Organohalides on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Halocarbon compounds are chemicals in which one or more carbon atoms are linked by
 Halocarbons are typically classified in the same ways as the similarly structured organic compounds that have hydrogen atoms occupying the
Halocarbons are typically classified in the same ways as the similarly structured organic compounds that have hydrogen atoms occupying the
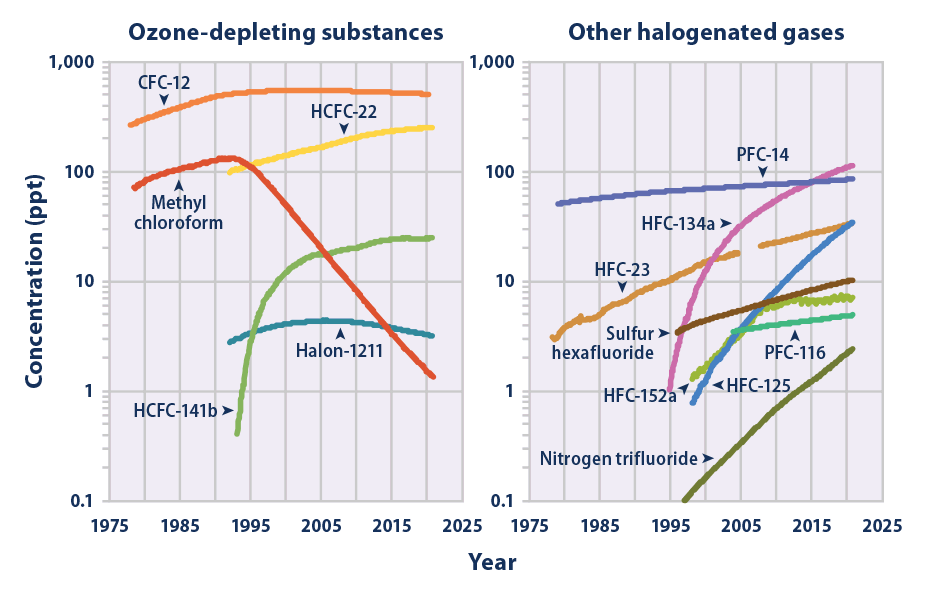 In 1962 a book by U.S. biologist Rachel Carson started a storm of concerns about environmental pollution, first focused on DDT and other
In 1962 a book by U.S. biologist Rachel Carson started a storm of concerns about environmental pollution, first focused on DDT and other
Chemical Industry Archives, Anniston Case
, by Environmental Working Group, Washington, DC, 2002 * * * * *
covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms ...
s with one or more halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is ...
atoms (fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reacti ...
, chlorine, bromine or iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a vi ...
– ) resulting in the formation of organofluorine compound
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of the organofluorines, organic compounds that contain the carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from oil and water repellents to pharmaceuticals, refri ...
s, organochlorine compounds, organobromine compounds, and organoiodine compounds. Chlorine halocarbons are the most common and are called organochlorides.
Many synthetic organic compounds such as plastic polymers, and a few natural ones, contain halogen atoms; they are known as ''halogenated'' compounds or ''organohalogens''. Organochlorides are the most common industrially used organohalides, although the other organohalides are used commonly in organic synthesis. Except for extremely rare cases, organohalides are not produced biologically, but many pharmaceuticals are organohalides. Notably, many pharmaceuticals such as Prozac have trifluoromethyl groups.
For information on inorganic halide chemistry, see halide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fluor ...
.
Chemical families
 Halocarbons are typically classified in the same ways as the similarly structured organic compounds that have hydrogen atoms occupying the
Halocarbons are typically classified in the same ways as the similarly structured organic compounds that have hydrogen atoms occupying the molecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
sites of the halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is ...
atoms in halocarbons. Among the chemical families are:M. Rossberg et al. “Chlorinated Hydrocarbons” in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2006, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.
*haloalkane
The haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are alkanes containing one or more halogen substituents. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely us ...
s—compounds with carbon atoms linked by single bonds
* haloalkenes—compounds with one or more double bonds between carbon atoms
* haloaromatics—compounds with carbons linked in one or more aromatic rings with a delocalised donut shaped pi cloud.
The halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is ...
atoms in halocarbon molecules are often called "substituent
A substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces (one or more) atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule. (In organic chemistry and biochemistry, the terms ''substituent'' and ''functional group'', as well as ''side ...
s," as though those atoms had been substituted for hydrogen atoms. However halocarbons are prepared in many ways that do not involve direct substitution of halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is ...
s for hydrogens.
History and context
A few halocarbons are produced in massive amounts by microorganisms. For example, several million tons ofmethyl bromide
Bromomethane, commonly known as methyl bromide, is an organobromine compound with formula C H3 Br. This colorless, odorless, nonflammable gas is produced both industrially and biologically. It has a tetrahedral shape and it is a recognized ozon ...
are estimated to be produced by marine organisms annually. Most of the halocarbons encountered in everyday life – solvents, medicines, plastics – are man-made. The first synthesis of halocarbons was achieved in the early 1800s. Production began accelerating when their useful properties as solvents and anesthetics were discovered. Development of plastics and synthetic elastomers has led to greatly expanded scale of production. A substantial percentage of drugs are halocarbons.
Natural halocarbons
A large amount of the naturally occurring halocarbons are created by wood fire,dioxine
Polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs), or simply dioxins, are a group of long-lived polyhalogenated organic compounds that are primarily anthropogenic, and contribute toxic, persistent organic pollution in the environment.
They are commonly ...
for example, or volcanic activities. A second large source are marine algae which produce several chlorinated methane and ethane containing compounds. There are several thousand complex halocarbons known, produced mainly by marine species. Although chlorine compounds are the majority of the discovered compounds, bromides, iodides and fluorides have also been found. The tyrian purple, which is a dibromoindigo, is representative of the bromides, while the thyroxine secreted from the thyroid gland
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobe (anatomy), lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of Connective tissue, tissue cal ...
, is an iodide, and the highly toxic fluoroacetate is one of the rare natural organofluorides. These three representatives, thyroxine from humans, tyrian purple from snails and fluoroacetate from plants, also show that unrelated species use halocarbons for several purposes....
Organoiodine compounds, including biological derivatives
Organoiodine compounds, called organic iodides, are similar in structure to organochlorine and organobromine compounds, but the C-I bond is weaker. Many organic iodides are known, but few are of major industrial importance. Iodide compounds are mainly produced as nutritional supplements. Thethyroxin
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4
rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone
rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone
rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus
rect 66 216 386 25 ...
hormones are essential for human health, hence the usefulness of iodized salt.
Six mg of iodide a day can be used to treat patients with hyperthyroidism due to its ability to inhibit the organification process in thyroid hormone synthesis, the so-called Wolff–Chaikoff effect
The Wolff–Chaikoff effect is a presumed reduction in thyroid hormone levels caused by ingestion of a large amount of iodine.
It was discovered by Drs. Jan Wolff and Israel Lyon Chaikoff at the University of California, Berkeley: in 1948, th ...
. Prior to 1940, iodides were the predominant antithyroid agents. In large doses, iodides inhibit proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called protease ...
of thyroglobulin, which permits TH to be synthesized and stored in colloid
A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others extend ...
, but not released into the bloodstream. This mechanism is referred to as Plummer effect
The Plummer effect is one of several physiological feedforward mechanisms taking place in follicular cells of the healthy thyroid gland and preventing the development of thyrotoxicosis in situations of extremely high supply with iodine.
Hist ...
.
This treatment is seldom used today as a stand-alone therapy despite the rapid improvement of patients immediately following administration. The major disadvantage of iodide treatment lies in the fact that excessive stores of TH accumulate, slowing the onset of action of thioamides (TH synthesis blockers). In addition, the functionality of iodides fades after the initial treatment period. An "escape from block" is also a concern, as extra stored TH may spike following discontinuation of treatment.
Uses
The first halocarbon commercially used was Tyrian purple, a natural organobromide of the '' Murex brandaris'' marine snail. Common uses for halocarbons have been as solvents,pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. This includes herbicide, insecticide, nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, microbicide, fungicide, and lampri ...
s, refrigerant
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the heat pump and refrigeration cycle, refrigeration cycle of air conditioning systems and heat pumps where in most cases they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Ref ...
s, fire-resistant oils, ingredients of elastomer
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of ''elastic p ...
s, adhesive
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
The use of adhesives offers certain advant ...
s and sealants, electrically insulating coatings, plasticizers, and plastics. Many halocarbons have specialized uses in industry. One halocarbon, sucralose
Sucralose is an artificial sweetener and sugar substitute. The majority of ingested sucralose is not broken down by the body, so it is noncaloric. In the European Union, it is also known under the E number E955. It is produced by chlorination of ...
