Oneida Carry on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
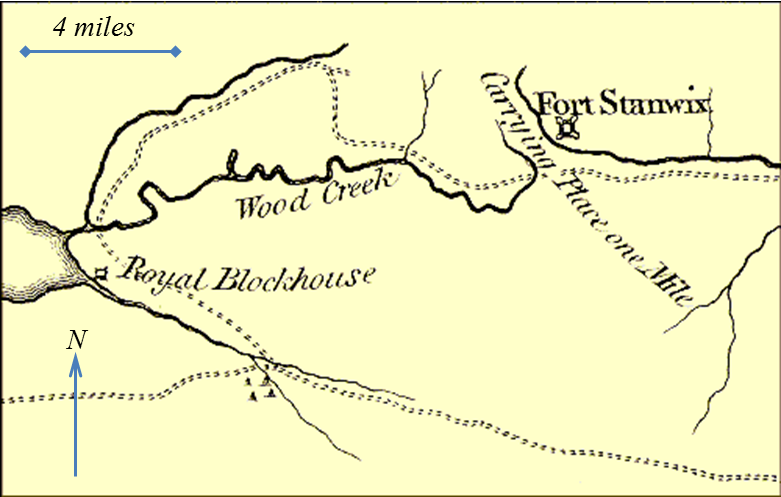
The Oneida Carry was an important link in the main 18th century
 After the war the Oneida Carry continued to be of economic importance. Established in 1792 the Western Inland Lock Navigation Company constructed a canal between the Mohawk River and Wood Creek. With this canal boats no longer had to be removed from the River and carried over the portage. These canals would have continued use until 1817 when the
After the war the Oneida Carry continued to be of economic importance. Established in 1792 the Western Inland Lock Navigation Company constructed a canal between the Mohawk River and Wood Creek. With this canal boats no longer had to be removed from the River and carried over the portage. These canals would have continued use until 1817 when the
trade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a sin ...
between the Atlantic seaboard of North America and interior of the continent. From Schenectady
Schenectady () is a city in Schenectady County, New York, United States, of which it is the county seat. As of the 2020 census, the city's population of 67,047 made it the state's ninth-largest city by population. The city is in eastern New Y ...
, near Albany, New York
Albany ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of New York, also the seat and largest city of Albany County. Albany is on the west bank of the Hudson River, about south of its confluence with the Mohawk River, and about north of New York City. ...
on the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between New ...
, cargo would be carried upstream along the Mohawk River
The Mohawk River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed October 3, 2011 river in the U.S. state of New York. It is the largest tributary of the Hudson River. The Mohawk fl ...
using boats known as ''bateau
A bateau or batteau is a shallow- draft, flat-bottomed boat which was used extensively across North America, especially in the colonial period and in the fur trade. It was traditionally pointed at both ends but came in a wide variety of sizes. T ...
x''. At the location at modern-day Rome, New York
Rome is a city in Oneida County, New York, United States, located in the central part of the state. The population was 32,127 at the 2020 census. Rome is one of two principal cities in the Utica–Rome Metropolitan Statistical Area, which li ...
, the cargo and boats would be portage
Portage or portaging (Canada: ; ) is the practice of carrying water craft or cargo over land, either around an obstacle in a river, or between two bodies of water. A path where items are regularly carried between bodies of water is also called a ...
d one to four miles overland to Wood Creek. This portage, which the Haudenosaunee
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
called ''De-o-Wain-Sta'', was known as the ''Oneida Carry'' or ''The Great Carrying Place'' in English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
, and as ''Trow Plat'' in Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People ...
. After relaunching into Wood Creek (called Kah-ne-go-dick by the Haudenosaunee), the ''bateaux'' would navigate downstream to Oneida Lake
Oneida Lake is the largest lake entirely within New York state, with a surface area of .
The lake is located northeast of Syracuse and near the Great Lakes. It feeds the Oneida River, a tributary of the Oswego River, which flows into Lake Ontari ...
, the Oswego River, and ultimately Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border span ...
at Oswego. Lake Ontario was the gateway to all the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
stretching another thousand miles inland.
The only other significant waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the continental interior was the Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting t ...
, which flows northeast out of Lake Ontario to Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple-pe ...
and Quebec City
Quebec City ( or ; french: Ville de Québec), officially Québec (), is the capital city of the Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the metropolitan area had a population of 839,311. It is th ...
