Peaking Power Station on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers", are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity. Because they supply power only occasionally, the power supplied commands a much higher price per kilowatt hour than base load power. Peak load power plants are dispatched in combination with base load power plants, which supply a dependable and consistent amount of electricity, to meet the minimum demand.
Although historically peaking power plants were frequently used in conjunction with coal baseload plants, peaking plants are now used less commonly. Combined cycle gas turbine plants have two or more cycles, the first of which is very similar to a peaking plant, with the second running on the waste heat of the first. That type of plant is often capable of rapidly starting up, albeit at reduced efficiency, and then over some hours transitioning to a more efficient baseload generation mode. Combined cycle plants have similar capital cost per watt to peaking plants, but run for much longer periods, and use less fuel overall, and hence give cheaper electricity.
As of 2020, open cycle gas turbines give an electricity cost of around $151–198/MWh.
Peaker plants are replaced with battery storage in some places. The New York Power Authority (NYPA) is seeking to replace gas peaker plants with battery storage, 142 Tesla Megapacks (providing 100 MW) replace a gas peaker plant in Ventura County, California and in Lessines, Belgium 40 Tesla Megapacks (50 MW) replaced a turbojet generator. Australia’s Clean Energy Council found in April 2021 that battery storage can be 30% cheaper than gas peaker plants.
Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers", are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity. Because they supply power only occasionally, the power supplied commands a much higher price per kilowatt hour than base load power. Peak load power plants are dispatched in combination with base load power plants, which supply a dependable and consistent amount of electricity, to meet the minimum demand.
Although historically peaking power plants were frequently used in conjunction with coal baseload plants, peaking plants are now used less commonly. Combined cycle gas turbine plants have two or more cycles, the first of which is very similar to a peaking plant, with the second running on the waste heat of the first. That type of plant is often capable of rapidly starting up, albeit at reduced efficiency, and then over some hours transitioning to a more efficient baseload generation mode. Combined cycle plants have similar capital cost per watt to peaking plants, but run for much longer periods, and use less fuel overall, and hence give cheaper electricity.
As of 2020, open cycle gas turbines give an electricity cost of around $151–198/MWh.
Peaker plants are replaced with battery storage in some places. The New York Power Authority (NYPA) is seeking to replace gas peaker plants with battery storage, 142 Tesla Megapacks (providing 100 MW) replace a gas peaker plant in Ventura County, California and in Lessines, Belgium 40 Tesla Megapacks (50 MW) replaced a turbojet generator. Australia’s Clean Energy Council found in April 2021 that battery storage can be 30% cheaper than gas peaker plants.
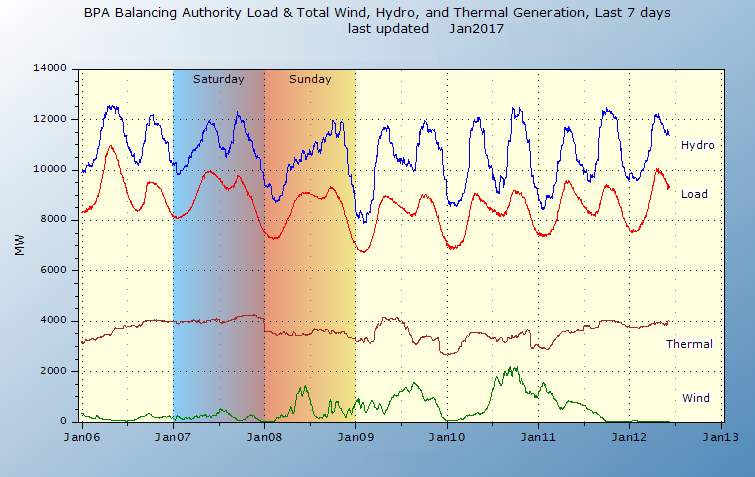 Hydroelectric dams are intentionally variable; they can generate less during off-peak and quickly respond to peak demands, consequently hydroelectricity may function as load following or a peaking plant and with sufficient water, a base-load plant. Natural gas turbines or pumped storage are often used where there is not enough hydroelectricity to respond to daily and weekly variations in generation and consumption. It is not unusual for a dam to be built with more capacity than can be sustained by the water supply, allowing for a higher peak output. Upgrading equipment at existing dams can be one of the least expensive ways of increasing peak generation. The ability to vary the amount of electricity generated is often limited by the requirement that minimum or maximum flows downstream are satisfied.
