Order-4 Dodecahedral Honeycomb on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In

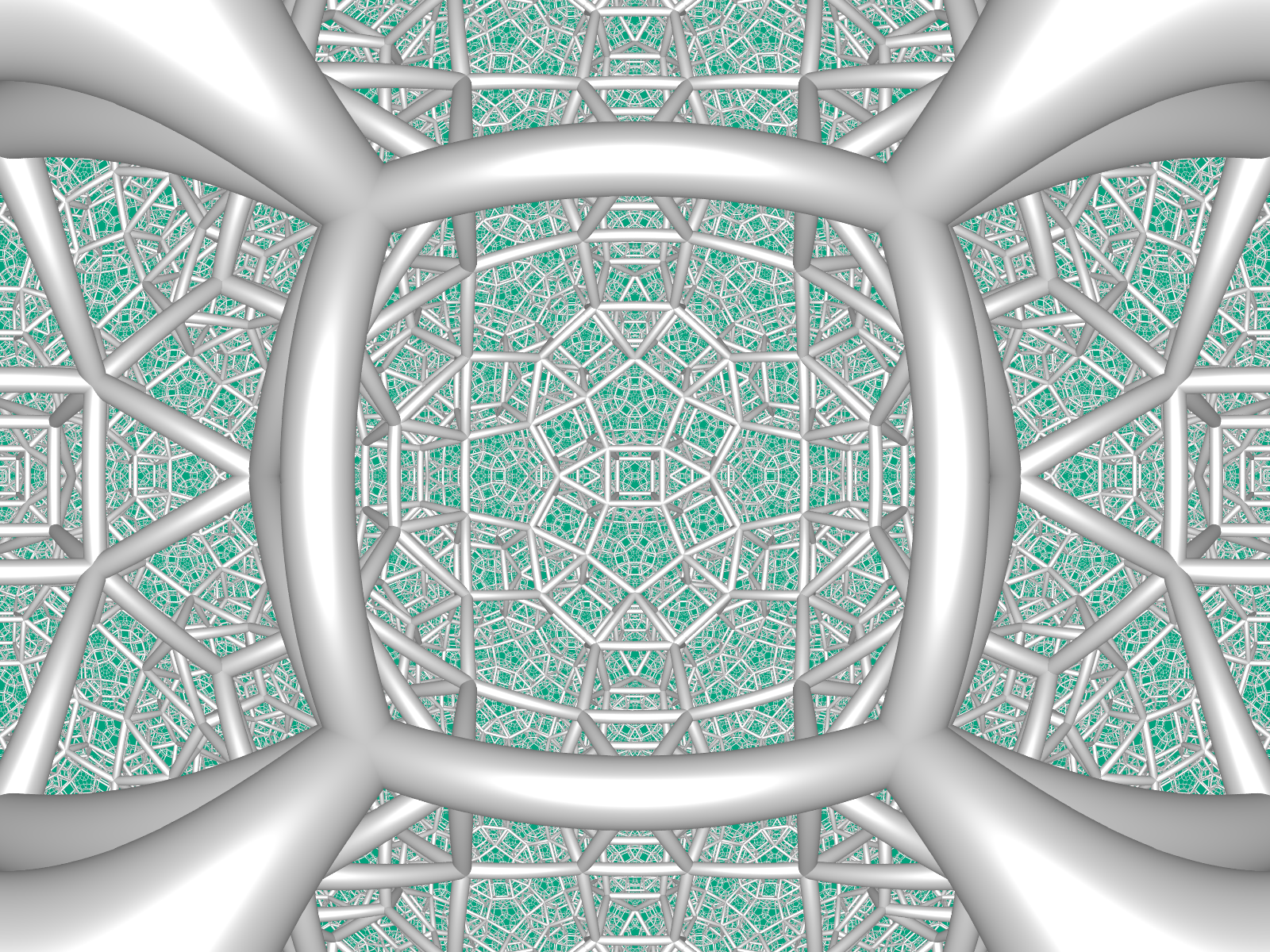
A view of the order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb under the Beltrami-Klein model



