Packaging Waste on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Packaging waste, the part of the
 According to the
According to the
 The Institute of Packaging Professionals defines ''overpackaging'' as “a condition where the methods and materials used to package an item exceed the requirements for adequate containment, protection, transport, and sale.” Overpackaging is an opportunity for
The Institute of Packaging Professionals defines ''overpackaging'' as “a condition where the methods and materials used to package an item exceed the requirements for adequate containment, protection, transport, and sale.” Overpackaging is an opportunity for







waste
Waste (or wastes) are unwanted or unusable materials. Waste is any substance discarded after primary use, or is worthless, defective and of no use. A by-product, by contrast is a joint product of relatively minor economic value. A waste prod ...
that consists of packaging
Packaging is the science, art and technology of enclosing or protecting products for distribution, storage, sale, and use. Packaging also refers to the process of designing, evaluating, and producing packages. Packaging can be described as a co ...
and packaging material
Packaging is the science, art and technology of enclosing or protecting products for distribution, storage, sale, and use. Packaging also refers to the process of designing, evaluating, and producing packages. Packaging can be described as a co ...
, is a major part of the total global waste, and the major part of the packaging waste consists of single-use
A disposable (also called disposable product) is a product designed for a single use after which it is recycled or is disposed as solid waste. The term is also sometimes used for products that may last several months (e.g. disposable air filte ...
plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptab ...
food packaging
Food packaging is a packaging system specifically designed for food and represents one of the most important aspects among the processes involved in the food industry, as it provides protection from chemical, biological and physical alteratio ...
, a hallmark of throwaway culture
The throw-away society is a generalised description of human social concept strongly influenced by consumerism, whereby the society tends to use items once only, from disposable packaging, and consumer products are not designed for reuse or life ...
. Notable examples for which the need for regulation was recognized early, are "containers of liquids for human consumption", i.e. plastic bottles
A plastic bottle is a bottle constructed from high-density or low density plastic. Plastic bottles are typically used to store liquids such as water, soft drinks, motor oil, cooking oil, medicine, shampoo, milk, and ink. The size ranges from v ...
and the like. In Europe, the Germans top the list of packaging waste producers with more than 220 kilos of packaging per capita.
Background
 According to the
According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it be ...
(EPA), defined containers and packaging
Packaging is the science, art and technology of enclosing or protecting products for distribution, storage, sale, and use. Packaging also refers to the process of designing, evaluating, and producing packages. Packaging can be described as a co ...
as products that are assumed to be discarded the same year the products they contain are purchased. The majority of the solid waste
Municipal solid waste (MSW), commonly known as trash or garbage in the United States and rubbish in Britain, is a waste type consisting of everyday items that are discarded by the public. "Garbage" can also refer specifically to food waste, ...
are packaging products, estimating to be about 77.9 million tons of generation in 2015 (29.7 percent of total generation). Packaging can come in all shapes and forms ranging from Amazon boxes to soda can
A drink can (or beverage can) is a metal container designed to hold a fixed portion of liquid such as carbonated soft drinks, alcoholic drinks, fruit juices, teas, herbal teas, energy drinks, etc. Drink cans are made of aluminum (75% of ...
s and are used to store, transport, contain, and protect goods to keep customer satisfaction. The type of packaging materials including glass, aluminum, steel, paper, cardboard, plastic, wood, and other miscellaneous packaging. Packaging waste is a dominant contributor in today's world and responsible for half of the waste in the globe.
The recycling rate in 2015 for containers and packaging was 53 percent. Furthermore, the process of burning of containers and packaging was 7.2 million tons (21.4 percent of total combustion with energy recovery
Energy recovery includes any technique or method of minimizing the input of energy to an overall system by the exchange of energy from one sub-system of the overall system with another. The energy can be in any form in either subsystem, but mos ...
). Following the landfill
A landfill site, also known as a tip, dump, rubbish dump, garbage dump, or dumping ground, is a site for the disposal of waste materials. Landfill is the oldest and most common form of waste disposal, although the systematic burial of the waste ...
s that received 29.4 million tons (21.4 percent of total land filling) within the same year.
