Operation Dexterity on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Operation Dexterity was a military operation, part of
 Like most of the islands of the South Pacific, the Islands of the Bismarck Archipelago are of volcanic origin with steep mountain slopes, jungle and treacherous marshes, where malaria was a problem for all deployed troops. The hot, tropical climate was rarely ameliorated by the torrential rain storms and dense clouds which afflicted the region. The inhabited islands had been managed by Australia as a League of Nations Mandate before the war, and there was only a settlement of Westerners originally settled by Imperial Germany before the First World War that was centered on coconut plantations and missionary complexes.
Like most of the islands of the South Pacific, the Islands of the Bismarck Archipelago are of volcanic origin with steep mountain slopes, jungle and treacherous marshes, where malaria was a problem for all deployed troops. The hot, tropical climate was rarely ameliorated by the torrential rain storms and dense clouds which afflicted the region. The inhabited islands had been managed by Australia as a League of Nations Mandate before the war, and there was only a settlement of Westerners originally settled by Imperial Germany before the First World War that was centered on coconut plantations and missionary complexes.
 The high command of the
The high command of the  General Sakai set up his headquarters at Malalia in the vicinity of
General Sakai set up his headquarters at Malalia in the vicinity of

Bismark Archipelago Campaign
part of the U.S. Army Campaigns of World War II series by the
Operation Cartwheel
Operation Cartwheel (1943–1944) was a major military operation for the Allies in the Pacific theatre of World War II. Cartwheel was an operation aimed at neutralising the major Japanese base at Rabaul. The operation was directed by the ...
in the South West Pacific Area
South West Pacific Area (SWPA) was the name given to the Allied supreme military command in the South West Pacific Theatre of World War II. It was one of four major Allied commands in the Pacific War. SWPA included the Philippines, Borneo, the D ...
(SWPA) for the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
in the Pacific theater
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. The operation was directed by the Supreme Allied Commander in the SWPA, General Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur (26 January 18805 April 1964) was an American military leader who served as General of the Army for the United States, as well as a field marshal to the Philippine Army. He had served with distinction in World War I, was C ...
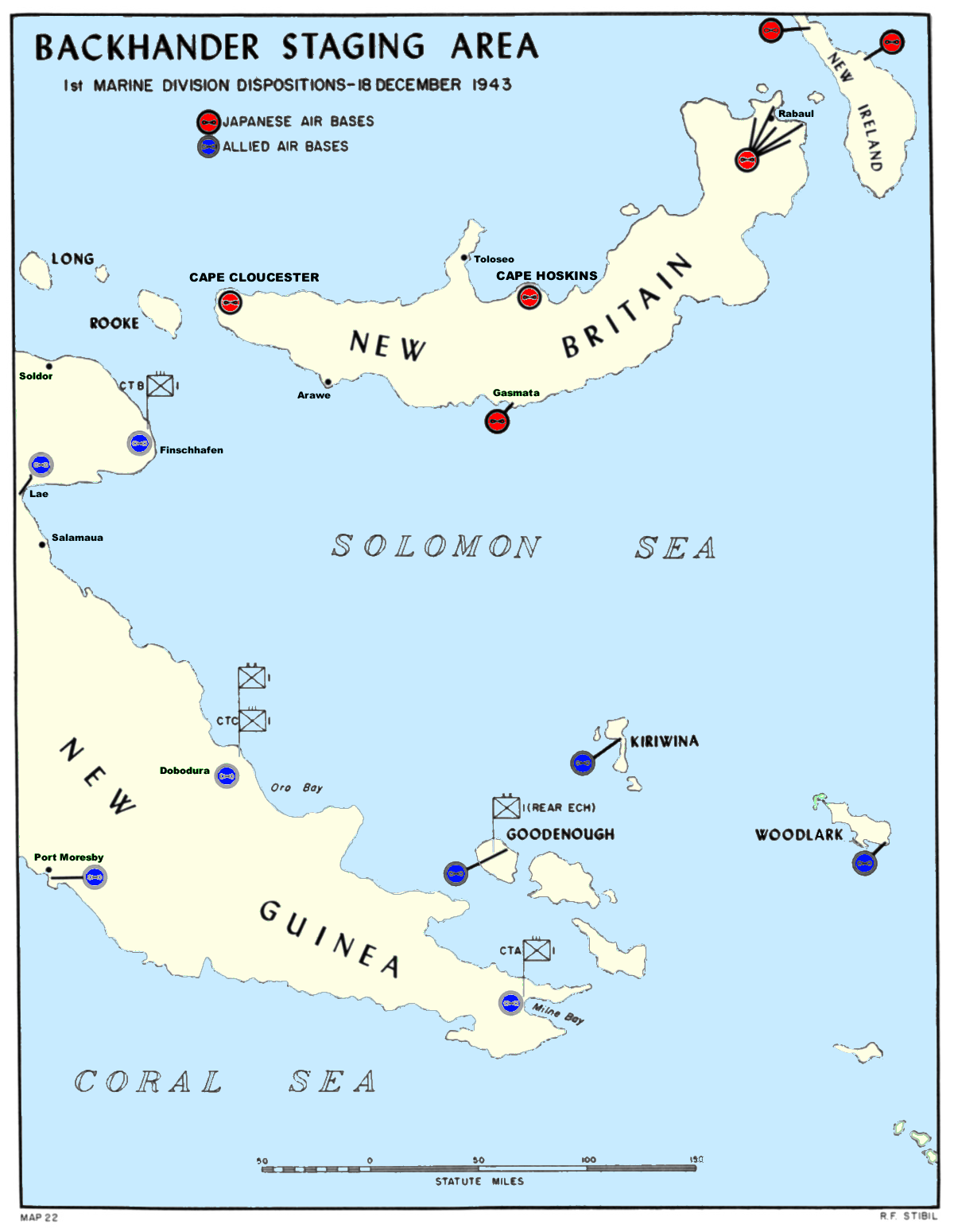
. Dexterity included amphibious landings at Arawe
Arawe is an island in Papua New Guinea, located on the southern coast of New Britain about from Cape Gloucester. It is also the name given to the island's surrounding area, which is also known as Cape Merkus. A small harbour known as Arawe Har ...
