Pannonia (Byzantine Province) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
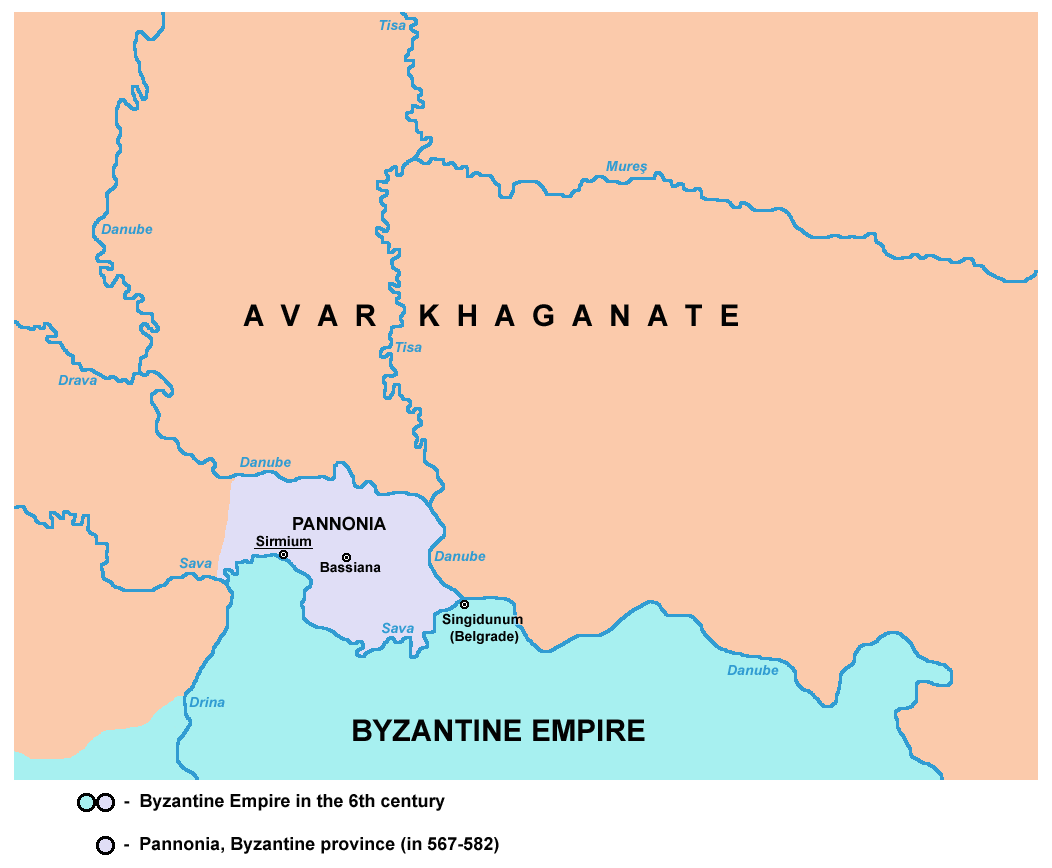 Pannonia was a
Pannonia was a
 Pannonia was a
Pannonia was a Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
province, which existed in present-day Syrmia
Syrmia ( sh, Srem/Срем or sh, Srijem/Сријем, label=none) is a region of the southern Pannonian Plain, which lies between the Danube and Sava rivers. It is divided between Serbia and Croatia. Most of the region is flat, with the exce ...
region of Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Bas ...
in the 6th century. Its capital was Sirmium
Sirmium was a city in the Roman province of Pannonia, located on the Sava river, on the site of modern Sremska Mitrovica in the Vojvodina autonomous provice of Serbia. First mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by Illyrians an ...
(modern-day Sremska Mitrovica
Sremska Mitrovica (; sr-Cyrl, Сремска Митровица, hu, Szávaszentdemeter, la, Sirmium) is a city and the administrative center of the Srem District in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. It is situated on the left bank ...
).