As packaging waste pollutes the Earth, all life on Earth experiences negative impacts that affected their lifestyle. Marine or land-living animals are suffocating due to the pollution of packaging waste. This is a major issue for low income countries who do not have an efficient waste management system to clean up their environments and being the main sources for the global ocean pollution
Marine pollution occurs when substances used or spread by humans, such as industrial, agricultural and residential waste, particles, noise, excess carbon dioxide or invasive organisms enter the ocean and cause harmful effects there. The majorit ...
. But 'litter louts', individuals who lack the motivation to recycle and instead leave their waste anywhere they want are also major contributors, especially in high income nations where such facilities are available. The current location with the greatest amount of solid waste that includes most of packaging products is the Great Pacific Garbage Patch located at West Coast of North America to Japan. Most packaging waste that eventually goes into the ocean often comes from places such as lakes, streams, and sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged from residenc ...
.
Possible solutions to reducing packaging waste are very simple and easy and could start with minimisation of packaging material
Packaging is the science, art and technology of enclosing or protecting products for distribution, storage, sale, and use. Packaging also refers to the process of designing, evaluating, and producing packages. Packaging can be described as a co ...
ranging up to a zero waste
Zero waste is a set of principles focused on waste prevention that encourages redesigning resource life cycles so that all products are reused. The goal of this movement is to avoid sending trash to landfills, incinerators, or the ocean. Curren ...
strategy (package-free products). The problem is mainly in a lack of motivation to start making a change. But examples of effective ways to help reduce packaging pollution include banning the use of single-use
A disposable (also called disposable product) is a product designed for a single use after which it is recycled or is disposed as solid waste. The term is also sometimes used for products that may last several months (e.g. disposable air filte ...
plastics, more social awareness and education, promotion of eco-friendly
Environment friendly processes, or environmental-friendly processes (also referred to as eco-friendly, nature-friendly, and green), are sustainability and marketing terms referring to goods and services, laws, guidelines and policies that clai ...
alternatives, public pressure, voluntary cleaning up, and adopting reusable or biodegradable
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradati ...
bags.
Overpackaging
 The Institute of Packaging Professionals defines ''overpackaging'' as “a condition where the methods and materials used to package an item exceed the requirements for adequate containment, protection, transport, and sale.” Overpackaging is an opportunity for
The Institute of Packaging Professionals defines ''overpackaging'' as “a condition where the methods and materials used to package an item exceed the requirements for adequate containment, protection, transport, and sale.” Overpackaging is an opportunity for source reduction Source reduction is activities designed to reduce the volume, mass, or toxicity of products throughout the life cycle. It includes the design and manufacture, use, and disposal of products with minimum toxic content, minimum volume of material, and ...
, reducing waste by proper package design and practice.
A classic example of a wasteful package design is a breakfast cereal box. This is typically a folding carton
The folding carton created the packaging industry as it is known today, beginning in the late 19th century. The process involves folding carton made of paperboard that is printed, laminated, cut, then folded and glued. The cartons are shipped fla ...
enclosing a plastic bag
A plastic bag, poly bag, or pouch is a type of container made of thin, flexible, plastic film, nonwoven fabric, or plastic textile. Plastic bags are used for containing and transporting goods such as foods, produce, powders, ice, magazines, c ...
of cereal. Cartons are typically tall and wide but very thin. This has an inefficient material-to-volume ratio; it is wasteful. Structural packaging engineer
Packaging engineering, also package engineering, packaging technology and packaging science, is a broad topic ranging from design conceptualization to product placement. All steps along the manufacturing process, and more, must be taken into ac ...
s are aware of the opportunity to save packaging costs, materials, and waste but marketers find benefit in a “billboard” style package for advertising and graphics. An optimized folding box would use much less paperboard for the same volume of cereal, but with reduced surface area for graphics. The use of a plastic bag without an enclosing box would use less material per unit of cereal.
''Slackfill'' packaging is that which is intentionally under-filled, resulting in non-functional headspace. Packagers doing this not only risk charges of ''deceptive packaging'' but are using excessive packaging: packaging waste.
With fragile items such as consumer electronics, engineers try to match the fragility of the product with the expected stresses of distribution handling. Package cushioning is used to help ensure safe delivery of the product. With overpackaging, excessive cushion and a larger corrugated box are used: wasteful packaging. Conversely, ''underpackaging'' would be the use of insufficient cushioning. Excessive product waste caused by underpackaging may be worse for the environment than the waste of the package.
