Ordinal Dot on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In written languages, an ordinal indicator is a
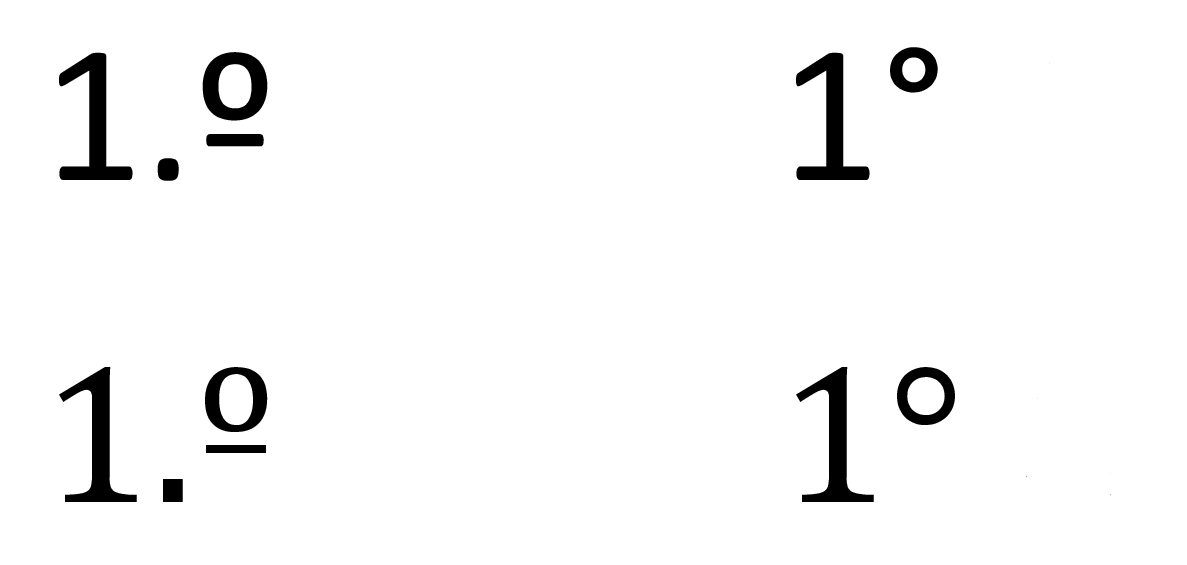 The masculine ordinal indicator may be confused with the
The masculine ordinal indicator may be confused with the 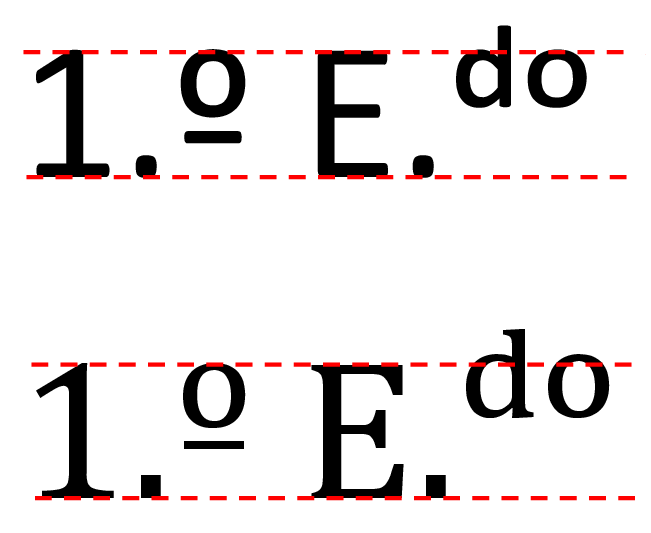 Also, the ordinal indicators should be distinguishable from superscript characters. The top of the ordinal indicators (i.e., the top of the elevated letter and letter ) must be aligned with the
Also, the ordinal indicators should be distinguishable from superscript characters. The top of the ordinal indicators (i.e., the top of the elevated letter and letter ) must be aligned with the  The line thickness of the ordinal indicators is always proportional to the line thickness of the other characters of the font. Many fonts just shrink the characters (making them thinner) to draw superscripts.
The line thickness of the ordinal indicators is always proportional to the line thickness of the other characters of the font. Many fonts just shrink the characters (making them thinner) to draw superscripts.
Windows keyboard layouts
Apple keyboard layouts
{{navbox punctuation Typographical symbols
character
Character or Characters may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''Character'' (novel), a 1936 Dutch novel by Ferdinand Bordewijk
* ''Characters'' (Theophrastus), a classical Greek set of character sketches attributed to The ...