It differed significantly in its area from the Roman province of Pannonia, and it was subordinate to the Diocese of Dacia
The Diocese of Dacia ( la, Dioecesis Daciae) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, in the area of modern western Bulgaria, central Serbia, Montenegro, northern Albania and northern North Macedonia. It was subordinate to the Praetorian prefectu ...
.
Geography
The province was located between theDanube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
river in the north-east and Sava
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally th ...
river in the south. The western border of Byzantine Pannonia stretched approximately to the estuary or river Drina
The Drina ( sr-Cyrl, Дрина, ) is a long Balkans river, which forms a large portion of the border between Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia. It is the longest tributary of the Sava River and the longest karst river in the Dinaric Alps whic ...
into Sava. Important cities in the area were Sirmium
Sirmium was a city in the Roman province of Pannonia, located on the Sava river, on the site of modern Sremska Mitrovica in the Vojvodina autonomous provice of Serbia. First mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by Illyrians an ...
and Bassianae
Bassianae or Bassiana ( Serbian: ''Basijana'' or Басијана) was an important ancient Roman town in Pannonia (today Syrmia region in Vojvodina province, Serbia). It was located near present-day Donji Petrovci, a village in the Ruma municip ...
. Byzantine Pannonia bordered Byzantine province of Moesia Prima
Moesia Prima (; Latin: ''Moesia''; el, Μοισία) was a frontier province of the late Roman Empire, situated in the central parts of present-day Serbia, along the south bank of the Danube River. Provincial capital was Viminacium, near modern K ...
in the south and Avar Khaganate
The Pannonian Avars () were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in chronicles of Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai ( el, Βαρχονίτες, Varchonítes), or Pseudo-Avars ...
in the west, north and east.
History
Background
Byzantine Pannonia succeeded the name of much bigger classical Roman province ofPannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
. In other words, The Byzantine one covered only a small eastern part of ancient Roman Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
. In the 2nd century, the original Roman province was divided into two ones: Pannonia Inferior
Pannonia Inferior, lit. Lower Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sirmium. It was one of the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pannonia ...
and Pannonia Superior
Pannonia Superior, lit. Upper Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Carnuntum. It was one on the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pannon ...
. Subsequently, the area was subdivided into four provinces finally: Pannonia Prima
Pannonia Prima was an ancient Roman province. It was formed in the year 296, during the reign of Emperor Diocletian. Previously, it was a part of the province of Pannonia Superior, which, along with Pannonia Inferior, was gradually divided into ...
, Pannonia Valeria
The Pannonia Valeria or simply Valeria, also known as Pannonia Ripensis, was one of the provinces of the Roman Empire. It was formed in the year 296, during the reign of emperor Diocletian, in a division of Pannonia Inferior. The capital of the pr ...
, Pannonia Savia
Pannonia Savia or simply Savia, also known as Pannonia Ripariensis, was a Late Roman province. It was formed in the year 295, during the Tetrarchy reform of Roman emperor Diocletian, and assigned to the civil diocese of Pannonia, which was atta ...
and Pannonia Secunda
Pannonia Secunda was one of the provinces of the Roman Empire. It was formed in the year 296, during the reign of emperor Diocletian. The capital of the province was Sirmium (today Sremska Mitrovica). Pannonia Secunda included parts of present-day ...
. Capital of Pannonia Secunda was Sirmium
Sirmium was a city in the Roman province of Pannonia, located on the Sava river, on the site of modern Sremska Mitrovica in the Vojvodina autonomous provice of Serbia. First mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by Illyrians an ...
.
In the middle of the 5th century, the territory of former Roman Pannonia was ceded to the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
by Theodosius II
Theodosius II ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος, Theodosios; 10 April 401 – 28 July 450) was Roman emperor for most of his life, proclaimed ''Augustus (title), augustus'' as an infant in 402 and ruling as the eastern Empire's sole emperor after ...
, and after the death of Attila
Attila (, ; ), frequently called Attila the Hun, was the ruler of the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European traditio ...
it successively passed (entirely or partially) into the hands of the Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the larg ...
, Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 and ...
and Gepids
The Gepids, ( la, Gepidae, Gipedae, grc, Γήπαιδες) were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion a ...
