Particle Collection In Wet Scrubbers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Particle collection in wet scrubbers capture relatively small
For example, particles produced by mechanical means (crushing or grinding) tend to be large (above 10 micrometres); whereas, particles produced from combustion or a chemical reaction will have a substantial portion of small (less than 5 micrometres) and submicrometre particles. The most critical sized particles are those in the 0.1 to 0.5 micrometres range because they are the most difficult for wet scrubbers to collect.
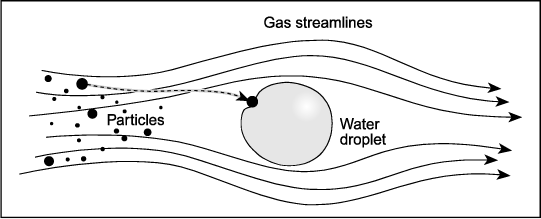 In a wet scrubbing system, dust particles will tend to follow the streamlines of the exhaust stream. However, when liquid droplets are introduced into the exhaust stream, particles cannot always follow these streamlines as they diverge around the droplet (Figure 1). The particle's mass causes it to break away from the streamlines and impact or hit the droplet.
Impaction increases as the diameter of the particle increases and as the relative velocity between the particle and droplets increases. As particles get larger they are less likely to follow the gas streamlines around droplets. Also, as particles move faster relative to the
liquid droplet, there is a greater chance that the particle will hit a droplet. Impaction is the predominant collection mechanism for scrubbers having gas stream velocities greater than 0.3 m/s (1 ft/s) (''Perry 1973'').
Most scrubbers operate with gas stream velocities well above 0.3 m/s. Therefore, at these velocities, particles having diameters greater than 1.0 µm are collected by this mechanism.
Impaction also increases as the size of the liquid droplet decreases because the presence of more droplets within the vessel increases the probability that particles will impact on the droplets.
In a wet scrubbing system, dust particles will tend to follow the streamlines of the exhaust stream. However, when liquid droplets are introduced into the exhaust stream, particles cannot always follow these streamlines as they diverge around the droplet (Figure 1). The particle's mass causes it to break away from the streamlines and impact or hit the droplet.
Impaction increases as the diameter of the particle increases and as the relative velocity between the particle and droplets increases. As particles get larger they are less likely to follow the gas streamlines around droplets. Also, as particles move faster relative to the
liquid droplet, there is a greater chance that the particle will hit a droplet. Impaction is the predominant collection mechanism for scrubbers having gas stream velocities greater than 0.3 m/s (1 ft/s) (''Perry 1973'').
Most scrubbers operate with gas stream velocities well above 0.3 m/s. Therefore, at these velocities, particles having diameters greater than 1.0 µm are collected by this mechanism.
Impaction also increases as the size of the liquid droplet decreases because the presence of more droplets within the vessel increases the probability that particles will impact on the droplets.
US EPA Air Pollution Training Institute
developed in collaboration with North Carolina State University, College of Engineering (NCSU)
The Encyclopedia Of Filters - Dust Collection
An overview of the science of dust collection systems, including Wet Scrubbers. Air pollution control systems Wet scrubbers
dust
Dust is made of fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in ho ...
particle
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass.
They vary greatly in size or quantity, from ...
s with the wet scrubber
The term wet scrubber describes a variety of devices that remove pollutants from a furnace flue gas or from other gas streams. In a wet scrubber, the polluted gas stream is brought into contact with the scrubbing liquid, by spraying it with the ...
's large liquid droplets. In most wet scrubbing systems, droplets produced are generally larger than 50 micrometres (in the 150 to 500 micrometres range). As a point of reference, human hair ranges in diameter from 50 to 100 micrometres. The size distribution of particles to be collected is source specific.For example, particles produced by mechanical means (crushing or grinding) tend to be large (above 10 micrometres); whereas, particles produced from combustion or a chemical reaction will have a substantial portion of small (less than 5 micrometres) and submicrometre particles. The most critical sized particles are those in the 0.1 to 0.5 micrometres range because they are the most difficult for wet scrubbers to collect.
Droplet production
Droplets are produced by several methods: #Injecting liquid at high pressure through specially designed nozzles #Aspirating the particle-laden gas stream through a liquid pool #Submerging a whirlingrotor
Rotor may refer to:
Science and technology
Engineering
* Rotor (electric), the non-stationary part of an alternator or electric motor, operating with a stationary element so called the stator
*Helicopter rotor, the rotary wing(s) of a rotorcraft ...
in a liquid pool.
These droplets collect particles by using one or more of several collection mechanisms such as impaction, direct interception, diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemica ...
, electrostatic attraction
Coulomb's inverse-square law, or simply Coulomb's law, is an experimental law of physics that quantifies the amount of force between two stationary, electrically charged particles. The electric force between charged bodies at rest is convention ...
, condensation, centrifugal force
In Newtonian mechanics, the centrifugal force is an inertial force (also called a "fictitious" or "pseudo" force) that appears to act on all objects when viewed in a rotating frame of reference. It is directed away from an axis which is parall ...
and gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stro ...
. However, impaction and diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemica ...
are the main ones.
Impaction
 In a wet scrubbing system, dust particles will tend to follow the streamlines of the exhaust stream. However, when liquid droplets are introduced into the exhaust stream, particles cannot always follow these streamlines as they diverge around the droplet (Figure 1). The particle's mass causes it to break away from the streamlines and impact or hit the droplet.
