OFDMA on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) is a multi-user version of the popular
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access: is it the multiple access system of the future?
S. Srikanth, V. Kumaran, C. Manikandan et al., AU-KBC Research Center, Anna University, India.
Short Introduction to OFDM
– Tutorial written by Prof. Debbah, head of the Alcatel-Lucent Chair on flexible radio. {{Channel access methods
orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing
In telecommunications, orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) is a type of digital transmission and a method of encoding digital data on multiple carrier frequencies. OFDM has developed into a popular scheme for wideband digital comm ...
(OFDM) digital modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the '' carrier signal'', with a separate signal called the ''modulation signal'' that typically contains informa ...
scheme. Multiple access
In telecommunications and computer networks, a channel access method or multiple access method allows more than two terminals connected to the same transmission medium to transmit over it and to share its capacity. Examples of shared physical med ...
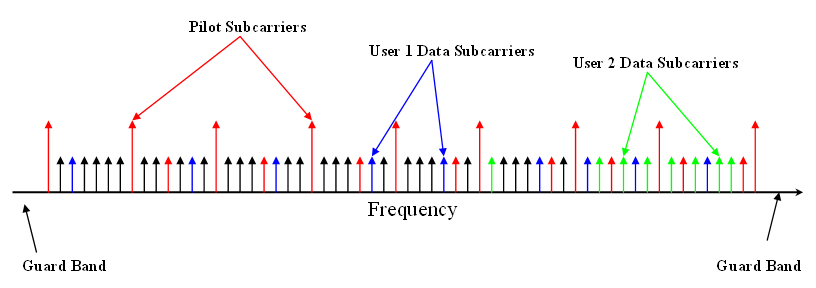
is achieved in OFDMA by assigning subsets of subcarriers
A subcarrier is a sideband of a radio frequency carrier wave, which is modulated to send additional information. Examples include the provision of colour in a black and white television system or the provision of stereo in a monophonic radio broa ...
to individual users. This allows simultaneous low-data-rate transmission from several users.
Comparisons
OFDMA is often compared to the combination of OFDM withstatistical time-division multiplexing
Statistical multiplexing is a type of communication link sharing, very similar to dynamic bandwidth allocation (DBA). In statistical multiplexing, a communication channel is divided into an arbitrary number of variable bitrate digital channels or ...
. The advantages and disadvantages summarized below are further discussed in the Characteristics and principles of operation section. See also the list of OFDM key features.
Advantages
* Allows simultaneous low-data-rate transmission from several users. * Pulsed carrier can be avoided. * Lower maximal transmission power for low-data-rate users. * Shorter delay and constant delay. * Contention-based multiple access (collision avoidance) is simplified. * Further improves OFDM robustness to fading and interference. * Combat narrow-band interference. * Flexibility of deployment across various frequency bands with little needed modification to the air interface. * Averaging interferences from neighboring cells, using different basic carrier permutations between users in different cells. * Interferences within the cell are averaged by using allocation with cyclic permutations. * Enables single-frequency network coverage, where coverage problem exists and gives excellent coverage. * Offers frequency diversity by spreading the carriers all over the used spectrum. * Allows per-channel or per-subchannel power.Disadvantages
* Higher sensitivity to frequency offsets and phase noise. * Asynchronous data communication services such as web access are characterised by short communication bursts at high data rate. Few users in a base station cell are transferring data simultaneously at low constant data rate. * The complex OFDM electronics, including the FFT algorithm andforward error correction
In computing, telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, an error correction code, sometimes error correcting code, (ECC) is used for controlling errors in data over unreliable or noisy communication channels. The central idea i ...
, are constantly active, thus consuming power, independent of the data rate, while OFDM combined with data packet scheduling may allow FFT algorithm to hibernate at times.
* The OFDM diversity gain and resistance to frequency-selective fading
In wireless communications, fading is variation of the attenuation of a signal with various variables. These variables include time, geographical position, and radio frequency. Fading is often modeled as a random process. A fading channel is a ...
may partly be lost if very few sub-carriers are assigned to each user, and if the same carrier is used in every OFDM symbol. Adaptive sub-carrier assignment based on fast feedback information about the channel, or sub-carrier frequency hopping, is therefore desirable.