Sometimes packaging is designed to protect its product for controlled distribution to a retail store. With online shopping
Online shopping is a form of electronic commerce which allows consumers to directly buy goods or services from a seller over the Internet using a web browser or a mobile app. Consumers find a product of interest by visiting the website of the r ...
or E-commerce
E-commerce (electronic commerce) is the activity of electronically buying or selling of products on online services or over the Internet. E-commerce draws on technologies such as mobile commerce, electronic funds transfer, supply chain manageme ...
, however, items packed for retail sale may be shipped individually by Fulfillment house
Fulfillment house and fulfillment center (in British English: fulfilment house and fulfilment centre) are modern terms for a packing warehouse. The terms were coined in the middle of the 1990s, and "fulfillment center" is usually used about an i ...
s by package delivery
Package delivery or parcel delivery is the delivery of shipping containers, parcels, or high value mail as single shipments. The service is provided by most postal systems, express mail, private courier companies, and less than truckload shi ...
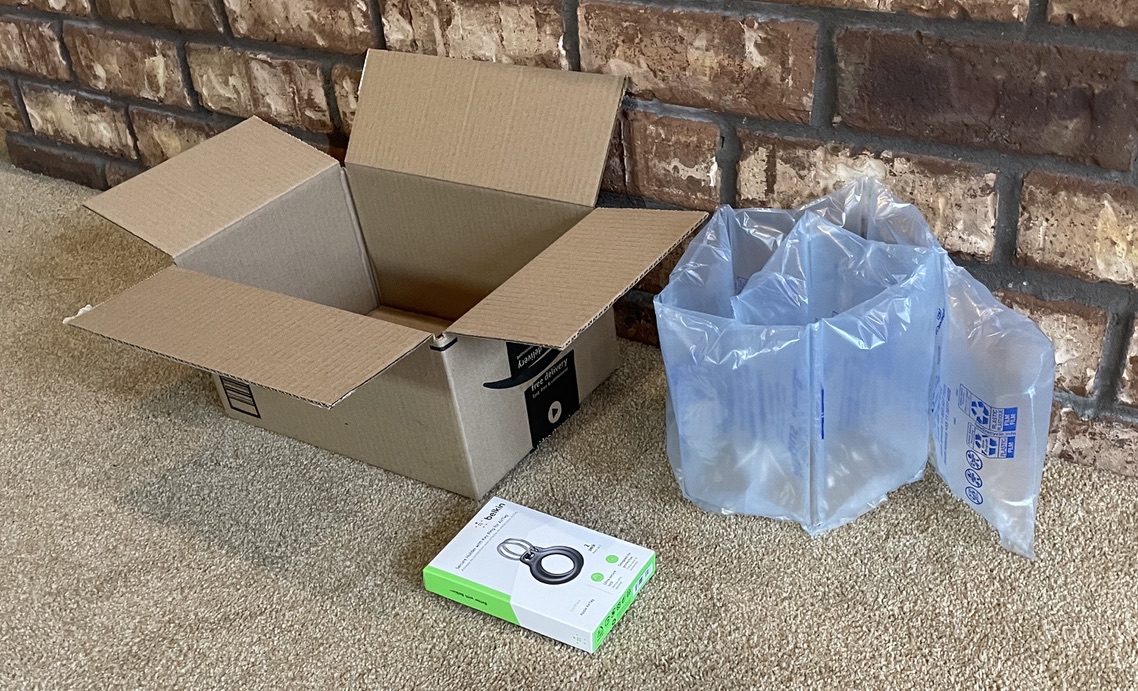
or small parcel carriers. Retail packages are frequently packed into a larger corrugated box for shipment. Often these secondary boxes are much larger than needed, thus use void-fill to immobilize the contents. This can have the appearance of gross overpackaging but is sometimes necessary. If the product packager designed all packaging to meet the requirements of individual shipment, then the portion delivered to a retail store would have excessive packaging. Sometimes two levels of packaging are needed for separate distribution, resulting in production inefficiencies.
