Pennsylvania House District 123 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pennsylvania (; (
/ref> By 1000 CE, in contrast to their nomadic
 Between 1730 and when the Pennsylvania Colony was shut down by Parliament with the Currency Act of 1764, the Pennsylvania Colony made its own paper money to account for the shortage of actual gold and silver. The paper money was called
Between 1730 and when the Pennsylvania Colony was shut down by Parliament with the Currency Act of 1764, the Pennsylvania Colony made its own paper money to account for the shortage of actual gold and silver. The paper money was called
 The General Assembly met in the old
The General Assembly met in the old
''ExplorePAHistory.com''. Retrieved February 18, 2022. later the
 At the beginning of the 20th century, Pennsylvania's economy centered on steel production, logging, coal mining, textile production, and other forms of industrial manufacturing. A surge in immigration to the U.S. during the late 19th and early 20th centuries provided a steady flow of cheap labor for these industries, which often employed children and people who could not speak English from Southern and
At the beginning of the 20th century, Pennsylvania's economy centered on steel production, logging, coal mining, textile production, and other forms of industrial manufacturing. A surge in immigration to the U.S. during the late 19th and early 20th centuries provided a steady flow of cheap labor for these industries, which often employed children and people who could not speak English from Southern and
 On September 11, 2001, during the terrorist attacks on the United States, the small town of
On September 11, 2001, during the terrorist attacks on the United States, the small town of
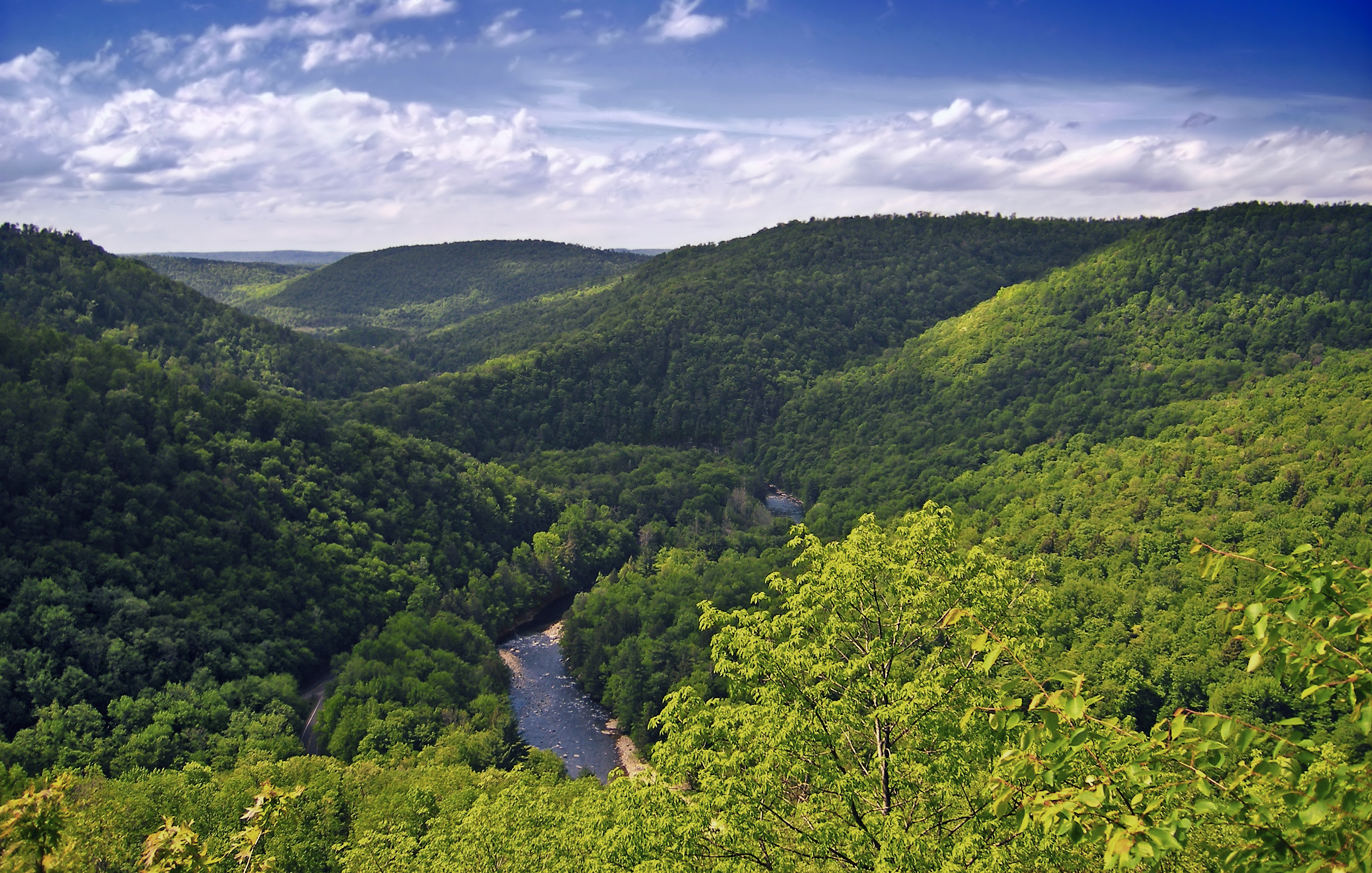 Pennsylvania is north to south and east to west. Of a total , are land, are inland waters, and are waters in
Pennsylvania is north to south and east to west. Of a total , are land, are inland waters, and are waters in
/ref> It is the 33rd-largest state in the
 Pennsylvania's diverse topography produces a variety of climates, though the entire state experiences cold winters and humid summers. Straddling two major zones, the majority of the state, except for the southeastern corner, has a
Pennsylvania's diverse topography produces a variety of climates, though the entire state experiences cold winters and humid summers. Straddling two major zones, the majority of the state, except for the southeastern corner, has a
 Among Pennsylvania residents, as of 2020, 74.5% were born in Pennsylvania, 18.4% were born in a different U.S. state, 1.5% were born in Puerto Rico], U.S. Island areas, or born abroad to American parent(s), and 5.6% were foreign born. Foreign-born Pennsylvanians are largely from Asia (36.0%), Europe (35.9%), and Latin America (30.6%) with the remainder from Africa (5%), North America (3.1%), and Oceania (0.4%).
The state's largest ancestry groups, expressed as a percentage of total people who responded with a particular ancestry for the 2010 census, are:
* German Americans, German 28.5%
* Irish Americans, Irish 18.2%
* Italian Americans, Italian 12.8%
* African Americans 9.6%
* English Americans, English 8.5%
* Polish Americans, Polish 7.2%
* French Americans, French 4.2%
Among Pennsylvania residents, as of 2020, 74.5% were born in Pennsylvania, 18.4% were born in a different U.S. state, 1.5% were born in Puerto Rico], U.S. Island areas, or born abroad to American parent(s), and 5.6% were foreign born. Foreign-born Pennsylvanians are largely from Asia (36.0%), Europe (35.9%), and Latin America (30.6%) with the remainder from Africa (5%), North America (3.1%), and Oceania (0.4%).
The state's largest ancestry groups, expressed as a percentage of total people who responded with a particular ancestry for the 2010 census, are:
* German Americans, German 28.5%
* Irish Americans, Irish 18.2%
* Italian Americans, Italian 12.8%
* African Americans 9.6%
* English Americans, English 8.5%
* Polish Americans, Polish 7.2%
* French Americans, French 4.2%
 Pennsylvania Dutch language, Pennsylvania German, spoken by nearly one percent of Pennsylvania's population as of 2010, is often misleadingly called Pennsylvania Dutch. The term Dutch was used to mean German, including the Netherlands, before the Latin name for them replaced it. When referring to the language spoken by the Pennsylvania Dutch, Pennsylvania Dutch people, Pennsylvania German, it means
Pennsylvania Dutch language, Pennsylvania German, spoken by nearly one percent of Pennsylvania's population as of 2010, is often misleadingly called Pennsylvania Dutch. The term Dutch was used to mean German, including the Netherlands, before the Latin name for them replaced it. When referring to the language spoken by the Pennsylvania Dutch, Pennsylvania Dutch people, Pennsylvania German, it means
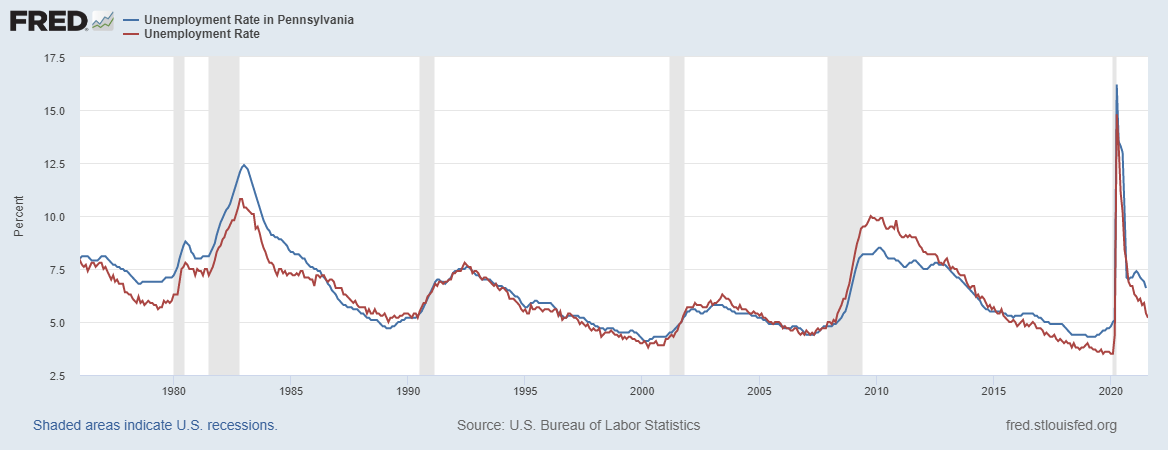
 As of 2021, Pennsylvania's gross state product (GSP) of $839.4 billion List of U.S. states and territories by GDP, ranks 6th among all U.S. states, behind California, Texas,
As of 2021, Pennsylvania's gross state product (GSP) of $839.4 billion List of U.S. states and territories by GDP, ranks 6th among all U.S. states, behind California, Texas,
 Casino gambling was legalized in Pennsylvania in 2004. As of 2022, there are List of casinos in Pennsylvania, 16 casinos in the state. Table games such as poker, roulette, blackjack, and craps were approved by the state legislature and signed into law in January 2010.
Casino gambling was legalized in Pennsylvania in 2004. As of 2022, there are List of casinos in Pennsylvania, 16 casinos in the state. Table games such as poker, roulette, blackjack, and craps were approved by the state legislature and signed into law in January 2010.
 Pennsylvania has a bicameral legislature set up by Commonwealth's constitution in 1790. The original Frame of Government of William Penn had a unicameral legislature. The Pennsylvania General Assembly, General Assembly includes 50 Pennsylvania Senate, Senators and 203 Pennsylvania House of Representatives, Representatives. Joseph B. Scarnati III, Joe Scarnati is currently President Pro Tempore of the State Senate, Jake Corman the Majority Leader, and Jay Costa the Minority Leader. Bryan Cutler is Speaker of the Pennsylvania House of Representatives, Speaker of the House of Representatives, with Kerry A. Benninghoff as Majority Leader and Frank Dermody as Minority Leader. As of the Pennsylvania House of Representatives election, 2018, 2018 elections, the Republicans hold the majority in the State House and Senate.
Pennsylvania has a bicameral legislature set up by Commonwealth's constitution in 1790. The original Frame of Government of William Penn had a unicameral legislature. The Pennsylvania General Assembly, General Assembly includes 50 Pennsylvania Senate, Senators and 203 Pennsylvania House of Representatives, Representatives. Joseph B. Scarnati III, Joe Scarnati is currently President Pro Tempore of the State Senate, Jake Corman the Majority Leader, and Jay Costa the Minority Leader. Bryan Cutler is Speaker of the Pennsylvania House of Representatives, Speaker of the House of Representatives, with Kerry A. Benninghoff as Majority Leader and Frank Dermody as Minority Leader. As of the Pennsylvania House of Representatives election, 2018, 2018 elections, the Republicans hold the majority in the State House and Senate.
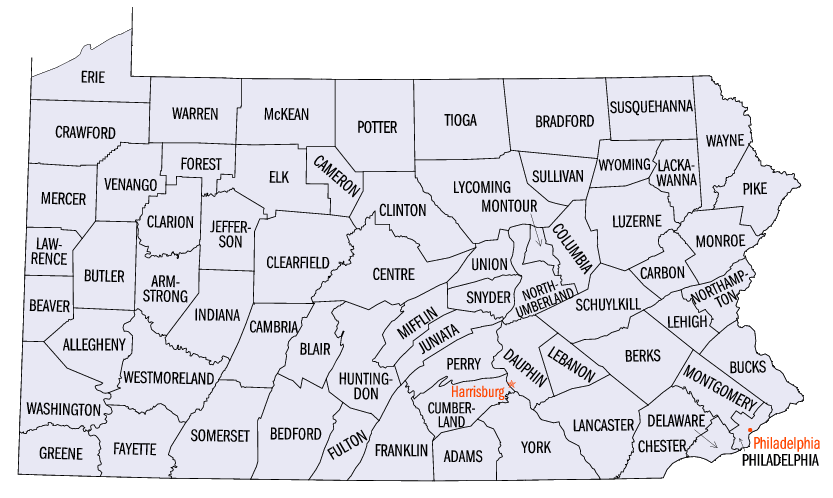 Pennsylvania is divided into 67 county (United States), counties.''The Pennsylvania Manual'', p. 6-3. Counties are further subdivided into municipalities that are either incorporated as cities, Borough (Pennsylvania), boroughs, or Township (Pennsylvania), townships.''Pennsylvania Manual'', p. 6-5. One county, Philadelphia County, Pennsylvania, Philadelphia County, is coterminous with the city of Philadelphia after it was Act of Consolidation, 1854, consolidated in 1854. The most populous county in Pennsylvania is Philadelphia, while the least populous is Cameron County, Pennsylvania, Cameron (4,547).
There are a total of 56 cities in Pennsylvania, which are classified, by population, as either first-, second-, or third-class cities. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania's largest city, has a population of 1.6 million and is the state's only first-class city.
Pennsylvania is divided into 67 county (United States), counties.''The Pennsylvania Manual'', p. 6-3. Counties are further subdivided into municipalities that are either incorporated as cities, Borough (Pennsylvania), boroughs, or Township (Pennsylvania), townships.''Pennsylvania Manual'', p. 6-5. One county, Philadelphia County, Pennsylvania, Philadelphia County, is coterminous with the city of Philadelphia after it was Act of Consolidation, 1854, consolidated in 1854. The most populous county in Pennsylvania is Philadelphia, while the least populous is Cameron County, Pennsylvania, Cameron (4,547).
There are a total of 56 cities in Pennsylvania, which are classified, by population, as either first-, second-, or third-class cities. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania's largest city, has a population of 1.6 million and is the state's only first-class city.
 Since the latter half of the 20th century, Pennsylvania has been perceived as a powerful swing state, and winning Pennsylvania has since been deemed as essential to President of the United States, U.S. presidential candidates. Only twice between 1932 to 1988 (1932 and 1968 with Herbert Hoover and Hubert Humphrey, respectively) has a winning presidential candidate failed to carry Pennsylvania.
Between 1992 and 2016, Pennsylvania trended Democratic Party (United States), Democratic in presidential elections; Bill Clinton won the state twice by large margins and Al Gore won it by a slightly closer margin in 2000. In the 2004 presidential election, John F. Kerry beat President George W. Bush in Pennsylvania, 2,938,095 (51%) to 2,793,847 (48%). In the 2008 presidential election, Democrat Barack Obama defeated
Since the latter half of the 20th century, Pennsylvania has been perceived as a powerful swing state, and winning Pennsylvania has since been deemed as essential to President of the United States, U.S. presidential candidates. Only twice between 1932 to 1988 (1932 and 1968 with Herbert Hoover and Hubert Humphrey, respectively) has a winning presidential candidate failed to carry Pennsylvania.
Between 1992 and 2016, Pennsylvania trended Democratic Party (United States), Democratic in presidential elections; Bill Clinton won the state twice by large margins and Al Gore won it by a slightly closer margin in 2000. In the 2004 presidential election, John F. Kerry beat President George W. Bush in Pennsylvania, 2,938,095 (51%) to 2,793,847 (48%). In the 2008 presidential election, Democrat Barack Obama defeated
 Under state law, school attendance in Pennsylvania is mandatory for a child from the age of 8until the age of 17, or until graduation from an accredited high school (whichever is earlier) unless students are Homeschooling in the United States, homeschooled. As of 2005, 83.8% of Pennsylvania residents age 18 to 24 are high school graduates; Among residents age 25 and over, 86.7% have graduated from high school.
The following are the four-year graduation rates for students completing high school in 2016:
Additionally, 27.5% of high school graduates in the state went on to obtain a bachelor's degree or higher, as of 2009. State students consistently do well in standardized testing. In 2007, Pennsylvania ranked 14th in mathematics, 12th in reading, and 10th in writing for 8th grade students. In 1988, the Pennsylvania General Assembly passed Act 169, which allows parents or guardians to homeschool their children as an option for compulsory school attendance. This law specifies the requirements and responsibilities of the parents and the school district where the family lives.
Under state law, school attendance in Pennsylvania is mandatory for a child from the age of 8until the age of 17, or until graduation from an accredited high school (whichever is earlier) unless students are Homeschooling in the United States, homeschooled. As of 2005, 83.8% of Pennsylvania residents age 18 to 24 are high school graduates; Among residents age 25 and over, 86.7% have graduated from high school.
The following are the four-year graduation rates for students completing high school in 2016:
Additionally, 27.5% of high school graduates in the state went on to obtain a bachelor's degree or higher, as of 2009. State students consistently do well in standardized testing. In 2007, Pennsylvania ranked 14th in mathematics, 12th in reading, and 10th in writing for 8th grade students. In 1988, the Pennsylvania General Assembly passed Act 169, which allows parents or guardians to homeschool their children as an option for compulsory school attendance. This law specifies the requirements and responsibilities of the parents and the school district where the family lives.
