Pantheon, Rome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Pantheon (, ; ,Although the spelling ''Pantheon'' is standard in English, only ''Pantheum'' is found in classical Latin; see, for example, Pliny, ''
36.38
"Agrippas Pantheum decoravit Diogenes Atheniensis". See also ''
"Pantheon"
"post-classical Latin ''pantheon'' a temple consecrated to all the gods (6th cent.; compare classical Latin ''pantheum'')". ) is an ancient 2nd century
 The name "Pantheon" is from the Ancient Greek "Pantheion" (Πάνθειον) meaning "of, relating to, or common to all the gods": (pan- / "παν-" meaning "all" + theion / "θεῖον"= meaning "of or sacred to a god"). The simplest explanation for the name is that the Pantheon was a temple dedicated to all the gods. However, the concept of a temple dedicated to all the gods has been questioned. Ziegler tried to collect evidence of pantheons, but his list consists of simple dedications "to all the gods" or "to the Twelve Gods", which are not necessarily true pantheons in the sense of a temple housing a cult that literally worships all the gods. The only definite pantheon recorded earlier than Agrippa's was at Antioch in Syria, though it is only mentioned by a sixth-century source.
The name "Pantheon" is from the Ancient Greek "Pantheion" (Πάνθειον) meaning "of, relating to, or common to all the gods": (pan- / "παν-" meaning "all" + theion / "θεῖον"= meaning "of or sacred to a god"). The simplest explanation for the name is that the Pantheon was a temple dedicated to all the gods. However, the concept of a temple dedicated to all the gods has been questioned. Ziegler tried to collect evidence of pantheons, but his list consists of simple dedications "to all the gods" or "to the Twelve Gods", which are not necessarily true pantheons in the sense of a temple housing a cult that literally worships all the gods. The only definite pantheon recorded earlier than Agrippa's was at Antioch in Syria, though it is only mentioned by a sixth-century source.
 :M·AGRIPPA·L·F·COS·TERTIVM·FECIT
or in full, "''M rcusAgrippa L ciif liusco ltertium fecit''," meaning " Marcus Agrippa, son of Lucius, made his buildingwhen consul for the third time." However, archaeological excavations have shown that the Pantheon of Agrippa had been completely destroyed except for the façade. Lise Hetland argues that the present construction began in 114, under
:M·AGRIPPA·L·F·COS·TERTIVM·FECIT
or in full, "''M rcusAgrippa L ciif liusco ltertium fecit''," meaning " Marcus Agrippa, son of Lucius, made his buildingwhen consul for the third time." However, archaeological excavations have shown that the Pantheon of Agrippa had been completely destroyed except for the façade. Lise Hetland argues that the present construction began in 114, under  The form of Agrippa's Pantheon is debated. As a result of excavations in the late 19th century, archaeologist Rodolfo Lanciani concluded that Agrippa's Pantheon was oriented so that it faced south, in contrast with the current layout that faces north, and that it had a shortened T-shaped plan with the entrance at the base of the "T". This description was widely accepted until the late 20th century. While more recent archaeological diggings have suggested that Agrippa's building might have had a circular form with a triangular porch, and it might have also faced north, much like the later rebuildings, Ziolkowski complains that their conclusions were based entirely on surmise; according to him, they did not find any new datable material, yet they attributed everything they found to the Agrippan phase, failing to account for the fact that
The form of Agrippa's Pantheon is debated. As a result of excavations in the late 19th century, archaeologist Rodolfo Lanciani concluded that Agrippa's Pantheon was oriented so that it faced south, in contrast with the current layout that faces north, and that it had a shortened T-shaped plan with the entrance at the base of the "T". This description was widely accepted until the late 20th century. While more recent archaeological diggings have suggested that Agrippa's building might have had a circular form with a triangular porch, and it might have also faced north, much like the later rebuildings, Ziolkowski complains that their conclusions were based entirely on surmise; according to him, they did not find any new datable material, yet they attributed everything they found to the Agrippan phase, failing to account for the fact that
 In 609, the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine emperor
In 609, the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine emperor

 The building was originally approached by a flight of steps. Later construction raised the level of the ground leading to the portico, eliminating these steps.
The pediment was decorated with relief sculpture, probably of gilded bronze. Holes marking the location of clamps that held the sculpture suggest that its design was likely an eagle within a wreath; ribbons extended from the wreath into the corners of the pediment.
On the intermediate block between the portico and the rotunda, the remains of a second pediment suggests that the existing portico is much shorter than originally intended. A portico aligned with the second pediment would fit columns with shafts 50 Roman feet (14.8 metres) tall and capitals 10 Roman feet tall (3 metres), whereas the existing portico has shafts 40 Roman feet (11.9 metres) tall and capitals eight Roman feet (2.4 metres) tall., pp. 199–206
Mark Wilson Jones has attempted to explain the design adjustments by suggesting that, once the higher pediment had been constructed, the required 50-foot columns failed to arrive (possibly as a result of logistical difficulties). The builders then had to make some awkward adjustments to fit the shorter columns and pediments. Rabun Taylor has noted that, even if the taller columns were delivered, basic construction constraints may have prevented their use. Assuming that each column would first be laid on the floor next to its pediment before being pivoted upright (using something like an
The building was originally approached by a flight of steps. Later construction raised the level of the ground leading to the portico, eliminating these steps.
The pediment was decorated with relief sculpture, probably of gilded bronze. Holes marking the location of clamps that held the sculpture suggest that its design was likely an eagle within a wreath; ribbons extended from the wreath into the corners of the pediment.
On the intermediate block between the portico and the rotunda, the remains of a second pediment suggests that the existing portico is much shorter than originally intended. A portico aligned with the second pediment would fit columns with shafts 50 Roman feet (14.8 metres) tall and capitals 10 Roman feet tall (3 metres), whereas the existing portico has shafts 40 Roman feet (11.9 metres) tall and capitals eight Roman feet (2.4 metres) tall., pp. 199–206
Mark Wilson Jones has attempted to explain the design adjustments by suggesting that, once the higher pediment had been constructed, the required 50-foot columns failed to arrive (possibly as a result of logistical difficulties). The builders then had to make some awkward adjustments to fit the shorter columns and pediments. Rabun Taylor has noted that, even if the taller columns were delivered, basic construction constraints may have prevented their use. Assuming that each column would first be laid on the floor next to its pediment before being pivoted upright (using something like an
 The weight of the Roman concrete dome is concentrated on a ring of voussoirs in diameter that form the oculus, while the downward thrust of the dome is carried by eight barrel vaults in the drum wall into eight piers. The thickness of the dome varies from at the base of the dome to around the oculus. The materials used in the concrete of the dome also vary. At its thickest point, the aggregate is travertine, then terracotta tiles, then at the very top, tufa and
The weight of the Roman concrete dome is concentrated on a ring of voussoirs in diameter that form the oculus, while the downward thrust of the dome is carried by eight barrel vaults in the drum wall into eight piers. The thickness of the dome varies from at the base of the dome to around the oculus. The materials used in the concrete of the dome also vary. At its thickest point, the aggregate is travertine, then terracotta tiles, then at the very top, tufa and


 The present high altars and the apses were commissioned by Pope Clement XI (1700–1721) and designed by Alessandro Specchi. Enshrined on the apse above the high altar is a 7th-century Byzantine icon of the Virgin and Child, given by Phocas to Pope Boniface IV on the occasion of the dedication of the Pantheon for Christian worship on 13 May 609. The choir was added in 1840, and was designed by Luigi Poletti.
The first niche to the right of the entrance holds a '' Madonna of the Girdle and St Nicholas of Bari'' (1686) painted by an unknown artist. The first chapel on the right, the Chapel of the Annunciation, has a fresco of the ''Annunciation'' attributed to
The present high altars and the apses were commissioned by Pope Clement XI (1700–1721) and designed by Alessandro Specchi. Enshrined on the apse above the high altar is a 7th-century Byzantine icon of the Virgin and Child, given by Phocas to Pope Boniface IV on the occasion of the dedication of the Pantheon for Christian worship on 13 May 609. The choir was added in 1840, and was designed by Luigi Poletti.
