Parliament Of The United Kingdom on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme
 The
The
 Upon the signal of the Monarch, the
Upon the signal of the Monarch, the
 Laws can be made by Acts of the United Kingdom Parliament. While Acts can apply to the whole of the United Kingdom including Scotland, due to the continuing separation of
Laws can be made by Acts of the United Kingdom Parliament. While Acts can apply to the whole of the United Kingdom including Scotland, due to the continuing separation of
 Prior to the creation of the
Prior to the creation of the
 In the United Kingdom, question time in the House of Commons lasts for an hour each day from Monday to Thursday (2:30 to 3:30 pm on Mondays, 11:30 am to 12:30 pm on Tuesdays and Wednesdays, and 9:30 to 10:30 am on Thursdays). Each Government department has its place in a rota which repeats every five weeks. The exception to this sequence are the Business Questions (Questions to the
In the United Kingdom, question time in the House of Commons lasts for an hour each day from Monday to Thursday (2:30 to 3:30 pm on Mondays, 11:30 am to 12:30 pm on Tuesdays and Wednesdays, and 9:30 to 10:30 am on Thursdays). Each Government department has its place in a rota which repeats every five weeks. The exception to this sequence are the Business Questions (Questions to the
 Several different views have been taken of Parliament's sovereignty. According to the jurist
Several different views have been taken of Parliament's sovereignty. According to the jurist
www.parliamentlive.tv
which maintains an archive dating back to 4 December 2007. There is also a related official
Public Policy Hub ŌĆō Parliament and law making
''Hansard'' from 1803 to 2005
Parliament Live TV
"AŌĆōZ of Parliament"
ĆöThe British Broadcasting Corporation (2005).
Topic: Politics
Ćö''The Guardian''
Topic: House of Lords
Ćö''The Guardian''
at Leeds University
British House of Commons people
(
legislative body
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known as p ...
of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs), also known as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are fourteen dependent territory, territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom. They are the last remna ...
. It meets at the Palace of Westminster
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Informally known as the Houses of Parli ...
, London. It alone possesses legislative supremacy and thereby ultimate power over all other political bodies in the UK and the overseas territories. Parliament is bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature, one divided into two separate assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate and vote as a single grou ...
but has three parts, consisting of the sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
(King-in-Parliament
The King-in-Parliament (or, during the reign of a female monarch, Queen-in-Parliament), sometimes referred neutrally as the Crown-in-Parliament, is a technical term of constitutional law in the Commonwealth realms that refers to the Crown in its ...
), the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the Bicameralism, upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by Life peer, appointment, Hereditary peer, heredity or Lords Spiritual, official function. Like the ...
, and the House of Commons (the primary chamber). In theory, power is officially vested in the King-in-Parliament
The King-in-Parliament (or, during the reign of a female monarch, Queen-in-Parliament), sometimes referred neutrally as the Crown-in-Parliament, is a technical term of constitutional law in the Commonwealth realms that refers to the Crown in its ...
. However, the Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has different ...
normally acts on the advice of the prime minister, and the powers of the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the Bicameralism, upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by Life peer, appointment, Hereditary peer, heredity or Lords Spiritual, official function. Like the ...
are limited to only delaying legislation; thus power is ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' vested in the House of Commons.
The House of Commons is an elected chamber with elections
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operate ...
to 650 single-member constituencies held at least every five years under the first-past-the-post system
In a first-past-the-post electoral system (FPTP or FPP), formally called single-member plurality voting (SMP) when used in single-member districts or informally choose-one voting in contrast to ranked voting, or score voting, voters cast their ...
. By constitutional convention Constitutional convention may refer to:
* Constitutional convention (political custom), an informal and uncodified procedural agreement
*Constitutional convention (political meeting), a meeting of delegates to adopt a new constitution or revise an e ...
, all government ministers
A minister is a politician who heads a ministry, making and implementing decisions on policies in conjunction with the other ministers. In some jurisdictions the head of government is also a minister and is designated the ŌĆśprime ministerŌĆÖ, Ō ...
, including prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
, are members of the House of Commons or, less commonly, the House of Lords and are thereby accountable to the respective branches of the legislature
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its p ...
. Most cabinet ministers
A cabinet is a body of high-ranking state officials, typically consisting of the executive branch's top leaders. Members of a cabinet are usually called cabinet ministers or secretaries. The function of a cabinet varies: in some countries ...
are from the Commons, whilst junior ministers can be from either house.
The House of Lords is the second chamber of Parliament. The House of Lords includes two different types of members. The most numerous are the Lords Temporal
The Lords Temporal are secular members of the House of Lords, the upper house of the British Parliament. These can be either life peers or hereditary peers, although the hereditary right to sit in the House of Lords was abolished for all but n ...
, consisting mainly of life peers
In the United Kingdom, life peers are appointed members of the Peerages in the United Kingdom, peerage whose titles cannot be inherited, in contrast to hereditary peers. In modern times, life peerages, always created at the rank of baron, are cr ...
appointed by the sovereign on the advice of the prime minister, and of 92 hereditary peer
The hereditary peers form part of the peerage in the United Kingdom. As of September 2022, there are 807 hereditary peers: 29 dukes (including five royal dukes), 34 marquesses, 190 earls, 111 viscounts, and 443 barons (disregarding subsid ...
s. The less numerous Lords Spiritual
The Lords Spiritual are the bishops of the Church of England who serve in the House of Lords of the United Kingdom. 26 out of the 42 diocesan bishops and archbishops of the Church of England serve as Lords Spiritual (not counting retired archbi ...
consist of the most senior bishops of the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britain ...
. Prior to the opening of the Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
in October 2009, the House of Lords also performed a judicial role through the Law Lords
Lords of Appeal in Ordinary, commonly known as Law Lords, were judges appointed under the Appellate Jurisdiction Act 1876 to the British House of Lords, as a committee of the House, effectively to exercise the judicial functions of the House of ...
.
With the global expansion of the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
, the UK Parliament has shaped the political systems of many countries as ex-colonies and so it has been called the "Mother of Parliaments
"The mother of parliaments" is a phrase coined by the British politician and reformer John Bright in a speech at Birmingham on 18 January 1865.
It was a reference to England. His actual words were: "England is the mother of parliaments". This ...
".
History
TheParliament of Great Britain
The Parliament of Great Britain was formed in May 1707 following the ratification of the Acts of Union by both the Parliament of England and the Parliament of Scotland. The Acts ratified the treaty of Union which created a new unified Kingdo ...
was formed in 1707 following the ratification of the Treaty of Union by Acts of Union passed by the Parliament of England
The Parliament of England was the legislature of the Kingdom of England from the 13th century until 1707 when it was replaced by the Parliament of Great Britain. Parliament evolved from the great council of bishops and peers that advised t ...
(established 1215) and the Parliament of Scotland
The Parliament of Scotland ( sco, Pairlament o Scotland; gd, P├Ārlamaid na h-Alba) was the legislature of the Kingdom of Scotland from the 13th century until 1707. The parliament evolved during the early 13th century from the king's council o ...
(c.1235), both Acts of Union stating, "That the United Kingdom of Great Britain be represented by one and the same Parliament to be styled The Parliament of Great Britain." At the start of the 19th century, Parliament was further enlarged by Acts of Union ratified by the Parliament of Great Britain and the Parliament of Ireland
The Parliament of Ireland ( ga, Parlaimint na h├ēireann) was the legislature of the Lordship of Ireland, and later the Kingdom of Ireland, from 1297 until 1800. It was modelled on the Parliament of England and from 1537 comprised two chamb ...
that abolished the latter and added 100 Irish MPs and 32 Lords to the former to create the Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The Royal and Parliamentary Titles Act 1927 formally amended the name to the "Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland", five years after the secession of the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorst├Īt ├ēireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between th ...
.
Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
 The
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was a sovereign state in the British Isles that existed between 1801 and 1922, when it included all of Ireland. It was established by the Acts of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Great B ...
was created on 1 January 1801, by the merger of the Kingdoms of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
and Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, ├ēire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
under the Acts of Union 1800. The principle of ministerial responsibility to the lower house
A lower house is one of two Debate chamber, chambers of a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house. Despite its official position "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide, the lower house has co ...
(Commons) did not develop until the 19th centuryŌĆöthe House of Lords was superior to the House of Commons both in theory and in practice. Members of the House of Commons (MPs) were elected in an antiquated electoral system
An electoral system or voting system is a set of rules that determine how elections and Referendum, referendums are conducted and how their results are determined. Electoral systems are used in politics to elect governments, while non-political ...
, under which constituencies of vastly different sizes existed. Thus, the borough of Old Sarum, with seven voters, could elect two members, as could the borough of Dunwich, which had almost completely disappeared into the sea due to land erosion.
Many small constituencies, known as pocket or rotten boroughs, were controlled by members of the House of Lords, who could ensure the election
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has opera ...
of their relatives or supporters. During the reforms of the 19th century, beginning with the Reform Act 1832
The Representation of the People Act 1832 (also known as the 1832 Reform Act, Great Reform Act or First Reform Act) was an Act of Parliament, Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom (indexed as 2 & 3 Will. IV c. 45) that introduced major chan ...
, the electoral system for the House of Commons was progressively regularised. No longer dependent on the Lords for their seats, MPs grew more assertive.
The supremacy of the British House of Commons was reaffirmed in the early 20th century. In 1909, the Commons passed the so-called "People's Budget
The 1909/1910 People's Budget was a proposal of the Liberal government that introduced unprecedented taxes on the lands and incomes of Britain's wealthy to fund new social welfare programmes. It passed the House of Commons in 1909 but was bloc ...
," which made numerous changes to the taxation system which were detrimental to wealthy landowners. The House of Lords, which consisted mostly of powerful landowners, rejected the Budget. On the basis of the Budget's popularity and the Lords' consequent unpopularity, the Liberal Party narrowly won two general elections in 1910.
Using the result as a mandate, the Liberal Prime Minister, H. H. Asquith
Herbert Henry Asquith, 1st Earl of Oxford and Asquith, (12 September 1852 ŌĆō 15 February 1928), generally known as H. H. Asquith, was a British statesman and Liberal Party politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom f ...