 The Pennsylvania State System of Higher Education (PASSHE) is the public university system of the Commonwealth, with 14 state-owned schools. West Chester University has by far the largest student body of the 14 universities. The Commonwealth System of Higher Education is an organizing body of the four state-related schools in Pennsylvania; these schools (Pennsylvania State University, Lincoln University (Pennsylvania), Lincoln University, the University of Pittsburgh, and Temple University) are independent institutions that receive some state funding. There are also 15 publicly funded two-year Community colleges in the United States, community colleges and technical schools that are separate from the PASSHE system. Additionally, there are many private two- and four-year technical schools, colleges, and universities.
Carnegie Mellon University, Pennsylvania State University, the
The Pennsylvania State System of Higher Education (PASSHE) is the public university system of the Commonwealth, with 14 state-owned schools. West Chester University has by far the largest student body of the 14 universities. The Commonwealth System of Higher Education is an organizing body of the four state-related schools in Pennsylvania; these schools (Pennsylvania State University, Lincoln University (Pennsylvania), Lincoln University, the University of Pittsburgh, and Temple University) are independent institutions that receive some state funding. There are also 15 publicly funded two-year Community colleges in the United States, community colleges and technical schools that are separate from the PASSHE system. Additionally, there are many private two- and four-year technical schools, colleges, and universities.
Carnegie Mellon University, Pennsylvania State University, the
 Pennsylvania is home to the nation's first zoo, the Philadelphia Zoo. Other long-accredited AZA zoos include the Erie Zoo and the Pittsburgh Zoo & PPG Aquarium. The Lehigh Valley Zoo and ZooAmerica are other notable zoos. The Commonwealth boasts some of the finest museums in the country, including the Allentown Art Museum in Allentown, Carnegie Museums in Pittsburgh, the Philadelphia Museum of Art, and :Museums in Pennsylvania, several others. One unique museum is the Houdini Museum in Scranton, the only building in the world devoted to the legendary magician. Pennsylvania is also home to the National Aviary, located in Pittsburgh.
All 121 List of Pennsylvania state parks, state parks in Pennsylvania feature free admission.
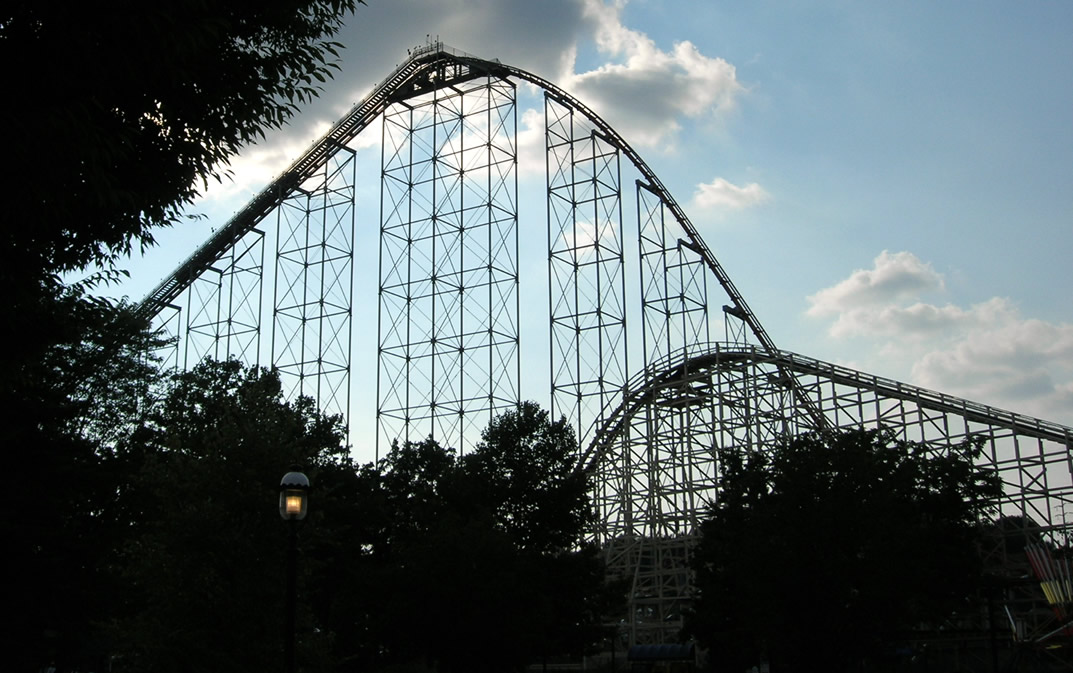
Pennsylvania's notable amusement parks include Conneaut Lake Park, Dorney Park & Wildwater Kingdom, Dutch Wonderland, DelGrosso's Amusement Park, Great Wolf Lodge, Hersheypark, Idlewild Park, Kalahari Resorts, Kalahari Resorts Poconos, Kennywood, Knoebels, Lakemont Park, Sandcastle Waterpark, Sesame Place (Philadelphia), Sesame Place, and Waldameer Park. Pennsylvania also is home to the largest indoor waterpark resort on the East Coast, Splash Lagoon in Erie.
The state's notable music festivals include Musikfest, the nation's largest free music festival held annually each August in
Pennsylvania is home to the nation's first zoo, the Philadelphia Zoo. Other long-accredited AZA zoos include the Erie Zoo and the Pittsburgh Zoo & PPG Aquarium. The Lehigh Valley Zoo and ZooAmerica are other notable zoos. The Commonwealth boasts some of the finest museums in the country, including the Allentown Art Museum in Allentown, Carnegie Museums in Pittsburgh, the Philadelphia Museum of Art, and :Museums in Pennsylvania, several others. One unique museum is the Houdini Museum in Scranton, the only building in the world devoted to the legendary magician. Pennsylvania is also home to the National Aviary, located in Pittsburgh.
All 121 List of Pennsylvania state parks, state parks in Pennsylvania feature free admission.
Pennsylvania's notable amusement parks include Conneaut Lake Park, Dorney Park & Wildwater Kingdom, Dutch Wonderland, DelGrosso's Amusement Park, Great Wolf Lodge, Hersheypark, Idlewild Park, Kalahari Resorts, Kalahari Resorts Poconos, Kennywood, Knoebels, Lakemont Park, Sandcastle Waterpark, Sesame Place (Philadelphia), Sesame Place, and Waldameer Park. Pennsylvania also is home to the largest indoor waterpark resort on the East Coast, Splash Lagoon in Erie.
The state's notable music festivals include Musikfest, the nation's largest free music festival held annually each August in


 The Pennsylvania Department of Transportation, abbreviated as PennDOT, is responsible for transport issues within the commonwealth.
The Pennsylvania Department of Transportation, abbreviated as PennDOT, is responsible for transport issues within the commonwealth.
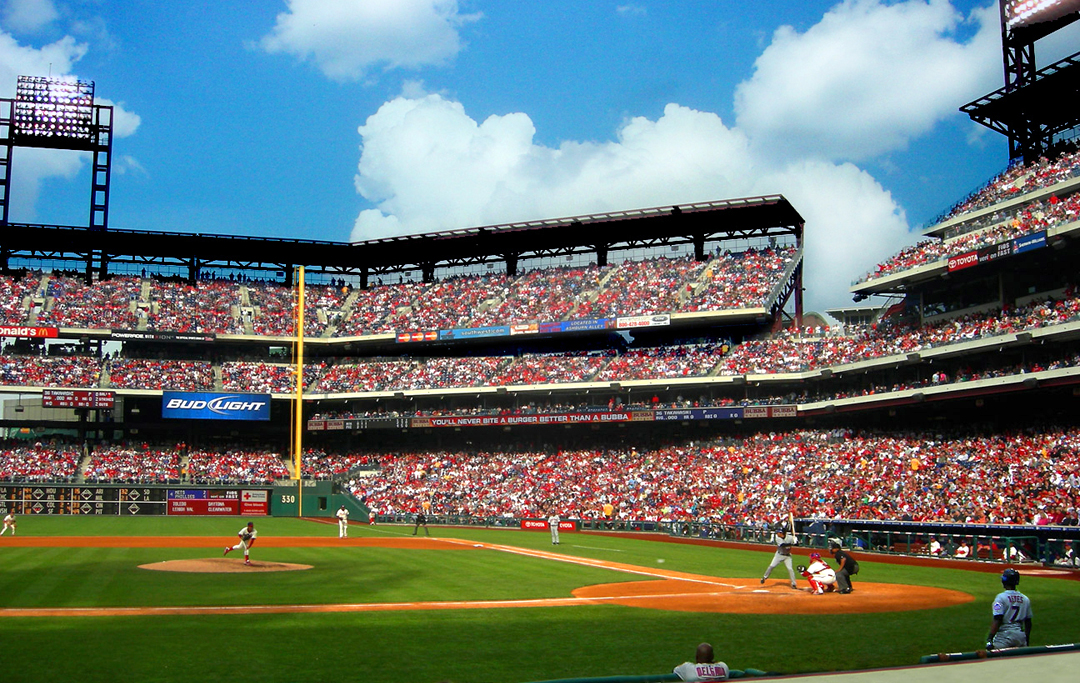



 Pennsylvania is home to eight major league professional sports teams: the Philadelphia Phillies and Pittsburgh Pirates of Major League Baseball, the Philadelphia 76ers of the National Basketball Association, NBA, the Philadelphia Eagles and Pittsburgh Steelers of the National Football League, NFL, the Philadelphia Flyers and Pittsburgh Penguins of the National Hockey League, NHL, and the Philadelphia Union of Major League Soccer. Among them, these teams have accumulated sevenWorld Series championships (with the Pirates winning five and Phillies winning two), 16 National League pennants (with the Pirates winning nine and Phillies winning seven), three pre-Super Bowl era NFL championships (all won by the Eagles), seven Super Bowl championships (with the Steelers winning six and the Eagles one), two NBA championships (both won by the 76ers), and seven Stanley Cup championships (with the Penguins winning five and Flyers winning two).
With Sports in Philadelphia, five professional sports teams and some of the most passionate sports fans in the nation,
Pennsylvania is home to eight major league professional sports teams: the Philadelphia Phillies and Pittsburgh Pirates of Major League Baseball, the Philadelphia 76ers of the National Basketball Association, NBA, the Philadelphia Eagles and Pittsburgh Steelers of the National Football League, NFL, the Philadelphia Flyers and Pittsburgh Penguins of the National Hockey League, NHL, and the Philadelphia Union of Major League Soccer. Among them, these teams have accumulated sevenWorld Series championships (with the Pirates winning five and Phillies winning two), 16 National League pennants (with the Pirates winning nine and Phillies winning seven), three pre-Super Bowl era NFL championships (all won by the Eagles), seven Super Bowl championships (with the Steelers winning six and the Eagles one), two NBA championships (both won by the 76ers), and seven Stanley Cup championships (with the Penguins winning five and Flyers winning two).
With Sports in Philadelphia, five professional sports teams and some of the most passionate sports fans in the nation,

 In 2008, author Sharon Hernes Silverman called Pennsylvania the snack food capital of the world. It leads all other states in the manufacture of pretzels and potato chips. The Sturgis Pretzel House introduced the pretzel to America, and companies like Anderson Bakery Company, Intercourse Pretzel Factory, and Snyder's of Hanover are leading manufacturers in the Commonwealth. Two of the three companies that define the U.S. potato chip industry are based in Pennsylvania: Utz Quality Foods, which started making chips in Hanover, Pennsylvania, in 1921 and Wise Foods, which started making chips in Berwick, Pennsylvania, Berwick also in 1921. The third, Frito-Lay is part of PepsiCo, and is based in Plano, Texas. Other companies such as Herr's Snacks, Martin's Potato Chips, Snyder's of Berlin (not associated with Snyder's of Hanover), Middleswarth Potato Chips (in Middleburg) and Troyer Farms Potato Products are popular chip manufacturers.
The U.S. chocolate industry is centered in
In 2008, author Sharon Hernes Silverman called Pennsylvania the snack food capital of the world. It leads all other states in the manufacture of pretzels and potato chips. The Sturgis Pretzel House introduced the pretzel to America, and companies like Anderson Bakery Company, Intercourse Pretzel Factory, and Snyder's of Hanover are leading manufacturers in the Commonwealth. Two of the three companies that define the U.S. potato chip industry are based in Pennsylvania: Utz Quality Foods, which started making chips in Hanover, Pennsylvania, in 1921 and Wise Foods, which started making chips in Berwick, Pennsylvania, Berwick also in 1921. The third, Frito-Lay is part of PepsiCo, and is based in Plano, Texas. Other companies such as Herr's Snacks, Martin's Potato Chips, Snyder's of Berlin (not associated with Snyder's of Hanover), Middleswarth Potato Chips (in Middleburg) and Troyer Farms Potato Products are popular chip manufacturers.
The U.S. chocolate industry is centered in
Gov. Andrew Curtin's Pennsylvania Reserve Volunteer Corps, Civil War 1861–1864
Official state government site
Pennsylvania Department of Transportation
Allegheny National Forest
Pennsylvania Wilds
USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Pennsylvania
Energy Data & Statistics for Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania State Facts from USDA
Official state tourism site
Free Original Documents Online: Pennsylvania State Archives 1600s to 1800s
Pennsylvania Department of Community and Economic Development
National Association of Counties (information on each Pennsylvania County)
* {{coord, 41, -78, dim:300000_region:US-PA_type:adm1st, name=Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, display=title Pennsylvania, 1787 establishments in the United States Articles containing video clips Contiguous United States Mid-Atlantic states Northeastern United States States and territories established in 1787 States of the United States States of the East Coast of the United States
Pennsylvania Dutch
The Pennsylvania Dutch ( Pennsylvania Dutch: ), also known as Pennsylvania Germans, are a cultural group formed by German immigrants who settled in Pennsylvania during the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries. They emigrated primarily from German-spe ...
: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each se ...
, Appalachia
Appalachia () is a cultural region in the Eastern United States that stretches from the Southern Tier of New York State to northern Alabama and Georgia. While the Appalachian Mountains stretch from Belle Isle in Newfoundland and Labrador, Ca ...
n, and Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
regions of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
. It borders Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
to its southeast, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
to its south, West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the Bur ...
to its southwest, Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
to its west, Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
and the Canadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
province of Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
to its northwest, New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
to its north, and the Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock (village), New York, Hancock, New York, the river flows for along the borders of N ...
and New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
to its east.
Pennsylvania is the fifth-most populous state in the nation with over 13 million residents as of 2020. It is the 33rd-largest state by area and ranks ninth among all states in population density. The southeastern Delaware Valley
The Delaware Valley is a metropolitan region on the East Coast of the United States that comprises and surrounds Philadelphia, the sixth most populous city in the nation and 68th largest city in the world as of 2020. The toponym Delaware Val ...
metropolitan area comprises and surrounds Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
, the state's largest
Large means of great size.
Large may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Arbitrarily large, a phrase in mathematics
* Large cardinal, a property of certain transfinite numbers
* Large category, a category with a proper class of objects and morphisms (o ...
and nation's sixth most populous city. Another 2.37 million reside in Greater Pittsburgh
Greater Pittsburgh is a populous region centered around its largest city and economic hub, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The region encompasses Pittsburgh's urban core county, Allegheny, and six adjacent Pennsylvania counties: Armstrong, Beaver, ...
in the southwest, centered around Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
, the state's second-largest and Western Pennsylvania
Western Pennsylvania is a region in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, covering the western third of the state. Pittsburgh is the region's principal city, with a metropolitan area population of about 2.4 million people, and serves as its economic ...
's largest city. The state's subsequent five most populous cities are: Allentown Allentown may refer to several places in the United States and topics related to them:
* Allentown, California, now called Toadtown, California
* Allentown, Georgia, a town in Wilkinson County
* Allentown, Illinois, an unincorporated community in T ...
, Reading
Reading is the process of taking in the sense or meaning of Letter (alphabet), letters, symbols, etc., especially by Visual perception, sight or Somatosensory system, touch.
For educators and researchers, reading is a multifaceted process invo ...
, Erie
Erie (; ) is a city on the south shore of Lake Erie and the county seat of Erie County, Pennsylvania, United States. Erie is the fifth largest city in Pennsylvania and the largest city in Northwestern Pennsylvania with a population of 94,831 a ...
, Scranton
Scranton is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania, Lackawanna County. With a population of 76,328 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 U ...
, and Bethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital o ...
. The state capital is Harrisburg
Harrisburg is the capital city of the Pennsylvania, Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Dauphin County, Pennsylvania, Dauphin County. With a population of 50,135 as of the 2021 census, Harrisburg is the List of c ...
.
Pennsylvania's geography is highly diverse: the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
run through the center of the state; the Allegheny and Pocono mountains span much of Northeast Pennsylvania
Northeastern Pennsylvania (NEPA) is a geographic region of the U.S. state of Pennsylvania that includes the Pocono Mountains, the Endless Mountains, and the industrial cities of Scranton, Wilkes-Barre, Pittston, Hazleton, Nanticoke, and Carbon ...
; close to 60% of the state is forested. While it has only of waterfront along Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
and the Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock (village), New York, Hancock, New York, the river flows for along the borders of N ...
, Pennsylvania has more navigable rivers than any other state in the nation, including the Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
, Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, and Pine Creek rivers.
Pennsylvania was founded in 1681 through a royal land grant
A land grant is a gift of real estate—land or its use privileges—made by a government or other authority as an incentive, means of enabling works, or as a reward for services to an individual, especially in return for military service. Grants ...
to William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer and religious thinker belonging to the Religious Society of Friends (Quakers), and founder of the Province of Pennsylvania, a North American colony of England. He was an early advocate of democracy a ...
, son of the state's namesake; a southeast portion of the state was once part of the colony of New Sweden
New Sweden ( sv, Nya Sverige) was a Swedish colony along the lower reaches of the Delaware River in what is now the United States from 1638 to 1655, established during the Thirty Years' War when Sweden was a great military power. New Sweden form ...
. Established as a haven for religious and political tolerance, the Province of Pennsylvania
The Province of Pennsylvania, also known as the Pennsylvania Colony, was a British North American colony founded by William Penn after receiving a land grant from Charles II of England in 1681. The name Pennsylvania ("Penn's Woods") refers to W ...
was known for its relatively peaceful relations with native tribes, innovative government system, and religious pluralism
Religious pluralism is an attitude or policy regarding the diversity of religious belief systems co-existing in society. It can indicate one or more of the following:
* Recognizing and tolerating the religious diversity of a society or countr ...
. Pennsylvania was one of thirteen British colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th centuri ...
from which the nation was formed.