 It can be seen as analogous to the 2D hyperbolic
It can be seen as analogous to the 2D hyperbolic 



hyperbolic geometry
In mathematics, hyperbolic geometry (also called Lobachevskian geometry or Bolyai–Lobachevskian geometry) is a non-Euclidean geometry. The parallel postulate of Euclidean geometry is replaced with:
:For any given line ''R'' and point ''P' ...
, the order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb is one of four compact regular
The term regular can mean normal or in accordance with rules. It may refer to:
People
* Moses Regular (born 1971), America football player
Arts, entertainment, and media Music
* "Regular" (Badfinger song)
* Regular tunings of stringed instrum ...
space-filling tessellation
A tessellation or tiling is the covering of a surface, often a plane, using one or more geometric shapes, called ''tiles'', with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellation can be generalized to higher dimensions and a variety of ge ...
s (or honeycombs
A honeycomb is a mass of hexagonal prismatic wax cells built by honey bees in their nests to contain their larvae and stores of honey and pollen.
Beekeepers may remove the entire honeycomb to harvest honey. Honey bees consume about of hone ...
) of hyperbolic 3-space. With Schläfli symbol
In geometry, the Schläfli symbol is a notation of the form \ that defines regular polytopes and tessellations.
The Schläfli symbol is named after the 19th-century Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli, who generalized Euclidean geometry to mor ...
it has four dodecahedra
In geometry, a dodecahedron (Greek , from ''dōdeka'' "twelve" + ''hédra'' "base", "seat" or "face") or duodecahedron is any polyhedron with twelve flat faces. The most familiar dodecahedron is the regular dodecahedron with regular pentag ...
around each edge
Edge or EDGE may refer to:
Technology Computing
* Edge computing, a network load-balancing system
* Edge device, an entry point to a computer network
* Adobe Edge, a graphical development application
* Microsoft Edge, a web browser developed b ...
, and 8 dodecahedra around each vertex
Vertex, vertices or vertexes may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics and computer science
*Vertex (geometry), a point where two or more curves, lines, or edges meet
*Vertex (computer graphics), a data structure that describes the position ...
in an octahedral
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at ea ...
arrangement. Its vertices are constructed from 3 orthogonal axes. Its dual
Dual or Duals may refer to:
Paired/two things
* Dual (mathematics), a notion of paired concepts that mirror one another
** Dual (category theory), a formalization of mathematical duality
*** see more cases in :Duality theories
* Dual (grammatical ...
is the order-5 cubic honeycomb
In hyperbolic geometry, the order-5 cubic honeycomb is one of four compact regular space-filling tessellations (or honeycombs) in hyperbolic 3-space. With Schläfli symbol it has five cubes around each edge, and 20 cubes around each vertex. It ...
.
Description
Thedihedral angle
A dihedral angle is the angle between two intersecting planes or half-planes. In chemistry, it is the clockwise angle between half-planes through two sets of three atoms, having two atoms in common. In solid geometry, it is defined as the un ...
of a regular dodecahedron
A regular dodecahedron or pentagonal dodecahedron is a dodecahedron that is regular, which is composed of 12 regular pentagonal faces, three meeting at each vertex. It is one of the five Platonic solids. It has 12 faces, 20 vertices, 30 edges, ...
is ~116.6°, so it is impossible to fit 4 of them on an edge in Euclidean 3-space. However in hyperbolic space a properly-scaled regular dodecahedron can be scaled so that its dihedral angles are reduced to 90 degrees, and then four fit exactly on every edge.
Symmetry
It has a half symmetry construction, , with two types (colors) of dodecahedra in theWythoff construction
In geometry, a Wythoff construction, named after mathematician Willem Abraham Wythoff, is a method for constructing a uniform polyhedron or plane tiling. It is often referred to as Wythoff's kaleidoscopic construction.
Construction process
...
. ↔ .
Images
A view of the order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb under the Beltrami-Klein model
Related polytopes and honeycombs
There are four regular compact honeycombs in 3D hyperbolic space: There are fifteen uniform honeycombs in the ,3,4Coxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H. S. M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of reflections (or kaleidoscopic mirrors). Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean ref ...
family, including this regular form.
There are eleven uniform honeycombs in the bifurcating ,31,1Coxeter group family, including this honeycomb in its alternated form.
This construction can be represented by alternation (checkerboard) with two colors of dodecahedral cells.
This honeycomb is also related to the 16-cell
In geometry, the 16-cell is the regular convex 4-polytope (four-dimensional analogue of a Platonic solid) with Schläfli symbol . It is one of the six regular convex 4-polytopes first described by the Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli in the m ...
, cubic honeycomb
The cubic honeycomb or cubic cellulation is the only proper regular space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb) in Euclidean 3-space made up of cubic cells. It has 4 cubes around every edge, and 8 cubes around each vertex. Its vertex figure is a ...
, and order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb
In the field of hyperbolic geometry, the order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb arises as one of 11 regular paracompact honeycombs in 3-dimensional hyperbolic space. It is ''paracompact'' because it has cells composed of an infinite number of faces. ...
all which have octahedral vertex figures:
This honeycomb is a part of a sequence of polychora and honeycombs with dodecahedral
In geometry, a dodecahedron (Greek , from ''dōdeka'' "twelve" + ''hédra'' "base", "seat" or "face") or duodecahedron is any polyhedron with twelve flat faces. The most familiar dodecahedron is the regular dodecahedron with regular pentag ...
cells:
Rectified order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb
The rectified order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb, , has alternatingoctahedron
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at e ...
and icosidodecahedron
In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty (''icosi'') triangular faces and twelve (''dodeca'') pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 ...
cells, with a square prism vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
.
: 

