

Pain management is an aspect of
medicine and
health care
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profe ...
involving relief of
pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
(pain relief, analgesia, pain control) in various dimensions, from
acute
Acute may refer to:
Science and technology
* Acute angle
** Acute triangle
** Acute, a leaf shape in the glossary of leaf morphology
* Acute (medicine), a disease that it is of short duration and of recent onset.
** Acute toxicity, the adverse eff ...
and simple to
chronic and challenging. Most
physicians and other
health professional
A health professional, healthcare professional, or healthcare worker (sometimes abbreviated HCW) is a provider of health care treatment and advice based on formal training and experience. The field includes those who work as a nurse, physician (suc ...
s provide some pain control in the normal course of their practice, and for the more complex instances of pain, they also call on additional help from a specific
medical specialty devoted to pain, which is called pain medicine.
Pain management often uses a
multidisciplinary approach for easing the suffering and improving the
quality of life of anyone experiencing pain, whether acute pain or
chronic pain. Relief of pain in general (analgesia) is often an acute affair, whereas managing chronic pain requires additional dimensions. The typical pain management team includes
medical practitioner
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through th ...
s,
pharmacist
A pharmacist, also known as a chemist (Commonwealth English) or a druggist (North American and, archaically, Commonwealth English), is a healthcare professional who prepares, controls and distributes medicines and provides advice and instructi ...
s,
clinical psychologist
Clinical psychology is an integration of social science, theory, and clinical knowledge for the purpose of understanding, preventing, and relieving psychologically based distress or dysfunction and to promote subjective well-being and persona ...
s,
physiotherapists,
occupational therapists,
recreational therapist
Recreational therapy or therapeutic recreation (TR) is a systematic process that utilizes recreation (leisure) and other activities as interventions to address the assessed needs of individuals with illnesses and/or disabling conditions, as a mea ...
s,
physician assistant
A physician assistant or physician associate (PA) is a type of Mid-level practitioner, mid-level health care provider. In North America PAs may diagnose illnesses, develop and manage treatment plans, prescribe medications, and may serve as a pri ...
s,
nurses, and
dentist
A dentist, also known as a dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry (the diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases and conditions of the mouth, oral cavity and other aspects of the craniofaci ...
s. The team may also include other
mental health specialists and
massage therapists. Pain sometimes resolves quickly once the underlying
trauma or
pathology has healed, and is treated by one practitioner, with drugs such as pain relievers (
analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It ...
s) and occasionally also
anxiolytics. Effective management of
chronic (long-term) pain, however, frequently requires the coordinated efforts of the pain management team. Effective pain management does not always mean total eradication of all pain. Rather, it often means achieving adequate quality of life in the presence of pain, through any combination of lessening the pain and/or better understanding it and being able to live happily despite it.
Medicine treats
injuries and diseases to support and speed healing. It treats distressing symptoms such as pain to relieve
suffering
Suffering, or pain in a broad sense, may be an experience of unpleasantness or aversion, possibly associated with the perception of harm or threat of harm in an individual. Suffering is the basic element that makes up the negative valence of a ...
during treatment, healing, and
dying. The task of medicine is to relieve suffering under three circumstances. The first is when a painful injury or pathology is resistant to treatment and persists. The second is when pain persists after the injury or pathology has healed. Finally, the third circumstance is when medical science cannot identify the cause of pain. Treatment approaches to chronic pain include
pharmacological measures, such as
analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It ...
s (pain killer drugs),
antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medication used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and to help manage addictions. Common side-effects of antidepressants include dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, hea ...
s, and
anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of b ...
s; interventional procedures, physical therapy,
physical exercise
Exercise is a body activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness.
It is performed for various reasons, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, hone athletic ...
, application of ice or heat; and
psychological
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between t ...
measures, such as
biofeedback
Biofeedback is the process of gaining greater awareness of many physiology, physiological functions of one's own body by using Electronics, electronic or other instruments, and with a goal of being able to Manipulation (psychology), manipulate t ...
and
cognitive behavioral therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a psycho-social intervention that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions, primarily depression and anxiety disorders. CBT focuses on challenging and changing cognitive distortions (suc ...
.
Defining pain
In the nursing profession, one common definition of pain is any problem that is "whatever the experiencing person says it is, existing whenever the experiencing person says it does".
Pain management includes patient and communication about the pain problem.
To define the pain problem, a health care provider will likely ask questions such as:
* How intense is the pain?
* How does the pain feel?
* Where is the pain?
* What, if anything, makes the pain lessen?
* What, if anything, makes the pain increase?
* When did the pain start?
After asking such questions, the health care provider will have a description of the pain.
Pain management will then be used to address that pain.
Adverse effects
There are many types of pain management. Each have their own benefits, drawbacks, and limits.
A common challenge in pain management is communication between the health care provider and the person experiencing pain.
People experiencing pain may have difficulty recognizing or describing what they feel and how intense it is.
Health care providers and patients may have difficulty communicating with each other about how pain responds to treatments.
There is a risk in many types of pain management for the patient to take treatment that is less effective than needed or which causes other difficulties and side effects.
Some treatments for pain can be harmful if overused.
A goal of pain management for the patient and their health care provider is to identify the amount of treatment needed to address the pain without going beyond that limit.
Another problem with pain management is that pain is the body's natural way of communicating a problem.
Pain is supposed to resolve as the body heals itself with time and pain management.
Sometimes pain management covers a problem, and the patient might be less aware that they need treatment for a deeper problem.
Physical approach
Physical medicine and rehabilitation
Physical medicine and rehabilitation uses a range of physical techniques such as heat and
electrotherapy, as well as therapeutic exercises and behavioral therapy. These techniques are usually part of an interdisciplinary or multidisciplinary program that might also include pharmaceutical medicines.
