Ozark Aquifer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The Ozarks, also known as the Ozark Mountains, Ozark Highlands or Ozark Plateau, is a
The Ozarks, also known as the Ozark Mountains, Ozark Highlands or Ozark Plateau, is a
"Ozarks geology: Clifty Creek Natural Area includes natural bridge"
, ''The Ozarks Chronicle'', Rolla, Mo. and Alum Cove in the
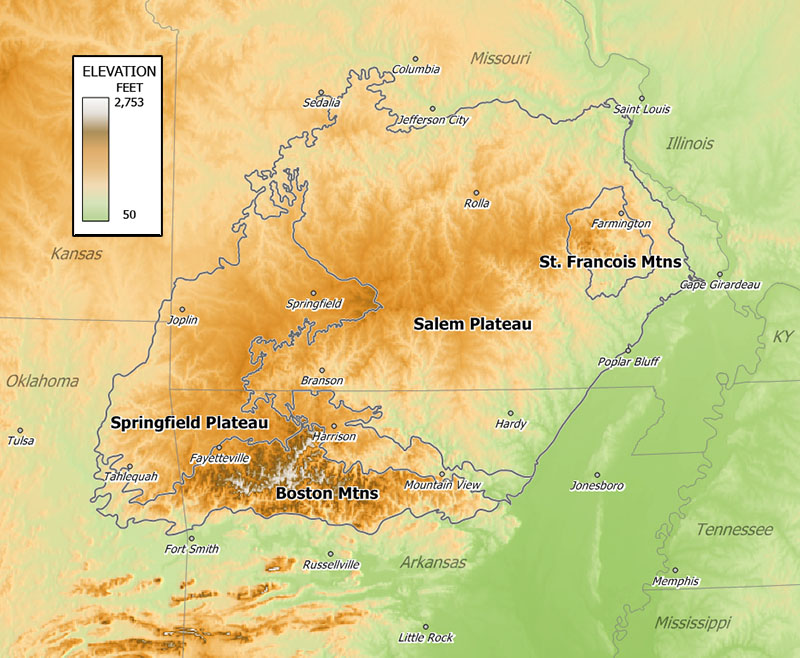 The Ozarks consist of five physiographic subregions: the
The Ozarks consist of five physiographic subregions: the
Missouri Department of Natural Resources Missouri is known as "The Cave State" with over 7,300 recorded caves, second in number only to Tennessee. The majority of these caves are found in the Ozark counties. The Ozark Plateaus aquifer system affects groundwater movement in all areas except the igneous core of the St. Francois Mountains.Rafferty, Milton
''OzarksWatch'', Vol. I, No. 4, Spring 1988.
United States Geological Survey.
United States Geological Survey. Geographic features include limestone and dolomite glades, which are rocky, desert-like areas on hilltops. Kept open by periodic fires that limit growth of
John Chase, Assistant Professor. Washington University in St. Louis. The Boston Mountains contain the highest elevations of the Ozarks, with peaks over , and form some of the greatest relief of any formation between the Appalachians and Rocky Mountains. The
 A major
A major  Sedimentation resumed in the Ordovician with the deposition of the Gunter sandstone, the Gasconade dolomite and the prominent Roubidoux sandstone and dolomite. The sandstone of the Roubidoux forms prominent bluffs along the streams eroding into the southern part of the Salem Plateau. The Roubidoux and Gunter sandstones serve as significant
Sedimentation resumed in the Ordovician with the deposition of the Gunter sandstone, the Gasconade dolomite and the prominent Roubidoux sandstone and dolomite. The sandstone of the Roubidoux forms prominent bluffs along the streams eroding into the southern part of the Salem Plateau. The Roubidoux and Gunter sandstones serve as significant
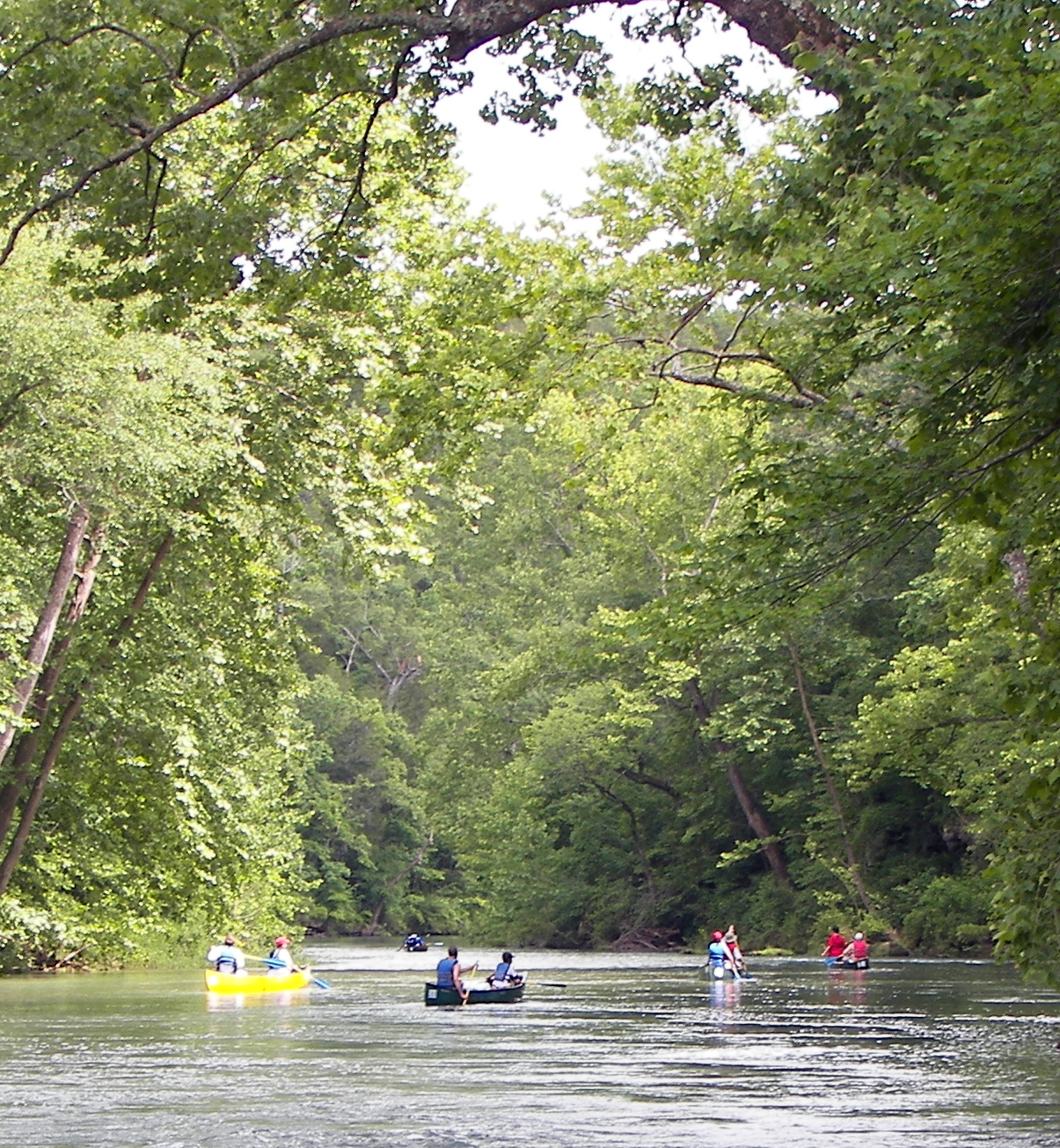

 Many of the rivers and streams in the Ozarks have been dammed. Most of the dams in the region were initially built for the dual purpose of flood control and hydropower generation but have also become major economic drivers through recreational use in places such as Branson, Missouri, and Mountain Home, Arkansas.
The United States Army Corps of Engineers, Army Corps of Engineers among others, operates multiple dams in the Ozarks region. Some of the largest lakes created by these dams are on the White River (Arkansas–Missouri), White River. Beginning in 1911 with the construction of Powersite Dam on the White River near Branson, Missouri and the impoundment of Lake Taneycomo the Ozarks rivers have been harnessed for electrical power, recreation, and flood control. After the President Franklin D, Roosevelt signed the Flood Control Act of 1938, six large flood control dams were constructed on the White River and its tributaries..
* Beaver Dam on the White River - Beaver Lake
* Table Rock Dam on the White River - Table Rock Lake
* Bull Shoals Dam on the White River - Bull Shoals Lake
* Norfork Dam on the North Fork River - Norfolk Lake
* Greers Ferry Lake on the Little Red River - Greers Ferry Lake
* Clearwater Dam on the Black River - Clearwater Lake
Multiple smaller lakes have been created by dams in the White River basin from 1911 through 1960. These smaller lakes include Lake Sequoyah,Boss, Stephen K., Heil-Chapdelaine, Vanessa M
Many of the rivers and streams in the Ozarks have been dammed. Most of the dams in the region were initially built for the dual purpose of flood control and hydropower generation but have also become major economic drivers through recreational use in places such as Branson, Missouri, and Mountain Home, Arkansas.
The United States Army Corps of Engineers, Army Corps of Engineers among others, operates multiple dams in the Ozarks region. Some of the largest lakes created by these dams are on the White River (Arkansas–Missouri), White River. Beginning in 1911 with the construction of Powersite Dam on the White River near Branson, Missouri and the impoundment of Lake Taneycomo the Ozarks rivers have been harnessed for electrical power, recreation, and flood control. After the President Franklin D, Roosevelt signed the Flood Control Act of 1938, six large flood control dams were constructed on the White River and its tributaries..