Types of packaging wastes

Glass containers
Bottles and jars for drinks and storing foods or juices are examples of glass containers. It's been estimated by the EPA that 9.1 million tons of glass containers were generated in 2015, or 3.5 percent of municipal solid waste (MSW). About 70 percent of glass consumption is used for containers and packaging purposes. At least 13.2 percent of the production of glass and containers are burned with energy recovery. The amount of glass containers and packaging going into the land fill is about 53 percent.
Aluminum containers and packaging
Aluminum container and packaging waste usually comes from cans from any kind of beverages, but foil can also be another that contributes it as well. It's been given that about 25 percent of aluminum is used for packaging purposes. Using the Aluminum Association Data, it has been calculated that at least 1.8 million tons of aluminum packaging were generated in 2015 or 0.8 percent MSW produced. Of those that are produced, only about 670,000 tons of aluminum containers and packaging were recycled, about 54.9 percent. And, the ones that ends up in the land fill is 50.6 percent.
Steel containers and packaging
The production of steel containers and packaging mostly comes in cans and other things like steel barrels. Only about 5 percent of steel use for packaging purposes of the total world of steel consumption which makes it the least amount wasted and the most recycled. It's totaled that 2.2 million tons or 0.9 percent of MSW generated in 2015. While according to the Steel Recycling Institute, an estimate of 1.6 million tons (73 percent) of steel packaging were recycled. Adding on, the steel packaging that were combusted with energy recover was about 5.4 percent and 21.6 percent were land filled.
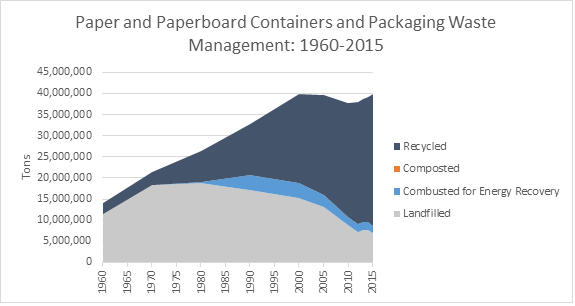
Paper and paperboard containers and packaging
The most of it being generated, and within the MSW in 2015, was corrugated boxes coming with at least 31.3 million tons (11.3 percent total) produced. However, it also the top most recycled at 28.9 million tons (92.3 percent) boxes being recycled in 2015. Later on, they are then combusted which makes 0.5 million tons and landfills received 1.9 million tons. Other than corrugated boxes, cartons, bags, sacks, wrapping papers, and other boxes used for shoes or cosmetics are other examples of paper and paperboard containers and packaging. The total amount of MSW generated for paper and paperboard containers and packaging was 39.9 million tons or 15.1 percent in 2015. Although, the recycled rate is about 78.2 percent and 4.3 percent of small proportions were combusted withenergy recovery
Energy recovery includes any technique or method of minimizing the input of energy to an overall system by the exchange of energy from one sub-system of the overall system with another. The energy can be in any form in either subsystem, but mos ...
and 17.6 percent in landfill.

Wood packaging
Wood packaging is anything that is made out of wood used for packaging purposes (e.g., wood crates, wood chips, boards, and planks). Wood packaging is still highly used in today's world for transporting goods. According to EPA's data that were borrowed from the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and theUnited States Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the United States federal executive departments, federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, ...
's Forest Service Southern Research Station, 9.8 million tons (3.7 percent of total MSW) of wood packaging were made in production in 2015. Also, in 2015, the amount that was recycled 2.7 million tons. Moreover, its estimated that 14.3 percent of the wood containers and packaging waste generated was combusted with energy recovery, while the 58.6 percent went to the land filled.

Plastic containers and packaging
Plastic container
Plastic containers are containers made exclusively or partially of plastic. Plastic containers are ubiquitous either as single-use or reuseable/durable plastic cups, plastic bottles, plastic bags, foam food containers, Tupperware, plastic tubes ...
s and packaging can be found in plastic bottles
A plastic bottle is a bottle constructed from high-density or low density plastic. Plastic bottles are typically used to store liquids such as water, soft drinks, motor oil, cooking oil, medicine, shampoo, milk, and ink. The size ranges from v ...
