Palace Of Sardar on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Palace of Sardar or Sardar Palace ( hy, Երեւանի սարդարի պալատ, az, Sərdər sarayı/سردر سارایی) is the former residence of Sardar, the ruler of the 
 The facade of the Mirror Hall of the palace was facing the Zange river (nowadays - Hrazdan). The walls of the hall were flush with the high steep wall above the river bank. To the left and to the right, the embankments rose from the crumbling clay walls of the Erivan fortress.
All the walls of the palace were covered with tiles with patterns and flowers. The walls between the tiles were covered with rough painting. In addition to the flowers, peacocks, lions and the sun were depicted there. The floor was glazed brick. The ceiling was covered with mirrors. There were also mirrors in the recesses along the walls and between the portraits.
The facade of the Mirror Hall of the palace was facing the Zange river (nowadays - Hrazdan). The walls of the hall were flush with the high steep wall above the river bank. To the left and to the right, the embankments rose from the crumbling clay walls of the Erivan fortress.
All the walls of the palace were covered with tiles with patterns and flowers. The walls between the tiles were covered with rough painting. In addition to the flowers, peacocks, lions and the sun were depicted there. The floor was glazed brick. The ceiling was covered with mirrors. There were also mirrors in the recesses along the walls and between the portraits.
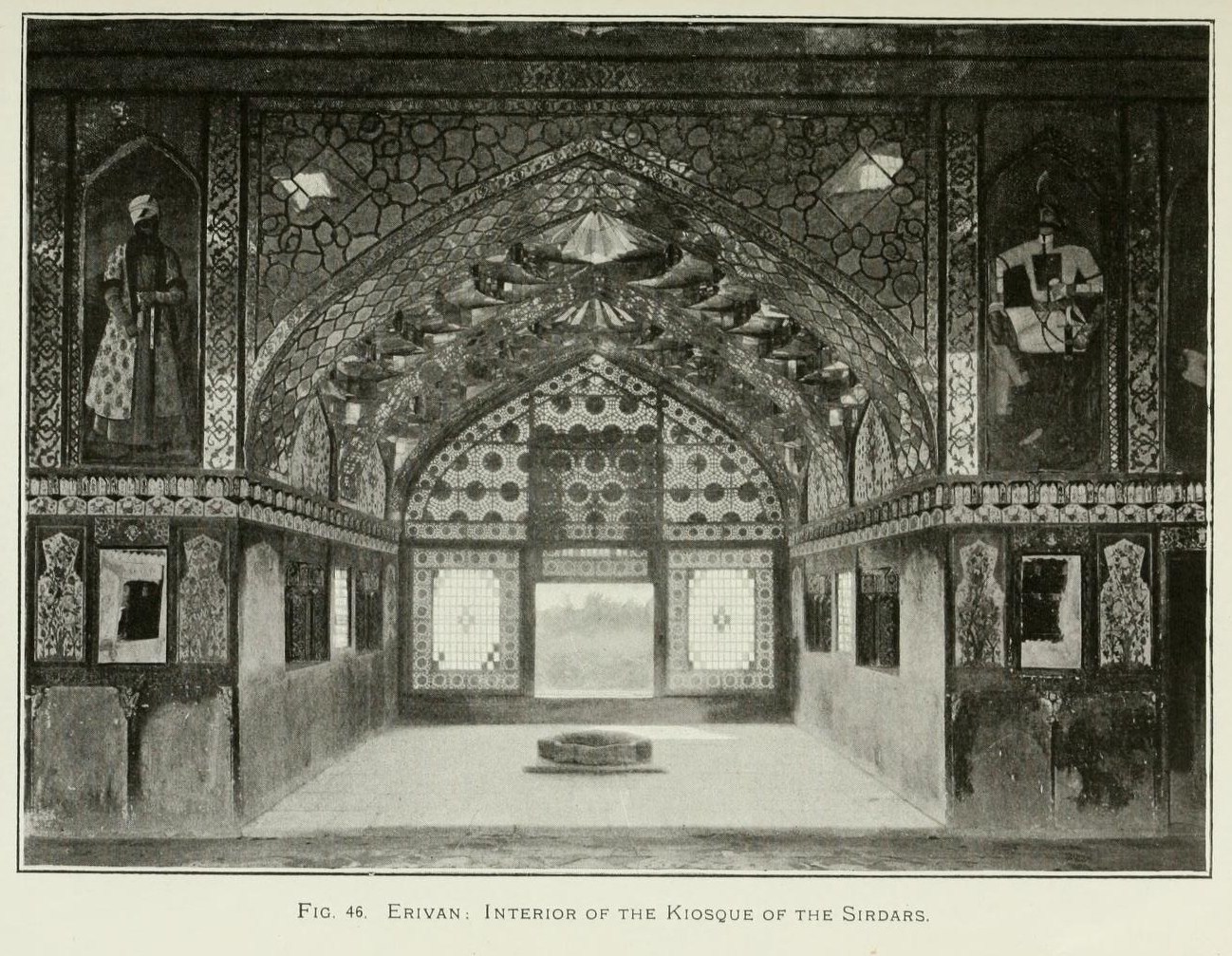 According to literary data, it is known that the Sardar Palace's walls of the Mirrored Hall were richly decorated with ornamental and thematic compositions. Scene murals were placed between the cornice and the ceiling of the palace, showing the legendary exploits of Rustam. On the first, Rustam hits a young warrior with a dagger, on the second he tears his clothes, learning that he has killed his son Zohrab; on the third – he pulls the enemy off the horse; on the fourth – he wins the diva and breaks his horns. According to the description of the eyewitnesses, in the palace, there was also depicted "a comic picture of an old man being kind to a young girl who serves him a glass of wine".
According to literary data, it is known that the Sardar Palace's walls of the Mirrored Hall were richly decorated with ornamental and thematic compositions. Scene murals were placed between the cornice and the ceiling of the palace, showing the legendary exploits of Rustam. On the first, Rustam hits a young warrior with a dagger, on the second he tears his clothes, learning that he has killed his son Zohrab; on the third – he pulls the enemy off the horse; on the fourth – he wins the diva and breaks his horns. According to the description of the eyewitnesses, in the palace, there was also depicted "a comic picture of an old man being kind to a young girl who serves him a glass of wine".