* Beaver Dam on the White River - Beaver Lake
* Table Rock Dam on the White River - Table Rock Lake
* Bull Shoals Dam on the White River - Bull Shoals Lake
* Norfork Dam on the North Fork River - Norfolk Lake
* Greers Ferry Lake on the Little Red River - Greers Ferry Lake
* Clearwater Dam on the Black River - Clearwater Lake
Multiple smaller lakes have been created by dams in the White River basin from 1911 through 1960. These smaller lakes include Lake Sequoyah,Boss, Stephen K., Heil-Chapdelaine, Vanessa M
"Mapping Landscape Change: An Historic and Bathymetric Study of Lake Sequoyah, Washington County, Arkansas"
a small recreational fishing lake east of Fayetteville, Arkansas, formed in 1961; Sequoyah is the uppermost impoundment on the White River. Below Sequoyah (northeast of Fayetteville) is Beaver Lake (Arkansas), Beaver Lake, formed in 1960. The White River continues northeasterly into Table Rock Lake (1958) in Missouri, which feeds directly into Lake Taneycomo, where the river zigzags southeasterly into Arkansas forming Bull Shoals Lake along the Arkansas-Missouri line. Completed in 1952, Bull Shoals is the furthest downstream lake on the White River proper. Norfork Dam, Norfork Lake was formed by damming the North Fork River (Missouri–Arkansas), North Fork River, a tributary of the White River, in 1941. Additional large lakes in the Ozarks region include
"The Meramec Basin Project: A Look Back 25 Years Later"
''Ozark Mountain Experience''. Article 69 & 70 Combined. 2006."Mountain Home (Baxter County)": ''The Encyclopedia of Arkansas History & Culture''
Campbell, Rex R. Campbell, Mary. Hughes, Colleen
"A Revolution in the Heartland: Changes in Rural Culture, Family and Communities, 1900–2000"
. University of Missouri: Department of Rural Sociology. Columbia, Missouri. 2004. The streams provided water and power to communities, farms and mills concentrated in the valleys prior to impoundment.E. Joan Wilson Miller
Abstract
"The Ozark Culture Region as Revealed by Traditional Materials". ''Annals of the Association of American Geographers'', Volume 58 Issue 1, Pages 51-77. January 3, 1967. Many cemeteries, farm roads, river fords and railways were lost when the lakes came, disrupting rural culture, travel and commerce. Baxter County, Arkansas, alone saw nearly 400 people displaced to make way for the reservoir created by Norfork Dam. The town of Forsyth, Missouri, was relocated in its entirety to a spot from its previous location. Prior to damming, rivers and streams in the White and Osage River basins were of similar character to the current conditions of the Buffalo, Elk River (Oklahoma), Elk, Niangua River, Niangua, Gasconade River, Gasconade, Big Piney River, Big Piney, Current River (Ozarks), Current, Jacks Fork River, Jacks Fork, Eleven Point River, Eleven Point and Meramec River, Meramec rivers. Because of the success of the Army Corps efforts to dam the large rivers in the Ozarks, the Ozarks Society began protests to keep the other rivers in the Ozarks free flowing. The Buffalo National River was created by an Act of Congress in 1972 as the nation's first List of areas in the United States National Park System#National rivers and national wild and scenic rivers, National River, administered by the National Park Service. The designation came after over a decade of battling a proposed Army Corps dam in the media, legislature, and courts to keep the Buffalo River free flowing. The Ozark Society, the main force behind the dam protest, still leads the fight to keep the Buffalo River pristine and protected. Today, the Buffalo River sees approximately 800,000 visitors camping, canoeing, floating, hiking, and tubing annually. In Missouri, the Ozark National Scenic Riverways was established in 1964 along the Current River (Ozarks), Current and Jacks Fork rivers as the first US national park based on a river system. The Eleven Point River is included in the National Wild and Scenic Rivers System established in 1968. These parks and rivers are a major economic driver for some of the least populated counties in Arkansas and Missouri, attracting up to 1.5 million tourists annually. Many other waterways and streams have their headwaters in the Boston Mountains portion of the Ozarks such as the Mulberry River (Arkansas), Mulberry River, the White River, War Eagle Creek, Little Mulberry Creek, Lee Creek, Big Piney Creek, and the Little Red River. To the south, the Arkansas River valley separates the Boston Mountains from the Ouachita Mountains. Missouri Ozark rivers include the Gasconade River, Gasconade, Big Piney River, Big Piney, and Niangua River, Niangua rivers in the north central region. The Meramec River and its tributaries Huzzah Creek (Meramec River tributary), Huzzah Creek and Courtois Creek are found in the northeastern Ozarks. The Black River (Arkansas–Missouri), Black and St. Francis River, St. Francis rivers mark the eastern crescent of the Ozarks. The James River (Missouri), James, Spring River (Arkansas), Spring and North Fork River (Missouri–Arkansas), North Fork rivers are in south-central Missouri. Forming the west central border of the Ozarks from Missouri through Kansas and into Oklahoma are the Spring River (Missouri), Spring River and its tributary, Center Creek. Grand Falls, Missouri's largest natural waterfall, a
"Hydraulic Modeling of In-channel Habitats in the Ozark Highlands of Missouri: Assessment of Physical Habitat Sensitivity to Environmental Change"
USGS-Biological Resources Division. Except during periods of heavy rain or snow melt – when water levels rise quite rapidly – their level of difficulty is suitable for most canoeing and tubing. Fish hatcheries are common due to the abundance of springs and waterways. The Neosho National Fish Hatchery was built in 1888; it was the first federal hatchery. The Arkansas Game and Fish Commission, Missouri Department of Conservation and United States Fish and Wildlife Service, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service operate numerous warm and cold water hatcheries and trout parks;
Missouri Fish Hatcheries and Trout Parks private hatcheries such as at Rockbridge, Missouri, Rockbridge are found throughout the region.
Tri-State and Viburnum Trend Districts
''Rocks & Minerals'', November 1, 1997.
, Kansas Geological Survey. Updated May 5, 2005. Much of the area supports beef cattle ranching, and dairy farming is common across the area. Dairy farms are usually cooperative affairs, with small farms selling to a corporate wholesaler, who packages product under a common brand for retail sales. Petroleum exploration and extraction also takes place in the Oklahoma portion of the Ozarks, as well as in the east half of the Boston Mountains in Arkansas. Logging of both softwood and hardwood timber species on both private land and in the United States National Forest, National Forests has long been an important economic activity. The majority of the Ozarks is forested. Oak–hickory forest, Oak-hickory is the predominant type; Juniperus virginiana, eastern junipers are common, with stands of List of Pinus species, pine often seen in the southern range. Less than a quarter of the region has been cleared for pasture and cropland.''Primary Distinguishing Characteristics of Level III Ecoregions of the Continental United States''
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Revised April 2000. Forests that were heavily logged during the early-to-mid-20th century have recovered; much of the remaining timber in the Ozarks is secondary forest, second-growth forest. However, deforestation of Old-growth forest, frontier forest contributed through erosion to increased gravel bars along Ozark waterways in logged areas; stream channels have become wider and shallower, and deepwater fish habitat has been lost. The numerous rivers and streams of the region saw hundreds of water-powered timber and grist mills."Index to the old mills of Missouri"
The numerous rivers and streams of the region saw hundreds of water-powered timber and grist mills."Index to the old mills of Missouri"
Hosted by rootsweb, this incomplete list includes almost 250 old mills in Missouri alone.
(Rootsweb) Mills were important centers of culture and commerce; dispersed widely throughout the region, mills served local needs, often thriving within a few miles of another facility. Few Ozark mills relied on inefficient water wheels for power; most utilized a dam, Sluice, millrace and water turbine.Suggs, George E., Jr. ''Water Mills of the Missouri Ozarks''. University of Oklahoma Press: Norman, Oklahoma. 1990 During the New Deal, the Civilian Conservation Corps employed hundreds in the construction of nearly 400 fire lookouts throughout the Ozarks at 121 known sites in Arkansas and 257 in Missouri. Of those lookouts, about half remain, and many of them are in use by the United States Forest Service, U.S. Forest Service. A 2007 report by the National Trust for Historic Preservation deemed these fire lookouts and related structures as one of America's 11 Most Endangered Historic Places. In the 1960s, federal activity promoted modernization, especially through better transportation and tourism. The Ozarks Regional Commission sponsored numerous projects.
Southwest Missouri Council of Governments White Paper.Snyder, Robert E. "Shepherd of the Hills Country: Tourism Transforms the Ozarks, 1880s-1930s". ''The Journal of American Culture'', Volume 27 Issue 1, Pages 117-119. The rapidly growing Northwest Arkansas, Northwest Arkansas metropolitan area has also become a tourist hub, drawing nationwide attention for the Crystal Bridges Museum of American Art in Bentonville, Arkansas. Poultry farming and food processing are significant industries throughout the region. The Tyson Foods corporation and ConAgra Foods each operates several hundred poultry farms and processing plants throughout the Ozarks. Schreiber Foods has operations throughout southern Missouri. The Trucking industry in the United States, trucking industry is important to the regional economy, with national carriers based there including J. B. Hunt, ABF Freight System, ABF, and Prime, Inc. Springfield remains an operational hub for the BNSF Railway. Logging and timber industries are also significant in the Ozark economy, with operations ranging from small family-run sawmills to large commercial concerns. Fortune 500 companies such as Wal-Mart, Leggett & Platt, Bass Pro Shops, and O'Reilly Auto Parts are based in the Ozarks. The area is home to several Missouri wine and spirit regions, including the Ozark Highlands AVA, Ozark Highlands and Ozark Mountain AVA, Ozark Mountain American Viticultural Areas, and the Ozark Highlands Spirits, Ozark Highland Spirits Region. There are a number of Craft brewery and microbrewery, microbreweries throughout the region.
