Optimal solutions for Rubik's Cube on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Optimal solutions for Rubik's Cube refer to solutions that are the shortest. There are two common ways to measure the length of a solution. The first is to count the number of quarter turns. The second is to count the number of outer-layer twists, called "face turns". A move to turn an outer layer two quarter (90°) turns in the same direction would be counted as two moves in the quarter turn metric (QTM), but as one turn in the face metric (FTM, or HTM "Half Turn Metric", or OBTM "Outer Block Turn Metric").
The maximal number of face turns needed to solve any instance of the Rubik's Cube is 20, and the maximal number of quarter turns is 26. These numbers are also the
Optimal solutions for Rubik's Cube refer to solutions that are the shortest. There are two common ways to measure the length of a solution. The first is to count the number of quarter turns. The second is to count the number of outer-layer twists, called "face turns". A move to turn an outer layer two quarter (90°) turns in the same direction would be counted as two moves in the quarter turn metric (QTM), but as one turn in the face metric (FTM, or HTM "Half Turn Metric", or OBTM "Outer Block Turn Metric").
The maximal number of face turns needed to solve any instance of the Rubik's Cube is 20, and the maximal number of quarter turns is 26. These numbers are also the
/ref> In 1992, a solution for the superflip with 20 face turns was found by Dik T. Winter, of which the minimality was shown in 1995 by Michael Reid, providing a new lower bound for the diameter of the cube group. Also in 1995, a solution for superflip in 24 quarter turns was found by Michael Reid, with its minimality proven by Jerry Bryan. In 1998, a new position requiring more than 24 quarter turns to solve was found. The position, which was called a 'superflip composed with four spot' needs 26 quarter turns.
 Although the whole cube group is very large (~4.3×1019), the right coset spaces and are much smaller.
The coset space is the largest and contains only 1082565 elements. The number of moves required by this algorithm is the sum of the largest process in each step.
Initially, Thistlethwaite showed that any configuration could be solved in at most 85 moves. In January 1980 he improved his strategy to yield a maximum of 80 moves. Later that same year, he reduced the number to 63, and then again to 52. By exhaustively searching the coset spaces it was later found that the worst possible number of moves for each stage was 7, 10, 13, and 15 giving a total of 45 moves at most. There have been implementations of Thistlewaite's algorithm in various computer languages.
Although the whole cube group is very large (~4.3×1019), the right coset spaces and are much smaller.
The coset space is the largest and contains only 1082565 elements. The number of moves required by this algorithm is the sum of the largest process in each step.
Initially, Thistlethwaite showed that any configuration could be solved in at most 85 moves. In January 1980 he improved his strategy to yield a maximum of 80 moves. Later that same year, he reduced the number to 63, and then again to 52. By exhaustively searching the coset spaces it was later found that the worst possible number of moves for each stage was 7, 10, 13, and 15 giving a total of 45 moves at most. There have been implementations of Thistlewaite's algorithm in various computer languages.
diameters
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest chord of the circle. Both definitions are also valid fo ...
of the corresponding Cayley graph
In mathematics, a Cayley graph, also known as a Cayley color graph, Cayley diagram, group diagram, or color group is a graph that encodes the abstract structure of a group. Its definition is suggested by Cayley's theorem (named after Arthur Cay ...
s of the Rubik's Cube group
The Rubik's Cube group is a group (G, \cdot ) that represents the structure of the Rubik's Cube mechanical puzzle. Each element of the set G corresponds to a cube move, which is the effect of any sequence of rotations of the cube's faces. With ...
. In STM (slice turn metric), the minimal number of turns is unknown.
There are many algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing ...
s to solve scrambled Rubik's Cubes. An algorithm that solves a cube in the minimum number of moves is known as God's algorithm
God's algorithm is a notion originating in discussions of ways to solve the Rubik's Cube puzzle, but which can also be applied to other combinatorial puzzles and mathematical games. It refers to any algorithm which produces a solution having the ...
.
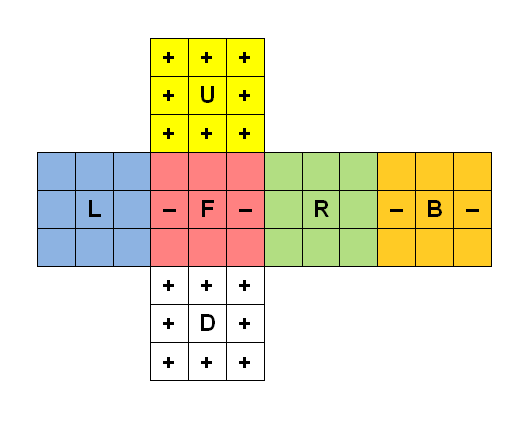
Move notation
To denote a sequence of moves on the 3×3×3 Rubik's Cube, this article uses "Singmaster notation", which was developed byDavid Singmaster
David Breyer Singmaster (born 1938) is an emeritus professor of mathematics at London South Bank University, England. A self-described metagrobologist, he has a huge personal collection of mechanical puzzles and books of brain teasers. He is mo ...
