PSORT on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 PSORT is a
PSORT is a
PSORT website
 PSORT is a
PSORT is a bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combi ...
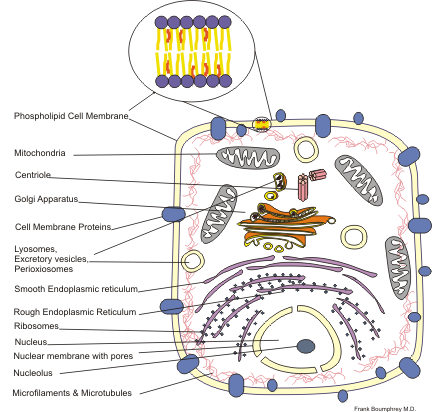
tool used for the prediction of protein localisation sites in cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
s. It receives the information
Information is an abstract concept that refers to that which has the power to inform. At the most fundamental level information pertains to the interpretation of that which may be sensed. Any natural process that is not completely random ...
of an amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
sequence and its taxon of origin (e.g. Gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall ...
) as inputs. Then it analyses the input sequence by applying the stored rules for various sequence features of known protein sorting signals. Finally, it reports the possibility for the input protein to be localised at each candidate site with additional information.
Researchers using this tool can predict with some degree of reason, where in a cell a protein is most likely to localise to. This is because proteins are localised by cell machinery that recognises signal peptide
A signal peptide (sometimes referred to as signal sequence, targeting signal, localization signal, localization sequence, transit peptide, leader sequence or leader peptide) is a short peptide (usually 16-30 amino acids long) present at the N-ter ...
sequences (similar to a postal address) and moves the protein the appropriate location. The signal peptide is often cleaved off after the destination is reached. PSORT uses known signal peptide sequences to analyse and predict what an input sequence is most likely to cause a localisation to.
Protein localisation is important because it supports a proposed role that a protein may have. For instance, catalase enzymes (proteins that convert peroxide into water and oxygen) should be expected to localise to a peroxisome because that is an area of high peroxide activity. By analysing a signal peptide sequence and visual localisation by GFP GFP may refer to:
Organisations
* Gaelic Football Provence, a French Gaelic Athletic Association club
* Geheime Feldpolizei, the German secret military police during the Second World War
* French Group for the Study of Polymers and their Applicat ...
expression, strong evidence is obtained for this role.
The program was written by Dr Kenta Nakai from the Human Genome Center at the Institute for Medical Science, University of Tokyo
, abbreviated as or UTokyo, is a public research university located in Bunkyō, Tokyo, Japan. Established in 1877, the university was the first Imperial University and is currently a Top Type university of the Top Global University Project by ...
, Japan and is available free for all users.
External Reference
PSORT website
References
{{Reflist Bioinformatics software Protein targeting