Pennsylvania played a vital and historic role in the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
and the ultimately successful quest for independence from the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
. Its largest city, Philadelphia, was the gathering place of the nation's Founding Fathers and home to much of the thinking, activism, and writing that inspired the American Revolution. Philadelphia hosted the First Continental Congress
The First Continental Congress was a meeting of delegates from 12 of the 13 British colonies that became the United States. It met from September 5 to October 26, 1774, at Carpenters' Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, after the British Navy ...
in Carpenters' Hall
Carpenters' Hall is the official birthplace of the Pennsylvania, Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and a key meeting place in the early history of the United States. Carpenters' Hall is located in Independence National Historical Park in Philadelphia, ...
in 1774, and, beginning the following year, the Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a late-18th-century meeting of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolutionary War. The Congress was creating a new country it first named "United Colonies" and in 1 ...
in Independence Hall
Independence Hall is a historic civic building in Philadelphia, where both the United States Declaration of Independence and the United States Constitution were debated and adopted by America's Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Fa ...
, which in 1776 unanimously adopted the Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence or declaration of statehood or proclamation of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the ...
, a document that historian Joseph Ellis
Joseph John-Michael Ellis III (born July 18, 1943) is an American historian whose work focuses on the lives and times of the founders of the United States of America. '' American Sphinx: The Character of Thomas Jefferson'' won a National Boo ...
has described as "the most potent and consequential words in American history" and which formally launched the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
.
On December 25 and 26, 1776, Washington secretly led a column of Continental Army troops across the Delaware River from Bucks County
Bucks County is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. As of the 2020 census, the population was 646,538, making it the fourth-most populous county in Pennsylvania. Its county seat is Doylestown. The county is named after the English ...
, launching a successful surprise attack against Hessian mercenaries
Hessians ( or ) were German soldiers who served as auxiliaries to the British Army during the American Revolutionary War. The term is an American synecdoche for all Germans who fought on the British side, since 65% came from the German states ...
at the Battle of Trenton
The Battle of Trenton was a small but pivotal American Revolutionary War battle on the morning of December 26, 1776, in Trenton, New Jersey. After General George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American m ...
. In 1777 and 1778, the national capital of Philadelphia fell under British control for nine months, and multiple Revolutionary War battles were fought in Pennsylvania. For six months, Washington and 12,000 Continental Army troops encamped at Valley Forge
Valley Forge functioned as the third of eight winter encampments for the Continental Army's main body, commanded by General George Washington, during the American Revolutionary War. In September 1777, Congress fled Philadelphia to escape the B ...
over a harsh winter with limited supplies; roughly 1,700 to 2,000 of them died at Valley Forge from disease and malnutrition.
In Philadelphia, the Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a late-18th-century meeting of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolutionary War. The Congress was creating a new country it first named "United Colonies" and in 1 ...
, on June 21, 1778, ratified the Articles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union was an agreement among the 13 Colonies of the United States of America that served as its first frame of government. It was approved after much debate (between July 1776 and November 1777) by ...
, which served as the foundation for the ultimate development and ratification of the U.S. Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the natio ...
. On December 12, 1787, Pennsylvania became the second state after Delaware, which had previously been part of Pennsylvania as the three lower counties, to ratify the Constitution. On eight separate occasions prior to the construction of Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
as the nation's capital, a Pennsylvania city served as the nation's capital (Philadelphia from 1775 to 1776, 1777, twice in 1778, 1781, and 1790; York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
in 1777; and Lancaster in 1777).
During the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
, Pennsylvania's 360,000 Union Army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union (American Civil War), Union of the collective U.S. st ...
volunteers proved influential in strengthening the Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
, successfully guarding the national capital of Washington, D.C., which was vulnerable following the fall of Fort Sumter
Fort Sumter is a sea fort built on an artificial island protecting Charleston, South Carolina from naval invasion. Its origin dates to the War of 1812 when the British invaded Washington by sea. It was still incomplete in 1861 when the Battl ...
, and later leading daring raids against Confederate Army
The Confederate States Army, also called the Confederate Army or the Southern Army, was the military land force of the Confederate States of America (commonly referred to as the Confederacy) during the American Civil War (1861–1865), fighting ...
strongholds in the Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion in the Southern United States. The term was first used to describe the states most dependent on plantations and slavery prior to the American Civil War. Following the war ...
. The bloodiest battle of the Civil War with over 50,000 casualties, and one of the Union Army's most important victories, was fought on Pennsylvania soil at Gettysburg over three days in July 1863. The Union Army's victory at Gettysburg is considered the turning point in the war, leading to the Union's preservation. President Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation throu ...
's 271-word address dedicating Gettysburg National Cemetery
Gettysburg National Cemetery is a United States national cemetery created for Union casualties from the Battle of Gettysburg in the American Civil War. The Battle of Gettysburg, which was fought between July 1 to 3, 1863, resulted in the large ...
on November 19, 1863, remains one of the best-known speeches in American history
The history of the lands that became the United States began with the arrival of the first people in the Americas around 15,000 BC. Numerous indigenous cultures formed, and many saw transformations in the 16th century away from more densely ...
.
In the late 19th and 20th centuries, Pittsburgh-based U.S. Steel
United States Steel Corporation, more commonly known as U.S. Steel, is an American integrated steel producer headquartered in Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, with production operations primarily in the United States of America and in severa ...
, Bethlehem-based Bethlehem Steel
The Bethlehem Steel Corporation was an American steelmaking company headquartered in Bethlehem, Pennsylvania. For most of the 20th century, it was one of the world's largest steel producing and shipbuilding companies. At the height of its succe ...
, and other Pennsylvania manufacturing companies inspired the American Industrial Revolution
The technological and industrial history of the United States describes the United States' emergence as one of the most technologically advanced nations in the world. The availability of land and literate labor, the absence of a landed arist ...
and contributed to the development of much of the nation's early infrastructure, including key bridges, skyscraper
A skyscraper is a tall continuously habitable building having multiple floors. Modern sources currently define skyscrapers as being at least or in height, though there is no universally accepted definition. Skyscrapers are very tall high-ris ...
s, and warships, tanks, and other military hardware used in U.S.-led victories in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, and the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
. Since Pennsylvania's 1787 founding, a number of influential Pennsylvanians have contributed significantly to the nation in many fields, including the military, politics, business, scientific innovation
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entity ...
, thought leadership, philanthropy, music, art, and sports.
History
Indigenous settlement
Pennsylvania's history of human habitation extends to thousands of years before the foundation of the colonialProvince of Pennsylvania
The Province of Pennsylvania, also known as the Pennsylvania Colony, was a British North American colony founded by William Penn after receiving a land grant from Charles II of England in 1681. The name Pennsylvania ("Penn's Woods") refers to W ...
in 1681. Archaeologist
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
s believe the first settlement of the Americas
The settlement of the Americas began when Paleolithic hunter-gatherers entered North America from the North Asian Mammoth steppe via the Beringia land bridge, which had formed between northeastern Siberia and western Alaska due to the lowering of ...
occurred at least 15,000 years ago during the last glacial period, though it is unclear when humans first entered the area now known as Pennsylvania. There also is open debate in the archaeological community regarding when ancestors of Native Americans expanded across the two continents down to the tip of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southe ...
; possibilities range between 30,000 and 10,500 years ago. Meadowcroft Rockshelter
Meadowcroft Rockshelter is an archaeological site located near Avella in Jefferson Township, Pennsylvania. The site is a rock shelter in a bluff overlooking Cross Creek (a tributary of the Ohio River), and contains evidence that the area may ha ...
in Jefferson Township, Washington County, Pennsylvania, Jefferson Township includes the earliest known signs of human activity in Pennsylvania and perhaps all of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
, including the remains of a civilization that existed over 10,000 years ago and possibly pre-dated the Clovis culture
The Clovis culture is a prehistoric Paleoamerican culture, named for distinct stone and bone tools found in close association with Pleistocene fauna, particularly two mammoths, at Blackwater Locality No. 1 near Clovis, New Mexico, in 1936 ...
.Ancient Pa. Dwelling Still Dividing Archaeologists/ref> By 1000 CE, in contrast to their nomadic
hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
ancestors
An ancestor, also known as a forefather, fore-elder or a forebear, is a parent or (recursively) the parent of an antecedent (i.e., a grandparent, great-grandparent, great-great-grandparent and so forth). ''Ancestor'' is "any person from whom ...
, the native population of Pennsylvania had developed agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating Plant, plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of Sedentism, sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of Domestication, domesticated species created food ...
techniques and a mixed food economy.
By the time European colonization of the Americas
During the Age of Discovery, a large scale European colonization of the Americas took place between about 1492 and 1800. Although the Norse had explored and colonized areas of the North Atlantic, colonizing Greenland and creating a short ter ...
began, at least two major Native American tribes inhabited Pennsylvania. The first, the Lenape
The Lenape (, , or Lenape , del, Lënapeyok) also called the Leni Lenape, Lenni Lenape and Delaware people, are an indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, who live in the United States and Canada. Their historical territory includ ...
, spoke an Algonquian language and inhabited the eastern region of the state, then known as Lenapehoking
Lenapehoking (Unami: ''Lënapehòkink'') is widely translated as ' homelands of the Lenape', which in the 16th and 17th centuries, ranged along the Eastern seaboard from western Connecticut to Delaware, and encompassed the territory adjacent to th ...
. It included most of New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
and most of the Lehigh Valley
The Lehigh Valley (), known colloquially as The Valley, is a geographic region formed by the Lehigh River in Lehigh County and Northampton County in eastern Pennsylvania. It is a component valley of the Great Appalachian Valley bound to the no ...
and Delaware Valley
The Delaware Valley is a metropolitan region on the East Coast of the United States that comprises and surrounds Philadelphia, the sixth most populous city in the nation and 68th largest city in the world as of 2020. The toponym Delaware Val ...
regions of eastern and southeastern Pennsylvania. The Lenape's territory ended somewhere between the Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock (village), New York, Hancock, New York, the river flows for along the borders of N ...
in the east and the Susquehanna River
The Susquehanna River (; Lenape: Siskëwahane) is a major river located in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, overlapping between the lower Northeast and the Upland South. At long, it is the longest river on the East Coast of the ...
in central Pennsylvania. The Susquehannock
The Susquehannock people, also called the Conestoga by some English settlers or Andastes were Iroquoian Native Americans who lived in areas adjacent to the Susquehanna River and its tributaries, ranging from its upper reaches in the southern p ...
, who spoke an Iroquoian language
The Iroquoian languages are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking.
As of 2020, all surviving Iroquoian ...
, were based in more western regions of Pennsylvania from New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
in the north to West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the Bur ...
in the southwest that included the Susquehanna River all the way to the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers near present day Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
. European disease and constant warfare with several neighbors and groups of Europeans weakened these tribes, and they were grossly outpaced financially as the Hurons
The Wyandot people, or Wyandotte and Waⁿdát, are Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands. The Wyandot are Iroquoian Indigenous peoples of North America who emerged as a confederacy of tribes around the north shore of Lake Ontario w ...
and Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
blocked them from proceeding west into Ohio during the Beaver Wars
The Beaver Wars ( moh, Tsianì kayonkwere), also known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars (french: Guerres franco-iroquoises) were a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America throughout t ...
. As they lost numbers and land, they abandoned much of their western territory and moved closer to the Susquehanna River and the Iroquois and Mohawk tribes located more to the north. Northwest of the Allegheny River was the Iroquoian Petun
The Petun (from french: pétun), also known as the Tobacco people or Tionontati ("People Among the Hills/Mountains"), were an indigenous Iroquoian people of the woodlands of eastern North America. Their last known traditional homeland was sout ...
, known mostly for their vast tobacco plantations, although this is believed to be complete fabrication. They were fragmented into three groups during the Beaver Wars: the Petun of New York, the Wyandot of Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, and the Tiontatecaga of the Kanawha River in southern West Virginia. South of the Allegheny River was a nation known as Calicua. They may have been the same as the Monongahela culture
The Monongahela culture were an Iroquoian Native American cultural manifestation of Late Woodland peoples from AD 1050 to 1635 in present-day western Pennsylvania, western Maryland, eastern Ohio, and West Virginia. The culture was named by Mary ...
and little is known about them except that they were probably a Siouan
Siouan or Siouan–Catawban is a language family of North America that is located primarily in the Great Plains, Ohio and Mississippi valleys and southeastern North America with a few other languages in the east.
Name
Authors who call the entire ...
culture. Archaeological sites from this time in this region are scarce.
17th century
In the 17th century, theDutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
and the English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
each claimed both sides of the Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock (village), New York, Hancock, New York, the river flows for along the borders of N ...
as part of their colonial lands in America. The Dutch were the first to take possession. By June 3, 1631, the Dutch began settling the Delmarva Peninsula
The Delmarva Peninsula, or simply Delmarva, is a large peninsula and proposed state on the East Coast of the United States, occupied by the vast majority of the state of Delaware and parts of the Eastern Shore regions of Maryland and Virginia ...
by establishing the Zwaanendael Colony
or was a short-lived Dutch colonial settlement in Delaware. It was built in 1631. The name is archaic Dutch for "swan valley." The site of the settlement later became the town of Lewes, Delaware.
History
Two directors of the Amsterdam ch ...
on the site of present-day Lewes, Delaware
Lewes ( ) is an incorporated city on the Delaware Bay in eastern Sussex County, Delaware, United States. According to the 2010 census, the population is 2,747. Along with neighboring Rehoboth Beach, Lewes is one of the principal cities of Delawar ...
. In 1638, Sweden established New Sweden Colony in the region of Fort Christina
Fort Christina (also called Fort Altena) was the first Swedish settlement in North America and the principal settlement of the New Sweden colony. Built in 1638 and named after Queen Christina of Sweden, it was located approximately 1 mi (1.6 ...
on the site of present-day Wilmington, Delaware
Wilmington ( Lenape: ''Paxahakink /'' ''Pakehakink)'' is the largest city in the U.S. state of Delaware. The city was built on the site of Fort Christina, the first Swedish settlement in North America. It lies at the confluence of the Christina ...
. New Sweden claimed and, for the most part, controlled the lower Delaware River region, including parts of present-day Delaware, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania, but settled few colonists there.
On March 12, 1664, King Charles II of England
Charles II (29 May 1630 – 6 February 1685) was King of Scotland from 1649 until 1651, and King of King of England, England, Scotland and King of Ireland, Ireland from the 1660 Restoration of the monarchy until his death in 1685.
Charles II ...
gave James, Duke of York
James VII and II (14 October 1633 16 September 1701) was King of England and King of Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was deposed in the Glorious Re ...
a grant that incorporated all lands included in the original Virginia Company of Plymouth Grant and other lands. This grant was in conflict with the Dutch claim for New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the East Coast of the United States, east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territor ...
, which included parts of today's Pennsylvania.
On June 24, 1664, the Duke of York sold the portion of his large grant that included present-day New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
to John Berkeley and George Carteret
Vice Admiral Sir George Carteret, 1st Baronet ( – 14 January 1680 N.S.) was a royalist statesman in Jersey and England, who served in the Clarendon Ministry as Treasurer of the Navy. He was also one of the original lords proprietor of the ...
for a proprietary colony. The land was not yet in British possession, but the sale boxed in the portion of New Netherland on the West side of the Delaware River. The British conquest of New Netherland began on August 29, 1664, when New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam ( nl, Nieuw Amsterdam, or ) was a 17th-century Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''factory'' gave rise ...
was coerced to surrender while facing cannons on British ships in New York Harbor
New York Harbor is at the mouth of the Hudson River where it empties into New York Bay near the East River tidal estuary, and then into the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast of the United States. It is one of the largest natural harbors in t ...
. This conquest continued, and was completed in October 1664, when the British captured Fort Casimir
Fort Casimir or Fort Trinity was a Dutch fort in the seventeenth-century colony of New Netherland. It was located on a no-longer existing barrier island at the end of Chestnut Street in what is now New Castle, Delaware.
Background
The Dutch c ...
in what today is New Castle, Delaware
New Castle is a city in New Castle County, Delaware, United States. The city is located six miles (10 km) south of Wilmington and is situated on the Delaware River. As of the 2010 census, the city's population was 5,285.
History
New Castl ...
.
The Peace of Breda
The Peace of Breda, or Treaty of Breda was signed in the Dutch city of Breda, on 31 July 1667. It consisted of three separate treaties between England and each of its opponents in the Second Anglo-Dutch War: the Dutch Republic, France, and Den ...
between England, France, and the Netherlands confirmed the English conquest on July 21, 1667, although there were temporary reversions.
On September 12, 1672, during the Third Anglo-Dutch War
The Third Anglo-Dutch War ( nl, Derde Engels-Nederlandse Oorlog), 27 March 1672 to 19 February 1674, was a naval conflict between the Dutch Republic and England, in alliance with France. It is considered a subsidiary of the wider 1672 to 1678 ...
, the Dutch reconquered New York Colony
The Province of New York (1664–1776) was a British proprietary colony and later royal colony on the northeast coast of North America. As one of the Middle Colonies, New York achieved independence and worked with the others to found the Uni ...
/New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam ( nl, Nieuw Amsterdam, or ) was a 17th-century Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''factory'' gave rise ...
, establishing three County Courts, which went on to become original Counties in present-day Delaware and Pennsylvania. The one that later transferred to Pennsylvania was Upland. This was partially reversed on February 9, 1674, when the Treaty of Westminster ended the Third Anglo-Dutch War and reverted all political situations to the ''status quo ante bellum''. The British retained the Dutch Counties with their Dutch names. By June 11, 1674, New York reasserted control over the outlying colonies, including Upland, and the names started to be changed to British names by November 11, 1674. Upland was partitioned on November 12, 1674, producing the general outline of the current border between Pennsylvania and Delaware.
On February 28, 1681, Charles II granted a land charter to Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belie ...
leader William Penn to repay a debt of £16,000 (around £2,100,000 in 2008, adjusting for retail inflation) owed to William's father. This transaction represents ne of the largest land grants to an individual in history. Penn proposed that the land be called New Wales, but there were objections to that name, so he recommended Sylvania (from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''silva'': "forest, woods"). The King named it Pennsylvania (literally "Penn's Woods") in honor of Admiral Penn. The younger Penn was embarrassed at this name, fearing that people would think he had named it after himself, but King Charles would not rename the grant. Penn established a government with two innovations that were much copied in the New World: the county commission
A county commission (or a board of county commissioners) is a group of elected officials (county commissioners) collectively charged with administering the county government in some states of the United States; such commissions usually comprise ...
and freedom of religious conviction.