* Dealing with co-channel interference from nearby cells is more complex in OFDM than in CDMA
Code-division multiple access (CDMA) is a channel access method used by various radio communication technologies. CDMA is an example of multiple access, where several transmitters can send information simultaneously over a single communicatio ...
. It would require dynamic channel allocation with advanced coordination among adjacent base stations.
* The fast channel feedback information and adaptive sub-carrier assignment is more complex than CDMA fast power control.
Characteristics and principles of operation
Based on feedback information about the channel conditions, adaptive user-to-subcarrier assignment can be achieved. If the assignment is done sufficiently fast, this further improves the OFDM robustness to fastfading
In wireless communications, fading is variation of the attenuation of a signal with various variables. These variables include time, geographical position, and radio frequency. Fading is often modeled as a random process. A fading channel is ...
and narrow-band cochannel interference, and makes it possible to achieve even better system spectral efficiency
Spectral efficiency, spectrum efficiency or bandwidth efficiency refers to the information rate that can be transmitted over a given bandwidth in a specific communication system. It is a measure of how efficiently a limited frequency spectrum is ut ...
.
Different numbers of sub-carriers can be assigned to different users, in view to support differentiated quality of service
Quality of service (QoS) is the description or measurement of the overall performance of a service, such as a telephony or computer network, or a cloud computing service, particularly the performance seen by the users of the network. To quantitat ...
(QoS), i.e. to control the data rate and error probability individually for each user.
OFDMA can be seen as an alternative to combining OFDM with time-division multiple access
Time-division multiple access (TDMA) is a channel access method for shared-medium networks. It allows several users to share the same frequency channel by dividing the signal into different time slots. The users transmit in rapid succession ...
(TDMA) or time-domain statistical multiplexing communication. Low-data-rate users can send continuously with low transmission power instead of using a "pulsed" high-power carrier. Constant delay, and shorter delay, can be achieved.
OFDMA can also be described as a combination of frequency-domain and time-domain multiple access, where the resources are partitioned in the time–frequency space, and slots are assigned along the OFDM symbol index, as well as OFDM sub-carrier index.
OFDMA is considered as highly suitable for broadband wireless networks, due to advantages including scalability and use of multiple antennas (MIMO
In radio, multiple-input and multiple-output, or MIMO (), is a method for multiplying the capacity of a radio link using multiple transmission and receiving antennas to exploit multipath propagation. MIMO has become an essential element of wi ...
)-friendliness, and ability to take advantage of channel frequency selectivity.
In spectrum sensing cognitive radio
A cognitive radio (CR) is a radio that can be programmed and configured dynamically to use the best wireless channels in its vicinity to avoid user interference and congestion. Such a radio automatically detects available channels in wireless spec ...
, OFDMA is a possible approach to filling free radio frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the up ...
bands adaptively. Timo A. Weiss and Friedrich K. Jondral of the University of Karlsruhe proposed a spectrum pooling system in which free bands sensed by nodes were immediately filled by OFDMA subbands.
Usage
OFDMA is used in: * the mobility mode of theIEEE 802.16
IEEE 802.16 is a series of wireless broadband standards written by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). The IEEE Standards Board established a working group in 1999 to develop standards for broadband for wireless metrop ...
Wireless MAN standard, commonly referred to as WiMAX,
* the wireless LAN
A wireless LAN (WLAN) is a wireless computer network that links two or more devices using wireless communication to form a local area network (LAN) within a limited area such as a home, school, computer laboratory, campus, or office buildi ...
(WLAN) standard IEEE 802.11ax (marketed as Wi-Fi 6 / Wi-Fi 6E),
* the IEEE 802.20
IEEE 802.20 or Mobile Broadband Wireless Access (MBWA) was a specification by the standard association of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for mobile broadband networks. The main standard was published in 2008. MBWA ...
mobile Wireless MAN standard, commonly referred to as MBWA,
* MoCA 2.0,
* the downlink of the 3GPP Long-Term Evolution
In telecommunications, long-term evolution (LTE) is a standard for wireless broadband communication for mobile devices and data terminals, based on the GSM/ EDGE and UMTS/HSPA standards. It improves on those standards' capacity and speed by ...
