on probability measures on semigroups led to a notion of "repetitive structure" and a novel treatment of sufficient statistics, in which one-parameter exponential families were characterized. He provided a category-theoretic approach to nested statistical models, using finite-sample principles. Before (and after) Martin-Löf, such nested models have often been tested using chi-square hypothesis tests, whose justifications are only asymptotic (and so irrelevant to real problems, which always have finite samples).
In the 1970s, Per Martin-Löf made important contributions to statistical theory and inspired further research, especially by Scandinavian statisticians including Rolf Sundberg, Thomas Höglund, and Steffan Lauritzen. In this work, Martin-Löf's previous research on probability measures on semigroups led to a notion of "repetitive structure" and a novel treatment of sufficient statistics, in which one-parameter exponential families were characterized. He provided a category-theoretic approach to nested statistical models, using finite-sample principles. Before (and after) Martin-Löf, such nested models have often been tested using chi-square hypothesis tests, whose justifications are only asymptotic (and so irrelevant to real problems, which always have finite samples).

"Gone Birdwatching"
''New Scientist'', 4 December 1999, magazine issue 2215. * *
An intuitionistic theory of types
'' In G. Sambin and J. Smith, editors, Twenty-Five Years of Constructive Type Theory. Oxford University Press, 1998. Reprinted version of an unpublished report from 1972. * Per Martin-Löf. An intuitionistic theory of types: Predicative part. In H. E. Rose and J. C. Shepherdson, editors, Logic Colloquium ‘73, pages 73–118. North Holland, 1975. * Per Martin-Löf.
Constructive mathematics and computer programming
'' In ''Logic, Methodology and Philosophy of Science VI, 1979''. Eds. Cohen, et al. North-Holland, Amsterdam. pp. 153–175, 1982. * Per Martin-Löf.
Intuitionistic type theory
'' (Notes by Giovanni Sambin of a series of lectures given in Padua, June 1980). Napoli, Bibliopolis, 1984. * Per Martin-Löf. ''Philosophical implications of type theory'', Unpublished notes, 1987? * Per Martin-Löf. ''Substitution calculus'', 1992. Notes from a lecture given in Göteborg. * Bengt Nordström, Kent Petersson, and Jan M. Smith. ''Programming in Martin-Löf's Type Theory''. Oxford University Press, 1990. (The book is out of print, bu
a free version
has been made available.) * Per Martin-Löf.
On the Meanings of the Logical Constants and the Justifications of the Logical Laws
'' '' Nordic Journal of Philosophical Logic'', 1(1): 11–60, 1996. * Per Martin-Löf.
Logic and Ethics
'' In T. Piecha and P. Schroeder-Heister, editors,
Proof-Theoretic Semantics: Assessment and Future Perspectives. Proceedings of the Third Tübingen Conference on Proof-Theoretic Semantics, 27–30 March 2019
', pages 227-235. URI:
http://dx.doi.org/10.15496/publikation-35319
'. University of Tübingen 2019.
philosopher
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
, and mathematical statistician. He is internationally renowned for his work on the foundations of probability
Probability is a branch of mathematics and statistics concerning events and numerical descriptions of how likely they are to occur. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1; the larger the probability, the more likely an e ...
, statistics, mathematical logic, and computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
. Since the late 1970s, Martin-Löf's publications have been mainly in logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure o ...
. In philosophical logic
Understood in a narrow sense, philosophical logic is the area of logic that studies the application of logical methods to philosophical problems, often in the form of extended logical systems like modal logic. Some theorists conceive philosophic ...
, Martin-Löf has wrestled with the philosophy of logical consequence
Logical consequence (also entailment or logical implication) is a fundamental concept in logic which describes the relationship between statement (logic), statements that hold true when one statement logically ''follows from'' one or more stat ...
and judgment
Judgement (or judgment) is the evaluation of given circumstances to make a decision. Judgement is also the ability to make considered decisions.
In an informal context, a judgement is opinion expressed as fact. In the context of a legal trial ...