Hydroelectric dams are intentionally variable; they can generate less during off-peak and quickly respond to peak demands, consequently hydroelectricity may function as load following or a peaking plant and with sufficient water, a base-load plant. Natural gas turbines or pumped storage are often used where there is not enough hydroelectricity to respond to daily and weekly variations in generation and consumption. It is not unusual for a dam to be built with more capacity than can be sustained by the water supply, allowing for a higher peak output. Upgrading equipment at existing dams can be one of the least expensive ways of increasing peak generation. The ability to vary the amount of electricity generated is often limited by the requirement that minimum or maximum flows downstream are satisfied.
 Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers", are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity. Because they supply power only occasionally, the power supplied commands a much higher price per kilowatt hour than base load power. Peak load power plants are dispatched in combination with base load power plants, which supply a dependable and consistent amount of electricity, to meet the minimum demand.
Although historically peaking power plants were frequently used in conjunction with coal baseload plants, peaking plants are now used less commonly. Combined cycle gas turbine plants have two or more cycles, the first of which is very similar to a peaking plant, with the second running on the waste heat of the first. That type of plant is often capable of rapidly starting up, albeit at reduced efficiency, and then over some hours transitioning to a more efficient baseload generation mode. Combined cycle plants have similar capital cost per watt to peaking plants, but run for much longer periods, and use less fuel overall, and hence give cheaper electricity.
As of 2020, open cycle gas turbines give an electricity cost of around $151–198/MWh.
Peaker plants are replaced with battery storage in some places. The New York Power Authority (NYPA) is seeking to replace gas peaker plants with battery storage, 142 Tesla Megapacks (providing 100 MW) replace a gas peaker plant in Ventura County, California and in Lessines, Belgium 40 Tesla Megapacks (50 MW) replaced a turbojet generator. Australia’s Clean Energy Council found in April 2021 that battery storage can be 30% cheaper than gas peaker plants.
Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers", are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity. Because they supply power only occasionally, the power supplied commands a much higher price per kilowatt hour than base load power. Peak load power plants are dispatched in combination with base load power plants, which supply a dependable and consistent amount of electricity, to meet the minimum demand.
Although historically peaking power plants were frequently used in conjunction with coal baseload plants, peaking plants are now used less commonly. Combined cycle gas turbine plants have two or more cycles, the first of which is very similar to a peaking plant, with the second running on the waste heat of the first. That type of plant is often capable of rapidly starting up, albeit at reduced efficiency, and then over some hours transitioning to a more efficient baseload generation mode. Combined cycle plants have similar capital cost per watt to peaking plants, but run for much longer periods, and use less fuel overall, and hence give cheaper electricity.
As of 2020, open cycle gas turbines give an electricity cost of around $151–198/MWh.
Peaker plants are replaced with battery storage in some places. The New York Power Authority (NYPA) is seeking to replace gas peaker plants with battery storage, 142 Tesla Megapacks (providing 100 MW) replace a gas peaker plant in Ventura County, California and in Lessines, Belgium 40 Tesla Megapacks (50 MW) replaced a turbojet generator. Australia’s Clean Energy Council found in April 2021 that battery storage can be 30% cheaper than gas peaker plants.
Peak hours
Peak hours usually occur in the morning or late afternoon/evening depending on location. In temperate climates, peak hours often occur when household appliances are heavily used in the evening after work hours. In hot climates, the peak is usually late afternoon when air conditioning load is high, during this time many workplaces are still open and consuming power. In cold climates, the peak is in the morning when space heating and industry are both starting up. A peaker plant may operate many hours a day, or it may operate only a few hours per year, depending on the condition of the region'selectrical grid
An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. It consists of:Kaplan, S. M. (2009). Smart Grid. Electrical Power ...
