Outline Of Bipolar Disorder on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The following
 Bipolar disorder can be described as all of the following:
* Disorder –
**
Bipolar disorder can be described as all of the following:
* Disorder –
**
 *
*
Bipolar UK
Bipolar Disorder overview
from the U.S. National Institute of Mental Health website
NICE Bipolar Disorder clinical guidelines
from the U.K. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence website *
outline
Outline or outlining may refer to:
* Outline (list), a document summary, in hierarchical list format
* Code folding, a method of hiding or collapsing code or text to see content in outline form
* Outline drawing, a sketch depicting the outer edge ...
is provided as an overview of and topical guide to bipolar disorder:
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with ...
– mental disorder
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness or psychiatric disorder, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. Such features may be persistent, relapsing and remitti ...
with periods of depression and periods of elevated mood. The elevated mood is significant and is known as mania
Mania, also known as manic syndrome, is a mental and behavioral disorder defined as a state of abnormally elevated arousal, affect, and energy level, or "a state of heightened overall activation with enhanced affective expression together wit ...
or hypomania
Hypomania (literally "under mania" or "less than mania") is a mental and behavioural disorder, characterised essentially by an apparently non-contextual elevation of mood (euphoria) that contributes to persistently disinhibited behaviour.
The ...
, depending on its severity, or whether symptoms of psychosis
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavior ...
are present. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy, or irritable. Individuals often make poorly thought out decisions with little regard to the consequences. The need for sleep is usually reduced during manic phases. During periods of depression, there may be crying, a negative outlook on life, and poor eye contact with others. The risk of suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and s ...
among those with the illness is high at greater than 6 percent over 20 years, while self-harm
Self-harm is intentional behavior that is considered harmful to oneself. This is most commonly regarded as direct injury of one's own skin tissues usually without a suicidal intention. Other terms such as cutting, self-injury and self-mutilatio ...
occurs in 30–40 percent. Other mental health issues such as anxiety disorder
Anxiety disorders are a cluster of mental disorders characterized by significant and uncontrollable feelings of anxiety and fear such that a person's social, occupational, and personal function are significantly impaired. Anxiety may cause physi ...
s and substance use disorder
Substance use disorder (SUD) is the persistent use of drugs (including alcohol) despite substantial harm and adverse consequences as a result of their use. Substance use disorders are characterized by an array of mental/emotional, physical, and ...