"Original Ozarks: Evidence of settlement before 1830 hard to find"
''Joplin Globe''. June 21, 2009. According to the National Register of Historic Places, the Rice-Upshaw House, ca.1826, "is one of the two oldest remaining standing buildings in Arkansas, and a rare surviving example of a building from Arkansas' territorial period"; Wolf House, ca. 1825, overlooks the junction of the Norfork and White rivers; the Craighead-Henry House, ca. 1816, is "one of the oldest known structures in the interior [Missouri] Ozarks." and Ozark English, dialect shared by the people who live on the plateau. Early settlers in Missouri were American pioneer, pioneers who came west from the Appalachia, Southern Appalachians at the beginning of the 19th century,Randolph, Vance. ''Ozark Magic and Folklore''. 367 pages. Courier Dover Publications, 1964. followed in the 1840s and 1850s by Irish Americans, Irish and German Americans, German immigrants. Much of the Ozark population is of English Americans, English, Scots-Irish Americans, Scots-Irish, and German descent, and the Ozark families from which the regional culture derived tend to have lived in the area since the 19th century.Rafferty, Milton D. ''The Ozarks: Land and Life'', University of Arkansas Press, 2nd ed., 2001. Early settlers relied on hunting, fishing, trapping, and foraging to supplement their diets and incomes. Today hunting and fishing for recreation are common activities and an important part of the tourist industry. Foraging for Edible mushroom, mushrooms (especially morels) and for American ginseng, ginseng is common and financially supported by established buyers in the area. Other forages include Phytolacca americana, poke, watercress, Diospyros virginiana, persimmons and Asimina triloba, pawpaw; wild berries such as blackberry, black raspberry, raspberry, Morus rubra, red mulberry, Prunus serotina, black cherry, Virginia strawberry, wild strawberry and dewberry; and wild nut (fruit), nuts such as Juglans nigra, black walnut and even acorns.Phillips, Jan. ''Wild Edibles of Missouri''. Missouri Department of Conservation, 2nd edition (1998)
Early settlers relied on hunting, fishing, trapping, and foraging to supplement their diets and incomes. Today hunting and fishing for recreation are common activities and an important part of the tourist industry. Foraging for Edible mushroom, mushrooms (especially morels) and for American ginseng, ginseng is common and financially supported by established buyers in the area. Other forages include Phytolacca americana, poke, watercress, Diospyros virginiana, persimmons and Asimina triloba, pawpaw; wild berries such as blackberry, black raspberry, raspberry, Morus rubra, red mulberry, Prunus serotina, black cherry, Virginia strawberry, wild strawberry and dewberry; and wild nut (fruit), nuts such as Juglans nigra, black walnut and even acorns.Phillips, Jan. ''Wild Edibles of Missouri''. Missouri Department of Conservation, 2nd edition (1998)
Cover, Introduction, Acknowledgments and Preface
Chapters
Color Plates
. Edible native plant, native legumes, grass, wild grasses and wildflowers are plentiful, and beekeeping is common.''The Naturalist''
High Plains Films. Doug Hawes-Davis, Director. 32 minutes, Color/B&W, 2001. Print and broadcast media have explored Ozark culture broadly. Books set in the Ozarks include ''Where the Red Fern Grows'', ''The Shepherd of the Hills (novel), The Shepherd of the Hills'', and ''As a Friend''.Forrest Gander, Gander, Forrest.
As a Friend
''. New York City: New Directions Publishers, New Directions Publishing Corporation. 2008. The 1999 film ''Ride with the Devil (film), Ride with the Devil'', based on the book ''Woe to Live On'', depicts conflict in southwest Missouri during the American Civil War, Civil War.Ward L. Schrantz. ''Jasper County, Missouri in the Civil War''. 1923. ''Winter's Bone'', a novel by Daniel Woodrell (author of ''Woe to Live On''), reflects on contemporary methamphetamine culture and its impact on families on the plateau. Released as a feature film in 2010, ''Winter's Bone'' received the Grand Jury Prize at the Sundance Film Festival, as well as other awards. Several early and influential country music, country-music television and radio programs originated from
Play Me Something Quick and Devilish: Bob Holt – Old-Time Square Dance Fiddler
''Musical Traditions'', Article MT021, June 1998. Netflix drama series ''Ozark (TV series), Ozark'' takes place in Osage Beach, Missouri and revolves around the well-to-do Byrde family as their lives are uprooted and they are forced to move from Chicago to the Ozarks after a money laundering scheme goes wrong. The series focuses on the Byrdes' dealings in the Ozarks, as well as their interactions with local Ozark crime families. The series premiered on July 21, 2017. Examples of commercial interpretations of traditional Ozark culture include the two major family theme parks in the region, Silver Dollar City and the now defunct Dogpatch USA, and the resort entertainment complex in
"How to Spot a Genuine Ozark Hillbilly"
October 23, 2008. Many of these tunes and tales can be traced to United Kingdom, British originsSmith, Vic
Review of Ozark Folksongs
''Musical Traditions'', January 2001. and to German folklore. Moreover, historian Vance Randolph attributes the formation of much Ozark lore to individual families when "backwoods parents begin by telling outrageous whoppers to their children and end by half believing the wildest of these tales themselves." Randolph collected Ozark folklore and lyrics in volumes such as the national bestseller ''Pissing in the Snow and Other Ozark Folktales'' (University of Illinois Press, 1976), ''Ozark Folksongs'' (University of Missouri Press, 1980), a four-volume anthology of regional songs and ballads collected in the 1920s and 1930s, and ''Ozark Magic and Folklore'' (Courier Dover Publications, 1964). Evidenced by Randolph's extensive field work, many Ozark anecdotes from the oral tradition are often Ribaldry, bawdy, full of wild embellishments on everyday themes.Florer, Faith L
"Book Review. Pissing in the snow and other Ozark folktales".
''Whole Earth Review''. Summer, 1987. "Because of their—ahem—subject matter, the tales contained in this volume could not be published with Randolph's four great collections of Ozark material published in the 1950s, and have until recently been circulating only in manuscript and on elusive microfilm." In 1941–42, commissioned by Alan Lomax of the Archive of Folk Culture, Randolph returned to the Ozarks with a portable recording machine from the Library of Congress and captured over 800 songs, ballads and instrumentals. Selected from among these several hundred recordings, 35 tracks were released on ''Various Artists: Ozark Folksongs'' (Rounder Records) in 2001. Traditional square dance, Square dances were an important social avenue throughout the Ozarks into the 20th century.Karen Mulrenin, Rita Saeger and Terry Brandt
Traditional square dance, Square dances were an important social avenue throughout the Ozarks into the 20th century.Karen Mulrenin, Rita Saeger and Terry Brandt
"Old-Time Ozark Square Dancing"
''Bittersweet'', Volume II, No. 1, Fall 1974.Foreman, Diana
''Bittersweet'', Volume V, No. 2, Winter 1977.Edited and photography by Allen Gage
''Bittersweet'', Volume IX, No. 3, Spring 1982. Square dances sprang up wherever people concentrated around mills and timber camps, springs, fords, and in towns small and large. Geographically isolated communities saw their own local dance tunes and variations develop. Of all the traditional musicians in the Ozarks, the fiddler holds a distinct place in both the community and folklore. Community fiddlers were revered for carrying local tunes; regionally, traveling fiddlers brought new tunes and entertainment, even while many viewed their arrival as a threat to morality. In 2007, Gordon McCann, a chronicler of Ozarks folklife and fiddle music for over four decades, donated a collection of audio recordings, fieldnotes and photographs to Missouri State University in Springfield.Gordon McCann pledges collection to Missouri State University: Four decades of material will be housed in Meyer Library
Missouri State University Press Release. September 26, 2007. The collection includes more than 3,000 hours of fiddle music and interviews recorded at jam sessions, music parties, concerts and dances in the Ozarks. Selected audio recordings along with biographical sketches, photographs and tune histories were published in Drew Beisswenger and Gordon McCann's 2008 book/37-track CD set ''Mel Bay Presents Ozarks Fiddle Music: 308 Tunes Featuring 30 Legendary Fiddlers With Selections from 50 Other Great Ozarks Fiddlers''. From 1973 to 1983, the Bittersweet project, which began as an English class at Lebanon High School (Missouri), Lebanon High School in Missouri, collected 476 taped and transcribed interviews, published 482 stories, and took over 50,000 photographs documenting traditional Ozark culture. Population influx since the 1950s, coupled with geographically lying in both the Midwest and Upper South, proximity to the Mississippi embayment, the Osage Plains, Osage and Northern Plains, contributes to changing cultural values in the Ozarks. Theme parks and theatres seen to reflect regional values have little in common with traditional Ozark culture. Community tradition bearers remain active, in decreasing numbers, far afield of commercial offers.
Mel Bay Presents Ozarks Fiddle Music: 308 Tunes Featuring 30 Legendary Fiddlers With Selections from 50 Other Great Ozarks Fiddlers
'' 2008. * Blevins, Brooks, ''A History of the Ozarks: Volume 1: The Old Ozarks.'' Urbana, IL: University of Illinois Press, 2018. * Rafferty, Milton D. ''The Ozarks: Land and Life.'' Fayetteville, AR: University of Arkansas Press, 2001. * Randolph, Vance. ''The Ozarks: An American Survival of Primitive Society.'' 1931. * Rossiter, Phyllis. ''A Living History of the Ozarks'' Gretna, LA: Pelican, 1992. * Phillips, Jared. ''Hipbillies: Deep Revolution in the Arkansas Ozarks'' Fayetteville, AR: University of Arkansas Press, 2019.
full text
Ozark National Scenic Riverways
*
Ozark Plateau National Wildlife Refuge
Ozark Mountains, Encyclopedia of Arkansas History & Culture, The Central Arkansas Library System.
The Intimate Wild: Ozark Highlands Trail, National Geographic, 10/2008.
"Closest to Everlastin'": Ozark Agricultural Biodiversity and Subsistence Traditions, 9/2010.
* {{Authority control Ozarks, Civilian Conservation Corps in Arkansas Civilian Conservation Corps in Missouri Mountain ranges of Arkansas Mountain ranges of Kansas Mountain ranges of Missouri Mountain ranges of Oklahoma Physiographic regions of the United States Plateaus of the United States Regions of Arkansas U.S. Interior Highlands

 The Ozarks, also known as the Ozark Mountains, Ozark Highlands or Ozark Plateau, is a
The Ozarks, also known as the Ozark Mountains, Ozark Highlands or Ozark Plateau, is a physiographic region
Physiographic regions of the world are a means of defining Earth's landforms into distinct regions, based upon the classic three-tiered approach by Nevin M. Fenneman in 1916, that separates landforms into physiographic divisions, physiographic pro ...
in the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sover ...
s of Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
, Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the Osage ...
, Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
and the extreme southeastern corner of Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the ...