, or group of characters, following a numeral denoting that it is an ordinal number
In set theory, an ordinal number, or ordinal, is a generalization of ordinal numerals (first, second, th, etc.) aimed to extend enumeration to infinite sets.
A finite set can be enumerated by successively labeling each element with the least n ...
, rather than a cardinal number
In mathematics, cardinal numbers, or cardinals for short, are a generalization of the natural numbers used to measure the cardinality (size) of sets. The cardinality of a finite set is a natural number: the number of elements in the set. Th ...
. In English orthography
English orthography is the writing system used to represent spoken English, allowing readers to connect the graphemes to sound and to meaning. It includes English's norms of spelling, hyphenation, capitalisation, word breaks, emphasis, and p ...
, this corresponds to the suffixes ''-st'', ''-nd'', ''-rd'', ''-th'' in written ordinals (represented either on the line ''1st'', ''2nd'', ''3rd'', ''4th'' or as superscript, ).
Also commonly encountered are the superscript
A subscript or superscript is a character (such as a number or letter) that is set slightly below or above the normal line of type, respectively. It is usually smaller than the rest of the text. Subscripts appear at or below the baseline, whil ...
or superior
Superior may refer to:
*Superior (hierarchy), something which is higher in a hierarchical structure of any kind
Places
*Superior (proposed U.S. state), an unsuccessful proposal for the Upper Peninsula of Michigan to form a separate state
*Lake ...
(and often underlined) masculine ordinal indicator, , and feminine ordinal indicator, , originally from Romance
Romance (from Vulgar Latin , "in the Roman language", i.e., "Latin") may refer to:
Common meanings
* Romance (love), emotional attraction towards another person and the courtship behaviors undertaken to express the feelings
* Romance languages, ...
and then via the cultural influence of Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
, as in 1º '' primo'' and 1ª '' prima''. In correct typography, the ordinal indicators and should be distinguishable from other characters.
The practice of underlined (or doubly underlined) superscripted abbreviations was common in 19th-century writing (not limited to ordinal indicators in particular, and also extant in the numero sign
The numero sign or numero symbol, №, (also represented as Nº, No, No. or no.), is a Typography, typographic abbreviation of the word ''number''(''s'') indicating ordinal number, ordinal numeration, especially in names and titles. For exampl ...
), and was also found in handwritten English until at least the late 19th century (e.g. "first" abbreviated or ''1'').
Usage
InSpanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
, Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
, Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
, and Galician, the ordinal indicators and are appended to the numeral depending on whether the grammatical gender
In linguistics, grammatical gender system is a specific form of noun class system, where nouns are assigned with gender categories that are often not related to their real-world qualities. In languages with grammatical gender, most or all nouns ...
is masculine or feminine. The indicator may be given an underline
An underscore, ; also called an underline, low line, or low dash; is a line drawn under a segment of text. In proofreading, underscoring is a convention that says "set this text in italic type", traditionally used on manuscript or typescript as ...
but this is not ubiquitous. In digital typography
Desktop publishing (DTP) is the creation of documents using page layout software on a personal ("desktop") computer. It was first used almost exclusively for print publications, but now it also assists in the creation of various forms of online ...
, this depends on the font: Cambria
Cambria is a name for Wales, being the Latinised form of the Welsh name for the country, . The term was not in use during the Roman period (when Wales had not come into existence as a distinct entity). It emerged later, in the medieval period, a ...
and Calibri
Calibri () is a digital sans-serif typeface family in the humanist or modern style. It was designed by Luc(as) de Groot in 2002–2004 and released to the general public in 2007, with Microsoft Office 2007 and Windows Vista. In Office 2007, it ...
, for example, have underlined ordinal indicators, while most other fonts do not.
Examples of the usage of ordinal indicators in Italian are:
*; ('first'),
*; ('second')
*; ('third')
Galician also forms its ordinal numbers this way, while Asturian follows a similar system where is used for the masculine gender, for the feminine gender and for the neuter gender.
In Spanish, using the two final letters of the word as it is spelled is not allowed, except in the cases of (an apocope
In phonology, apocope () is the loss (elision) of a word-final vowel. In a broader sense, it can refer to the loss of any final sound (including consonants) from a word.
Etymology
''Apocope'' comes from the Greek () from () "cutting off", from ...
of ) before singular masculine nouns, which is not abbreviated as but as , of (an apocope of ) before singular masculine nouns, which is not abbreviated as but as , and of compound ordinal numbers ending in "" or "". For instance, "twenty-first" is before a masculine noun, and its abbreviation is . Since none of these words are shortened before feminine nouns, their correct forms for those cases are and . These can be represented as and . As with other abbreviations in Spanish, the ordinal numbers have a period ".", which is placed ''before'' the indicator. Portuguese follows the same method.