, is a sweetener.
Before they became strictly regulated, the general public often encountered haloalkane
The haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are alkanes containing one or more halogen substituents. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely us ...
s as paint and cleaning solvents such as trichloroethane (1,1,1-trichloroethane) and carbon tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride, also known by many other names (such as tetrachloromethane, also IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry, recognised by the IUPAC, carbon tet in the cleaning industry, Halon-104 in firefighting, and Refrigerant-10 in HVAC ...
(tetrachloromethane), pesticides like 1,2-dibromoethane
1,2-Dibromoethane, also known as ethylene dibromide (EDB), is an organobromine compound with the chemical formula . Although trace amounts occur naturally in the ocean, where it is formed probably by algae and kelp, it is mainly synthetic. It is a ...
(EDB, ethylene dibromide), and refrigerants like Freon-22 (duPont
DuPont de Nemours, Inc., commonly shortened to DuPont, is an American multinational chemical company first formed in 1802 by French-American chemist and industrialist Éleuthère Irénée du Pont de Nemours. The company played a major role in ...
trademark for chlorodifluoromethane). Some haloalkanes are still widely used for industrial cleaning, such as methylene chloride (dichloromethane), and as refrigerants, such as R-134a (1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane
1,1,1,2-Tetrafluoroethane (also known as norflurane (INN), R-134a, Freon 134a, Forane 134a, Genetron 134a, Green Gas, Florasol 134a, Suva 134a, or HFC-134a) is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) and haloalkane refrigerant with thermodynamic properties s ...
).
Haloalkenes have also been used as solvents, including perchloroethylene (Perc, tetrachloroethene), widespread in dry cleaning, and trichloroethylene (TCE, 1,1,2-trichloroethene). Other haloalkenes have been chemical building blocks of plastics such as polyvinyl chloride ("vinyl" or PVC, polymerized chloroethene) and Teflon (duPont
DuPont de Nemours, Inc., commonly shortened to DuPont, is an American multinational chemical company first formed in 1802 by French-American chemist and industrialist Éleuthère Irénée du Pont de Nemours. The company played a major role in ...
trademark for polymerized tetrafluoroethene, PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene that has numerous applications. It is one of the best-known and widely applied PFAS. The commonly known brand name of PTFE-based composition is Teflon by Chemour ...
).
Haloaromatics include the former Aroclor
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are highly carcinogenic chemical compounds, formerly used in industrial and consumer products, whose production was banned in the United States by the Toxic Substances Control Act in 1979 and internationally by t ...
s (Monsanto Company
The Monsanto Company () was an American agrochemical and agricultural biotechnology corporation founded in 1901 and headquartered in Creve Coeur, Missouri. Monsanto's best known product is Roundup (herbicide), Roundup, a glyphosate-based herbic ...
trademark for polychlorinated biphenyls, PCBs), once widely used in power transformers and capacitors and in building caulk, the former Halowax
Halowax is a New York-based company that was later owned by Union Carbide. It was subsequently taken over by Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania-based Koppers, which was later renamed Beazer East. It is the largest US producer of polychlorinated naphthalenes ...
es ( Union Carbide trademark for polychlorinated naphthalenes, PCNs), once used for electrical insulation, and the chlorobenzenes and their derivatives, used for disinfectant
A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than st ...
s, pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. This includes herbicide, insecticide, nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, microbicide, fungicide, and lampri ...
s such as dichloro-diphenyl-trichloroethane ( DDT, 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethane), herbicides
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weedkillers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page fo ...
such as 2,4-D (2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid), askarel
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are highly carcinogenic chemical compounds, formerly used in industrial and consumer products, whose production was banned in the United States by the Toxic Substances Control Act of 1976, Toxic Substances Contro ...
dielectrics (mixed with PCBs, no longer used in most countries), and chemical feedstocks.