Spa therapy has showed positive effects in reducing pain among patients with chronic low back pain. However, there are limited studies looking at this approach. Studies have shown that
kinesiotape could be used on individuals with chronic low back pain to reduce pain. The Center for Disease Control recommends that physical therapy and exercise can be prescribed as a positive alternative to
opioids for decreasing one's pain in multiple injuries, illnesses, or diseases.
This can include chronic low back pain, osteoarthritis of the hip and knee, or
fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a medical condition defined by the presence of chronic widespread pain, fatigue, waking unrefreshed, cognitive symptoms, lower abdominal pain or cramps, and depression. Other symptoms include insomnia and a general hyp ...
.
Exercise alone or with other rehabilitation disciplines (such as psychologically based approaches) can have a positive effect on reducing pain.
In addition to improving pain, exercise also can improve one's well-being and general health.
and
mobilization therapy are safe interventions that likely reduce pain for patients with chronic low back pain. However, manipulation produces a larger effect than mobilization.
Specifically in chronic low back pain, education about the way the brain processes pain in conjunction with routine physiotherapy interventions may provide short term relief of disability and pain.
Exercise interventions
Physical activity interventions, such as tai chi, yoga and Pilates, promote harmony of the mind and body through total body awareness. These practices incorporate breathing techniques, meditation and a wide variety of movements, while training the body to perform functionally by increasing strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
Physical activity and exercise may improve chronic pain (pain lasting more than 12 weeks), and overall quality of life, while minimizing the need for pain medications.
More specifically, walking has been effective in improving pain management in chronic low back pain.
TENS
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) is a self-operated portable device intended to help regulate and create chronic pain via electrical impulses.
Limited research has explored the effectiveness of TENS in relation to pain management of Multiple Sclerosis (MS). MS is a chronic autoimmune neurological disorder, which consists of the demyelination of the nerve axons and disruption of nerve conduction velocity and efficiency.
In one study, electrodes were placed over the lumbar spine and participants received treatment twice a day and at any time when they experienced a painful episode.
This study found that TENS would be beneficial to MS patients who reported localized or limited symptoms to one limb.
The research is mixed with whether or not TENS helps manage pain in MS patients.
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation has been found to be ineffective for
lower back pain. However, it might help with
diabetic neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is various types of nerve damage associated with diabetes mellitus. Symptoms depend on the site of nerve damage and can include motor changes such as weakness; sensory symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or pain; or autonomic c ...
as well as other illnesses.
tDCS
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a non-invasive technique of brain stimulation that can modulate activity in specific brain cortex regions, and it involves the application of low-intensity (up to 2 mA) constant direct current to the scalp through electrodes in order to modulate excitability of large cortical areas.
tDCS may have a role in pain assessment by contributing to efforts in distinguishing between somatic and affective aspects of pain experience.
Zaghi and colleagues (2011) found that the motor cortex, when stimulated with tDCS, increases the threshold for both the perception of non-painful and painful stimuli.
Although there is a greater need for research examining the mechanism of electrical stimulation in relation to pain treatment, one theory suggests that the changes in thalamic activity may be due the influence of motor cortex stimulation on the decrease in pain sensations.
In relation to MS, a study found that after daily tDCS sessions resulted in an individual's subjective report of pain to decrease when compared to a sham condition.
In addition, the study found a similar improvement at 1 to 3 days before and after each tDCS session.
Fibromyalgia is a disorder in which an individual experiences dysfunctional brain activity, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness in localized areas.
Research examining tDCS for pain treatment in Fibromyalgia has found initial evidence for pain decreases.
Specifically, the stimulation of the primary motor cortex resulted in significantly greater pain improvement in comparison to the control group (e.g., sham stimulation, stimulation of the DLPFC).
However, this effect decreased after treatment ended, but remained significant for three weeks following the extinction of treatment.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture involves the insertion and manipulation of needles into specific points on the body to relieve pain or for therapeutic purposes. An analysis of the 13 highest quality studies of pain treatment with acupuncture, published in January 2009 in the ''
British Medical Journal
''The BMJ'' is a weekly peer-reviewed medical trade journal, published by the trade union the British Medical Association (BMA). ''The BMJ'' has editorial freedom from the BMA. It is one of the world's oldest general medical journals. Origi ...
'', was unable to quantify the difference in the effect on pain of real,
sham and no acupuncture. A systematic review in 2019 reported that acupuncture injection therapy was an effective treatment for patients with nonspecific chronic low back pain, and is widely used in Southeast Asian countries.
Light therapy
Research has not found evidence that
light therapy such as
low level laser therapy
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT), cold laser therapy, or photobiomodulation (PBM) is a form of medicine that applies low-level (low-power) lasers or light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to the surface of the body. Whereas high-power lasers are used in la ...
is an effective therapy for relieving
low back pain.
Sound therapy
Audioanalgesia
Audioanalgesia (or audio-analgesia) is the relief of pain (analgesia) using white noise or music (that is, via audio equipment) without using pharmacological agents (that is, without analgesic drugs), usually during painful medical procedures such ...
and
music therapy are both examples of using
auditory stimuli
In physiology, a stimulus is a detectable change in the physical or chemical structure of an organism's internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to detect external stimuli, so that an appropriate reaction can be ma ...
to manage pain or other distress. They are generally viewed as (1) not sufficient when used alone, but also (2) helpful
adjuncts
In brewing, adjuncts are unmalted grains (such as corn, rice, rye, oats, barley, and wheat) or grain products used in brewing beer which supplement the main mash ingredient (such as malted barley). This is often done with the intention of cut ...
to other forms of
therapy.
Interventional procedures
Interventional radiology
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs bo ...
procedures for pain control, typically used for
chronic back pain
Back pain is pain felt in the back. It may be classified as neck pain (cervical), middle back pain (thoracic), lower back pain (lumbar) or coccydynia (tailbone or sacral pain) based on the segment affected. The lumbar area is the most common area ...