 In the 1850s, the Azerbaijani artist Mirza Kadym Erivani painted 4 large (1x2 m) oil portraits for the restored palace. In essence, these portraits made on canvas with oil paints were the first easel works in the Azerbaijani painting. The portraits were placed in the second niches' tier of the palace's large hall. With the complete destruction of the palace in 1914, these portraits were removed from the walls and can be currently found in the State Museum of Georgia. From the relatives' memoirs, it is known that in Mirza Kadim's room there were four more similar portraits depicting armed soldiers (it is assumed that these were the artist's versions of portraits of the sardars).
The portraits occupied a dominant place in the architectural decoration of the palace's interior. Here were portraits of Fatali Shah, his heir Abbas Mirza, Sardar Huseyn-Quli and his brother. Judging by the sketches of the Russian artists V. Moshkov and G. Gagarin, who visited this palace in the first half of the 19th century, and by to the descriptions of other travelers, these portraits were distinguished by their liveliness and great similarity, although in general, they also wore a decorative, somewhat a conditional character. There were eight large portraits in the Mirror Hall of the palace. Some of them had inscriptions in the Azerbaijani language.
The hall continued with a platform and a fountain in the middle, both marble paved. In the entire height of the site, from the side of the river, there was a huge wooden window with a frame of openwork with multi-colored glass inserted.
On the sides of the marble platform there were two small rooms and their doors opened onto the Hall of Mirrors. The ceilings and the walls of these rooms were motley decorated with simple paintings. The back side of the Hall of Mirrors, facing the courtyard, was glazed and entirely in small frames. Before the renovation of the 1850s, this whole side was in the same frames with whimsical patterns and multi-colored glass as on the marble platform. During the renovation, the remnants of these frames were destroyed, and ordinary frames, painted with red paint, were inserted in their place. During the renovation, the hall was covered with an iron roof, painted in red, and the marble pool located in the courtyard, in the front of the hall, was destroyed.
At the time of the Sardars, the entire back side of the Hall of Mirrors was hung with a large "golden curtain", which was pulled back by eight people. By the beginning of the 20th century, the cornice with the iron blocks of this curtain was preserved.
The palace's architecture was stylistically connected with the one of the Sheki Khans Palace and the late Fevid Garden and park pavilions.