What had been Upland on the Pennsylvania side of the Pennsylvania-Delaware border was renamed as Chester County Chester County may refer to:
* Chester County, Pennsylvania, United States
* Chester County, South Carolina, United States
* Chester County, Tennessee
Chester County is a county located in the U.S. state of Tennessee. As of the 2020 census, th ...
when Pennsylvania instituted their colonial governments on March 4, 1681. Penn signed a peace treaty with Tamanend
Tamanend (historically also known as Taminent, Tammany, Saint Tammany or King Tammany, "the Affable," ) (–) was the Chief of Chiefs and Chief of the Turtle Clan of the Lenni-Lenape nation in the Delaware Valley signing the Peace Treaty with ...
, leader of the Lenape, which began a long period of friendly relations between the Quakers and the Indians. Additional treaties between Quakers and other tribes followed. The treaty
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations
An international organization or international o ...
of William Penn was never violated.
18th century
Colonial Scrip
Early American currency went through several stages of development during the colonial and post-Revolutionary history of the United States. John Hull was authorized by the Massachusetts legislature to make the earliest coinage of the colony (the ...
. The Colony issued bills of credit, which were as good as gold or silver coins because of their legal tender status. Since they were issued by the government and not a banking institution, it was an interest-free proposition, largely defraying the expense of the government and therefore taxation of the people. It also promoted general employment and prosperity, since the government used discretion and did not issue excessive amounts that inflated the currency. Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading inte ...
had a hand in creating this currency, whose utility, he said, was never to be disputed. The currency also met with "cautious approval" by Adam Smith
Adam Smith (baptized 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the thinking of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as "The Father of Economics"——— ...
.
The University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (also known as Penn or UPenn) is a private research university in Philadelphia. It is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and is ranked among the highest-regarded universitie ...
in Philadelphia was founded by Benjamin Franklin in 1740, becoming one of the nine colonial colleges
The colonial colleges are nine institutions of higher education chartered in the Thirteen Colonies before the United States of America became a sovereign nation after the American Revolution. These nine have long been considered together, notably ...
and the first college established in the state and one of the first in the nation; today, it is an Ivy League
The Ivy League is an American collegiate athletic conference comprising eight private research universities in the Northeastern United States. The term ''Ivy League'' is typically used beyond the sports context to refer to the eight schools ...
university that is ranked one the world's best universities. Dickinson College
, mottoeng = Freedom is made safe through character and learning
, established =
, type = Private liberal arts college
, endowment = $645.5 million (2022)
, president = J ...
in Carlisle
Carlisle ( , ; from xcb, Caer Luel) is a city that lies within the Northern England, Northern English county of Cumbria, south of the Anglo-Scottish border, Scottish border at the confluence of the rivers River Eden, Cumbria, Eden, River C ...
was the first college founded after the states united. Established in 1773, Dickinson was ratified five days after the Treaty of Paris Treaty of Paris may refer to one of many treaties signed in Paris, France:
Treaties
1200s and 1300s
* Treaty of Paris (1229), which ended the Albigensian Crusade
* Treaty of Paris (1259), between Henry III of England and Louis IX of France
* Trea ...
on September 9, 1783, and was founded by Benjamin Rush
Benjamin Rush (April 19, 1813) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father of the United States who signed the United States Declaration of Independence, and a civic leader in Philadelphia, where he was a physician, politician, ...
and named after John Dickinson
John Dickinson (November 13 Julian_calendar">/nowiki>Julian_calendar_November_2.html" ;"title="Julian_calendar.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Julian calendar">/nowiki>Julian calendar November 2">Julian_calendar.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Julian calendar" ...
.
James Smith wrote that in 1763, "the Indians again commenced hostilities, and were busily engaged in killing and scalping the frontier inhabitants in various parts of Pennsylvania." Further, "This state was then a Quaker government, and at the first of this war the frontiers received no assistance from the state." The ensuing hostilities became known as Pontiac's War
Pontiac's War (also known as Pontiac's Conspiracy or Pontiac's Rebellion) was launched in 1763 by a loose confederation of Native Americans dissatisfied with British rule in the Great Lakes region following the French and Indian War (1754–176 ...
.
After the Stamp Act Congress
The Stamp Act Congress (October 7 – 25, 1765), also known as the Continental Congress of 1765, was a meeting held in New York, New York, consisting of representatives from some of the British colonies in North America. It was the first gat ...
of 1765, Delegate John Dickinson
John Dickinson (November 13 Julian_calendar">/nowiki>Julian_calendar_November_2.html" ;"title="Julian_calendar.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Julian calendar">/nowiki>Julian calendar November 2">Julian_calendar.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Julian calendar" ...
of Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
wrote the ''Declaration of Rights and Grievances
In response to the Stamp and Tea Acts, the Declaration of Rights and Grievances was a document written by the Stamp Act Congress and passed on October 14, 1765. American colonists opposed the acts because they were passed without the consideration ...
''. The Congress was the first meeting of the Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of Kingdom of Great Britain, British Colony, colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Fo ...
, called at the request of the Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
Assembly, but only nine colonies sent delegates. Dickinson then wrote '' Letters from a Farmer in Pennsylvania, To the Inhabitants of the British Colonies'', which were published in the Pennsylvania Chronicle between December 2, 1767, and February 15, 1768.
When the Founding Fathers convened in Philadelphia in 1774, 12 colonies sent representatives to the First Continental Congress
The First Continental Congress was a meeting of delegates from 12 of the 13 British colonies that became the United States. It met from September 5 to October 26, 1774, at Carpenters' Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, after the British Navy ...
. The Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a late-18th-century meeting of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolutionary War. The Congress was creating a new country it first named "United Colonies" and in 1 ...
, which also met in Philadelphia (in May 1775), authored and signed the Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence or declaration of statehood or proclamation of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the ...
in Philadelphia, but when Philadelphia was captured by the British in the Philadelphia Campaign
The Philadelphia campaign (1777–1778) was a British effort in the American Revolutionary War to gain control of Philadelphia, which was then the seat of the Second Continental Congress. British General William Howe, after failing to draw ...
, the Continental Congress moved west, meeting at the Lancaster courthouse on Saturday, September 27, 1777, and then to York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
. In York, they adopted the Articles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union was an agreement among the 13 Colonies of the United States of America that served as its first frame of government. It was approved after much debate (between July 1776 and November 1777) by ...
, largely authored by John Dickinson, that formed 13 independent States into a new union. Later, the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of Legal entity, entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When ...
was written, and Philadelphia was once again chosen to be cradle to the new nation. The Constitution was drafted and signed at the Pennsylvania State House
The Pennsylvania House of Representatives is the lower house of the bicameral Pennsylvania General Assembly, the legislature of the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. There are 203 members, elected for two-year terms from single member districts.
It ...
, now known as Independence Hall
Independence Hall is a historic civic building in Philadelphia, where both the United States Declaration of Independence and the United States Constitution were debated and adopted by America's Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Fa ...
, and the same building where the Declaration of Independence was signed in 1776.
Pennsylvania became the second state to ratify the U.S. Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the natio ...
on December 12, 1787, five days after Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
became the first. At the time, Pennsylvania was the most ethnically and religiously diverse of the thirteen colonies. Because a third of Pennsylvania's population spoke German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
, the Constitution was presented in German so those citizens could participate in the discussion about it. Reverend Frederick Muhlenberg, a Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
minister and the first Speaker of the U.S. House of Representatives, acted as chairman of Pennsylvania's ratifying convention.
For half a century, the Pennsylvania General Assembly
The Pennsylvania General Assembly is the legislature of the U.S. commonwealth of Pennsylvania. The legislature convenes in the State Capitol building in Harrisburg. In colonial times (1682–1776), the legislature was known as the Pennsylvania ...
met at various places in the Philadelphia area before it began meeting regularly in Independence Hall in Philadelphia for 63 years. However, events such as the Paxton Boys
The Paxton Boys were Pennsylvania's most aggressive colonists according to historian Kevin Kenny. While not many specifics are known about the individuals in the group their overall profile is clear. Paxton Boys Lived in hill country northwest of ...
massacres of 1763 had made the legislature aware of the need for a central capital. In 1799 the General Assembly moved to the Lancaster Courthouse.
19th century
 The General Assembly met in the old
The General Assembly met in the old Dauphin County
Dauphin County (; Pennsylvania Dutch: Daffin Kaundi) is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. As of the 2020 census, the population was 286,401. The county seat and the largest city is Harrisburg, Pennsylvania's state capital and ninth ...
Court House until December 1821 when the Federal
Federal or foederal (archaic) may refer to:
Politics
General
*Federal monarchy, a federation of monarchies
*Federation, or ''Federal state'' (federal system), a type of government characterized by both a central (federal) government and states or ...
-style Hills Capitol, named for Lancaster architect Stephen Hills, was constructed on a hilltop land grant of four acres set aside for a seat of state government in Harrisburg
Harrisburg is the capital city of the Pennsylvania, Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Dauphin County, Pennsylvania, Dauphin County. With a population of 50,135 as of the 2021 census, Harrisburg is the List of c ...
by the son and namesake of John Harris, Sr.
John Harris Sr. (1673 – December 1748) was an American businessman who emigrated from Britain to America late in the 17th century. Harris would later settle and establish Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, which was later named in his honor.
Biograp ...
, a Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a Historic counties of England, historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other Eng ...
native who founded a trading post and ferry on the east shore of the Susquehanna River
The Susquehanna River (; Lenape: Siskëwahane) is a major river located in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, overlapping between the lower Northeast and the Upland South. At long, it is the longest river on the East Coast of the ...
in 1705. The Hills Capitol burned down on February 2, 1897, during a heavy snowstorm, presumably because of a faulty flue
A flue is a duct, pipe, or opening in a chimney for conveying exhaust gases from a fireplace, furnace, water heater, boiler, or generator to the outdoors. Historically the term flue meant the chimney itself. In the United States, they are al ...
.
The General Assembly met at a nearby Methodist Church
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related Christian denomination, denominations of Protestantism, Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John W ...
until a new capitol could be built. Following an architectural selection contest that some alleged had been rigged, Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
architect Henry Ives Cobb
Henry Ives Cobb (August 19, 1859 – March 27, 1931) was an architect from the United States. Based in Chicago in the last decades of the 19th century, he was known for his designs in the Richardsonian Romanesque and Victorian Gothic styles. ...
was asked to design and build a replacement building. However, the legislature had little money to allocate to the project. When they dubbed the roughly finished somewhat industrial Cobb Capitol building complete, the General Assembly refused to occupy the building. In 1901, political and popular indignation prompted a second contest that was restricted to Pennsylvania architects; Joseph Miller Huston
Joseph Miller Huston (February 23, 1866 – 1940) was an architect notable for designing the third (and current) Pennsylvania State Capitol in Harrisburg. Construction started in 1902 of his '' Beaux-Arts'' design. He was one of five peopl ...
of Philadelphia was chosen to design the present Pennsylvania State Capitol
The Pennsylvania State Capitol is the seat of government for the U.S. state of Pennsylvania located in downtown Harrisburg which was designed by architect Joseph Miller Huston in 1902 and completed in 1906 in a Beaux-Arts style with decorative ...
that incorporated Cobb's building into a magnificent public work, finished and dedicated in 1907.
James Buchanan
James Buchanan Jr. ( ; April 23, 1791June 1, 1868) was an American lawyer, diplomat and politician who served as the 15th president of the United States from 1857 to 1861. He previously served as secretary of state from 1845 to 1849 and repr ...
, a Franklin County native, served as the 15th U.S. president and was the first president to be born in Pennsylvania. The Battle of Gettysburg
The Battle of Gettysburg () was fought July 1–3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, by Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War. In the battle, Union Major General George Meade's Army of the Po ...
, the major turning point of the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
, took place near Gettysburg in July 1863. An estimated 350,000 Pennsylvanians served in the Union Army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union (American Civil War), Union of the collective U.S. st ...
forces, including 8,600 African American military volunteer
A military volunteer (or ''war volunteer'') is a person who enlists in military service by free will, and is not a conscript, mercenary, or a foreign legionnaire. Volunteers sometimes enlist to fight in the armed forces of a foreign country, fo ...
s.
The politics of Pennsylvania were for decades dominated by the financially conservative Republican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
-aligned Cameron machine
The Cameron machine, later known as the Quay machine and Penrose machine, was a Republican political machine in Pennsylvania that controlled much of the state's politics for seven decades. Founded by antislavery Know Nothing and Republican Simon ...
, established by U.S. Senator Simon Cameron,Chapter One: 1. Pennsylvania's Bosses and Political Machines''ExplorePAHistory.com''. Retrieved February 18, 2022. later the
Secretary of War
The secretary of war was a member of the U.S. president's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War", had been appointed to serve the Congress of the ...
under President Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation throu ...
. Control of the machine was subsequently passed on to Cameron's son J. Donald Cameron
James Donald Cameron (May 14, 1833 – August 30, 1918) was an American politician from Pennsylvania who served as Secretary of War under President Ulysses S. Grant and in the United States Senate for nearly twenty years. In May, 1876 Cameron was ...
, whose ineffectiveness resulted in a transfer of power to the more shrewd Matthew Quay
Matthew Stanley "Matt" Quay (September 30, 1833May 28, 1904) was an American politician of the Republican Party who represented Pennsylvania in the United States Senate from 1887 until 1899 and from 1901 until his death in 1904. Quay's control ...
and finally to Boies Penrose
Boies Penrose (November 1, 1860 – December 31, 1921) was an American lawyer and Republican politician from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
After serving in both houses of the Pennsylvania legislature, he represented Pennsylvania in the United ...
.
The post-Civil War era, known as the Gilded Age
In United States history, the Gilded Age was an era extending roughly from 1877 to 1900, which was sandwiched between the Reconstruction era and the Progressive Era. It was a time of rapid economic growth, especially in the Northern and Weste ...
, saw the continued rise of industry in Pennsylvania. Pennsylvania was home to some of the largest steel companies in the world. Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie (, ; November 25, 1835August 11, 1919) was a Scottish-American industrialist and philanthropist. Carnegie led the expansion of the American steel industry in the late 19th century and became one of the richest Americans i ...
founded the Carnegie Steel Company
Carnegie Steel Company was a steel-producing company primarily created by Andrew Carnegie and several close associates to manage businesses at steel mills in the Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania area in the late 19th century. The company was forme ...
in Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
and Charles M. Schwab founded Bethlehem Steel
The Bethlehem Steel Corporation was an American steelmaking company headquartered in Bethlehem, Pennsylvania. For most of the 20th century, it was one of the world's largest steel producing and shipbuilding companies. At the height of its succe ...
in Bethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital o ...
. Other titans of industry, including ohn D. Rockefeller Ohn is a Burmese name, used by people from Myanmar. Notable people with the name include:
* Daw Ohn (1913–2003), Burmese professor in Pali
* Ohn Gyaw (born 1932), Burmese Minister of Foreign Affairs from 1991 to 1998
* Ohn Kyaing (born 1944), Bur ...
and Jay Gould
Jason Gould (; May 27, 1836 – December 2, 1892) was an American railroad magnate and financial speculator who is generally identified as one of the robber barons of the Gilded Age. His sharp and often unscrupulous business practices made hi ...
, also operated in Pennsylvania. In the latter half of the 19th century, the U.S. oil industry
The petroleum industry, also known as the oil industry or the oil patch, includes the global processes of exploration, extraction, refining, transportation (often by oil tankers and pipelines), and marketing of petroleum products. The larges ...
was born in Western Pennsylvania
Western Pennsylvania is a region in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, covering the western third of the state. Pittsburgh is the region's principal city, with a metropolitan area population of about 2.4 million people, and serves as its economic ...
, which supplied the vast majority of kerosene
Kerosene, paraffin, or lamp oil is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in aviation as well as households. Its name derives from el, κηρός (''keros'') meaning "wax", and was regi ...
for years thereafter. As the Pennsylvania oil rush
The oil rush in America started in Titusville, Pennsylvania, in the Oil Creek (Allegheny River), Oil Creek Valley when Edwin L. Drake struck "rock oil" there in 1859. Titusville and other towns on the shores of Oil Creek expanded rapidly as oil w ...
developed, Pennsylvania's oil boom towns, such as Titusville, rose and later fell. Coal mining, primarily in the Northeastern Pennsylvania
Northeastern Pennsylvania (NEPA) is a geographic region of the U.S. state of Pennsylvania that includes the Pocono Mountains, the Endless Mountains, and the industrial cities of Scranton, Wilkes-Barre, Pittston, Hazleton, Nanticoke, and Carbon ...
Coal Region
The Coal Region is a region of Northeastern Pennsylvania. It is known for being home to the largest known deposits of anthracite, anthracite coal in the world with an estimated reserve of seven billion short tons.
The region is typically define ...
, also was a major industry in the state. In 1903, Milton S. Hershey
Milton Snavely Hershey (September 13, 1857 – October 13, 1945) was an American chocolatier, businessman, and philanthropist.
Trained in the confectionery business, Hershey pioneered the manufacture of caramel, using fresh milk. He launched t ...
began construction on a chocolate factory in Hershey, Pennsylvania
Hershey is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Derry Township, Dauphin County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is home to The Hershey Company, which was founded by candy magnate Milton S. Hershey.
The community is lo ...
; The Hershey Company
The Hershey Company, commonly known as Hershey's, is an American multinational company and one of the largest chocolate manufacturers in the world. It also manufactures baked products, such as cookies and cakes, and sells beverages like milksh ...
grew to become the largest chocolate manufacturer in North America. Heinz Company
The H. J. Heinz Company is an American food processing company headquartered at One PPG Place in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The company was founded by Henry J. Heinz in 1869. Heinz manufactures thousands of food products in plants on six contine ...
was also founded during this period. These huge companies exercised a large influence on the politics of Pennsylvania; as Henry Demarest Lloyd
Henry Demarest Lloyd (May 1, 1847 – September 28, 1903) was a 19th-century American progressive political activist and pioneer muckraking journalist. He is best remembered for his exposés of the Standard Oil Company, which were written before ...
put it, oil baron John D. Rockefeller "had done everything with the Pennsylvania legislature except refine it". Pennsylvania created a Department of Highways and engaged in a vast program of road-building, while railroads continued to see heavy usage.