, include
epidural steroid injections,
facet joint injection
Facet joint injections are used to alleviate symptoms of Facet syndrome. The procedure is an outpatient surgery, so that the patient can go home on the same day. It usually takes 10–20 minutes, but may take up to 30 minutes if the patient needs ...
s,
neurolytic blocks,
spinal cord stimulators and
intrathecal drug delivery system implants.
Pulsed radiofrequency,
neuromodulation, direct introduction of medication and nerve
ablation may be used to target either the tissue structures and organ/systems responsible for persistent
nociception
Nociception (also nocioception, from Latin ''nocere'' 'to harm or hurt') is the sensory nervous system's process of encoding noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, co ...
or the
nociceptors from the structures implicated as the source of chronic pain.
Radiofrequency treatment has been seen to improve pain in patients for facet joint low back pain. However, continuous radiofrequency is more effective in managing pain than pulsed radiofrequency.
An
intrathecal pump used to deliver very small quantities of medications directly to the spinal fluid. This is similar to epidural infusions used in
labour
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the labour ...
and postoperatively. The major differences are that it is much more common for the drug to be delivered into the spinal fluid (intrathecal) rather than epidurally, and the pump can be fully implanted under the skin.
A
spinal cord stimulator is an implantable medical device that creates electric impulses and applies them near the dorsal surface of the spinal cord provides a
paresthesia
Paresthesia is an abnormal sensation of the skin (tingling, pricking, chilling, burning, numbness) with no apparent physical cause. Paresthesia may be transient or chronic, and may have any of dozens of possible underlying causes. Paresthesias ar ...
("tingling") sensation that alters the perception of pain by the patient.
Intra-articular ozone therapy
Intra-articular ozone therapy has been seen to efficiently alleviate chronic pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis.
Psychological approach
Acceptance and commitment therapy
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is a form of cognitive behavioral therapy that focuses on behavior change rather than symptom change, includes methods designed to alter the context around psychological experiences rather than to alter the makeup of the experiences, and emphasizes the use of experiential behavior change methods.
The central process in ACT revolves around psychological flexibility, which in turn includes processes of acceptance, awareness, a present-oriented quality in interacting with experiences, an ability to persist or change behavior, and an ability to be guided by one's values.
ACT has an increased evidence base for range of health and behavior problems, including chronic pain.
ACT influences patients to adopt a tandem process to acceptance and change, which allows for a greater flexibility in the focus of treatment.
Recent research has applied ACT successfully to chronic pain in older adults due to in part of its direction from individual values and being highly customizable to any stage of life.
In line with the therapeutic model of ACT, significant increases in process variables, pain acceptance, and mindfulness were also observed in a study applying ACT to chronic pain in older adults.
In addition, these primary results suggested that an ACT based treatment may significantly improve levels of physical disability, psychosocial disability, and depression post-treatment and at a three-month follow-up for older adults with chronic pain.
Cognitive behavioral therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a psycho-social intervention that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions, primarily depression and anxiety disorders. CBT focuses on challenging and changing cognitive distortions (suc ...
(CBT) helps patients with pain to understand the relationship between their pain, thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. A main goal in treatment is cognitive (thinking, reasoning or remembering) restructuring to encourage helpful thought patterns. This will target healthy activities such as regular exercise and pacing. Lifestyle changes are also trained to improve sleep patterns and to develop better coping skills for pain and other stressors using various techniques (e.g., relaxation, diaphragmatic breathing, and even biofeedback).
Studies have demonstrated the usefulness of cognitive behavioral therapy in the management of chronic low back pain, producing significant decreases in physical and psychosocial disability. CBT is significantly more effective than standard care in treatment of people with body-wide pain, like fibromyalgia. Evidence for the usefulness of CBT in the management of adult chronic pain is generally poorly understood, due partly to the proliferation of techniques of doubtful quality, and the poor quality of reporting in clinical trials. The crucial content of individual interventions has not been isolated and the important contextual elements, such as therapist training and development of treatment manuals, have not been determined. The widely varying nature of the resulting data makes useful
systematic review
A systematic review is a Literature review, scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from publ ...
and
meta-analysis within the field very difficult.
In 2020, a
systematic review
A systematic review is a Literature review, scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from publ ...
of
randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluated the clinical effectiveness of psychological therapies for the management of adult chronic pain (excluding headaches). There is no evidence that
behaviour therapy (BT) is effective for reducing this type of pain, however BT may be useful for improving a persons mood immediately after treatment. This improvement appears to be small, and is short term in duration.
CBT may have a small positive short-term effect on pain immediately following treatment. CBT may also have a small effect on reducing
disability and potential
catastrophizing
Exaggeration is the representation of something as more extreme or dramatic than it really is. Exaggeration may occur intentionally or unintentionally.
Exaggeration can be a rhetorical device or figure of speech. It may be used to evoke stron ...
that may be associated with adult chronic pain. These benefits do not appear to last very long following the therapy.
CBT may contribute towards improving the mood of an adult who experiences chronic pain, which could possibility be maintained for longer periods of time.
For children and adolescents, a review of RCTs evaluating the effectiveness of psychological therapy for the management of chronic and recurrent pain found that psychological treatments are effective in reducing pain when people under 18 years old have headaches. This beneficial effect may be maintained for at least three months following the therapy.
Psychological treatments may also improve pain control for children or adolescents who experience pain not related to headaches. It is not known if psychological therapy improves a child or adolescents mood and the potential for disability related to their chronic pain.
Hypnosis
A 2007 review of 13 studies found evidence for the efficacy of
hypnosis in the reduction of pain in some conditions. However the studies had some limitations like small study sizes, bringing up issues of power to detect group differences, and lacking credible controls for placebo or expectation. The authors concluded that "although the findings provide support for the general applicability of hypnosis in the treatment of chronic pain, considerably more research will be needed to fully determine the effects of hypnosis for different chronic-pain conditions."