.
A contract from 510 assigned most of the territory of former Roman Pannonia (including Sirmium
Sirmium was a city in the Roman province of Pannonia, located on the Sava river, on the site of modern Sremska Mitrovica in the Vojvodina autonomous provice of Serbia. First mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by Illyrians an ...
) to the Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the larg ...
, while the eastern part of present-day Syrmia
Syrmia ( sh, Srem/Срем or sh, Srijem/Сријем, label=none) is a region of the southern Pannonian Plain, which lies between the Danube and Sava rivers. It is divided between Serbia and Croatia. Most of the region is flat, with the exce ...
(which included the city of Bassianae
Bassianae or Bassiana ( Serbian: ''Basijana'' or Басијана) was an important ancient Roman town in Pannonia (today Syrmia region in Vojvodina province, Serbia). It was located near present-day Donji Petrovci, a village in the Ruma municip ...
) was assigned to the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. In 536, Sirmium was placed under the control of the Gepids
The Gepids, ( la, Gepidae, Gipedae, grc, Γήπαιδες) were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion a ...
. The Lombard–Gepid War (567)
In 566, Lombard king Alboin concluded a treaty with the Pannonian Avars, to whom he promised the Gepids' land if they defeated them. The Gepids were destroyed by the Avars and the Lombards in 567. Gepid King Cunimund was killed by Alboin himself. T ...
ended with a Lombard- Avar victory and annihilation of Gepids, while Sirmium was retaken by the Byzantine Empire.
Under the Byzantine Empire
From 567 to 573,Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
was in a war with the Avars, who aimed to conquer Byzantine Pannonia. Temporary truce was declared in 573, but the war was resumed. Due to the fact that Byzantine-Persian war also started in this time, the Byzantine Empire was not able to defend Pannonia. The city of Sirmium
Sirmium was a city in the Roman province of Pannonia, located on the Sava river, on the site of modern Sremska Mitrovica in the Vojvodina autonomous provice of Serbia. First mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by Illyrians an ...
was finally conquered by the Avars in 582, thus marking end of Roman control of Pannonia since Classical Antiquity.
Legacy
The Byzantine Empire re-established control over Pannonia in the 11th century, leading to the creation of theTheme of Sirmium
The Theme of Sirmium ( el, θέμα Σιρμίου) was a Byzantine administrative unit ( theme), which existed in present-day Serbia, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina in the 11th century. Its capital was Sirmium (today Sremska Mitrovica).
Backg ...
to administer the region, but not lasting long.
References
*Prof. Dr. Radmilo Petrović, Vojvodina - petnaest milenijuma kulturne istorije, Beograd, 2003. *Dr Petar Milošević, Arheologija i istorija Sirmijuma, Novi Sad, 2001.See also
*Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
*Pannonia Inferior
Pannonia Inferior, lit. Lower Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sirmium. It was one of the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pannonia ...
*Pannonia Secunda
Pannonia Secunda was one of the provinces of the Roman Empire. It was formed in the year 296, during the reign of emperor Diocletian. The capital of the province was Sirmium (today Sremska Mitrovica). Pannonia Secunda included parts of present-day ...
*Theme of Sirmium
The Theme of Sirmium ( el, θέμα Σιρμίου) was a Byzantine administrative unit ( theme), which existed in present-day Serbia, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina in the 11th century. Its capital was Sirmium (today Sremska Mitrovica).
Backg ...
*History of Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( Serbian: Војводина or ''Vojvodina''; hu, Vajdaság; sk, Vojvodina; ro, Voivodina; hr, Vojvodina; Rusyn: Войводина) is an autonomous province that comprises northern Serbia. It consists of the southern part of ...
*History of Serbia
The history of Serbia covers the historical development of Serbia and of its predecessor states, from the Early Stone Age to the present state, as well as that of the Serbian people and of the areas they ruled historically. Serbian habitation ...
{{Coord missing, Serbia
Provinces of the Byzantine Empire
6th century in Serbia
Byzantine Serbia
History of Syrmia
Medieval history of Vojvodina