In 1827, in one of the palace's rooms, Alexander Griboyedov took part in the production of his comedy the "Grief from the Mind" performed by the officers of the Russian army. In 1864, after the relocation of the governor's residence from the Sardar Palace to the center of Erivan, the fortress was abolished, its walls and buildings, including the palace gradually were destroyed. The old building was left unattended and the local population pulled it apart piece by piece. At the beginning of the 20th century, the palace was under the jurisdiction of the military engineer of the Alexandropol distance, however this did not lead to the safety maintenance of the palace. On its territory lived a watchman who looked after the Hall of Mirrors and once a year wiped the portraits with kerosene to avoid their damage. According to the published notes of Alexander Kolchinsky, from his travel to the Caucasus in 1902, during the renovation of the Mirror Hall, the original interior elements were replaced with modern ones, the hall was covered with an iron roof and painted in red, while the pool was destroyed. The walls of the palace "were full of all kinds of names, surnames and obscene inscriptions". In 1914 the palace was completely ruined.
The National Gallery of Georgia keeps items of the Qajar period from the Sardar Palace related to the Erivan Khanate. Among them there are household items, paintings, as well as marble slabs that were part of the decor of the palace's complex. In 2019, these items were restored and exhibited for the first time in Baku, at the Heydar Aliyev Cultural Center.
During the desolation times, the palace was covered with inscriptions made by travelers and tourists. One of the inscriptions was a kind of poem left on 20 March 1895, according to the watchman, by a certain lady who was traveling from
In the 1850s, the Azerbaijani artist Mirza Kadym Erivani painted 4 large (1x2 m) oil portraits for the restored palace. In essence, these portraits made on canvas with oil paints were the first easel works in the Azerbaijani painting. The portraits were placed in the second niches' tier of the palace's large hall. With the complete destruction of the palace in 1914, these portraits were removed from the walls and can be currently found in the State Museum of Georgia. From the relatives' memoirs, it is known that in Mirza Kadim's room there were four more similar portraits depicting armed soldiers (it is assumed that these were the artist's versions of portraits of the sardars).
The portraits occupied a dominant place in the architectural decoration of the palace's interior. Here were portraits of Fatali Shah, his heir Abbas Mirza, Sardar Huseyn-Quli and his brother. Judging by the sketches of the Russian artists V. Moshkov and G. Gagarin, who visited this palace in the first half of the 19th century, and by to the descriptions of other travelers, these portraits were distinguished by their liveliness and great similarity, although in general, they also wore a decorative, somewhat a conditional character. There were eight large portraits in the Mirror Hall of the palace. Some of them had inscriptions in the Azerbaijani language.
The hall continued with a platform and a fountain in the middle, both marble paved. In the entire height of the site, from the side of the river, there was a huge wooden window with a frame of openwork with multi-colored glass inserted.
On the sides of the marble platform there were two small rooms and their doors opened onto the Hall of Mirrors. The ceilings and the walls of these rooms were motley decorated with simple paintings. The back side of the Hall of Mirrors, facing the courtyard, was glazed and entirely in small frames. Before the renovation of the 1850s, this whole side was in the same frames with whimsical patterns and multi-colored glass as on the marble platform. During the renovation, the remnants of these frames were destroyed, and ordinary frames, painted with red paint, were inserted in their place. During the renovation, the hall was covered with an iron roof, painted in red, and the marble pool located in the courtyard, in the front of the hall, was destroyed.
At the time of the Sardars, the entire back side of the Hall of Mirrors was hung with a large "golden curtain", which was pulled back by eight people. By the beginning of the 20th century, the cornice with the iron blocks of this curtain was preserved.
The palace's architecture was stylistically connected with the one of the Sheki Khans Palace and the late Fevid Garden and park pavilions.