The first niche to the right of the entrance holds a '' Madonna of the Girdle and St Nicholas of Bari'' (1686) painted by an unknown artist. The first chapel on the right, the Chapel of the Annunciation, has a fresco of the ''Annunciation'' attributed to
File:Pantheon (J).jpg, Pantheon during a cloudy day
File:Oculus photographed in fisheye by Victor Grigas, Pantheon, Rome.tif, The dome photographed with a
Official webpage from Vicariate of Rome website
(archived 16 September 2015)
"Beggar's Rome"
– A self-directed virtual tour of St. Maria ad Martyres (Pantheon) and other Roman churches
Live streaming Video of the Pantheon
Virtual Panorama and photo gallery
article in Platner's ''Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome''
Pantheon Rome vs Pantheon Paris
.
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20080315223914/http://www.greatbuildings.com/buildings/Pantheon.html Pantheonat Great Buildings/Architecture Week website (archived 15 March 2008)
Art & History Pantheon
.
Summer solstice at the Pantheon
(archived 15 July 2011) *
Video Introduction to the Pantheon
Panoramic Virtual Tour inside the Pantheon
* High-resolution 360° Panoramas and Images o
Pantheon, Art Atlas
audio guide Pantheon Rome
* * * {{Authority control 126 120s establishments in the Roman Empire 2nd-century religious buildings and structures 7th-century churches in Italy Basilica churches in Rome Temples in the Campus Martius Ancient Roman buildings and structures in Rome Concrete shell structures Church buildings with domes Round churches Conversion of non-Christian religious buildings and structures into churches Tourist attractions in Rome Rome R. IX Pigna Centralized-plan churches in Italy Hadrian Roman temples by deity Buildings converted to Catholic church buildings Burial sites of the House of Savoy Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa Burned buildings and structures in Italy Rotundas in Europe
Natural History
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi, and plants, in their natural environment, leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is cal ...
'36.38
"Agrippas Pantheum decoravit Diogenes Atheniensis". See also ''
Oxford Latin Dictionary
The ''Oxford Latin Dictionary'' (or ''OLD'') is the standard English lexicon of Classical Latin, compiled from sources written before AD 200. Begun in 1933, it was published in fascicles between 1968 and 1982; a lightly revised second edition ...
'', s.v. "Pantheum"; ''Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the principal historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP), a University of Oxford publishing house. The dictionary, which published its first editio ...
'', s.v"Pantheon"
"post-classical Latin ''pantheon'' a temple consecrated to all the gods (6th cent.; compare classical Latin ''pantheum'')". ) is an ancient 2nd century
Roman temple
Ancient Roman temples were among the most important buildings in culture of ancient Rome, Roman culture, and some of the richest buildings in Architecture of ancient Rome, Roman architecture, though only a few survive in any sort of complete ...
and, since AD 609, a Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
church called the Basilica of St. Mary and the Martyrs () in Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
, Italy. It is perhaps the most famous, and architecturally most influential, rotunda.
The Pantheon was built on the site of an earlier temple, which had been commissioned by Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa during the reign of Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
(27 BC – AD 14). After the original burnt down, the present building was ordered by the emperor Hadrian
Hadrian ( ; ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. Hadrian was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic peoples, Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, Aelia '' ...
and probably dedicated AD 126. Its date of construction is uncertain, because Hadrian chose to re-inscribe the new temple with Agrippa's original date inscription from the older temple.
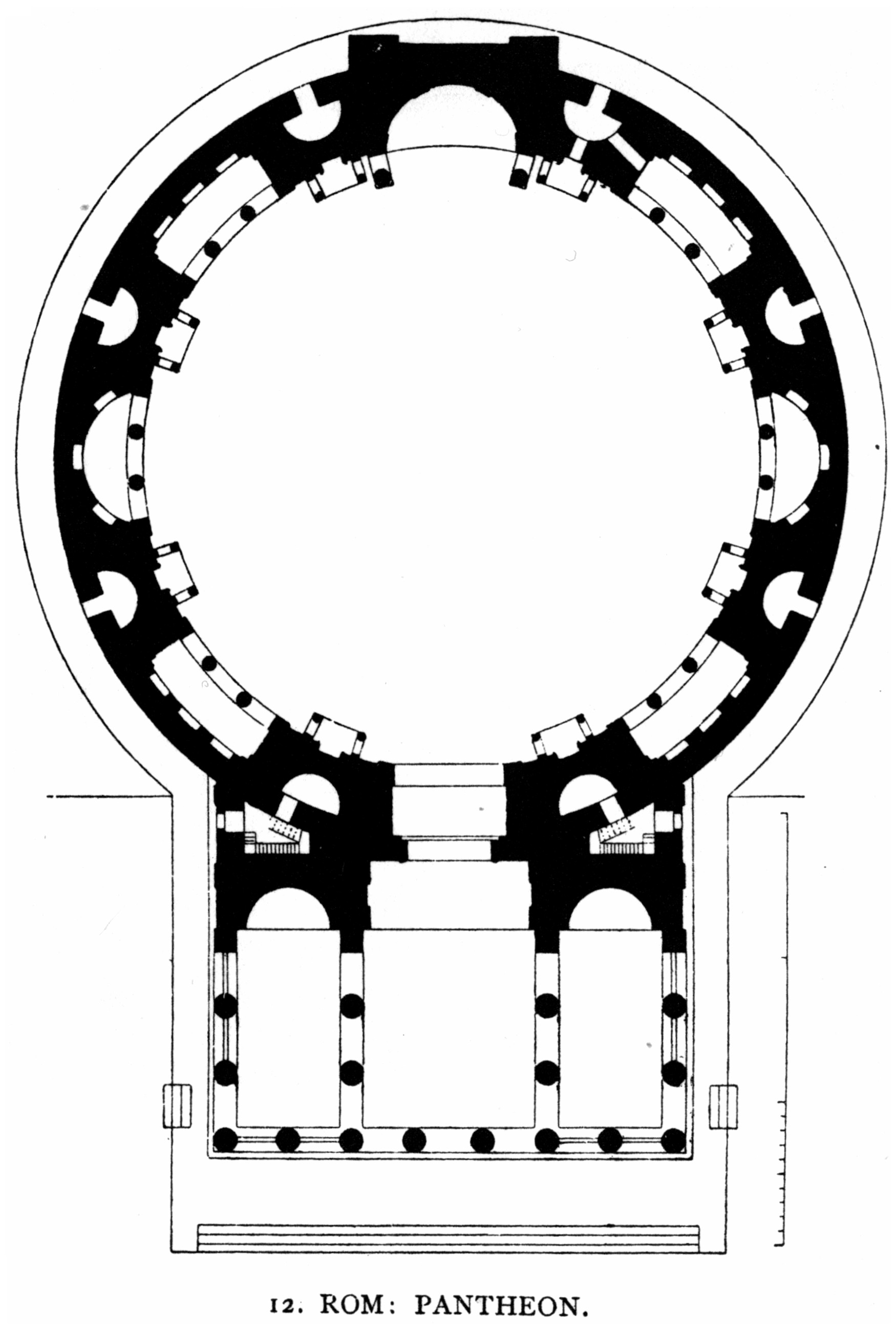
The building is round in plan, except for the portico with large granite Corinthian columns (eight in the first rank and two groups of four behind) under a pediment
Pediments are a form of gable in classical architecture, usually of a triangular shape. Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the cornice (an elaborated lintel), or entablature if supported by columns.Summerson, 130 In an ...
. A rectangular vestibule links the porch to the rotunda, which is under a coffered concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of aggregate bound together with a fluid cement that cures to a solid over time. It is the second-most-used substance (after water), the most–widely used building material, and the most-manufactur ...
dome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a m ...
, with a central opening ( oculus) to the sky. Almost two thousand years after it was built, the Pantheon's dome is still the world's largest unreinforced concrete dome. The height to the oculus and the diameter of the interior circle are the same, .
It is one of the best-preserved of all Ancient Roman buildings, in large part because it has been in continuous use throughout its history. Since the 7th century, it has been a church dedicated to St. Mary and the Martyrs (), known as "Santa Maria Rotonda". The square in front of the Pantheon is called Piazza della Rotonda. The Pantheon is a state property, managed by Italy's Ministry of Cultural Heritage and Activities and Tourism through the Polo Museale del Lazio. In 2013, it was visited by over six million people.