Origins
The practice of indicating ordinals with superscript suffixes may originate with the practice of writing a superscript ''o'' to indicate a Latin ablative in pre-modern scribal practice. This ablativedesinence
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns, adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can carry gr ...
happened to be frequently combined with ordinal numerals indicating dates (as in ''tertio die'' (written ''iiio die'') "on the third day" or in Anno Domini
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used to label or number years in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means 'in the year of the Lord', but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", ...
years, as in (written or similarly) "in the thousandth ..year after the incarnation of our lord Jesus Christ").
The usage of terminals in the vernacular
A vernacular or vernacular language is in contrast with a "standard language". It refers to the language or dialect that is spoken by people that are inhabiting a particular country or region. The vernacular is typically the native language, n ...
languages of Europe derives from Latin usage, as practised by scribes in monasteries and chanceries before writing in the vernacular became established. The terminal letters used depend on the gender of the item to be ordered and the case in which the ordinal adjective is stated, for example ("the first day", nominative case, masculine), but ("on the first day", ablative case masculine), shown as Io or io. As monumental inscriptions often refer to days on which events happened, e.g. "he died on the tenth of June", the ablative case is generally used: Xo () with the month stated in the genitive case. Examples:
*Io , "on the first day of July"
*Xo
*XXo
*Lo
*Co
*Mo
Design
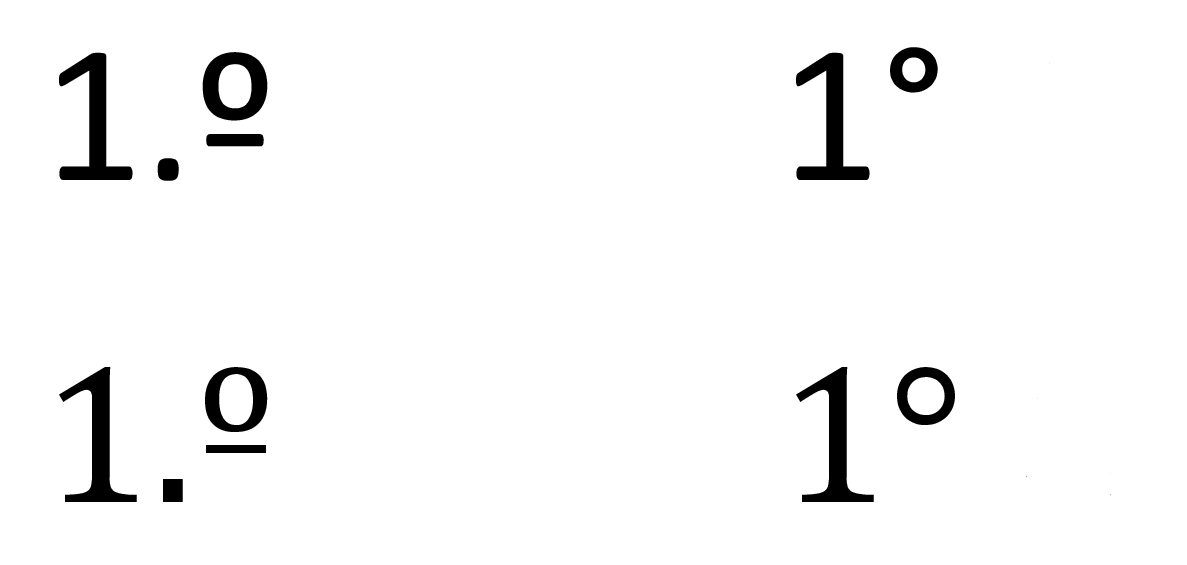 The masculine ordinal indicator may be confused with the
The masculine ordinal indicator may be confused with the degree sign
The degree symbol or degree sign, , is a typographical symbol that is used, among other things, to represent degrees of arc (e.g. in geographic coordinate systems), hours (in the medical field), degrees of temperature or alcohol proof. The sym ...
(U+00B0), which looks very similar and which is provided on the Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
and Latin American keyboard layouts. It was common in the early days of computers to use the same character for both. The degree sign is a uniform circle and is never underlined. The masculine ordinal indicator is the shape of a lower-case letter , and thus may be oval
An oval () is a closed curve in a plane which resembles the outline of an egg. The term is not very specific, but in some areas (projective geometry, technical drawing, etc.) it is given a more precise definition, which may include either one or ...
or elliptical
Elliptical may mean:
* having the shape of an ellipse, or more broadly, any oval shape
** in botany, having an elliptic leaf shape
** of aircraft wings, having an elliptical planform
* characterised by ellipsis (the omission of words), or by conc ...