. Because of the cost of building an efficient power plant, if a peaker plant is only going to be run for a short or highly variable time, it does not make economic sense to make it as efficient as a base load power plant. In addition, the equipment and fuels used in base load plants are often unsuitable for use in peaker plants because the fluctuating conditions would severely strain the equipment. For these reasons, nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
* Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
, waste-to-energy, coal and biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
are rarely, if ever, operated as peaker plants.
Renewable energy
As countries trend away from fossil fuel-fired base load plants and towards renewable but intermittent energy sources such as wind and solar, there is a corresponding increase in the need forgrid energy storage
Grid energy storage (also called large-scale energy storage) is a collection of methods used for energy storage on a large scale within an electrical power grid. Electrical energy is stored during times when electricity is plentiful and inexp ...
systems, as renewable alternatives to building more peaking or load following power plants. Another option is broader distribution of generating capacity, through the use of grid interties, such as the WECC Intertie Paths.
Types
Peaker plants are generally gas turbines orgas engine
A gas engine is an internal combustion engine that runs on a gaseous fuel, such as coal gas, producer gas, biogas, landfill gas or natural gas. In the United Kingdom, the term is unambiguous. In the United States, due to the widespread use of ...
s that burn natural gas. A few burn biogas or petroleum-derived liquids, such as diesel
Diesel may refer to:
* Diesel engine, an internal combustion engine where ignition is caused by compression
* Diesel fuel, a liquid fuel used in diesel engines
* Diesel locomotive, a railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engin ...
oil and jet fuel
Jet fuel or aviation turbine fuel (ATF, also abbreviated avtur) is a type of aviation fuel designed for use in aircraft powered by gas-turbine engines. It is colorless to straw-colored in appearance. The most commonly used fuels for commercial a ...
, but they are generally more expensive than natural gas, so their use is limited to areas not supplied with natural gas. However, many peaker plants are able to use petroleum as a backup fuel, as storing oil in tanks is easy. The thermodynamic efficiency of simple-cycle gas turbine power plants ranges from 20 to 42%, with between 30 and 42% being average for a new plant.
For greater efficiency, a heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) is added at the exhaust. This is known as a combined cycle
A combined cycle power plant is an assembly of heat engines that work in tandem from the same source of heat, converting it into mechanical energy. On land, when used to make electricity the most common type is called a combined cycle gas turb ...
plant. Cogeneration uses waste exhaust heat for process, district heating or other heating uses. Both of these options are used only in plants that are intended to be operated for longer periods than usual. Natural gas and diesel generators with reciprocating engines are sometimes used for grid support using smaller plants.
Another option for increased efficiency and power output in gas turbines is installing a turbine inlet air cooling system, that cools down the inlet air temperature increasing mass flow ratio. This option, in combination with a thermal energy storage tank, can increase the turbine power output in on-peak periods up to 30%.
 Hydroelectric dams are intentionally variable; they can generate less during off-peak and quickly respond to peak demands, consequently hydroelectricity may function as load following or a peaking plant and with sufficient water, a base-load plant. Natural gas turbines or pumped storage are often used where there is not enough hydroelectricity to respond to daily and weekly variations in generation and consumption. It is not unusual for a dam to be built with more capacity than can be sustained by the water supply, allowing for a higher peak output. Upgrading equipment at existing dams can be one of the least expensive ways of increasing peak generation. The ability to vary the amount of electricity generated is often limited by the requirement that minimum or maximum flows downstream are satisfied.
Hydroelectric dams are intentionally variable; they can generate less during off-peak and quickly respond to peak demands, consequently hydroelectricity may function as load following or a peaking plant and with sufficient water, a base-load plant. Natural gas turbines or pumped storage are often used where there is not enough hydroelectricity to respond to daily and weekly variations in generation and consumption. It is not unusual for a dam to be built with more capacity than can be sustained by the water supply, allowing for a higher peak output. Upgrading equipment at existing dams can be one of the least expensive ways of increasing peak generation. The ability to vary the amount of electricity generated is often limited by the requirement that minimum or maximum flows downstream are satisfied.