, partly inspired by the work of Brentano, Frege, and Husserl. In mathematical logic
Mathematical logic is the study of Logic#Formal logic, formal logic within mathematics. Major subareas include model theory, proof theory, set theory, and recursion theory (also known as computability theory). Research in mathematical logic com ...
, Martin-Löf has been active in developing intuitionistic type theory
Intuitionistic type theory (also known as constructive type theory, or Martin-Löf type theory (MLTT)) is a type theory and an alternative foundation of mathematics.
Intuitionistic type theory was created by Per Martin-Löf, a Swedish mathematicia ...
as a constructive foundation of mathematics; Martin-Löf's work on type theory has influenced computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
.
Until his retirement in 2009, Per Martin-Löf held a joint chair for Mathematics and Philosophy at Stockholm University
Stockholm University (SU) () is a public university, public research university in Stockholm, Sweden, founded as a college in 1878, with university status since 1960. With over 33,000 students at four different faculties: law, humanities, social ...
.Member profileAcademia Europaea
The Academia Europaea is a pan-European Academy of humanities, letters, law, and sciences.
The Academia was founded in 1988 as a functioning Europe-wide Academy that encompasses all fields of scholarly inquiry. It acts as co-ordinator of Europe ...
, retrieved 2014-01-26.
His brother Anders Martin-Löf is now emeritus professor of mathematical statistics at Stockholm University; the two brothers have collaborated in research in probability and statistics. The research of Anders and Per Martin-Löf has influenced statistical theory, especially concerning exponential families, the expectation–maximization method for missing data
In statistics, missing data, or missing values, occur when no data value is stored for the variable in an observation. Missing data are a common occurrence and can have a significant effect on the conclusions that can be drawn from the data.
Mi ...
, and model selection
Model selection is the task of selecting a model from among various candidates on the basis of performance criterion to choose the best one.
In the context of machine learning and more generally statistical analysis, this may be the selection of ...
.
Per Martin-Löf received his PhD in 1970 from Stockholm University
Stockholm University (SU) () is a public university, public research university in Stockholm, Sweden, founded as a college in 1878, with university status since 1960. With over 33,000 students at four different faculties: law, humanities, social ...
, under Andrey Kolmogorov
Andrey Nikolaevich Kolmogorov ( rus, Андре́й Никола́евич Колмого́ров, p=ɐnˈdrʲej nʲɪkɐˈlajɪvʲɪtɕ kəlmɐˈɡorəf, a=Ru-Andrey Nikolaevich Kolmogorov.ogg, 25 April 1903 – 20 October 1987) was a Soviet ...
.
Martin-Löf is an enthusiastic bird-watcher; his first scientific publication was on the mortality rates of ringed birds..
Randomness and Kolmogorov complexity
In 1964 and 1965, Martin-Löf studied in Moscow under the supervision of Andrei N. Kolmogorov. He wrote a 1966 article ''The definition of random sequences'' that gave the first suitable definition of a random sequence. Earlier researchers such as Richard von Mises had attempted to formalize the notion of a test for randomness in order to define a random sequence as one that passed all tests for randomness; however, the precise notion of a randomness test was left vague. Martin-Löf's key insight was to use thetheory of computation
In theoretical computer science and mathematics, the theory of computation is the branch that deals with what problems can be solved on a model of computation, using an algorithm, how efficiently they can be solved or to what degree (e.g., app ...
to define formally the notion of a test for randomness. This contrasts with the idea of randomness in probability
Probability is a branch of mathematics and statistics concerning events and numerical descriptions of how likely they are to occur. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1; the larger the probability, the more likely an e ...
; in that theory, no particular element of a sample space can be said to be random.
Martin-Löf randomness has since been shown to admit many equivalent characterizations — in terms of compression, randomness tests, and gambling
Gambling (also known as betting or gaming) is the wagering of something of Value (economics), value ("the stakes") on a Event (probability theory), random event with the intent of winning something else of value, where instances of strategy (ga ...