The Pantheon's large circular domed cella, with a conventional temple portico front, was unique in Roman architecture. Nevertheless, it became a standard exemplar when classical styles were revived, and has been copied many times by later architects.
Etymology
 The name "Pantheon" is from the Ancient Greek "Pantheion" (Πάνθειον) meaning "of, relating to, or common to all the gods": (pan- / "παν-" meaning "all" + theion / "θεῖον"= meaning "of or sacred to a god"). The simplest explanation for the name is that the Pantheon was a temple dedicated to all the gods. However, the concept of a temple dedicated to all the gods has been questioned. Ziegler tried to collect evidence of pantheons, but his list consists of simple dedications "to all the gods" or "to the Twelve Gods", which are not necessarily true pantheons in the sense of a temple housing a cult that literally worships all the gods. The only definite pantheon recorded earlier than Agrippa's was at Antioch in Syria, though it is only mentioned by a sixth-century source.
The name "Pantheon" is from the Ancient Greek "Pantheion" (Πάνθειον) meaning "of, relating to, or common to all the gods": (pan- / "παν-" meaning "all" + theion / "θεῖον"= meaning "of or sacred to a god"). The simplest explanation for the name is that the Pantheon was a temple dedicated to all the gods. However, the concept of a temple dedicated to all the gods has been questioned. Ziegler tried to collect evidence of pantheons, but his list consists of simple dedications "to all the gods" or "to the Twelve Gods", which are not necessarily true pantheons in the sense of a temple housing a cult that literally worships all the gods. The only definite pantheon recorded earlier than Agrippa's was at Antioch in Syria, though it is only mentioned by a sixth-century source. Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history of ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
, a Roman senator
The Roman Senate () was the highest and Roman constitution, constituting assembly of ancient Rome and its aristocracy. With different powers throughout its existence it lasted from the first days of the Rome, city of Rome (traditionally founded ...
who wrote in Greek, speculated that the name of the Pantheon comes either from the statues of many gods placed around this building, or from the resemblance of the dome to the heavens. According to Adam Ziolkowski, this uncertainty strongly suggests that "Pantheon" (or Pantheum) was merely a nickname, not the formal name of the building.
Godfrey and Hemsoll point out that ancient authors never refer to Hadrian's Pantheon with the word ''aedes
''Aedes'' (also known as the tiger mosquito) is a genus of mosquitoes originally found in tropical and subtropical zones, but now found on all continents except Antarctica. Some species have been spread by human activity: ''Aedes albopictus'', ...
'', as they do with other temples, and the Severan inscription carved on the architrave uses simply "Pantheum", not "Aedes Panthei" (temple of all the gods). Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding i ...
wrote that it had been decreed that temple buildings (or perhaps temple cellae) should only be dedicated to single divinities, so that it would be clear who would be offended if, for example, the building was struck by lightning, and because it was only appropriate to offer sacrifice to a specific deity (27.25.7–10). Godfrey and Hemsoll maintain that the word Pantheon "need not denote a particular group of gods, or, indeed, even all the gods, since it could well have had other meanings. ... Certainly the word pantheus or pantheos, could be applicable to individual deities. ... Bearing in mind also that the Greek word θεῖος (theios) need not mean 'of a god' but could mean 'superhuman
The term superhuman refers to humans, humanoids or other beings with abilities and other qualities that exceed those naturally found in humans. These qualities may be acquired through natural ability, self-actualization or technological aids. ...
', or even 'excellent'."
Since the French Revolution, when the church of Sainte-Geneviève in Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
was deconsecrated and turned into the secular monument called the Panthéon of Paris, the generic term ''pantheon'' has sometimes been applied to other buildings in which illustrious dead are honoured or buried.
History

Ancient
In the aftermath of the Battle of Actium (31 BC), Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa started an impressive building program. The Pantheon was a part of the complex created by him on his own property in the Campus Martius in 29–19 BC, which included three buildings aligned from south to north: the Baths of Agrippa, the Basilica of Neptune, and the Pantheon. It seems likely that the Pantheon and the Basilica of Neptune were Agrippa's ''sacra privata'', not ''aedes publicae'' (public temples). The former would help explain how the building could have so easily lost its original name and purpose (Ziolkowski contends that it was originally the Temple of Mars in Campo) in such a relatively short period of time. It had long been thought that the current building was built by Agrippa, with later alterations undertaken, and this was in part because of the Latin inscription on the front of the temple which reads: :M·AGRIPPA·L·F·COS·TERTIVM·FECIT
or in full, "''M rcusAgrippa L ciif liusco ltertium fecit''," meaning " Marcus Agrippa, son of Lucius, made his buildingwhen consul for the third time." However, archaeological excavations have shown that the Pantheon of Agrippa had been completely destroyed except for the façade. Lise Hetland argues that the present construction began in 114, under
:M·AGRIPPA·L·F·COS·TERTIVM·FECIT
or in full, "''M rcusAgrippa L ciif liusco ltertium fecit''," meaning " Marcus Agrippa, son of Lucius, made his buildingwhen consul for the third time." However, archaeological excavations have shown that the Pantheon of Agrippa had been completely destroyed except for the façade. Lise Hetland argues that the present construction began in 114, under Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier ...
, four years after it was destroyed by fire for the second time (Oros. 7.12). She reexamined Herbert Bloch's 1959 paper, which is responsible for the commonly maintained Hadrianic date, and maintains that he should not have excluded all of the Trajanic-era bricks from his brick-stamp study. Her argument is particularly interesting in light of Heilmeyer's argument that, based on stylistic evidence, Apollodorus of Damascus, Trajan's architect, was the obvious architect.
 The form of Agrippa's Pantheon is debated. As a result of excavations in the late 19th century, archaeologist Rodolfo Lanciani concluded that Agrippa's Pantheon was oriented so that it faced south, in contrast with the current layout that faces north, and that it had a shortened T-shaped plan with the entrance at the base of the "T". This description was widely accepted until the late 20th century. While more recent archaeological diggings have suggested that Agrippa's building might have had a circular form with a triangular porch, and it might have also faced north, much like the later rebuildings, Ziolkowski complains that their conclusions were based entirely on surmise; according to him, they did not find any new datable material, yet they attributed everything they found to the Agrippan phase, failing to account for the fact that
The form of Agrippa's Pantheon is debated. As a result of excavations in the late 19th century, archaeologist Rodolfo Lanciani concluded that Agrippa's Pantheon was oriented so that it faced south, in contrast with the current layout that faces north, and that it had a shortened T-shaped plan with the entrance at the base of the "T". This description was widely accepted until the late 20th century. While more recent archaeological diggings have suggested that Agrippa's building might have had a circular form with a triangular porch, and it might have also faced north, much like the later rebuildings, Ziolkowski complains that their conclusions were based entirely on surmise; according to him, they did not find any new datable material, yet they attributed everything they found to the Agrippan phase, failing to account for the fact that Domitian
Domitian ( ; ; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was Roman emperor from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Flavian dynasty. Described as "a r ...
, known for his enthusiasm for building and known to have restored the Pantheon after 80 AD, might well have been responsible for everything they found. Ziolkowski argues that Lanciani's initial assessment is still supported by all of the finds to date, including theirs; he expresses scepticism because the building they describe, "a single building composed of a huge pronaos and a circular cella of the same diameter, linked by a relatively narrow and very short passage (much thinner than the current intermediate block), has no known parallels in classical architecture and would go against everything we know of Roman design principles in general and of Augustan architecture in particular."
The only passages referring to the decoration of the Agrippan Pantheon written by an eyewitness are in Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
's ''Natural History
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi, and plants, in their natural environment, leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is cal ...
''. From him we know that "the capitals, too, of the pillars, which were placed by M. Agrippa in the Pantheon, are made of Syracusan bronze", that "the Pantheon of Agrippa has been decorated by Diogenes of Athens, and the Caryatides, by him, which form the columns of that temple, are looked upon as masterpieces of excellence: the same, too, with the statues that are placed upon the roof," and that one of Cleopatra's pearls was cut in half so that each half "might serve as pendants for the ears of Venus, in the Pantheon at Rome".
The Augustan Pantheon was destroyed along with other buildings in a fire in 80 AD. Domitian
Domitian ( ; ; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was Roman emperor from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Flavian dynasty. Described as "a r ...
rebuilt the Pantheon, which was burnt again in 110 AD.
