Oskar Backlund on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
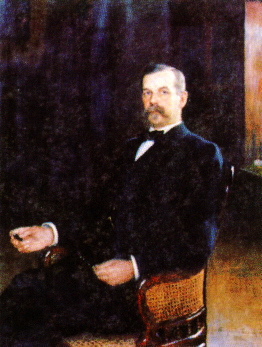 Johan Oskar Backlund (28 April 1846 – 29 August 1916) was a
Johan Oskar Backlund (28 April 1846 – 29 August 1916) was a
Bruce Medal page
in
I:56 (Svenskt biografiskt handlexikon)
in Project Runeberg (in Swedish)
in Project Runeberg (in Swedish)
(in German)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Backlund, Oskar 1846 births 1916 deaths 19th-century Swedish astronomers Uppsala University alumni Members of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences Foreign Members of the Royal Society Foreign associates of the National Academy of Sciences Recipients of the Bruce Medal Recipients of the Gold Medal of the Royal Astronomical Society Fellows of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences Full members of the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences Academic staff of the University of Tartu Recipients of the Lalande Prize Privy Councillor (Russian Empire) 20th-century Swedish astronomers
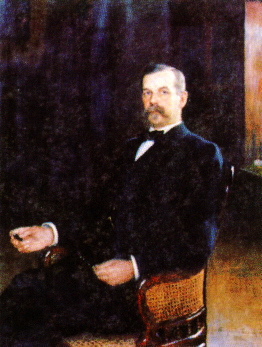 Johan Oskar Backlund (28 April 1846 – 29 August 1916) was a
Johan Oskar Backlund (28 April 1846 – 29 August 1916) was a Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
-Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
n astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, moons, comets and galaxies – in either ...
. His name is sometimes given as Jöns Oskar Backlund, however even contemporary Swedish sources give "Johan". In Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
, where he spent his entire career, he is known as Oskar Andreevich Baklund (Оскар Андреевич Баклунд). Russian sources sometimes give his dates of birth and death as 16 April 1846 and 16 August 1916, since Russia still used the Julian calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandr ...
at the time.
Life
He was born in Länghem, inVästergötland
Västergötland (), also known as West Gothland or the Latinized version Westrogothia in older literature, is one of the 25 traditional non-administrative provinces of Sweden (''landskap'' in Swedish), situated in the southwest of Sweden.
Väs ...
, Sweden and graduated from Uppsala University
Uppsala University ( sv, Uppsala universitet) is a public research university in Uppsala, Sweden. Founded in 1477, it is the oldest university in Sweden and the Nordic countries still in operation.
The university rose to significance during ...
in 1872. After getting his doctorate in 1875, he emigrated to Russia in 1876. He worked at Dorpat Observatory
The Tartu Observatory ( et, Tartu Observatoorium) is the largest astronomical observatory in Estonia. On 1 January 2018, Tartu Observatory was joined again to the University of Tartu, and the observatory is now an institute of the university. I ...
, in today's Tartu, Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
, and then in 1879 worked at Pulkovo Observatory
The Pulkovo Astronomical Observatory (russian: Пулковская астрономическая обсерватория, Pulkovskaya astronomicheskaya observatoriya), officially named the Central Astronomical Observatory of the Russian Academ ...
, becoming director of the observatory from 1895 until his death.
He specialized in celestial mechanics
Celestial mechanics is the branch of astronomy that deals with the motions of objects in outer space. Historically, celestial mechanics applies principles of physics (classical mechanics) to astronomical objects, such as stars and planets, to ...
, and notably worked on calculating the orbit of Comet Encke
Comet Encke , or Encke's Comet (official designation: 2P/Encke), is a periodic comet that completes an orbit of the Sun once every 3.3 years. (This is the shortest period of a reasonably bright comet; the faint main-belt comet 311P/PanSTARRS ha ...
, taking into account the perturbations of various planets. He used observations of Comet Encke to try estimate the mass of Mercury. Russian sources sometimes referred to the comet as Comet Encke-Backlund. He also carried out geodesic studies in Spitzbergen from 1898 to 1900. He became a member of the Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
Academy of Sciences in 1883, member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences in 1897 and Fellow of the Royal Society
Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the judges of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural knowledge, including mathemat ...
in 1911. He was elected a Foreign Honorary Member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (abbreviation: AAA&S) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, a ...
in 1914.
Family
He was married to Ulrika Catharina Widebeck. Their daughter Elsa Celsing became a well-known artist, and their son Helge Gotrik Backlund (3 September 1878 – 1958) was a geologist and explorer.Honors
Awards *Gold Medal of the Royal Astronomical Society
The Gold Medal of the Royal Astronomical Society is the highest award given by the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS). The RAS Council have "complete freedom as to the grounds on which it is awarded" and it can be awarded for any reason. Past awar ...
(1909)
*Bruce Medal
The Catherine Wolfe Bruce Gold Medal is awarded every year by the Astronomical Society of the Pacific for outstanding lifetime contributions to astronomy. It is named after Catherine Wolfe Bruce, an American patroness of astronomy, and was fi ...
(1914)
Named after him
*The crater Backlund on the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
* Asteroid 856 Backlunda
* Backlundtoppen, a mountain in Olav V Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard.
References
External links
Bruce Medal page
in
Project Runeberg
Project Runeberg ( sv, Projekt Runeberg) is a digital cultural archive initiative that publishes free electronic versions of books significant to the culture and history of the Nordic countries. Patterned after Project Gutenberg, it was founded ...
(in Swedish)I:56 (Svenskt biografiskt handlexikon)
in Project Runeberg (in Swedish)
in Project Runeberg (in Swedish)
Obituaries
(in German)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Backlund, Oskar 1846 births 1916 deaths 19th-century Swedish astronomers Uppsala University alumni Members of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences Foreign Members of the Royal Society Foreign associates of the National Academy of Sciences Recipients of the Bruce Medal Recipients of the Gold Medal of the Royal Astronomical Society Fellows of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences Full members of the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences Academic staff of the University of Tartu Recipients of the Lalande Prize Privy Councillor (Russian Empire) 20th-century Swedish astronomers