Oramics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
__NOTOC__
Oramics is a drawn sound technique designed in 1957 by musician
 * ANS synthesizer
* Variophone
*
* ANS synthesizer
* Variophone
*
Mini Oramics machine
;Video * * ;BBC News * * {{citation , title = How Daphne Oram's Oramic machine changed electro music , url = https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/technology-12956702 , date = 4 April 2011 Graphical sound Articles containing video clips
Daphne Oram
Daphne Blake Oram (31 December 1925 – 5 January 2003) was a British composer and electronic musician. She was one of the first British composers to produce electronic sound, and was an early practitioner of musique concrète in the UK. As a co ...
. The machine was further developed in 1962 after receiving a grant from the Gulbenkian Foundation
The Calouste Gulbenkian Foundation ( pt, Fundação Calouste Gulbenkian), commonly referred to simply as the Gulbenkian Foundation, is a Portuguese institution dedicated to the promotion of the arts, philanthropy, science, and education. One o ...
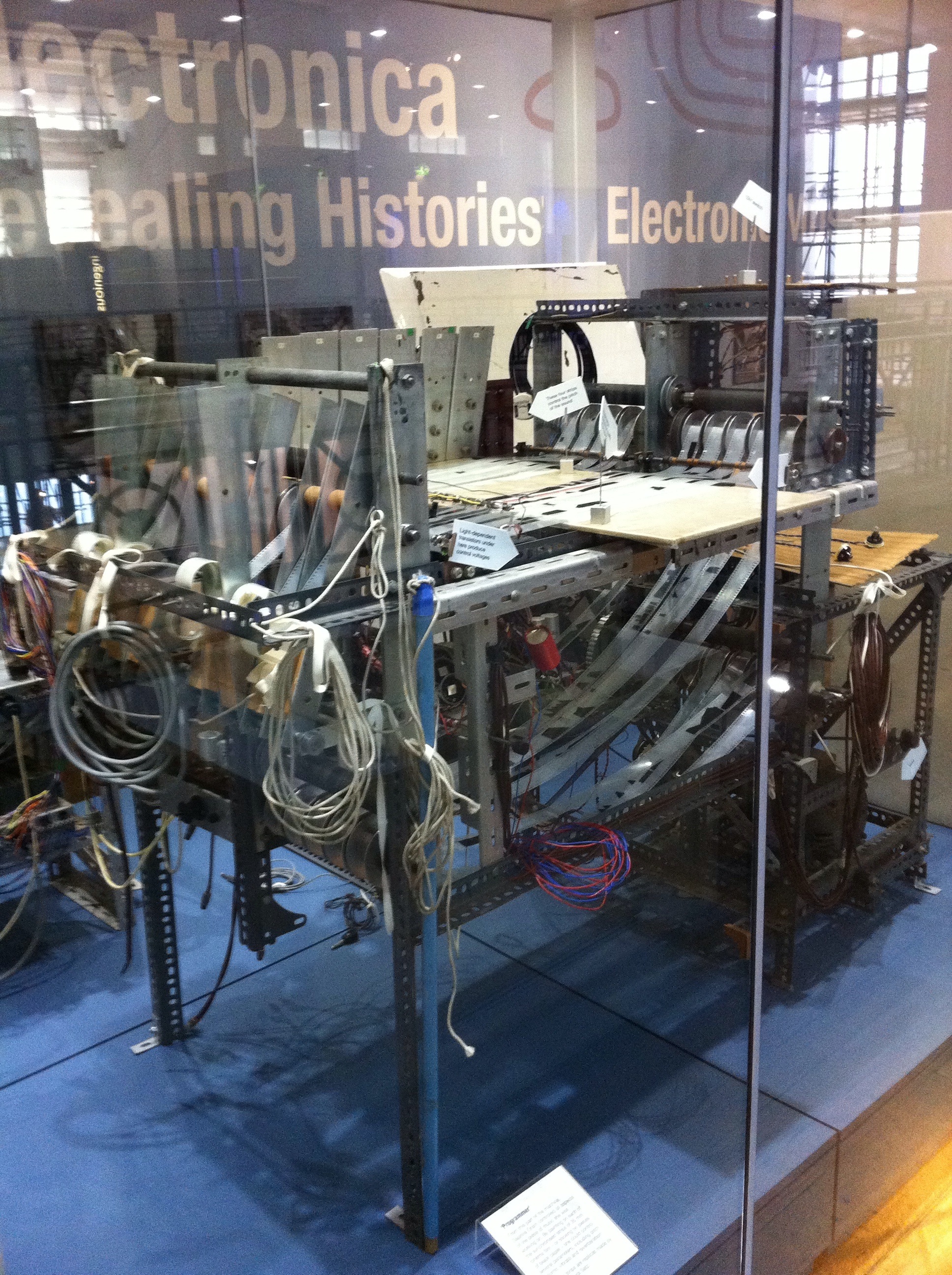
. The technique involves drawing on 35mm film strips to control the sound produced. Oramics was also the name used by Oram to refer to her studio and business interests generally.
Oram's composition machine consisted of a large rectangular metal frame, providing a table-like surface traversed by ten synchronised strips of clear, sprocketed 35mm film. The musician drew shapes on the film to create a mask, which modulated the light received by photocells. Although the output from the machine was monophonic, the sounds could be added to multitrack tapes to provide more texture and create polyphony
Polyphony ( ) is a type of musical texture consisting of two or more simultaneous lines of independent melody, as opposed to a musical texture with just one voice, monophony, or a texture with one dominant melodic voice accompanied by chords, ...
.
The original machine was exhibited at the Science Museum
A science museum is a museum devoted primarily to science. Older science museums tended to concentrate on static displays of objects related to natural history, paleontology, geology, industry and industrial machinery, etc. Modern trends in ...
in London between 2011 and 2015.
Related techniques
The Oramics machine, which creates music from graphic elements uses similar principles to Yevgeny Sholpo's " Variophone", which produces sound by reading shapes cut into and drawings on cardboard. Canadian filmmakers Norman McLaren andEvelyn Lambart
Evelyn Lambart (23 July 1914 – 3 April 1999) was a Canadian animator and technical director with the National Film Board of Canada, known for her early collaborations with Norman McLaren as well as her later films, as sole director.
In 19 ...
have made films that feature sounds created by drawing or printing various patterns, such as triangles and circles, along the optical soundtrack area of the film.
In 2016 Tom Richards, a PhD Student at Goldsmiths, University of London
Goldsmiths, University of London, officially the Goldsmiths' College, is a constituent research university of the University of London in England. It was originally founded in 1891 as The Goldsmiths' Technical and Recreative Institute by the Wo ...
, re-imagined and built a working Mini-Oramics machine.
See also
 * ANS synthesizer
* Variophone
*
* ANS synthesizer
* Variophone
* RCA Synthesizer
The RCA Mark II Sound Synthesizer (nicknamed ''Victor'') was the first programmable electronic synthesizer and the flagship piece of equipment at the Columbia-Princeton Electronic Music Center. Designed by Herbert Belar and Harry Olson at RCA, wi ...
References
Further reading
*External links
* * * () *Mini Oramics machine
;Video * * ;BBC News * * {{citation , title = How Daphne Oram's Oramic machine changed electro music , url = https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/technology-12956702 , date = 4 April 2011 Graphical sound Articles containing video clips