Parliament Of Normandy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

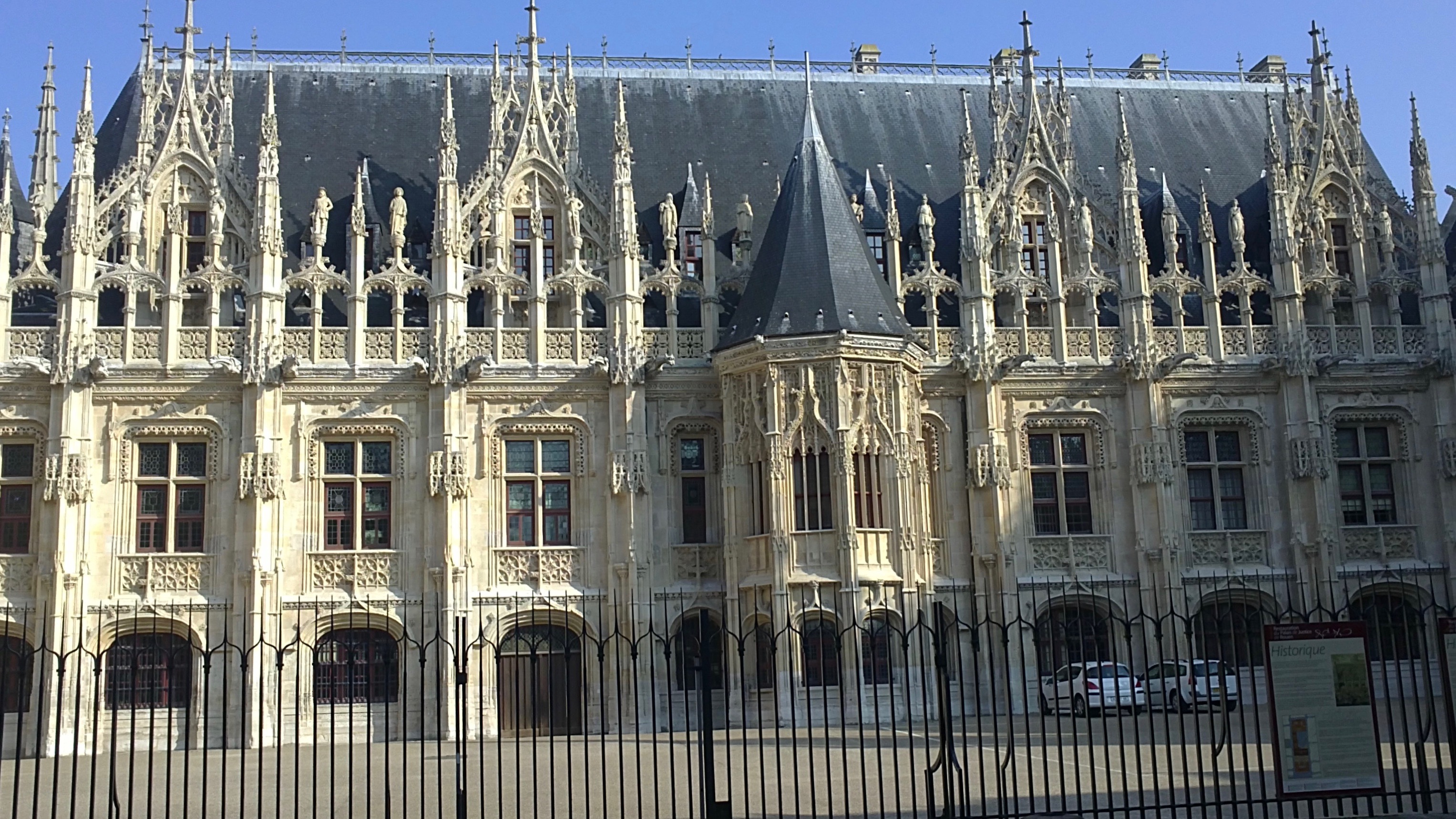 The Parliament of Normandy (''parlement de Normandie''), also known as the Parliament of Rouen (''parlement de
The Parliament of Normandy (''parlement de Normandie''), also known as the Parliament of Rouen (''parlement de
 Raised to a sovereign court and given a base in Rouen by
Raised to a sovereign court and given a base in Rouen by

 The Parliament of Normandy (''parlement de Normandie''), also known as the Parliament of Rouen (''parlement de
The Parliament of Normandy (''parlement de Normandie''), also known as the Parliament of Rouen (''parlement de Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the Regions of France, region of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the Departments of France, department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of ...