— that bear little outward resemblance to the original definition, but each of which satisfies our intuitive notion of properties that random sequences ought to have: random sequences should be incompressible, they should pass statistical tests for randomness, and it should be impossible to make money betting on them. The existence of these multiple definitions of Martin-Löf randomness, and the stability of these definitions under different models of computation, give evidence that Martin-Löf randomness is a fundamental property of mathematics and not an accident of Martin-Löf's particular model. The thesis that the definition of Martin-Löf randomness "correctly" captures the intuitive notion of randomness has been called the "Martin-Löf– Chaitin Thesis"; it is somewhat similar to the Church–Turing thesis
In Computability theory (computation), computability theory, the Church–Turing thesis (also known as computability thesis, the Turing–Church thesis, the Church–Turing conjecture, Church's thesis, Church's conjecture, and Turing's thesis) ...
.
Following Martin-Löf's work, algorithmic information theory defines a random string as one that cannot be produced from any computer program that is shorter than the string ( Chaitin–Kolmogorov randomness); i.e. a string whose Kolmogorov complexity
In algorithmic information theory (a subfield of computer science and mathematics), the Kolmogorov complexity of an object, such as a piece of text, is the length of a shortest computer program (in a predetermined programming language) that prod ...
is at least the length of the string. This is a different meaning from the usage of the term in statistics. Whereas statistical randomness refers to the ''process'' that produces the string (e.g. flipping a coin to produce each bit will randomly produce a string), algorithmic randomness refers to the ''string itself''. Algorithmic information theory separates random from nonrandom strings in a way that is relatively invariant to the model of computation
In computer science, and more specifically in computability theory and computational complexity theory, a model of computation is a model which describes how an output of a mathematical function is computed given an input. A model describes how ...
being used.
An algorithmically random sequence
Intuitively, an algorithmically random sequence (or random sequence) is a sequence of binary digits that appears random to any algorithm running on a (prefix-free or not) universal Turing machine. The notion can be applied analogously to sequen ...
is an ''infinite'' sequence of characters, all of whose prefixes (except possibly a finite number of exceptions) are strings that are "close to" algorithmically random (their length is within a constant of their Kolmogorov complexity).
Mathematical statistics
Per Martin-Löf has done important research inmathematical statistics
Mathematical statistics is the application of probability theory and other mathematical concepts to statistics, as opposed to techniques for collecting statistical data. Specific mathematical techniques that are commonly used in statistics inc ...
, which (in the Swedish tradition) includes probability theory
Probability theory or probability calculus is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations, probability theory treats the concept in a rigorous mathematical manner by expre ...
and statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
.
Bird-watching and sex determination
 Per Martin-Löf began bird watching in his youth and remains an enthusiastic bird-watcher. As a teenager, he published an article on estimating the
Per Martin-Löf began bird watching in his youth and remains an enthusiastic bird-watcher. As a teenager, he published an article on estimating the mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular Statistical population, population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically ...
s of birds, using data from bird ringing
Bird ringing (UK) or bird banding (US) is the attachment of a small, individually numbered metal or plastic tag to the leg or wing of a wild bird to enable individual identification. This helps in keeping track of the movements of the bird an ...
, in a Swedish zoological journal: This paper was soon cited in leading international journals, and this paper continues to be cited.
In the biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
and statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
of birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
, there are several problems of missing data
In statistics, missing data, or missing values, occur when no data value is stored for the variable in an observation. Missing data are a common occurrence and can have a significant effect on the conclusions that can be drawn from the data.
Mi ...
. Martin-Löf's first paper discussed the problem of estimating the mortality rates of the Dunlin species, using capture-recapture
Mark and recapture is a method commonly used in ecology to estimate an animal population's size where it is impractical to count every individual. A portion of the population is captured, marked, and released. Later, another portion will be captu ...
methods. The problem of determining the biological sex of a bird, which is extremely difficult for humans, is one of the first examples in Martin-Löf's lectures on statistical model
A statistical model is a mathematical model that embodies a set of statistical assumptions concerning the generation of Sample (statistics), sample data (and similar data from a larger Statistical population, population). A statistical model repre ...
s.