.
The letters L, R, F, B, U, and D indicate a clockwise quarter turn of the left, right, front, back, up, and down face respectively. Half turns are indicated by appending a 2. A counterclockwise quarter turn is indicated by appending a prime symbol
The prime symbol , double prime symbol , triple prime symbol , and quadruple prime symbol are used to designate units and for other purposes in mathematics, science, linguistics and music.
Although the characters differ little in appearance fr ...
( ′ ).
The letters M, S and E are used to denote the turning of a middle layer. M represents turning the layer between the R and L faces 1 quarter turn top to bottom. S represents turning the layer between the F and B faces 1 quarter turn clockwise, as seen from the front. E represents turning the layer between the U and D faces 1 quarter turn left to right, clockwise as seen from the bottom. As with regular turns, a 2 signifies a double turn and a prime (') indicates a quarter turn anticlockwise.
The letters X, Y and Z are used to signify cube rotations. X signifies rotating the cube in the R direction. Y signifies the rotation of the cube in the U direction. Z signifies the rotation of the cube on the F direction . These cube rotations are used in algorithms to make the algorithms smoother and faster. As with regular turns, a 2 signifies a half rotation and a prime (') indicates a quarter rotation in the opposite direction. Note that these letters are usually lowercase instead.
Lower bounds
It can be proven by counting arguments that there exist positions needing at least 18 moves to solve. To show this, first count the number of cube positions that exist in total, then count the number of positions achievable using at most 17 moves starting from a solved cube. It turns out that the latter number is smaller. This argument was not improved upon for many years. Also, it is not aconstructive proof
In mathematics, a constructive proof is a method of proof that demonstrates the existence of a mathematical object by creating or providing a method for creating the object. This is in contrast to a non-constructive proof (also known as an existenc ...
: it does not exhibit a concrete position that needs this many moves. It was conjectured that the so-called superflip would be a position that is very difficult. A Rubik's Cube is in the superflip pattern when each corner piece is in the correct position, but each edge piece is incorrectly oriented.Michael Reid's Rubik's Cube page M-symmetric positions/ref> In 1992, a solution for the superflip with 20 face turns was found by Dik T. Winter, of which the minimality was shown in 1995 by Michael Reid, providing a new lower bound for the diameter of the cube group. Also in 1995, a solution for superflip in 24 quarter turns was found by Michael Reid, with its minimality proven by Jerry Bryan. In 1998, a new position requiring more than 24 quarter turns to solve was found. The position, which was called a 'superflip composed with four spot' needs 26 quarter turns.
Upper bounds
The first upper bounds were based on the 'human' algorithms. By combining the worst-case scenarios for each part of these algorithms, the typical upper bound was found to be around 100. Perhaps the first concrete value for an upper bound was the 277 moves mentioned byDavid Singmaster
David Breyer Singmaster (born 1938) is an emeritus professor of mathematics at London South Bank University, England. A self-described metagrobologist, he has a huge personal collection of mechanical puzzles and books of brain teasers. He is mo ...
in early 1979. He simply counted the maximum number of moves required by his cube-solving algorithm. Later, Singmaster reported that Elwyn Berlekamp
Elwyn Ralph Berlekamp (September 6, 1940 – April 9, 2019) was a professor of mathematics and computer science at the University of California, Berkeley.Contributors, ''IEEE Transactions on Information Theory'' 42, #3 (May 1996), p. 1048. DO10. ...
, John Conway
John Horton Conway (26 December 1937 – 11 April 2020) was an English mathematician active in the theory of finite groups, knot theory, number theory, combinatorial game theory and coding theory. He also made contributions to many branches ...
, and Richard K. Guy had come up with a different algorithm that took at most 160 moves. Soon after, Conway’s Cambridge Cubists reported that the cube could be restored in at most 94 moves.
Thistlethwaite's algorithm
The breakthrough, known as "descent through nested sub-groups" was found byMorwen Thistlethwaite
Morwen Bernard Thistlethwaite is a knot theorist and professor of mathematics for the University of Tennessee in Knoxville. He has made important contributions to both knot theory and Rubik's Cube group theory.
