Ordvac on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
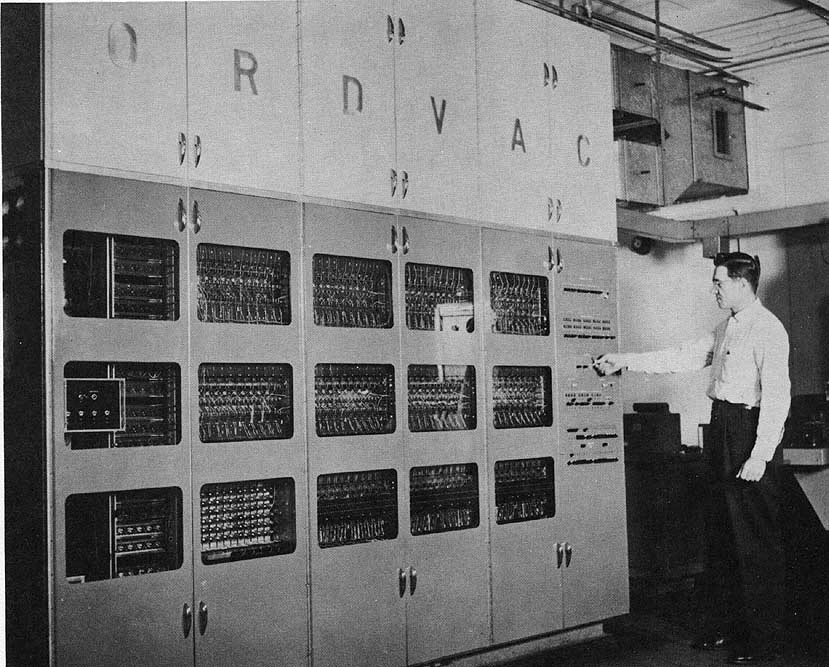 The ORDVAC (''Ordnance Discrete Variable Automatic Computer)'', is an early
The ORDVAC (''Ordnance Discrete Variable Automatic Computer)'', is an early
/ref> * Arithmetic unit uses 1100 vacuum tubes, * Control, uses about 500 vacuum tubes, Total of 2718 vacuum tubes, weight .
ORDVAC documentation
at bitsavers.org {{Mainframes IAS architecture computers United States Army equipment Vacuum tube computers
 The ORDVAC (''Ordnance Discrete Variable Automatic Computer)'', is an early
The ORDVAC (''Ordnance Discrete Variable Automatic Computer)'', is an early computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as C ...
built by the University of Illinois
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (U of I, Illinois, University of Illinois, or UIUC) is a public land-grant research university in Illinois in the twin cities of Champaign and Urbana. It is the flagship institution of the University ...
for the Ballistic Research Laboratory
The Ballistic Research Laboratory (BRL) was a leading U.S. Army research establishment situated at Aberdeen Proving Ground, Maryland that specialized in ballistics ( interior, exterior, and terminal) as well as vulnerability and lethality analysis. ...
at Aberdeen Proving Ground
Aberdeen Proving Ground (APG) (sometimes erroneously called Aberdeen Proving ''Grounds'') is a U.S. Army facility located adjacent to Aberdeen, Harford County, Maryland, United States. More than 7,500 civilians and 5,000 military personnel work at ...
. A successor to the ENIAC
ENIAC (; Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was the first programmable, electronic, general-purpose digital computer, completed in 1945. There were other computers that had these features, but the ENIAC had all of them in one packa ...
(along with EDVAC built earlier). It was based on the IAS IAS may refer to:
Science
* Institute for Advanced Study, in Princeton, New Jersey, United States
* Image Analysis & Stereology, the official journal of the International Society for Stereology & Image Analysis.
* Iowa Archeological Society, Uni ...
architecture developed by John von Neumann
John von Neumann (; hu, Neumann János Lajos, ; December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian-American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist, engineer and polymath. He was regarded as having perhaps the widest cove ...
, which came to be known as the von Neumann architecture
The von Neumann architecture — also known as the von Neumann model or Princeton architecture — is a computer architecture based on a 1945 description by John von Neumann, and by others, in the ''First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC''. The ...
. The ORDVAC was the first computer to have a compiler
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primarily used for programs that ...
. ORDVAC passed its acceptance tests on March 6, 1952, at Aberdeen Proving Ground in Maryland. Its purpose was to perform ballistic trajectory calculations for the US Military. In 1992, the Ballistic Research Laboratory
The Ballistic Research Laboratory (BRL) was a leading U.S. Army research establishment situated at Aberdeen Proving Ground, Maryland that specialized in ballistics ( interior, exterior, and terminal) as well as vulnerability and lethality analysis. ...
became a part of the U.S. Army Research Laboratory
The U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command Army Research Laboratory (DEVCOM ARL) is the U.S. Army's foundational research laboratory. ARL is headquartered at the Adelphi Laboratory Center (ALC) in Adelphi, Maryland. Its largest singl ...
.
Unlike the other computers of its era, the ORDVAC and ILLIAC I
The ILLIAC I (Illinois Automatic Computer), a pioneering computer in the ILLIAC series of computers built in 1952 by the University of Illinois, was the first computer built and owned entirely by a United States educational institution.
Computer ...
were twins and could exchange programs with each other. The later SILLIAC
The SILLIAC (''Sydney version of the Illinois Automatic Computer'', i.e. the ''Sydney ILLIAC''), an early computer built by the University of Sydney, Australia, was based on the ILLIAC and ORDVAC computers developed at the University of Illin ...
computer was a copy of the ORDVAC/ILLIAC series. J. P. Nash of the University of Illinois was a developer of both the ORDVAC and of the university's own identical copy, the ILLIAC
ILLIAC (Illinois Automatic Computer) was a series of supercomputers built at a variety of locations, some at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign. In all, five computers were built in this series between 1951 and 1974. Some more modern ...