, and may have a varying line thickness.
Ordinal indicators may also be underlined. It is not mandatory in Portugal nor in Brazil, but it is preferred in some fonts to avoid confusion with the degree sign.
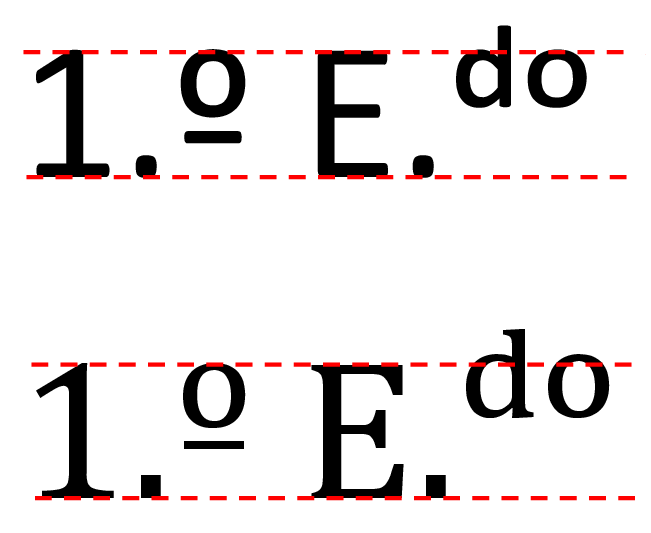 Also, the ordinal indicators should be distinguishable from superscript characters. The top of the ordinal indicators (i.e., the top of the elevated letter and letter ) must be aligned with the
Also, the ordinal indicators should be distinguishable from superscript characters. The top of the ordinal indicators (i.e., the top of the elevated letter and letter ) must be aligned with the cap height
In typography, cap height is the height of a capital letter above the baseline for a particular typeface.http://pfaedit.sourceforge.net/glossary.html Glossary of (some) Typographic Terms It specifically is the height of capital letters that are f ...
of the font. The alignment of the top of superscripted letters and will depend on the font.
 The line thickness of the ordinal indicators is always proportional to the line thickness of the other characters of the font. Many fonts just shrink the characters (making them thinner) to draw superscripts.
The line thickness of the ordinal indicators is always proportional to the line thickness of the other characters of the font. Many fonts just shrink the characters (making them thinner) to draw superscripts.
Encoding
The Romance feminine and masculine ordinal indicators were adopted into the 8-bitECMA-94
ISO/IEC 8859 is a joint ISO and IEC series of standards for 8-bit character encodings. The series of standards consists of numbered parts, such as ISO/IEC 8859-1, ISO/IEC 8859-2, etc. There are 15 parts, excluding the abandoned ISO/IEC 8859-12. ...
encoding in 1985 and the ISO 8859-1
ISO/IEC 8859-1:1998, ''Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 1: Latin alphabet No. 1'', is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1 ...
encoding in 1987 (both based on DEC's Multinational Character Set
The Multinational Character Set (DMCS or MCS) is a character encoding created in 1983 by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) for use in the popular VT220 computer terminal, terminal. It was an 8-bit extension of ASCII that added accented character ...
designed for VT220
The VT220 is a computer terminal introduced by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in November 1983. The VT240 added monochrome ReGIS vector graphics support to the base model, while the VT241 did the same in color. The 200 series replaced the s ...
), at positions 170 (xAA) and 186 (xBA), respectively.
ISO 8859-1 was incorporated as the first 256 code points of ISO/IEC 10646
ISO/IEC JTC 1, entitled "Information technology", is a joint technical committee (JTC) of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Its purpose is to develop, maintain and pr ...
and Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology Technical standard, standard for the consistent character encoding, encoding, representation, and handling of Character (computing), text expre ...
in 1991.
The Unicode characters are thus:
*
*
There are superscript versions of the letters and in Unicode, these are different characters and should not be used as ordinal indicators.
The majority of character sets intended to support Galician, Portuguese and/or Spanish have those two characters encoded. In detail (in hexadecimal):
Typing
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
and Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
keyboard layouts are the only ones on which the characters are directly accessible through a dedicated key: for "º" and for "ª". On other keyboard layouts these characters are accessible only through a set of keystrokes.
On Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for serv ...
can be obtained by and by .