'') after the place where it sat (the provincial capital of Normandy), was a provincial parlement
A ''parlement'' (), under the French Ancien RĆ©gime, was a provincial appellate court of the Kingdom of France. In 1789, France had 13 parlements, the oldest and most important of which was the Parlement of Paris. While both the modern Fre ...
of the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. ...
. It replaced the ancient court of the exchequer of Normandy
The Exchequer of Normandy (''Ɖchiquier de Normandie'') or Exchequer of Rouen (''Ɖchiquier de Rouen'') was the fiscal and administrative court of the Duchy of Normandy until the early 16th century.
Surviving records show that the Exchequer of N ...
, set up by Rollo, first duke of Normandy
In the Middle Ages, the duke of Normandy was the ruler of the Duchy of Normandy in north-western Kingdom of France, France. The duchy arose out of a grant of land to the Viking leader Rollo by the French king Charles the Simple, Charles III in ...
.
The parlement was built in a mixing of the French Flamboyant
Flamboyant (from ) is a form of late Gothic architecture that developed in Europe in the Late Middle Ages and Renaissance, from around 1375 to the mid-16th century. It is characterized by double curves forming flame-like shapes in the bar-tr ...
style and Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
architecture by Roger Ango and Roulland le Roux, between 1499 and 1508, during the reign of the king Louis XII of France
Louis XII (27 June 14621 January 1515), was King of France from 1498 to 1515 and King of Naples from 1501 to 1504. The son of Charles, Duke of OrlƩans, and Maria of Cleves, he succeeded his 2nd cousin once removed and brother in law at the tim ...
. Today, the building is the seat of the courthouse of the city of Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the Regions of France, region of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the Departments of France, department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of ...
.
History
 Raised to a sovereign court and given a base in Rouen by
Raised to a sovereign court and given a base in Rouen by Louis XII of France
Louis XII (27 June 14621 January 1515), was King of France from 1498 to 1515 and King of Naples from 1501 to 1504. The son of Charles, Duke of OrlƩans, and Maria of Cleves, he succeeded his 2nd cousin once removed and brother in law at the tim ...
, this court's name was changed from ''Ć©chiquier'' to ''parlement'' by Francis I of France
Francis I (french: FranƧois Ier; frm, Francoys; 12 September 1494 ā€“ 31 March 1547) was King of France from 1515 until his death in 1547. He was the son of Charles, Count of AngoulĆŖme, and Louise of Savoy. He succeeded his first cousin once ...
on his accession in 1515. The parlement de Rouen had responsibility for the seven great bailliages of Normandy ā€“ Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the Regions of France, region of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the Departments of France, department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of ...
, Caudebec-en-Caux, Ɖvreux, Les Andelys
Les Andelys (; Norman: ''Les Aundelys'') is a commune in the northern French department of Eure, in Normandy.
Geography
It lies on the Seine, about northeast of Ɖvreux.
The commune is divided into two parts, Grand-Andely (located about from ...
, Caen
Caen (, ; nrf, Kaem) is a commune in northwestern France. It is the prefecture of the department of Calvados. The city proper has 105,512 inhabitants (), while its functional urban area has 470,000,Coutances and

Histoire du parlement de Normandie
', 7 volumes, Rouen,
AlenƧon
AlenƧon (, , ; nrf, AlenƧoun) is a commune in Normandy, France, capital of the Orne department. It is situated west of Paris. AlenƧon belongs to the intercommunality of AlenƧon (with 52,000 people).