. Thus for nearly a hundred years movement of military goods, trade goods, and other supplies into and out of the continental interior required control over the Oneida Carry. The Carry was strategically important in the colonial wars between Great Britain and France, in the American Revolution, and in the War of 1812 between Great Britain and the United States, and the City of Rome, New York
Rome is a city in Oneida County, New York, United States, located in the central part of the state. The population was 32,127 at the 2020 census. Rome is one of two principal cities in the Utica–Rome Metropolitan Statistical Area, which li ...
was founded there in 1796. Its military importance declined with the completion of the Erie Canal
The Erie Canal is a historic canal in upstate New York that runs east-west between the Hudson River and Lake Erie. Completed in 1825, the canal was the first navigable waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes, vastly reducing ...
in 1825, after which it became just one of many "ports".
Early development and the French and Indian War
Interest in improving transportation across the Oneida Carry began as early as 1702 when native Americans petitioned GovernorCornbury
Edward Hyde, 3rd Earl of Clarendon (28 November 1661 – 31 March 1723), styled Viscount Cornbury between 1674 and 1709, was an English aristocrat and politician. Better known by his noble title Lord Cornbury, he was propelled into the forefr ...
to have improvements made to allow easier passage of boats. As at this time the Oneida Carry was nothing more than a path between the two bodies of water. Although important to trade it wasn't until the beginning of the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the s ...
that the Oneida Carry was finally improved with fortifications, supplies, and dams.
Following the failure of British campaign plans in 1755, a chain of forts along the Mohawk River
The Mohawk River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed October 3, 2011 river in the U.S. state of New York. It is the largest tributary of the Hudson River. The Mohawk fl ...
and up to Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border span ...
were garrisoned during the winter of 1755–1756 to protect the route from a French Invasion and provide a staging area for the invasion of New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spai ...
. The largest garrison was left at Fort Oswego
Fort Oswego was an 18th-century trading post in the Great Lakes region in North America, which became the site of a battle between French and British forces in 1756 during the French and Indian War. The fort was established in 1727 on the orders o ...
, at the end of the chain, which depended on the others for its supplies. The two forts occupying either end of the Oneida Carry were a key element of this supply chain. Fort Williams, on the Mohawk, was the larger of the two, while Fort Bull, on Wood Creek, was little more than a palisade surrounding storehouses. In March 1756 this palisade, holding a large amount of supplies for Fort Oswego, would be the scene of the first battle, known to history, to take place on the Oneida Carry. The Battle of Fort Bull
The Battle of Fort Bull was a French attack on the British-held Fort Bull on 27 March 1756, early in the French and Indian War. The fort was built to defend a portion of the waterway connecting Albany, New York to Lake Ontario via the Mohawk Rive ...
lasted only one day, but saw the entire fortification, and the supplies within, destroyed when its Powder Magazine exploded.
Starting in May 1756 the British refortified the Oneida Carry by adding Fort Craven, Fort Newport, and Fort Wood Creek. However, these forts would only remain until August 1756, when they were destroyed by the British themselves in anticipation of a massive attack by the French Army and Marines after the capture of Fort Oswego.
Direct control of the Oneida Carry by the British would not be re-established until two years later with the construction of Fort Stanwix Fort Stanwix was a colonial fort whose construction commenced on August 26, 1758, under the direction of British General John Stanwix, at the location of present-day Rome, New York, but was not completed until about 1762. The bastion fort was built ...
in August 1758.
American Revolution
Between the end of theFrench and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the s ...
and the beginning of the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
the Oneida Carry transformed from a place of war to a place of peace. After Pontiac's Rebellion
Pontiac's War (also known as Pontiac's Conspiracy or Pontiac's Rebellion) was launched in 1763 by a loose confederation of Native Americans dissatisfied with British rule in the Great Lakes region following the French and Indian War (1754–176 ...
the British slowly abandoned Fort Stanwix Fort Stanwix was a colonial fort whose construction commenced on August 26, 1758, under the direction of British General John Stanwix, at the location of present-day Rome, New York, but was not completed until about 1762. The bastion fort was built ...
; its believed the last Half Pay Officer left the Fort in June 1774 when Governor William Tryon declared the fort "dismantled". During the inter-war period the carry also became home to the Roof Family- who would establish a tavern, continued to be utilized by merchants to move trade goods into the interior of the continent, and in 1768 saw the signing of the Treaty of Fort Stanwix
The Treaty of Fort Stanwix was a treaty signed between representatives from the Iroquois and Great Britain (accompanied by negotiators from New Jersey, Virginia and Pennsylvania) in 1768 at Fort Stanwix. It was negotiated between Sir William Jo ...
.
