Pacific Northwest languages on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
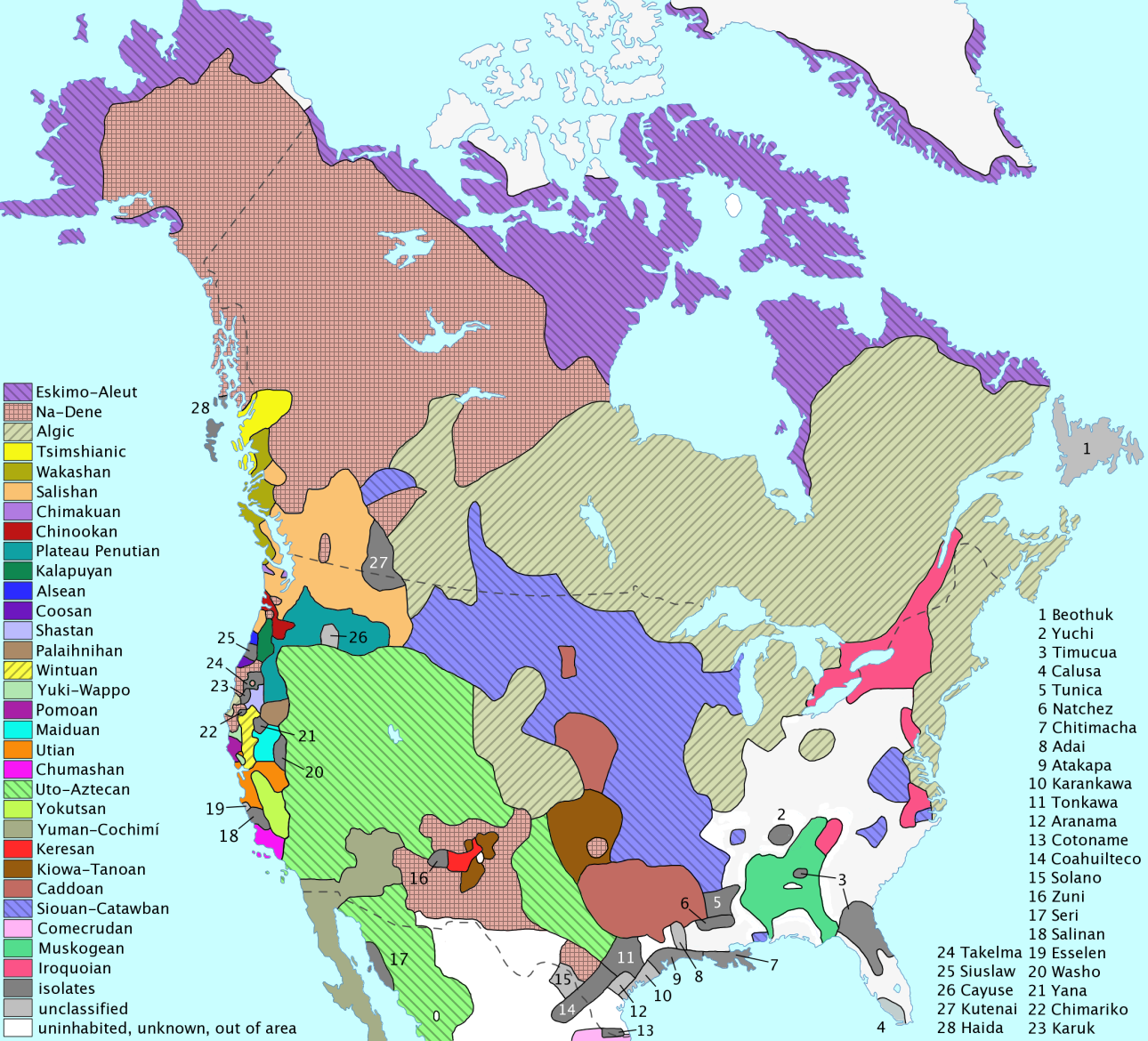 The Pacific Northwest languages are the indigenous languages of the
The Pacific Northwest languages are the indigenous languages of the
 The Pacific Northwest languages are the indigenous languages of the
The Pacific Northwest languages are the indigenous languages of the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Tho ...
of North America. This is a geographic term and does not imply any common heritage for these languages. In fact, the Pacific Northwest is an area of exceptional linguistic diversity and contains languages belonging to a large number of (apparently) unrelated families
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideal ...