Hypnosis has reduced the pain of some harmful medical procedures in children and adolescents.
In clinical trials addressing other patient groups, it has significantly reduced pain compared to no treatment or some other non-hypnotic interventions.
The effects of self hypnosis on chronic pain are roughly comparable to those of progressive muscle relaxation.
Hypnosis with analgesic (painkiller) has been seen to relieve chronic pain for most people and may be a safe and effective alternative to medications. However, high quality clinical data is needed to generalize to the whole chronic pain population.
Mindfulness meditation
A 2013 meta-analysis of studies that used techniques centered around the concept of
mindfulness
Mindfulness is the practice of purposely bringing one's attention to the present-moment experience without evaluation, a skill one develops through meditation or other training. Mindfulness derives from ''sati'', a significant element of Hind ...
, concluded, "that MBIs
indfulness-based interventionsdecrease the intensity of pain for chronic pain patients." A 2019 review of studies of brief mindfulness-based interventions (BMBI) concluded that BMBI are not recommended as a first-line treatment and could not confirm their efficacy in managing chronic or acute pain.
Mindfulness-based pain management
Mindfulness-based pain management (MBPM) is a mindfulness-based intervention (MBI) providing specific applications for people living with chronic pain and illness.
Adapting the core concepts and practices of
mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) and
mindfulness-based cognitive therapy
Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) is an approach to psychotherapy that uses cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) methods in collaboration with mindfulness meditative practices and similar psychological strategies. The origins to its concept ...
(MBCT), MBPM includes a distinctive emphasis on the practice of '
loving-kindness Loving-kindness may refer to:
* an English translation of Chesed
( he, חֶסֶד, also Romanized: ) is a Hebrew word that means 'kindness or love between people', specifically of the devotional piety of people towards God as well as of love o ...
', and has been seen as sensitive to concerns about removing mindfulness teaching from its original ethical framework within
Buddhism.
It was developed by
Vidyamala Burch and is delivered through the programs of
Breathworks.
It has been subject to a range of clinical studies demonstrating its effectiveness.
Medications
The
World Health Organization (WHO) recommends a ''
pain ladder
"Pain ladder", or analgesic ladder, was created by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a guideline for the use of drugs in the management of pain. Originally published in 1986 for the management of cancer pain, it is now widely used by medical p ...
'' for managing pain relief with pharmaceutical medicine. It was first described for use in
cancer pain. However it can be used by medical professionals as a general principle when managing any type of pain.
In the treatment of chronic pain, the three-step WHO Analgesic Ladder provides guidelines for selecting the appropriate medicine. The exact medications recommended will vary by country and the individual treatment center, but the following gives an example of the WHO approach to treating chronic pain with medications. If, at any point, treatment fails to provide adequate pain relief, then the doctor and patient move onto the next step.
Mild pain
Paracetamol
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol.
At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferior ...
(acetaminophen), or a
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
(NSAID) such as
ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used for treating pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to close a patent ductus arte ...
will relieve mild pain.
Mild to moderate pain
Paracetamol, an NSAID or paracetamol in a combination product with a weak
opioid such as
tramadol
Tramadol, sold under the brand name Ultram among others, is an opioid pain medication used to treat moderate to moderately severe pain. When taken by mouth in an immediate-release formulation, the onset of pain relief usually begins within an h ...
, may provide greater relief than their separate use. A combination of opioid with
acetaminophen
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol.
At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferior ...
can be frequently used such as Percocet,
Vicodin, or Norco.
Moderate to severe pain
When treating moderate to severe pain, the type of the pain, acute or chronic, needs to be considered. The type of pain can result in different medications being prescribed. Certain medications may work better for acute pain, others for chronic pain, and some may work equally well on both. Acute pain medication is for rapid onset of pain such as from an inflicted
trauma or to treat
post-operative pain.
Chronic pain medication is for alleviating long-lasting, ongoing pain.
Morphine is the
gold standard to which all
narcotic
The term narcotic (, from ancient Greek ναρκῶ ''narkō'', "to make numb") originally referred medically to any psychoactive compound with numbing or paralyzing properties. In the United States, it has since become associated with opiates ...
s are compared. Semi-synthetic derivatives of morphine such as
hydromorphone (Dilaudid),
oxymorphone
Oxymorphone (sold under the brand names Numorphan and Opana among others) is a highly potent opioid analgesic indicated for treatment of severe pain. Pain relief after injection begins after about 5–10 minutes, after oral administration it beg ...
(Numorphan, Opana),
nicomorphine (Vilan),
hydromorphinol
Hydromorphinol (RAM-320, 14-Hydroxydihydromorphine), also is an opiate analogue that is a derivative of morphine, where the 14-position has been hydroxylated and the 7,8- double bond saturated. It has similar effects to morphine such as sedation ...
and others vary in such ways as duration of action, side effect profile and milligramme potency.
Fentanyl has the benefit of less
histamine release and thus fewer
side effects. It can also be administered via
transdermal patch which is convenient for chronic pain management. In addition to the intrathecal patch and injectable fentanyl formulations, the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) has approved various immediate release fentanyl products for breakthrough cancer pain (Actiq/OTFC/Fentora/Onsolis/Subsys/Lazanda/Abstral).
Oxycodone is used across the Americas and Europe for relief of serious chronic pain. Its main slow-release formula is known as
OxyContin. Short-acting tablets, capsules, syrups and
ampule
An ampoule (also ampul and ampule) is a small sealed vial which is used to contain and preserve a sample, usually a solid or liquid. Ampoules are usually made of glass.
Modern ampoules are most commonly used to contain pharmaceuticals and chem ...
s which contain OxyContin are available making it suitable for acute intractable pain or
breakthrough pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
.
Diamorphine, and
methadone are used less frequently. Clinical studies have shown that transdermal
Buprenorphine is effective at reducing chronic pain.
Pethidine, known in North America as meperidine, is not recommended for pain management due to its low potency, short duration of action, and toxicity associated with repeated use.