However, during the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
the Oneida Carry once again became a battle ground. With Patriot Forces occupying the carry in August 1776 the Army only had a year to reconstruct Fort Stanwix Fort Stanwix was a colonial fort whose construction commenced on August 26, 1758, under the direction of British General John Stanwix, at the location of present-day Rome, New York, but was not completed until about 1762. The bastion fort was built ...
before the British arrived and laid siege to Fort Stanwix (August 2, 1777 to August 22, 1777). After the successful defense of Fort Stanwix the Oneida Carry saw little military action. In the spring of 1779, as a part of the Sullivan Expedition
The 1779 Sullivan Expedition (also known as the Sullivan-Clinton Expedition, the Sullivan Campaign, and the Sullivan-Clinton Genocide) was a United States military campaign during the American Revolutionary War, lasting from June to October 1779 ...
of 1779, the American Army used the fort as a staging ground for the destruction of Onondaga Castle. In 1780 the garrison was attacked by a large force of Natives led by Joseph Brant
Thayendanegea or Joseph Brant (March 1743 – November 24, 1807) was a Mohawk military and political leader, based in present-day New York, who was closely associated with Great Britain during and after the American Revolution. Perhaps t ...
forcing a three-day standoff between the Patriot Troops in the well-defended Fort Stanwix and the poorly defended Loyalist
Loyalism, in the United Kingdom, its overseas territories and its former colonies, refers to the allegiance to the British crown or the United Kingdom. In North America, the most common usage of the term refers to loyalty to the British Cro ...
Natives. In general the most military action seen by the garrison was the occasional harassment by bands of Loyalist
Loyalism, in the United Kingdom, its overseas territories and its former colonies, refers to the allegiance to the British crown or the United Kingdom. In North America, the most common usage of the term refers to loyalty to the British Cro ...
Raiding Parties moving into the Mohawk Valley. Which is not to downplay the many lives lost by those soldiers who were unexpectedly attacked, but to re-enforce the idea that garrison duty on the carry became extremely boring. Finally, in the spring of 1781, when flood and fire (most likely arson
Arson is the crime of willfully and deliberately setting fire to or charring property. Although the act of arson typically involves buildings, the term can also refer to the intentional burning of other things, such as motor vehicles, wat ...
) destroyed most of the fort, the American Troops evacuated the post; only to return in 1784 to sign the Second Treaty of Fort Stanwix, ending the American Revolution with those Native Americans who sided with the British.
19th Century and Beyond
 After the war the Oneida Carry continued to be of economic importance. Established in 1792 the Western Inland Lock Navigation Company constructed a canal between the Mohawk River and Wood Creek. With this canal boats no longer had to be removed from the River and carried over the portage. These canals would have continued use until 1817 when the
After the war the Oneida Carry continued to be of economic importance. Established in 1792 the Western Inland Lock Navigation Company constructed a canal between the Mohawk River and Wood Creek. With this canal boats no longer had to be removed from the River and carried over the portage. These canals would have continued use until 1817 when the Erie Canal
The Erie Canal is a historic canal in upstate New York that runs east-west between the Hudson River and Lake Erie. Completed in 1825, the canal was the first navigable waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes, vastly reducing ...
began construction within the new City of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
.
The carry also saw a continuation of its military importance throughout the 1800s and up to the 21st Century. Built in 1813 and used until 1873, the Rome Arsenal was a three-acre fortification complex which included barracks, arsenal, magazine, workshops, and other buildings, built to support American forces waging the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States, United States of America and its Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom ...
, Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
, and the American Civil War. This post actually replaced an early armory, constructed and utilized in the late 1790s which was located on the site of, the then demolished, Fort Stanwix.
Starting on 3 April 1941, the War Department began looking for an area to construct an Air Depot in central New York and thus the Oneida Carry would once again become an important part of the Nations Defense. Opened in February 1942 Griffiss Air Force Base
Griffiss Air Force Base is a former United States Air Force installation in the northeastern United States, located in Central New York state at Rome, about northwest of Utica.
Missions included fighter interceptors, electronic research ...
would become home to the Rome Labs, the 416th Air Expeditionary Group 416th may refer to:
*416th Air Expeditionary Operations Group, provisional unit assigned to the United States Air Force Air Mobility Command
*416th Bombardment Wing, inactive United States Air Force unit
*416th Engineer Command (TEC), US Army Reser ...
and Strategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was both a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile c ...
. Currently the now closed Air Force Base is the home for the Northeast Air Defense Sector
The Eastern Air Defense Sector (EADS) is a United States Air Force unit of Air Combat Command (ACC), permanently assigned to the North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD). A joint, bi-national military organization, EADS is composed of US ...
facilities which provides detection and air defense for the entire eastern half of the United States.
The city of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, with a population of 33,725 at the 2010 census and the second largest city in the State of New York by area (75.7 square miles), now encompasses most of what was once the Oneida Carry.
References
{{authority control Colonization history of the United States Portages in the United States Trade routes Water transportation in New York (state) Rivers of New York (state) French and Indian War Anglo-French wars Rivers of Oneida County, New York Transportation in Rome, New York