, which was later renamed the ILLIAC I. Abe Taub, Sylvian Ray, and Donald B. Gillies
Donald Bruce Gillies (October 15, 1928 – July 17, 1975) was a Canadian computer scientist and mathematician who worked in the fields of computer design, game theory, and minicomputer programming environments.
Early life and education ...
assisted in the checkout of ORDVAC at Aberdeen Proving Ground. After ORDVAC was moved to Aberdeen, it was used remotely by telephone by the University of Illinois for up to eight hours per night. It was one of the first computers to be used remotely and probably the first to routinely be used remotely.
The ORDVAC used 2178 vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied.
The type kn ...
s. Its addition time was 72 microseconds
A microsecond is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one millionth (0.000001 or 10−6 or ) of a second. Its symbol is μs, sometimes simplified to us when Unicode is not available.
A microsecond is equal to 1000 n ...
and the multiplication time was 732 microseconds. Its main memory
Computer data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers.
The central processing unit (CPU) of a computer ...
consisted of 1024 words
A word is a basic element of language that carries an objective or practical meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no consen ...
of 40 bit
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communications. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represente ...
s each, stored using Williams tube
The Williams tube, or the Williams–Kilburn tube named after inventors Freddie Williams and Tom Kilburn, is an early form of computer memory. It was the first random-access digital storage device, and was used successfully in several early co ...
s. It was a rare asynchronous
Asynchrony is the state of not being in synchronization.
Asynchrony or asynchronous may refer to:
Electronics and computing
* Asynchrony (computer programming), the occurrence of events independent of the main program flow, and ways to deal with ...
machine, meaning that there was no central clock regulating the timing of the instructions. One instruction started executing when the previous one finished.
Among the ORDVAC programmers were Martin Davis and Elsie Shutt
Elsie Shutt (born 1928) is an American computer programmer and entrepreneur who founded Computations Incorporated (CompInc) in 1957 when she was not permitted to work part-time at home after she became pregnant. Shutt was notably one of the first ...
.
ORDVAC and its successor at Aberdeen Proving Ground, BRLESC
The BRLESC I (Ballistic Research Laboratories Electronic Scientific Computer) was one of the last of the first-generation electronic computers. It was built by the United States Army's Ballistic Research Laboratory (BRL) at Aberdeen Proving Gro ...
, used their own unique notation for hexadecimal
In mathematics and computing, the hexadecimal (also base-16 or simply hex) numeral system is a positional numeral system that represents numbers using a radix (base) of 16. Unlike the decimal system representing numbers using 10 symbols, hexa ...
numbers. Instead of the sequence A B C D E F universally used today, the digits ten to fifteen were represented by the letters K S N J F L (King Sized Numbers Just for Laughs), corresponding to the teleprinter
A teleprinter (teletypewriter, teletype or TTY) is an electromechanical device that can be used to send and receive typed messages through various communications channels, in both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint configurations. Initia ...
characters on five-track paper tape
Five- and eight-hole punched paper tape
Paper tape reader on the Harwell computer with a small piece of five-hole tape connected in a circle – creating a physical program loop
Punched tape or perforated paper tape is a form of data storage ...
. The manual that was used by the military in 1958 used the name sexadecimal for the base 16 number system.
Commissioning
When ORDVAC was completed, it was tested at the University of Illinois and then disassembled and shipped toAberdeen Proving Ground
Aberdeen Proving Ground (APG) (sometimes erroneously called Aberdeen Proving ''Grounds'') is a U.S. Army facility located adjacent to Aberdeen, Harford County, Maryland, United States. More than 7,500 civilians and 5,000 military personnel work at ...
in Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
. Three faculty members including Sylvian Ray and Abe Taub drove to Maryland to help assemble the machine, which was reconstructed and passed its validation tests in just a week. It was expected that assembly and testing would take over a month. When some military officers came to check on the progress of Ordvac assembly, they asked, "Who is in charge here?", and were told, "It's the guy who is holding the broom!", as Abe Taub—the head of The University of Illinois Digital Computer Laboratory—was sweeping up after having completed all the necessary tasks.
Details
* Memory uses 40 cathode ray tubes and 800 vacuum tubes,manual Vol 1/ref> * Arithmetic unit uses 1100 vacuum tubes, * Control, uses about 500 vacuum tubes, Total of 2718 vacuum tubes, weight .
See also
*ILLIAC II
The ILLIAC II was a revolutionary super-computer built by the University of Illinois that became operational in 1962.
Description
The concept, proposed in 1958, pioneered Emitter-coupled logic (ECL) circuitry, pipelining, and transistor memory ...
* ILLIAC III The ILLIAC III was a fine-grained SIMD pattern recognition computer built by the University of Illinois in 1966.
This ILLIAC's initial task was image processing of bubble chamber experiments used to detect nuclear particles. Later it was used on bi ...
* ILLIAC IV
The ILLIAC IV was the first massively parallel computer. The system was originally designed to have 256 64-bit floating point units (FPUs) and four central processing units (CPUs) able to process 1 billion operations per second. Due to budget con ...
* History of computing hardware
The history of computing hardware covers the developments from early simple devices to aid calculation to modern day computers. Before the 20th century, most calculations were done by humans.
The first aids to computation were purely mechan ...
* List of vacuum tube computers
Vacuum-tube computers, now called first-generation computers, are programmable digital computers using vacuum-tube logic circuitry. They were preceded by systems using electromechanical relays and followed by systems built from discrete transis ...
References
External links
ORDVAC documentation
at bitsavers.org {{Mainframes IAS architecture computers United States Army equipment Vacuum tube computers