Ovarian mucinous tumor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mucinous tumors are part of the surface epithelial-stromal tumor group of ovarian neoplasms, and account for approximately 36% of all ovarian 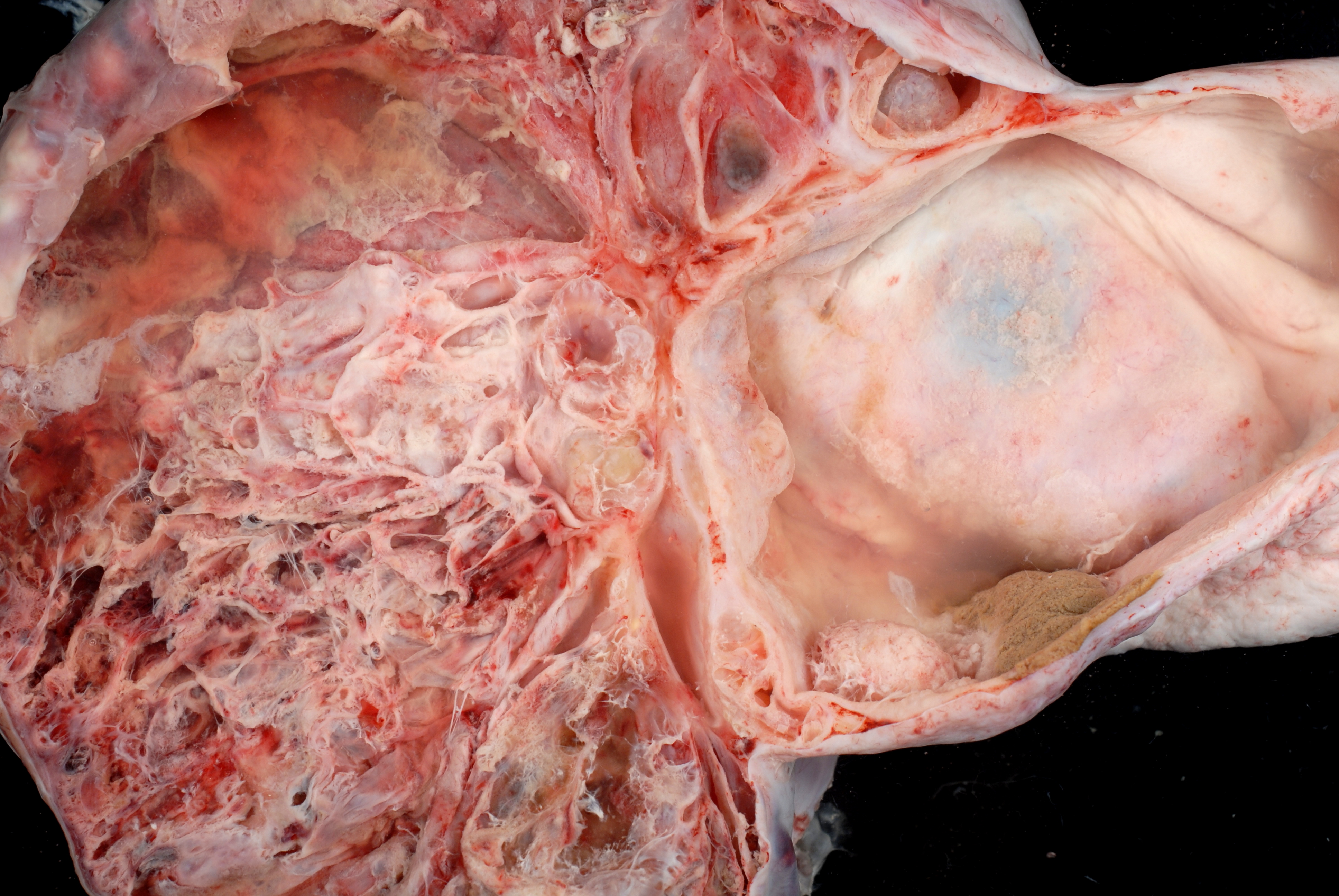 It is well documented that malignancy may be only focally present in mucinous neoplasms of the ovary, so thorough sampling is imperative.
The major distinguishing features of mucinous tumors are that the tumors are filled with a mucus-like material, which gives them their name; this mucus is produced by mucus-secreting goblet cells very similar to the cells lining normal intestine.