are commonly associated. Also known as manic depression.
What type of thing is bipolar disorder?
 Bipolar disorder can be described as all of the following:
* Disorder –
**
Bipolar disorder can be described as all of the following:
* Disorder –
** Mental disorder
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness or psychiatric disorder, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. Such features may be persistent, relapsing and remitti ...
– functional abnormality or disturbance characterized by a behavioral or mental pattern that may cause suffering or a poor ability to function in life. Such features may be persistent, relapsing and remitting, or occur as a single episode.
Bipolar spectrum
Bipolar spectrum
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with ...
–
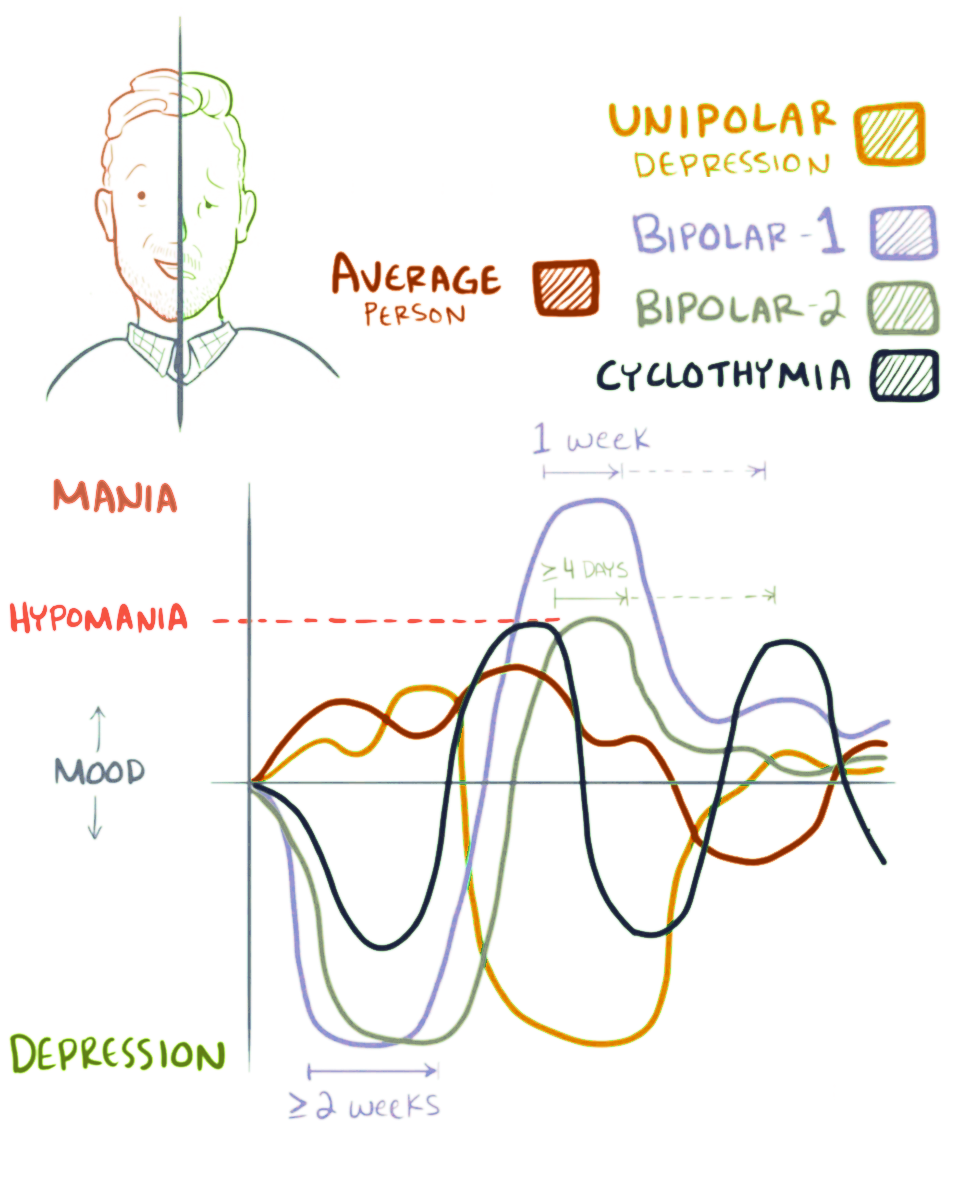
* Bipolar I – bipolar disorder with at least one manic episode (with or without psychosis), possibly with hypomanic and/or depressive episodes as well
* Bipolar II – bipolar disorder with at least one depressive and at least one hypomanic episode, without any full mania
* Cyclothymia
Cyclothymia ( ), also known as cyclothymic disorder, psychothemia/psychothymia, bipolar III, affective personality disorder and cyclothymic personality disorder, is a mental and behavioural disorder that involves numerous periods of symptoms of ...
– "mild" bipolar disorder, with symptoms of hypomania and depression not severe enough to be classified as bipolar I or II
* Dysthymia
Dysthymia ( ), also known as persistent depressive disorder (PDD), is a mental and behavioral disorder, specifically a disorder primarily of mood, consisting of similar cognitive and physical problems as major depressive disorder, but with lon ...
– akin to depression, with symptoms that are long-lasting but less severe
* Major depressive disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Introdu ...
– a mood disorder involving low mood, low energy, poor self-esteem, lack of interest in enjoyable activities, and/or aches and pains
* Schizoaffective disorder – mood swings combined with psychosis
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavior ...
; has subtypes bipolar type and depressive type
* Mania
Mania, also known as manic syndrome, is a mental and behavioral disorder defined as a state of abnormally elevated arousal, affect, and energy level, or "a state of heightened overall activation with enhanced affective expression together wit ...
– a state of hyperactivity, heightened mood (euphoric or irritable), low sleep, pressured speech, grandiosity, and/or racing thoughts; may include psychotic features like delusion
A delusion is a false fixed belief that is not amenable to change in light of conflicting evidence. As a pathology, it is distinct from a belief based on false or incomplete information, confabulation, dogma, illusion, hallucination, or some o ...
s or hallucinations
A hallucination is a perception in the absence of an external stimulus that has the qualities of a real perception. Hallucinations are vivid, substantial, and are perceived to be located in external objective space. Hallucination is a combinatio ...