, introduced the Parliament Bill, which sought to restrict the powers of the House of Lords. (He did not reintroduce the land tax provision of the People's Budget.) When the Lords refused to pass the bill, Asquith countered with a promise extracted from the King in secret before the second general election of 1910 and requested the creation of several hundred Liberal peers, so as to erase the Conservative majority in the House of Lords. In the face of such a threat, the House of Lords narrowly passed the bill.
The Parliament Act 1911
The Parliament Act 1911 (1 & 2 Geo. 5 c. 13) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It is constitutionally important and partly governs the relationship between the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two Houses of Parlia ...
, as it became, prevented the Lords from blocking a money bill (a bill dealing with taxation), and allowed them to delay any other bill for a maximum of three sessions (reduced to two sessions in 1949), after which it could become law over their objections. However, regardless of the Parliament Acts of 1911 and 1949, the House of Lords has always retained the unrestricted power to veto any bill outright which attempts to extend the life of a parliament.
Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
The result of the 1918 general election in Ireland showed a landslide victory for theIrish republican
Irish republicanism ( ga, poblacht├Īnachas ├ēireannach) is the political movement for the unity and independence of Ireland under a republic. Irish republicans view British rule in any part of Ireland as inherently illegitimate.
The develop ...
party Sinn F├®in
Sinn F├®in ( , ; en, " eOurselves") is an Irish republican and democratic socialist political party active throughout both the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland.
The original Sinn F├®in organisation was founded in 1905 by Arthur Gri ...
, who vowed in their manifesto
A manifesto is a published declaration of the intentions, motives, or views of the issuer, be it an individual, group, political party or government. A manifesto usually accepts a previously published opinion or public consensus or promotes a ...
to establish an independent Irish Republic. Accordingly, Sinn F├®in MPs, though ostensively elected to sit in the House of Commons, refused to take their seats in Westminster, and instead assembled in 1919 to proclaim Irish independence and form a revolutionary unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature, which consists of one house or assembly, that legislates and votes as one.
Unicameral legislatures exist when there is no widely perceived need for multic ...
parliament for the independent Irish Republic, called D├Īil ├ēireann
D├Īil ├ēireann ( , ; ) is the lower house, and principal chamber, of the Oireachtas (Irish legislature), which also includes the President of Ireland and Seanad ├ēireann (the upper house).Article 15.1.2┬║ of the Constitution of Ireland read ...
.
In 1920, in parallel to the D├Īil, the Government of Ireland Act 1920 created home rule
Home rule is government of a colony, dependent country, or region by its own citizens. It is thus the power of a part (administrative division) of a state or an external dependent country to exercise such of the state's powers of governance wit ...
parliaments of Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart ├ēireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
and Southern Ireland
Southern Ireland, South Ireland or South of Ireland may refer to:
*The southern part of the island of Ireland
*Southern Ireland (1921ŌĆō1922), a former constituent part of the United Kingdom
*Republic of Ireland, which is sometimes referred to as ...
and reduced the representation of both parts at Westminster. The number of Northern Ireland seats was increased again after the introduction of direct rule Direct rule is when an imperial or central power takes direct control over the legislature, executive and civil administration of an otherwise largely self-governing territory.
Examples Chechnya
In 1991, Chechen separatists declared independence o ...
in 1973.
The Irish republicans responded by declaring the elections to these home rule Parliaments, held on the same day in 1921, to be the basis of membership for a new D├Īil ├ēireann. While the elections in Northern Ireland were both contested and won by Unionist parties, in Southern Ireland, all 128 candidates for the Southern Irish seats were returned unopposed. Of these, 124 were won by Sinn F├®in and four by independent Unionists representing Dublin University
The University of Dublin ( ga, Ollscoil Átha Cliath), corporately designated the Chancellor, Doctors and Masters of the University of Dublin, is a university located in Dublin, Ireland. It is the degree-awarding body for Trinity College Dubl ...
(Trinity College). Since only four MPs sat in the home rule Southern Irish parliament, with the remaining 124 being in the Republic's Second D├Īil
The Second D├Īil () was D├Īil ├ēireann as it convened from 16 August 1921 until 8 June 1922. From 1919 to 1922, D├Īil ├ēireann was the revolutionary parliament of the self-proclaimed Irish Republic. The Second D├Īil consisted of members elected ...
, the home rule parliament was adjourned ''sine die
In mathematics, sine and cosine are trigonometric functions of an angle. The sine and cosine of an acute angle are defined in the context of a right triangle: for the specified angle, its sine is the ratio of the length of the side that is oppo ...
'' without ever having operated.
In 1922, pursuant to the Anglo-Irish Treaty
The 1921 Anglo-Irish Treaty ( ga , An Conradh Angla-├ēireannach), commonly known in Ireland as The Treaty and officially the Articles of Agreement for a Treaty Between Great Britain and Ireland, was an agreement between the government of the ...
, the revolutionary Irish Republic was replaced by the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorst├Īt ├ēireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between th ...
, recognised by Westminster as independent, while Northern Ireland would remain British, and in 1927 parliament was renamed the Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Further reforms to the House of Lords were made in the 20th century. The Life Peerages Act 1958
The Life Peerages Act 1958 established the modern standards for the creation of life peers by the Sovereign of the United Kingdom.
Background
This Act was made during the Conservative governments of 1957ŌĆō1964, when Harold Macmillan was Prime M ...
authorised the regular creation of life peerage dignities. By the 1960s, the regular creation of hereditary peerage dignities had ceased; thereafter, almost all new peers were life peers only.
The House of Lords Act 1999 removed the automatic right of hereditary peers to sit in the House of Lords, although it made an exception for 92 of them to be elected to life-terms by the other hereditary peers, with by-elections upon their death. The House of Lords is now a chamber that is subordinate to the House of Commons. Additionally, the Constitutional Reform Act 2005 led to abolition of the judicial functions of the House of Lords
Whilst the House of Lords of the United Kingdom is the upper chamber of Parliament and has government ministers, it for many centuries had a judicial function. It functioned as a court of first instance for the trials of peers, for impeachments, ...
with the creation of the new Supreme Court of the United Kingdom
The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom (initialism: UKSC or the acronym: SCOTUK) is the final court of appeal in the United Kingdom for all civil cases, and for criminal cases originating in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. As the Unite ...
in October 2009.
Composition and powers
The legislative authority, theKing-in-Parliament
The King-in-Parliament (or, during the reign of a female monarch, Queen-in-Parliament), sometimes referred neutrally as the Crown-in-Parliament, is a technical term of constitutional law in the Commonwealth realms that refers to the Crown in its ...
, has three separate elements: the Monarch, the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the Bicameralism, upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by Life peer, appointment, Hereditary peer, heredity or Lords Spiritual, official function. Like the ...
, and the House of Commons. No individual may be a member of both Houses, and members of the House of Lords are legally barred from voting in elections for members of the House of Commons. Formerly, no-one could be a Member of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members of ...
(MP) while holding an office of profit under the Crown, thus maintaining the separation of powers
Separation of powers refers to the division of a state's government into branches, each with separate, independent powers and responsibilities, so that the powers of one branch are not in conflict with those of the other branches. The typic ...
, but the principle has been gradually eroded. Until 1919, Members of Parliament who were appointed to ministerial office lost their seats in the House of Commons and had to seek re-election; the rule was abolished in 1926. Holders of offices are ineligible to serve as a Member of Parliament under the House of Commons Disqualification Act 1975
The House of Commons Disqualification Act 1975 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that prohibits certain categories of people from becoming members of the House of Commons. It is an updated version of similar older acts, known col ...
.
Royal Assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in other ...
of the Monarch is required for all Bills to become law, and certain delegated legislation must be made by the Monarch by Order in Council. The Crown also has executive powers which do not depend on Parliament, through prerogative powers
The royal prerogative is a body of customary authority, privilege and immunity, recognized in common law and, sometimes, in civil law jurisdictions possessing a monarchy, as belonging to the sovereign and which have become widely vested in the ...
, including the power to make treaties, declare war, award honours, and appoint officers and civil servants. In practice these are always exercised by the monarch on the advice of the Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
and the other ministers of HM Government
ga, Rialtas a Shoilse gd, Riaghaltas a Mh├▓rachd
, image = HM Government logo.svg
, image_size = 220px
, image2 = Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (HM Government).svg
, image_size2 = 180px
, caption = Royal coat of arms of t ...
. The Prime Minister and government are directly accountable to Parliament, through its control of public finances, and to the public, through the election of members of parliament.
The Monarch also appoints the Prime Minister, who then forms a government from members of the Houses of Parliament. This must be someone who could command a majority in a confidence vote in the House of Commons. In the past the monarch has occasionally had to make a judgement, as in the appointment of Alec Douglas-Home
Alexander Frederick Douglas-Home, Baron Home of the Hirsel (; 2 July 1903 ŌĆō 9 October 1995), styled as Lord Dunglass between 1918 and 1951 and being The 14th Earl of Home from 1951 till 1963, was a British Conservative politician who se ...
in 1963 when it was thought that the incumbent Prime Minister, Harold Macmillan
Maurice Harold Macmillan, 1st Earl of Stockton, (10 February 1894 ŌĆō 29 December 1986) was a British Conservative statesman and politician who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1957 to 1963. Caricatured as "Supermac", he ...
, had become ill with terminal cancer. However, today the outgoing Prime Minister advises the monarch who should be offered the position.
The House of Lords is known formally as "The Right Honourable The Lords Spiritual and Temporal in Parliament Assembled", the Lords Spiritual being bishops of the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britain ...
and the Lords Temporal being Peers of the Realm
A peer of the realm is a member of the highest aristocratic social order outside the ruling dynasty of the kingdom.
Notable examples are:
* a member of the peerages in the United Kingdom, who is a hereditary peer or a life peer
* a member of the ...
. The Lords Spiritual and Lords Temporal are considered separate " estates", but they sit, debate and vote together.
Since the Parliament Acts 1911 and 1949
The Parliament Acts 1911 and 1949 are two Act of Parliament, Acts of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, which form part of the constitution of the United Kingdom. Section 2(2) of the Parliament Act 1949 provides that the two Acts are to be St ...