Biography
Morwen Thistlethwait ...
; details of Thistlethwaite's algorithm were published in ''Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it ...
'' in 1981 by Douglas Hofstadter. The approaches to the cube that led to algorithms with very few moves are based on group theory
In abstract algebra, group theory studies the algebraic structures known as group (mathematics), groups.
The concept of a group is central to abstract algebra: other well-known algebraic structures, such as ring (mathematics), rings, field ...
and on extensive computer searches. Thistlethwaite's idea was to divide the problem into subproblems. Where algorithms up to that point divided the problem by looking at the parts of the cube that should remain fixed, he divided it by restricting the type of moves that could be executed. In particular he divided the cube group into the following chain of subgroups:
*
*
*
*
*
Next he prepared tables for each of the right coset
In mathematics, specifically group theory, a subgroup of a group may be used to decompose the underlying set of into disjoint, equal-size subsets called cosets. There are ''left cosets'' and ''right cosets''. Cosets (both left and right) ...
spaces . For each element he found a sequence of moves that took it to the next smaller group. After these preparations he worked as follows. A random cube is in the general cube group . Next he found this element in the right coset
In mathematics, specifically group theory, a subgroup of a group may be used to decompose the underlying set of into disjoint, equal-size subsets called cosets. There are ''left cosets'' and ''right cosets''. Cosets (both left and right) ...
space . He applied the corresponding process to the cube. This took it to a cube in . Next he looked up a process that takes the cube to , next to and finally to .
 Although the whole cube group is very large (~4.3×1019), the right coset spaces and are much smaller.
The coset space is the largest and contains only 1082565 elements. The number of moves required by this algorithm is the sum of the largest process in each step.
Initially, Thistlethwaite showed that any configuration could be solved in at most 85 moves. In January 1980 he improved his strategy to yield a maximum of 80 moves. Later that same year, he reduced the number to 63, and then again to 52. By exhaustively searching the coset spaces it was later found that the worst possible number of moves for each stage was 7, 10, 13, and 15 giving a total of 45 moves at most. There have been implementations of Thistlewaite's algorithm in various computer languages.
Although the whole cube group is very large (~4.3×1019), the right coset spaces and are much smaller.
The coset space is the largest and contains only 1082565 elements. The number of moves required by this algorithm is the sum of the largest process in each step.
Initially, Thistlethwaite showed that any configuration could be solved in at most 85 moves. In January 1980 he improved his strategy to yield a maximum of 80 moves. Later that same year, he reduced the number to 63, and then again to 52. By exhaustively searching the coset spaces it was later found that the worst possible number of moves for each stage was 7, 10, 13, and 15 giving a total of 45 moves at most. There have been implementations of Thistlewaite's algorithm in various computer languages.
Kociemba's algorithm
Thistlethwaite's algorithm was improved by Herbert Kociemba in 1992. He reduced the number of intermediate groups to only two: * * * As with Thistlethwaite's algorithm, he would search through the right coset space to take the cube to group . Next he searched the optimal solution for group . The searches in and were both done with a method equivalent toIDA*
Iterative deepening A* (IDA*) is a graph traversal and path search algorithm that can find the shortest path between a designated start node and any member of a set of goal nodes in a weighted graph. It is a variant of iterative deepening depth ...
. The search in needs at most 12 moves and the search in at most 18 moves, as Michael Reid showed in 1995. By also generating suboptimal solutions that take the cube to group and looking for short solutions in , much shorter overall solutions are usually obtained. Using this algorithm solutions are typically found of fewer than 21 moves, though there is no proof that it will always do so.
In 1995 Michael Reid proved that using these two groups every position can be solved in at most 29 face turns, or in 42 quarter turns. This result was improved by Silviu Radu in 2005 to 40.
At first glance, this algorithm appears to be practically inefficient: if contains 18 possible moves (each move, its prime, and its 180-degree rotation), that leaves (over 1 quadrillion) cube states to be searched. Even with a heuristic
A heuristic (; ), or heuristic technique, is any approach to problem solving or self-discovery that employs a practical method that is not guaranteed to be optimal, perfect, or rational, but is nevertheless sufficient for reaching an immediate ...
-based computer algorithm like IDA*
Iterative deepening A* (IDA*) is a graph traversal and path search algorithm that can find the shortest path between a designated start node and any member of a set of goal nodes in a weighted graph. It is a variant of iterative deepening depth ...