Pentazocine
Pentazocine, sold under the brand name Talwin among others, is a painkiller used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is believed to work by activating (agonizing) κ-opioid receptors (KOR) and μ-opioid receptors (MOR). As such it is called an ...
,
dextromoramide and
dipipanone are also not recommended in new patients except for acute pain where other analgesics are not tolerated or are inappropriate, for pharmacological and misuse-related reasons. In some countries potent synthetics such as
piritramide
Piritramide(R-3365, trade names Dipidolor, Piridolan, Pirium and others) is a synthetic opioid analgesic (narcotic painkiller) that is marketed in certain European countries including: Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Slovenia, Germany and the ...
and
ketobemidone are used for severe pain.
Tapentadol
Tapentadol, brand names Nucynta among others, is a centrally acting opioid analgesic of the benzenoid class with a dual mode of action as an agonist of the μ-opioid receptor and as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI). Analgesia occurs wit ...
is a newer agent introduced in the last decade.
For moderate pain,
tramadol
Tramadol, sold under the brand name Ultram among others, is an opioid pain medication used to treat moderate to moderately severe pain. When taken by mouth in an immediate-release formulation, the onset of pain relief usually begins within an h ...
,
codeine
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, ''Papaver somniferum''. It is typically use ...
,
dihydrocodeine, and
hydrocodone are used, with
nicocodeine
Nicocodeine (Lyopect, Tusscodin) is an opioid analgesic and cough suppressant, an ester of codeine closely related to dihydrocodeine and the codeine analogue of nicomorphine. It is not commonly used in most countries, but has activity similar to ...
,
ethylmorphine
Ethylmorphine (also known as codethyline, dionine, and ethyl morphine) is an opioid analgesic and antitussive.
Side effects
Adverse effects are similar to other opioids and include drowsiness, constipation, vertigo, nausea, vomiting, and respirat ...
and
propoxyphene or
dextropropoxyphene (less commonly).
Drugs of other types can be used to help opioids combat certain types of pain.
Amitriptyline is prescribed for chronic muscular pain in the arms, legs, neck and lower back with an opiate, or sometimes without it or with an NSAID.
While
opiate
An opiate, in classical pharmacology, is a substance derived from opium. In more modern usage, the term ''opioid'' is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain (including antagonis ...
s are often used in the management of chronic pain, high doses are associated with an increased risk of
opioid overdose.
Opioids
In 2009, the
Food and Drug Administration stated: "According to the
National Institutes of Health, studies have shown that properly managed medical use of opioid analgesic compounds (taken exactly as prescribed) is safe, can manage pain effectively, and rarely causes addiction." In 2013, the FDA stated that "abuse and misuse of these products have created a serious and growing public health problem".
Opioid medications can provide short, intermediate or long acting analgesia depending upon the specific properties of the medication and whether it is formulated as an extended release drug. Opioid medications may be administered orally, by injection, via nasal mucosa or oral mucosa, rectally, transdermally, intravenously, epidurally and intrathecally. In chronic pain conditions that are opioid responsive, a combination of a long-acting (OxyContin, MS Contin, Opana ER, Exalgo and Methadone) or
extended release
Modified-release dosage is a mechanism that (in contrast to immediate-release dosage) delivers a drug with a delay after its administration (delayed-release dosage) or for a prolonged period of time (extended-release R, XR, XLdosage) or to a sp ...
medication is often prescribed along with a shorter-acting medication (oxycodone, morphine or hydromorphone) for breakthrough pain, or exacerbations.
Most opioid treatment used by patients outside of healthcare settings is oral (
tablet
Tablet may refer to:
Medicine
* Tablet (pharmacy), a mixture of pharmacological substances pressed into a small cake or bar, colloquially called a "pill"
Computing
* Tablet computer, a mobile computer that is primarily operated by touching the s ...
,
capsule or liquid), but
suppositories
A suppository is a dosage form used to deliver medications by insertion into a body orifice where it dissolves or melts to exert local or systemic effects. There are three types of suppositories, each to insert into a different sections: rectal su ...
and skin patches can be prescribed. An opioid
injection is rarely needed for patients with chronic pain.
Although opioids are strong analgesics, they do not provide complete analgesia regardless of whether the pain is acute or chronic in origin. Opioids are effective analgesics in chronic malignant pain and modestly effective in nonmalignant pain management. However, there are associated adverse effects, especially during the commencement or change in dose. When
opioids
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use ...
are used for prolonged periods
drug tolerance
Drug tolerance or drug insensitivity is a pharmacological concept describing subjects' reduced reaction to a drug following its repeated use. Increasing its dosage may re-amplify the drug's effects; however, this may accelerate tolerance, further ...
,
chemical dependency
Substance dependence, also known as drug dependence, is a biopsychological situation whereby an individual's functionality is dependent on the necessitated re-consumption of a psychoactive substance because of an adaptive state that has develope ...
,
diversion and
addiction may occur.
Clinical guidelines for prescribing opioids for chronic pain have been issued by the
American Pain Society
The American Pain Society (APS) was a professional membership organization and a national chapter of the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP).
History
Around the time of Purdue Pharma
Purdue Pharma L.P., formerly the Purdue ...
and the American Academy of Pain Medicine. Included in these guidelines is the importance of assessing the patient for the risk of substance abuse, misuse, or addiction. Factors correlated with an elevated risk of opioid misuse include a history of substance use disorder, younger age, major depression, and the use of psychotropic medications. Physicians who prescribe opioids should integrate this treatment with any psychotherapeutic intervention the patient may be receiving. The guidelines also recommend monitoring not only the pain but also the level of functioning and the achievement of therapeutic goals. The prescribing physician should be suspicious of abuse when a patient reports a reduction in pain but has no accompanying improvement in function or progress in achieving identified goals.
The list below consists of commonly used opioid analgesics which have long-acting formulations. Common brand names for the extended release formulation are in parentheses.