History
The name of AlenƧon is firs ...
. It was thus made up of 4 presidents (of which the first and third were clergy and the other two laymen), 13 clergy councillors, 15 lay councillors, 2 ''greffiers'' (a secretary for civil law and one for criminal law), a ''huissier audiencier'' (the bailiff who officially assigns documents between lawyers and introduces the judges in the public court room), 6 other '' huissiers de justice'', 2 advocates general and 1 procurator general. Following letters patent of 1507 from Louis XII, the archbishop of Rouen and the abbot of Saint-Ouen were 'ex officio' honorary councillors to the parlement.
When the court of the Ć©chiquier was made permanent, it was divided into two chambers, one to sit in the morning and the other in the afternoon. This second chamber later became known as the premiĆØre des enquĆŖtes. The chambre de la Tournelle, entrusted with criminal cases, was built in 1519 and the chambre des vacations was not set up until 1547. Until 1 October 1506, the parlement de Normandie sat in the chĆ¢teau de Rouen
Rouen Castle (''ChĆ¢teau Bouvreuil'') was a fortified ducal and royal residence in the city of Rouen, capital of the duchy of Normandy, now in France. With the exception of the tower wrongly associated with Joan of Arc, which was restored by Vi ...
then in the palais (which was begun in 1499 and only completed long afterwards).
Many kings of France held lits de justice at the parlement de Normandie. Charles VIII held one on 27 April 1485 and at it confirmed Normandy's privileges. Louis XII was accompanied there by the main officers of his court on 24 October 1508. On 2 August 1517, Francis I held one there, accompanied by chancellor Duprat and many officers of his court. Some days later, the dauphin came to the parliament, where he was granted the same honors as the king himself, as the king had ordered. In January 1518, he granted the parlement de Normandie the same privileges as that of the parlement de Paris and, by another edict the following February, temporarily exempted it from the arriĆØre-ban In medieval and early modern France, the arriĆØre-ban (Latin ''retrobannum'') was a general proclamation whereby the king (or duke) summoned to war all the vassals of his vassals.. The term is a folk-etymological correction of Old French ''herban'' ...
.
On 8 October 1550, Henri II held a lit de justice at the parlement de Rouen, accompanied by the cardinals, king Henry II of Navarre, many dukes, constable Anne de Montmorency
Anne, Duke of Montmorency, Honorary Knight of the Garter (15 March 1493, Chantilly, Oise12 November 1567, Paris) was a French soldier, statesman and diplomat. He became Marshal of France and Constable of France and served five kings.
Early lif ...
, the admiral, the duc de Longueville, chancellor Olivier, and many other lords. Charles IX was declared of age at the parlement, accompanied by chancellor Michel de L'Hospital
Michel may refer to:
* Michel (name), a given name or surname of French origin (and list of people with the name)
* MĆchel (nickname), a nickname (a list of people with the nickname, mainly Spanish footballers)
* MĆchel (footballer, born 1963), S ...
.
In 1523, Francis I exempted the parlement from the gabelle and ordained that it would issue to each of his officers and his widow as much salt as it had for his household, without fixing the quantity, paying only the market price, on the condition it did not abuse this privilege. In 1540 chancellor Guillaume Poyet
Guillaume Poyet (c. 1473 ā€“ April 1548) was a French magistrate born in Angers. After practising successfully as a barrister at Angers and Paris, he was instructed by Louise of Savoy, mother of the king Francis I, to uphold her rights against the ...
set the king against the parlement de Rouen, and the king banned it. Commissaires were named for the Tournelle, and a president and 12 councillors sent to Bayeux
Bayeux () is a Communes of France, commune in the Calvados (department), Calvados Departments of France, department in Normandy (administrative region), Normandy in northwestern France.
Bayeux is the home of the Bayeux Tapestry, which depicts ...
, to give justice to the subjects of basse-Normandie until the king raised his ban; and wishing to give to this court's officers a mark of his satisfaction with their conduct, in June 1542 he made the arriĆØre-ban exemption general and perpetual via an edict.