. The Ozarks cover a significant portion of northern Arkansas and most of the southern half of Missouri, extending from Interstate 40
Interstate 40 (I-40) is a major east–west Interstate Highway running through the south-central portion of the United States. At a length of , it is the third-longest Interstate Highway in the country, after I-90 and I-80. From west to ea ...
in central Arkansas to Interstate 70
Interstate 70 (I-70) is a major east–west Interstate Highway System, Interstate Highway in the United States that runs from Interstate 15, I-15 near Cove Fort, Utah, to a park and ride lot just east of Interstate 695 (Maryland), I-695 in ...
in central Missouri.
There are two mountain ranges in the Ozarks: the Boston Mountains
The Boston Mountains is a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the U.S. states of Arkansas and Oklahoma. Part of the Ozarks, the Boston Mountains are a deeply dissected plateau. The ecoregion is steeper ...
of Arkansas and the St. Francois Mountains
The St. Francois Mountains in southeast Missouri are a mountain range of Precambrian igneous mountains rising over the Ozark Plateau. This range is one of the oldest exposures of igneous rock in North America.
The name of the range is spelled out ...
of Missouri. Buffalo Lookout, the highest point in the Ozarks, is located in the Boston Mountains. Geologically, the area is a broad dome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a m ...
with the exposed core in the ancient St. Francois Mountains. The Ozarks cover nearly , making it the most extensive highland
Highlands or uplands are areas of high elevation such as a mountainous region, elevated mountainous plateau or high hills. Generally speaking, upland (or uplands) refers to ranges of hills, typically from up to while highland (or highlands) is ...
region between the Appalachians
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
and Rockies
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Can ...
. Together with the Ouachita Mountains
The Ouachita Mountains (), simply referred to as the Ouachitas, are a mountain range in western Arkansas and southeastern Oklahoma. They are formed by a thick succession of highly deformed Paleozoic strata constituting the Ouachita Fold and Thru ...
, the area is known as the U.S. Interior Highlands.
The Salem Plateau, named after Salem, Missouri
Salem is the county seat of Dent County, Missouri, United States. The population was 4,608 at the 2020 census, which allows Salem to become a Class 3 city in Missouri; however, the city has chosen to remain a Class 4 city under Missouri Revise ...
, makes up the largest geologic area of the Ozarks. The second largest is the Springfield Plateau, named after Springfield, Missouri
Springfield is the third largest city in the U.S. state of Missouri and the county seat of Greene County. The city's population was 169,176 at the 2020 census. It is the principal city of the Springfield metropolitan area, which had an estimat ...
, nicknamed the "Queen City of the Ozarks". On the northern Ozark border are the cities of St. Louis
St. Louis () is the second-largest city in Missouri, United States. It sits near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri Rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a population of 301,578, while the bi-state metropolitan area, which e ...
and Columbia, Missouri
Columbia is a city in the U.S. state of Missouri. It is the county seat of Boone County and home to the University of Missouri. Founded in 1821, it is the principal city of the five-county Columbia metropolitan area. It is Missouri's fourth ...
. Significant Ozark cities in Arkansas include Fayetteville, Bentonville, Springdale, Eureka Springs
Eureka Springs is a city in Carroll County, Arkansas, United States, and one of two county seats for the county. It is located in the Ozark Mountains of northwest Arkansas, near the border with Missouri. As of the 2020 census, the city populati ...
, and Fort Smith. Branson Branson may refer to:
Places
;Canada
* Branson, Toronto
;United States
* Branson, Missouri, a popular tourist destination in the Ozark Mountains
* Branson, Colorado
* Branson City, California
* The Branson School, in Ross, California
* Warrenpoi ...
, just north of the Arkansas–Missouri border, is a tourist destination and popularizer of Ozark culture.
Etymology
''Ozarks'' is atoponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
believed to be derived as an English-language adaptation of the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
abbreviation ''aux Arcs'' (short for ''aux Arcansas'', meaning "of/at/to the Arcansas lural). Originally, in the decades prior to the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
, ''aux Arkansas'' referred to the trading post
A trading post, trading station, or trading house, also known as a factory, is an establishment or settlement where goods and services could be traded.
Typically the location of the trading post would allow people from one geographic area to tr ...
at Arkansas Post
The Arkansas Post (french: Poste de Arkansea) (Spanish: ''Puesto de Arkansas''), formally the Arkansas Post National Memorial, was the first European settlement in the Mississippi Alluvial Plain and present-day U.S. state of Arkansas. In 168 ...
, located in wooded Arkansas Delta
The Arkansas Delta is one of the six natural regions of the state of Arkansas. Willard B. Gatewood Jr., author of ''The Arkansas Delta: Land of Paradox'', says that rich cotton lands of the Arkansas Delta make that area "The Deepest of the Deep ...
lowland area above the confluence of the Arkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in the western United Stat ...
with the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
.
Other possible derivations include ''aux arcs'' meaning "and
or AND may refer to:
Logic, grammar, and computing
* Conjunction (grammar), connecting two words, phrases, or clauses
* Logical conjunction in mathematical logic, notated as "∧", "⋅", "&", or simple juxtaposition
* Bitwise AND, a boole ...
of the arches", in reference to the dozens of natural bridges
A natural arch, natural bridge, or (less commonly) rock arch is a natural landform where an arch has formed with an opening underneath. Natural arches commonly form where inland cliffs, coastal cliffs, fins or stacks are subject to erosion ...
formed by erosion and collapsed caves in the Ozark region. These include Clifty Hollow Natural Bridge (actually a series of arches) in Missouri,Watkins, Conor"Ozarks geology: Clifty Creek Natural Area includes natural bridge"
, ''The Ozarks Chronicle'', Rolla, Mo. and Alum Cove in the
Ozark–St. Francis National Forest
The Ozark – St. Francis National Forest is a United States National Forest that is located in the U.S. state, state of Arkansas. It is composed of two separate forests, Ozark National Forest in the Ozark Mountains; and St. Francis National Fore ...
. By the early 20th century, the "Ozarks" had become a generic and widely used term.McMillen, Margot Ford. ''A to Z Missouri: The Dictionary of Missouri Place Names'', Columbia, Missouri: Pebble Publishing, 1996.
Physiographic subregions
 The Ozarks consist of five physiographic subregions: the
The Ozarks consist of five physiographic subregions: the Boston Mountains
The Boston Mountains is a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the U.S. states of Arkansas and Oklahoma. Part of the Ozarks, the Boston Mountains are a deeply dissected plateau. The ecoregion is steeper ...
of north Arkansas and Cookson Hills The Cookson Hills are in eastern Oklahoma. They are an extension of the Boston Mountains of Arkansas to the east and the southwestern margin of the Ozark Plateau. They lie generally between Stilwell, Sallisaw and Tahlequah. The area became part ...
of east Oklahoma; the Springfield Plateau
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
of southwest Missouri, northeast Oklahoma, and northwest Arkansas and including Springfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
, Joplin and Monett
Monett is the most-populous city in the Barry County, Missouri, Barry and Lawrence County, Missouri, Lawrence counties in the U.S. state of Missouri. The city is located in the Ozark Mountains, Ozarks, just south of Interstate 44 in Missouri, Inte ...
/Aurora
An aurora (plural: auroras or aurorae), also commonly known as the polar lights, is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly seen in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). Auroras display dynamic patterns of bri ...
in Missouri, Tahlequah
Tahlequah ( ; ''Cherokee'': ᏓᎵᏆ, ''daligwa'' ) is a city in Cherokee County, Oklahoma located at the foothills of the Ozark Mountains. It is part of the Green Country region of Oklahoma and was established as a capital of the 19th-century ...
in Oklahoma, and Fayetteville and Harrison
Harrison may refer to:
People
* Harrison (name)
* Harrison family of Virginia, United States
Places
In Australia:
* Harrison, Australian Capital Territory, suburb in the Canberra district of Gungahlin
In Canada:
* Inukjuak, Quebec, or "Po ...
in Arkansas; the White River Hills along the White River, including Branson Branson may refer to:
Places
;Canada
* Branson, Toronto
;United States
* Branson, Missouri, a popular tourist destination in the Ozark Mountains
* Branson, Colorado
* Branson City, California
* The Branson School, in Ross, California
* Warrenpoi ...
and Mountain Home to Batesville; the Salem Plateau
Salem may refer to: Places
Canada
Ontario
* Bruce County
** Salem, Arran–Elderslie, Ontario, in the municipality of Arran–Elderslie
** Salem, South Bruce, Ontario, in the municipality of South Bruce
* Salem, Dufferin County, Ontario, part ...
or Central Plateau, which includes a broad band across south central Missouri and north central Arkansas including the Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus li ...
, Salem
Salem may refer to: Places
Canada
Ontario
* Bruce County
** Salem, Arran–Elderslie, Ontario, in the municipality of Arran–Elderslie
** Salem, South Bruce, Ontario, in the municipality of South Bruce
* Salem, Dufferin County, Ontario, part ...
and West Plains
West Plains is a city in, and the county seat of Howell County, Missouri, United States. The population was 12,184 at the 2020 census.
History
The history of West Plains can be traced back to 1832, when settler Josiah Howell (after whom Howell ...
areas; the Courtois Hills
The Courtois Hills region is an area of the Ozark Mountains in southeast Missouri. It is one of several mountainous regions that surround the Ozarks's Salem (or Central) Plateau.
Geography
Although it does not contain the highest peak, the Cour ...
of southeastern Missouri; the Osage-Gasconade Hills around the Lake of the Ozarks
Lake of the Ozarks is a reservoir created by impounding the Osage River in the northern part of the Ozarks in central Missouri. Parts of three smaller tributaries to the Osage are included in the impoundment: the Niangua River, Grandglaize Creek ...
; the Saint Francois Mountains
The St. Francois Mountains in southeast Missouri are a mountain range of Precambrian igneous mountains rising over the Ozark Plateau. This range is one of the oldest exposures of igneous rock in North America.
The name of the range is spelled out ...
; and the Missouri River and Mississippi River border areas along the eastern and northeastern flanks.