In MacOS
macOS (; previously OS X and originally Mac OS X) is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac computers. Within the market of desktop and lapt ...
keyboards, can be obtained by pressing and can be obtained by pressing .
In Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which ...
, can be obtained by or , and by or . On ChromeOS
ChromeOS, sometimes stylized as chromeOS and formerly styled as Chrome OS, is a Linux-based operating system designed by Google. It is derived from the open-source ChromiumOS and uses the Google Chrome web browser as its principal user interfac ...
, the same , facilities are included in the UK-Extended language setting but the Compose function requires a (Google) add-on to Chrome.
On many mobile devices keyboards ( tablets, smartphone
A smartphone is a portable computer device that combines mobile telephone and computing functions into one unit. They are distinguished from feature phones by their stronger hardware capabilities and extensive mobile operating systems, whic ...
s, etc.) and can be obtained by holding the keys and , respectively, and then selecting the desired character. For this option to appear, the selected input language may need to be changed to one where these symbols are used natively. For example, on Microsoft Swiftkey, both are available when 'Italian' is enabled, but not when only 'English' is.
Similar conventions
Some languages usesuperior letter
In typography and handwriting, a superior letter is a lower-case letter placed above the baseline and made smaller than ordinary script. The style has traditionally been distinct from superscript. Formerly quite common in abbreviations, the orig ...
s as a typographic convention for abbreviations. Oftentimes, the ordinal indicators and are used in this sense, and not to indicate ordinal numbers. Some might say that this is a misuse of ordinal indicators:
* Spanish uses superscript letters and ordinal indicators in some abbreviations, such as for ("approved"); for ("number"); for (an honorific
An honorific is a title that conveys esteem, courtesy, or respect for position or rank when used in addressing or referring to a person. Sometimes, the term "honorific" is used in a more specific sense to refer to an honorary academic title. It ...
); for , a Spanish name
Spanish names are the traditional way of identifying, and the official way of registering, a person in Spain. They comprise a given name (simple or composite) and two surnames (the first surname of each parent). Traditionally, the first surname ...
frequently used in compounds like ; and for , administrator. The superscript characters and indicators are always preceded by a period. Traditionally they have been underlined, but this is optional and less frequent today. Portuguese forms some abbreviations in the same manner. For example: for (an honorific
An honorific is a title that conveys esteem, courtesy, or respect for position or rank when used in addressing or referring to a person. Sometimes, the term "honorific" is used in a more specific sense to refer to an honorary academic title. It ...
), for (Ltd.
A private company limited by shares is a class of private limited company incorporated under the laws of England and Wales, Northern Ireland, Scotland, certain Commonwealth countries, and the Republic of Ireland. It has shareholders with limit ...
), and for (Ms.
Ms. (American English) or Ms (British English; normally , but also , or when unstressed)''Oxford English Dictionary'' online, Ms, ''n.2''. Etymology: "An orthographic and phonetic blend of Mrs ''n.1'' and miss ''n.2'' Compare mizz ''n.'' The pr ...
).
* English has borrowed the "No." abbreviation from the Romance-language word ''numero'', which itself derives from the Latin word ''numero'', the ablative case
In grammar, the ablative case (pronounced ; sometimes abbreviated ) is a grammatical case for nouns, pronouns, and adjectives in the grammars of various languages; it is sometimes used to express motion away from something, among other uses. T ...
of the word ''numerus'' ("number"). This is sometimes written as "No", with the superscript ''o'' optionally underlined, or sometimes with the ordinal indicator. In this case the ordinal indicator would simply represent the letter "o" in ''numero''; see numero sign
The numero sign or numero symbol, №, (also represented as Nº, No, No. or no.), is a Typography, typographic abbreviation of the word ''number''(''s'') indicating ordinal number, ordinal numeration, especially in names and titles. For exampl ...
.
Ordinal dot
InBasque
Basque may refer to:
* Basques, an ethnic group of Spain and France
* Basque language, their language
Places
* Basque Country (greater region), the homeland of the Basque people with parts in both Spain and France
* Basque Country (autonomous co ...
, Serbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian () – also called Serbo-Croat (), Serbo-Croat-Bosnian (SCB), Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian (BCS), and Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS) – is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and ...
, Czech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus'
Places
*Czech, ...
, Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish a ...
, Estonian
Estonian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Estonia, a country in the Baltic region in northern Europe
* Estonians, people from Estonia, or of Estonian descent
* Estonian language
* Estonian cuisine
* Estonian culture
See also ...