The degree to which the decorative scheme should be credited to Hadrian's architects is uncertain. Finished by Hadrian but not claimed as one of his works, it used the text of the original inscription on the new façade
A façade or facade (; ) is generally the front part or exterior of a building. It is a loanword from the French language, French (), which means "frontage" or "face".
In architecture, the façade of a building is often the most important asp ...
(a common practice in Hadrian's rebuilding projects all over Rome; the only building on which Hadrian put his own name was the Temple to the Deified Trajan). How the building was actually used is not known. The Historia Augusta
The ''Historia Augusta'' (English: ''Augustan History'') is a late Roman collection of biographies, written in Latin, of the Roman emperors, their junior colleagues, Caesar (title), designated heirs and Roman usurper, usurpers from 117 to 284. S ...
says that Hadrian dedicated the Pantheon (among other buildings) in the name of the original builder (Hadr. 19.10), but the current inscription could not be a copy of the original; it does not tell us to whom Agrippa's foundation was dedicated, and, in Ziolkowski's opinion, it was highly unlikely that in 25 BC Agrippa would have presented himself as "consul tertium." On coins, the same words, "M. Agrippa L.f cos. tertium", were the ones used to refer to him after his death; consul tertium serving as "a sort of posthumous cognomen ex virtute, a remembrance of the fact that, of all the men of his generation apart from Augustus himself, he was the only one to hold the consulship thrice." Whatever the cause of the alteration of the inscription might have been, the new inscription reflects the fact that there was a change in the building's purpose.
Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history of ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
, a Graeco-Roman senator, consul and author of a comprehensive ''History of Rome'', writing approximately 75 years after the Pantheon's reconstruction, mistakenly attributed the domed building to Agrippa rather than Hadrian. Dio appears to be the only near-contemporaneous writer to mention the Pantheon. Even by 200, there was uncertainty about the origin of the building and its purpose:
In 202, the building was repaired by the joint emperors Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; ; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through cursus honorum, the ...
and his son Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname Caracalla (; ), was Roman emperor from 198 to 217 AD, first serving as nominal co-emperor under his father and then r ...
(fully ''Marcus Aurelius Antoninus''), for which there is another, smaller inscription on the architrave of the façade, under the aforementioned larger text. This now-barely legible inscription reads:
:IMP · CAES · L · SEPTIMIVS · SEVERVS · PIVS · PERTINAX · ARABICVS · ADIABENICVS · PARTHICVS · MAXIMVS · PONTIF · MAX · TRIB · POTEST · X · IMP · XI · COS · III · P · P · PROCOS ET
:IMP · CAES · M · AVRELIVS · ANTONINVS · PIVS · FELIX · AVG · TRIB · POTEST · V · COS · PROCOS · PANTHEVM · VETVSTATE · CORRVPTVM · CVM · OMNI · CVLTV · RESTITVERVNT
In English, this means:
:Emp rorCaes r L ciusSeptimius Severus Pius Pertinax, victorious in Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
, victor of Adiabene, the greatest victor in Parthia
Parthia ( ''Parθava''; ''Parθaw''; ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Medes during the 7th century BC, was incorporated into the subsequent Achaemeni ...
, Pontif xMax mus.html" ;"title="xMax[imus">xMax[imus 10 times tribune, 11 times proclaimed emperor, three times consul, Pater Patriae">P[aterP[atriae">mus">mus.html" ;"title="xMax[imus">xMax[imus 10 times tribune, 11 times proclaimed emperor, three times consul, Pater Patriae">P[aterP[atriae], proconsul, and
:Emp rorCaes rCaracalla, M rcusAurelius Antoninus Pius Felix Aug stus], five times tribune, consul, proconsul, have carefully restored the Pantheon ruined by age.
Medieval
 In 609, the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine emperor
In 609, the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine emperor Phocas
Phocas (; ; 5475 October 610) was Eastern Roman emperor from 602 to 610. Initially a middle-ranking officer in the East Roman army, Roman army, Phocas rose to prominence as a spokesman for dissatisfied soldiers in their disputes with the cour ...
gave the building to Pope Boniface IV, who converted it into a Christian church and consecrated it to St. Mary and the Martyrs on 13 May 609: "Another Pope, Boniface, asked the same mperor Phocas, in Constantinopleto order that in the old temple called the Pantheon, after the pagan filth was removed, a church should be made, to the holy virgin Mary and all the martyrs, so that the commemoration of the saints would take place henceforth where not gods but demons were formerly worshipped." Twenty-eight cartloads of holy relics of martyrs were said to have been removed from the catacombs
Catacombs are man-made underground passages primarily used for religious purposes, particularly for burial. Any chamber used as a burial place is considered a catacomb, although the word is most commonly associated with the Roman Empire.
Etym ...
and placed in a porphyry basin beneath the high altar. On its consecration, Boniface placed an icon of the Mother of God as ' Panagia Hodegetria' (All Holy Directress) within the new sanctuary.
The building's consecration as a church saved it from the abandonment, destruction, and the worst of the spoliation that befell the majority of ancient Rome's buildings during the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start o ...
. However, Paul the Deacon
Paul the Deacon ( 720s 13 April in 796, 797, 798, or 799 AD), also known as ''Paulus Diaconus'', ''Warnefridus'', ''Barnefridus'', or ''Winfridus'', and sometimes suffixed ''Cassinensis'' (''i.e.'' "of Monte Cassino"), was a Benedictine monk, sc ...
records the spoliation of the building by the Emperor Constans II, who visited Rome in July 663:
Remaining at Rome twelve days he pulled down everything that in ancient times had been made of metal for the ornament of the city, to such an extent that he even stripped off the roof of the church f the blessed Mary which at one time was called the Pantheon, and had been founded in honour of all the gods and was now by the consent of the former rulers the place of all the martyrs; and he took away from there the bronze tiles and sent them with all the other ornaments to Constantinople.Much fine external marble has been removed over the centuries – for example, capitals from some of the
pilaster
In architecture, a pilaster is both a load-bearing section of thickened wall or column integrated into a wall, and a purely decorative element in classical architecture which gives the appearance of a supporting column and articulates an ext ...
s are in the British Museum
The British Museum is a Museum, public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is the largest in the world. It documents the story of human cu ...
. Two columns were swallowed up in the medieval buildings that abutted the Pantheon on the east and were lost. In the early 17th century, Urban VIII Barberini tore away the bronze ceiling of the portico, and replaced the medieval campanile with the famous twin towers (often wrongly attributed to Bernini) called "the ass's ears", which were not removed until the late 19th century. The only other loss has been the external sculptures, which adorned the pediment
Pediments are a form of gable in classical architecture, usually of a triangular shape. Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the cornice (an elaborated lintel), or entablature if supported by columns.Summerson, 130 In an ...
above Agrippa's inscription. The marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is ty ...
interior has largely survived, although with extensive restoration.
Renaissance
Since the Renaissance the Pantheon has been the site of several important burials. Among those buried there are the paintersRaphael
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino (; March 28 or April 6, 1483April 6, 1520), now generally known in English as Raphael ( , ), was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. List of paintings by Raphael, His work is admired for its cl ...
and Annibale Carracci
Annibale Carracci ( , , ; November 3, 1560 – July 15, 1609) was an Italian painter and instructor, active in Bologna and later in Rome. Along with his brother Agostino Carracci, Agostino and cousin Ludovico Carracci, Ludovico (with whom the Ca ...
, the composer Arcangelo Corelli
Arcangelo Corelli (, also , ; ; 17 February 1653 – 8 January 1713) was an List of Italian composers, Italian composer and violinist of the middle Baroque music, Baroque era. His music was key in the development of the modern genres of Sonata a ...
, and the architect
An architect is a person who plans, designs, and oversees the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to provide services in connection with the design of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the buildings that h ...
Baldassare Peruzzi. In the 15th century, the Pantheon was adorned with paintings: the best-known is the ''Annunciation'' by Melozzo da Forlì
Melozzo da Forlì ( – 8 November 1494) was an Italian Renaissance painter and architect. His fresco paintings are notable for the use of foreshortening. He was the most important member of the Forlì painting school.
Biography
Melozzo was s ...
. Filippo Brunelleschi, among other architects, looked to the Pantheon as inspiration for their works.