Probability on algebraic structures
Martin-Löf wrote a licenciate thesis on probability on algebraic structures, particularly semigroups, while a student ofUlf Grenander
Ulf Grenander (23 July 1923 – 12 May 2016) was a Swedish statistician and professor of applied mathematics at Brown University.
His early research was in probability theory, stochastic processes, time series analysis, and statistical theory (pa ...
at Stockholm University.
Statistical models
Martin-Löf developed innovative approaches tostatistical theory
The theory of statistics provides a basis for the whole range of techniques, in both study design and data analysis, that are used within applications of statistics.
The theory covers approaches to statistical-decision problems and to statistica ...
. In his paper "On Tables of Random Numbers", Kolmogorov observed that the frequency probability
Frequentist probability or frequentism is an interpretation of probability; it defines an event's probability (the ''long-run probability'') as the limit of a sequence, limit of its Empirical probability, relative frequency in infinitely many E ...
notion of the limiting properties of infinite sequences failed to provide a foundation for statistics, which considers only finite samples. Much of Martin-Löf's work in statistics was to provide a finite-sample foundation for statistics.
Model selection and hypothesis testing
 In the 1970s, Per Martin-Löf made important contributions to statistical theory and inspired further research, especially by Scandinavian statisticians including Rolf Sundberg, Thomas Höglund, and Steffan Lauritzen. In this work, Martin-Löf's previous research on probability measures on semigroups led to a notion of "repetitive structure" and a novel treatment of sufficient statistics, in which one-parameter exponential families were characterized. He provided a category-theoretic approach to nested statistical models, using finite-sample principles. Before (and after) Martin-Löf, such nested models have often been tested using chi-square hypothesis tests, whose justifications are only asymptotic (and so irrelevant to real problems, which always have finite samples).
In the 1970s, Per Martin-Löf made important contributions to statistical theory and inspired further research, especially by Scandinavian statisticians including Rolf Sundberg, Thomas Höglund, and Steffan Lauritzen. In this work, Martin-Löf's previous research on probability measures on semigroups led to a notion of "repetitive structure" and a novel treatment of sufficient statistics, in which one-parameter exponential families were characterized. He provided a category-theoretic approach to nested statistical models, using finite-sample principles. Before (and after) Martin-Löf, such nested models have often been tested using chi-square hypothesis tests, whose justifications are only asymptotic (and so irrelevant to real problems, which always have finite samples).
Expectation–maximization method for exponential families
Martin-Löf's student, Rolf Sundberg, developed a detailed analysis of the expectation–maximization (EM) method for estimation using data from exponential families, especially withmissing data
In statistics, missing data, or missing values, occur when no data value is stored for the variable in an observation. Missing data are a common occurrence and can have a significant effect on the conclusions that can be drawn from the data.
Mi ...
. Sundberg credits a formula, later known as the Sundberg formula, to previous manuscripts of the Martin-Löf brothers, Per and Anders
Anders is a male name in Scandinavian languages and Fering, Fering North Frisian, an equivalent of the Greek Andreas ("manly") and the English Andrew. It originated from Andres (name), Andres via metathesis (linguistics), metathesis.
In Sweden, A ...
. Many of these results reached the international scientific community through the 1976 paper on the expectation–maximization (EM) method by Arthur P. Dempster, Nan Laird, and Donald Rubin, which was published in a leading international journal, sponsored by the Royal Statistical Society.
Logic

Philosophical logic
Inphilosophical logic
Understood in a narrow sense, philosophical logic is the area of logic that studies the application of logical methods to philosophical problems, often in the form of extended logical systems like modal logic. Some theorists conceive philosophic ...
, Per Martin-Löf has published papers on the theory of logical consequence
Logical consequence (also entailment or logical implication) is a fundamental concept in logic which describes the relationship between statement (logic), statements that hold true when one statement logically ''follows from'' one or more stat ...
, on judgment
Judgement (or judgment) is the evaluation of given circumstances to make a decision. Judgement is also the ability to make considered decisions.