Karst
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathering-resistant ro ...
features such as spring
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season), a season of the year
* Spring (device), a mechanical device that stores energy
* Spring (hydrology), a natural source of water
* Spring (mathematics), a geometric surface in the shape of a ...
s, losing stream
A losing stream, disappearing stream, influent stream or sinking river is a stream or river that loses water as it flows downstream. The water infiltrates into the ground recharging the local groundwater, because the water table is below the bo ...
s, sinkhole
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are locally also known as ''vrtače'' and shakeholes, and to openi ...
s and cave
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea ...
s are common in the limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
s of the Springfield Plateau and abundant in the dolomite Dolomite may refer to:
*Dolomite (mineral), a carbonate mineral
*Dolomite (rock), also known as dolostone, a sedimentary carbonate rock
*Dolomite, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community
*Dolomite, California, United States, an unincor ...
bedrock of the Salem Plateau and Boston Mountains.''Karst, Springs and Caves in Missouri''Missouri Department of Natural Resources Missouri is known as "The Cave State" with over 7,300 recorded caves, second in number only to Tennessee. The majority of these caves are found in the Ozark counties. The Ozark Plateaus aquifer system affects groundwater movement in all areas except the igneous core of the St. Francois Mountains.Rafferty, Milton
''OzarksWatch'', Vol. I, No. 4, Spring 1988.
United States Geological Survey.
United States Geological Survey. Geographic features include limestone and dolomite glades, which are rocky, desert-like areas on hilltops. Kept open by periodic fires that limit growth of
grasses
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and ...
and forb
A forb or phorb is an herbaceous flowering plant that is not a graminoid (grass, sedge, or rush). The term is used in biology and in vegetation ecology, especially in relation to grasslands and understory. Typically these are dicots without woo ...
s in shallow soil, glades are home to collared lizards, tarantulas, scorpions, cacti and other species more typical of the Desert Southwest
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural list of regions of the United States, region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacen ...
."Spatial Interaction Webs in Ozark Glades"John Chase, Assistant Professor. Washington University in St. Louis. The Boston Mountains contain the highest elevations of the Ozarks, with peaks over , and form some of the greatest relief of any formation between the Appalachians and Rocky Mountains. The
Ouachita Mountains
The Ouachita Mountains (), simply referred to as the Ouachitas, are a mountain range in western Arkansas and southeastern Oklahoma. They are formed by a thick succession of highly deformed Paleozoic strata constituting the Ouachita Fold and Thru ...
to the south rise a few hundred feet higher, but are not geographically associated with the Ozarks. The Boston Mountains portion of the Ozarks extends north of the Arkansas River Valley , is approximately long, and is bordered by the Springfield and Salem Plateau to the north of the White River. Summits can reach elevations of just over , with valleys deep. Turner Ward Knob is the highest named peak. Found in western Newton County, Arkansas
Newton County is a County (United States), county in the U.S. state of Arkansas. As of the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census, the population was 8,330. The county seat is Jasper, Arkansas, Jasper. Newton County is Arkansas's 46th county, f ...
, its elevation is . Nearby, five unnamed peaks have elevations at or slightly above . Drainage is primarily to the White River, with the exception of the Illinois River
The Illinois River ( mia, Inoka Siipiiwi) is a principal tributary of the Mississippi River and is approximately long. Located in the U.S. state of Illinois, it has a drainage basin of . The Illinois River begins at the confluence of the D ...
, although there also is considerable drainage from the south slopes of the Boston Mountains to the Arkansas River. Major streams of this type include Lee Creek, Frog Bayou, Mulberry River, Spadra Creek, Big Piney Creek, Little Piney Creek, Illinois Bayou, Point Remove Creek, and Cadron Creek. Many Ozark waterways have their headwaters in the uplands of the Boston formation, including the Buffalo, Kings
Kings or King's may refer to:
*Monarchs: The sovereign heads of states and/or nations, with the male being kings
*One of several works known as the "Book of Kings":
**The Books of Kings part of the Bible, divided into two parts
**The ''Shahnameh'' ...
, Mulberry
''Morus'', a genus of flowering plants in the family Moraceae, consists of diverse species of deciduous trees commonly known as mulberries, growing wild and under cultivation in many temperate world regions. Generally, the genus has 64 identif ...
, Little Red and White rivers.
Topography is mostly gently rolling in the Springfield and Salem plateaus, whereas the Saint Francois Mountains
The St. Francois Mountains in southeast Missouri are a mountain range of Precambrian igneous mountains rising over the Ozark Plateau. This range is one of the oldest exposures of igneous rock in North America.
The name of the range is spelled out ...
are more rugged. Although the Springfield formation's surface is primarily Mississippian limestone and chert
Chert () is a hard, fine-grained sedimentary rock composed of microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz, the mineral form of silicon dioxide (SiO2). Chert is characteristically of biological origin, but may also occur inorganically as a prec ...
, the Salem Plateau is made of older Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start ...
dolomites, limestones, and sandstones. Both are rife with karst topography and form long, flat plains. The formations are separated by steep escarpments that dramatically interrupt the rolling hills. Although much of the Springfield Plateau has been denuded
Denudation is the geological processes in which moving water, ice, wind, and waves erode the Earth's surface, leading to a reduction in elevation and in relief of landforms and landscapes. Although the terms erosion and denudation are used interch ...
of the surface layers of the Boston Mountains, large remnants of these younger layers are present throughout the southern end of the formation, possibly suggesting a peneplain
390px, Sketch of a hypothetical peneplain formation after an orogeny.
In geomorphology and geology, a peneplain is a low-relief plain formed by protracted erosion. This is the definition in the broadest of terms, albeit with frequency the usage ...
process. The Springfield Plateau drains through wide, mature streams ultimately feeding the White River.
Geology
TheSt. Francois Mountains
The St. Francois Mountains in southeast Missouri are a mountain range of Precambrian igneous mountains rising over the Ozark Plateau. This range is one of the oldest exposures of igneous rock in North America.
The name of the range is spelled out ...
in the northeastern Ozarks are the eroded remnants of an ancient range which form the geological core of the highland dome. The igneous
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or ...
and volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates a ...
rocks of the St. Francois Mountains are the exposed remains of a Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
mountain range hundreds of millions of years old. The remaining hills are the exposed portion of an extensive terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its own ...
(the Spavinaw terrane in part) of granitic
A granitoid is a generic term for a diverse category of coarse-grained igneous rocks that consist predominantly of quartz, plagioclase, and alkali feldspar. Granitoids range from plagioclase-rich tonalites to alkali-rich syenites and from quart ...
and rhyolitic
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The mineral ...
rocks dating from 1485 to 1350 mya that stretches from Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
to western Oklahoma.Denison, Rodger E., et al., ''Geology and Geochemistry of the Precambrian Rocks in the Central Interior Region of the United States'', Geological Survey Professional Paper 1241-C, 1984 The core of the range existed as an island in the Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
seas. Reef
A reef is a ridge or shoal of rock, coral or similar relatively stable material, lying beneath the surface of a natural body of water. Many reefs result from natural, abiotic processes— deposition of sand, wave erosion planing down rock out ...
complexes occur in the sedimentary layers surrounding this ancient island. These flanking reefs were points of concentration for later ore
Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals, typically containing metals, that can be mined, treated and sold at a profit.Encyclopædia Britannica. "Ore". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 7 April 2 ...
-bearing fluids which formed the rich lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
-zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
ores that have been and continue to be mined in the area. The igneous and volcanic rocks extend at depth under the relatively thin veneer of Paleozoic sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic matter, organic particles at Earth#Surface, Earth's surface, followed by cementation (geology), cementation. Sedimentati ...
rocks and form the basal crust of the entire region.A. G. Unklesbay, Jerry D. Vineyard. ''Missouri Geology — Three Billion Years of Volcanoes, Seas, Sediments, and Erosion'', University of Missouri Press, 1992.
 A major
A major unconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval o ...
in the region attests that the Ozarks were above sea level for several hundred million years from the time of the volcanism in the Precambrian until the mid-Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million ...
with an erosionally produced relief of up to . The seas encroached during the late Cambrian producing the Lamotte Sandstone
Lamotte, LaMotte or La Motte may refer to:
Places Canada
* La Motte, Quebec
France
* La Grande-Motte, in the Hérault département
* La Motte, Côtes-d'Armor, in the Côtes-d'Armor ''département''
* La Motte, Var, in the Var ''département''
...
, thick, followed by carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate g ...
sedimentation. Coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
Co ...
s formed around the granite and rhyolite islands in this Cambrian sea. This carbonate formation, the Bonneterre, now mostly dolomite Dolomite may refer to:
*Dolomite (mineral), a carbonate mineral
*Dolomite (rock), also known as dolostone, a sedimentary carbonate rock
*Dolomite, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community
*Dolomite, California, United States, an unincor ...
, is exposed around the St. Francis Mountains, but extends in the subsurface throughout the Ozarks and reaches a thickness of . The Bonneterre is overlain by of dolomite, often sandy, silty or cherty, forming the Elvins Group
The Elvins Group is a geologic group in Missouri. It preserves fossils dating back to the Cambrian period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, an ...
and the Potosi and Eminence formations. Withdrawal of the seas resulted in another unconformity during the latest Cambrian and early Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start ...
periods. Hydrothermal
Hydrothermal circulation in its most general sense is the circulation of hot water (Ancient Greek ὕδωρ, ''water'',Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with th ...
mineralizing fluids formed the rich lead ore deposits of the Lead Belt
The Southeast Missouri Lead District, commonly called the Lead Belt, is a lead mining district in the southeastern part of Missouri. Counties in the Lead Belt include Saint Francois, Crawford, Dent, Iron, Madison, Reynolds, and Washingt ...
during this time.
aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characterist ...
s when present in the subsurface. The source of the sands is considered to be the emerging Wisconsin Dome
Wisconsin () is a U.S. state, state in the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 25th-largest state by total area and the List of U.S. states and territories by populatio ...
to the northeast. The Ozark region remained as a subsiding shallow carbonate shelf environment with a significant thickness of cherty dolomites such as the Jefferson City
Jefferson City, informally Jeff City, is the capital of Missouri, United States. It had a population of 43,228 at the 2020 census, ranking as the 15th most populous city in the state. It is also the county seat of Cole County and the principa ...
, Cotter and Powell formations.
Portions of the Ozark Plateau, the Springfield Plateau of southwest Missouri and northern Arkansas, are underlain by Mississippian cherty limestones locally referred to as "Boone chert", consisting of limestone and chert layers. These are eroded and form steep hills, valleys and bluffs.