The growth of industry eventually provided middle class incomes to working-class households after the development of labor unions helped them gain living wages. However, the rise of unions also led to a rise of union busting
Union busting is a range of activities undertaken to disrupt or prevent the formation of trade unions or their attempts to grow their membership in a workplace.
Union busting tactics can refer to both legal and illegal activities, and can range ...
with several private police forces springing up. Pennsylvania was the location of the first documented organized strike in North America, and Pennsylvania was the location of two hugely prominent strikes, the Great Railroad Strike of 1877
The Great Railroad Strike of 1877, sometimes referred to as the Great Upheaval, began on July 14 in Martinsburg, West Virginia, after the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) cut wages for the third time in a year. This strike finally ended 52 day ...
and the Coal Strike of 1902
The Coal strike of 1902 (also known as the anthracite coal strike) was a strike by the United Mine Workers of America in the anthracite coalfields of eastern Pennsylvania. Miners struck for higher wages, shorter workdays, and the recognition of ...
. The eight-hour day was eventually adopted, and the coal and iron police were banned.
20th century
 At the beginning of the 20th century, Pennsylvania's economy centered on steel production, logging, coal mining, textile production, and other forms of industrial manufacturing. A surge in immigration to the U.S. during the late 19th and early 20th centuries provided a steady flow of cheap labor for these industries, which often employed children and people who could not speak English from Southern and
At the beginning of the 20th century, Pennsylvania's economy centered on steel production, logging, coal mining, textile production, and other forms of industrial manufacturing. A surge in immigration to the U.S. during the late 19th and early 20th centuries provided a steady flow of cheap labor for these industries, which often employed children and people who could not speak English from Southern and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
. Thousands of Pennsylvanians volunteered during the Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (clock ...
. Pennsylvania was an important industrial center in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, and the state provided over 300,000 soldiers for the military. On May 31, 1918, the Pittsburgh Agreement
The Pittsburgh Agreement was a memorandum of understanding completed on 31 May 1918 between members of Czech and Slovak expatriate communities in the United States of America. It replaced the Cleveland Agreement of October 22, 1915.
It is name ...
was signed in Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
to declare the formation of the independent state of Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
with future Czechoslovak president Tomáš Masaryk
Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk (7 March 185014 September 1937) was a Czechoslovak politician, statesman, sociologist, and philosopher. Until 1914, he advocated restructuring the Austro-Hungarian Empire into a federal state. With the help of t ...
.
In 1923, President Calvin Collidge established the Allegheny National Forest
The Allegheny National Forest is a National Forest in Northwestern Pennsylvania, about 100 miles northeast of Pittsburgh. The forest covers of land. Within the forest is Kinzua Dam, which impounds the Allegheny River to form Allegheny Reservoir ...
under the authority of the Weeks Act
The Weeks Act is a federal law (36 Stat. 961) enacted by the United States Congress on March 1, 1911. Introduced by Massachusetts Congressman John W. Weeks and signed into law by President William Howard Taft, the law authorized the United States S ...
of 1911. The forest is located in the northwest part of the state in Elk
The elk (''Cervus canadensis''), also known as the wapiti, is one of the largest species within the deer family, Cervidae, and one of the largest terrestrial mammals in its native range of North America and Central and East Asia. The common ...
, Forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
, McKean, and Warren
A warren is a network of wild rodent or lagomorph, typically rabbit burrows. Domestic warrens are artificial, enclosed establishment of animal husbandry dedicated to the raising of rabbits for meat and fur. The term evolved from the medieval A ...
Counties for the purposes of timber production and watershed protection in the Allegheny River
The Allegheny River ( ) is a long headwater stream of the Ohio River in western Pennsylvania and New York (state), New York. The Allegheny River runs from its headwaters just below the middle of Pennsylvania's northern border northwesterly into ...
basin. The Allegheny is the state's only national forest.
Pennsylvania manufactured 6.6 percent of total U.S. military armaments produced during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, ranking sixth among the 48 states. The Philadelphia Naval Shipyard
The Philadelphia Naval Shipyard was an important naval shipyard of the United States for almost two centuries.
Philadelphia's original navy yard, begun in 1776 on Front Street and Federal Street in what is now the Pennsport section of the cit ...
served as an important naval base, and Pennsylvania produced important military leaders, including George C. Marshall
George Catlett Marshall Jr. (December 31, 1880 – October 16, 1959) was an American army officer and statesman. He rose through the United States Army to become Chief of Staff of the United States Army, Chief of Staff of the US Army under Pre ...
, Hap Arnold
Henry Harley Arnold (June 25, 1886 – January 15, 1950) was an American general officer holding the ranks of General of the Army and later, General of the Air Force. Arnold was an aviation pioneer, Chief of the Air Corps (1938–1941), ...
, Jacob Devers
Jacob Loucks Devers (; 8 September 1887 – 15 October 1979) was a general in the United States Army who commanded the 6th Army Group in the European Theater during World War II. He was involved in the development and adoption of numerous ...
, and Carl Spaatz
Carl Andrew Spaatz (born Spatz; June 28, 1891 – July 14, 1974), nicknamed "Tooey", was an American World War II general. As commander of Strategic Air Forces in Europe in 1944, he successfully pressed for the bombing of the enemy's oil product ...
. During the war, over a million Pennsylvanians served in the armed forces, and more Medals of Honor
The Medal of Honor (MOH) is the United States Armed Forces' highest military decoration and is awarded to recognize American soldiers, sailors, marines, airmen, guardians and coast guardsmen who have distinguished themselves by acts of valor. Th ...
were awarded to Pennsylvanians than to individuals from any other state.
The Three Mile Island accident
The Three Mile Island accident was a partial meltdown of the Three Mile Island, Unit 2 (TMI-2) reactor in Pennsylvania, United States. It began at 4 a.m. on March 28, 1979. It is the most significant accident in U.S. commercial nuclea ...
was the most significant nuclear accident
A nuclear and radiation accident is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "an event that has led to significant consequences to people, the environment or the facility. Examples include lethal effects to individuals, lar ...
in U.S. commercial nuclear power plant history. The state was hard-hit by the decline and restructuring of the steel industry and other heavy industries during the late 20th century. With job losses came heavy population losses, especially in the state's largest cities. Pittsburgh lost its place among the top ten most populous cities in the United States by 1950, and Philadelphia dropped to the fifth and later sixth largest city after decades of being among the top three.
After 1990, as information-based industries became more important in the economy, state and local governments put more resources into the old, well-established public library system. Some localities, however, used new state funding to cut local taxes. New ethnic groups, especially Hispanics and Latinos, began entering the state to fill low-skill jobs in agriculture and service industries. For example, in Chester County Chester County may refer to:
* Chester County, Pennsylvania, United States
* Chester County, South Carolina, United States
* Chester County, Tennessee
Chester County is a county located in the U.S. state of Tennessee. As of the 2020 census, th ...
, Mexican immigrants brought the Spanish language
Spanish ( or , Castilian) is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from colloquial Latin spoken on the Iberian peninsula. Today, it is a world language, global language with more than 500 millio ...
, increased Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, high birth rates, and cuisine when they were hired as agricultural laborers; in some rural localities, they made up half or more of the population. Meanwhile, Stateside Puerto Ricans
Stateside Puerto Ricans ( es, link=no, Puertorriqueños de Estados Unidos), also ambiguously known as Puerto Rican Americans ( es, link=no, puertorriqueño-americanos,), or Puerto Ricans in the United States, are Puerto Ricans who are in the ...
built a large community in the state's third largest city, Allentown Allentown may refer to several places in the United States and topics related to them:
* Allentown, California, now called Toadtown, California
* Allentown, Georgia, a town in Wilkinson County
* Allentown, Illinois, an unincorporated community in T ...
. They comprised over 40% of the city's population by 2000.
In the 20th century, as Pennsylvania's historical national and even global leadership in mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic via ...
largely ceased and its steelmaking
Steelmaking is the process of producing steel from iron ore and carbon/or scrap. In steelmaking, impurities such as nitrogen, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur and excess carbon (the most important impurity) are removed from the sourced iron, and all ...
and other heavy manufacturing sectors slowed, the state sought to grow its service and other industries to replace the jobs and economic productivity lost from the downturn of these industries. Pittsburgh's concentration of universities has enabled it to be a leader in technology and healthcare. Similarly, Philadelphia has a concentration of university expertise. Healthcare, retail, transportation, and tourism are some of the state's growing industries of the postindustrial era. As in the rest of the nation, most residential population growth has occurred in suburban rather than central city areas, although both major cities have had significant revitalization in their downtown areas. Philadelphia anchors the seventh-largest metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually com ...
in the country, while Pittsburgh is the center of the twenty-seventh largest metro area in the country. The growth of the Lehigh Valley
The Lehigh Valley (), known colloquially as The Valley, is a geographic region formed by the Lehigh River in Lehigh County and Northampton County in eastern Pennsylvania. It is a component valley of the Great Appalachian Valley bound to the no ...
has made it one of the seventy most populous metro areas in the country, while Pennsylvania also has six other metro areas among the top 200 most populous American metro areas. Philadelphia forms part of the Northeast megalopolis
The Northeast megalopolis, also known as the Northeast Corridor, Acela Corridor, Boston–Washington corridor, or BosWash, is the world's largest megalopolis in terms of economic output and the second most populous megalopolis in the United St ...
and is associated with the Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States, also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast, is a geographic region of the United States. It is located on the Atlantic coast of North America, with Canada to its north, the Southe ...
, while Pittsburgh is part of the Great Lakes megalopolis and is often associated with the Midwestern United States
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. I ...
and the Rust Belt
The Rust Belt is a region of the United States that experienced industrial decline starting in the 1950s. The U.S. manufacturing sector as a percentage of the U.S. GDP peaked in 1953 and has been in decline since, impacting certain regions and ...
.
21st century
 On September 11, 2001, during the terrorist attacks on the United States, the small town of
On September 11, 2001, during the terrorist attacks on the United States, the small town of Shanksville, Pennsylvania
Shanksville is a borough in Somerset County, Pennsylvania. It has a population of 197 as of the 2020 U.S. census. It is part of the Somerset, Pennsylvania Micropolitan Statistical Area and is located southeast of Pittsburgh and west of Philade ...
received worldwide attention after United Airlines Flight 93 crashed into a field in Stonycreek Township, north of the town, killing all 40 civilians and four Al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda (; , ) is an Islamic extremism, Islamic extremist organization composed of Salafist jihadists. Its members are mostly composed of Arab, Arabs, but also include other peoples. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian and military ta ...
hijackers on board. The hijackers had intended to crash the plane into either the United States Capitol
The United States Capitol, often called The Capitol or the Capitol Building, is the seat of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, which is formally known as the United States Congress. It is located on Capitol Hill ...
or The White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in 1800. ...
. After learning from family members via air phone of the earlier attacks on the World Trade Center
World Trade Centers are sites recognized by the World Trade Centers Association.
World Trade Center may refer to:
Buildings
* List of World Trade Centers
* World Trade Center (2001–present), a building complex that includes five skyscrapers, a ...
, however, Flight 93 passengers on board revolted against the hijackers and fought for control of the plane, causing it to crash. It was the only one of the four aircraft hijacked that day that never reached its intended target and the heroism of the passengers has been commemorated.
Beginning in 2003, the Tekko
The , are weaponized stirrups and horseshoes which originated in Okinawa, Japan, and they fall into the category of "fist-load weapons". By definition, a fist-load weapon increases the mass of the hand so that, given the physical proportional ...
anime
is Traditional animation, hand-drawn and computer animation, computer-generated animation originating from Japan. Outside of Japan and in English, ''anime'' refers specifically to animation produced in Japan. However, in Japan and in Japane ...
convention is held annually in Pittsburgh. In October 2018, the Tree of Life – Or L'Simcha Congregation
Tree of Life – Or L'Simcha Congregation () is a Conservative Jewish synagogue in the Squirrel Hill neighborhood of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The congregation moved into its present synagogue building in 1953. It merged with Congregation Or L'S ...
experienced the Pittsburgh synagogue shooting
The Pittsburgh synagogue shooting was an antisemitic terrorist attack which took place at the Tree of Life – Or L'Simcha Congregation synagogue in the Squirrel Hill neighborhood of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. The congregation, alo ...
.
Geography
 Pennsylvania is north to south and east to west. Of a total , are land, are inland waters, and are waters in
Pennsylvania is north to south and east to west. Of a total , are land, are inland waters, and are waters in Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
.2006 Statistical Abstract: Geography & Environment: Land and Land Use/ref> It is the 33rd-largest state in the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
. Pennsylvania has of coastline along Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
and of shoreline along the Delaware Estuary. Of the original Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of Kingdom of Great Britain, British Colony, colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Fo ...
, Pennsylvania is the only state that does not border the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
.
The boundaries of the state are the Mason–Dixon line
The Mason–Dixon line, also called the Mason and Dixon line or Mason's and Dixon's line, is a demarcation line separating four U.S. states, forming part of the borders of Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware, and West Virginia (part of Virginia ...
(39°43' N) to the south, Twelve-Mile Circle
The Twelve-Mile Circle is an approximately circular arc which forms most of the boundary between Pennsylvania and Delaware. It is not actually a circle, but rather a combination of different circular arcs that have been feathered together.
It is ...
on the Pennsylvania-Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
border, the Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock (village), New York, Hancock, New York, the river flows for along the borders of N ...
to the east, 80°31' W to the west, and the 42° N to the north, except for a short segment on the western end where a triangle extends north to Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
. The state has five geographical regions: Allegheny Plateau
The Allegheny Plateau , in the United States, is a large dissected plateau area of the Appalachian Mountains in western and central New York, northern and western Pennsylvania, northern and western West Virginia, and eastern Ohio. It is divide ...
, Ridge and Valley
The Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians, also called the Ridge and Valley Province or the Valley and Ridge Appalachians, are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian division and are also a belt within the Appalachian Mountains extending ...
, Atlantic Coastal Plain
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Afr ...
, Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
, and Erie Plain
The Erie Plain is a lacustrine plain that borders Lake Erie in North America. From Buffalo, New York, to Cleveland, Ohio, it is quite narrow (at best only a few miles/kilometers wide), but broadens considerably from Cleveland around Lake Erie to S ...
.
Climate
 Pennsylvania's diverse topography produces a variety of climates, though the entire state experiences cold winters and humid summers. Straddling two major zones, the majority of the state, except for the southeastern corner, has a
Pennsylvania's diverse topography produces a variety of climates, though the entire state experiences cold winters and humid summers. Straddling two major zones, the majority of the state, except for the southeastern corner, has a humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
''Dfb''). The southern portion of the state has a humid subtropical
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
climate. The largest city, Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
, has a humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
(Köppen ''Cfa'').
Summers are generally hot and humid. Moving toward the mountainous interior of the state, the winter climate becomes colder, the number of cloudy days increases, and snowfall amounts are greater. Western areas of the state, particularly locations near Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
, can receive over of snowfall annually, and the entire state receives plentiful precipitation throughout the year. The state may be subject to severe weather from spring through summer into autumn. Tornadoes occur annually in the state, sometimes in large numbers, such as 30 recorded tornadoes in 2011; generally speaking, these tornadoes do not cause significant damage.
Municipalities
Cities in Pennsylvania includePhiladelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
, Reading
Reading is the process of taking in the sense or meaning of Letter (alphabet), letters, symbols, etc., especially by Visual perception, sight or Somatosensory system, touch.
For educators and researchers, reading is a multifaceted process invo ...
, Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus li ...
and Lancaster in the southeast, Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
in the southwest, and the tri-cities of Allentown Allentown may refer to several places in the United States and topics related to them:
* Allentown, California, now called Toadtown, California
* Allentown, Georgia, a town in Wilkinson County
* Allentown, Illinois, an unincorporated community in T ...
, Bethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital o ...
, and Easton in the central east, known as the Lehigh Valley
The Lehigh Valley (), known colloquially as The Valley, is a geographic region formed by the Lehigh River in Lehigh County and Northampton County in eastern Pennsylvania. It is a component valley of the Great Appalachian Valley bound to the no ...
. The northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each se ...
includes the former anthracite coal
Anthracite, also known as hard coal, and black coal, is a hard, compact variety of coal that has a submetallic luster. It has the highest carbon content, the fewest impurities, and the highest energy density of all types of coal and is the high ...
mining cities of Scranton
Scranton is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania, Lackawanna County. With a population of 76,328 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 U ...
, Wilkes-Barre
Wilkes-Barre ( or ) is a city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Luzerne County. Located at the center of the Wyoming Valley in Northeastern Pennsylvania, it had a population of 44,328 in the 2020 census. It is the secon ...
, Pittston
Pittston is a city in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is situated between Scranton and Wilkes-Barre in Northeastern Pennsylvania. The city gained prominence in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as an active anthracite coal ...
, Nanticoke Nanticoke may refer to:
* Nanticoke people in Delaware, United States
* Nanticoke language, an Algonquian language
* Nanticoke Lenni-Lenape, a state-recognized tribe in New Jersey
Place names Canada
* Nanticoke, Ontario
** Nanticoke Generating S ...
, and Hazleton Hazleton may refer to:
Places
* Hazleton, British Columbia, Canada
* Hazleton, Gloucestershire, a village in Gloucestershire, England
** Hazleton long barrows, Neolithic burial mounds at Hazleton, Gloucestershire, England
** Hazleton Abbey, a me ...
. Erie
Erie (; ) is a city on the south shore of Lake Erie and the county seat of Erie County, Pennsylvania, United States. Erie is the fifth largest city in Pennsylvania and the largest city in Northwestern Pennsylvania with a population of 94,831 a ...
is located in the northwest. State College is located in the central region. Williamsport is in the north-central region with York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
, Carlisle
Carlisle ( , ; from xcb, Caer Luel) is a city that lies within the Northern England, Northern English county of Cumbria, south of the Anglo-Scottish border, Scottish border at the confluence of the rivers River Eden, Cumbria, Eden, River C ...
, and the state capital Harrisburg
Harrisburg is the capital city of the Pennsylvania, Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Dauphin County, Pennsylvania, Dauphin County. With a population of 50,135 as of the 2021 census, Harrisburg is the List of c ...
on the Susquehanna River
The Susquehanna River (; Lenape: Siskëwahane) is a major river located in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, overlapping between the lower Northeast and the Upland South. At long, it is the longest river on the East Coast of the ...
in the east-central region of the state. Altoona, Pennsylvania, Altoona and Johnstown, Pennsylvania, Johnstown are in the state's west-central region.