In an informal context, a judgement is opinion expressed as fact. In the context of a legal trial ...
s, etc. He has been interested in Central-European philosophical traditions, especially of the German-language writings of Franz Brentano
Franz Clemens Honoratus Hermann Josef Brentano (; ; 16 January 1838 – 17 March 1917) was a German philosopher and psychologist. His 1874 '' Psychology from an Empirical Standpoint'', considered his magnum opus, is credited with having reintrod ...
, Gottlob Frege
Friedrich Ludwig Gottlob Frege (; ; 8 November 1848 – 26 July 1925) was a German philosopher, logician, and mathematician. He was a mathematics professor at the University of Jena, and is understood by many to be the father of analytic philos ...
, and of Edmund Husserl
Edmund Gustav Albrecht Husserl (; 8 April 1859 – 27 April 1938) was an Austrian-German philosopher and mathematician who established the school of Phenomenology (philosophy), phenomenology.
In his early work, he elaborated critiques of histori ...
.
Type theory
Martin-Löf has worked inmathematical logic
Mathematical logic is the study of Logic#Formal logic, formal logic within mathematics. Major subareas include model theory, proof theory, set theory, and recursion theory (also known as computability theory). Research in mathematical logic com ...
for many decades.
From 1968 to '69 he worked as an assistant professor at the University of Chicago
The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, or UChi) is a Private university, private research university in Chicago, Illinois, United States. Its main campus is in the Hyde Park, Chicago, Hyde Park neighborhood on Chicago's South Side, Chic ...
where he met William Alvin Howard
William Alvin Howard (born 1926) is an American mathematician and proof theorist best known for his work demonstrating formal similarity between intuitionistic logic and the simply typed lambda calculus that has come to be known as the Curry–Ho ...
with whom he discussed issues related to the Curry–Howard correspondence
In programming language theory and proof theory, the Curry–Howard correspondence is the direct relationship between computer programs and mathematical proofs. It is also known as the Curry–Howard isomorphism or equivalence, or the proofs-as-p ...
. Martin-Löf's first draft article on type theory dates back to 1971. This impredicative theory generalized Girard's System F
System F (also polymorphic lambda calculus or second-order lambda calculus) is a typed lambda calculus that introduces, to simply typed lambda calculus, a mechanism of universal quantification over types. System F formalizes parametric polymorph ...
. However, this system turned out to be inconsistent
In deductive logic, a consistent theory is one that does not lead to a logical contradiction. A theory T is consistent if there is no formula \varphi such that both \varphi and its negation \lnot\varphi are elements of the set of consequences o ...
due to Girard's paradox which was discovered by Girard when studying System U, an inconsistent extension of System F. This experience led Per Martin-Löf to develop the philosophical foundations of type theory
In mathematics and theoretical computer science, a type theory is the formal presentation of a specific type system. Type theory is the academic study of type systems.
Some type theories serve as alternatives to set theory as a foundation of ...
, his ''meaning explanation'', a form of proof-theoretic semantics, which justifies predicative type theory as presented in his 1984 Bibliopolis book, and extended in a number of increasingly philosophical texts, such as his influential ''On the Meanings of the Logical Constants and the Justifications of the Logical Laws''.
The 1984 type theory was extensional while the type theory presented in the book by Nordström ''et al.'' in 1990, which was heavily influenced by his later ideas, intensional, and more amenable to being implemented on a computer.
Martin-Löf's intuitionistic type theory developed the notion of dependent type
In computer science and logic, a dependent type is a type whose definition depends on a value. It is an overlapping feature of type theory and type systems. In intuitionistic type theory, dependent types are used to encode logic's quantifiers lik ...
s and directly influenced the development of the calculus of constructions
In mathematical logic and computer science, the calculus of constructions (CoC) is a type theory created by Thierry Coquand. It can serve as both a typed programming language and as constructive foundation for mathematics. For this second reaso ...
and the logical framework LF. A number of popular computer-based proof systems are based on type theory, for example NuPRL, LEGO, Coq, ALF, Agda, Twelf, Epigram
An epigram is a brief, interesting, memorable, sometimes surprising or satirical statement. The word derives from the Greek (, "inscription", from [], "to write on, to inscribe"). This literary device has been practiced for over two millennia ...
, and Idris (programming language), Idris.