, Faroese, Finnish
Finnish may refer to:
* Something or someone from, or related to Finland
* Culture of Finland
* Finnish people or Finns, the primary ethnic group in Finland
* Finnish language, the national language of the Finnish people
* Finnish cuisine
See also ...
, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
, Hungarian, Icelandic, Latvian, Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
*Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
*Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including the ...
, Slovak, Slovene, Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
, among other languages, a period or full stop
The full stop (Commonwealth English), period (North American English), or full point , is a punctuation mark. It is used for several purposes, most often to mark the end of a declarative sentence (as distinguished from a question or exclamation ...
is written after the numeral. In Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
the period can be omitted if there is no ambiguity whether a given numeral is ordinal or cardinal. The only exception are variables in mathematics ("k+1-szy" — "(k+1)st").
Writing out the endings
End, END, Ending, or variation, may refer to:
End
*In mathematics:
**End (category theory)
**End (topology)
**End (graph theory)
** End (group theory) (a subcase of the previous)
**End (endomorphism)
*In sports and games
**End (gridiron football) ...
for various cases, as sometimes happens in Czech and Slovak, is considered incorrect and uneducated. Should a period or full stop follow this dot, it is omitted. In Czech and Slovak, numerals with ordinal dot are mostly used only in tables, lists etc., or in case of large (or long) numbers; within a sentence it is recommended to write out the form with letters in full.
The Serbian standard of Serbo-Croatian (unlike the Croatian and Bosnian standards) uses the dot in role of the ordinal indicator only past Arabic numerals, while Roman numerals are used without a dot.
There is a problem with autocorrection, mobile editors etc. which often forces a capital initial letter to the word following the ordinal number.
Other suffixes
English
* ''-st'' is used with numbers ending in ''1'' (e.g. ''1st'', pronounced ''first'') * ''-nd'' is used with numbers ending in ''2'' (e.g. ''92nd'', pronounced ''ninety-second'') * ''-rd'' is used with numbers ending in ''3'' (e.g. ''33rd'', pronounced ''thirty-third'') * As an exception to the above rules, all the "teen" numbers ending with ''11'', ''12'', etc. use ''-th'' (e.g. ''11th'', pronounced ''eleventh'', ''112th'', pronounced ''one hundred ndth'') * ''-th'' is used for all other numbers (e.g. 9th, pronounced ''ninth''). * One archaic variant uses a singular ''-d'' for numbers ending in 2 or 3 (e.g. ''92d'' or ''33d'') In 19th-century handwriting, these terminals were often elevated, that is to say written as superscripts (e.g. ). With the gradual introduction of thetypewriter
A typewriter is a mechanical or electromechanical machine for typing characters. Typically, a typewriter has an array of keys, and each one causes a different single character to be produced on paper by striking an inked ribbon selectivel ...
in the late 19th century, it became common to write them on the baseline in typewritten texts,
and this usage even became recommended in certain 20th-century style guides.
Thus, the 17th edition of ''The Chicago Manual of Style
''The Chicago Manual of Style'' (abbreviated in writing as ''CMOS'' or ''CMS'', or sometimes as ''Chicago'') is a style guide for American English published since 1906 by the University of Chicago Press. Its 17 editions have prescribed writi ...
'' states: "The letters in ordinal numbers should not appear as superscripts (e.g., 122nd not )", as do the ''Bluebook
''The Bluebook: A Uniform System of Citation'' is a style guide that prescribes the most widely used legal citation system in the United States. It is taught and used at a majority of U.S. law schools and is also used in a majority of federal ...
'' and style guides by the ''Council of Science Editors
The Council of Science Editors (CSE), formerly the Council of Biology Editors (CBE; 1965–2000) and originally the Conference of Biology Editors (CBE; 1957–1965), is a United States-based nonprofit organization that supports editorial practic ...
'', Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washing ...
, and Yahoo
Yahoo! (, styled yahoo''!'' in its logo) is an American web services provider. It is headquartered in Sunnyvale, California and operated by the namesake company Yahoo! Inc. (2017–present), Yahoo Inc., which is 90% owned by investment funds ma ...
. Two problems are that superscripts are used "most often in citations" and are "tiny and hard to read". Some word processor
A word processor (WP) is a device or computer program that provides for input, editing, formatting, and output of text, often with some additional features.
Word processor (electronic device), Early word processors were stand-alone devices ded ...
s format ordinal indicators as superscripts by default (e.g. Microsoft Word
Microsoft Word is a word processing software developed by Microsoft. It was first released on October 25, 1983, under the name ''Multi-Tool Word'' for Xenix systems. Subsequent versions were later written for several other platforms includin ...