The state's three most populated cities, in order of size, are Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
, Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
, and Allentown Allentown may refer to several places in the United States and topics related to them:
* Allentown, California, now called Toadtown, California
* Allentown, Georgia, a town in Wilkinson County
* Allentown, Illinois, an unincorporated community in T ...
.
Adjacent states and province
*Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
(Province of Canada) (Northwest)
* New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
(North and Northeast)
* New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
(East and Southeast)
* Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
(Extreme Southeast)
* Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
(South)
* West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the Bur ...
(Southwest)
* Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
(West)
Demographics
As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 U.S. census, Pennsylvania had a population of 13,011,844, up from 12,702,379 in 2010. In 2019, net Human migration, migration to other states resulted in a decrease of 27,718, and Immigration to the United States, immigration from other countries resulted in an increase of 127,007. Net migration to the Commonwealth was 98,289. Migration of native Pennsylvanians resulted in a decrease of 100,000 people. From 2008 to 2012, 5.8% of the population was foreign-born. Pennsylvania is the List of U.S. states and territories by population, fifth most populated state in the U.S. after California, Florida,New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
, and Texas.
Place of origin
 Among Pennsylvania residents, as of 2020, 74.5% were born in Pennsylvania, 18.4% were born in a different U.S. state, 1.5% were born in Puerto Rico], U.S. Island areas, or born abroad to American parent(s), and 5.6% were foreign born. Foreign-born Pennsylvanians are largely from Asia (36.0%), Europe (35.9%), and Latin America (30.6%) with the remainder from Africa (5%), North America (3.1%), and Oceania (0.4%).
The state's largest ancestry groups, expressed as a percentage of total people who responded with a particular ancestry for the 2010 census, are:
* German Americans, German 28.5%
* Irish Americans, Irish 18.2%
* Italian Americans, Italian 12.8%
* African Americans 9.6%
* English Americans, English 8.5%
* Polish Americans, Polish 7.2%
* French Americans, French 4.2%
Among Pennsylvania residents, as of 2020, 74.5% were born in Pennsylvania, 18.4% were born in a different U.S. state, 1.5% were born in Puerto Rico], U.S. Island areas, or born abroad to American parent(s), and 5.6% were foreign born. Foreign-born Pennsylvanians are largely from Asia (36.0%), Europe (35.9%), and Latin America (30.6%) with the remainder from Africa (5%), North America (3.1%), and Oceania (0.4%).
The state's largest ancestry groups, expressed as a percentage of total people who responded with a particular ancestry for the 2010 census, are:
* German Americans, German 28.5%
* Irish Americans, Irish 18.2%
* Italian Americans, Italian 12.8%
* African Americans 9.6%
* English Americans, English 8.5%
* Polish Americans, Polish 7.2%
* French Americans, French 4.2%
Race and ethnicity
Pennsylvania's Hispanic or Latino American population grew by 82.6% between 2000 and 2010, marking one of the largest increases in a state's Hispanic population. The significant growth of the Hispanic or Latino population is due to migration to the state mainly from Puerto Rico, a U.S. territory, and to a lesser extent immigration from countries such as the Dominican Republic, Mexico, and various Central and South American nations and a wave of Hispanic and Latinos leaving New York and New Jersey for safer and more affordable living. The Asian population swelled by almost 60%, fueled by Indian, Vietnamese, and Chinese immigration, and many Asian transplants moving toPhiladelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
from New York. The rapid growth of this community has given Pennsylvania one of the largest Asian populations in the nation. The African American population grew by 13%, which was the largest increase in that population among the state's peers (New York, New Jersey, Ohio, Illinois, and Michigan). Pennsylvania has a high in-migration of black and Hispanic people from other nearby states with the eastern and south-central portions of the state seeing the bulk of the increases.
The majority of Hispanic or Latino Americans in Pennsylvania are of Puerto Rican American, Puerto Rican descent. Most of the remaining Hispanic or Latino population is made up of Mexican American, Mexicans and Dominican American, Dominicans. Most Hispanic or Latinos are concentrated in Philadelphia, Lehigh Valley
The Lehigh Valley (), known colloquially as The Valley, is a geographic region formed by the Lehigh River in Lehigh County and Northampton County in eastern Pennsylvania. It is a component valley of the Great Appalachian Valley bound to the no ...
, and South Central Pennsylvania. The Hispanic or Latino population is greatest in Bethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital o ...
, Allentown Allentown may refer to several places in the United States and topics related to them:
* Allentown, California, now called Toadtown, California
* Allentown, Georgia, a town in Wilkinson County
* Allentown, Illinois, an unincorporated community in T ...
, Reading
Reading is the process of taking in the sense or meaning of Letter (alphabet), letters, symbols, etc., especially by Visual perception, sight or Somatosensory system, touch.
For educators and researchers, reading is a multifaceted process invo ...
, Lancaster, York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
, and around Philadelphia. It is not clear how much of this change reflects a changing population and how much reflects increased willingness to self-identify minority status. As of 2010, it is estimated that about 85% of all Hispanics or Latino Americans in Pennsylvania live within a radius of Philadelphia, with about 20% living within the city itself.
Among the state's black population, the vast majority in the state are African American. There are also a growing number of blacks of West Indian American, West Indian, African immigration to the United States, recent African, and Black Hispanic, Hispanic or Latino origins. Most blacks live in the Philadelphia area, Pittsburgh, and South Central Pennsylvania. Non-Hispanic whites make up the majority of Pennsylvania; they are mostly descended from German, Irish, Scottish, Welsh, Italian, and English immigrants. Rural portions of South Central Pennsylvania are recognized nationally for their notable Amish#Population and distribution, Amish communities. Wyoming Valley, including Scranton
Scranton is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania, Lackawanna County. With a population of 76,328 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 U ...
and Wilkes-Barre
Wilkes-Barre ( or ) is a city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Luzerne County. Located at the center of the Wyoming Valley in Northeastern Pennsylvania, it had a population of 44,328 in the 2020 census. It is the secon ...
, has the highest percentage of white residents of any metropolitan area with a population of 500,000 or above in the U.S.; in Wyoming Valley, 96.2% of the population claim to be white with no Hispanic background. The center of population of Pennsylvania is in Perry County, Pennsylvania, Perry County in Duncannon, Pennsylvania, Duncannon.
Age and poverty
As of the 2010 census, Pennsylvania had the fourth-highest proportion of elderly (65+) citizens in the nation at 15.4%, compared to a national average of 13.0%. According to U.S. Census Bureau estimates, the state's poverty rate was 12.5% in 2017 compared to 13.4% for the U.S. as a whole.Languages
As of 2010, 90.2% (10,710,239) of Pennsylvania residents age five and older spoke English language, English at home as a primary language while 4.1% (486,058) spoke Spanish language, Spanish, 0.9% (103,502) spokeGerman
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
including Pennsylvania Dutch
The Pennsylvania Dutch ( Pennsylvania Dutch: ), also known as Pennsylvania Germans, are a cultural group formed by German immigrants who settled in Pennsylvania during the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries. They emigrated primarily from German-spe ...
, and 0.5% (56,052) spoke Chinese language, Chinese, which includes Standard Chinese, Mandarin of the population over the age of five. In total, 9.9% (1,170,628) of Pennsylvania's population age5 and older spoke a mother tongue other than English.
Pennsylvania Dutch language
 Pennsylvania Dutch language, Pennsylvania German, spoken by nearly one percent of Pennsylvania's population as of 2010, is often misleadingly called Pennsylvania Dutch. The term Dutch was used to mean German, including the Netherlands, before the Latin name for them replaced it. When referring to the language spoken by the Pennsylvania Dutch, Pennsylvania Dutch people, Pennsylvania German, it means
Pennsylvania Dutch language, Pennsylvania German, spoken by nearly one percent of Pennsylvania's population as of 2010, is often misleadingly called Pennsylvania Dutch. The term Dutch was used to mean German, including the Netherlands, before the Latin name for them replaced it. When referring to the language spoken by the Pennsylvania Dutch, Pennsylvania Dutch people, Pennsylvania German, it means German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
". In fact, Germans, in their own language, call themselves Deutsch, (Pennsylvania German: "Deitsch"). Pennsylvania Dutch is a descendant of German in the West Central German dialect family and is closest to Palatine German language, Palatine German. Pennsylvania German is still very vigorous as a first language among Amish, Old Order Amish and Old Order Mennonites, principally in the Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, Lancaster County and Berks County, Pennsylvania, Berks County areas; it is almost extinct as an everyday language outside the Plain people, plain communities, though a few words have passed into English usage.
Religion
Of the originalThirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of Kingdom of Great Britain, British Colony, colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Fo ...
, Pennsylvania and Rhode Island had the most religious freedom. Voltaire, writing of William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer and religious thinker belonging to the Religious Society of Friends (Quakers), and founder of the Province of Pennsylvania, a North American colony of England. He was an early advocate of democracy a ...
in 1733, observed: "The new sovereign also enacted several wise and wholesome laws for his colony, which have remained invariably the same to this day. The chief is, to ill-treat no person on account of religion, and to consider as brethren all those who believe in one God." One result of this uncommon freedom was a wide religious Multiculturalism, diversity, which continues to the present.
Pennsylvania's population in 2010 was 12,702,379; of these, 6,838,440 (53.8%) were estimated to belong to some sort of organized religion. According to the Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA) at Pennsylvania State University, the largest religious bodies in Pennsylvania by adherents were the Roman Catholic Church with 3,503,028 adherents, the United Methodist Church with 591,734 members, and the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America with 501,974 members. Since 2014, among the state's religious population, 73% were Christianity, Christian, according to Pew Research Center. In 2020, the Public Religion Research Institute estimated 68% of the population identified with Christianity. As of 2014, 47% of all Pennsylvanians identified as Protestantism in the United States, Protestants, making Protestantism far and away the most prominent religious affiliation among Pennsylvanians. Among all self-identified Christians in the state, however, 24% identified as Catholic Church, Catholics, the most of any Christian religious affiliation.
Pennsylvania, especially in the Greater Pittsburgh
Greater Pittsburgh is a populous region centered around its largest city and economic hub, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The region encompasses Pittsburgh's urban core county, Allegheny, and six adjacent Pennsylvania counties: Armstrong, Beaver, ...
area, has one of the largest communities of Presbyterianism, Presbyterians in the nation, the third highest by percentage of population and the largest outright in membership as Protestant Christians. The Presbyterian Church (USA), American Presbyterian Church, with about 250,000 members and 1,011 congregations, is the largest Presbyterian denomination while the Presbyterian Church in America is also significant, with 112 congregations and approximately 23,000 adherents; the Evangelical Presbyterian Church (United States), EPC has around 50 congregations, including the Evangelical Covenant Order of Presbyterians, ECO, according to 2010 estimates. The fourth-largest Protestantism, Protestant denomination, the United Church of Christ, has 180,000 members and 627 congregations in the state. The American Baptist Churches USA, American Baptist Churches, also referred to as the Northern Baptist Convention is based in King of Prussia, Pennsylvania, King of Prussia.
Pennsylvania was the center state of the Evangelical and Reformed Church, German Reformed denomination from the 1700s. Bethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital o ...
is one of the headquarters of the Moravian Church in the U.S. Pennsylvania also has a very large Amish population, second only to Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
among U.S. states. As of 2000, there was a total Amish population of 47,860 in Pennsylvania and an additional 146,416 Mennonites and 91,200 Schwarzenau Brethren, Brethren. The total Anabaptism, Anabapist population including Bruderhof Communities, Bruderhof was 232,631, about two percent of the population. While Pennsylvania owes its existence to Quakers, and much of the historic character of the Commonwealth is ideologically rooted in the teachings of the Religious Society of Friends (as they are officially known), practicing Quakers are a small minority of about 10,000 adherents as of 2010.
Economy

 As of 2021, Pennsylvania's gross state product (GSP) of $839.4 billion List of U.S. states and territories by GDP, ranks 6th among all U.S. states, behind California, Texas,
As of 2021, Pennsylvania's gross state product (GSP) of $839.4 billion List of U.S. states and territories by GDP, ranks 6th among all U.S. states, behind California, Texas, New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
, Florida, and Illinois. As of 2021, if Pennsylvania were an independent country, its economy would rank as the 22nd largest in the world. On a per capita basis, Pennsylvania's 2021 per capita GSP of $64,751 ranks 24th among the fifty states. As of 2016, there were 5,354,964 people in employment in Pennsylvania with 301,484 total employer establishments. As of May 2020, the state's unemployment rate is 13.1%.
Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
in the southeast corner, Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
in the southwest corner, Erie in the northwest corner, Wyoming Valley, Scranton-Wilkes-Barre in the northeast corner, and Lehigh Valley, Allentown-Bethlehem-Easton in the east central region are urban manufacturing centers. Much of Pennsylvania is rural; this dichotomy affects state politics and the state economy. Philadelphia is home to six Fortune 500 companies, with more located in suburbs like King of Prussia, Pennsylvania, King of Prussia; it is a leader in the financial and insurance industries.
Pittsburgh is home to eight Fortune 500 companies, including U.S. Steel
United States Steel Corporation, more commonly known as U.S. Steel, is an American integrated steel producer headquartered in Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, with production operations primarily in the United States of America and in severa ...
, PPG Industries, and H.J. Heinz. In all, Pennsylvania is home to 50 Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 companies. Hershey is home to The Hershey Company
The Hershey Company, commonly known as Hershey's, is an American multinational company and one of the largest chocolate manufacturers in the world. It also manufactures baked products, such as cookies and cakes, and sells beverages like milksh ...
, one of the largest chocolate manufacturers in the world. Erie is home to GE Transportation, the nation's largest manufacturer of train locomotives.
As in the U.S. as a whole and in most states, the largest private employer in Pennsylvania is Walmart, followed by the University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (also known as Penn or UPenn) is a private research university in Philadelphia. It is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and is ranked among the highest-regarded universitie ...
, an Ivy League
The Ivy League is an American collegiate athletic conference comprising eight private research universities in the Northeastern United States. The term ''Ivy League'' is typically used beyond the sports context to refer to the eight schools ...
private Research university, research university in Philadelphia. Pennsylvania is home to the oldest investor-owned utility company in the U.S., The York Water Company.
Banking
The first nationally chartered bank in the U.S., the Bank of North America, was founded in 1781 in Philadelphia. After a series of mergers, the Bank of North America is now part of Wells Fargo. Pennsylvania is home to the first nationally-chartered bank under the 1863 National Banking Act. That year, the Pittsburgh Savings & Trust Company received a national charter and renamed itself the First National Bank of Pittsburgh as part of the National Banking Act. That bank is still in existence today as PNC Financial Services, PNC and remains based in Pittsburgh. PNC is currently the state's largest bank and the nation's sixth largest bank.Agriculture
Pennsylvania ranks 19th overall among all states in agricultural production. Its leading agricultural products are fungiculture, mushrooms, apples, Christmas trees, Egg (food), layer chickens, Nursery (horticulture), nursery, sod, milk, maize, corn for silage, grapes (including Grape juice, juice grapes), and horses production. Pennsylvania ranks eighth in the nation in winemaking. The Pennsylvania Department of Agriculture worked with private companies to establish "PA Preferred" as a way to brand agricultural products grown or made in the state. The financial impact of agriculture in Pennsylvania includes employment of more than 66,800 people employed by the food manufacturing industry and over $1.7 billion in food product export as of 2011.Gambling
 Casino gambling was legalized in Pennsylvania in 2004. As of 2022, there are List of casinos in Pennsylvania, 16 casinos in the state. Table games such as poker, roulette, blackjack, and craps were approved by the state legislature and signed into law in January 2010.
Casino gambling was legalized in Pennsylvania in 2004. As of 2022, there are List of casinos in Pennsylvania, 16 casinos in the state. Table games such as poker, roulette, blackjack, and craps were approved by the state legislature and signed into law in January 2010.
Film
The Pennsylvania Film Production Tax Credit began in 2004 and stimulated the development of a film industry in the state.Governance
Pennsylvania has had five Pennsylvania Constitution, constitutions during its statehood: 1776, 1790, 1838, 1874, and 1968. Before that the province of Pennsylvania was governed for a century by a Frame of Government of Pennsylvania, Frame of Government, of which there were four versions: 1682, 1683, 1696, and 1701. The capital of Pennsylvania isHarrisburg
Harrisburg is the capital city of the Pennsylvania, Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Dauphin County, Pennsylvania, Dauphin County. With a population of 50,135 as of the 2021 census, Harrisburg is the List of c ...
. The legislature meets there in the Pennsylvania State Capitol, State Capitol.
In a 2020 study, Pennsylvania was ranked as the 19th hardest state for citizens to vote in.
Executive
The current Governor is Tom Wolf. The other elected officials composing the executive branch are the Lieutenant Governor of Pennsylvania, Lieutenant Governor John Fetterman, Pennsylvania Attorney General, Attorney General Joshua Shapiro, Pennsylvania Auditor General, Auditor General Timothy DeFoor, and Pennsylvania Treasurer Stacy Garrity. The Governor and Lieutenant Governor run as a ticket in the general election and are up for re-election every four years during the midterm elections. The elections for Attorney General, Auditor General, and Treasurer are held every four years coinciding with a Presidential election.Legislative
 Pennsylvania has a bicameral legislature set up by Commonwealth's constitution in 1790. The original Frame of Government of William Penn had a unicameral legislature. The Pennsylvania General Assembly, General Assembly includes 50 Pennsylvania Senate, Senators and 203 Pennsylvania House of Representatives, Representatives. Joseph B. Scarnati III, Joe Scarnati is currently President Pro Tempore of the State Senate, Jake Corman the Majority Leader, and Jay Costa the Minority Leader. Bryan Cutler is Speaker of the Pennsylvania House of Representatives, Speaker of the House of Representatives, with Kerry A. Benninghoff as Majority Leader and Frank Dermody as Minority Leader. As of the Pennsylvania House of Representatives election, 2018, 2018 elections, the Republicans hold the majority in the State House and Senate.
Pennsylvania has a bicameral legislature set up by Commonwealth's constitution in 1790. The original Frame of Government of William Penn had a unicameral legislature. The Pennsylvania General Assembly, General Assembly includes 50 Pennsylvania Senate, Senators and 203 Pennsylvania House of Representatives, Representatives. Joseph B. Scarnati III, Joe Scarnati is currently President Pro Tempore of the State Senate, Jake Corman the Majority Leader, and Jay Costa the Minority Leader. Bryan Cutler is Speaker of the Pennsylvania House of Representatives, Speaker of the House of Representatives, with Kerry A. Benninghoff as Majority Leader and Frank Dermody as Minority Leader. As of the Pennsylvania House of Representatives election, 2018, 2018 elections, the Republicans hold the majority in the State House and Senate.