* Mixed affective state – a state with traits of both mania and depression (e.g. irritability, low mood, suicidality, and racing thoughts at the same time)
* Hypomania
Hypomania (literally "under mania" or "less than mania") is a mental and behavioural disorder, characterised essentially by an apparently non-contextual elevation of mood (euphoria) that contributes to persistently disinhibited behaviour.
The ...
– a state of high mood similar to that of mania but less severe
* Major depressive episode – an episode with signs of major depressive disorder
Symptoms of bipolar disorder
*Anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
– a state of increased stress and worry
* Emotional dysregulation – difficulty regulating one's mood, resulting in mood swings
* Sleep disorder – disordered sleeping habits
Signs typical of mania
*Delusion
A delusion is a false fixed belief that is not amenable to change in light of conflicting evidence. As a pathology, it is distinct from a belief based on false or incomplete information, confabulation, dogma, illusion, hallucination, or some o ...
– fixed belief that cannot be changed despite reason or evidence, not explained by common cultural beliefs
* Hallucination – perceiving something that is not actually present
* Insomnia
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder in which people have trouble sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low energy, ...
– difficulty falling and/or staying asleep
* Pressured speech
Pressure of speech or pressured speech is a tendency to speak rapidly and frenziedly. Pressured speech is motivated by an urgency that may not be apparent to the listener. The speech produced is difficult to interpret.
Such speech may be too fas ...
– rapid, erratic, and/or frenzied speech that can be difficult for others to understand and interrupt
* Psychosis
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavior ...
– inability to distinguish between reality and fantasy
* Racing thoughts
Racing thoughts refers to the rapid thought patterns that often occur in manic, hypomanic, or mixed episodes. While racing thoughts are most commonly described in people with bipolar disorder and sleep apnea, they are also common with anxiety diso ...
– rapid thinking, sometimes experienced as distracting or distressing
Signs typical of depression
*Anhedonia
Anhedonia is a diverse array of deficits in hedonic function, including reduced motivation or ability to experience pleasure. While earlier definitions emphasized the inability to experience pleasure, anhedonia is currently used by researchers t ...
– reduced ability to experience pleasure
* Dysphoria – a state of profound unhappiness or discomfort
* Hypersomnia
Hypersomnia is a neurological disorder of excessive time spent sleeping or excessive sleepiness. It can have many possible causes (such as seasonal affective disorder) and can cause distress and problems with functioning. In the fifth edition ...
– excessive sleeping and/or sleepiness
* Self harm – causing intentional pain or injury to the body, often as self-punishment or emotional release
* Suicidal ideation
Suicidal ideation, or suicidal thoughts, means having thoughts, ideas, or ruminations about the possibility of ending one's own life.World Health Organization, ''ICD-11 for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics'', ver. 09/2020MB26.A Suicidal ideatio ...
– considering committing suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and s ...
Treatment of bipolar disorder
 *
* Treatment of bipolar disorder The emphasis of the treatment of bipolar disorder is on effective management of the long-term course of the illness, which can involve treatment of emergent symptoms. Treatment methods include pharmacological and psychological techniques.
Bipolar D ...
–
* Treatment of bipolar disorder – Mood stabilizers – medication that reduces mood swings and allows the user to experience a more typical range of moods
* Anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of b ...
s –
* Carbamazepine –
* Gabapentin –
* Lamotrigine
Lamotrigine, sold under the brand name Lamictal among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy and stabilize mood in bipolar disorder. For epilepsy, this includes focal seizures, tonic-clonic seizures, and seizures in Lennox-Gastaut synd ...
(Lamictal) –
* Oxcarbazepine –
* Topiramate
Topiramate, sold under the brand name Topamax among others, is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor medication used to treat epilepsy and prevent migraines. It has also been used in alcohol dependence. For epilepsy this includes treatment for gener ...
–
* Valproic acid –
* Sodium valproate
Valproate (VPA) and its valproic acid, sodium valproate, and valproate semisodium forms are medications primarily used to treat epilepsy and bipolar disorder and prevent migraine headaches. They are useful for the prevention of seizures in those ...
–
* Valproate semisodium
Valproate (VPA) and its valproic acid, sodium valproate, and valproate semisodium forms are medications primarily used to treat epilepsy and bipolar disorder and prevent migraine headaches. They are useful for the prevention of seizures in thos ...
–
* Lithium pharmacology –
* Lithium carbonate
Lithium carbonate is an inorganic compound, the lithium salt (chemistry), salt of carbonate with the chemical formula, formula . This white Salt (chemistry), salt is widely used in the processing of metal oxides. It is listed on the World Health O ...