, supermarket bags, milk and water jugs, and more. EPA used data from the American Chemistry Council
American Chemistry Council (ACC), formerly known as the Manufacturing Chemists' Association (at its founding in 1872) and then as the Chemical Manufacturers' Association (from 1978 until 2000), is an industry trade association for American chemic ...
to estimate that 14.7 million tons (5.5 percent of MSW generation) of plastic container
Plastic containers are containers made exclusively or partially of plastic. Plastic containers are ubiquitous either as single-use or reuseable/durable plastic cups, plastic bottles, plastic bags, foam food containers, Tupperware, plastic tubes ...
s and packaging
Packaging is the science, art and technology of enclosing or protecting products for distribution, storage, sale, and use. Packaging also refers to the process of designing, evaluating, and producing packages. Packaging can be described as a co ...
were created in 2015. The overall amount that is recycled is about 2.2 million tons (14.6 percent). In addition, 16.8 percent were combusted with energy recover and 68.6 percent went straight into the land fill. Most of the plastics are made from polyethylene terephthalate
Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and foods ...
(PET), high-density polyethylene
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polyethylene high-density (PEHD) is a thermoplastic polymer produced from the monomer ethylene. It is sometimes called "alkathene" or "polythene" when used for HDPE pipes. With a high strength-to-density ratio, ...
(HDPE), low-density polyethylene
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic made from the monomer ethylene. It was the first grade of polyethylene, produced in 1933 by Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) using a high pressure process via free radical polymerization. Its ...
(LDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a ...
(PS), polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.
Polypropylene
belongs to the group of polyolefins and ...
(PP) and other resins. That being said, the recycling rate for PET bottle
Although PET is used in several applications, (principally textile fibres for apparel and upholstery, bottles and other rigid packaging, flexible packaging and electrical and electronic goods), as of 2022 only bottles are collected at a substa ...
s and jars was 29.9 percent (890,000 tons) and the recycling of HDPE water and milk jugs was 30.3 percent (230,000 tons).

Role of packaging waste in pollution
Litter
Litter
Litter consists of waste products that have been discarded incorrectly, without consent, at an unsuitable location. Litter can also be used as a verb; to litter means to drop and leave objects, often man-made, such as aluminum cans, paper cups, ...
mostly consists of packaging waste. Besides the disfigurement of the landscape, it also poses a health hazard for various life forms. Packaging materials such as glass and plastic bottles are the main constituents of litter. It has a huge impact on the marine environment as well, when animals are caught in or accidentally consume plastic packaging.
Air pollution
The production of packaging material is the main source of the air pollution that is being spread globally. Some emissions comes from accidental fires or activities that includes incineration of packaging waste that releases vinyl chloride, CFC, and hexane. For a more direct course, emissions can originate in land fill sites which could release and methane. Most comes from steel and glass packaging manufacturing.Water pollution
Packaging waste can come from land based or marine sources. The current location that makes up the large of amount of water pollution is the Great Pacific Garbage Patch located at West Coast of North America to Japan. Marine sources such as rivers that caught packaging materials eventually lead to the oceans. In global standards, about 80 percent of packaging waste in ocean comes from land based sources and 20 percent comes from marine sources. The 20 percent of packaging waste that comes from marine sources comes from the rivers of China starting from least to greatest contributors, the Hanjiang, Zhujiang, Dong, Huangpu, Xi, and Yangtze river. All other marine sources comes from rivers of Africa and Southeast Asia.
Impacts on marine species and wildlife species
Most marine species and wildlife species suffer from the following: * Entanglement: At least 344 species are entangled by packaging waste, specifically the ones that are plastics. Most of the victims are marine species like whales, seabirds, turtles, and fish. * Ingestion: 233 marine species are recorded that had consumed plastic packaging waste of either unintentionally, intentionally, or indirectly. Again, the following victims would be whales, fish, mammals, seabirds, and turtles. The effects of eating plastic packaging waste could lead to greatly reduced stomach capacity, leading to poor appetite and false sense of satiation. Whats worse is that the size of the ingested material is ultimately limited by the size of the organism. For example, microplastics consumed by planktons and fishes can consume cigarettes boxes. Plastic can also obstruct or perforate the gut, cause ulcerative lesions, or gastric rupture. This can ultimately lead to death. * Interaction: Animals contacting with packaging waste includes collisions, obstructions, abrasions or use as substrate.Impacts on human health
Bisphenol A
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a chemical compound primarily used in the manufacturing of various plastics. It is a colourless solid which is soluble in most common organic solvents, but has very poor solubility in water. BPA is produced on an industrial s ...