, the powers of the House of Lords have been very much less than those of the House of Commons. All bills except money bills
In the Westminster system (and, colloquially, in the United States), a money bill or supply bill is a bill that solely concerns taxation or government spending (also known as appropriation of money), as opposed to changes in public law.
Conv ...
are debated and voted upon in the House of Lords; however, by voting against a bill, the House of Lords can only delay it for a maximum of two parliamentary sessions over a year. After that time, the House of Commons can force the Bill through without the Lords' consent, under the Parliament Acts. The House of Lords can also hold the government to account through questions to government ministers and the operation of a small number of select committees. The highest court in England & Wales and in Northern Ireland used to be a committee of the House of Lords, but it became an independent supreme court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
in 2009.
The Lords Spiritual formerly included all of the senior clergymen of the Church of EnglandŌĆöarchbishops, bishops, abbots and mitred priors. Upon the Dissolution of the Monasteries under Henry VIII the abbots and mitred priors lost their positions in Parliament. All diocesan bishops continued to sit in Parliament, but the Bishopric of Manchester Act 1847
The Ecclesiastical Commissioners Act 1847 (10 & 11 Vict c 108), sometimes called the Bishopric of Manchester Act 1847, is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom with the principal purpose of delegating to the Ecclesiastical Commissioners ...
, and later Acts, provide that only the 26 most senior are Lords Spiritual. These always include the incumbents of the "five great sees", namely the Archbishop of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Canterbury. The current archbishop is Justi ...
, the Archbishop of York
The archbishop of York is a senior bishop in the Church of England, second only to the archbishop of Canterbury. The archbishop is the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of York and the metropolitan bishop of the province of York, which covers th ...
, the Bishop of London
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
, the Bishop of Durham
The Bishop of Durham is the Anglican bishop responsible for the Diocese of Durham in the Province of York. The diocese is one of the oldest in England and its bishop is a member of the House of Lords. Paul Butler has been the Bishop of Durham ...
and the Bishop of Winchester
The Bishop of Winchester is the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Winchester in the Church of England. The bishop's seat (''cathedra'') is at Winchester Cathedral in Hampshire. The Bishop of Winchester has always held ''ex officio'' (except dur ...
. The remaining 21 Lords Spiritual are the most senior diocesan bishops, ranked in order of consecration
Consecration is the solemn dedication to a special purpose or service. The word ''consecration'' literally means "association with the sacred". Persons, places, or things can be consecrated, and the term is used in various ways by different grou ...
, although the Lords Spiritual (Women) Act 2015
The Lords Spiritual (Women) Act 2015 is an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom. It stipulates that whenever a vacancy arises among the Lords Spiritual during the next ten years after the Act comes into force, the position has to be filled by ...
makes time-limited provision for vacancies to be filled by women who are bishops.
The Lords Temporal are life peers created under the Appellate Jurisdiction Act 1876 and the Life Peerages Act 1958
The Life Peerages Act 1958 established the modern standards for the creation of life peers by the Sovereign of the United Kingdom.
Background
This Act was made during the Conservative governments of 1957ŌĆō1964, when Harold Macmillan was Prime M ...
, in addition to 92 hereditary peers under the House of Lords Act 1999. Formerly, the Lords Temporal were exclusively hereditary peers. The right of some hereditary peers to sit in Parliament was not automatic: after Scotland and England united into Great Britain in 1707, it was provided that all peers whose dignities had been created by English kings could sit in Parliament, but those whose dignities had been created by Scottish kings were to elect a limited number of " representative peers." A similar arrangement was made in respect of Ireland when it was united with Great Britain in 1801, but when southern Ireland left the United Kingdom in 1922 the election of Irish representative peers ceased. By the Peerage Act 1963
The Peerage Act 1963 (c. 48) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that permits women peeresses and all Scottish hereditary peers to sit in the House of Lords and allows newly inherited hereditary peerages to be disclaimed.
Backgro ...
, the election of Scottish representative peers also ended, and all Scottish peers were granted the right to sit in Parliament. Under the House of Lords Act 1999, only life peerages (that is to say, peerage dignities which cannot be inherited) automatically entitle their holders to seats in the House of Lords. Of the hereditary peers, only 92ŌĆöthe Earl Marshal, the Lord Great Chamberlain
The Lord Great Chamberlain of England is the sixth of the Great Officers of State (United Kingdom), Great Officers of State, ranking beneath the Lord Privy Seal, Lord Keeper of the Privy Seal and above the Lord High Constable of England, Lord Hi ...
and the 90 elected by other peersŌĆöretain their seats in the House.
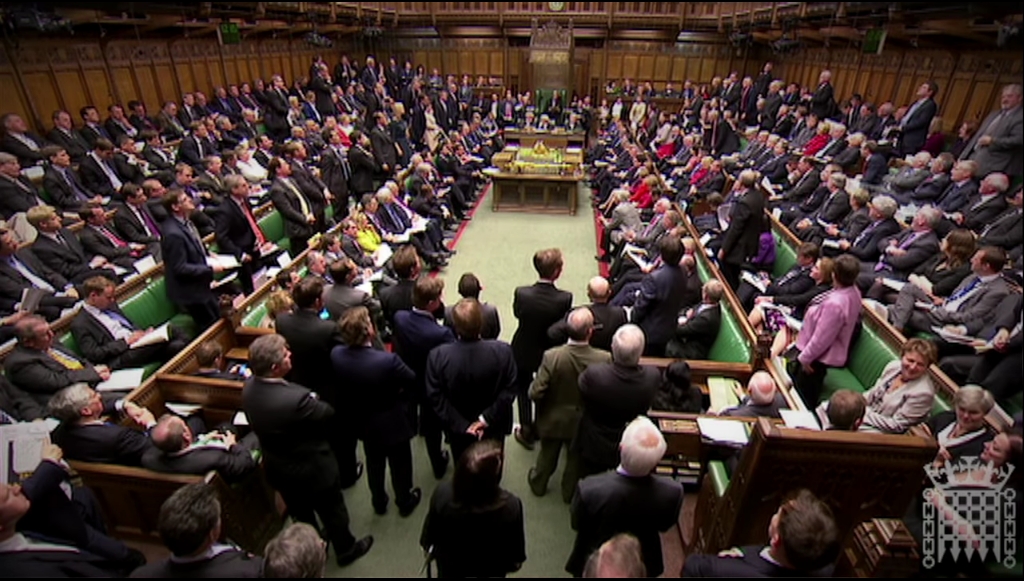
The Commons, the last of the "estates" of the Kingdom, are represented in the House of Commons, which is known formally as, "The Honourable The Commons in Parliament Assembled" ("commons" coming not from the term "commoner", but from ', the old French term for a municipality or local district). As of 2019, the House consists of 650 members, however one seat is left vacant by the Speaker of the House, who must remain politically impartial, and so does not get a vote on the passing of bills. Each Member of Parliament (MP) is chosen by a single constituency by the First-Past-the-Post
In a first-past-the-post electoral system (FPTP or FPP), formally called single-member plurality voting (SMP) when used in single-member districts or informally choose-one voting in contrast to ranked voting, or score voting, voters cast their ...
electoral system. There are 650 constituencies in the United Kingdom, each made up of an average of 65,925 voters. The First-Past-the-Post system means that every constituency elects one MP each (except the constituency of the Speaker, whose seat is uncontested). Each voter assigns one vote for one candidate, and the candidate with the most votes in each constituency is elected as MP to represent their constituency. A party needs to win 326 constituencies (known as "seats") to win a majority in the House of Commons. If no party achieves a majority, then a situation of no overall control occurs ŌĆō commonly known as a "Hung Parliament". In case of a Hung Parliament, the party with the most seats has the opportunity to form a coalition with other parties, so their combined seat tally extends past the 326-seat majority. Universal adult suffrage
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise, is the right to vote in representative democracy, public, political elections and referendums (although the term is sometimes used for any right to vote). In some languages, and occasionally i ...
exists for those 18 and over; citizens of the United Kingdom, and those of the Republic of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, ├ēire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern side of the island. A ...
and Commonwealth nations resident in the United Kingdom, are qualified to vote, unless they are in prison at the time of the election. The term of members of the House of Commons depends on the term of Parliament, a maximum of five years; a general election, during which all the seats are contested, occurs after each dissolution (see below).
All legislation must be passed by the House of Commons to become law and it controls taxation and the supply of money to the government. Government ministers (including the Prime Minister) must regularly answer questions in the House of Commons and there are a number of select committees that scrutinise particular issues and the workings of the government. There are also mechanisms that allow members of the House of Commons to bring to the attention of the government particular issues affecting their constituents.
State Opening of Parliament
The State Opening of Parliament is an annual event that marks the commencement of a session of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It is held in theHouse of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the Bicameralism, upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by Life peer, appointment, Hereditary peer, heredity or Lords Spiritual, official function. Like the ...
Chamber. Before 2012, it took place in November or December, or, in a general election year, when the new Parliament first assembled. From 2012 onwards, the ceremony has taken place in May or June.
 Upon the signal of the Monarch, the
Upon the signal of the Monarch, the Lord Great Chamberlain
The Lord Great Chamberlain of England is the sixth of the Great Officers of State (United Kingdom), Great Officers of State, ranking beneath the Lord Privy Seal, Lord Keeper of the Privy Seal and above the Lord High Constable of England, Lord Hi ...
raises their wand of office to signal to Black Rod
Black Rod (officially known as the Lady Usher of the Black Rod or, if male, the Gentleman Usher of the Black Rod) is an official in the parliaments of several Commonwealth countries. The position originates in the House of Lords of the Parliam ...
, who is charged with summoning the House of Commons and has been waiting in the Commons lobby. Black Rod turns and, under the escort of the Door-keeper of the House of Lords and an inspector of police
Inspector, also police inspector or inspector of police, is a police rank. The rank or position varies in seniority depending on the organization that uses it.
Australia
In Australian police forces, the rank of inspector is generally the ne ...