These tumors may become very large, some have been weighed as large as 25 kilograms.
Cystadenocarcinomas (malignant tumors) contain a more solid growth pattern with the hallmarks of malignancy: cellular
It is well documented that malignancy may be only focally present in mucinous neoplasms of the ovary, so thorough sampling is imperative.
The major distinguishing features of mucinous tumors are that the tumors are filled with a mucus-like material, which gives them their name; this mucus is produced by mucus-secreting goblet cells very similar to the cells lining normal intestine.
These tumors may become very large, some have been weighed as large as 25 kilograms.
Cystadenocarcinomas (malignant tumors) contain a more solid growth pattern with the hallmarks of malignancy: cellular
tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s.
Approximately 75% are benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malign ...
, 10% are borderline and 15% are malignant
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not s ...
.
Rarely, the tumor is seen bilaterally; approximately 5% of primary mucinous tumors are bilateral.
''Benign'' mucinous tumors are typically multilocular (have several lobes), and the cysts have a smooth lining of epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
that resembles endocervical
The cervical canal is the spindle-shaped, flattened canal of the cervix, the neck of the uterus.
Anatomy
The cervical canal communicates with the uterine cavity via the internal orifice of the uterus (or internal os) and with the vagina via the ...
epithelial cell
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellula ...
s with small numbers of gastrointestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and ...
-type epithelial cells.
''Borderline'' and ''malignant'' mucinous tumors often have papillae and solid areas.
There may also be hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vag ...
and necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated dige ...
.
 It is well documented that malignancy may be only focally present in mucinous neoplasms of the ovary, so thorough sampling is imperative.
The major distinguishing features of mucinous tumors are that the tumors are filled with a mucus-like material, which gives them their name; this mucus is produced by mucus-secreting goblet cells very similar to the cells lining normal intestine.
These tumors may become very large, some have been weighed as large as 25 kilograms.
Cystadenocarcinomas (malignant tumors) contain a more solid growth pattern with the hallmarks of malignancy: cellular
It is well documented that malignancy may be only focally present in mucinous neoplasms of the ovary, so thorough sampling is imperative.
The major distinguishing features of mucinous tumors are that the tumors are filled with a mucus-like material, which gives them their name; this mucus is produced by mucus-secreting goblet cells very similar to the cells lining normal intestine.
These tumors may become very large, some have been weighed as large as 25 kilograms.
Cystadenocarcinomas (malignant tumors) contain a more solid growth pattern with the hallmarks of malignancy: cellular atypia
Atypia (from Greek, ''a'' + ''typos'', without type; a condition of being irregular or nonstandard) is a histopathologic term for a structural abnormality in a cell, i.e. it is used to describe atypical cells.
Atypia can be caused by an infection ...
and stratification, loss of the normal architecture of the tissue, and necrosis. The appearance can look similar to colonic cancer.
Clear stromal invasion is used to differentiate borderline tumors from malignant tumors.
Pseudomyxoma peritonei
Pseudomyxoma peritonei (PMP) is a clinical condition caused by cancerous cells (mucinous adenocarcinoma) that produce abundant mucin or gelatinous ascites. The tumors cause fibrosis of tissues and impede digestion or organ function, and if left unt ...
may present as a result of an ovarian mucinous tumor, however this is a rare cause of this condition, which is a rare condition. A more common cause of pseudomyxoma peritonei is a mucin-producing tumor of the appendix.
Since mucinous tumors arising from the ovary usually only involve one ovary, the presence of involvement in both ovaries with a mucinous tumor suggests that the tumor may have arisen in another location, and further study is warranted.
The risk of mucinous tumors is significantly associated with smoking: relative risk for current smokers 2.22 (2.22 times the risk for non-smokers) and 2.02 for past smokers. Risk is also associated with smoking duration: relative risk per 20 years was 1.44. See article by Tworoger SS in Cancer March 1, 2008 using data from the Nurses Health Study.
Prognosis
10-year survival rates for mucinous tumors is excellent in the absence of invasion. In the case of borderline tumors confined to the ovary and malignant tumors without invasion, the survival rates are 90% or greater. In invasive mucinous cystadenocarcinomas, the survival is approximately 30%. Survival in metastasis is between 12 and 30 months.References