on 15 December 1943, and Cape Gloucester on 26 December 1943 in the northwest of New Britain
New Britain ( tpi, Niu Briten) is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago, part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from New Guinea by a northwest corner of the Solomon Sea (or with an island hop of Umboi the Dam ...
, the capture of the Imperial Japanese
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent forma ...
held Tuluvu aerodrome on the 30 December 1943 and the amphibious landing at Saidor
The landing at Saidor, codenamed Operation Michaelmas, was an Allied amphibious landing at Saidor, Papua New Guinea on 2 January 1944 as part of Operation Dexterity during World War II. In Allied hands, Saidor was a stepping stone towards Ma ...
on 2 January 1944. The operation ended on 10 February 1944.
History and planning
TheEmpire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent fo ...
had largely achieved its objectives in the Pacific region in the spring of 1942, with almost the entire area between Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
and the Bismarck Archipelago
The Bismarck Archipelago (, ) is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. Its area is about 50,000 square km.
History
The first inhabitants o ...
under Japanese control. Further Japanese offensives against the Allied lines were planned to force them into a single decisive battle and then request negotiations for their surrender. The initial Japanese offensive failed during the Battle of Midway
The Battle of Midway was a major naval battle in the Pacific Theater of World War II that took place on 4–7 June 1942, six months after Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor and one month after the Battle of the Coral Sea. The U.S. Navy under Adm ...
in June 1942 and subsequently the Japanese attempt to also capture Port Moresby
(; Tok Pisin: ''Pot Mosbi''), also referred to as Pom City or simply Moresby, is the capital and largest city of Papua New Guinea. It is one of the largest cities in the southwestern Pacific (along with Jayapura) outside of Australia and New Z ...
in New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu
Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of Port Moresby (Capital of Papua New Guinea).
It is a simplified version of ...
collapsed, ending the Japanese offensive run in the Pacific theater of operations for the rest of the war. The allies in the South Pacific began their first counter-offensive against the Japanese-held island Guadalcanal in August 1942 and the Japanese forces were forced onto the defensive.
To keep the Japanese cowed and begin the Allied advance towards the Japanese home islands, the Allied military leadership envisaged an advance through the Pacific over two main lines of attack. Admiral Chester W. Nimitz would lead Allied forces in the Pacific and General Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur (26 January 18805 April 1964) was an American military leader who served as General of the Army for the United States, as well as a field marshal to the Philippine Army. He had served with distinction in World War I, was C ...
would advance Allied operations against the Japanese in the Southwest Pacific. Landings along the coast of New Guinea were planned which constituted the first step towards a return to the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
and the conquest of the Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands ( gil, Tungaru;Reilly Ridgell. ''Pacific Nations and Territories: The Islands of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia.'' 3rd. Ed. Honolulu: Bess Press, 1995. p. 95. formerly Kingsmill or King's-Mill IslandsVery often, this n ...
. The operation in New Guinea was known as Operation Cartwheel
Operation Cartwheel (1943–1944) was a major military operation for the Allies in the Pacific theatre of World War II. Cartwheel was an operation aimed at neutralising the major Japanese base at Rabaul. The operation was directed by the ...
which began on 30 June 1943 with the objective to conquer New Guinea, the Bismarck Archipelago
The Bismarck Archipelago (, ) is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. Its area is about 50,000 square km.