Judiciary
Pennsylvania is divided into 60 judicial districts, most of which (except Philadelphia County, Pennsylvania, Philadelphia) have magisterial district judges (formerly called district justices and justices of the peace), who preside mainly over preliminary hearings in felony and misdemeanor offenses, all minor (summary) criminal offenses, and small civil claims. Most criminal and civil cases originate in the Courts of Common Pleas, which also serve as appellate courts to the district judges and for local agency decisions. The Superior Court of Pennsylvania, Superior Court hears all appeals from the Courts of Common Pleas not expressly designated to the Commonwealth Court of Pennsylvania, Commonwealth Court or Supreme Court. It also has original jurisdiction to review Warrant (law), warrants for Telephone tapping, wiretap surveillance. The Commonwealth Court is limited to appeals from final orders of certain state agencies and certain designated cases from the Courts of Common Pleas. The Supreme Court of Pennsylvania is the final appellate court. All judges in Pennsylvania are elected; the chief justice is determined by seniority.Local government
 Pennsylvania is divided into 67 county (United States), counties.''The Pennsylvania Manual'', p. 6-3. Counties are further subdivided into municipalities that are either incorporated as cities, Borough (Pennsylvania), boroughs, or Township (Pennsylvania), townships.''Pennsylvania Manual'', p. 6-5. One county, Philadelphia County, Pennsylvania, Philadelphia County, is coterminous with the city of Philadelphia after it was Act of Consolidation, 1854, consolidated in 1854. The most populous county in Pennsylvania is Philadelphia, while the least populous is Cameron County, Pennsylvania, Cameron (4,547).
There are a total of 56 cities in Pennsylvania, which are classified, by population, as either first-, second-, or third-class cities. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania's largest city, has a population of 1.6 million and is the state's only first-class city.
Pennsylvania is divided into 67 county (United States), counties.''The Pennsylvania Manual'', p. 6-3. Counties are further subdivided into municipalities that are either incorporated as cities, Borough (Pennsylvania), boroughs, or Township (Pennsylvania), townships.''Pennsylvania Manual'', p. 6-5. One county, Philadelphia County, Pennsylvania, Philadelphia County, is coterminous with the city of Philadelphia after it was Act of Consolidation, 1854, consolidated in 1854. The most populous county in Pennsylvania is Philadelphia, while the least populous is Cameron County, Pennsylvania, Cameron (4,547).
There are a total of 56 cities in Pennsylvania, which are classified, by population, as either first-, second-, or third-class cities. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania's largest city, has a population of 1.6 million and is the state's only first-class city. Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
(303,000) and Scranton
Scranton is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania, Lackawanna County. With a population of 76,328 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 U ...
(76,000) are second-class and second-class 'A' cities, respectively. The rest of the cities, like the third and fourth-largest—Allentown Allentown may refer to several places in the United States and topics related to them:
* Allentown, California, now called Toadtown, California
* Allentown, Georgia, a town in Wilkinson County
* Allentown, Illinois, an unincorporated community in T ...
(126,000) and Reading
Reading is the process of taking in the sense or meaning of Letter (alphabet), letters, symbols, etc., especially by Visual perception, sight or Somatosensory system, touch.
For educators and researchers, reading is a multifaceted process invo ...
(95,000)—to the smallest—Parker, Pennsylvania, Parker with a population of only 820—are third-class cities. First- and second-class cities are governed by a "strong mayor" form of mayor–council government, whereas third-class cities are governed by either a "weak mayor" form of government or a council–manager government.
Boroughs are generally smaller than cities, with most Pennsylvania cities having been incorporated as a borough before being incorporated as a city. There are 958 boroughs in Pennsylvania, all of which are governed by the "weak mayor" form of mayor-council government. The largest borough in Pennsylvania is State College (40,501) and the smallest is Centralia, Pennsylvania, Centralia.
Townships are the third type of municipality in Pennsylvania and are classified as either first-class or second-class townships. There are 1,454 second-class townships and 93 first-class townships.''The Pennsylvania Manual'', p. 6-6. Second-class townships can become first-class townships if they have a population density greater than and a referendum is passed supporting the change. Pennsylvania's largest township is Upper Darby Township, Delaware County, Pennsylvania, Upper Darby Township (85,681), and the smallest is East Keating Township, Clinton County, Pennsylvania, East Keating Township.
There is one exception to the types of municipalities in Pennsylvania: Bloomsburg, Pennsylvania, Bloomsburg was incorporated as a town in 1870 and is, officially, the only town in the state. In 1975, McCandless Township, Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, McCandless Township adopted a home-rule charter under the name of "Town of McCandless", but is, legally, still a first-class township. The state has 56 cities, 958 boroughs, 93 first-class townships, 1,454 second-class townships, and one town (Bloomsburg) for a total of 2,562 municipalities.
Taxation
Pennsylvania had the 15th-highest state and local tax burden in the nation as of 2012, according to the Tax Foundation. Residents paid a total of $83.7 billion in state and local taxes with a per capita average of $4,589 annually. Residents share 76% of the total tax burden. Many state politicians have tried to increase the share of taxes paid by out-of-state sources. Suggested revenue sources include taxing natural gas drilling as Pennsylvania is the only state without such a tax on gas drilling. Additional revenue prospects include trying to place tolls on interstate highways; specifically Interstate 80 in Pennsylvania, Interstate 80, which is used heavily by out of state commuters with high maintenance costs. Sales taxes provide 39% of the Commonwealth's revenue; State income tax, personal income taxes 34%; motor vehicle taxes about 12%, and taxes on Cigarette tax#Taxation, cigarettes and alcoholic beverages 5%. The personal income tax is a flat 3.07%. An individual's taxable income is based on the following eight types of income: compensation (salary); interest; dividends; net profits from the operation of a business, profession or farm; net gains or income from the dispositions of property; net gains or income from rents, royalties, patents and copyrights; income derived through estates or trusts; and gambling and lottery winnings (other than Pennsylvania Lottery winnings). Counties, municipalities, and school districts levy taxes on real estate. In addition, some local bodies assess a income tax, wage tax on personal income. Generally, the total wage tax rate is capped at 1% of income but some municipalities with home rule charters may charge more than 1%. Thirty-two of the Commonwealth's sixty-seven counties levy a property tax, personal property tax on stocks, bonds, and similar holdings. With the exception of the city ofPhiladelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
, Pennsylvania, municipalities and school districts are allowed to enact a local earned income tax within the purview of Act 32. Residents of these municipalities and school districts are required to file a local income tax return in addition to federal and state returns. This local return is filed with the local income tax collector, a private collection agency appointed by a particular county to collect the local earned income and local services tax (the latter a flat fee deducted from salaried employees working within a particular municipality or school district).
The City of Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
has its own local income taxation system. Philadelphia-based employers are required to withhold the Philadelphia wage tax from the salaries of their employees. Residents of Philadelphia working for an employer are not required to file a local return as long as their Philadelphia wage tax is fully withheld by their employer. If their employer does not withhold the Philadelphia wage tax, residents are required to register with the Revenue Department and file an Earnings Tax return. Residents of Philadelphia with self-employment income are required to file a Net Profits Tax (NPT) return, while those with business income from Philadelphia sources are required to obtain a Commercial Activity License (CAL) and pay the Business Income and Receipts Tax (BIRT) and the NPT. Residents with unearned income (except for interest from checking and savings accounts) are required to file and pay the School Income-tax (SIT).
The complexity of Pennsylvania's local tax filing system has been criticized by experts, who note that the outsourcing of collections to private entities is akin to tax farming and that many new residents are caught off guard and end up facing failure to file penalties even if they did not owe any tax. Attempts to transfer local income tax collections to the state level (i.e. by having a separate local section on the state income tax return, currently the method used to collect local income taxes in New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, Indiana, and Iowa) have been unsuccessful.
State law enforcement
The Pennsylvania State Police is the chief law enforcement agency in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania.Politics
Republican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
John McCain in Pennsylvania, 3,276,363 (54%) to 2,655,885 (44%).
In the 2016 presidential election, however, Republican Donald Trump broke the Democratic streak in the state, winning by 2,970,733 (48%) votes to 2,926,441 (47%) votes. The state returned to the Democratic column in 2020 United States presidential election in Pennsylvania, 2020 by voting for Joe Biden over Trump, 3,458,229 (50%) to 3,377,674 (49%). The state holds 20 United States Electoral College, electoral votes.
In recent national elections since 1992, Pennsylvania had leaned Democrat. The state voted for the Democratic ticket for president in every election between 1992 and 2012. During the 2008 election campaign, a recruitment drive saw registered Democrats outnumber registered Republicans by 1.2 million. However, Pennsylvania has a history of electing Republican U.S. Senators. From 2009 to 2011, the state was represented by two Democratic senators for the first time since 1947 after Republican Senator Arlen Specter switched party affiliation. In 2010, Republicans recaptured a U.S. Senate seat and a majority of the state's congressional seats, control of both chambers of the state legislature, and the governorship. Democrats won back the governorship, however, four years later in the Pennsylvania gubernatorial election, 2014, 2014 election. It was the first time since a governor became eligible for reelection that an incumbent governor had been defeated in a reelection bid.
Historically, Democratic strength was concentrated in Philadelphia in the southeast, the Pittsburgh and Johnstown, Pennsylvania, Johnstown areas in the southwest, and Scranton/Wilkes-Barre in the northeast. Republican strength was concentrated in the Philadelphia suburbs and the more rural areas in the state's central, northeastern, and western portions, some of which have long been considered among the nation's most conservative areas. Since 1992, however, the Philadelphia suburbs have swung Democratic; the brand of Republicanism there was traditionally a moderate one. In the 21st century, however, Pittsburgh suburbs, which historically had been Democrat strongholds, have swung more Republican.
Democratic political consultant James Carville once pejoratively described Pennsylvania as "Philadelphia in the east, Pittsburgh in the west, and Alabama in the middle", suggesting that political power in the state was based in its two largest cities, which have been reliably Democrat, offset by the state's large rural power base, which has proven equally reliably Republican. Political analysts and editorials refer to central Pennsylvania as the "T" in statewide elections. The state's three valleys (Delaware Valley, Delaware, Lehigh Valley, Lehigh, and Wyoming Valley, Wyoming Valleys) and Greater Pittsburgh
Greater Pittsburgh is a populous region centered around its largest city and economic hub, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The region encompasses Pittsburgh's urban core county, Allegheny, and six adjacent Pennsylvania counties: Armstrong, Beaver, ...
generally vote Democrat, while the majority of the counties in the central part of the state vote Republican. As a result, maps showing the results of statewide elections invariably form a shape that resembles a "T".
Federal representation
Pennsylvania's two United States Senate, U.S. Senators are Democratic Party (United States), Democrat Bob Casey Jr. andRepublican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
Pat Toomey. Casey would seek reelection in 2024 should he seek another term. Toomey, meanwhile, chose not to run for reelection in 2022, and Democrat John Fetterman will succeed Toomey in 2023.
Pennsylvania has Pennsylvania's congressional districts, 18 seats in the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives as of 2022.
Education
Pennsylvania has 500 public school districts, thousands of private schools, publicly funded colleges and universities, and over 100 private institutions of higher education.Primary and secondary education
Higher education
University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (also known as Penn or UPenn) is a private research university in Philadelphia. It is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and is ranked among the highest-regarded universitie ...
, and the University of Pittsburgh are members of the Association of American Universities, an invitation-only organization of leading research universities. Lehigh University is a private research university located in Bethlehem. The Pennsylvania State University is the Commonwealth's land-grant university, National Sea Grant College Program, Sea Grant College and, National Space Grant College and Fellowship Program, Space Grant College. The University of Pennsylvania, located in Philadelphia, is considered the first university in the United States and established the country's First university in the United States#Establishment of quarterly-education schools, issuance of any kind of "doctoral" degree, first medical school in the United States, medical school. The University of Pennsylvania is also the Commonwealth's only, and geographically most southern, Ivy League
The Ivy League is an American collegiate athletic conference comprising eight private research universities in the Northeastern United States. The term ''Ivy League'' is typically used beyond the sports context to refer to the eight schools ...
school. The Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine (LECOM) is a private graduate school of medicine, dentistry, and pharmacy with a main campus in Erie, and a branch campus located in Greensburg (with two other campuses outside of Pennsylvania). With over 2,200 enrolled medical students, the College of Osteopathic Medicine at LECOM is the largest medical school in the United States. The Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts is the first and oldest art school in the United States. Philadelphia College of Pharmacy, now a part of University of the Sciences, University of the Sciences in Philadelphia, was the first pharmacy school in the United States.
Recreation
 Pennsylvania is home to the nation's first zoo, the Philadelphia Zoo. Other long-accredited AZA zoos include the Erie Zoo and the Pittsburgh Zoo & PPG Aquarium. The Lehigh Valley Zoo and ZooAmerica are other notable zoos. The Commonwealth boasts some of the finest museums in the country, including the Allentown Art Museum in Allentown, Carnegie Museums in Pittsburgh, the Philadelphia Museum of Art, and :Museums in Pennsylvania, several others. One unique museum is the Houdini Museum in Scranton, the only building in the world devoted to the legendary magician. Pennsylvania is also home to the National Aviary, located in Pittsburgh.
All 121 List of Pennsylvania state parks, state parks in Pennsylvania feature free admission.
Pennsylvania's notable amusement parks include Conneaut Lake Park, Dorney Park & Wildwater Kingdom, Dutch Wonderland, DelGrosso's Amusement Park, Great Wolf Lodge, Hersheypark, Idlewild Park, Kalahari Resorts, Kalahari Resorts Poconos, Kennywood, Knoebels, Lakemont Park, Sandcastle Waterpark, Sesame Place (Philadelphia), Sesame Place, and Waldameer Park. Pennsylvania also is home to the largest indoor waterpark resort on the East Coast, Splash Lagoon in Erie.
The state's notable music festivals include Musikfest, the nation's largest free music festival held annually each August in
Pennsylvania is home to the nation's first zoo, the Philadelphia Zoo. Other long-accredited AZA zoos include the Erie Zoo and the Pittsburgh Zoo & PPG Aquarium. The Lehigh Valley Zoo and ZooAmerica are other notable zoos. The Commonwealth boasts some of the finest museums in the country, including the Allentown Art Museum in Allentown, Carnegie Museums in Pittsburgh, the Philadelphia Museum of Art, and :Museums in Pennsylvania, several others. One unique museum is the Houdini Museum in Scranton, the only building in the world devoted to the legendary magician. Pennsylvania is also home to the National Aviary, located in Pittsburgh.
All 121 List of Pennsylvania state parks, state parks in Pennsylvania feature free admission.
Pennsylvania's notable amusement parks include Conneaut Lake Park, Dorney Park & Wildwater Kingdom, Dutch Wonderland, DelGrosso's Amusement Park, Great Wolf Lodge, Hersheypark, Idlewild Park, Kalahari Resorts, Kalahari Resorts Poconos, Kennywood, Knoebels, Lakemont Park, Sandcastle Waterpark, Sesame Place (Philadelphia), Sesame Place, and Waldameer Park. Pennsylvania also is home to the largest indoor waterpark resort on the East Coast, Splash Lagoon in Erie.
The state's notable music festivals include Musikfest, the nation's largest free music festival held annually each August in Bethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital o ...
, the Philadelphia Folk Festival, Creation Festival, and Purple Door. The Great Allentown Fair, held annually at the Allentown Fairgrounds since the 19th century, is one of the nation's longest-running annual fairs.
There are nearly one million licensed hunters in Pennsylvania. Whitetail deer, black bear, cottontail rabbits, squirrel, turkey, and grouse are common game species. Pennsylvania is considered one of the finest wild turkey hunting states in the Union, alongside Texas and Alabama. Sport hunting in Pennsylvania provides a massive boost for the Commonwealth's economy. A report from The Center for Rural Pennsylvania (a Legislative Agency of the Pennsylvania General Assembly) reported that hunting, fishing, and furtaking generated a total of $9.6 billion statewide.
The Boone and Crockett Club reports that five of the ten largest (skull size) American black bear, black bear entries came from the state. The state also has a tied record for the largest hunter shot black bear in the Boone & Crockett books at and a skull of 23 3/16 tied with a bear shot in California in 1993. The largest bear ever found dead was in Utah in 1975, and the second-largest was shot by a Poaching, poacher in the state in 1987. As of 2007, Pennsylvania has the second highest number of Boone and Crockett-recorded record black bears at 183, behind Wisconsin's 299.
Transportation



 The Pennsylvania Department of Transportation, abbreviated as PennDOT, is responsible for transport issues within the commonwealth.
The Pennsylvania Department of Transportation, abbreviated as PennDOT, is responsible for transport issues within the commonwealth.
Air
Pennsylvania has seven major airports: Philadelphia International Airport, Philadelphia International, Pittsburgh International Airport, Pittsburgh International, Lehigh Valley International Airport, Lehigh Valley International, Harrisburg International Airport, Harrisburg International, Wilkes-Barre/Scranton International Airport, Wilkes-Barre/Scranton International, Erie International Airport, Erie International, and University Park Airport. A total of 134 public-use airports are located in the state.Bus and coach
Intercity bus service is provided between cities in Pennsylvania and other major points in the Northeast by Bolt Bus, Fullington Trailways, Greyhound Lines, Martz Trailways, Megabus (North America), Megabus, OurBus, Trans-Bridge Lines, and various Chinatown bus lines, Chinatown bus companies. In 2018, OurBus began offering service from West Chester, Pennsylvania, West Chester, Malvern, Pennsylvania, Malvern, King of Prussia, Pennsylvania, King of Prussia, and Fort Washington, Pennsylvania, Fort Washington to New York City.Rail
The SEPTA, Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA) is the sixth-largest transit agency in the United States and operates the commuter rail, commuter, heavy rail, heavy and light rail transit, and transit bus service in the Philadelphia metropolitan area. Pittsburgh Regional Transit is the 25th-largest transit agency and provides transit bus and light rail service in and around Pittsburgh. Intercity passenger rail transit is provided by Amtrak, with the majority of traffic occurring on the ''Keystone Service'' in the high-speed Keystone Corridor between Harrisburg and Philadelphia's 30th Street Station before heading north to New York City, as well as the ''Northeast Regional'' providing frequent high-speed service up and down the Northeast Corridor. The ''Pennsylvanian (Amtrak), Pennsylvanian'' follows the same route from New York City to Harrisburg, but extends out to Pittsburgh. The ''Capitol Limited (Amtrak train), Capitol Limited'' also passes through Pittsburgh, as well as Connellsville, Pennsylvania, Connellsville, on its way from Chicago toWashington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
Traveling between Chicago and New York City, the ''Lake Shore Limited'' passes through Erie once in each direction. There are 67 short-line railroad, short-line, freight railroads operating in Pennsylvania, the highest number in any U.S. state."Pennsylvania Department of Transportation Fact Book", p. 10. With more than four million inter-city rail passengers in 2018, Philadelphia's 30th Street Station is Amtrak's third busiest train station in the nation after Pennsylvania Station (New York), Penn Station in Manhattan and Washington Union Station, Union Station in Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
and North America's List of busiest railway stations in North America, 12th-busiest train station overall.