Awards
Martin-Löf is a member of theRoyal Swedish Academy of Sciences
The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences () is one of the Swedish Royal Academies, royal academies of Sweden. Founded on 2 June 1739, it is an independent, non-governmental scientific organization that takes special responsibility for promoting nat ...
(elected 1990) and of the Academia Europaea
The Academia Europaea is a pan-European Academy of humanities, letters, law, and sciences.
The Academia was founded in 1988 as a functioning Europe-wide Academy that encompasses all fields of scholarly inquiry. It acts as co-ordinator of Europe ...
(elected 1989).
See also
*Franz Brentano
Franz Clemens Honoratus Hermann Josef Brentano (; ; 16 January 1838 – 17 March 1917) was a German philosopher and psychologist. His 1874 '' Psychology from an Empirical Standpoint'', considered his magnum opus, is credited with having reintrod ...
* Rudolf Carnap
Rudolf Carnap (; ; 18 May 1891 – 14 September 1970) was a German-language philosopher who was active in Europe before 1935 and in the United States thereafter. He was a major member of the Vienna Circle and an advocate of logical positivism.
...
* Michael Dummett
Sir Michael Anthony Eardley Dummett (; 27 June 1925 – 27 December 2011) was an English academic described as "among the most significant British philosophers of the last century and a leading campaigner for racial tolerance and equality." H ...
* Gottlob Frege
Friedrich Ludwig Gottlob Frege (; ; 8 November 1848 – 26 July 1925) was a German philosopher, logician, and mathematician. He was a mathematics professor at the University of Jena, and is understood by many to be the father of analytic philos ...
* Ulf Grenander
Ulf Grenander (23 July 1923 – 12 May 2016) was a Swedish statistician and professor of applied mathematics at Brown University.
His early research was in probability theory, stochastic processes, time series analysis, and statistical theory (pa ...
* Jaakko Hintikka
* Edmund Husserl
Edmund Gustav Albrecht Husserl (; 8 April 1859 – 27 April 1938) was an Austrian-German philosopher and mathematician who established the school of Phenomenology (philosophy), phenomenology.
In his early work, he elaborated critiques of histori ...
* Andrei N. Kolmogorov
* Anders Martin-Löf
* John von Neumann
John von Neumann ( ; ; December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian and American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist and engineer. Von Neumann had perhaps the widest coverage of any mathematician of his time, in ...
* Peter Pagin
* Dag Prawitz
Dag Prawitz (born 1936, Stockholm) is a Swedish philosopher and logician. He is best known for his work on proof theory and the foundations of natural deduction, and for his contributions to proof-theoretic semantics.
Prawitz is a member of the ...
* Charles Sanders Peirce
Charles Sanders Peirce ( ; September 10, 1839 – April 19, 1914) was an American scientist, mathematician, logician, and philosopher who is sometimes known as "the father of pragmatism". According to philosopher Paul Weiss (philosopher), Paul ...
* Frank P. Ramsey
Frank Plumpton Ramsey (; 22 February 1903 – 19 January 1930) was a British people, British philosopher, mathematician, and economist who made major contributions to all three fields before his death at the age of 26. He was a close friend of ...
* Bertrand Russell
Bertrand Arthur William Russell, 3rd Earl Russell, (18 May 1872 – 2 February 1970) was a British philosopher, logician, mathematician, and public intellectual. He had influence on mathematics, logic, set theory, and various areas of analytic ...
* Dana Scott
Dana Stewart Scott (born October 11, 1932) is an American logician who is the emeritus Hillman University Professor of Computer Science, Philosophy, and Mathematical Logic at Carnegie Mellon University; he is now retired and lives in Berkeley, C ...
* Alfred Tarski
Alfred Tarski (; ; born Alfred Teitelbaum;School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of St Andrews ''School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of St Andrews''. January 14, 1901 – October 26, 1983) was a Polish-American logician ...
* Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher and theoretical biologist. He was highly influential in the development of theoretical computer ...