In 1827, in one of the palace's rooms, Alexander Griboyedov took part in the production of his comedy the "Grief from the Mind" performed by the officers of the Russian army. In 1864, after the relocation of the governor's residence from the Sardar Palace to the center of Erivan, the fortress was abolished, its walls and buildings, including the palace gradually were destroyed. The old building was left unattended and the local population pulled it apart piece by piece. At the beginning of the 20th century, the palace was under the jurisdiction of the military engineer of the Alexandropol distance, however this did not lead to the safety maintenance of the palace. On its territory lived a watchman who looked after the Hall of Mirrors and once a year wiped the portraits with kerosene to avoid their damage. According to the published notes of Alexander Kolchinsky, from his travel to the Caucasus in 1902, during the renovation of the Mirror Hall, the original interior elements were replaced with modern ones, the hall was covered with an iron roof and painted in red, while the pool was destroyed. The walls of the palace "were full of all kinds of names, surnames and obscene inscriptions". In 1914 the palace was completely ruined.
The National Gallery of Georgia keeps items of the Qajar period from the Sardar Palace related to the Erivan Khanate. Among them there are household items, paintings, as well as marble slabs that were part of the decor of the palace's complex. In 2019, these items were restored and exhibited for the first time in Baku, at the Heydar Aliyev Cultural Center.
During the desolation times, the palace was covered with inscriptions made by travelers and tourists. One of the inscriptions was a kind of poem left on 20 March 1895, according to the watchman, by a certain lady who was traveling from
Erivan Khanate
The Erivan Khanate ( fa, خانات ایروان, translit=Xānāt-e Iravān; hy, Երեւանի խանութիւն, translit=Yerevani xanut'iwn; az, ایروان خانلیغی, translit=İrəvan xanlığı), also known as Chokhur-e Sa'd, was ...
. It was located in the northeastern part of the Erivan Fortress
Erivan Fortress ( hy, Երևանի բերդը; ''Yerevani berdë''; fa, قلعه ایروان, ''Ghaleh-ye Iravân''; russian: Эриванская крепость ''E'rivanskaya krepost' '') was a 16th-century fortress in Yerevan.
History
...
in Yerevan
Yerevan ( , , hy, Երևան , sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia and one of the world's List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Y ...
, on the left bank of the Hrazdan river
The Hrazdan ( hy, Հրազդան գետ, ) is a major river and the second largest in Armenia. It originates at the northwest extremity of Lake Sevan and flows south through the Kotayk Province and Armenia's capital, Yerevan; the lake in turn is f ...
.
During the Russian-Qajar War of 1827, the fortress was destroyed, and the palace itself was in ruins, with the exception of the personal pavilion of the Sardar. During 1914–1918, the remains of the ruined palace were also destroyed. Later, on the site of the palace, according to the project of R. Israelian, the building of the “Ararat” winery rose.

Legends
According to a popular legend recorded at the beginning of the 20th century, the Sardar Palace was built around 1600 by the Safavid hero Arus, his sons Zorab and Faramos, and his daughter, the evil sorceress, Luthera.Palace’s interior
 The facade of the Mirror Hall of the palace was facing the Zange river (nowadays - Hrazdan). The walls of the hall were flush with the high steep wall above the river bank. To the left and to the right, the embankments rose from the crumbling clay walls of the Erivan fortress.
All the walls of the palace were covered with tiles with patterns and flowers. The walls between the tiles were covered with rough painting. In addition to the flowers, peacocks, lions and the sun were depicted there. The floor was glazed brick. The ceiling was covered with mirrors. There were also mirrors in the recesses along the walls and between the portraits.
The facade of the Mirror Hall of the palace was facing the Zange river (nowadays - Hrazdan). The walls of the hall were flush with the high steep wall above the river bank. To the left and to the right, the embankments rose from the crumbling clay walls of the Erivan fortress.
All the walls of the palace were covered with tiles with patterns and flowers. The walls between the tiles were covered with rough painting. In addition to the flowers, peacocks, lions and the sun were depicted there. The floor was glazed brick. The ceiling was covered with mirrors. There were also mirrors in the recesses along the walls and between the portraits.
 According to literary data, it is known that the Sardar Palace's walls of the Mirrored Hall were richly decorated with ornamental and thematic compositions. Scene murals were placed between the cornice and the ceiling of the palace, showing the legendary exploits of Rustam. On the first, Rustam hits a young warrior with a dagger, on the second he tears his clothes, learning that he has killed his son Zohrab; on the third – he pulls the enemy off the horse; on the fourth – he wins the diva and breaks his horns. According to the description of the eyewitnesses, in the palace, there was also depicted "a comic picture of an old man being kind to a young girl who serves him a glass of wine".