History
The first inhabitants o ...
and Rabaul
Rabaul () is a township in the East New Britain province of Papua New Guinea, on the island of New Britain. It lies about 600 kilometres to the east of the island of New Guinea. Rabaul was the provincial capital and most important settlement in ...
. Until mid-September 1943, the fighting focused on the eastern part of New Guinea, while a decision was made on 22 September 1943 to land in West New Britain
West New Britain is a province of Papua New Guinea on the islands of New Britain. The provincial capital is Kimbe. The area of the province is 20,387 km² with a population of 264,264 as of the 2011 census. The province's only land border is w ...
.
Operation Dexterity was to be conducted in three separate phases:
* Operation Lazaretto – Planned landing in southern New Britain at the plantation of Lindenhafen, approximately 5 km from Gasmata Gasmata is a village on the southern coast of New Britain, Papua New Guinea located at 6° 16' 60S 150° 19' 60E. There is a Gasmata Airport in Surumi Peninsula area adjacent. The village is administered under Gasmata Rural LLG in East New Britain ...
on 14 November 1943 and the neutralization of Japanese base at Gasmata for protection of eastern flank for the subsequent operation. This operation was never undertaken and replaced by Operation Director.
::Units: 126th Regimental Combat Team (RCT) and elements of the 32nd Infantry Division and the Sixth Army.
*Operation Director
The Battle of Arawe (also known as Operation Director) was fought between Allied and Japanese forces during the New Britain campaign of World War II. The battle formed part of the Allied Operation Cartwheel, and had the objective of serving a ...
– Landing in southwestern New Britain at Arawe as a diversion for Operation Backhander, Arawe was planned as patrol boat base.
::Units: 112th Regimental Combat Team
* Operation Backhander – Landing in northwestern New Britain at Cape Gloucester to capture local Japanese airfields and convert them into a major Allied airbase.
::Units: 1st Marine Division.
* Operation Michaelmas – Landing in New Guinea at Saidor to prevent the withdrawal of Japanese troops retreating in the advance of the Australian Army
The Australian Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of Australia, a part of the Australian Defence Force (ADF) along with the Royal Australian Navy and the Royal Australian Air Force. The Army is commanded by the Chief of Army (Austral ...
from Finschhafen
Finschhafen is a town east of Lae on the Huon Peninsula in Morobe Province of Papua New Guinea. The town is commonly misspelt as Finschafen or Finschaven. During World War II, the town was also referred to as Fitch Haven in the logs of some U.S ...
.
::Units: 32nd Infantry Division
Geography and Environment
 Like most of the islands of the South Pacific, the Islands of the Bismarck Archipelago are of volcanic origin with steep mountain slopes, jungle and treacherous marshes, where malaria was a problem for all deployed troops. The hot, tropical climate was rarely ameliorated by the torrential rain storms and dense clouds which afflicted the region. The inhabited islands had been managed by Australia as a League of Nations Mandate before the war, and there was only a settlement of Westerners originally settled by Imperial Germany before the First World War that was centered on coconut plantations and missionary complexes.
Like most of the islands of the South Pacific, the Islands of the Bismarck Archipelago are of volcanic origin with steep mountain slopes, jungle and treacherous marshes, where malaria was a problem for all deployed troops. The hot, tropical climate was rarely ameliorated by the torrential rain storms and dense clouds which afflicted the region. The inhabited islands had been managed by Australia as a League of Nations Mandate before the war, and there was only a settlement of Westerners originally settled by Imperial Germany before the First World War that was centered on coconut plantations and missionary complexes.
The Japanese on New Britain
 The high command of the
The high command of the 8th Area Army
The was a field army of the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II.
History
The Japanese 8th Area Army was formed on November 16, 1942 under the Southern Expeditionary Army Group for the specific task of opposing landings by Allied forces i ...
of the Japanese Imperial Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor o ...
in Rabaul
Rabaul () is a township in the East New Britain province of Papua New Guinea, on the island of New Britain. It lies about 600 kilometres to the east of the island of New Guinea. Rabaul was the provincial capital and most important settlement in ...
controlled the Japanese actions in the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capita ...
, New Guinea and the Bismarck Islands
The Bismarck Archipelago (, ) is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. Its area is about 50,000 square km.
History
The first inhabitants o ...
. In January 1942, the Japanese had taken the strategically important port of Rabaul in northeastern New Britain and in subsequent months the largest and most important Japanese naval and air base in the Pacific was constructed at that location. The 8th Area Army was commanded by General Hitoshi Imamura
was a Japanese general who served in the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II, and was subsequently convicted of war crimes.
Early career
A native of Sendai city, Miyagi Prefecture, Imamura's father was a judge. Imamura graduated from t ...
who had at his disposal nearly 200,000 men. In early 1943, the Japanese leadership had expected that the Allies would attempt to break the inner Japanese defensive belt in the Pacific and attack the bases on New Guinea, the Mariana Islands
The Mariana Islands (; also the Marianas; in Chamorro: ''Manislan Mariånas'') are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, betw ...