, approaches the doors to the Chamber of the Commons. In 1642, King Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742ŌĆō814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226ŌĆō1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
stormed into the House of Commons in an unsuccessful attempt to arrest the Five Members
The Five Members were Members of Parliament whom King Charles I attempted to arrest on 4 January 1642. King Charles I entered the English House of Commons, accompanied by armed soldiers, during a sitting of the Long Parliament, although the Fi ...
, who included the celebrated English patriot and leading Parliamentarian John Hampden
John Hampden (24 June 1643) was an English landowner and politician whose opposition to arbitrary taxes imposed by Charles I made him a national figure. An ally of Parliamentarian leader John Pym, and cousin to Oliver Cromwell, he was one of th ...
. This action sparked the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642ŌĆō1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of re ...
. The wars established the constitutional rights of Parliament, a concept legally established in the Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, R├©abhlaid Ghl├▓rmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and ...
in 1688 and the subsequent Bill of Rights 1689. Since then, no British monarch has entered the House of Commons when it is in session. On Black Rod's approach, the doors are slammed shut against them, symbolising the rights of parliament and its independence from the monarch. They then strike, with the end of their ceremonial staff (the Black Rod), three times on the closed doors of the Commons Chamber. They are then admitted, and announce the command of the monarch for the attendance of the Commons.
The monarch reads a speech, known as the Speech from the Throne
A speech from the throne, or throne speech, is an event in certain monarchies in which the reigning sovereign, or a representative thereof, reads a prepared speech to members of the nation's legislature when a session is opened, outlining th ...
, which is prepared by the Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
and the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
, outlining the Government's agenda for the coming year. The speech reflects the legislative agenda for which the Government intends to seek the agreement of both Houses of Parliament.
After the monarch leaves, each Chamber proceeds to the consideration of an "Address in Reply to His Majesty's Gracious Speech." But, first, each House considers a bill '' pro forma'' to symbolise their right to deliberate independently of the monarch. In the House of Lords, the bill is called the Select Vestries Bill
A bill for the better regulating of Select Vestries, usually referred to as the Select Vestries Bill, is customarily the first bill introduced and debated in the United Kingdom's House of Lords at the start of each session of Parliament. The equiva ...
, while the Commons equivalent is the Outlawries Bill
A Bill for the more effectual preventing clandestine Outlawries, usually referred to as the Outlawries Bill, is customarily the first bill on the agenda of the United Kingdom's House of Commons at the start of each session of Parliament. It is use ...
. The Bills are considered for the sake of form only, and do not make any actual progress.
Legislative procedure
:''See also the stages of a bill section inActs of Parliament in the United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom an act of Parliament is primary legislation passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom.
An act of Parliament can be enforced in all four of the UK constituent countries (England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Irelan ...
''
Both houses of the British Parliament are presided over by a speaker, the Speaker of the House
The speaker of a deliberative assembly, especially a legislative body, is its presiding officer, or the chair. The title was first used in 1377 in England.
Usage
The title was first recorded in 1377 to describe the role of Thomas de Hungerf ...
for the Commons and the Lord Speaker
The Lord Speaker is the presiding officer, chairman and highest authority of the House of Lords in the Parliament of the United Kingdom. The office is analogous to the Speaker of the House of Commons: the Lord Speaker is elected by the members ...
in the House of Lords.
For the Commons, the approval of the Sovereign is theoretically required before the election of the Speaker becomes valid, but it is, by modern convention, always granted. The Speaker's place may be taken by the Chairman of Ways and Means, the First Deputy Chairman, or the Second Deputy Chairman. (The titles of those three officials refer to the Committee of Ways and Means, a body which no longer exists.)
Prior to July 2006, the House of Lords was presided over by a Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. The ...
(a Cabinet member), whose influence as Speaker was very limited (whilst the powers belonging to the Speaker of the House of Commons are vast). However, as part of the Constitutional Reform Act 2005, the position of Speaker of the House of Lords (as it is termed in the Act) was separated from the office of Lord Chancellor (the office which has control over the judiciary as a whole), though the Lords remain largely self-governing. Decisions on points of order and on the disciplining of unruly members are made by the whole body, but by the Speaker alone in the Lower House. Speeches in the House of Lords are addressed to the House as a whole (using the words "My Lords"), but those in the House of Commons are addressed to the Speaker alone (using "Mr Speaker" or "Madam Speaker"). Speeches may be made to both Houses simultaneously.
Both Houses may decide questions by voice vote
In parliamentary procedure, a voice vote (from the Latin ''viva voce'', meaning "live voice") or acclamation is a voting method in deliberative assemblies (such as legislatures) in which a group vote is taken on a topic or motion by responding vo ...
; members shout out "Aye!" and "No!" in the CommonsŌĆöor "Content!" and "Not-Content!" in the LordsŌĆöand the presiding officer declares the result. The pronouncement of either Speaker may be challenged, and a recorded vote (known as a division) demanded. (The Speaker of the House of Commons may choose to overrule a frivolous request for a division, but the Lord Speaker does not have that power.) In each House, a division requires members to file into one of the two lobbies alongside the Chamber; their names are recorded by clerks, and their votes are counted as they exit the lobbies to re-enter the Chamber. The Speaker of the House of Commons is expected to be non-partisan, and does not cast a vote except in the case of a tie; the Lord Speaker, however, votes along with the other Lords.
Both Houses normally conduct their business in public, and there are galleries where visitors may sit.
Duration
Originally there was no fixed limit on the length of a Parliament, but theTriennial Act 1694
The Meeting of Parliament Act 1694 (6 & 7 Will & Mary c 2), also known as the Triennial Act 1694, is an Act of the Parliament of England. This Act is Chapter II Rot. Parl. pt. 1. nu. 2. The act currently requires that Parliament hold a session a ...
set the maximum duration at three years. As the frequent elections were deemed inconvenient, the Septennial Act 1715
The Septennial Act 1715 (1 Geo 1 St 2 c 38), sometimes called the Septennial Act 1716, was an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain. It was passed in May 1716. It increased the maximum length of a parliament (and hence the maximum period between ...
extended the maximum to seven years, but the Parliament Act 1911
The Parliament Act 1911 (1 & 2 Geo. 5 c. 13) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It is constitutionally important and partly governs the relationship between the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two Houses of Parlia ...
reduced it to five. During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesŌĆöincluding all of the great powersŌĆöforming two opposin ...
, the term was temporarily extended to ten years by Acts of Parliament. Since the end of the war the maximum has remained five years. Modern Parliaments, however, rarely continued for the maximum duration; normally, they were dissolved earlier. For instance, the 52nd, which assembled in 1997, was dissolved after four years. The Septennial Act was repealed by the Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011
The Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011 (c. 14) (FTPA) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that for the first time set in legislation a default fixed election date for a general election to the Westminster parliament. Since the repeal ...
, which established a presumption that a Parliament will last for five years, unless two thirds of the House of Commons votes for an early general election, or the government loses the confidence of the House.
Summary history of terms of the Parliament of the United Kingdom
Following a general election, a new Parliamentary session begins. Parliament is formally summoned 40 days in advance by the Sovereign, who is the source of parliamentary authority. On the day indicated by the Sovereign's proclamation, the two Houses assemble in their respective chambers. The Commons are then summoned to the House of Lords, where Lords Commissioners
The Lords Commissioners are privy counsellors appointed by the monarch of the United Kingdom to exercise, on his or her behalf, certain functions relating to Parliament which would otherwise require the monarch's attendance at the Palace of Wes ...
(representatives of the Sovereign) instruct them to elect a Speaker. The Commons perform the election; on the next day, they return to the House of Lords, where the Lords Commissioners confirm the election and grant the new Speaker the royal approval in the Sovereign's name.
The business of Parliament for the next few days of its session involves the taking of the oaths of allegiance
An oath of allegiance is an oath whereby a subject or citizen acknowledges a duty of allegiance and swears loyalty to a monarch or a country. In modern republics, oaths are sworn to the country in general, or to the country's constitution. For ...
. Once a majority of the members have taken the oath in each House, the State Opening of Parliament may take place. The Lords take their seats in the House of Lords Chamber, the Commons appear at the Bar (at the entrance to the Chamber), and the Sovereign takes the seat on the throne. The Sovereign then reads the Speech from the Throne
A speech from the throne, or throne speech, is an event in certain monarchies in which the reigning sovereign, or a representative thereof, reads a prepared speech to members of the nation's legislature when a session is opened, outlining th ...
ŌĆöthe content of which is determined by the Ministers of the CrownŌĆöoutlining the Government's legislative agenda for the upcoming year. Thereafter, each House proceeds to the transaction of legislative business.
By custom, before considering the Government's legislative agenda, a bill is introduced ''pro forma'' in each HouseŌĆöthe Select Vestries Bill
A bill for the better regulating of Select Vestries, usually referred to as the Select Vestries Bill, is customarily the first bill introduced and debated in the United Kingdom's House of Lords at the start of each session of Parliament. The equiva ...
in the House of Lords and the Outlawries Bill
A Bill for the more effectual preventing clandestine Outlawries, usually referred to as the Outlawries Bill, is customarily the first bill on the agenda of the United Kingdom's House of Commons at the start of each session of Parliament. It is use ...
in the House of Commons. These bills do not become laws; they are ceremonial indications of the power of each House to debate independently of the Crown. After the ''pro forma'' bill is introduced, each House debates the content of the Speech from the Throne for several days. Once each House formally sends its reply to the Speech, legislative business may commence, appointing committees, electing officers, passing resolutions and considering legislation.
A session of Parliament is brought to an end by a prorogation. There is a ceremony similar to the State Opening, but much less well known to the general public. Normally, the Sovereign does not personally attend the prorogation ceremony in the House of Lords and is represented by Lords Commissioners. The next session of Parliament begins under the procedures described above, but it is not necessary to conduct another election of a Speaker or take the oaths of allegiance afresh at the beginning of such subsequent sessions. Instead, the State Opening of Parliament proceeds directly. To avoid the delay of opening a new session in the event of an emergency during the long summer recess, Parliament is no longer prorogued beforehand, but only after the Houses have reconvened in the autumn; the State Opening follows a few days later.