According to literary data, it is known that the Sardar Palace's walls of the Mirrored Hall were richly decorated with ornamental and thematic compositions. Scene murals were placed between the cornice and the ceiling of the palace, showing the legendary exploits of Rustam. On the first, Rustam hits a young warrior with a dagger, on the second he tears his clothes, learning that he has killed his son Zohrab; on the third – he pulls the enemy off the horse; on the fourth – he wins the diva and breaks his horns. According to the description of the eyewitnesses, in the palace, there was also depicted "a comic picture of an old man being kind to a young girl who serves him a glass of wine".
 In the 1850s, the Azerbaijani artist Mirza Kadym Erivani painted 4 large (1x2 m) oil portraits for the restored palace. In essence, these portraits made on canvas with oil paints were the first easel works in the Azerbaijani painting. The portraits were placed in the second niches' tier of the palace's large hall. With the complete destruction of the palace in 1914, these portraits were removed from the walls and can be currently found in the State Museum of Georgia. From the relatives' memoirs, it is known that in Mirza Kadim's room there were four more similar portraits depicting armed soldiers (it is assumed that these were the artist's versions of portraits of the sardars).
The portraits occupied a dominant place in the architectural decoration of the palace's interior. Here were portraits of Fatali Shah, his heir Abbas Mirza, Sardar Huseyn-Quli and his brother. Judging by the sketches of the Russian artists V. Moshkov and G. Gagarin, who visited this palace in the first half of the 19th century, and by to the descriptions of other travelers, these portraits were distinguished by their liveliness and great similarity, although in general, they also wore a decorative, somewhat a conditional character. There were eight large portraits in the Mirror Hall of the palace. Some of them had inscriptions in the Azerbaijani language.
The hall continued with a platform and a fountain in the middle, both marble paved. In the entire height of the site, from the side of the river, there was a huge wooden window with a frame of openwork with multi-colored glass inserted.
On the sides of the marble platform there were two small rooms and their doors opened onto the Hall of Mirrors. The ceilings and the walls of these rooms were motley decorated with simple paintings. The back side of the Hall of Mirrors, facing the courtyard, was glazed and entirely in small frames. Before the renovation of the 1850s, this whole side was in the same frames with whimsical patterns and multi-colored glass as on the marble platform. During the renovation, the remnants of these frames were destroyed, and ordinary frames, painted with red paint, were inserted in their place. During the renovation, the hall was covered with an iron roof, painted in red, and the marble pool located in the courtyard, in the front of the hall, was destroyed.
At the time of the Sardars, the entire back side of the Hall of Mirrors was hung with a large "golden curtain", which was pulled back by eight people. By the beginning of the 20th century, the cornice with the iron blocks of this curtain was preserved.
The palace's architecture was stylistically connected with the one of the Sheki Khans Palace and the late Fevid Garden and park pavilions.
In 1827, in one of the palace's rooms, Alexander Griboyedov took part in the production of his comedy the "Grief from the Mind" performed by the officers of the Russian army. In 1864, after the relocation of the governor's residence from the Sardar Palace to the center of Erivan, the fortress was abolished, its walls and buildings, including the palace gradually were destroyed. The old building was left unattended and the local population pulled it apart piece by piece. At the beginning of the 20th century, the palace was under the jurisdiction of the military engineer of the Alexandropol distance, however this did not lead to the safety maintenance of the palace. On its territory lived a watchman who looked after the Hall of Mirrors and once a year wiped the portraits with kerosene to avoid their damage. According to the published notes of Alexander Kolchinsky, from his travel to the Caucasus in 1902, during the renovation of the Mirror Hall, the original interior elements were replaced with modern ones, the hall was covered with an iron roof and painted in red, while the pool was destroyed. The walls of the palace "were full of all kinds of names, surnames and obscene inscriptions". In 1914 the palace was completely ruined.
The National Gallery of Georgia keeps items of the Qajar period from the Sardar Palace related to the Erivan Khanate. Among them there are household items, paintings, as well as marble slabs that were part of the decor of the palace's complex. In 2019, these items were restored and exhibited for the first time in Baku, at the Heydar Aliyev Cultural Center.
