PRESS Statistic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 In
In statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
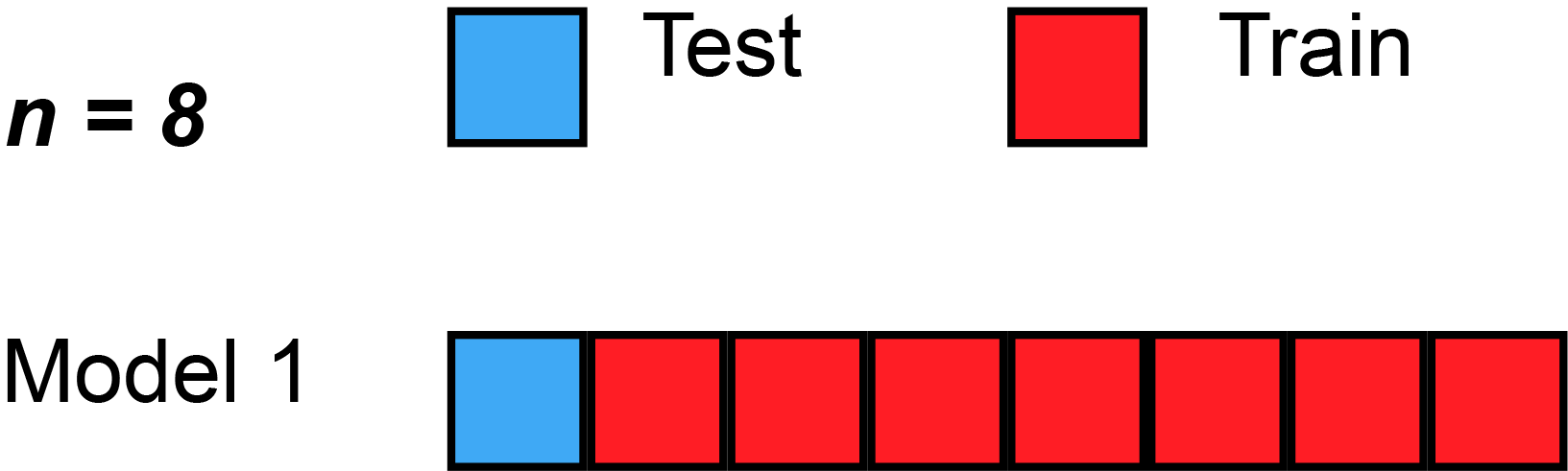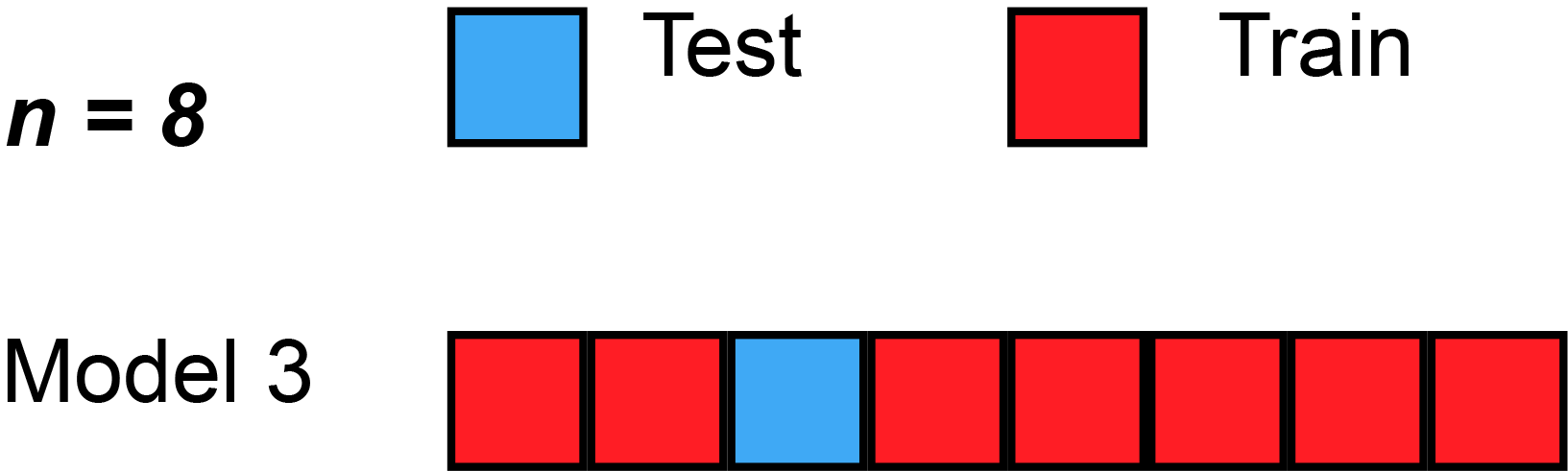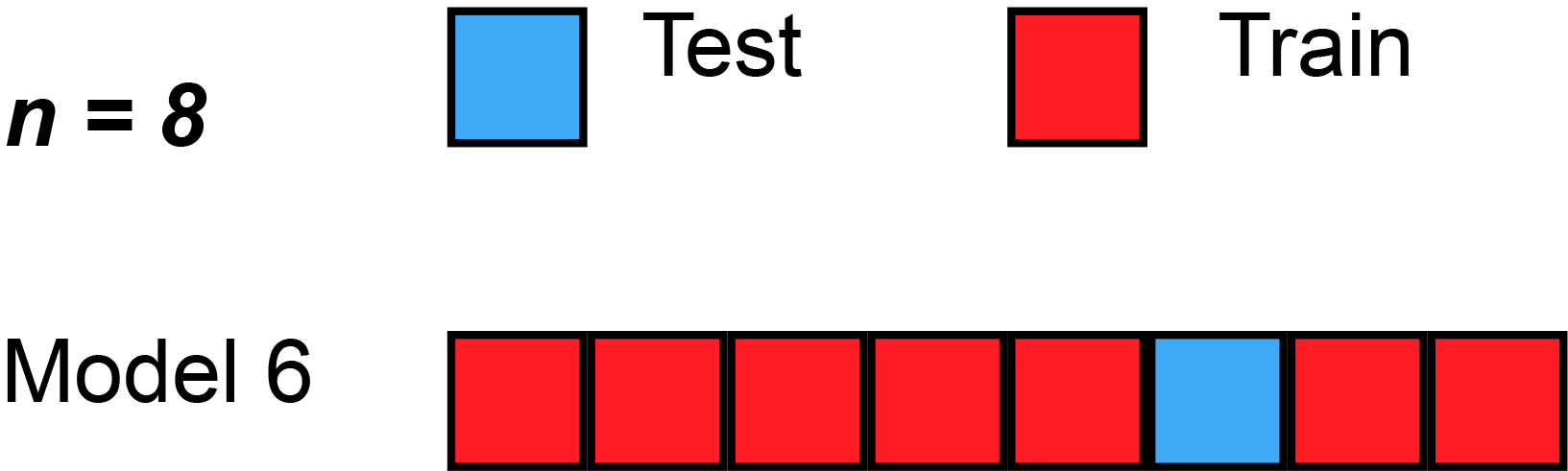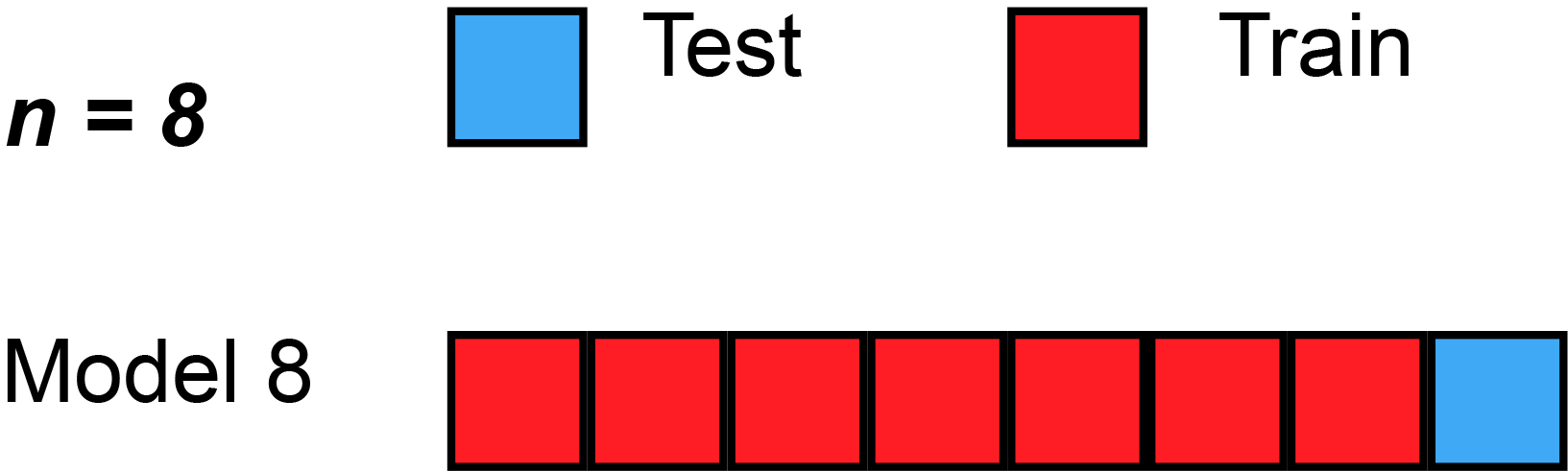
, the predicted residual error sum of squares (PRESS) is a form of cross-validation used in regression analysis to provide a summary measure of the fit of a model to a sample of observations that were not themselves used to estimate the model. It is calculated as the sum of squares of the prediction residuals for those observations. Specifically, the PRESS statistic is an exhaustive form of cross-validation, as it tests all the possible ways that the original data can be divided into a training and a validation set.
Procedure
Instead of ''fitting'' only one model on all data, leave-one-out cross-validation is used to fit N models (on N observations) where for each model one data point is left out from thetraining set
In machine learning, a common task is the study and construction of algorithms that can learn from and make predictions on data. Such algorithms function by making data-driven predictions or decisions, through building a mathematical model from ...
. The out-of-sample predicted value is calculated for the omitted observation in each case, and the PRESS statistic is calculated as the sum of the squares of all the resulting prediction errors:
:
Usage
Given this procedure, the PRESS statistic can be calculated for a number of candidate model structures for the same dataset, with the lowest values of PRESS indicating the best structures. Models that are over-parameterised ( over-fitted) would tend to give small residuals for observations included in the model-fitting but large residuals for observations that are excluded. The PRESS statistic has been extensively used in lazy learning and locally linear learning to speed-up the assessment and the selection of the neighbourhood size.See also
*Model selection
Model selection is the task of selecting a model from among various candidates on the basis of performance criterion to choose the best one.
In the context of machine learning and more generally statistical analysis, this may be the selection of ...
* Stepwise regression
In statistics, stepwise regression is a method of fitting regression models in which the choice of predictive variables is carried out by an automatic procedure. In each step, a variable is considered for addition to or subtraction from the set of ...
* Cross-validation (statistics)
Cross-validation, sometimes called rotation estimation or out-of-sample testing, is any of various similar model validation techniques for assessing how the results of a statistics, statistical analysis will Generalization error, generalize to ...
References
Regression diagnostics Model selection {{statistics-stub