–
* Lithium citrate
Lithium citrate (Li3C6H5O7) is a chemical compound of lithium and citrate that is used as a mood stabilizer in psychiatric treatment of manic states and bipolar disorder. There is extensive pharmacology of lithium, the active component of this s ...
–
* Lithium sulfate
Lithium sulfate is a white inorganic salt with the formula Li2 S O4. It is the lithium salt of sulfuric acid.
Properties
Physical properties
Lithium sulfate is soluble in water, though it does not follow the usual trend of increasing solubilit ...
–
* Antipsychotic
Antipsychotics, also known as neuroleptics, are a class of Psychiatric medication, psychotropic medication primarily used to manage psychosis (including delusions, hallucinations, paranoia or disordered thought), principally in schizophrenia but ...
s –
* Treatment of bipolar disorder – Anxiety –
* Alprazolam (Solanax and Xanax) –
* List of benzodiazepines
The below tables contain a sample list of benzodiazepines and benzodiazepine analogs that are commonly prescribed, with their basic pharmacological characteristics, such as half-life and equivalent doses to other benzodiazepines, also listed, al ...
–
Non-pharmaceutical treatment of bipolar disorder
*Clinical psychology
Clinical psychology is an integration of social science, theory, and clinical knowledge for the purpose of understanding, preventing, and relieving psychologically based distress or dysfunction and to promote subjective well-being and persona ...
–
* Electroconvulsive therapy –
* Involuntary commitment
Involuntary commitment, civil commitment, or involuntary hospitalization/hospitalisation is a legal process through which an individual who is deemed by a qualified agent to have symptoms of severe mental disorder is detained in a psychiatric hos ...
–
* Light therapy –
* Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy (also psychological therapy, talk therapy, or talking therapy) is the use of psychological methods, particularly when based on regular personal interaction, to help a person change behavior, increase happiness, and overcome pro ...
–
* Transcranial magnetic stimulation –
History of bipolar disorder
History of bipolar disorder – * Emil Kraepelin – * Karl Leonhard – * John Cade – *Mogens Schou
Mogens Schou (24 November 1918 – 29 September 2005) was a Denmark, Danish psychiatrist whose research into Lithium pharmacology, lithium led to its utilization as a treatment for bipolar disorder.
Early years
Schou was born in Copenhagen ...
–
* Frederick K. Goodwin
Frederick King Goodwin (April 21, 1936 – September 10, 2020) was an American psychiatrist and Clinical Professor of Psychiatry at the George Washington University Medical Center, where he was also director of the Center on Neuroscience, Medica ...
–
* Kay Redfield Jamison –
Organisations
*International Society for Bipolar Disorders
The International Society for Bipolar Disorders (ISBD) is a nonprofit organization based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, where it was founded June 17, 1999. The society focuses on research and education in bipolar disorders.
The society has a members ...
–
* Icarus Project
The Icarus Project (2002-2020) was a network of peer-support groups and media projects with the stated aim of changing the language and culture of what gets called mental health and mental illness. The name is derived from Icarus, a hero in Greek ...
–Bipolar UK
See also
*Affective spectrum
The affective spectrum is a spectrum of affective disorders (mood disorders). It is a grouping of related psychiatric and medical disorders which may accompany bipolar, unipolar, and schizoaffective disorders at statistically higher rates than ...
– spectrum of mood disorders, including disorders that impact other areas in addition to mood (e.g. ADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by excessive amounts of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that are pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and otherwise age-inapp ...
and migraine
Migraine (, ) is a common neurological disorder characterized by recurrent headaches. Typically, the associated headache affects one side of the head, is pulsating in nature, may be moderate to severe in intensity, and could last from a few hou ...
s)
* List of people with bipolar disorder –
* Bipolar disorder in children
Bipolar disorder in children, or pediatric bipolar disorder (PBD), is a controversial mental disorder in children and adolescents that is mainly diagnosed in the United States, and is hypothesized to be like bipolar disorder (BD) in adults, thus i ...
– pediatric bipolar disorder, which sometimes involves more rapid shifting and mixed states
References
External links
{{sisterlinks, Bipolar disorderBipolar Disorder overview
from the U.S. National Institute of Mental Health website
NICE Bipolar Disorder clinical guidelines
from the U.K. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence website *
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with ...
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with ...