Pancreatoblastoma on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
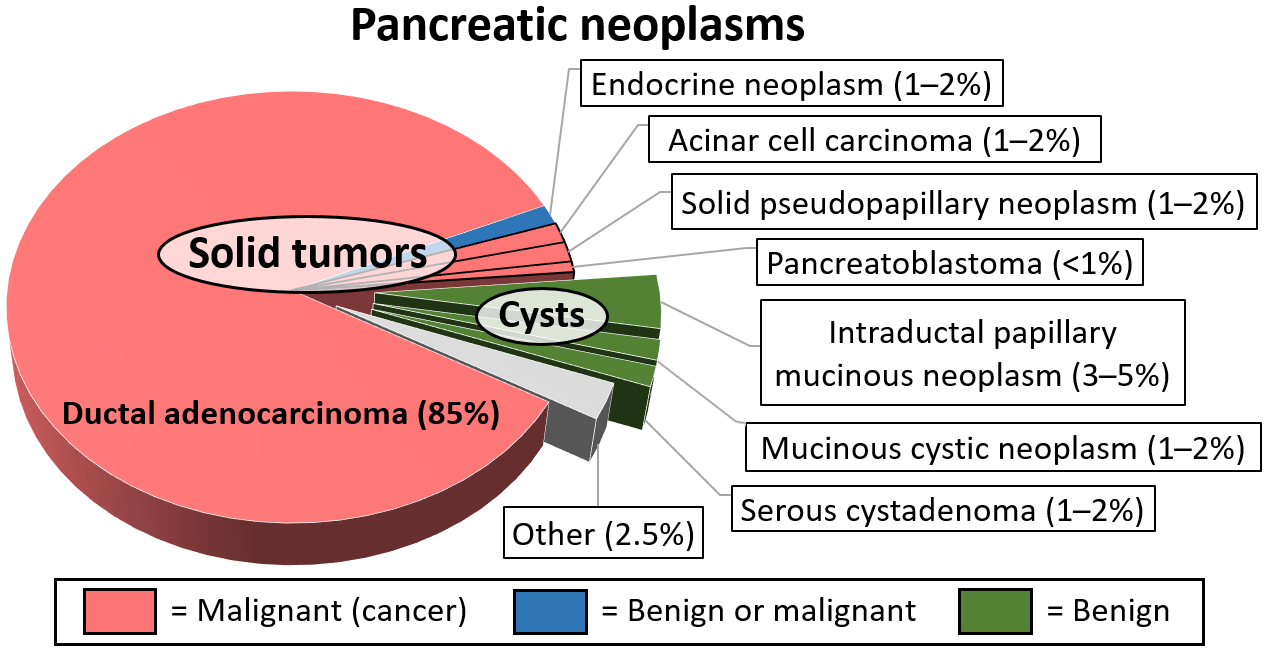 Pancreatoblastoma is a rare type of pancreatic cancer. It occurs mainly in childhood and has a relatively good prognosis.
Pancreatoblastoma is a rare type of pancreatic cancer. It occurs mainly in childhood and has a relatively good prognosis.
 Pancreatoblastoma is a rare type of pancreatic cancer. It occurs mainly in childhood and has a relatively good prognosis.
Pancreatoblastoma is a rare type of pancreatic cancer. It occurs mainly in childhood and has a relatively good prognosis.
Symptoms
Children with pancreatoblastoma rarely present with early-stage disease, instead, most present with locally advanced ormetastatic
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, ...
disease. Common presenting symptoms include abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a m ...
, emesis
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteriti ...
, and jaundice. A multidisciplinary approach
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several other fields like sociology, anthropology, psychology, ec ...
including good clinical history, state of the art imaging, and careful pathology is often needed to establish the correct diagnosis.
Pathology
Resected pancreatoblastomas can be quite large, ranging from 2 centimeters to 20 centimeters in size (1 to 8 inches). They are typically solid, soft masses. Under the microscope, at least two cell types are seen: cells with “acinar” differentiation, and cells forming small “squamoid” nests. The cells with acinar differentiation have some features of the normal acinar cell of the pancreas (the most common cell in the normal pancreas).Diagnosis
Treatment
If the tumor is operable, the first line of therapy should be surgical resection. Then, after surgical resection, adjuvant chemotherapy should be given, even in stage I disease. In patients with inoperable disease, chemotherapy alone should be given.http://www.orpha.net/data/patho/GB/uk-pancrea.pdf - A multi-disciplinary approach to the treatment, including surgeons, oncologists, pathologists, radiologists, and radiation oncologists, is often the best approach to managing these patients.See also
* Grayson GilbertReferences
External links
{{Soft tissue tumors and sarcomas Digestive system neoplasia Pancreas disorders Pancreatic cancer