(BPA), styrene
Styrene () is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. This derivative of benzene is a colorless oily liquid, although aged samples can appear yellowish. The compound evaporates easily and has a sweet smell, although high concen ...
and benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, ...
can be found in certain packaging waste. BPA can affect the hearts of women, permanently damage the DNA of mice, and appear to be entering the human body from a variety of unknown sources. Studies from Journal of American Association shows that higher bisphenol A levels were significantly associated with heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, hea ...
s, diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
, and abnormally high levels of certain liver enzyme
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin tim ...
s. Toxins such as these are found within our food chains. When fish or plankton consume microplastics
Microplastics are fragments of any type of plastic less than in length, according to the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the European Chemicals Agency. They cause pollution by entering natural ecosystems from a v ...
, it can also enter our food chain. Microplastics was also found in common table salt and in both tap and bottled water
Bottled water is drinking water (e.g., well water, distilled water, mineral water, or spring water) packaged in plastic or glass water bottles. Bottled water may be carbonated or not. Sizes range from small single serving bottles to large car ...
. Microplastics are dangerous as the toxins can affect the human body's nervous, respiratory, and reproductive system.
Actions to reduce packaging wastes
Waste management system improvements
* Segregation of waste at sources: plastics, organic, metals, paper, etc. * Effective collection of the segregated waste, transport and safe storage * Cost-effective recycling of materials (including plastics) * Less land filling and dumping in the environmentPromotion of eco-friendly alternatives
Governments working with industries could support the development and promotion of sustainable alternatives in order to phase out single-use plastics progressively. If governments were to introduce economic incentives, supporting projects which upscale or recycle single-use items and stimulating the creation of micro-enterprises, they could contribute to the uptake of eco-friendly alternatives to single-use plastics.Social awareness and education
Social awareness and education is also one of the ways to help contribute to issues similar to helping reducing packaging waste. Using the media gives quick access for the individuals or groups to spread information and awareness in regarding to letting the public know what is going on in the world and ways that others can contribute to assist in fixing problems of packaging wastes. Schools are also good for spreading the education with factual knowledge, possible outcomes for the increase of packaging waste, and provide ways to get individuals to give a helping hand in keeping our planet clean. Public awareness strategies can include a wide range of activities designed to persuade and educate. These strategies may focus not only on the reuse and recycling of resources, but also on encouraging responsible use and minimization of waste generation and litter.Voluntarily actions to reduce packaging waste
* Reuse bags * Bring reusable bags to supermarkets * Repair broken objects instead of throwing them away * Exchange packaging materials on BoxGiver * Recycle * Clean up in coastal areas * Do community services to clean up parks and streets from packaging wasteSee also
*Plastic waste
Plastic pollution is the accumulation of plastic objects and particles (e.g. plastic bottles, bags and microbeads) in the Earth's environment that adversely affects humans, wildlife and their habitat. Plastics that act as pollutants are catego ...
* Waste & Resources Action Programme
WRAP (Waste & Resources Action Programme) is a British registered charity. It works with businesses, individuals and communities to achieve a circular economy, by helping them reduce waste, develop sustainable products and use resources in an eff ...
* Packaging Recovery Note
* Packaging and packaging waste directive
* Producer Responsibility Obligations (Packaging Waste) Regulations 2007
* Reusable packaging Reusable packaging is manufactured of durable materials and is specifically designed for multiple trips and extended life. A ''reusable package'' or container is “designed for reuse without impairment of its protective function.” The term ret ...
* Sustainable packaging
* Fast food
Fast food is a type of mass-produced food designed for commercial resale, with a strong priority placed on speed of service. It is a commercial term, limited to food sold in a restaurant or store with frozen, preheated or precooked ingredien ...
* Waste minimization
Waste minimisation is a set of processes and practices intended to reduce the amount of waste produced. By reducing or eliminating the generation of harmful and persistent wastes, waste minimisation supports efforts to promote a more sustainab ...
* Circular economy
A circular economy (also referred to as circularity and CE) is a model of production and consumption, which involves sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing and recycling existing materials and products as long as possible. CE aims ...
References