. However, the close proximity of multiple languages has created many opportunities for mutual interaction, with the result that the Pacific Northwest forms a linguistic area, with many areal feature
In geolinguistics, areal features are elements shared by languages or dialects in a geographic area, particularly when such features are not descended from a proto-language, or, common ancestor language. That is, an areal feature is contrasted to ...
s that are shared across language families. These include animacy hierarchies and case markers that cliticize to the end of the word before the noun phrase being marked for case.
The linguistic area is centered on the Salishan
The Salishan (also Salish) languages are a family of languages of the Pacific Northwest in North America (the Canadian province of British Columbia and the American states of Washington, Oregon, Idaho and Montana). They are characterised by ...
, Wakashan and Chimakuan
The Chimakuan languages are a group of extinct languages that were spoken in northwestern Washington state, United States, on the Olympic Peninsula. They were spoken by Chimakum, Quileute and Hoh tribes. They are part of the Mosan sprachbund, ...
families. Some features are also shared with Tsimshianic, Chinookan
The Chinookan languages were a small family of languages spoken in Oregon and Washington along the Columbia River by Chinook peoples. Although the last known native speaker of any Chinookan language died in 2012, the 2009-2013 American Community ...
and Sahaptian
Sahaptian (also Sahaptianic, Sahaptin, Shahaptian) is a two-language branch of the Plateau Penutian family spoken by Native Americans in the United States, Native American peoples in the Columbia Plateau region of Washington (state), Washington, ...
languages, as well as Kutenai
The Kutenai ( ), also known as the Ktunaxa ( ; ), Ksanka ( ), Kootenay (in Canada) and Kootenai (in the United States), are an indigenous people of Canada and the United States. Kutenai bands live in southeastern British Columbia, northern ...
, a language isolate.
These languages are well known for their complex phonetic
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that studies how humans produce and perceive sounds, or in the case of sign languages, the equivalent aspects of sign. Linguists who specialize in studying the physical properties of speech are phoneticians. ...
systems, particularly their large number of dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
* Dorsal c ...
obstruents. Tlingit
The Tlingit ( or ; also spelled Tlinkit) are indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast of North America. Their language is the Tlingit language (natively , pronounced ),
, for example, has about 24 different stop consonants and fricative
A fricative is a consonant produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of ; the back of the tongue against the soft palate in t ...
s in the velar
Velars are consonants articulated with the back part of the tongue (the dorsum) against the soft palate, the back part of the roof of the mouth (known also as the velum).
Since the velar region of the roof of the mouth is relatively extensive a ...
, uvular
Uvulars are consonants articulated with the back of the tongue against or near the uvula, that is, further back in the mouth than velar consonants. Uvulars may be stops, fricatives, nasals, trills, or approximants, though the IPA does not prov ...
, and glottal areas (as well as five different lateral
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Healthcare
*Lateral (anatomy), an anatomical direction
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
* Lateral release (surgery), a surgical procedure on the side of a kneecap
Phonetics
*Lateral co ...
obstruents). Also common are a number of other consonants that are unfamiliar to English speakers, such as pharyngeal consonants and ejective
In phonetics, ejective consonants are usually voiceless consonants that are pronounced with a glottalic egressive airstream. In the phonology of a particular language, ejectives may contrast with aspirated, voiced and tenuis consonants. Some ...
s.
References
* Northwest Coast Sprachbund (North America) {{na-lang-stub