Each Parliament comes to an end, after a number of sessions, in anticipation of a general election. Parliament is dissolved by virtue of the Dissolution and Calling of Parliament Act 2022
The Dissolution and Calling of Parliament Act 2022 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that repealed the Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011 and reinstated the prior constitutional situation, by reviving the prerogative powers of the m ...
and previously the Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011
The Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011 (c. 14) (FTPA) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that for the first time set in legislation a default fixed election date for a general election to the Westminster parliament. Since the repeal ...
. Prior to that, dissolution was effected by the Sovereign, always on the advice of the Prime Minister. The Prime Minister could seek dissolution at a time politically advantageous to their party. If the Prime Minister loses the support of the House of Commons, Parliament will dissolve and a new election will be held. Parliaments can also be dissolved if two-thirds of the House of Commons votes for an early election.
Formerly, the demise of the Sovereign automatically brought a Parliament to an end, the Crown being seen as the ' (beginning, basis and end) of the body, but this is no longer the case. The first change was during the reign of William and Mary, when it was seen to be inconvenient to have no Parliament at a time when succession to the Crown could be disputed, and an Act was passed that provided that a Parliament was to continue for six months after the death of a Sovereign, unless dissolved earlier. Under the Representation of the People Act 1867
The Representation of the People Act 1867, 30 & 31 Vict. c. 102 (known as the Reform Act 1867 or the Second Reform Act) was a piece of British legislation that enfranchised part of the urban male working class in England and Wales for the first ...
Parliament can now continue for as long as it would otherwise have done in the event of the death of the Sovereign.
After each Parliament concludes, the Crown issues writs to hold a general election and elect new members of the House of Commons, though membership of the House of Lords does not change.
Legislative functions
 Laws can be made by Acts of the United Kingdom Parliament. While Acts can apply to the whole of the United Kingdom including Scotland, due to the continuing separation of
Laws can be made by Acts of the United Kingdom Parliament. While Acts can apply to the whole of the United Kingdom including Scotland, due to the continuing separation of Scots law
Scots law () is the legal system of Scotland. It is a hybrid or mixed legal system containing civil law and common law elements, that traces its roots to a number of different historical sources. Together with English law and Northern Ireland l ...
many Acts do not apply to Scotland and may be matched either by equivalent Acts that apply to Scotland alone or, since 1999, by legislation set by the Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( gd, P├Ārlamaid na h-Alba ; sco, Scots Pairlament) is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. Located in the Holyrood area of the capital city, Edinburgh, it is frequently referred to by the metonym Holyro ...
relating to devolved matters.
This has led to a paradox known as the West Lothian question. The existence of a devolved Scottish Parliament means that while Westminster MPs from Scotland may vote directly on matters that affect English constituencies, they may not have much power over their laws affecting their own constituency. Since there is no devolved "English Parliament", the converse is not true. While any Act of the Scottish Parliament may be overturned, amended or ignored by Westminster, in practice this has yet to happen. Legislative Consent Motion
A legislative consent motion (LCM, also known as a Sewel motion in Scotland) is a motion passed by either the Scottish Parliament, Senedd, or Northern Ireland Assembly, in which it consents that the Parliament of the United Kingdom may (or ...
s enables the UK Parliament to vote on issues normally devolved to Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland, as part of United Kingdom legislation.
Laws, in draft form known as bills, may be introduced by any member of either House. A bill introduced by a Minister is known as a "Government Bill"; one introduced by another member is called a "Private Member's Bill
A private member's bill is a bill (proposed law) introduced into a legislature by a legislator who is not acting on behalf of the executive branch. The designation "private member's bill" is used in most Westminster system jurisdictions, in whi ...
". A different way of categorising bills involves the subject. Most bills, involving the general public, are called " public bills". A bill that seeks to grant special rights to an individual or small group of individuals, or a body such as a local authority, is called a " Private Bill". A Public Bill which affects private rights (in the way a Private Bill would) is called a " Hybrid Bill", although those that draft bills take pains to avoid this.
Private Members' Bills make up the majority of bills, but are far less likely to be passed than government bills. There are three methods for an MP to introduce a Private Member's Bill. The Private Members' Ballot (once per Session) put names into a ballot, and those who win are given time to propose a bill. The Ten Minute Rule
The Ten Minute Rule, also known as Standing Order No. 23, is a procedure in the Parliament of the United Kingdom for the introduction of Private Member's Bills in addition to the 20 per session normally permissible. It is one of the ways in whi ...
is another method, where MPs are granted ten minutes to outline the case for a new piece of legislation. Standing Order 57 is the third method, which allows a bill to be introduced without debate if a day's notice is given to the Table Office. Filibuster
A filibuster is a political procedure in which one or more members of a legislative body prolong debate on proposed legislation so as to delay or entirely prevent decision. It is sometimes referred to as "talking a bill to death" or "talking out ...
ing is a danger, as an opponent of a bill can waste much of the limited time allotted to it. Private Members' Bills have no chance of success if the current government opposes them, but they are used in moral issues: the bills to decriminalise homosexuality and abortion were Private Members' Bills, for example. Governments can sometimes attempt to use Private Members' Bills to pass things it would rather not be associated with. "Handout bills" are bills which a government hands to MPs who win Private Members' Ballots.
Each Bill goes through several stages in each House. The first stage, called the first reading, is a formality. At the second reading
A reading of a bill is a stage of debate on the bill held by a general body of a legislature.
In the Westminster system, developed in the United Kingdom, there are generally three readings of a bill as it passes through the stages of becoming, ...
, the general principles of the bill are debated, and the House may vote to reject the bill, by not passing the motion "That the Bill be now read a second time." Defeats of Government Bills in the Commons are extremely rare, the last being in 2005, and may constitute a motion of no confidence
A motion of no confidence, also variously called a vote of no confidence, no-confidence motion, motion of confidence, or vote of confidence, is a statement or vote about whether a person in a position of responsibility like in government or mana ...
. (Defeats of Bills in the Lords never affect confidence and are much more frequent.)
Following the second reading, the bill is sent to a committee. In the House of Lords, the Committee of the Whole House
A committee of the whole is a meeting of a legislative or deliberative assembly using procedural rules that are based on those of a committee, except that in this case the committee includes all members of the assembly. As with other (standing) c ...
or the Grand Committee are used. Each consists of all members of the House; the latter operates under special procedures, and is used only for uncontroversial bills. In the House of Commons, the bill is usually committed to a Public Bill Committee, consisting of between 16 and 50 members, but the Committee of the Whole House is used for important legislation. Several other types of committees, including Select Committees, may be used, but rarely. A committee considers the bill clause by clause, and reports the bill as amended to the House, where further detailed consideration ("consideration stage" or "report stage") occurs. However, a practice which used to be called the "kangaroo" (Standing Order 32) allows the Speaker to select which amendments are debated. This device is also used under Standing Order 89 by the committee chairman, to restrict debate in committee. The Speaker, who is impartial as between the parties, by convention selects amendments for debate which represent the main divisions of opinion within the House. Other amendments can technically be proposed, but in practice have no chance of success unless the parties in the House are closely divided. If pressed they would normally be casually defeated by acclamation.
Once the House has considered the bill, the third reading follows. In the House of Commons, no further amendments may be made, and the passage of the motion "That the Bill be now read a third time" is passage of the whole bill. In the House of Lords further amendments to the bill may be moved. After the passage of the third reading motion, the House of Lords must vote on the motion "That the Bill do now pass." Following its passage in one House, the bill is sent to the other House. If passed in identical form by both Houses, it may be presented for the Sovereign's Assent. If one House passes amendments that the other will not agree to, and the two Houses cannot resolve their disagreements, the bill will normally fail.
Since the passage of the Parliament Act 1911 the power of the House of Lords to reject bills passed by the House of Commons has been restricted, with further restrictions were placed by the Parliament Act 1949. If the House of Commons passes a public bill in two successive sessions, and the House of Lords rejects it both times, the Commons may direct that the bill be presented to the Sovereign for his or her Assent, disregarding the rejection of the Bill in the House of Lords. In each case, the bill must be passed by the House of Commons at least one calendar month before the end of the session. The provision does not apply to Private bills or to Public bills if they originated in the House of Lords or if they seek to extend the duration of a Parliament beyond five years. A special procedure applies in relation to bills classified by the Speaker of the House of Commons as "Money Bills". A Money Bill concerns ''solely'' national taxation or public funds; the Speaker's certificate is deemed conclusive under all circumstances. If the House of Lords fails to pass a Money Bill within one month of its passage in the House of Commons, the Lower House may direct that the Bill be submitted for the Sovereign's Assent immediately.
Even before the passage of the Parliament Acts, the Commons possessed pre-eminence in cases of financial matters. By ancient custom, the House of Lords may not introduce a bill relating to taxation or Supply, nor amend a bill so as to insert a provision relating to taxation or Supply, nor amend a Supply Bill in any way. The House of Commons is free to waive this privilege, and sometimes does so to allow the House of Lords to pass amendments with financial implications. The House of Lords remains free to reject bills relating to Supply and taxation, but may be over-ruled easily if the bills are Money Bills. (A bill relating to revenue and Supply may not be a Money Bill if, for example, it includes subjects other than national taxation and public funds).
The last stage of a bill involves the granting of the Royal Assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in other ...
. Theoretically, the Sovereign may either grant or withhold Royal Assent (make the bill a law or veto the bill). In modern times the Sovereign always grants the Royal Assent, using the Norman French
Norman or Norman French (, french: Normand, Guern├®siais: , J├©rriais: ) is a Romance language which can be classified as one of the O├»l languages along with French, Picard and Walloon. The name "Norman French" is sometimes used to descri ...
words " Le Roy le veult" (the King wishes it; "La Reyne" in the case of a Queen). The last refusal to grant the Assent was in 1708, when Queen Anne withheld her Assent from a bill "for the settling of Militia in Scotland", in the words "" (the Queen will think it over).
Thus, every bill obtains the assent of all three components of Parliament before it becomes law (except where the House of Lords is over-ridden under the Parliament Acts 1911 and 1949
The Parliament Acts 1911 and 1949 are two Act of Parliament, Acts of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, which form part of the constitution of the United Kingdom. Section 2(2) of the Parliament Act 1949 provides that the two Acts are to be St ...