The Boston Mountains are a high and deeply dissected plateau. The rocks of the region are essentially little disturbed, flat-lying sedimentary layers of Paleozoic age. The highest ridges and peaks are capped by Pennsylvanian sandstone such as the basal Atoka and the "Middle Bloyd". The deeply eroded valleys are cut into Mississippian limestone and below that layer Ordovician dolomite.
During the Pennsylvanian period the Ozark Plateau was uplifted as a result of the Ouachita orogeny
The Ouachita orogeny was a mountain-building event that resulted in the folding and faulting of strata currently exposed in the Ouachita Mountains. The more extensive Ouachita system extends from the current range in Arkansas and Oklahoma south ...
. During the late Paleozoic the deep ocean basin that existed in central and southern Arkansas was lifted when South America collided with North America, creating the folded Ouachita Mountains and uplifting the Ozark plateau to the north.
Ecology and conservation
Formal conservation in the region began when theOzark National Forest
The Ozarks, also known as the Ozark Mountains, Ozark Highlands or Ozark Plateau, is a physiographic region in the U.S. states of Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma and the extreme southeastern corner of Kansas. The Ozarks cover a significant port ...
was created by proclamation of President Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
in 1908 to preserve across five Arkansas counties. Another were added the following year. The initial forest included area as far south as Mount Magazine and as far east as Sylamore, Arkansas, Sylamore.
In 1939, Congress established Mark Twain National Forest at nine sites in Missouri. Wildlife management areas were founded in the 1920s and '30s to restore populations to viable numbers. In the 1930s and 1940s Aldo Leopold, Arthur Carhart and Bob Marshall (wilderness activist), Bob Marshall developed a "wilderness" policy for the Forest Service. Their efforts bore fruit with The Wilderness Act of 1964 which designated wilderness areas "where the earth and its community of life are untrammeled by men, where man himself is a visitor and does not remain", though this included secondary forest, second growth public forests like the Mark Twain National Forest.
Land was also added to Ozark National Forest during this period, with over in total additions. Some land was reclaimed by the government through the Resettlement Administration during the Great Depression in the United States, Great Depression. In 1976, Congress established the Hercules Glades Wilderness, the first of 13 designated wilderness areas in the Ozarks. In 1986, Congress established the Ozark Plateau National Wildlife Refuge in northeast Oklahoma. Protected areas ensure the recovery of endangered and threatened species of animals and plants, including the red wolf, Ozark big-eared bat, Indiana bat, eastern small-footed bat, southeastern bat, southeastern big-eared bat; longnose darter, Ozark cavefish, Ozark cave crayfish, Bowman's cave amphipod, Ozark cave amphipod, bat cave isopod; and Ozark Castanea pumila, chinquapin. It is a habitat of migratory birds and contains geological, archeological, historical, and paleontological resources.
Commercial farms and processing operations are known to raise levels of chemical and biological contaminants in Ozark streams, threatening water supplies, recreational use and endangered native species.
Lakes and streams

 Many of the rivers and streams in the Ozarks have been dammed. Most of the dams in the region were initially built for the dual purpose of flood control and hydropower generation but have also become major economic drivers through recreational use in places such as Branson, Missouri, and Mountain Home, Arkansas.
The United States Army Corps of Engineers, Army Corps of Engineers among others, operates multiple dams in the Ozarks region. Some of the largest lakes created by these dams are on the White River (Arkansas–Missouri), White River. Beginning in 1911 with the construction of Powersite Dam on the White River near Branson, Missouri and the impoundment of Lake Taneycomo the Ozarks rivers have been harnessed for electrical power, recreation, and flood control. After the President Franklin D, Roosevelt signed the Flood Control Act of 1938, six large flood control dams were constructed on the White River and its tributaries..
* Beaver Dam on the White River - Beaver Lake
* Table Rock Dam on the White River - Table Rock Lake
* Bull Shoals Dam on the White River - Bull Shoals Lake
* Norfork Dam on the North Fork River - Norfolk Lake
* Greers Ferry Lake on the Little Red River - Greers Ferry Lake
* Clearwater Dam on the Black River - Clearwater Lake
Multiple smaller lakes have been created by dams in the White River basin from 1911 through 1960. These smaller lakes include Lake Sequoyah,Boss, Stephen K., Heil-Chapdelaine, Vanessa M
Many of the rivers and streams in the Ozarks have been dammed. Most of the dams in the region were initially built for the dual purpose of flood control and hydropower generation but have also become major economic drivers through recreational use in places such as Branson, Missouri, and Mountain Home, Arkansas.
The United States Army Corps of Engineers, Army Corps of Engineers among others, operates multiple dams in the Ozarks region. Some of the largest lakes created by these dams are on the White River (Arkansas–Missouri), White River. Beginning in 1911 with the construction of Powersite Dam on the White River near Branson, Missouri and the impoundment of Lake Taneycomo the Ozarks rivers have been harnessed for electrical power, recreation, and flood control. After the President Franklin D, Roosevelt signed the Flood Control Act of 1938, six large flood control dams were constructed on the White River and its tributaries..
* Beaver Dam on the White River - Beaver Lake
* Table Rock Dam on the White River - Table Rock Lake
* Bull Shoals Dam on the White River - Bull Shoals Lake
* Norfork Dam on the North Fork River - Norfolk Lake
* Greers Ferry Lake on the Little Red River - Greers Ferry Lake
* Clearwater Dam on the Black River - Clearwater Lake
Multiple smaller lakes have been created by dams in the White River basin from 1911 through 1960. These smaller lakes include Lake Sequoyah,Boss, Stephen K., Heil-Chapdelaine, Vanessa M"Mapping Landscape Change: An Historic and Bathymetric Study of Lake Sequoyah, Washington County, Arkansas"
a small recreational fishing lake east of Fayetteville, Arkansas, formed in 1961; Sequoyah is the uppermost impoundment on the White River. Below Sequoyah (northeast of Fayetteville) is Beaver Lake (Arkansas), Beaver Lake, formed in 1960. The White River continues northeasterly into Table Rock Lake (1958) in Missouri, which feeds directly into Lake Taneycomo, where the river zigzags southeasterly into Arkansas forming Bull Shoals Lake along the Arkansas-Missouri line. Completed in 1952, Bull Shoals is the furthest downstream lake on the White River proper. Norfork Dam, Norfork Lake was formed by damming the North Fork River (Missouri–Arkansas), North Fork River, a tributary of the White River, in 1941. Additional large lakes in the Ozarks region include
Lake of the Ozarks
Lake of the Ozarks is a reservoir created by impounding the Osage River in the northern part of the Ozarks in central Missouri. Parts of three smaller tributaries to the Osage are included in the impoundment: the Niangua River, Grandglaize Creek ...
, Pomme de Terre Lake, and Truman Lake in the northern Ozarks. These three lakes were formed by impounding the Osage River and its tributary the Pomme de Terre River (Missouri), Pomme de Terre River in 1931, 1961 and 1979 respectively.
Grand Lake o' the Cherokees, Grand Lake o' the Cherokee in northeast Oklahoma, on the western portion of the Ozark Plateau, was created in 1940 with the damming of the Grand River. Stockton Lake was formed in 1969 by damming the Sac River near the city of Stockton, Missouri, and supplements the water supply of Springfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
in nearby Greene County, Missouri, Greene County. .
The creation of the lakes significantly altered the Ozark landscape and affected traditional Ozark culture through displacement.Watkins, Conor"The Meramec Basin Project: A Look Back 25 Years Later"
''Ozark Mountain Experience''. Article 69 & 70 Combined. 2006."Mountain Home (Baxter County)": ''The Encyclopedia of Arkansas History & Culture''
Campbell, Rex R. Campbell, Mary. Hughes, Colleen
"A Revolution in the Heartland: Changes in Rural Culture, Family and Communities, 1900–2000"
. University of Missouri: Department of Rural Sociology. Columbia, Missouri. 2004. The streams provided water and power to communities, farms and mills concentrated in the valleys prior to impoundment.E. Joan Wilson Miller
Abstract
"The Ozark Culture Region as Revealed by Traditional Materials". ''Annals of the Association of American Geographers'', Volume 58 Issue 1, Pages 51-77. January 3, 1967. Many cemeteries, farm roads, river fords and railways were lost when the lakes came, disrupting rural culture, travel and commerce. Baxter County, Arkansas, alone saw nearly 400 people displaced to make way for the reservoir created by Norfork Dam. The town of Forsyth, Missouri, was relocated in its entirety to a spot from its previous location. Prior to damming, rivers and streams in the White and Osage River basins were of similar character to the current conditions of the Buffalo, Elk River (Oklahoma), Elk, Niangua River, Niangua, Gasconade River, Gasconade, Big Piney River, Big Piney, Current River (Ozarks), Current, Jacks Fork River, Jacks Fork, Eleven Point River, Eleven Point and Meramec River, Meramec rivers. Because of the success of the Army Corps efforts to dam the large rivers in the Ozarks, the Ozarks Society began protests to keep the other rivers in the Ozarks free flowing. The Buffalo National River was created by an Act of Congress in 1972 as the nation's first List of areas in the United States National Park System#National rivers and national wild and scenic rivers, National River, administered by the National Park Service. The designation came after over a decade of battling a proposed Army Corps dam in the media, legislature, and courts to keep the Buffalo River free flowing. The Ozark Society, the main force behind the dam protest, still leads the fight to keep the Buffalo River pristine and protected. Today, the Buffalo River sees approximately 800,000 visitors camping, canoeing, floating, hiking, and tubing annually. In Missouri, the Ozark National Scenic Riverways was established in 1964 along the Current River (Ozarks), Current and Jacks Fork rivers as the first US national park based on a river system. The Eleven Point River is included in the National Wild and Scenic Rivers System established in 1968. These parks and rivers are a major economic driver for some of the least populated counties in Arkansas and Missouri, attracting up to 1.5 million tourists annually. Many other waterways and streams have their headwaters in the Boston Mountains portion of the Ozarks such as the Mulberry River (Arkansas), Mulberry River, the White River, War Eagle Creek, Little Mulberry Creek, Lee Creek, Big Piney Creek, and the Little Red River. To the south, the Arkansas River valley separates the Boston Mountains from the Ouachita Mountains. Missouri Ozark rivers include the Gasconade River, Gasconade, Big Piney River, Big Piney, and Niangua River, Niangua rivers in the north central region. The Meramec River and its tributaries Huzzah Creek (Meramec River tributary), Huzzah Creek and Courtois Creek are found in the northeastern Ozarks. The Black River (Arkansas–Missouri), Black and St. Francis River, St. Francis rivers mark the eastern crescent of the Ozarks. The James River (Missouri), James, Spring River (Arkansas), Spring and North Fork River (Missouri–Arkansas), North Fork rivers are in south-central Missouri. Forming the west central border of the Ozarks from Missouri through Kansas and into Oklahoma are the Spring River (Missouri), Spring River and its tributary, Center Creek. Grand Falls, Missouri's largest natural waterfall, a
chert
Chert () is a hard, fine-grained sedimentary rock composed of microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz, the mineral form of silicon dioxide (SiO2). Chert is characteristically of biological origin, but may also occur inorganically as a prec ...
outcropping, includes bluffs and glades on Shoal Creek south of Joplin. All these river systems see heavy recreational use in season, including the Elk River (Oklahoma), Elk River in southwestern Missouri and its tributary Big Sugar Creek.