A few halocarbons, including acid halides like acetyl chloride, are highly reactive; these are rarely found outside chemical processing. The widespread uses of halocarbons were often driven by observations that most of them were more stable than other substances. They may be less affected by acids or alkalis; they may not burn as readily; they may not be attacked by bacteria or molds; or they may not be affected as much by sun exposure.
Hazards
The stability of halocarbons tended to encourage beliefs that they were mostly harmless, although in the mid-1920s physicians reported workers in polychlorinated naphthalene (PCN) manufacturing suffering from chloracne , and by the late 1930s it was known that workers exposed to PCNs could die from liver disease and that DDT would kill mosquitos and other insects . By the 1950s, there had been several reports and investigations of workplace hazards. In 1956, for example, after testing hydraulic oils containing polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB)s, the U.S. Navy found that skin contact caused fatal liver disease in animals and rejected them as "too toxic for use in asubmarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
" .
 In 1962 a book by U.S. biologist Rachel Carson started a storm of concerns about environmental pollution, first focused on DDT and other
In 1962 a book by U.S. biologist Rachel Carson started a storm of concerns about environmental pollution, first focused on DDT and other pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. This includes herbicide, insecticide, nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, microbicide, fungicide, and lampri ...
s, some of them also halocarbons. These concerns were amplified when in 1966 Swedish chemist Soren Jensen reported widespread residues of PCBs among Arctic and sub-Arctic fish and birds . In 1974, Mexican chemist Mario Molina and U.S. chemist Sherwood Rowland
Frank Sherwood "Sherry" Rowland (June 28, 1927 – March 10, 2012) was an American Nobel laureate and a professor of chemistry at the University of California, Irvine. His research was on atmospheric chemistry and chemical kinetics. His best ...
predicted that common halocarbon refrigerant
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the heat pump and refrigeration cycle, refrigeration cycle of air conditioning systems and heat pumps where in most cases they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Ref ...
s, the chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), would accumulate in the upper atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
and destroy protective ozone . Within a few years, ozone depletion was being observed above Antarctica, leading to bans on production and use of chlorofluorocarbons in many countries. In 2007, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) said halocarbons were a direct cause of global warming.
Since the 1970s there have been longstanding, unresolved controversies over potential health hazards of trichloroethylene (TCE) and other halocarbon solvents that had been widely used for industrial cleaning . More recently perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), a precursor in the most common manufacturing process for Teflon and also used to make coatings for fabrics and food packaging, became a health and environmental concern starting in 2006 , suggesting that halocarbons, though thought to be among the most inert, may also present hazards.
Halocarbons, including those that might not be hazards in themselves, can present waste disposal issues. Because they do not readily degrade in natural environments, halocarbons tend to accumulate. Incineration and accidental fires can create corrosive byproducts such as hydrochloric acid and hydrofluoric acid
Hydrofluoric acid is a Solution (chemistry), solution of hydrogen fluoride (HF) in water. Solutions of HF are colourless, acidic and highly Corrosive substance, corrosive. It is used to make most fluorine-containing compounds; examples include th ...
, and poison
Poison is a chemical substance that has a detrimental effect to life. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figuratively, with a broa ...
s like halogenated dioxins
Dioxin may refer to:
* 1,2-Dioxin or 1,4-Dioxin, two unsaturated heterocyclic 6-membered rings where two carbon atoms have been replaced by oxygen atoms, giving the molecular formula C4H4O2
*Dibenzo-1,4-dioxin, the parent compound also known as ...
and furan
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.
Furan is a colorless, flammable, highly ...
s. Species of Desulfitobacterium are being investigated for their potential in the bioremediation of halogenic organic compounds.
See also
*Halogenation
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction that entails the introduction of one or more halogens into a compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, ...
* Carbon–fluorine bond
* Fluorinated gases
Fluorinated gases (F-gases) are chemical compounds containing fluorine that are gases near room temperature.
Types of F-gases
The most common F-gases are hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which contain hydrogen, fluorine, and carbon. They are used in ...
* List of refrigerants
Notes
References
*, settled between the parties, reviewed in * * * * * *, cited iChemical Industry Archives, Anniston Case
, by Environmental Working Group, Washington, DC, 2002 * * * * *
External links
* {{Authority control