(LTE) fourth-generation mobile broadband standard. The radio interface was formerly named ''High Speed OFDM Packet Access'' (HSOPA), now named Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA).
* the downlink and the uplink of the 3GPP 5G New Radio (5G NR) fifth-generation mobile network standard. 5G NR is the successor to LTE.
* the Qualcomm Flarion Technologies Mobile Flash-OFDM
* the now defunct Qualcomm
Qualcomm () is an American multinational corporation headquartered in San Diego, California, and incorporated in Delaware. It creates semiconductors, software, and services related to wireless technology. It owns patents critical to the 5G, ...
/3GPP2
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project 2 (3GPP2) is a collaboration between telecommunications associations to make a globally applicable third generation ( 3G) mobile phone system specification within the scope of the ITU's IMT-2000 project. In ...
Ultra Mobile Broadband
Evolution-Data Optimized (EV-DO, EVDO, etc.) is a telecommunications standard for the wireless transmission of data through radio signals, typically for broadband Internet access. EV-DO is an evolution of the CDMA2000 (IS-2000) standard which su ...
(UMB) project, intended as a successor of CDMA2000
CDMA2000 (also known as C2K or IMT Multi‑Carrier (IMT‑MC)) is a family of 3G mobile technology standards for sending voice, data, and Signaling (telecommunication), signaling data between mobile phones and cell sites. It is developed by 3GP ...
, but replaced by LTE.
OFDMA is also a candidate access method for the IEEE 802.22 ''Wireless Regional Area Networks'' (WRAN), a cognitive radio
A cognitive radio (CR) is a radio that can be programmed and configured dynamically to use the best wireless channels in its vicinity to avoid user interference and congestion. Such a radio automatically detects available channels in wireless spec ...
technology which uses white spaces in the television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
(TV) frequency spectrum, and the proposed access method for DECT
Digital enhanced cordless telecommunications (Digital European cordless telecommunications), usually known by the acronym DECT, is a standard primarily used for creating cordless telephone systems. It originated in Europe, where it is the common ...
-5G specification which aims to fulfill IMT-2020 requirements for high-throughput mobile broadband (eMMB) and ultra reliable low latency (URLLC) applications.

See also
*Code-division multiple access
Code-division multiple access (CDMA) is a channel access method used by various radio communication technologies. CDMA is an example of multiple access, where several transmitters can send information simultaneously over a single communicatio ...
* Frequency-division multiple access
Frequency-division multiple access (FDMA) is a channel access method used in some multiple-access protocols. FDMA allows multiple users to send data through a single communication channel, such as a coaxial cable or microwave beam, by dividing ...
* Time-division multiple access
Time-division multiple access (TDMA) is a channel access method for shared-medium networks. It allows several users to share the same frequency channel by dividing the signal into different time slots. The users transmit in rapid succession ...
* Single-carrier FDMA
Single-carrier FDMA (SC-FDMA) is a frequency-division multiple access scheme. It is also called linearly precoded OFDMA (LP-OFDMA). Like other multiple access schemes (TDMA, FDMA, CDMA, OFDMA), it deals with the assignment of multiple users to a ...
(SC-FDMA), a.k.a. linearly precoded OFDMA ( LP-OFDMA)
* 3GPP Long-Term Evolution
* WiMAX
Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX) is a family of wireless broadband communication standards based on the IEEE 802.16 set of standards, which provide physical layer (PHY) and media access control (MAC) options.
The WiMAX ...
* WiBro
WiBro (''wireless broadband'') is a wireless broadband Internet technology developed by the South Korean telecoms industry. WiBro is the South Korean service name for IEEE 802.16e (mobile WiMAX) international standard. By the end of 2012, t ...
References
External links
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access: is it the multiple access system of the future?
S. Srikanth, V. Kumaran, C. Manikandan et al., AU-KBC Research Center, Anna University, India.
Short Introduction to OFDM
– Tutorial written by Prof. Debbah, head of the Alcatel-Lucent Chair on flexible radio. {{Channel access methods