Ozark rivers and streams are typically clear water, with baseflows sustained by many seep (hydrology), seeps and spring (hydrology), springs, and flow through forests along limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
and dolomite Dolomite may refer to:
*Dolomite (mineral), a carbonate mineral
*Dolomite (rock), also known as dolostone, a sedimentary carbonate rock
*Dolomite, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community
*Dolomite, California, United States, an unincor ...
bluffs. Gravel bars are common along shallow banks, while deep holes are found along bluffs.MS Panfil, RB Jacobson"Hydraulic Modeling of In-channel Habitats in the Ozark Highlands of Missouri: Assessment of Physical Habitat Sensitivity to Environmental Change"
USGS-Biological Resources Division. Except during periods of heavy rain or snow melt – when water levels rise quite rapidly – their level of difficulty is suitable for most canoeing and tubing. Fish hatcheries are common due to the abundance of springs and waterways. The Neosho National Fish Hatchery was built in 1888; it was the first federal hatchery. The Arkansas Game and Fish Commission, Missouri Department of Conservation and United States Fish and Wildlife Service, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service operate numerous warm and cold water hatcheries and trout parks;
Missouri Fish Hatcheries and Trout Parks private hatcheries such as at Rockbridge, Missouri, Rockbridge are found throughout the region.
Regional economy
Traditional economic activity
The Ozarks contain ore deposits oflead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, iron and barite. Many of these deposits have been depleted by historic mining activities, but much remains and is currently being mined in the Southeast Missouri Lead District, Lead Belt of southeast Missouri. Historically, the lead belt around the Saint Francois Mountains and the Tri-State district lead-zinc mining area around Joplin, Missouri, have been important sources of metals. Mining practices common in the early 20th century left significant abandoned underground mine problems and heavy metals, heavy metal contamination in topsoil and groundwater in the Tri-State district.Lasmanis, RaymondTri-State and Viburnum Trend Districts
''Rocks & Minerals'', November 1, 1997.
, Kansas Geological Survey. Updated May 5, 2005. Much of the area supports beef cattle ranching, and dairy farming is common across the area. Dairy farms are usually cooperative affairs, with small farms selling to a corporate wholesaler, who packages product under a common brand for retail sales. Petroleum exploration and extraction also takes place in the Oklahoma portion of the Ozarks, as well as in the east half of the Boston Mountains in Arkansas. Logging of both softwood and hardwood timber species on both private land and in the United States National Forest, National Forests has long been an important economic activity. The majority of the Ozarks is forested. Oak–hickory forest, Oak-hickory is the predominant type; Juniperus virginiana, eastern junipers are common, with stands of List of Pinus species, pine often seen in the southern range. Less than a quarter of the region has been cleared for pasture and cropland.''Primary Distinguishing Characteristics of Level III Ecoregions of the Continental United States''
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Revised April 2000. Forests that were heavily logged during the early-to-mid-20th century have recovered; much of the remaining timber in the Ozarks is secondary forest, second-growth forest. However, deforestation of Old-growth forest, frontier forest contributed through erosion to increased gravel bars along Ozark waterways in logged areas; stream channels have become wider and shallower, and deepwater fish habitat has been lost.
 The numerous rivers and streams of the region saw hundreds of water-powered timber and grist mills."Index to the old mills of Missouri"
The numerous rivers and streams of the region saw hundreds of water-powered timber and grist mills."Index to the old mills of Missouri"Hosted by rootsweb, this incomplete list includes almost 250 old mills in Missouri alone.
(Rootsweb) Mills were important centers of culture and commerce; dispersed widely throughout the region, mills served local needs, often thriving within a few miles of another facility. Few Ozark mills relied on inefficient water wheels for power; most utilized a dam, Sluice, millrace and water turbine.Suggs, George E., Jr. ''Water Mills of the Missouri Ozarks''. University of Oklahoma Press: Norman, Oklahoma. 1990 During the New Deal, the Civilian Conservation Corps employed hundreds in the construction of nearly 400 fire lookouts throughout the Ozarks at 121 known sites in Arkansas and 257 in Missouri. Of those lookouts, about half remain, and many of them are in use by the United States Forest Service, U.S. Forest Service. A 2007 report by the National Trust for Historic Preservation deemed these fire lookouts and related structures as one of America's 11 Most Endangered Historic Places. In the 1960s, federal activity promoted modernization, especially through better transportation and tourism. The Ozarks Regional Commission sponsored numerous projects.
Current economic activities
Tourism is the growth industry of the Ozarks as evidenced by the growth of the Branson, Missouri, entertainment center celebrating traditional Ozark culture.''Area and Economic Overview: Southwest Missouri Overall Economic Development Program''Southwest Missouri Council of Governments White Paper.Snyder, Robert E. "Shepherd of the Hills Country: Tourism Transforms the Ozarks, 1880s-1930s". ''The Journal of American Culture'', Volume 27 Issue 1, Pages 117-119. The rapidly growing Northwest Arkansas, Northwest Arkansas metropolitan area has also become a tourist hub, drawing nationwide attention for the Crystal Bridges Museum of American Art in Bentonville, Arkansas. Poultry farming and food processing are significant industries throughout the region. The Tyson Foods corporation and ConAgra Foods each operates several hundred poultry farms and processing plants throughout the Ozarks. Schreiber Foods has operations throughout southern Missouri. The Trucking industry in the United States, trucking industry is important to the regional economy, with national carriers based there including J. B. Hunt, ABF Freight System, ABF, and Prime, Inc. Springfield remains an operational hub for the BNSF Railway. Logging and timber industries are also significant in the Ozark economy, with operations ranging from small family-run sawmills to large commercial concerns. Fortune 500 companies such as Wal-Mart, Leggett & Platt, Bass Pro Shops, and O'Reilly Auto Parts are based in the Ozarks. The area is home to several Missouri wine and spirit regions, including the Ozark Highlands AVA, Ozark Highlands and Ozark Mountain AVA, Ozark Mountain American Viticultural Areas, and the Ozark Highlands Spirits, Ozark Highland Spirits Region. There are a number of Craft brewery and microbrewery, microbreweries throughout the region.
Culture
"Ozark" also refers to the distinctive culture, architecture,Andy Ostmeyer"Original Ozarks: Evidence of settlement before 1830 hard to find"
''Joplin Globe''. June 21, 2009. According to the National Register of Historic Places, the Rice-Upshaw House, ca.1826, "is one of the two oldest remaining standing buildings in Arkansas, and a rare surviving example of a building from Arkansas' territorial period"; Wolf House, ca. 1825, overlooks the junction of the Norfork and White rivers; the Craighead-Henry House, ca. 1816, is "one of the oldest known structures in the interior [Missouri] Ozarks." and Ozark English, dialect shared by the people who live on the plateau. Early settlers in Missouri were American pioneer, pioneers who came west from the Appalachia, Southern Appalachians at the beginning of the 19th century,Randolph, Vance. ''Ozark Magic and Folklore''. 367 pages. Courier Dover Publications, 1964. followed in the 1840s and 1850s by Irish Americans, Irish and German Americans, German immigrants. Much of the Ozark population is of English Americans, English, Scots-Irish Americans, Scots-Irish, and German descent, and the Ozark families from which the regional culture derived tend to have lived in the area since the 19th century.Rafferty, Milton D. ''The Ozarks: Land and Life'', University of Arkansas Press, 2nd ed., 2001.
 Early settlers relied on hunting, fishing, trapping, and foraging to supplement their diets and incomes. Today hunting and fishing for recreation are common activities and an important part of the tourist industry. Foraging for Edible mushroom, mushrooms (especially morels) and for American ginseng, ginseng is common and financially supported by established buyers in the area. Other forages include Phytolacca americana, poke, watercress, Diospyros virginiana, persimmons and Asimina triloba, pawpaw; wild berries such as blackberry, black raspberry, raspberry, Morus rubra, red mulberry, Prunus serotina, black cherry, Virginia strawberry, wild strawberry and dewberry; and wild nut (fruit), nuts such as Juglans nigra, black walnut and even acorns.Phillips, Jan. ''Wild Edibles of Missouri''. Missouri Department of Conservation, 2nd edition (1998)
Early settlers relied on hunting, fishing, trapping, and foraging to supplement their diets and incomes. Today hunting and fishing for recreation are common activities and an important part of the tourist industry. Foraging for Edible mushroom, mushrooms (especially morels) and for American ginseng, ginseng is common and financially supported by established buyers in the area. Other forages include Phytolacca americana, poke, watercress, Diospyros virginiana, persimmons and Asimina triloba, pawpaw; wild berries such as blackberry, black raspberry, raspberry, Morus rubra, red mulberry, Prunus serotina, black cherry, Virginia strawberry, wild strawberry and dewberry; and wild nut (fruit), nuts such as Juglans nigra, black walnut and even acorns.Phillips, Jan. ''Wild Edibles of Missouri''. Missouri Department of Conservation, 2nd edition (1998)Cover, Introduction, Acknowledgments and Preface
Chapters
Color Plates
. Edible native plant, native legumes, grass, wild grasses and wildflowers are plentiful, and beekeeping is common.''The Naturalist''
High Plains Films. Doug Hawes-Davis, Director. 32 minutes, Color/B&W, 2001. Print and broadcast media have explored Ozark culture broadly. Books set in the Ozarks include ''Where the Red Fern Grows'', ''The Shepherd of the Hills (novel), The Shepherd of the Hills'', and ''As a Friend''.Forrest Gander, Gander, Forrest.