). The words "BE IT ENACTED by the King's most Excellent Majesty, by and with the advice and consent of the Lords Spiritual and Temporal, and Commons, in this present Parliament assembled, and by the authority of the same, as follows:-," or, where the House of Lords' authority has been over-ridden by use of the Parliament Acts, the words "BE IT ENACTED by King's most Excellent Majesty, by and with the advice and consent of the Commons in this present Parliament assembled, in accordance with the provisions of the Parliament Acts 1911 and 1949, and by the authority of the same, as follows:-" appear near the beginning of each Act of Parliament. These words are known as the enacting formula
An enacting clause is a short phrase that introduces the main provisions of a law enacted by a legislature. It is also called enacting formula or enacting words. It usually declares the source from which the law claims to derive its authority. In ...
.
Judicial functions
 Prior to the creation of the
Prior to the creation of the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom
The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom (initialism: UKSC or the acronym: SCOTUK) is the final court of appeal in the United Kingdom for all civil cases, and for criminal cases originating in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. As the Unite ...
in 2009, Parliament was the highest court in the realm for most purposes, but the Privy Council
A privy council is a body that advises the head of state of a state, typically, but not always, in the context of a monarchic government. The word "privy" means "private" or "secret"; thus, a privy council was originally a committee of the mon ...
had jurisdiction in some cases (for instance, appeals from ecclesiastical courts). The jurisdiction of Parliament arose from the ancient custom of petitioning the Houses to redress grievances and to do justice. The House of Commons ceased considering petitions to reverse the judgements of lower courts in 1399, effectively leaving the House of Lords as the court of last resort. In modern times, the judicial functions of the House of Lords
Whilst the House of Lords of the United Kingdom is the upper chamber of Parliament and has government ministers, it for many centuries had a judicial function. It functioned as a court of first instance for the trials of peers, for impeachments, ...
were performed not by the whole House, but by the Lords of Appeal in Ordinary
Lords of Appeal in Ordinary, commonly known as Law Lords, were judges appointed under the Appellate Jurisdiction Act 1876 to the British House of Lords, as a committee of the House, effectively to exercise the judicial functions of the House of ...
(judges granted life peerage dignities under the Appellate Jurisdiction Act 1876) and by Lords of Appeal (other peers with experience in the judiciary). However, under the Constitutional Reform Act 2005, these judicial functions were transferred to the newly created Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
in 2009, and the Lords of Appeal in Ordinary became the first Justices of the Supreme Court. Peers who hold high judicial office are no longer allowed to vote or speak in the Lords until they retire as justices.
In the late 19th century, Acts allowed for the appointment of ''Scottish Lords of Appeal in Ordinary'' and ended appeal in Scottish criminal matters to the House of Lords, so that the High Court of Justiciary became the highest criminal court in Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
. There is an argument that the provisions of Article XIX of the Union with England Act 1707 prevent any Court outside Scotland from hearing any appeal in criminal cases: "And that the said Courts or any other of the like nature after the Unions shall have no power to Cognosce Review or Alter the Acts or Sentences of the Judicatures within Scotland or stop the Execution of the same." The House of Lords judicial committee usually had a minimum of two Scottish Judges to ensure that some experience of Scots law
Scots law () is the legal system of Scotland. It is a hybrid or mixed legal system containing civil law and common law elements, that traces its roots to a number of different historical sources. Together with English law and Northern Ireland l ...
was brought to bear on Scottish appeals in civil cases, from the Court of Session
The Court of Session is the supreme civil court of Scotland and constitutes part of the College of Justice; the supreme criminal court of Scotland is the High Court of Justiciary. The Court of Session sits in Parliament House in Edinburgh ...
. The Supreme Court now usually has at least two Scottish judges, together with at least one from Northern Ireland. As Wales is developing its own judicature, it is likely that the same principle will be applied.
Certain other judicial functions have historically been performed by the House of Lords. Until 1948, it was the body in which peers had to be tried for felonies or high treason; now, they are tried by normal juries. The last occasion of the trial of a peer in the House of Lords was in 1935. When the House of Commons impeaches an individual, the trial takes place in the House of Lords. Impeachments are now possibly defunct, as the last one occurred in 1806. In 2006, a number of MPs attempted to revive the custom, having signed a motion for the impeachment of Tony Blair
Sir Anthony Charles Lynton Blair (born 6 May 1953) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1997 to 2007 and Leader of the Labour Party from 1994 to 2007. He previously served as Leader of th ...
, but this was unsuccessful.
Relationship with the UK Government
The British Government is answerable to the House of Commons. However, neither the Prime Minister nor members of the Government are elected by the House of Commons. Instead, the King requests the person most likely to command the support of a majority in the House, normally the leader of the largest party in the House of Commons, to form a government. So that they may be accountable to the Lower House, the Prime Minister and most members of theCabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
are, by convention, members of the House of Commons. The last Prime Minister to be a member of the House of Lords was Alec Douglas-Home, 14th Earl of Home
Alexander Frederick Douglas-Home, Baron Home of the Hirsel (; 2 July 1903 ŌĆō 9 October 1995), styled as Lord Dunglass between 1918 and 1951 and being The 14th Earl of Home from 1951 till 1963, was a British Conservative Party (UK), Conse ...
, who became Prime Minister in 1963. To adhere to the convention under which he was responsible to the Lower House, he disclaimed his peerage and procured election to the House of Commons within days of becoming Prime Minister.
Governments have a tendency to dominate the legislative functions of Parliament, by using their in-built majority in the House of Commons, and sometimes using their patronage power to appoint supportive peers in the Lords. In practice, governments can pass any legislation (within reason) in the Commons they wish, unless there is major dissent by MPs in the governing party.
But even in these situations, it is highly unlikely a bill will be defeated, though dissenting MPs may be able to extract concessions from the government. In 1976, Quintin Hogg, Lord Hailsham of St Marylebone created a now widely used name for this behaviour, in an academic paper called "elective dictatorship
The phrase "elective dictatorship" (also called executive dominance in political science) describes the state in which a typical Westminster system state's parliament is dominated by the government of the day. It refers to the fact that the legis ...
".
Parliament controls the executive by passing or rejecting its Bills and by forcing Ministers of the Crown to answer for their actions, either at "Question Time" or during meetings of the parliamentary committees
A committee or commission is a body of one or more persons subordinate to a deliberative assembly. A committee is not itself considered to be a form of assembly. Usually, the assembly sends matters into a committee as a way to explore them more ...
. In both cases, Ministers are asked questions by members of their Houses, and are obliged to answer.
Although the House of Lords may scrutinise the executive through Question Time and through its committees, it cannot bring down the Government. A ministry must always retain the confidence and support of the House of Commons. The Lower House may indicate its lack of support by rejecting a Motion of Confidence
A motion of no confidence, also variously called a vote of no confidence, no-confidence motion, motion of confidence, or vote of confidence, is a statement or vote about whether a person in a position of responsibility like in government or mana ...
or by passing a Motion of No Confidence
A motion of no confidence, also variously called a vote of no confidence, no-confidence motion, motion of confidence, or vote of confidence, is a statement or vote about whether a person in a position of responsibility like in government or mana ...
. Confidence Motions are generally originated by the Government to reinforce its support in the House, whilst No Confidence Motions are introduced by the Opposition. The motions sometimes take the form "That this House has oconfidence in His Majesty's Government" but several other varieties, many referring to specific policies supported or opposed by Parliament, are used. For instance, a Confidence Motion of 1992 used the form, "That this House expresses the support for the economic policy of His Majesty's Government." Such a motion may theoretically be introduced in the House of Lords, but, as the Government need not enjoy the confidence of that House, would not be of the same effect as a similar motion in the House of Commons; the only modern instance of such an occurrence involves the 'No Confidence' motion that was introduced in 1993 and subsequently defeated.
Many votes are considered votes of confidence, although not including the language mentioned above. Important bills that form part of the Government's agenda (as stated in the Speech from the Throne) are generally considered matters of confidence. The defeat of such a bill by the House of Commons indicates that a Government no longer has the confidence of that House. The same effect is achieved if the House of Commons " withdraws Supply," that is, rejects the budget.
Where a Government has lost the confidence of the House of Commons, in other words has lost the ability to secure the basic requirement of the authority of the House of Commons to tax and to spend Government money, the Prime Minister is obliged either to resign, or seek the dissolution of Parliament and a new general election. Otherwise the machinery of government grinds to a halt within days. The third choice ŌĆō to mount a coup d'├®tat or an anti-democratic revolution ŌĆō is hardly to be contemplated in the present age. Though all three situations have arisen in recent years even in developed economies, international relations have allowed a disaster to be avoided.
Where a Prime Minister has ceased to retain the necessary majority and requests a dissolution, the Sovereign can in theory reject his or her request, forcing a resignation and allowing the Leader of the Opposition
The Leader of the Opposition is a title traditionally held by the leader of the largest political party not in government, typical in countries utilizing the parliamentary system form of government. The leader of the opposition is typically se ...
to be asked to form a new government. This power is used extremely rarely. The conditions that should be met to allow such a refusal are known as the Lascelles Principles
The Lascelles Principles are a constitutional convention in the United Kingdom beginning in 1950, under which the sovereign can refuse a request from the prime minister to dissolve Parliament if three conditions are met:
#if the existing Parlia ...
. These conditions and principles are constitutional conventions arising from the Sovereign's reserve powers as well as longstanding tradition and practice, not laid down in law.
In practice, the House of Commons' scrutiny of the Government is very weak. Since the first-past-the-post
In a first-past-the-post electoral system (FPTP or FPP), formally called single-member plurality voting (SMP) when used in single-member districts or informally choose-one voting in contrast to ranked voting, or score voting, voters cast their ...
electoral system is employed in elections, the governing party tends to enjoy a large majority in the Commons; there is often limited need to compromise with other parties. Modern British political parties are so tightly organised that they leave relatively little room for free action by their MPs. In many cases, MPs may be expelled from their parties for voting against the instructions of party leaders. During the 20th century, the Government has lost confidence issues only three timesŌĆötwice in 1924, and once in 1979.