, Palau
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the Caro ...
and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
. General Imamura therefore foresaw an attack on New Britain, at the latest after the Allies had occupied New Ireland, which was expected in February or March 1944.
The 8th Area Army relied exclusively on barge and submarine traffic from Rabaul to New Guinea, because of Allied air superiority. In September 1943, Major General Iwao Matsuda
was a Japanese politician of the Liberal Democratic Party who was a member of the House of Councillors in the Diet (national legislature). A native of Gifu, Gifu, Japan, and graduate of the University of Tokyo, he joined the Ministry of Intern ...
took over the 65th Brigade, the various pioneers and debarkation units, and a number of troops of the 51st Division, whose main units were on New Guinea in the fight against Australian troops. Two companies of 115th Division and provisional infantry companies formed from artillery and engineer elements of the 66th Division, and about half of the 51st Reconnaissance Regiment belonged to General Matsuda's command. General Matsuda, a highly experienced officer, established his headquarters near the airfield of Cape Gloucester. On 5 October 1943, all of Matsuda's units came under the command of the 17th Division which was commanded by Lieutenant General Yasushi Sakai, who had arrived in December 1943 from the Japanese theater of operations in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
.
 General Sakai set up his headquarters at Malalia in the vicinity of
General Sakai set up his headquarters at Malalia in the vicinity of Cape Hoskins
Cape Hoskins is located on the north coast of New Britain in the West New Britain Province.
History
Hoskinos, as locals are known, regularly find arrowheads and spears just below the surface soil. When villagers were building state of the art ou ...
on the East Williaumez Peninsula. The 17th Division's troops began immediately ordering the expansions of the defensive lines. The Japanese headquarters was established in an existing concrete bunker at the foot of Talawe Mountain, which was surrounded by dense, tropical vegetation. Smaller bunkers and shelters for machine gun positions were sited at possible Allied landing beaches five miles southeast of Cape Gloucester. Two hills known later as ''Target-Hill'' and ''Hill 660'' served as focal points for the Japanese defenses. Thus about half of all available Japanese troops in the west of the island were in positions that could effectively contribute to the defense of Cape Gloucester.
On 12 December 1943, General Yasushi Sakai advised all commanders of his units about an imminent Allied invasion. The large volumes of Allied landing ships along the ports of New Guinea did not convince the Japanese of the scheduled operations of Allied forces. False invasion alarms were commonplace up to the end of 1943. With the Allies' air superiority increasing, the bombing of Rabaul and Wewak
Wewak is the capital of the East Sepik province of Papua New Guinea. It is on the northern coast of the island of New Guinea. It is the largest town between Madang and Jayapura. It is the see city (seat) of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Wewak. ...
brought the realization that the invasion of New Britain was imminent.
Preparatory actions
Reconnaissance
Two days after the decision to proceed with the operation was taken by the Allied commanders, the US 6th Army'sAlamo Scouts
The Alamo Scouts (U.S. 6th Army Special Reconnaissance Unit) was a reconnaissance unit of the Sixth United States Army in the Pacific Theater of Operations during World War II. The unit is best known for its role in liberating American prisoner ...
began to deploy in the area of Cape Gloucester. They neared the coast by torpedo boat, then transferred to dinghies and landed on the beaches. From there they reconnoitered the Japanese defenses by direct observations or through contact with the local aboriginal population of New Britain.


Citations
Film
* ''Attack: The Battle for New Britain (1944)'', Produzent:Frank Capra
Frank Russell Capra (born Francesco Rosario Capra; May 18, 1897 – September 3, 1991) was an Italian-born American film director, producer and writer who became the creative force behind some of the major award-winning films of the 1930s ...
– Documentary, DVD
The DVD (common abbreviation for Digital Video Disc or Digital Versatile Disc) is a digital optical disc data storage format. It was invented and developed in 1995 and first released on November 1, 1996, in Japan. The medium can store any kind ...
, USA, (2003)
Further reading
Bismark Archipelago Campaign
part of the U.S. Army Campaigns of World War II series by the
United States Army Center of Military History
The United States Army Center of Military History (CMH) is a directorate within the United States Army Training and Doctrine Command. The Institute of Heraldry remains within the Office of the Administrative Assistant to the Secretary of the Arm ...
External links
* http://www.ibiblio.org/hyperwar/USMC/II/USMC-II-IV-1.html * http://www.ibiblio.org/hyperwar/USMC/USMC-C-Gloucester/index.html * http://www.hmasshropshire.com/chapter5.htm * http://www.cronab.demon.co.uk/sallet6.htm {{coord missing, Papua New Guinea South West Pacific theatre of World War II