Pope Urban VIII
Pope Urban VIII (; ; baptised 5 April 1568 – 29 July 1644), born Maffeo Vincenzo Barberini, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 6 August 1623 to his death, in July 1644. As pope, he expanded the papal terri ...
(1623 to 1644) ordered the bronze ceiling of the Pantheon's portico melted down. Most of the bronze was used to make bombards for the fortification of Castel Sant'Angelo, with the rest used by the Apostolic Camera for other works. It is also said that the bronze was used by Bernini in creating his famous baldachin above the high altar
An altar is a table or platform for the presentation of religion, religious offerings, for sacrifices, or for other ritualistic purposes. Altars are found at shrines, temples, Church (building), churches, and other places of worship. They are use ...
of St. Peter's Basilica, though the archaeologist Carlo Fea discovered from the Pope's accounts that about 90% of the bronze was used for the cannon, and that the bronze for the baldachin came from Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
. Concerning this, an anonymous contemporary Roman satirist quipped in a pasquinade (a publicly posted poem) that ''quod non fecerunt barbari fecerunt Barberini'' ("What the barbarians did not do the Barberinis rban VIII's family namedid").
In 1747, the broad frieze below the dome with its false windows was "restored," but bore little resemblance to the original. In the early decades of the 20th century, a piece of the original, as far as could be reconstructed from Renaissance drawings and paintings, was recreated in one of the panels.
Modern
Two monarchs of theKingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
are buried in the Pantheon: King Vittorio Emanuele II and King Umberto I, as well as Umberto's Queen Consort
A queen consort is the wife of a reigning king, and usually shares her spouse's social Imperial, royal and noble ranks, rank and status. She holds the feminine equivalent of the king's monarchical titles and may be crowned and anointed, but hi ...
, Margherita. It was supposed to be the final resting place for the Monarchs of Italy of the House of Savoy
The House of Savoy (, ) is a royal house (formally a dynasty) of Franco-Italian origin that was established in 1003 in the historical region of Savoy, which was originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy and now lies mostly within southeastern F ...
, but the Monarchy was abolished in June 1946 and the authorities have refused to grant a burial to the former kings who died in exile ( King Vittorio Emanuele III and King Umberto II). The National Institute for the Honour Guard of the Royal Tombs of the Pantheon, which was originally chartered by the House of Savoy
The House of Savoy (, ) is a royal house (formally a dynasty) of Franco-Italian origin that was established in 1003 in the historical region of Savoy, which was originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy and now lies mostly within southeastern F ...
, and has subsequently operated with the authorisation of the Italian Republic, mounts a guard of honour
A guard of honour (Commonwealth English), honor guard (American English) or ceremonial guard, is a group of people, typically drawn from the military, appointed to perform ceremonial duties – for example, to receive or guard a head of state ...
in front of the Royal tombs.
The Pantheon is in use as a Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
church, and as such, visitors are asked to keep an appropriate level of deference. Masses are celebrated there on Sundays and holy days of obligation. Weddings are also held there from time to time.
Structure
Portico

 The building was originally approached by a flight of steps. Later construction raised the level of the ground leading to the portico, eliminating these steps.
The pediment was decorated with relief sculpture, probably of gilded bronze. Holes marking the location of clamps that held the sculpture suggest that its design was likely an eagle within a wreath; ribbons extended from the wreath into the corners of the pediment.
On the intermediate block between the portico and the rotunda, the remains of a second pediment suggests that the existing portico is much shorter than originally intended. A portico aligned with the second pediment would fit columns with shafts 50 Roman feet (14.8 metres) tall and capitals 10 Roman feet tall (3 metres), whereas the existing portico has shafts 40 Roman feet (11.9 metres) tall and capitals eight Roman feet (2.4 metres) tall., pp. 199–206
Mark Wilson Jones has attempted to explain the design adjustments by suggesting that, once the higher pediment had been constructed, the required 50-foot columns failed to arrive (possibly as a result of logistical difficulties). The builders then had to make some awkward adjustments to fit the shorter columns and pediments. Rabun Taylor has noted that, even if the taller columns were delivered, basic construction constraints may have prevented their use. Assuming that each column would first be laid on the floor next to its pediment before being pivoted upright (using something like an
The building was originally approached by a flight of steps. Later construction raised the level of the ground leading to the portico, eliminating these steps.
The pediment was decorated with relief sculpture, probably of gilded bronze. Holes marking the location of clamps that held the sculpture suggest that its design was likely an eagle within a wreath; ribbons extended from the wreath into the corners of the pediment.
On the intermediate block between the portico and the rotunda, the remains of a second pediment suggests that the existing portico is much shorter than originally intended. A portico aligned with the second pediment would fit columns with shafts 50 Roman feet (14.8 metres) tall and capitals 10 Roman feet tall (3 metres), whereas the existing portico has shafts 40 Roman feet (11.9 metres) tall and capitals eight Roman feet (2.4 metres) tall., pp. 199–206
Mark Wilson Jones has attempted to explain the design adjustments by suggesting that, once the higher pediment had been constructed, the required 50-foot columns failed to arrive (possibly as a result of logistical difficulties). The builders then had to make some awkward adjustments to fit the shorter columns and pediments. Rabun Taylor has noted that, even if the taller columns were delivered, basic construction constraints may have prevented their use. Assuming that each column would first be laid on the floor next to its pediment before being pivoted upright (using something like an A-frame
An A-frame is a basic structure designed to bear a Structural load, load in a lightweight economical manner. The simplest form of an A-frame is two similarly sized Beam (structure), beams, arranged in an angle of 45 degrees or less, attached a ...
), there would be a space requirement of a column-length on one side of the pediment, and at least a column-length on the opposite side for the pivoting equipment and ropes. With 50-foot columns, "there was no way to sequence the erection of he columnswithout creating a hopeless snarl. The shafts were simply too long to be positioned on the floor in a workable configuration, regardless of sequence." Specifically, the innermost row of columns would be blocked by the main body of the temple, and in the later stages of construction some already-erected columns would inevitably obstruct the erection of further columns.
It has also been argued that the scale of the portico was related to the urban design of the space in front of the temple.
The grey granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
columns that were used in the Pantheon's pronaos were quarried in Egypt at Mons Claudianus in the eastern mountains. Each was tall, in diameter, and in weight. These were dragged more than from the quarry to the river on wooden sledges. They were floated by barge down the Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
when the water level was high during the spring floods, and then transferred to vessels to cross the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
to the Roman port of Ostia. There, they were transferred back onto barges and pulled up the Tiber River
The Tiber ( ; ; ) is the List of rivers of Italy, third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the R ...
to Rome. After being unloaded near the Mausoleum of Augustus, the site of the Pantheon was still about 700 metres away. Thus, it was necessary to either drag them or to move them on rollers to the construction site.
In the walls at the back of the Pantheon's portico are two huge niches, perhaps intended for statues of Augustus Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
and Agrippa.
The large bronze doors to the cella, measuring wide by high, are the oldest in Rome. These were thought to be a 15th-century replacement for the original, mainly because they were deemed by contemporary architects to be too small for the door frames. Later analysis of the fusion technique confirmed that these are the original Roman doors, a rare example of Roman monumental bronze surviving, despite cleaning and the application of Christian motifs over the centuries.
Rotunda
pumice
Pumice (), called pumicite in its powdered or dust form, is a volcanic rock that consists of extremely vesicular rough-textured volcanic glass, which may or may not contain crystals. It is typically light-colored. Scoria is another vesicula ...
, both porous light stones. At the very top, where the dome would be at its weakest and vulnerable to collapse, the oculus lightens the load.
No tensile test results are available on the concrete used in the Pantheon; however, Cowan discussed tests on ancient concrete from Roman ruins in Libya, which gave a compressive strength of . An empirical relationship gives a tensile strength of for this specimen. Finite element analysis of the structure by Mark and Hutchison found a maximum tensile stress of only at the point where the dome joins the raised outer wall.
The stresses in the dome were found to be substantially reduced by the use of successively less dense aggregate stones, such as small pots or pieces of pumice, in higher layers of the dome. Mark and Hutchison estimated that, if normal weight concrete had been used throughout, the stresses in the arch would have been some 80% greater. Hidden chambers engineered within the rotunda form a sophisticated structural system. This reduced the weight of the roof, as did the oculus eliminating the apex.