Impaction increases as the diameter of the particle increases and as the relative velocity between the particle and droplets increases. As particles get larger they are less likely to follow the gas streamlines around droplets. Also, as particles move faster relative to the
liquid droplet, there is a greater chance that the particle will hit a droplet. Impaction is the predominant collection mechanism for scrubbers having gas stream velocities greater than 0.3 m/s (1 ft/s) (''Perry 1973'').
Most scrubbers operate with gas stream velocities well above 0.3 m/s. Therefore, at these velocities, particles having diameters greater than 1.0 µm are collected by this mechanism.
Impaction also increases as the size of the liquid droplet decreases because the presence of more droplets within the vessel increases the probability that particles will impact on the droplets.
In a wet scrubbing system, dust particles will tend to follow the streamlines of the exhaust stream. However, when liquid droplets are introduced into the exhaust stream, particles cannot always follow these streamlines as they diverge around the droplet (Figure 1). The particle's mass causes it to break away from the streamlines and impact or hit the droplet.
Impaction increases as the diameter of the particle increases and as the relative velocity between the particle and droplets increases. As particles get larger they are less likely to follow the gas streamlines around droplets. Also, as particles move faster relative to the
liquid droplet, there is a greater chance that the particle will hit a droplet. Impaction is the predominant collection mechanism for scrubbers having gas stream velocities greater than 0.3 m/s (1 ft/s) (''Perry 1973'').
Most scrubbers operate with gas stream velocities well above 0.3 m/s. Therefore, at these velocities, particles having diameters greater than 1.0 µm are collected by this mechanism.
Impaction also increases as the size of the liquid droplet decreases because the presence of more droplets within the vessel increases the probability that particles will impact on the droplets.
Diffusion
Very small particles (less than 0.1 µm in diameter) experiencerandom movement
Random Movement is the stage name of DJ and drum and bass musician Michael Richards. As a recording artist, he has many releases on Innerground Records, Fokuz Recordings, V Recordings, and his own label, Flight Pattern.
Biography
In 2003, Ri ...
in an exhaust stream. These particles are so tiny that they are bumped by gas molecules as they move in the exhaust stream. This bumping, or bombardment, causes them to first move one way and then another in a random manner, or to diffuse
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
, through the gas. This irregular motion can cause the particles to collide with a droplet and be collected (Figure 2). Because of this, diffusion is the primary collection mechanism in wet scrubbers for particles smaller than 0.1 µm.
The rate of diffusion depends on the following:
#The relative velocity between the particle and droplet
#The particle diameter
#The liquid-droplet diameter.
For both impaction and diffusion, collection efficiency increases with an increase in relative velocity (liquid- or gas-pressure input) and a decrease in liquid-droplet size.
However, collection by diffusion increases as particle size decreases. This mechanism enables certain scrubbers to effectively remove the very tiny particles (less than 0.1 µm).
In the particle size range of approximately 0.1 to 1.0 µm, neither of these two collection mechanisms (impaction or diffusion) dominates. This relationship is illustrated in Figure 3.
Other collection mechanisms
In recent years, some scrubber manufacturers have utilized other collection mechanisms such aselectrostatic attraction
Coulomb's inverse-square law, or simply Coulomb's law, is an experimental law of physics that quantifies the amount of force between two stationary, electrically charged particles. The electric force between charged bodies at rest is convention ...
and condensation to enhance particle collection without increasing power consumption.
In electrostatic attraction
Coulomb's inverse-square law, or simply Coulomb's law, is an experimental law of physics that quantifies the amount of force between two stationary, electrically charged particles. The electric force between charged bodies at rest is convention ...
, particles are captured by first inducing a charge on them. Then, the charged particles are either attracted to each other, forming larger, easier-to-collect particles, or they are collected on a surface.
Condensation of water vapor on particles promotes collection by adding mass to the particles. Other mechanisms such as gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stro ...
, centrifugal force
In Newtonian mechanics, the centrifugal force is an inertial force (also called a "fictitious" or "pseudo" force) that appears to act on all objects when viewed in a rotating frame of reference. It is directed away from an axis which is parall ...
, and direct interception slightly affect particle collection. developed in collaboration with North Carolina State University, College of Engineering (NCSU)
Bibliography
*Bethea, R. M. 1978. Air Pollution Control Technology. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold. *National Asphalt Pavement Association. 1978. The Maintenance and Operation of Exhaust Systems in the Hot Mix Batch Plant. 2nd ed. Information Series 52. *Perry, J. H. (Ed.). 1973. Chemical Engineers’ Handbook. 5th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill. *Richards, J. R. 1995. Control of Particulate Emissions (APTI Course 413). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. *Richards, J. R. 1995. Control of Gaseous Emissions. (APTI Course 415). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. *Schifftner, K. C. 1979, April. Venturi scrubber operation and maintenance. Paper presented at the U.S. EPA Environmental Research Information Center. Atlanta, GA. *Semrau, K. T. 1977. Practical process design of particulate scrubbers. Chemical Engineering. 84:87-91. *U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 1982, September. Control Techniques for Particulate Emissions from Stationary Sources. Vol. 1. EPA 450/3-81-005a. *Wechselblatt, P. M. 1975. Wet scrubbers (particulates). In F. L. Cross and H. E. Hesketh (Eds.), Handbook for the Operation and Maintenance of Air Pollution Control Equipment. Westport: Technomic Publishing.References
External links
The Encyclopedia Of Filters - Dust Collection
An overview of the science of dust collection systems, including Wet Scrubbers. Air pollution control systems Wet scrubbers