During the desolation times, the palace was covered with inscriptions made by travelers and tourists. One of the inscriptions was a kind of poem left on 20 March 1895, according to the watchman, by a certain lady who was traveling from
In the 1850s, the Azerbaijani artist Mirza Kadym Erivani painted 4 large (1x2 m) oil portraits for the restored palace. In essence, these portraits made on canvas with oil paints were the first easel works in the Azerbaijani painting. The portraits were placed in the second niches' tier of the palace's large hall. With the complete destruction of the palace in 1914, these portraits were removed from the walls and can be currently found in the State Museum of Georgia. From the relatives' memoirs, it is known that in Mirza Kadim's room there were four more similar portraits depicting armed soldiers (it is assumed that these were the artist's versions of portraits of the sardars).
The portraits occupied a dominant place in the architectural decoration of the palace's interior. Here were portraits of Fatali Shah, his heir Abbas Mirza, Sardar Huseyn-Quli and his brother. Judging by the sketches of the Russian artists V. Moshkov and G. Gagarin, who visited this palace in the first half of the 19th century, and by to the descriptions of other travelers, these portraits were distinguished by their liveliness and great similarity, although in general, they also wore a decorative, somewhat a conditional character. There were eight large portraits in the Mirror Hall of the palace. Some of them had inscriptions in the Azerbaijani language.
The hall continued with a platform and a fountain in the middle, both marble paved. In the entire height of the site, from the side of the river, there was a huge wooden window with a frame of openwork with multi-colored glass inserted.
On the sides of the marble platform there were two small rooms and their doors opened onto the Hall of Mirrors. The ceilings and the walls of these rooms were motley decorated with simple paintings. The back side of the Hall of Mirrors, facing the courtyard, was glazed and entirely in small frames. Before the renovation of the 1850s, this whole side was in the same frames with whimsical patterns and multi-colored glass as on the marble platform. During the renovation, the remnants of these frames were destroyed, and ordinary frames, painted with red paint, were inserted in their place. During the renovation, the hall was covered with an iron roof, painted in red, and the marble pool located in the courtyard, in the front of the hall, was destroyed.
At the time of the Sardars, the entire back side of the Hall of Mirrors was hung with a large "golden curtain", which was pulled back by eight people. By the beginning of the 20th century, the cornice with the iron blocks of this curtain was preserved.
The palace's architecture was stylistically connected with the one of the Sheki Khans Palace and the late Fevid Garden and park pavilions.
In 1827, in one of the palace's rooms, Alexander Griboyedov took part in the production of his comedy the "Grief from the Mind" performed by the officers of the Russian army. In 1864, after the relocation of the governor's residence from the Sardar Palace to the center of Erivan, the fortress was abolished, its walls and buildings, including the palace gradually were destroyed. The old building was left unattended and the local population pulled it apart piece by piece. At the beginning of the 20th century, the palace was under the jurisdiction of the military engineer of the Alexandropol distance, however this did not lead to the safety maintenance of the palace. On its territory lived a watchman who looked after the Hall of Mirrors and once a year wiped the portraits with kerosene to avoid their damage. According to the published notes of Alexander Kolchinsky, from his travel to the Caucasus in 1902, during the renovation of the Mirror Hall, the original interior elements were replaced with modern ones, the hall was covered with an iron roof and painted in red, while the pool was destroyed. The walls of the palace "were full of all kinds of names, surnames and obscene inscriptions". In 1914 the palace was completely ruined.
The National Gallery of Georgia keeps items of the Qajar period from the Sardar Palace related to the Erivan Khanate. Among them there are household items, paintings, as well as marble slabs that were part of the decor of the palace's complex. In 2019, these items were restored and exhibited for the first time in Baku, at the Heydar Aliyev Cultural Center.
During the desolation times, the palace was covered with inscriptions made by travelers and tourists. One of the inscriptions was a kind of poem left on 20 March 1895, according to the watchman, by a certain lady who was traveling from Qajar Empire
Qajar Iran (), also referred to as Qajar Persia, the Qajar Empire, '. Sublime State of Persia, officially the Sublime State of Iran ( fa, دولت علیّه ایران ') and also known then as the Guarded Domains of Iran ( fa, ممالک م ...
:
References
Sources
* * {{coord missing, Armenia Russian Empire Former palaces Demolished buildings and structures in Armenia Erivan Khanate Persian-Caucasian architecture Buildings of the Qajar period