*
Oxycodone (OxyContin)
*
Hydromorphone (Exalgo, Hydromorph Contin)
*
Morphine (M-Eslon, MS Contin)
*
Oxymorphone
Oxymorphone (sold under the brand names Numorphan and Opana among others) is a highly potent opioid analgesic indicated for treatment of severe pain. Pain relief after injection begins after about 5–10 minutes, after oral administration it beg ...
(Opana ER)
*
Fentanyl, transdermal (Duragesic)
*
Buprenorphine*, transdermal (Butrans)
*
Tramadol
Tramadol, sold under the brand name Ultram among others, is an opioid pain medication used to treat moderate to moderately severe pain. When taken by mouth in an immediate-release formulation, the onset of pain relief usually begins within an h ...
(Ultram ER)
*
Tapentadol
Tapentadol, brand names Nucynta among others, is a centrally acting opioid analgesic of the benzenoid class with a dual mode of action as an agonist of the μ-opioid receptor and as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI). Analgesia occurs wit ...
(Nucynta ER)
*
Methadone* (Metadol, Methadose)
*
Hydrocodone bitartrate (Hysingla ER) and bicarbonate (Zohydro ER)
*Methadone and buprenorphine are each used both for the treatment of
opioid addiction and as analgesics
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
The other major group of analgesics are
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
s (NSAID). They work by inhibiting the release of
prostaglandin
The prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derive ...
s, which cause inflammatory pain.
Acetaminophen
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol.
At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferior ...
/paracetamol is not always included in this class of medications. However, acetaminophen may be administered as a single medication or in combination with other analgesics (both NSAIDs and opioids). The alternatively prescribed NSAIDs such as
ketoprofen and
piroxicam have limited benefit in chronic pain disorders and with long-term use are associated with significant
adverse effects. The use of selective NSAIDs designated as
selective COX-2 inhibitors have significant cardiovascular and cerebrovascular risks which have limited their utilization.
Common NSAIDs include
aspirin,
ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used for treating pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to close a patent ductus arte ...
, and
naproxen. There are many NSAIDs such as parecoxib (selective COX-2 inhibitor) with proven effectiveness after different surgical procedures. Wide use of non-opioid analgesics can reduce opioid-induced side-effects.
Antidepressants and antiepileptic drugs
Some
antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medication used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and to help manage addictions. Common side-effects of antidepressants include dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, hea ...
and
antiepileptic
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of b ...
drugs are used in chronic pain management and act primarily within the pain pathways of the central nervous system, though peripheral mechanisms have been attributed as well. They are generally used to treat nerve brain that results from injury to the nervous system.
Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, is a general term describing disease affecting the peripheral nerves, meaning nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. Damage to peripheral nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland, or o ...
can be due to chronic high blood sugar levels (
diabetic neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is various types of nerve damage associated with diabetes mellitus. Symptoms depend on the site of nerve damage and can include motor changes such as weakness; sensory symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or pain; or autonomic c ...
). These drugs also reduce pain from viruses such as shingles,
phantom limb pain and post-stroke pain. These mechanisms vary and in general are more effective in
neuropathic pain disorders as well as
complex regional pain syndrome
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is any of several painful conditions that are characterized by a continuing (spontaneous and/or evoked) regional pain that is seemingly disproportionate in time or degree to the usual course of any known trau ...
.
A common anti-epileptic drug is
gabapentin, and an example of an antidepressant would be
amitriptyline.
Cannabinoids
Evidence of medical marijuana's effect on reducing pain is generally conclusive. Detailed in a 1999 report by the
Institute of Medicine
The National Academy of Medicine (NAM), formerly called the Institute of Medicine (IoM) until 2015, is an American nonprofit, non-governmental organization. The National Academy of Medicine is a part of the National Academies of Sciences, E ...
, "the available evidence from animal and human studies indicates that cannabinoids can have a substantial analgesic effect". In a 2013 review study published in ''Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology'', various studies were cited in demonstrating that cannabinoids exhibit comparable effectiveness to opioids in models of acute pain and even greater effectiveness in models of chronic pain. It is mainly the THC strain of medical marijuana that provide analgesic benefits, as opposed to the CBD strain.
Ketamine
Ketamine is a safe, effective alternative to opioids in the treatment of acute pain in the ED.
What's the ED? Ketamine probably
? reduces pain more than opioids and with less nausea and vomiting.
Other analgesics
Other drugs which can potentiate conventional analgesics or have analgesic properties in certain circumstances are called
analgesic adjuvant
An analgesic adjuvant is a medication that is typically used for indications other than pain control but provides control of pain in some painful diseases. For instance, caffeine has minimal analgesic effect on its own, but may have an adjuvant ...
medications.
, an anticonvulsant, can reduce neuropathic pain itself and can also potentiate opiates.
Drugs with
anticholinergic activity, such as
orphenadrine
Orphenadrine (sold under many brand names) is an anticholinergic drug of the ethanolamine antihistamine class; it is closely related to diphenhydramine. It is a muscle relaxant that is used to treat muscle pain and to help with motor control in Pa ...
,
cyclobenzaprine
Cyclobenzaprine (sold under the brand name Flexeril, among others) is a medication used for muscle spasms from musculoskeletal conditions of sudden onset. It is not useful in cerebral palsy. It is taken by mouth. Use is not recommended for mor ...
, and
trazodone, are given in conjunction with opioids for neuropathic pain. Orphenadrine and cyclobenzaprine are also
muscle relaxants, and are useful in painful musculoskeletal conditions.
Clonidine
Clonidine, sold under the brand name Catapres among others, is an α2-adrenergic agonist medication used to treat high blood pressure, ADHD, drug withdrawal ( alcohol, opioids, or nicotine), menopausal flushing, diarrhea, spasticity, and c ...
, an alpha-2 receptor agonist, is another drug that has found use as an analgesic adjuvant.