Road
PennDOT owns of the of roadway in the state, making it the fifth-largest state highway system in the United States."Pennsylvania Department of Transportation Fact Book", p. 7. The Pennsylvania Turnpike system is long, with the mainline portion stretching from Ohio to Philadelphia and New Jersey. It is overseen by the Pennsylvania Turnpike Commission. Another major east–west route is Interstate 80 in Pennsylvania, Interstate 80, which runs primarily in the northern tier of the state from Ohio to New Jersey at the Delaware Water Gap. Interstate 90 in Pennsylvania, Interstate 90 travels the relatively short distance between Ohio and New York through Erie County, Pennsylvania, Erie County, in the extreme northwestern part of the state. Primary north–south highways are Interstate 79 in Pennsylvania, Interstate 79 from its terminus in Erie through Pittsburgh to West Virginia, Interstate 81 in Pennsylvania, Interstate 81 from New York through Scranton, Pennsylvania, Scranton, Lackawanna County and Harrisburg to Maryland and Interstate 476, which begins north of theDelaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
border, in Chester, Pennsylvania, Chester, Delaware County and travels to Clarks Summit, Pennsylvania, Clarks Summit, where it joins I-81. All but of I-476 is the Northeast Extension of the Pennsylvania Turnpike. The highway south of the Pennsylvania Turnpike is officially called the "Veterans Memorial Highway", but is commonly referred to colloquially as the "Blue Route".
Water
The port of Pittsburgh is the second-largest inland port in the United States and the 18th-largest port overall; the Port of Philadelphia is the 24th-largest port in the United States. Pennsylvania's only port on the Great Lakes is located in Erie. The Allegheny River Lock and Dam Two is the most-used Lock (water transport), lock operated by the United States Army Corps of Engineers of its 255 nationwide. The dam impounds theAllegheny River
The Allegheny River ( ) is a long headwater stream of the Ohio River in western Pennsylvania and New York (state), New York. The Allegheny River runs from its headwaters just below the middle of Pennsylvania's northern border northwesterly into ...
near Downtown Pittsburgh.
Culture
Sports
Professional sports



 Pennsylvania is home to eight major league professional sports teams: the Philadelphia Phillies and Pittsburgh Pirates of Major League Baseball, the Philadelphia 76ers of the National Basketball Association, NBA, the Philadelphia Eagles and Pittsburgh Steelers of the National Football League, NFL, the Philadelphia Flyers and Pittsburgh Penguins of the National Hockey League, NHL, and the Philadelphia Union of Major League Soccer. Among them, these teams have accumulated sevenWorld Series championships (with the Pirates winning five and Phillies winning two), 16 National League pennants (with the Pirates winning nine and Phillies winning seven), three pre-Super Bowl era NFL championships (all won by the Eagles), seven Super Bowl championships (with the Steelers winning six and the Eagles one), two NBA championships (both won by the 76ers), and seven Stanley Cup championships (with the Penguins winning five and Flyers winning two).
With Sports in Philadelphia, five professional sports teams and some of the most passionate sports fans in the nation,
Pennsylvania is home to eight major league professional sports teams: the Philadelphia Phillies and Pittsburgh Pirates of Major League Baseball, the Philadelphia 76ers of the National Basketball Association, NBA, the Philadelphia Eagles and Pittsburgh Steelers of the National Football League, NFL, the Philadelphia Flyers and Pittsburgh Penguins of the National Hockey League, NHL, and the Philadelphia Union of Major League Soccer. Among them, these teams have accumulated sevenWorld Series championships (with the Pirates winning five and Phillies winning two), 16 National League pennants (with the Pirates winning nine and Phillies winning seven), three pre-Super Bowl era NFL championships (all won by the Eagles), seven Super Bowl championships (with the Steelers winning six and the Eagles one), two NBA championships (both won by the 76ers), and seven Stanley Cup championships (with the Penguins winning five and Flyers winning two).
With Sports in Philadelphia, five professional sports teams and some of the most passionate sports fans in the nation, Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
is often described as the nation's best sports city.
In baseball, in addition to its two MLB franchises, Pennsylvania has Minor League Baseball, minor league and semi-pro sports teams: the Triple-A (baseball), Triple-A baseball Lehigh Valley IronPigs and the Scranton/Wilkes-Barre RailRiders of the Triple-A East; the Double-A (baseball), Double-A baseball Altoona Curve, Erie SeaWolves, Harrisburg Senators, and Reading Fightin Phils of the Double-A Northeast; the collegiate summer baseball State College Spikes and Williamsport Crosscutters of the MLB Draft League; the independent baseball Lancaster Barnstormers and York Revolution of the Atlantic League of Professional Baseball; the independent baseball Washington Wild Things of the Frontier League; the Erie BayHawks (2019–), Erie BayHawks of the NBA G League; the Lehigh Valley Phantoms, Wilkes-Barre/Scranton Penguins, and Hershey Bears of the American Hockey League; the Reading Royals and of the ECHL; and the Philadelphia Soul of the Arena Football League. Among them, these teams have accumulated 12 triple and double-A baseball league titles (RailRiders 1, Senators 6, Fightin Phils 4Curve 1), 3Arena Bowl Championships (Soul), and 11 Calder Cups (Bears).
The first World Series between the Boston Americans (which later became the Boston Red Sox) and Pittsburgh Pirates was played in Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
in 1903. Since 1959, the Little League World Series has been held each August in South Williamsport, Pennsylvania, South Williamsport near where Little League Baseball was founded in Williamsport.
With the addition of the Philadelphia Union of the MLS, Pennsylvania now boasts three teams that are eligible to compete for the Lamar Hunt U.S. Open Cup annually. The other two teams are Philadelphia Union II and the Pittsburgh Riverhounds. Both of the United Soccer League (USL). Within the American Soccer Pyramid, the MLS takes the first tier while the USL-2 claims the third tier.
Arnold Palmer, one of the 20th century's most accomplished professional golfers, comes from Latrobe, Pennsylvania, Latrobe, and Jim Furyk, a current Professional Golfers' Association of America, PGA member grew up near in Manheim Township, Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, Lancaster. PGA tournaments in Pennsylvania include the 84 Lumber Classic played at Nemacolin Woodlands Resort, in Farmington, Pennsylvania, Farmington and the Northeast Pennsylvania Classic played at Glenmaura National Golf Club in Moosic, Pennsylvania, Moosic.
Philadelphia is home to LOVE Park across from Philadelphia City Hall, City Hall, a popular location for skateboard, skateboarding and host to ESPN's X Games in 2001 and 2002.
Motorsports
In motorsports, the Mario Andretti dynasty of race drivers hails from Nazareth, Pennsylvania, Nazareth in theLehigh Valley
The Lehigh Valley (), known colloquially as The Valley, is a geographic region formed by the Lehigh River in Lehigh County and Northampton County in eastern Pennsylvania. It is a component valley of the Great Appalachian Valley bound to the no ...
. Pennsylvania racetracks include Jennerstown Speedway in Jennerstown, Pennsylvania, Jennerstown, Lake Erie Speedway in North East, Pennsylvania, North East, Lernerville Speedway in Sarver, Pennsylvania, Sarver, and Pocono Raceway in Long Pond, Pennsylvania, Long Pond, which is home to two NASCAR Cup Series races and an IndyCar Series race. The state is also home to Maple Grove Raceway, near Reading
Reading is the process of taking in the sense or meaning of Letter (alphabet), letters, symbols, etc., especially by Visual perception, sight or Somatosensory system, touch.
For educators and researchers, reading is a multifaceted process invo ...
, which hosts major National Hot Rod Association-sanctioned drag racing events each year.
There are also two motocross race tracks that host a round of the AMA Toyota Motocross Championships in Pennsylvania. High Point Raceway is located in Mount Morris, Pennsylvania, and Steel City is located in Delmont, Pennsylvania.
Horse racing courses in Pennsylvania consist of The Meadows Racetrack and Casino, The Meadows near Pittsburgh, Mohegan Sun Pocono in Wilkes-Barre, and Harrah's Philadelphia in Chester, which offer harness racing, and Penn National Race Course in Grantville, Pennsylvania, Grantville, Parx Casino and Racing, Parx Racing (formerly Philadelphia Park) in Bensalem, Pennsylvania, Bensalem, and Presque Isle Downs near Erie, which offer thoroughbred racing. Smarty Jones, the 2004 Kentucky Derby and Preakness Stakes winner, had Philadelphia Park as his home course.
College sports
In college football, three Pennsylvania universities compete in NCAA Division I, the highest level of sanctioned collegiate play in the sport: Penn State Nittany Lions football, Penn State in the Big Ten Conference, Pittsburgh Panthers football, Pitt in the Atlantic Coast Conference, and Temple Owls football, Temple in the American Athletic Conference. Over their respective college football histories, Penn State claims two College football national championships in NCAA Division I FBS, national championships (1982 and 1986) and seven undefeated seasons (1887, 1912, 1968, 1969, 1973, 1986, and 1994) and Pitt has won nine national championships (1915, 1916, 1918, 1929, 1931, 1934, 1936, 1937, and 1976) and had eight undefeated seasons (1904, 1910, 1915, 1916, 1917, 1920, 1937, and 1976). Penn State plays its home games at Beaver Stadium, a 106,572-capacity stadium that is the List of North American stadiums by capacity, second largest stadium in the nation; the team is coached by James Franklin (American football coach), James Franklin. Pitt plays its home games at Acrisure Stadium, a 68,400-capacity stadium it shares with the Pittsburgh Steelers; the team is coached by Pat Narduzzi. Over their respective histories, four additional Pennsylvania universities and colleges have won national college football championships: Lafayette Leopards football, Lafayette in Easton (1896), Villanova Wildcats football, Villanova in Villanova, Pennsylvania, Villanova (2009), Penn Quakers football, Penn in Philadelphia (1895, 1897, 1904, and 1908), and Washington & Jefferson Presidents, Washington & Jefferson in Washington, Pennsylvania, Washington (1921). In college basketball, five Philadelphia and Delaware Valley, Philadelphia-area universities, collectively known as the Philadelphia Big 5, Big Five, have a rich tradition in NCAA Division I basketball. National titles in college basketball have been won by La Salle Explorers men's basketball, La Salle (1954), Temple Owls men's basketball, Temple (1938), Penn Quakers men's basketball, Penn (1920 and 1921), Pittsburgh Panthers men's basketball, Pitt (1928 and 1930), and Villanova Wildcats men's basketball, Villanova (1985, 2016, and 2018). Pennsylvania has several universities and colleges known as national leaders in college wrestling. Penn State Nittany Lions wrestling, Penn State, coached by Cael Sanderson, has won ten NCAA Division I Wrestling Championships in its history, second most among all universities and colleges after Oklahoma State Cowboys wrestling, Oklahoma State. Lehigh Mountain Hawks, Lehigh inBethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital o ...
has had 28 NCAA Division I individual champions over its history.
Food

 In 2008, author Sharon Hernes Silverman called Pennsylvania the snack food capital of the world. It leads all other states in the manufacture of pretzels and potato chips. The Sturgis Pretzel House introduced the pretzel to America, and companies like Anderson Bakery Company, Intercourse Pretzel Factory, and Snyder's of Hanover are leading manufacturers in the Commonwealth. Two of the three companies that define the U.S. potato chip industry are based in Pennsylvania: Utz Quality Foods, which started making chips in Hanover, Pennsylvania, in 1921 and Wise Foods, which started making chips in Berwick, Pennsylvania, Berwick also in 1921. The third, Frito-Lay is part of PepsiCo, and is based in Plano, Texas. Other companies such as Herr's Snacks, Martin's Potato Chips, Snyder's of Berlin (not associated with Snyder's of Hanover), Middleswarth Potato Chips (in Middleburg) and Troyer Farms Potato Products are popular chip manufacturers.
The U.S. chocolate industry is centered in
In 2008, author Sharon Hernes Silverman called Pennsylvania the snack food capital of the world. It leads all other states in the manufacture of pretzels and potato chips. The Sturgis Pretzel House introduced the pretzel to America, and companies like Anderson Bakery Company, Intercourse Pretzel Factory, and Snyder's of Hanover are leading manufacturers in the Commonwealth. Two of the three companies that define the U.S. potato chip industry are based in Pennsylvania: Utz Quality Foods, which started making chips in Hanover, Pennsylvania, in 1921 and Wise Foods, which started making chips in Berwick, Pennsylvania, Berwick also in 1921. The third, Frito-Lay is part of PepsiCo, and is based in Plano, Texas. Other companies such as Herr's Snacks, Martin's Potato Chips, Snyder's of Berlin (not associated with Snyder's of Hanover), Middleswarth Potato Chips (in Middleburg) and Troyer Farms Potato Products are popular chip manufacturers.
The U.S. chocolate industry is centered in Hershey, Pennsylvania
Hershey is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Derry Township, Dauphin County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is home to The Hershey Company, which was founded by candy magnate Milton S. Hershey.
The community is lo ...
, with Mars, Incorporated, Mars, Godiva Chocolatier, Godiva, and Wilbur Chocolate Company nearby, and smaller manufacturers such as Asher's in Souderton, Pennsylvania, Souderton, and Gertrude Hawk Chocolates of Dunmore, Pennsylvania, Dunmore. Other notable companies include Just Born in Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, makers of Hot Tamales, Mike and Ikes, the Easter favorite marshmallow Peeps, and Boyer Brothers of Altoona, Pennsylvania, which is well known for its Mallo Cups. Auntie Anne's, Auntie Anne's Pretzels began as a market-stand in Downingtown, Pennsylvania, and now has corporate headquarters in Lancaster City. Traditional Pennsylvania Dutch foods include chicken potpie, ham potpie, schnitz un knepp (dried apples, ham, and dumplings), Fasnacht (doughnut), fasnachts (raised doughnuts), scrapple, pretzels, bologna, chow-chow, and Shoofly pie. Martin's Famous Pastry Shoppe, headquartered in Chambersburg, Pennsylvania, specializes in potato bread, another Cuisine of the Pennsylvania Dutch, traditional Pennsylvania Dutch food. D.G. Yuengling & Son, America's oldest brewery, has been brewing beer in Pottsville, Pennsylvania, Pottsville since 1829.
Among the regional foods associated with Philadelphia are cheesesteaks, hoagies, soft pretzels, Italian water ice, Irish potato candy, scrapple, Tastykake, and Stromboli (food), strombolis. In Pittsburgh, tomato ketchup was improved by H. J. Heinz Company, Henry John Heinz from 1876 to the early 20th century. Famous to a lesser extent than Heinz ketchup is the Pittsburgh's Primanti Brothers Restaurant sandwiches, pierogies, and city chicken. Outside of Scranton, in Old Forge, Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania, Old Forge, there are dozens of Italian restaurants specializing in pizza made unique by thick, light crust, and American cheese. Erie also has its share of unique foods, including Greek sauce and sponge candy. Sauerkraut along with pork and mashed potatoes is a traditional meal on New Year's Day in Pennsylvania; its tradition began with the Pennsylvania Dutch who believe the meal leads to good luck in the new year to come.
Nicknames
Pennsylvania has been known as the keystone (architecture), Keystone State since 1802, based in part upon its central location among the originalThirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of Kingdom of Great Britain, British Colony, colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Fo ...
forming the United States, and also in part because of the number of important American documents signed in the state (such as the Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence or declaration of statehood or proclamation of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the ...
). It was also a keystone state economically, having both the industry common to the Northern United States, North (making such wares as Conestoga wagons and Long rifle, rifles) and the agriculture common to the Southern United States, South (producing feed, fiber, food, and tobacco).
Another one of Pennsylvania's nicknames is the Quakers, Quaker State; in colonial times, it was known officially as the Province of Pennsylvania, Quaker Province, in recognition of Quaker William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer and religious thinker belonging to the Religious Society of Friends (Quakers), and founder of the Province of Pennsylvania, a North American colony of England. He was an early advocate of democracy a ...
's Frame of Government of Pennsylvania, First Frame of Government constitution for Pennsylvania that guaranteed Freedom (political), liberty of conscience. He knew of the hostility Quakers faced when they opposed religious ritual, taking oaths, violence, war and military service, and what they viewed as ostentatious wikt:frippery, frippery.
"The Coal State", "The Oil State", "The Chocolate State", and "The Steel State" were adopted when those were the state's greatest industries. "The State of Independence" currently appears on many road signs entering the state.
Notable people
Sister regions
* Matanzas Province, Cuba * Rhône-Alpes, FranceSee also
* Index of Pennsylvania-related articles * List of cathedrals in Pennsylvania * Outline of PennsylvaniaNotes
References
Citations
Sources
Web sources
* * *Books
*External links
*Gov. Andrew Curtin's Pennsylvania Reserve Volunteer Corps, Civil War 1861–1864
Official state government site
Pennsylvania Department of Transportation
Allegheny National Forest
Pennsylvania Wilds
USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Pennsylvania
Energy Data & Statistics for Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania State Facts from USDA
Official state tourism site
Free Original Documents Online: Pennsylvania State Archives 1600s to 1800s
Pennsylvania Department of Community and Economic Development
National Association of Counties (information on each Pennsylvania County)
* {{coord, 41, -78, dim:300000_region:US-PA_type:adm1st, name=Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, display=title Pennsylvania, 1787 establishments in the United States Articles containing video clips Contiguous United States Mid-Atlantic states Northeastern United States States and territories established in 1787 States of the United States States of the East Coast of the United States