Notes
References
Bird watching and missing data
* * George A. Barnard"Gone Birdwatching"
''New Scientist'', 4 December 1999, magazine issue 2215. * *
Probability foundations
* Per Martin-Löf. "The Definition of Random Sequences." ''Information and Control'', 9(6): 602–619, 1966. * Li, Ming and Vitányi, Paul, ''An Introduction to Kolmogorov Complexity and Its Applications'', Springer, 1997Probability on algebraic structures, following Ulf Grenander
* Grenander, Ulf. ''Probability on Algebraic Structures''. (Dover reprint) * Martin-Löf, P. The continuity theorem on a locally compact group. ''Teor. Verojatnost. i Primenen.'' 10 1965 367–371. * Martin-Löf, Per. Probability theory on discrete semigroups. ''Z. Wahrscheinlichkeitstheorie und Verw. Gebiete'' 4 1965 78—102 * Nitis Mukhopadhyay. "A Conversation with Ulf Grenander". ''Statist. Sci.'' Volume 21, Number 3 (2006), 404–426.Statistics foundations
* Anders Martin-Löf. 1963. "Utvärdering av livslängder i subnanosekundsområdet" ("Evaluation of lifetimes in time-lengths below one nanosecond"). ("Sundberg formula", according to Sundberg 1971) * Per Martin-Löf. 1966. ''Statistics from the point of view of statistical mechanics''. Lecture notes, Mathematical Institute, Aarhus University. ("Sundberg formula" credited to Anders Martin-Löf, according to Sundberg 1971) * Per Martin-Löf. 1970. ''Statistika Modeller (Statistical Models): Anteckningar fran seminarier läsåret 1969–1970 (Notes from seminars in the academic year 1969–1970), with the assistance of Rolf Sundberg.'' Stockholm University. * Martin-Löf, P. "Exact tests, confidence regions and estimates", with a discussion byA. W. F. Edwards
Anthony William Fairbank Edwards, Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from the royalsociety.org website where: (born 1935) is a British statistician, geneticist and evolutionary biologist. Ed ...
, G. A. Barnard, D. A. Sprott, O. Barndorff-Nielsen, D. Basu and G. Rasch. ''Proceedings of Conference on Foundational Questions in Statistical Inference'' (Aarhus, 1973), pp. 121–138. Memoirs, No. 1, Dept. Theoret. Statist., Inst. Math., Univ. Aarhus, Aarhus, 1974.
* Martin-Löf, P. Repetitive structures and the relation between canonical and microcanonical distributions in statistics and statistical mechanics. With a discussion by D. R. Cox and G. Rasch and a reply by the author. ''Proceedings of Conference on Foundational Questions in Statistical Inference'' (Aarhus, 1973), pp. 271–294. Memoirs, No. 1, Dept. Theoret. Statist., Inst. Math., Univ. Aarhus, Aarhus, 1974.
* Martin-Löf, P. The notion of redundancy and its use as a quantitative measure of the deviation between a statistical hypothesis and a set of observational data. With a discussion by F. Abildgård, A. P. Dempster, D. Basu, D. R. Cox, A. W. F. Edwards
Anthony William Fairbank Edwards, Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from the royalsociety.org website where: (born 1935) is a British statistician, geneticist and evolutionary biologist. Ed ...
, D. A. Sprott, G. A. Barnard, O. Barndorff-Nielsen, J. D. Kalbfleisch and G. Rasch and a reply by the author. ''Proceedings of Conference on Foundational Questions in Statistical Inference'' (Aarhus, 1973), pp. 1–42. Memoirs, No. 1, Dept. Theoret. Statist., Inst. Math., Univ. Aarhus, Aarhus, 1974.
* Martin-Löf, Per The notion of redundancy and its use as a quantitative measure of the discrepancy between a statistical hypothesis and a set of observational data. ''Scand. J. Statist.'' 1 (1974), no. 1, 3—18.
* Sverdrup, Erling. "Tests without power." ''Scand. J. Statist.'' 2 (1975), no. 3, 158–160.
* Martin-Löf, Per Reply to Erling Sverdrup's polemical article: ''Tests without power'' (''Scand. J. Statist.'' 2 (1975), no. 3, 158–160). ''Scand. J. Statist.'' 2 (1975), no. 3, 161–165.