In 2021, researchers described a novel type of pain therapy – a
CRISPR-dCas9 epigenome editing
Epigenome editing or Epigenome engineering is a type of genetic engineering in which the epigenome is modified at specific sites using engineered molecules targeted to those sites (as opposed to whole-genome modifications). Whereas gene editing inv ...
method for repressing
Nav1.7 gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. The ...
which showed therapeutic potential in three mouse models of chronic pain.
Self-management
Self-management of chronic pain has been described as the individual's ability to manage various aspects of their chronic pain.
Self-management can include building
self-efficacy
In psychology, self-efficacy is an individual's belief in their capacity to act in the ways necessary to reach specific goals. The concept was originally proposed by the psychologist Albert Bandura.
Self-efficacy affects every area of human endea ...
, monitoring one's own symptoms, goal setting and action planning. It also includes patient-physician shared decision-making, among others.
The benefits of self-management vary depending on self-management techniques used. They only have marginal benefits in management of chronic musculoskeletal pain. Some research has shown that self-management of pain can use different approaches. Those approaches can range from different therapies such as yoga, acupuncture,exercise and other relaxation techniques. Patients could also take a more natural approach by taking different minerals, vitamins or herbs. However, research has shown there is a difference between rural patients and non-rural patients having more access to different self-management approaches. Physicians in these areas may be readily prescribing more pain medication in these rural cities due to being less experienced with pain management. Simply put, it is sometimes easier for rural patients to get a prescription that insurance pays for instead of natural approaches that cost more money than they can afford to spend on their pain management. Self-management may be a more expensive alternative.
Society and culture
The medical treatment of pain as practiced in
Greece and
Turkey is called algology (from the Greek άλγος,
algos, "
pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
"). The Hellenic Society of Algology and the Turkish Algology-Pain Society are the relevant local bodies affiliated to the
International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP).
Undertreatment
Undertreatment of pain is the absence of pain management therapy for a person in
pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
when treatment is
indicated
In medicine, an indication is a valid reason to use a certain test, medication, procedure, or surgery. There can be multiple indications to use a procedure or medication. An indication can commonly be confused with the term diagnosis. A diagnosis ...
.
Consensus in
evidence-based medicine
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) is "the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients". The aim of EBM is to integrate the experience of the clinician, the values of t ...
and the recommendations of
medical specialty organizations establish guidelines to determine the treatment for pain which health care providers ought to offer.
For various social reasons, persons in pain may not seek or may not be able to access treatment for their pain.
Health care providers may not provide the treatment which authorities recommend.
Some studies about gender biases have concluded that female pain recipients are often over looked when it comes to the perception of their pain. Whether they appeared to be in high levels of pain didn't make a difference for their observers. The women participants in the studies were still ''perceived'' to be in less pain than they actually were. Men participants on the other hand were offered pain relief while their self reporting indicated that their pain levels didn't necessarily warrant treatment. Biases exist when it comes to gender. Prescribers have been seen over and under prescribing treatment to individuals based on them being male or female .There are other prevalent reasons that undertreatment of pain occurs. Gender is a factor as well as race. When it comes to prescribers treating patients racial disparities has become a real factor. Research has shown that non-white individuals pain perception has affected their pain treatment. The
African-American community has been shown to suffer significantly when it comes to trusting the medical community to treat them. Oftentimes medication although available to be prescribed is dispensed in less quantities due to their pain being perceived on a smaller scale. The black community could be undermined by physicians thinking they are not in as much pain as they are reporting. Another occurrence may be physicians simply making the choice not to treat the patient accordingly in spite of the self-reported pain level. Racial disparity is definitely a real issue in the world of pain management.
In children
Acute pain is common in children and adolescents as a result of injury, illness, or necessary medical procedures.
is present in approximately 15–25% of children and adolescents. It may be caused by an underlying disease, such as
sickle cell anemia,
cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. O ...
,
rheumatoid arthritis. Cancer or
functional disorder
‘Functional disorder’ is an umbrella term for a group of recognisable medical conditions which are due to changes to the functioning of the systems of the body rather than due to a disease affecting the structure of the body.
Functional disord ...
s such as migraines,
fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a medical condition defined by the presence of chronic widespread pain, fatigue, waking unrefreshed, cognitive symptoms, lower abdominal pain or cramps, and depression. Other symptoms include insomnia and a general hyp ...
, and complex regional pain could also cause chronic pain in children.
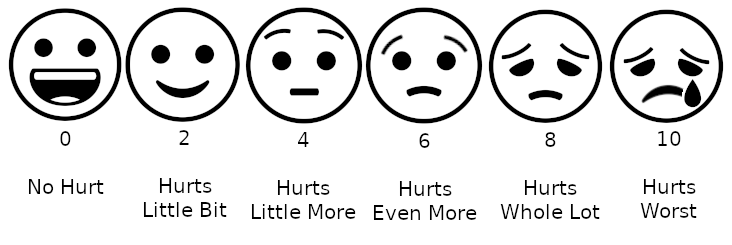
Pain assessment in children is often challenging due to limitations in developmental level, cognitive ability, or their previous pain experiences. Clinicians must observe physiological and behavioral cues exhibited by the child to make an assessment. Self-report, if possible, is the most accurate measure of pain. Self-report pain scales involve younger kids matching their pain intensity to photographs of other children's faces, such as the Oucher Scale, pointing to schematics of faces showing different pain levels, or pointing out the location of pain on a body outline.
Questionnaires for older children and adolescents include the Varni-Thompson Pediatric Pain Questionnaire (PPQ) and the Children's Comprehensive Pain Questionnaire. They are often utilized for individuals with chronic or persistent pain.
Acetaminophen,
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
, and
opioid analgesics are commonly used to treat acute or chronic pain symptoms in children and adolescents. However a pediatrician should be consulted before administering any medication.