The top of the rotunda wall features a series of brick relieving arches, visible on the outside and built into the mass of the brickwork. The Pantheon is full of such devices – for example, there are relieving arches over the recesses inside – but all these arches were hidden by marble facing on the interior and possibly by stone revetment or stucco on the exterior.
The height to the oculus and the diameter of the interior circle are the same, , so the whole interior would fit exactly within a cube (or, a 43.3-m sphere could fit within the interior). These dimensions make more sense when expressed in ancient Roman units of measurement
The units of measurement of ancient Rome were generally consistent and well documented.
Length
The basic unit of Roman linear measurement was the ''pes'' (plural: ''pedes'') or Roman foot. Investigation of its relation to the English foot goes ...
: The dome spans 150 Roman feet; the oculus is 30 Roman feet in diameter; the doorway is 40 Roman feet high. The Pantheon still holds the record for the world's largest unreinforced concrete dome. It is also substantially larger than earlier domes. It is the only masonry dome to not require reinforcement. All other extant ancient domes were either designed with tie-rods, chains and banding or have been retrofitted with such devices to prevent collapse.
Though often drawn as a free-standing building, there was a building at its rear which abutted it. While this building helped buttress the rotunda, there was no interior passage from one to the other.
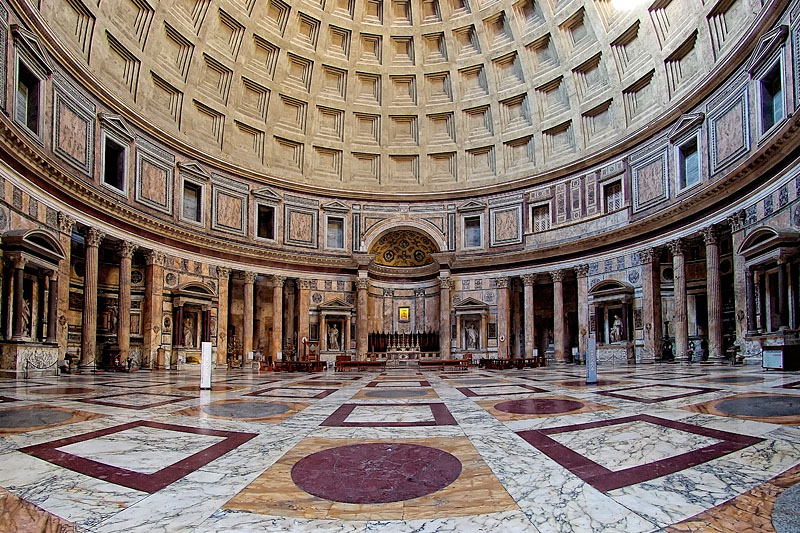
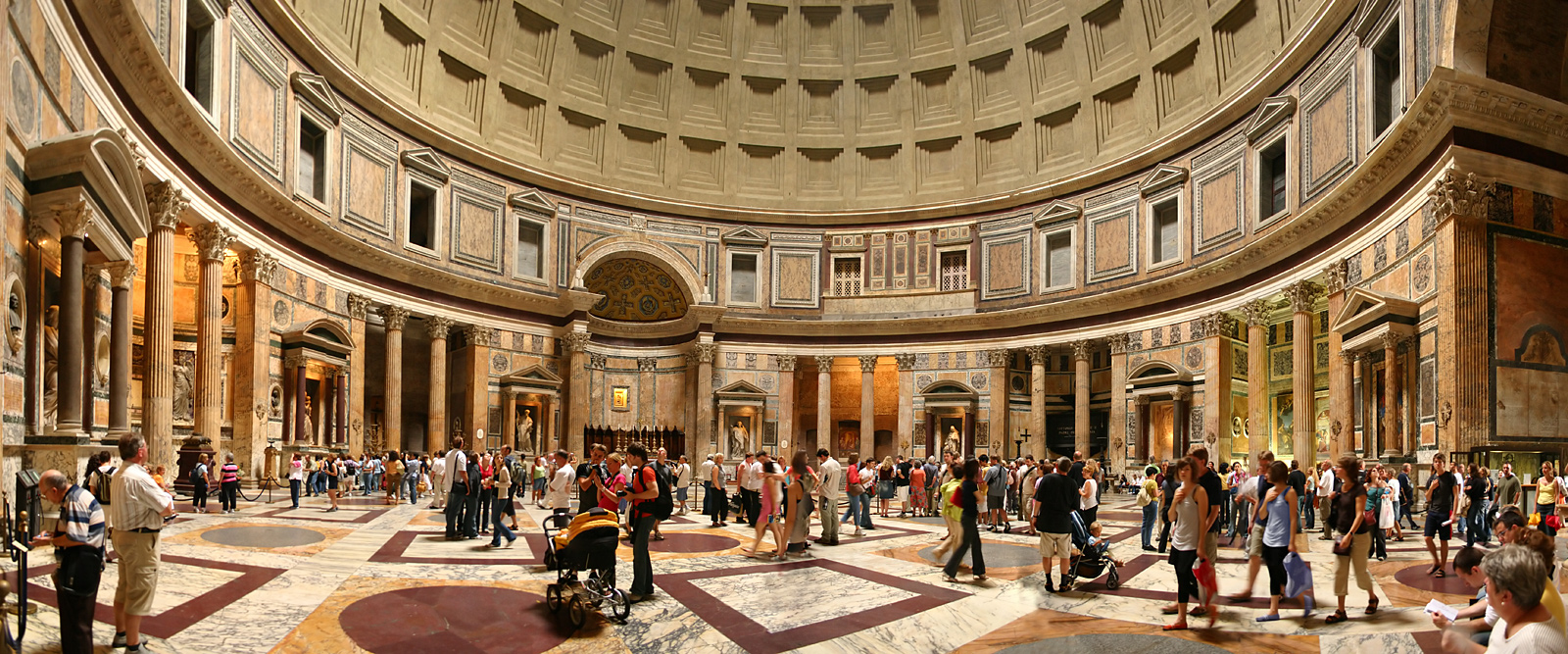
Interior
Upon entry, visitors are greeted by an enormous rounded room covered by the dome. The oculus at the top of the dome was never covered, allowing rainfall through the ceiling and onto the floor. Because of this, the interior floor is equipped with drains and has been built with an incline of about to promote water runoff. The interior of the dome was possibly intended to symbolize the arched vault of the heavens. The oculus at the dome's apex and the entry door are the only natural sources of light in the interior. Throughout the day, light from the oculus moves around this space in a reversesundial
A sundial is a horology, horological device that tells the time of day (referred to as civil time in modern usage) when direct sunlight shines by the position of the Sun, apparent position of the Sun in the sky. In the narrowest sense of the ...
effect: marking time with light rather than shadow. The oculus also offers cooling and ventilation; during storms, a drainage system below the floor handles rain falling through the oculus. On Pentecost
Pentecost (also called Whit Sunday, Whitsunday or Whitsun) is a Christianity, Christian holiday which takes place on the 49th day (50th day when inclusive counting is used) after Easter Day, Easter. It commemorates the descent of the Holy Spiri ...
, huge quantities of red rose
A rose is either a woody perennial plant, perennial flowering plant of the genus ''Rosa'' (), in the family Rosaceae (), or the flower it bears. There are over three hundred Rose species, species and Garden roses, tens of thousands of cultivar ...
petals are thrown through the oculus by firefighters of the Vigili del Fuoco on the roof.
The dome features sunken panels ( coffers), in five rings of 28. This evenly spaced layout was difficult to achieve and, it is presumed, had symbolic meaning, either numerical, geometric, or lunar. In antiquity, the coffers may have contained bronze rosettes symbolising the starry firmament.
Circles and squares form the unifying theme of the interior design. The checkerboard floor pattern contrasts with the concentric circles of square coffers in the dome. Each zone of the interior, from floor to ceiling, is subdivided according to a different scheme. As a result, the interior decorative zones do not line up. The overall effect is immediate viewer orientation according to the major axis of the building, even though the cylindrical space topped by a hemispherical dome is inherently ambiguous. This discordance has not always been appreciated, and the attic level was redone according to Neoclassical taste in the 18th century.