* Sverdrup, Erling. A rejoinder to: ''Tests without power'' (''Scand. J. Statist.'' 2 (1975), 161—165) by P. Martin-Löf. ''Scand. J. Statist.'' 4 (1977), no. 3, 136—138.
* Martin-Löf, P. Exact tests, confidence regions and estimates. Foundations of probability and statistics. II. ''Synthese'' 36 (1977), no. 2, 195—206.
* Rolf Sundberg. 1971. ''Maximum likelihood theory and applications for distributions generated when observing a function of an exponential family variable''. Dissertation, Institute for Mathematical Statistics, Stockholm University.
* Sundberg, Rolf. Maximum likelihood theory for incomplete data from an exponential family. ''Scand. J. Statist.'' 1 (1974), no. 2, 49—58.
* Sundberg, Rolf An iterative method for solution of the likelihood equations for incomplete data from exponential families. Comm. Statist.—Simulation Comput. B5 (1976), no. 1, 55—64.
* Sundberg, Rolf Some results about decomposable (or Markov-type) models for multidimensional contingency tables: distribution of marginals and partitioning of tests. Scand. J. Statist. 2 (1975), no. 2, 71—79.
* Höglund, Thomas. The exact estimate — a method of statistical estimation. ''Z. Wahrscheinlichkeitstheorie und Verw. Gebiete'' 29 (1974), 257—271.
* Lauritzen, Steffen L. ''Extremal families and systems of sufficient statistics''. Lecture Notes in Statistics, 49. Springer-Verlag, New York, 1988. xvi+268 pp.
Foundations of mathematics, logic, and computer science
* Per Martin-Löf. A theory of types. Preprint, Stockholm University, 1971. * Per Martin-Löf.An intuitionistic theory of types
'' In G. Sambin and J. Smith, editors, Twenty-Five Years of Constructive Type Theory. Oxford University Press, 1998. Reprinted version of an unpublished report from 1972. * Per Martin-Löf. An intuitionistic theory of types: Predicative part. In H. E. Rose and J. C. Shepherdson, editors, Logic Colloquium ‘73, pages 73–118. North Holland, 1975. * Per Martin-Löf.
Constructive mathematics and computer programming
'' In ''Logic, Methodology and Philosophy of Science VI, 1979''. Eds. Cohen, et al. North-Holland, Amsterdam. pp. 153–175, 1982. * Per Martin-Löf.
Intuitionistic type theory
'' (Notes by Giovanni Sambin of a series of lectures given in Padua, June 1980). Napoli, Bibliopolis, 1984. * Per Martin-Löf. ''Philosophical implications of type theory'', Unpublished notes, 1987? * Per Martin-Löf. ''Substitution calculus'', 1992. Notes from a lecture given in Göteborg. * Bengt Nordström, Kent Petersson, and Jan M. Smith. ''Programming in Martin-Löf's Type Theory''. Oxford University Press, 1990. (The book is out of print, bu
a free version
has been made available.) * Per Martin-Löf.
On the Meanings of the Logical Constants and the Justifications of the Logical Laws
'' '' Nordic Journal of Philosophical Logic'', 1(1): 11–60, 1996. * Per Martin-Löf.
Logic and Ethics
'' In T. Piecha and P. Schroeder-Heister, editors,
Proof-Theoretic Semantics: Assessment and Future Perspectives. Proceedings of the Third Tübingen Conference on Proof-Theoretic Semantics, 27–30 March 2019
', pages 227-235. URI:
http://dx.doi.org/10.15496/publikation-35319
'. University of Tübingen 2019.
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Martin-Lof, Per Members of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences Members of Academia Europaea Mathematical logicians Swedish logicians Swedish statisticians 20th-century Swedish philosophers 21st-century Swedish philosophers Swedish information theorists 20th-century Swedish mathematicians 21st-century Swedish mathematicians Academic staff of Stockholm University Birdwatchers Swedish ornithologists 1942 births Living people Proof theorists People from Stockholm