). Style guide author Jack Lynch (Rutgers
Rutgers University (; RU), officially Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, is a public land-grant research university consisting of four campuses in New Jersey. Chartered in 1766, Rutgers was originally called Queen's College, and was a ...
) recommends turning off automatic superscripting of ordinals in Microsoft Word
Microsoft Word is a word processing software developed by Microsoft. It was first released on October 25, 1983, under the name ''Multi-Tool Word'' for Xenix systems. Subsequent versions were later written for several other platforms includin ...
, because "no professionally printed books use superscripts".
French
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
uses the ordinal indicators (), in feminine (), (). French also uses the indicator for the variant ; in feminine this indicator becomes : . In plural, all these indicators take a S: (), (), (), (), ().
These indicators use superscript formatting whenever it is available.
Catalan
The rule inCatalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
is to follow the number with the last letter in the singular and the last two letters in the plural. Most numbers follow the pattern exemplified by "20" ( '' '', '' '', '' '', '' ''), but the first few ordinals are irregular, affecting the abbreviations of the masculine forms. Superscripting is not standard.
Dutch
Unlike otherGermanic languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, Engli ...
, Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
is similar to English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
in this respect: the French layout with ' used to be popular, but the recent spelling changes now prescribe the suffix . Optionally and may be used, but this is more complex: (), (), (), ()...
Finnish
InFinnish orthography
Finnish orthography is based on the Latin script, and uses an alphabet derived from the Swedish alphabet, officially comprising twenty-nine letters but also including two additional letters found in some loanwords. The Finnish orthography striv ...
, when the numeral is followed by its head
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals may ...
noun (which indicates the grammatical case
A grammatical case is a category of nouns and noun modifiers (determiners, adjectives, participles, and Numeral (linguistics), numerals), which corresponds to one or more potential grammatical functions for a nominal group in a wording. In vari ...
of the ordinal), it is sufficient to write a period or full stop
The full stop (Commonwealth English), period (North American English), or full point , is a punctuation mark. It is used for several purposes, most often to mark the end of a declarative sentence (as distinguished from a question or exclamation ...
after the numeral: "In the competition, I finished in 2nd place". However, if the head noun is omitted, the ordinal indicator takes the form of a morphological suffix, which is attached to the numeral with a colon. In the nominative case
In grammar, the nominative case (abbreviated ), subjective case, straight case or upright case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb or (in Latin and formal variants of Engl ...
, the suffix is for 1 and 2, and for larger numerals: "I came 2nd, and my brother came 3rd". This is derived from the endings of the spelled-out ordinal numbers: , , '', '', , , ...
The system becomes rather complicated when the ordinal needs to be inflected
In linguistic morphology, inflection (or inflexion) is a process of word formation in which a word is modified to express different grammatical categories such as tense, case, voice, aspect, person, number, gender, mood, animacy, and defini ...
, as the ordinal suffix is adjusted according to the case ending: (nominative case, which has no ending), (genitive case
In grammar, the genitive case (abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can al ...
with ending ), (partitive case
The partitive case (abbreviated , , or more ambiguously ) is a grammatical case which denotes "partialness", "without result", or "without specific identity". It is also used in contexts where a subgroup is selected from a larger group, or with nu ...
with ending ), (inessive case
In grammar, the inessive case (abbreviated ; from la, inesse "to be in or at") is a locative grammatical case. This case carries the basic meaning of "in": for example, "in the house" is in Finnish, in Estonian, () in Moksha, in Basque, in ...
with ending ), (illative case
In grammar, the illative case (; abbreviated ; from la, illatus "brought in") is a grammatical case used in the Finnish, Estonian, Lithuanian, Latvian and Hungarian languages. It is one of the locative cases, and has the basic meaning of "into ...
with ending ), etc. Even native speakers sometimes find it difficult to exactly identify the ordinal suffix, as its borders with the word stem
In linguistics, a word stem is a part of a word responsible for its lexical meaning. The term is used with slightly different meanings depending on the morphology of the language in question. In Athabaskan linguistics, for example, a verb stem is ...
and the case ending may appear blurred. In such cases it may be preferable to write the ordinal word entirely with letters
Letter, letters, or literature may refer to:
Characters typeface
* Letter (alphabet), a character representing one or more of the sounds used in speech; any of the symbols of an alphabet.
* Letterform, the graphic form of a letter of the alphabe ...
and particularly is rare even in the nominative case, as it is not significantly shorter than the full word .