Catholic additions

 The present high altars and the apses were commissioned by Pope Clement XI (1700–1721) and designed by Alessandro Specchi. Enshrined on the apse above the high altar is a 7th-century Byzantine icon of the Virgin and Child, given by Phocas to Pope Boniface IV on the occasion of the dedication of the Pantheon for Christian worship on 13 May 609. The choir was added in 1840, and was designed by Luigi Poletti.
The first niche to the right of the entrance holds a '' Madonna of the Girdle and St Nicholas of Bari'' (1686) painted by an unknown artist. The first chapel on the right, the Chapel of the Annunciation, has a fresco of the ''Annunciation'' attributed to
The present high altars and the apses were commissioned by Pope Clement XI (1700–1721) and designed by Alessandro Specchi. Enshrined on the apse above the high altar is a 7th-century Byzantine icon of the Virgin and Child, given by Phocas to Pope Boniface IV on the occasion of the dedication of the Pantheon for Christian worship on 13 May 609. The choir was added in 1840, and was designed by Luigi Poletti.
The first niche to the right of the entrance holds a '' Madonna of the Girdle and St Nicholas of Bari'' (1686) painted by an unknown artist. The first chapel on the right, the Chapel of the Annunciation, has a fresco of the ''Annunciation'' attributed to Melozzo da Forlì
Melozzo da Forlì ( – 8 November 1494) was an Italian Renaissance painter and architect. His fresco paintings are notable for the use of foreshortening. He was the most important member of the Forlì painting school.
Biography
Melozzo was s ...
. On the left side is a canvas by Clement Maioli of ''St Lawrence and St Agnes'' (1645–1650). On the right wall is the ''Incredulity of St Thomas'' (1633) by Pietro Paolo Bonzi.
The second niche has a 15th-century fresco of the Tuscan school, depicting the ''Coronation of the Virgin''. In the second chapel is the tomb of King Victor Emmanuel II (died 1878). It was originally dedicated to the Holy Spirit
The Holy Spirit, otherwise known as the Holy Ghost, is a concept within the Abrahamic religions. In Judaism, the Holy Spirit is understood as the divine quality or force of God manifesting in the world, particularly in acts of prophecy, creati ...
. A competition was held to decide which architect should design it. Giuseppe Sacconi participated, but lost – he would later design the tomb of Umberto I in the opposite chapel.
Manfredo Manfredi won the competition, and started work in 1885. The tomb consists of a large bronze plaque surmounted by a Roman eagle and the arms of the house of Savoy
The House of Savoy (, ) is a royal house (formally a dynasty) of Franco-Italian origin that was established in 1003 in the historical region of Savoy, which was originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy and now lies mostly within southeastern F ...
. The golden lamp above the tomb burns in honor of Victor Emmanuel III
Victor Emmanuel III (; 11 November 1869 – 28 December 1947) was King of Italy from 29 July 1900 until his abdication on 9 May 1946. A member of the House of Savoy, he also reigned as Emperor of Ethiopia from 1936 to 1941 and King of the Albani ...
, who died in exile in 1947.
The third niche has a sculpture by Il Lorenzone of ''St Anne and the Blessed Virgin''. In the third chapel is a 15th-century painting of the Umbrian school, ''The Madonna of Mercy between St Francis and St John the Baptist''. It is also known as the Madonna of the Railing, because it originally hung in the niche on the left-hand side of the portico, where it was protected by a railing. It was moved to the ''Chapel of the Annunciation'', and then to its present position sometime after 1837. The bronze epigram commemorated Pope Clement XI's restoration of the sanctuary. On the right wall is the canvas ''Emperor Phocas presenting the Pantheon to Pope Boniface IV'' (1750) by an unknown. There are three memorial plaques in the floor, one conmmemorating a Gismonda written in the vernacular. The final niche on the right side has a statue of ''St. Anastasius'' (''Sant'Anastasio'') (1725) by Bernardino Cametti.
On the first niche to the left of the entrance is an ''Assumption'' (1638) by Andrea Camassei. The first chapel on the left, the Chapel of St Joseph in the Holy Land, is the chapel of the Confraternity of the , a confraternity
A confraternity (; ) is generally a Christian voluntary association of laypeople created for the purpose of promoting special works of Christian charity or piety, and approved by the Church hierarchy. They are most common among Catholics, Lu ...
of artists and musicians formed by a 16th-century canon, Desiderio da Segni, to ensure that worship was maintained in the chapel.
The first members were, among others, Antonio da Sangallo the younger, Jacopo Meneghino, Giovanni Mangone, Zuccari, Domenico Beccafumi, and Flaminio Vacca. The confraternity continued to draw members from the elite of Rome's artists and architects, and among later members we find Bernini, Cortona
Cortona (, ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Arezzo, in Tuscany, Italy. It is the main cultural and artistic centre of the Val di Chiana after Arezzo.
Toponymy
Cortona is derived from Latin Cortōna, and from Etruscan language, Etr ...
, Algardi, and many others. The institution still exists, and is now called the ''Academia Ponteficia di Belle Arti'' (The Pontifical Academy of Fine Arts), based in the palace of the Cancelleria. The altar in the chapel is covered with false marble. On the altar is a statue of ''St Joseph and the Holy Child'' by Vincenzo de' Rossi.
To the sides are paintings (1661) by Francesco Cozza, one of the Virtuosi: ''Adoration of the Shepherds'' on left side and ''Adoration of the Magi'' on right. The stucco relief on the left, ''Dream of St Joseph'', is by Paolo Benaglia, and the one on the right, ''Rest during the flight from Egypt'', is by Carlo Monaldi. On the vault are several 17th-century canvases, from left to right: ''Cumean Sibyl'' by Ludovico Gimignani; Moses by Francesco Rosa; ''Eternal Father'' by Giovanni Peruzzini; ''David'' by Luigi Garzi
Luigi Garzi (1638–1721) was an Italian painter of the Baroque period whose style was strongly influenced by the work of the Bolognese painter Guido Reni.
Biography
He was born in Pistoia. He started learning from a poorly known landscape paint ...
; and ''Eritrean Sibyl'' by Giovanni Andrea Carlone.
The second niche has a statue of ''St Agnes'', by Vincenzo Felici. The bust on the left is a portrait of Baldassare Peruzzi, derived from a plaster portrait by Giovanni Duprè. The tomb of King Umberto I and his wife Margherita di Savoia is in the next chapel. The chapel was originally dedicated to St Michael the Archangel, and then to St. Thomas the Apostle. The present design is by Giuseppe Sacconi, completed after his death by his pupil Guido Cirilli. The tomb consists of a slab of alabaster mounted in gilded bronze. The frieze has allegorical representations of ''Generosity'', by Eugenio Maccagnani, and ''Munificence'', by Arnaldo Zocchi. The royal tombs are maintained by the National Institute of Honour Guards to the Royal Tombs, founded in 1878. They also organize picket guards at the tombs. The altar with the royal arms is by Cirilli.
The third niche holds the mortal remains – his Ossa et cineres, "Bones and ashes", as the inscription on the sarcophagus says – of the great artist Raphael
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino (; March 28 or April 6, 1483April 6, 1520), now generally known in English as Raphael ( , ), was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. List of paintings by Raphael, His work is admired for its cl ...
. His fiancée, Maria Bibbiena is buried to the right of his sarcophagus; she died before they could marry. The sarcophagus was given by Pope Gregory XVI
Pope Gregory XVI (; ; born Bartolomeo Alberto Cappellari; 18 September 1765 – 1 June 1846) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 2 February 1831 to his death in June 1846. He had adopted the name Mauro upon enteri ...
, and its inscription reads ''ILLE HIC EST RAPHAEL TIMUIT QUO SOSPITE VINCI / RERUM MAGNA PARENS ET MORIENTE MORI'', meaning "Here lies Raphael, by whom the great mother of all things (Nature) feared to be overcome while he was living, and while he was dying, herself to die". The epigraph was written by Pietro Bembo
Pietro Bembo, (; 20 May 1470 – 18 January 1547) was a Venetian scholar, poet, and literary theory, literary theorist who also was a member of the Knights Hospitaller and a cardinal of the Catholic Church. As an intellectual of the Italian Re ...
.