Caregivers may provide nonpharmacological treatment for children and adolescents because it carries minimal risk and is cost effective compared to pharmacological treatment. Nonpharmacologic interventions vary by age and developmental factors. Physical interventions to ease pain in infants include swaddling, rocking, or sucrose via a pacifier. For children and adolescents physical interventions include hot or cold application,
massage, or
acupuncture.
Cognitive behavioral therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a psycho-social intervention that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions, primarily depression and anxiety disorders. CBT focuses on challenging and changing cognitive distortions (suc ...
(CBT) aims to reduce the emotional distress and improve the daily functioning of school-aged children and adolescents with pain by changing the relationship between their thoughts and emotions. In addition this therapy teaches them adaptive
coping strategies. Integrated interventions in CBT include
relaxation technique,
mindfulness
Mindfulness is the practice of purposely bringing one's attention to the present-moment experience without evaluation, a skill one develops through meditation or other training. Mindfulness derives from ''sati'', a significant element of Hind ...
,
biofeedback
Biofeedback is the process of gaining greater awareness of many physiology, physiological functions of one's own body by using Electronics, electronic or other instruments, and with a goal of being able to Manipulation (psychology), manipulate t ...
, and
acceptance
Acceptance in human psychology is a person's assent to the reality of a situation, recognizing a process or condition (often a negative or uncomfortable situation) without attempting to change it or protest it. The concept is close in meaning to ...
(in the case of chronic pain).
Many therapists will hold sessions for caregivers to provide them with effective management strategies.
Professional certification
Pain management practitioners come from all fields of medicine. In addition to medical practitioners, a pain management team may often benefit from the input of
pharmacists,
physiotherapists,
clinical psychologist
Clinical psychology is an integration of social science, theory, and clinical knowledge for the purpose of understanding, preventing, and relieving psychologically based distress or dysfunction and to promote subjective well-being and persona ...
s and
occupational therapists, among others. Together the multidisciplinary team can help create a package of care suitable to the patient.
Pain medicine in the United States
Pain physicians are often fellowship-trained
board-certified anesthesiologists,
neurologists,
physiatrists,
emergency physicians, or
psychiatrists.
Palliative care doctors are also specialists in pain management. The
American Society of Interventional Pain Physicians
The American Society of Interventional Pain Physicians (ASIPP) is a not-for-profit organization that represents nearly 4,500 interventional pain management specialists. It has its headquarters in Paducah, Kentucky. Its current Chairman of the Boa ...
, the
American Board of Anesthesiology, the
American Osteopathic Board of Anesthesiology
The American Osteopathic Board of Anesthesiology (AOBA) is an organization that provides board certification to qualified Doctors of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) who specialize in the administration of anesthetic agents and perioperative medicine ( ...
(recognized by the
AOABOS
Established in 1939, the American Osteopathic Association Bureau of Osteopathic Specialists (AOABOS) is a non-profit umbrella organization for 18 medical specialty boards in the United States. Along with the American Board of Medical Specialties (A ...
), the American Board of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, the
American Board of Emergency Medicine and the
American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology each provide certification for a subspecialty in pain management following fellowship training. The fellowship training is recognized by the
American Board of Medical Specialties (ABMS) or the
American Osteopathic Association Bureau of Osteopathic Specialists (AOABOS). As the field of pain medicine has grown rapidly, many practitioners have entered the field, some non-ACGME board-certified.
See also
*
Equianalgesic
*
Opioid comparison
An equianalgesic chart is a conversion chart that lists equivalent doses of analgesics (drugs used to relieve pain). Equianalgesic charts are used for calculation of an equivalent dose (a dose which would offer an equal amount of analgesia) betwe ...
, an example of an
equianalgesic chart
*
Pain Catastrophizing Scale
Catastrophic thinking has widely been recognized in the development and maintenance of hypochondriasis and anxiety disorders. This broadly accepted understanding has classified catastrophizing as a tendency to misinterpret and exaggerate situati ...
*
Pain ladder
"Pain ladder", or analgesic ladder, was created by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a guideline for the use of drugs in the management of pain. Originally published in 1986 for the management of cancer pain, it is now widely used by medical p ...
*
Pain management during childbirth
*
Pain psychology
Pain psychology is the study of psychological and behavioral processes in chronic pain. Pain psychology involves the implementation of treatments for chronic pain. Pain psychology can also be regarded as a branch of medical psychology, as many co ...
References
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
*
World Health Organization (WHO) Treatment Guidelines on Pain
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pain Management
Palliative care
Acute pain

 Pain management is an aspect of medicine and
Pain management is an aspect of medicine and  Pain assessment in children is often challenging due to limitations in developmental level, cognitive ability, or their previous pain experiences. Clinicians must observe physiological and behavioral cues exhibited by the child to make an assessment. Self-report, if possible, is the most accurate measure of pain. Self-report pain scales involve younger kids matching their pain intensity to photographs of other children's faces, such as the Oucher Scale, pointing to schematics of faces showing different pain levels, or pointing out the location of pain on a body outline. Questionnaires for older children and adolescents include the Varni-Thompson Pediatric Pain Questionnaire (PPQ) and the Children's Comprehensive Pain Questionnaire. They are often utilized for individuals with chronic or persistent pain.
Acetaminophen,
Pain assessment in children is often challenging due to limitations in developmental level, cognitive ability, or their previous pain experiences. Clinicians must observe physiological and behavioral cues exhibited by the child to make an assessment. Self-report, if possible, is the most accurate measure of pain. Self-report pain scales involve younger kids matching their pain intensity to photographs of other children's faces, such as the Oucher Scale, pointing to schematics of faces showing different pain levels, or pointing out the location of pain on a body outline. Questionnaires for older children and adolescents include the Varni-Thompson Pediatric Pain Questionnaire (PPQ) and the Children's Comprehensive Pain Questionnaire. They are often utilized for individuals with chronic or persistent pain.
Acetaminophen,