Irish
Numerals from ''3'' up form their ordinals uniformly by adding the suffix : , etc. When the ordinal is written out, the suffix adheres to the spelling restrictions imposed by the broad/slender difference in consonants and is written after slender consonants; but when written as numbers, only the suffix itself () is written. In the case of ''4'' (), the final syllable issyncopated
In music, syncopation is a variety of rhythms played together to make a piece of music, making part or all of a tune or piece of music off-beat. More simply, syncopation is "a disturbance or interruption of the regular flow of rhythm": a "place ...
before the suffix, and in the case of ''9'' (), ''20'' (), and ''1000'' (), the final vowel is assimilated into the suffix.
Most multiples of ten end in a vowel in their cardinal form and form their ordinal form by adding the suffix to their genitive singular form, which ends in ; this is not reflected in writing. Exceptions are ''20'' () and ''40'' (), both of whom form their ordinals by adding the suffix directly to the cardinal ( and ).
When counting objects (2) becomes and (4) becomes .
As in French, the vigesimal system is widely used, particularly in people's ages. – 95.
The numbers ''1'' () and ''2'' () both have two separate ordinals: one regularly formed by adding , and one suppletive In linguistics and etymology, suppletion is traditionally understood as the use of one word as the inflected form of another word when the two words are not cognate. For those learning a language, suppletive forms will be seen as "irregular" or even ...
form (). The regular forms are restricted in their usage to actual numeric contexts, when counting. The latter are also used in counting, especially , but are used in broader, more abstract senses of 'first' and 'second' (or 'other'). In their broader senses, and are not written as and , though and may in a numeric context be read aloud as and (e.g., may be read as or as ).
Russian
One or two letters of the spelled-out numeral are appended to it (either after a hyphen or, rarely, in superscript). The rule is to take the minimal number of letters that include at least one consonant phoneme. Examples: 2-му второму , 2-я вторая , 2-й второй (note that in the second example the vowel letter я represents two phonemes, one of which () is ''consonant'').Swedish
The general rule is that (for 1 and 2) or (for all other numbers, except , et cetera, but including and ) is appended to the numeral. The reason is that and respectively end the ordinal number words. The ordinals for 1 and 2 may however be given an form ( and instead of and ) when used about a male person (masculine natural gender), and if so they are written and . When indicating dates, suffixes are never used. Examples: (first grade (in elementary school)), (third edition), but . Furthermore, suffixes can be left out if the number obviously is an ordinal number, example: (3rd ed). Using afull stop
The full stop (Commonwealth English), period (North American English), or full point , is a punctuation mark. It is used for several purposes, most often to mark the end of a declarative sentence (as distinguished from a question or exclamation ...
as an ordinal indicator is considered archaic, but still occurs in military contexts. Example: (5th company).
Representation as prefix
Numbers inMalay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
and Indonesian
Indonesian is anything of, from, or related to Indonesia, an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It may refer to:
* Indonesians, citizens of Indonesia
** Native Indonesians, diverse groups of local inhabitants of the archipelago
** Indonesian ...
are preceded by the ordinal prefix ; for example, , "seventh". The exception is which means "first".
Numbers in Filipino
Filipino may refer to:
* Something from or related to the Philippines
** Filipino language, standardized variety of 'Tagalog', the national language and one of the official languages of the Philippines.
** Filipinos, people who are citizens of th ...
are preceded by the ordinal prefix or (the latter subject to sandhi
Sandhi ( sa, सन्धि ' , "joining") is a cover term for a wide variety of sound changes that occur at morpheme or word boundaries. Examples include fusion of sounds across word boundaries and the alteration of one sound depending on near ...
; for example, or , "seventh". The exception is , which means "first".
In Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
and Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
, an ordinal number is prefixed by / ; for example, "first", "second".
In Korean
Korean may refer to:
People and culture
* Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula
* Korean cuisine
* Korean culture
* Korean language
**Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chosŏn'gŭl
**Korean dialects and the Jeju language
** ...
, an ordinal number is prefixed by or suffixed by ; for example, "first", "second".
See also
*Numero sign
The numero sign or numero symbol, №, (also represented as Nº, No, No. or no.), is a Typography, typographic abbreviation of the word ''number''(''s'') indicating ordinal number, ordinal numeration, especially in names and titles. For exampl ...
* Superior letter
In typography and handwriting, a superior letter is a lower-case letter placed above the baseline and made smaller than ordinary script. The style has traditionally been distinct from superscript. Formerly quite common in abbreviations, the orig ...
References
External links
* .Windows keyboard layouts
Apple keyboard layouts
{{navbox punctuation Typographical symbols