Pumped-storage hydroelectricity
Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH), or pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES), is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by electric power systems for load balancing. The method stores energy in the form of gravitational potential ...
is the largest-capacity form of grid energy storage available, used for averaging off-peak and peak electrical demands. The site stores energy using the gravitational potential of water stored in a reservoir. Low-cost off-peak electric power from base load or intermittent sources is used to pump water at a low elevation to storage in a high elevation reservoir. During periods of high electrical demand, the stored water is released through turbines to produce electric power. Start up times are only a few minutes, and some can start in a few tens of seconds.
Batteries
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
are used in some cases where conditions favor it to smooth flow (avoiding a costly power line upgrade) as well as supplying peak power and other grid services Ancillary services are the services necessary to support the transmission of electric power from generators to consumers given the obligations of control areas and transmission utilities within those control areas to maintain reliable operations of ...
such as operating reserve
In electricity networks, the operating reserve is the generating capacity available to the system operator within a short interval of time to meet demand in case a generator goes down or there is another disruption to the supply. Most power sys ...
, sometimes in hybrid configuration with turbines or diesel engines. Battery power is by far the fastest responding of all powerplants, and can respond to grid conditions at millisecond timescales, giving slower responding equipment a chance to react to outages.
Pumped-storage and batteries are net consumers, as they have no inherent energy source, and the conversion between electricity and storage and back incurs some losses.
Solar thermal peaker plants were proposed in 2017, under a US Department of Energy Technology 2 Market award to Hank Price of SolarDynamics, whose paper "Dispatchable Solar Power Plant" proposed utilizing the thermal energy storage inherent in a solar thermal energy power plant, that enables this heat-based form of solar to generate like a gas peaker, to supply power on demand day or night, and in return be controlled by the utility and paid in capacity payments to be available when needed, like a traditional peaker plant. A solar thermal power plant makes electricity in a steam cycle power plant like a traditional power plant but the heat for steam is supplied by solar energy heating a material such as molten salts and storing the heat until needed to make steam for power generation.
Base load power plants
An economical electrical supply system will also include base load power plants. These generating units will emphasize low incremental fuel cost, but may use a higher capital investment to improve efficiency. For example, a peaking plant might use only a gas turbine, while a base load plant might also add a steam "bottom cycle" to improve the overall plant fuel consumption per unit of electricity produced. Nuclear and coal burning plants generally operate continuously, stopping only for maintenance or unexpected outages. The low incremental fuel cost of nuclear power plants compared with high capital cost makes it most economic for them to be used for base load supply. Hydroelectric plants with few restrictions on water supply may be used for base load as their incremental fuel cost is zero. Since a steam cycle power plant may take hours to go from cold standby to full rating, they are not usually used to provide peak load service.Donald G. Fink, H. Wayne Beaty, ''Standard Handbook for Electrical Engineers, Eleventh Edition'', McGraw Hill, 1978, , "Generating Capacity Mix" page 12–18 Intermediate load following power plants such as hydroelectric operate between these extremes, curtailing their output on nights and weekends when demand is low. Base load and intermediate plants are used preferentially to meet electrical demand because the lower efficiencies of peaker plants make them more expensive to operate.See also
*Geothermal power
Geothermal power is electrical power generated from geothermal energy. Technologies in use include dry steam power stations, flash steam power stations and binary cycle power stations. Geothermal electricity generation is currently used in 2 ...
* List of energy storage projects
This is a list of energy storage power plants worldwide, other than pumped hydro storage.
Many individual energy storage plants augment electrical grids by capturing excess electrical energy during periods of low demand and storing it in oth ...
* Smart grid
A smart grid is an electrical grid which includes a variety of operation and energy measures including:
*Advanced metering infrastructure (of which smart meters are a generic name for any utility side device even if it is more capable e.g. a f ...
* Vehicle-to-grid
* Turbine inlet air cooling
* Load following power plant
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Peaking Power Plant Power station technology