Parliamentary questions
 In the United Kingdom, question time in the House of Commons lasts for an hour each day from Monday to Thursday (2:30 to 3:30 pm on Mondays, 11:30 am to 12:30 pm on Tuesdays and Wednesdays, and 9:30 to 10:30 am on Thursdays). Each Government department has its place in a rota which repeats every five weeks. The exception to this sequence are the Business Questions (Questions to the
In the United Kingdom, question time in the House of Commons lasts for an hour each day from Monday to Thursday (2:30 to 3:30 pm on Mondays, 11:30 am to 12:30 pm on Tuesdays and Wednesdays, and 9:30 to 10:30 am on Thursdays). Each Government department has its place in a rota which repeats every five weeks. The exception to this sequence are the Business Questions (Questions to the Leader of House of Commons
The leader of the House of Commons is a minister of the Crown of the Government of the United Kingdom whose main role is organising government business in the House of Commons. The leader is generally a member or attendee of the cabinet of th ...
), in which questions are answered each Thursday about the business of the House the following week. Also, Questions to the Prime Minister
Prime Minister's Questions (PMQs, officially known as Questions to the Prime Minister, while colloquially known as Prime Minister's Question Time) is a constitutional convention in the United Kingdom, currently held as a single session every W ...
takes place each Wednesday from noon to 12:30 pm.
In addition to government departments, there are also questions to the Church commissioners. Additionally, each Member of Parliament is entitled to table questions for written answer. Written questions are addressed to the Ministerial head of a government department, usually a Secretary of State, but they are often answered by a Minister of State
Minister of State is a title borne by politicians in certain countries governed under a parliamentary system. In some countries a Minister of State is a Junior Minister of government, who is assigned to assist a specific Cabinet Minister. In o ...
or Parliamentary Under Secretary of State. Written Questions are submitted to the Clerks of the Table Office, either on paper or electronically, and answers are recorded in '' The Official Report (Hansard)'' so as to be widely available and accessible.
In the House of Lords, a half-hour is set aside each afternoon at the start of the day's proceedings for Lords' oral questions. A peer submits a question in advance, which then appears on the Order Paper
The Order Paper is a daily publication in the Westminster system of government which lists the business of parliament for that day's sitting. A separate paper is issued daily for each house of the legislature.
The Order Paper provides members ...
for the day's proceedings. The peer shall say: "''My Lords, I beg leave to ask the Question standing in my name on the Order Paper''." The Minister responsible then answers the question. The peer is then allowed to ask a supplementary question and other peers ask further questions on the theme of the original put down on the order paper. (For instance, if the question regards immigration, peers can ask the Minister any question related to immigration during the allowed period.)
Parliamentary sovereignty
Sir William Blackstone
Sir William Blackstone (10 July 1723 ŌĆō 14 February 1780) was an English jurist, judge and Tory politician of the eighteenth century. He is most noted for writing the '' Commentaries on the Laws of England''. Born into a middle-class family ...
, "It has sovereign and uncontrollable authority in making, confirming, enlarging, restraining, abrogating, repealing, reviving, and expounding of laws, concerning matters of all possible denominations, ecclesiastical, or temporal, civil, military, maritime, or criminalŌĆ” it can, in short, do every thing that is not naturally impossible."
A different view has been taken by the Scottish judge Thomas Cooper, 1st Lord Cooper of Culross. When he decided the 1953 case of ''MacCormick v. Lord Advocate
''MacCormick v Lord Advocate'' 1953 SC 396 was a Scottish constitutional law case and Scots law, Scottish legal action on whether Queen Elizabeth II was entitled to use the numeral "II" as her regnal number in Scotland, as there had never been an ...
'' as Lord President of the Court of Session, he stated, "The principle of unlimited sovereignty of Parliament is a distinctively English principle and has no counterpart in Scottish constitutional law." He continued, "Considering that the Union legislation extinguished the Parliaments of Scotland and England and replaced them by a new Parliament, I have difficulty in seeing why the new Parliament of Great Britain must inherit all the peculiar characteristics of the English Parliament but none of the Scottish." Nevertheless, he did not give a conclusive opinion on the subject.
Thus, the question of Parliamentary sovereignty appears to remain unresolved. Parliament has not passed any Act defining its own sovereignty. The European Union (Withdrawal Agreement) Act 2020
The European Union (Withdrawal Agreement) Act 2020 (c. 1) is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that makes legal provision for ratifying the Brexit Withdrawal Agreement and incorporating it into the domestic law of the United Ki ...
states "It is recognised that the Parliament of the United Kingdom is sovereign." without qualification or definition. A related possible limitation on Parliament relates to the Scottish legal system and Presbyterian faith, preservation of which were Scottish preconditions to the creation of the unified Parliament. Since the Parliament of the United Kingdom was set up in reliance on these promises, it may be that it has no power to make laws that break them.
Parliament's power has often been eroded by its own Acts. Acts passed in 1921
Events
January
* January 2
** The Association football club Cruzeiro Esporte Clube, from Belo Horizonte, is founded as the multi-sports club Palestra Italia by Italian expatriates in First Brazilian Republic, Brazil.
** The Spanish lin ...
and 1925 granted the Church of Scotland
The Church of Scotland ( sco, The Kirk o Scotland; gd, Eaglais na h-Alba) is the national church in Scotland.
The Church of Scotland was principally shaped by John Knox, in the Scottish Reformation, Reformation of 1560, when it split from t ...
complete independence in ecclesiastical matters. From 1973 to 2020, its power had been restricted by membership of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
, which has the power to make laws enforceable in each member state. In the Factortame case, the European Court of Justice
The European Court of Justice (ECJ, french: Cour de Justice europ├®enne), formally just the Court of Justice, is the supreme court of the European Union in matters of European Union law. As a part of the Court of Justice of the European Un ...
ruled that British courts could have powers to overturn British legislation contravening European law.
Parliament has also created national devolved parliaments and an assembly with differing degrees of legislative authority in Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
, Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the WalesŌĆōEngland border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
and Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart ├ēireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
, but not in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
, which continues to be governed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Parliament still has the power over areas for which responsibility lies with the devolved institutions, but would ordinarily gain the agreement of those institutions to act on their behalf. Similarly, it has granted the power to make regulations to Ministers of the Crown, and the power to enact religious legislation to the General Synod of the Church of England. (Measures of the General Synod and, in some cases proposed statutory instrument
In many countries, a statutory instrument is a form of delegated legislation.
United Kingdom
Statutory instruments are the principal form of delegated or secondary legislation in the United Kingdom.
National government
Statutory instrument ...
s made by ministers, must be approved by both Houses before they become law.)
In every case aforementioned, authority has been conceded by Act of Parliament and may be taken back in the same manner. It is entirely within the authority of Parliament, for example, to abolish the devolved governments in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland, or ŌĆö as happened in 2020 ŌĆö to leave the EU. However, Parliament also revoked its legislative competence over Australia and Canada with the Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
and Canada Acts: although the Parliament of the United Kingdom could pass an Act reversing its action, it would not take effect in Australia or Canada as the competence of the Imperial Parliament is no longer recognised there in law.
One well-recognised consequence of Parliament's sovereignty is that it cannot bind future Parliaments; that is, no Act of Parliament may be made secure from amendment or repeal by a future Parliament. For example, although the Act of Union 1800
The Acts of Union 1800 (sometimes incorrectly referred to as a single 'Act of Union 1801') were parallel acts of the Parliament of Great Britain and the Parliament of Ireland which united the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Irela ...
states that the Kingdoms of Great Britain and Ireland are to be united "forever," Parliament permitted southern Ireland to leave the United Kingdom in 1922.
Privileges
Each House of Parliament possesses and guards various ancient privileges. The House of Lords relies on inherent right. In the case of the House of Commons, the Speaker goes to the Lords' Chamber at the beginning of each new Parliament and requests representatives of the Sovereign to confirm the Lower House's "undoubted" privileges and rights. The ceremony observed by the House of Commons dates to the reign of King Henry VIII. Each House is the guardian of its privileges, and may punish breaches thereof. The extent of parliamentary privilege is based on law and custom. Sir William Blackstone states that these privileges are "very large and indefinite," and cannot be defined except by the Houses of Parliament themselves. The foremost privilege claimed by both Houses is that offreedom of speech
Freedom of speech is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or a community to articulate their opinions and ideas without fear of retaliation, censorship, or legal sanction. The right to freedom of expression has been recogni ...
in debate; nothing said in either House may be questioned in any court or other institution outside Parliament. Another privilege claimed is that of freedom from arrest; at one time this was held to apply for any arrest except for high treason, felony
A felony is traditionally considered a crime of high seriousness, whereas a misdemeanor is regarded as less serious. The term "felony" originated from English common law (from the French medieval word "f├®lonie") to describe an offense that resu ...
or breach of the peace
Breach of the peace, or disturbing the peace, is a legal term used in constitutional law in English-speaking countries and in a public order sense in the several jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It is a form of disorderly conduct.
Public ord ...
but it now excludes any arrest on criminal charges; it applies during a session of Parliament, and 40 days before or after such a session. Members of both Houses are no longer privileged from service on juries
A jury is a sworn body of people (jurors) convened to hear evidence and render an impartial verdict (a finding of fact on a question) officially submitted to them by a court, or to set a penalty or judgment.
Juries developed in England durin ...
.
Both Houses possess the power to punish breaches of their privilege. Contempt of ParliamentŌĆöfor example, disobedience of a subpoena issued by a committeeŌĆömay also be punished. The House of Lords may imprison an individual for any fixed period of time, but an individual imprisoned by the House of Commons is set free upon prorogation. The punishments imposed by either House may not be challenged in any court, and the Human Rights Act does not apply.
Until at least 2015, members of the House of Commons also had the privilege of a separate seating area in the Palace of Westminster canteen, protected by a false partition labelled "MPs only beyond this point," so that they did not have to sit with canteen staff taking a break. This provoked mockery from a newly elected 20-year-old MP who described it as "ridiculous" snobbery.
Emblem
The quasi-official emblem of the Houses of Parliament is a crownedportcullis
A portcullis (from Old French ''porte coleice'', "sliding gate") is a heavy vertically-closing gate typically found in medieval fortifications, consisting of a latticed grille made of wood, metal, or a combination of the two, which slides down gr ...