In 1560, the parlement de Normandie and the other provincial parlements were suppressed before being reestablished in June 1568 by Charles IX. In February 1589, an edict of the month by Henry IV of France
Henry IV (french: Henri IV; 13 December 1553 ā€“ 14 May 1610), also known by the epithets Good King Henry or Henry the Great, was King of Navarre (as Henry III) from 1572 and King of France from 1589 to 1610. He was the first monarc ...
transferred the parlement to Caen
Caen (, ; nrf, Kaem) is a commune in northwestern France. It is the prefecture of the department of Calvados. The city proper has 105,512 inhabitants (), while its functional urban area has 470,000,revolt of the va-nu-pieds
The Revolt of the ''va-nu-pieds'' (, ''barefooted ones'') was a popular uprising in Normandy in 1639 following King Louis XIII's decision to set up the gabelle salt tax in Cotentin in place of the privilege of the quart-bouillon.
Context
The Nu-P ...
strongly enough, it as replaced by commissaires from the parlement de Paris until its reestablishment in January 1641.Pierre Miquel, ''Les Guerres de religion'', Club France Loisirs, 1980, () p. 367
In April 1545, Francis I had set up a criminal chamber here to judge cases relating to Protestants, which was replaced by a chambre de lā€™Ć©dit, as part of the execution of the edict of Nantes
The Edict of Nantes () was signed in April 1598 by King Henry IV and granted the Calvinist Protestants of France, also known as Huguenots, substantial rights in the nation, which was in essence completely Catholic. In the edict, Henry aimed pr ...
of April 1598, suppressed in its turn in January 1685 as part of the edict of Fontainebleau
The Edict of Fontainebleau (22 October 1685) was an edict issued by French King Louis XIV and is also known as the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes. The Edict of Nantes (1598) had granted Huguenots the right to practice their religion without s ...
. Made up at this time of 57 councillors and 2 presidents, an edict of July 1680 created a second chambre des enquĆŖtes, after which the parlement was made up of five chambers, the grand-chambre, the Tournelle, two chambres des enquĆŖtes and the chambre des requĆŖtes du palais right up until the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
. It was at the parlement de Normandie that, from 1728, the general assemblies of dƩputƩs of different courts and other notables met to discuss public affairs such as hospitals' needs and other necessities.
Organisation

Notes
Sources
* ''EncyclopƩdie ou Dictionnaire raisonnƩ des sciences, des arts et des mƩtiers
''EncyclopƩdie, ou dictionnaire raisonnƩ des sciences, des arts et des mƩtiers'' (English: ''Encyclopedia, or a Systematic Dictionary of the Sciences, Arts, and Crafts''), better known as ''EncyclopƩdie'', was a general encyclopedia publi ...
'' by Diderot
Denis Diderot (; ; 5 October 171331 July 1784) was a French philosopher, art critic, and writer, best known for serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the ''EncyclopƩdie'' along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. He was a prominen ...
& dā€™Alembert, vol. 12, p. 60
References
* Amable Floquet,Histoire du parlement de Normandie
', 7 volumes, Rouen,
Ɖdouard FrĆØre
Ɖdouard FrĆØre (27 September 1797, Rouen ā€“ 7 April 1874, Rouen) was a French bookseller, archivist, biographer, and historian specialized in the Normandy area.
Life
The son and grandson of booksellers, FrĆØre's father, Jacques-Christophe oper ...
, 1840ā€“1842
* Olivier Chaline
Olivier Chaline (29 December 1964, Neuilly-sur-Seine) is a contemporary French historian, a specialist of the history of Central Europe.
Biography
The son of Jean-Pierre Chaline, himself an historian (a specialist on the French Third Republic), ...
, ''Godart de Belbeuf : le parlement, le roi et les Normands'', Luneray, Bertout, 1996,
* (ed. Nicolas Plantrou), ''Du Parlement de Normandie Ć la Cour d'appel de Rouen 1499ā€“1999'', Rouen, 1999
{{Authority control
History of Normandy
Nor