As a Friend
''. New York City: New Directions Publishers, New Directions Publishing Corporation. 2008. The 1999 film ''Ride with the Devil (film), Ride with the Devil'', based on the book ''Woe to Live On'', depicts conflict in southwest Missouri during the American Civil War, Civil War.Ward L. Schrantz. ''Jasper County, Missouri in the Civil War''. 1923. ''Winter's Bone'', a novel by Daniel Woodrell (author of ''Woe to Live On''), reflects on contemporary methamphetamine culture and its impact on families on the plateau. Released as a feature film in 2010, ''Winter's Bone'' received the Grand Jury Prize at the Sundance Film Festival, as well as other awards. Several early and influential country music, country-music television and radio programs originated from
Springfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
in the 1950s and '60s, including ABC-TV's ''Ozark Jubilee'' and ''The Slim Wilson Show'' on KYTV (TV), KYTV. The Clampett clan of ''The Beverly Hillbillies'' TV show provide a stereotypical depiction of Ozark people. Ozark musicians include Porter Wagoner and Old-time music, old-time fiddler Bob Holt (fiddler), Bob Holt.Henigan, JuliePlay Me Something Quick and Devilish: Bob Holt – Old-Time Square Dance Fiddler
''Musical Traditions'', Article MT021, June 1998. Netflix drama series ''Ozark (TV series), Ozark'' takes place in Osage Beach, Missouri and revolves around the well-to-do Byrde family as their lives are uprooted and they are forced to move from Chicago to the Ozarks after a money laundering scheme goes wrong. The series focuses on the Byrdes' dealings in the Ozarks, as well as their interactions with local Ozark crime families. The series premiered on July 21, 2017. Examples of commercial interpretations of traditional Ozark culture include the two major family theme parks in the region, Silver Dollar City and the now defunct Dogpatch USA, and the resort entertainment complex in
Branson Branson may refer to:
Places
;Canada
* Branson, Toronto
;United States
* Branson, Missouri, a popular tourist destination in the Ozark Mountains
* Branson, Colorado
* Branson City, California
* The Branson School, in Ross, California
* Warrenpoi ...
. Ozark Folkways in Winslow, Arkansas, and Ozark Folk Center State Park in Mountain View, Arkansas, interpret regional culture through musical performance and exhibitions of pioneer skills and crafts.
Traditional Ozark culture includes stories and tunes passed orally between generations through community music parties and other informal gatherings.Aunt Shelle Stormoe"How to Spot a Genuine Ozark Hillbilly"
October 23, 2008. Many of these tunes and tales can be traced to United Kingdom, British originsSmith, Vic
Review of Ozark Folksongs
''Musical Traditions'', January 2001. and to German folklore. Moreover, historian Vance Randolph attributes the formation of much Ozark lore to individual families when "backwoods parents begin by telling outrageous whoppers to their children and end by half believing the wildest of these tales themselves." Randolph collected Ozark folklore and lyrics in volumes such as the national bestseller ''Pissing in the Snow and Other Ozark Folktales'' (University of Illinois Press, 1976), ''Ozark Folksongs'' (University of Missouri Press, 1980), a four-volume anthology of regional songs and ballads collected in the 1920s and 1930s, and ''Ozark Magic and Folklore'' (Courier Dover Publications, 1964). Evidenced by Randolph's extensive field work, many Ozark anecdotes from the oral tradition are often Ribaldry, bawdy, full of wild embellishments on everyday themes.Florer, Faith L
"Book Review. Pissing in the snow and other Ozark folktales".
''Whole Earth Review''. Summer, 1987. "Because of their—ahem—subject matter, the tales contained in this volume could not be published with Randolph's four great collections of Ozark material published in the 1950s, and have until recently been circulating only in manuscript and on elusive microfilm." In 1941–42, commissioned by Alan Lomax of the Archive of Folk Culture, Randolph returned to the Ozarks with a portable recording machine from the Library of Congress and captured over 800 songs, ballads and instrumentals. Selected from among these several hundred recordings, 35 tracks were released on ''Various Artists: Ozark Folksongs'' (Rounder Records) in 2001.
"Old-Time Ozark Square Dancing"
''Bittersweet'', Volume II, No. 1, Fall 1974.Foreman, Diana
''Bittersweet'', Volume V, No. 2, Winter 1977.Edited and photography by Allen Gage
''Bittersweet'', Volume IX, No. 3, Spring 1982. Square dances sprang up wherever people concentrated around mills and timber camps, springs, fords, and in towns small and large. Geographically isolated communities saw their own local dance tunes and variations develop. Of all the traditional musicians in the Ozarks, the fiddler holds a distinct place in both the community and folklore. Community fiddlers were revered for carrying local tunes; regionally, traveling fiddlers brought new tunes and entertainment, even while many viewed their arrival as a threat to morality. In 2007, Gordon McCann, a chronicler of Ozarks folklife and fiddle music for over four decades, donated a collection of audio recordings, fieldnotes and photographs to Missouri State University in Springfield.Gordon McCann pledges collection to Missouri State University: Four decades of material will be housed in Meyer Library
Missouri State University Press Release. September 26, 2007. The collection includes more than 3,000 hours of fiddle music and interviews recorded at jam sessions, music parties, concerts and dances in the Ozarks. Selected audio recordings along with biographical sketches, photographs and tune histories were published in Drew Beisswenger and Gordon McCann's 2008 book/37-track CD set ''Mel Bay Presents Ozarks Fiddle Music: 308 Tunes Featuring 30 Legendary Fiddlers With Selections from 50 Other Great Ozarks Fiddlers''. From 1973 to 1983, the Bittersweet project, which began as an English class at Lebanon High School (Missouri), Lebanon High School in Missouri, collected 476 taped and transcribed interviews, published 482 stories, and took over 50,000 photographs documenting traditional Ozark culture. Population influx since the 1950s, coupled with geographically lying in both the Midwest and Upper South, proximity to the Mississippi embayment, the Osage Plains, Osage and Northern Plains, contributes to changing cultural values in the Ozarks. Theme parks and theatres seen to reflect regional values have little in common with traditional Ozark culture. Community tradition bearers remain active, in decreasing numbers, far afield of commercial offers.
Religion
Ozark religion, like that of Appalachia, was predominantly Baptist and Methodist during periods of early settlement; it tends to the social conservatism, conservative or individualistic, with Episcopal Church (United States), Episcopalians, Assemblies of God, Baptists including Southern Baptist Convention, Southern Baptists, Churches of Christ, Church of Christ, pentecostalism, Pentecostals, and other Protestant denominations present, as well as Roman Catholic Church, Catholics. Religious organizations headquartered in the Ozarks include the Assemblies of God and Baptist Bible Fellowship International inSpringfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
and the General Association of General Baptists in Poplar Bluff, Missouri, Poplar Bluff.
See also
;National Forests of the Ozarks * * ;Ozark National Rivers and Wild Scenic Riverways * * * ;Hiking Trail Systems of the Ozarks * * * * * * * * * ;Ships named Ozark * * *References
Further reading
* Beisswenger, Drew & Gordon McCann,Mel Bay Presents Ozarks Fiddle Music: 308 Tunes Featuring 30 Legendary Fiddlers With Selections from 50 Other Great Ozarks Fiddlers
'' 2008. * Blevins, Brooks, ''A History of the Ozarks: Volume 1: The Old Ozarks.'' Urbana, IL: University of Illinois Press, 2018. * Rafferty, Milton D. ''The Ozarks: Land and Life.'' Fayetteville, AR: University of Arkansas Press, 2001. * Randolph, Vance. ''The Ozarks: An American Survival of Primitive Society.'' 1931. * Rossiter, Phyllis. ''A Living History of the Ozarks'' Gretna, LA: Pelican, 1992. * Phillips, Jared. ''Hipbillies: Deep Revolution in the Arkansas Ozarks'' Fayetteville, AR: University of Arkansas Press, 2019.
Folklore
* Gilmore, Robert Karl. ''Ozark Baptizings, Hangings, and Other Diversions: Theatrical Folkways of Rural Missouri, 1885-1910'' Norman, OK: University of Oklahoma Press, 1984. * Morrow, Lynn, and James Keefe, eds. ''White River Chronicles.'' Fayetteville, AR: University of Arkansas Press, 1994. * McNeil, W. K.''Ozark Country.'' Jackson, MS: University Press of Mississippi, 1995. * Randolph, Vance. ''Ozark Folksongs.'' In four volumes. Columbia, MO: University of Missouri Press, 1980)History
* ''A reminiscent history of the Ozark region: comprising a condensed general history, a brief descriptive history of each county, and numerous biographical sketches of prominent citizens of such counties'' (1894full text
Tourism
* Morrow, Lynn, and Linda Myers-Phinney. ''Shepherd of the Hills Country: Tourism Transforms the Ozarks, 1880s–1930s.'' Fayetteville, AR: University of Arkansas Press, 1999.External links
*Ozark National Scenic Riverways
*
Ozark Plateau National Wildlife Refuge
Ozark Mountains, Encyclopedia of Arkansas History & Culture, The Central Arkansas Library System.
The Intimate Wild: Ozark Highlands Trail, National Geographic, 10/2008.
"Closest to Everlastin'": Ozark Agricultural Biodiversity and Subsistence Traditions, 9/2010.
* {{Authority control Ozarks, Civilian Conservation Corps in Arkansas Civilian Conservation Corps in Missouri Mountain ranges of Arkansas Mountain ranges of Kansas Mountain ranges of Missouri Mountain ranges of Oklahoma Physiographic regions of the United States Plateaus of the United States Regions of Arkansas U.S. Interior Highlands