. The portcullis was originally the badge of various English noble families from the 14th century. It went on to be adopted by the kings of the Tudor dynasty
The House of Tudor was a royal house of largely Welsh and English origin that held the English throne from 1485 to 1603. They descended from the Tudors of Penmynydd and Catherine of France. Tudor monarchs ruled the Kingdom of England and it ...
in the 16th century, under whom the Palace of Westminster became the regular meeting place of Parliament. The crown was added to make the badge a specifically royal symbol.
The portcullis probably first came to be associated with the Palace of Westminster
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Informally known as the Houses of Parli ...
through its use as decoration in the rebuilding of the Palace after the fire of 1512. However, at the time it was only one of many symbols. The widespread use of the portcullis throughout the Palace dates from the 19th century, when Charles Barry
Sir Charles Barry (23 May 1795 ŌĆō 12 May 1860) was a British architect, best known for his role in the rebuilding of the Palace of Westminster (also known as the Houses of Parliament) in London during the mid-19th century, but also responsi ...
and Augustus Pugin
Augustus Welby Northmore Pugin ( ; 1 March 181214 September 1852) was an English architect, designer, artist and critic with French and, ultimately, Swiss origins. He is principally remembered for his pioneering role in the Gothic Revival st ...
used it extensively as a decorative feature in their designs for the new Palace built following the disastrous 1834 fire.
The crowned portcullis came to be accepted during the 20th century as the emblem of both houses of parliament. This was simply a result of custom and usage rather than a specific decision. The emblem now appears on official stationery, publications and papers, and is stamped on various items in use in the Palace of Westminster, such as cutlery, silverware and china. Various shades of red and green are used for visual identification of the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the Bicameralism, upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by Life peer, appointment, Hereditary peer, heredity or Lords Spiritual, official function. Like the ...
and the House of Commons.
Broadcast media
All public events are broadcast live and on-demand viwww.parliamentlive.tv
which maintains an archive dating back to 4 December 2007. There is also a related official
YouTube
YouTube is a global online video platform, online video sharing and social media, social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by ...
channel. They are also broadcast live by the independent Euronews
Euronews (styled on-air in lowercase as euronews) is a European television news network, headquartered in Lyon, France. The network began broadcasting on 1 January 1993 and covers world news from a European perspective.
The majority of Eurone ...
English channel. In the UK the BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board ex ...
has its own dedicated parliament channel, BBC Parliament
BBC Parliament is a British free-to-air public broadcast television channel from the BBC that broadcasts live and recorded coverage of the House of Commons, House of Lords and Select Committees of the British Parliament, the Scottish Parliament ...
, which broadcasts 24 hours a day and is also available on BBC iPlayer
BBC iPlayer (stylised as iPLAYER or BBC iPLAYER) is a video on demand service from the BBC. The service is available on a wide range of devices, including mobile phones and tablets, personal computers and smart televisions. iPlayer services del ...
. It shows live coverage from the House of Commons, House of Lords, the Scottish Parliament, the Northern Ireland Assembly and the Senedd.
See also
*Act of Parliament
Acts of Parliament, sometimes referred to as primary legislation, are texts of law passed by the Legislature, legislative body of a jurisdiction (often a parliament or council). In most countries with a parliamentary system of government, acts of ...
* Acts of Parliament of the United Kingdom relating to the European Communities and the European Union
This is a list of current, amended, spent and repealed Acts of the Parliament of the United Kingdom relating to its former membership and current relationship to the European Communities and the European Union from 1972 onwards.
Some of the ...
* History of democracy
A democracy is a political system, or a system of decision-making within an institution or organization or a country, in which all members have an equal share of power. Modern democracies are characterized by two capabilities that differentiate ...
* ''The History of Parliament
The History of Parliament is a project to write a complete history of the United Kingdom Parliament and its predecessors, the Parliament of Great Britain and the Parliament of England. The history will principally consist of a prosopography, in w ...
''
* List of Acts of the Parliament of the United Kingdom
{{British legislation lists
This is an ''incomplete'' list of Acts of the Parliament of the United Kingdom from its establishment in 1801 up until the present.
Lists of Acts by Year
* List of Acts of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, 1801ŌĆ ...
* List of British governments
* List of parliaments of the United Kingdom
* Parliament in the Making
Parliament in the Making was a programme of events organised by the Parliament of the United Kingdom to commemorate a series of anniversaries in 2015 including:
* the sealing of ''Magna Carta'', on 15 June 1215, 800 years earlier
* the first repr ...
, a programme of anniversary events in 2015
* Parliament of the United Kingdom relocation
Several parties have advocated the relocation of the Parliament of the United Kingdom from its current location at the Palace of Westminster, London, to the English Midlands or Northern England, for economic or other reasons.
A contributing fact ...
* Parliamentary agent
Parliamentary agents are solicitors who are licensed (together with the firms they belong to) by the Houses of Parliament in the United Kingdom to draft, promote or oppose private bills. Private bills are a specific class of legislation promoted ...
* ''Parliamentary Brief
First published in 1992, ''Parliamentary Brief'' is a monthly British political magazine circulated by request to members of the British House of Commons, members of the House of Lords, senior civil servants, and political journalists. Reports&md ...
''
* Parliamentary Information and Communication Technology Service
Parliamentary Information and Communication Technology Service or PICT provides IT services to MPs, Peers and staff across the UK Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the ...
* Parliamentary Office of Science and Technology
The Parliamentary Office of Science and Technology (POST) is the Parliament of the United Kingdom's in-house source of independent, balanced and accessible analysis of public policy issues related to science and technology. POST serves both Hous ...
* Parliamentary records of the United Kingdom
Parliamentary records of the United Kingdom covers the period from the creation of the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1707, including records from the Parliament of Great Britain and of the Parliament of the United Kingdom.
Longest Parliament
The lo ...
* Records of members of parliament of the United Kingdom
This article about records of members of parliament of the United Kingdom and of England includes a variety of lists of MPs by age, period and other circumstances of service, familiar sets, ethnic or religious minorities, physical attributes, and ...
* TheyWorkForYou
* United Kingdom Parliament constituencies
* UK Parliament Week
UK Parliament Week, previously called Parliament Week, is an annual series of events in the United Kingdom that aim to inspire interest in parliament, Politics of the United Kingdom, politics and democracy and encourage young people and the publi ...
Lists of MPs elected
*List of MPs elected in the 1966 United Kingdom general election
This is a list of Members of Parliament elected at the 1966 general election, held on 31 March.
By nation
* List of MPs for constituencies in Scotland (1966ŌĆō1970
Composition
These representative diagrams show the composition of the part ...
* List of MPs elected in the 1970 United Kingdom general election
This is a list of Members of Parliament elected at the 1970 general election, held on 18 June.
Composition
These representative diagrams show the composition of the parties in the 1970 general election.
Note: This is not the official seatin ...
* List of MPs elected in the February 1974 United Kingdom general election
* List of MPs elected in the October 1974 United Kingdom general election
This is a list of Members of Parliament (MPs) elected in the October 1974 United Kingdom general election, October 1974 general election, held on 10 October. This Parliament was dissolved in 1979.
Composition
These representative diagrams show ...
* List of MPs elected in the 1979 United Kingdom general election
This is a list of Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Members of Parliament (MPs) elected in the 1979 United Kingdom general election, 1979 general election, held on 3 May. This Parliament was dissolved in 1983 United Kingdom general electio ...
* List of MPs elected in the 1983 United Kingdom general election
This is a list of Members of Parliament (MPs) elected in the 1983 general election, held on 9 June. This Parliament was dissolved in 1987.
During 1983-1987 Bernard Weatherill was the speaker, Margaret Thatcher served as Prime Minister, Michae ...
* List of MPs elected in the 1987 United Kingdom general election
* List of MPs elected in the 1992 United Kingdom general election
This is a list of Members of Parliament (MPs) elected in the 1992 general election, held on 9 April.
During the 1992ŌĆō97 Parliament, Betty Boothroyd was the Speaker, John Major served as Prime Minister, and Neil Kinnock, John Smith, Margaret ...
* List of MPs elected in the 1997 United Kingdom general election
This is a list of Members of Parliament (MPs) elected to the House of Commons at the 1997 general election, held on 1 May.
The list is arranged by constituency. New MPs elected since the general election are noted at the bottom of the page. ...
* List of MPs elected in the 2001 United Kingdom general election
This is a list of Members of Parliament (MPs) elected to the House of Commons at the 2001 general election, held on 7 June.
The list is arranged by constituency. New MPs elected since the general election and changes in party allegiance are no ...
* List of MPs elected in the 2005 United Kingdom general election
This is a list of Members of Parliament (MPs) elected to the House of Commons at the 2005 general election, held on 5 May. The list is arranged by constituency. New MPs elected since the general election and changes in party allegiance are note ...
* List of MPs elected in the 2010 United Kingdom general election
The 2010 general election took place on 6 May 2010 and saw each of Parliament's 650 constituencies return one Member of Parliament (MP) to the House of Commons. Parliament, which consists of the House of Lords and the elected House of Commons, ...
* List of MPs elected in the 2015 United Kingdom general election
* List of MPs elected in the 2017 United Kingdom general election
* List of MPs elected in the 2019 United Kingdom general election
In the United Kingdom's (UK) 2019 general election, 650 Members of Parliament (MPs) were elected to the House of Commons ŌĆō one for each parliamentary constituency.
The UK Parliament comprises the elected House of Commons, the House of Lords ...
Notes
References
Footnotes
Sources
* * * * * * * * * *External links
*Public Policy Hub ŌĆō Parliament and law making
''Hansard'' from 1803 to 2005
Parliament Live TV
"AŌĆōZ of Parliament"
ĆöThe British Broadcasting Corporation (2005).
Topic: Politics
Ćö''The Guardian''
Topic: House of Lords
Ćö''The Guardian''
at Leeds University
British House of Commons people
(
C-SPAN
Cable-Satellite Public Affairs Network (C-SPAN ) is an American cable and satellite television network that was created in 1979 by the cable television industry as a nonprofit public service. It televises many proceedings of the United States ...
)
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Parliament of United Kingdom
1801 establishments in the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
Politics of the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...