The present arrangement is from 1811, designed by Antonio Muñoz. The bust of Raphael (1833) is by Giuseppe Fabris. The two plaques commemorate Maria Bibbiena and Annibale Carracci
Annibale Carracci ( , , ; November 3, 1560 – July 15, 1609) was an Italian painter and instructor, active in Bologna and later in Rome. Along with his brother Agostino Carracci, Agostino and cousin Ludovico Carracci, Ludovico (with whom the Ca ...
. Behind the tomb is the statue known as the ''Madonna del Sasso'' (Madonna of the Rock) so named because she rests one foot on a boulder. It was commissioned by Raphael and made by Lorenzetto in 1524.
In the Chapel of the Crucifixion, the Roman brick wall is visible in the niches. The wooden crucifix on the altar is from the 15th century. On the left wall is a ''Descent of the Holy Ghost'' (1790) by Pietro Labruzi. On the right side is the low relief ''Cardinal Consalvi presents to Pope Pius VII the five provinces restored to the Holy See'' (1824) made by the Danish sculptor Bertel Thorvaldsen. The bust is a portrait of Cardinal Agostino Rivarola. The final niche on this side has a statue of ''St. Evasius'' (''Sant'Evasio'') (1727) by Francesco Moderati.
Gallery
fisheye lens
A fisheye lens is an ultra wide angle lens, ultra wide-angle lens that produces strong Distortion (optics), visual distortion intended to create a wide panorama, panoramic or Sphere#Hemisphere, hemispherical image. Fisheye lenses achieve extremel ...
in 2016
File:Pantheon 0918 2013.jpg, Pantheon 2013
File:Pantheon 0935 2013.jpg, Tomb of King Victor Emmanuel II, "Father of the Country"
File:Rome Pantheon 2020 P05.jpg, The icon of the Madonna which was given by Phocas to Pope Boniface IV
File:2025-03-09 Rome Pantheon.jpg, Exterior
Cardinal deaconry
On 23 July 1725, the Pantheon was established as Cardinal-deaconry of S. Maria ad Martyres, i.e. a titular church for a cardinal-deacon. On 26 May 1929, this deaconry was suppressed to establish the Cardinal Deaconry of S. Apollinare alle Terme Neroniane-Alessandrine. The following cardinals were cardinal deacons of Santa Maria ad Martyres : * Nicola del Giudice 1725–1743 * Alessandro Albani 1743–1747 * Carlo Maria Sacripante 1747–1751 * Mario Bolognetti 1751–1756 * Prospero Colonna di Sciarra 1756–1763 * Domenico Orsini d'Aragona 1763–1777 * Antonio Casali 1777–1787 * Ignazio Boncompagni-Ludovisi 1787–1789 * Antonio Doria Pamphili 1789–1800 * Romoaldo Braschi-Onesti 1800–1817 * Ercole Consalvi 1817–1824 * Stanislao Sanseverino 1825–1826 * Agostino Rivarola 1826–1842 * Adriano Fieschi 1843–1853 * Vincenzo Santucci 1854–1861 * Roberto Roberti 1863–1867 * Gaspare Grassellini 1867–1875 * Enea Sbarretti 1877–1884 * Carmine Gori-Merosi 1884–1886 * Luigi Pallotti 1887–1890 * ''vacant'' (1890–1901) * Felice Cavagnis 1901–1906 * ''vacant'' (1906–1929)Influence on architecture
The Pantheon remains the largestdome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a m ...
constructed by concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of aggregate bound together with a fluid cement that cures to a solid over time. It is the second-most-used substance (after water), the most–widely used building material, and the most-manufactur ...
that is not reinforced. As the best-preserved example of an Ancient Roman monumental building, the Pantheon has been enormously influential in Western architecture from at least the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
. Starting with Brunelleschi
Filippo di ser Brunellesco di Lippo Lapi (1377 – 15 April 1446), commonly known as Filippo Brunelleschi ( ; ) and also nicknamed Pippo by Leon Battista Alberti, was an Italian architect, designer, goldsmith and sculptor. He is considered to ...
's dome of Santa Maria del Fiore in Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
, completed in 1436. Among the most notable versions are the church of Santa Maria Assunta (1664) in Ariccia by Gian Lorenzo Bernini
Gian Lorenzo (or Gianlorenzo) Bernini (, ; ; Italian Giovanni Lorenzo; 7 December 1598 – 28 November 1680) was an Italians, Italian sculptor and Italian architect, architect. While a major figure in the world of architecture, he was more prom ...
, which followed his work restoring the Roman original.Summerson (1980) 38–39 The 1774 Belle Isle House in England is also considered to be a version of the Pantheon. Other domes inspired by the Pantheon include the Rotunda of Mosta in Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
(1833).
The portico-and-dome form of the Pantheon can be detected in many buildings of the 19th and 20th centuries, including government and public buildings, city hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or municipal hall (in the Philippines) is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses the city o ...
s, university
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
buildings, and public libraries. The Rotunda built in the 19th century as library at the University of Virginia
The University of Virginia (UVA) is a Public university#United States, public research university in Charlottesville, Virginia, United States. It was founded in 1819 by Thomas Jefferson and contains his The Lawn, Academical Village, a World H ...
was constructed so that students of architecture could learn from it. Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
relied on paintings by Andrea Palladio of the Pantheon. The 1824 Henriette Wegner Pavilion in Oslo
Oslo ( or ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of 1,064,235 in 2022 ...
's famous Frogner Park features a painted miniature copy of the Pantheon dome. The architect Carl Ludvig Engel also took influences from the structure of the Pantheon for the 1837 Nokia Church. Other notable replicas, such as The Rotunda gallery that opened 1818 in New York City, have not survived. The Pantheon's dome was also an inspiration for the '' Volkshalle'', an assembly hall planned but never built by the Nazi German
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a totalitarian dictat ...
architect Albert Speer
Berthold Konrad Hermann Albert Speer (; ; 19 March 1905 – 1 September 1981) was a German architect who served as Reich Ministry of Armaments and War Production, Minister of Armaments and War Production in Nazi Germany during most of W ...
for Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
's intended rebuilding of Berlin as "Germania
Germania ( ; ), also more specifically called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman provinces of Germania Inferior and Germania Superio ...
".
See also
*Romanian Athenaeum
The Romanian Athenaeum () is a concert hall in the center of Bucharest, Romania, and a landmark of the Romanian capital city. Opened in 1888, the ornate, domed, circular building is the city's most prestigious concert hall and home of the "Geor ...
* Panthéon, Paris
* Pantheon, Moscow (never built)
* Manchester Central Library
* The Rotunda (University of Virginia), United States
General:
* List of Roman domes
This is a list of Roman domes. The Romans were the first builders in the history of architecture
The history of architecture traces the changes in architecture through various traditions, regions, overarching stylistic trends, and dates. ...
* History of Roman and Byzantine domes
* List of largest domes
* List of tourist attractions in Rome
Notes
Footnotes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Summerson, John (1980), '' The Classical Language of Architecture'', 1980 edition, Thames and Hudson ''World of Art'' series, * *External links
Official webpage from Vicariate of Rome website
(archived 16 September 2015)
"Beggar's Rome"
– A self-directed virtual tour of St. Maria ad Martyres (Pantheon) and other Roman churches
Live streaming Video of the Pantheon
Virtual Panorama and photo gallery
article in Platner's ''Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome''
Pantheon Rome vs Pantheon Paris
.
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20080315223914/http://www.greatbuildings.com/buildings/Pantheon.html Pantheonat Great Buildings/Architecture Week website (archived 15 March 2008)
Art & History Pantheon
.
Summer solstice at the Pantheon
(archived 15 July 2011) *
Video Introduction to the Pantheon
Panoramic Virtual Tour inside the Pantheon
* High-resolution 360° Panoramas and Images o
Pantheon, Art Atlas
audio guide Pantheon Rome
* * * {{Authority control 126 120s establishments in the Roman Empire 2nd-century religious buildings and structures 7th-century churches in Italy Basilica churches in Rome Temples in the Campus Martius Ancient Roman buildings and structures in Rome Concrete shell structures Church buildings with domes Round churches Conversion of non-Christian religious buildings and structures into churches Tourist attractions in Rome Rome R. IX Pigna Centralized-plan churches in Italy Hadrian Roman temples by deity Buildings converted to Catholic church buildings Burial sites of the House of Savoy Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa Burned buildings and structures in Italy Rotundas in Europe