, which may narrow it down considerably, searching through that many states is likely not practical. To solve this problem, Kociemba devised a lookup table that provides an exact heuristic for . When the exact number of moves needed to reach is available, the search becomes virtually instantaneous: one need only generate 18 cube states for each of the 12 moves and choose the one with the lowest heuristic each time. This allows the second heuristic, that for , to be less precise and still allow for a solution to be computed in reasonable time on a modern computer.
Korf's algorithm
Using these group solutions combined with computer searches will generally quickly give very short solutions. But these solutions do not always come with a guarantee of their minimality. To search specifically for minimal solutions a new approach was needed. In 1997 Richard Korf announced an algorithm with which he had optimally solved random instances of the cube. Of the ten random cubes he did, none required more than 18 face turns. The method he used is calledIDA*
Iterative deepening A* (IDA*) is a graph traversal and path search algorithm that can find the shortest path between a designated start node and any member of a set of goal nodes in a weighted graph. It is a variant of iterative deepening depth ...
and is described in his paper "Finding Optimal Solutions to Rubik's Cube Using Pattern Databases". Korf describes this method as follows
: IDA* is a depth-first search that looks for increasingly longer solutions in a series of iterations, using a lower-bound heuristic to prune branches once a lower bound on their length exceeds the current iterations bound.
It works roughly as follows. First he identified a number of subproblems that are small enough to be solved optimally. He used:
#The cube restricted to only the corners, not looking at the edges
#The cube restricted to only 6 edges, not looking at the corners nor at the other edges.
#The cube restricted to the other 6 edges.
Clearly the number of moves required to solve any of these subproblems is a lower bound for the number of moves needed to solve the entire cube.
Given a random
In common usage, randomness is the apparent or actual lack of pattern or predictability in events. A random sequence of events, symbols or steps often has no order and does not follow an intelligible pattern or combination. Individual ra ...
cube C, it is solved as iterative deepening. First all cubes are generated that are the result of applying 1 move to them. That is C * F, C * U, … Next, from this list, all cubes are generated that are the result of applying two moves. Then three moves and so on. If at any point a cube is found that needs too many moves based on the lower bounds to still be optimal it can be eliminated from the list.
Although this algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing ...
will always find optimal solutions, there is no worst case analysis. It is not known how many moves this algorithm might need. An implementation of this algorithm can be found here.
Further improvements, and finding God's Number
In 2006, Silviu Radu further improved his methods to prove that every position can be solved in at most 27 face turns or 35 quarter turns. Daniel Kunkle and Gene Cooperman in 2007 used a supercomputer to show that all unsolved cubes can be solved in no more than 26 moves (in face-turn metric). Instead of attempting to solve each of the billions of variations explicitly, the computer was programmed to bring the cube to one of 15,752 states, each of which could be solved within a few extra moves. All were proved solvable in 29 moves, with most solvable in 26. Those that could not initially be solved in 26 moves were then solved explicitly, and shown that they too could be solved in 26 moves. Tomas Rokicki reported in a 2008 computational proof that all unsolved cubes could be solved in 25 moves or fewer. This was later reduced to 23 moves. In August 2008 Rokicki announced that he had a proof for 22 moves. Finally, in 2010, Tomas Rokicki, Herbert Kociemba, Morley Davidson, and John Dethridge gave the finalcomputer-assisted proof
A computer-assisted proof is a mathematical proof that has been at least partially generated by computer.
Most computer-aided proofs to date have been implementations of large proofs-by-exhaustion of a mathematical theorem. The idea is to use a ...
that all cube positions could be solved with a maximum of 20 face turns.
In 2009, Tomas Rokicki proved that 29 moves in the quarter-turn metric is enough to solve any scrambled cube. And in 2014, Tomas Rokicki and Morley Davidson proved that the maximum number of quarter-turns needed to solve the cube is 26.
The face-turn and quarter-turn metrics differ in the nature of their antipodes.
An antipode is a scrambled cube that is maximally far from solved, one that requires the maximum number of moves to solve. In the half-turn metric with a maximum number of 20, there are hundreds of millions of such positions. In the quarter-turn metric, only a single position (and its two rotations) is known that requires the maximum of 26 moves. Despite significant effort, no additional quarter-turn distance-26 positions have been found. Even at distance 25, only two positions (and their rotations) are known to exist. At distance 24, perhaps 150,000 positions exist.
References
Further reading
*External links
* How to solve the Rubik's Cube, a Wikibooks article that gives an overview over several algorithms that are simple enough to be memorizable by humans. However, such algorithms will usually not give an ''optimal'' solution which only uses the minimum possible number of moves. {{Rubik's Cube Rubik's Cube Computer-assisted proofs