Related honeycombs
There are four rectified compact regular honeycombs:Truncated order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb
The truncated order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb, , hasoctahedron
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at e ...
and truncated dodecahedron
In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.
Geometric relations
This polyhedron can be formed from a regular dodecahedron by tru ...
cells, with a square pyramid
In geometry, a square pyramid is a pyramid having a square base. If the apex is perpendicularly above the center of the square, it is a right square pyramid, and has symmetry. If all edge lengths are equal, it is an equilateral square pyramid ...
vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
.
 It can be seen as analogous to the 2D hyperbolic
It can be seen as analogous to the 2D hyperbolic truncated order-4 pentagonal tiling
In geometry, the truncated order-4 pentagonal tiling is a uniform tiling of the Hyperbolic geometry, hyperbolic plane. It has Schläfli symbol of t0,1.
Uniform colorings
A half symmetry +,4,5= ,5coloring can be constructed with two color ...
, t with truncated pentagon and square faces:
: Related honeycombs
Bitruncated order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb
The bitruncated order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb, or bitruncated order-5 cubic honeycomb, , hastruncated octahedron
In geometry, the truncated octahedron is the Archimedean solid that arises from a regular octahedron by removing six pyramids, one at each of the octahedron's vertices. The truncated octahedron has 14 faces (8 regular hexagons and 6 squares), 36 ...
and truncated icosahedron
In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of 13 convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose 32 faces are two or more types of regular polygons. It is the only one of these shapes that does not contain triangles or squa ...
cells, with a digonal disphenoid
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the o ...
vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
.

Related honeycombs
Cantellated order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb
The cantellated order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb, , hasrhombicosidodecahedron
In geometry, the rhombicosidodecahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed of two or more types of regular polygon faces.
It has 20 regular triangular faces, 30 square faces, 12 regular ...
, cuboctahedron
A cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with 8 triangular faces and 6 square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with 2 triangles and 2 squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such, it ...
, and cube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross.
The cube is the on ...
cells, with a wedge vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
.

Related honeycombs
Cantitruncated order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb
The cantitruncated order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb, , hastruncated icosidodecahedron
In geometry, a truncated icosidodecahedron, rhombitruncated icosidodecahedron,Wenninger Model Number 16 great rhombicosidodecahedron,Williams (Section 3-9, p. 94)Cromwell (p. 82) omnitruncated dodecahedron or omnitruncated icosahedronNorman Wood ...
, truncated octahedron
In geometry, the truncated octahedron is the Archimedean solid that arises from a regular octahedron by removing six pyramids, one at each of the octahedron's vertices. The truncated octahedron has 14 faces (8 regular hexagons and 6 squares), 36 ...
, and cube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross.
The cube is the on ...
cells, with a mirrored sphenoid vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
.

Related honeycombs
Runcinated order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb
The runcinated order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb is the same as the runcinated order-5 cubic honeycomb.Runcitruncated order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb
The runcitruncated order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb, , hastruncated dodecahedron
In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.
Geometric relations
This polyhedron can be formed from a regular dodecahedron by tru ...
, rhombicuboctahedron
In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is a polyhedron with eight triangular, six square, and twelve rectangular faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle, one square, and two rectangles meeting at ...
, decagonal prism
In geometry, the decagonal prism is the eighth in the infinite set of prisms, formed by ten square side faces and two regular decagon caps. With twelve faces, it is one of many nonregular dodecahedra. The decagonal prism has 12 faces, 30 edges, an ...
, and cube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross.
The cube is the on ...
cells, with an isosceles-trapezoidal pyramid
A pyramid (from el, πυραμίς ') is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge to a single step at the top, making the shape roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be trilateral, quadrila ...
vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines ...
.

Related honeycombs
Runcicantellated order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb
The runcicantellated order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb is the same as the runcitruncated order-5 cubic honeycomb.Omnitruncated order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb
The omnitruncated order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb is the same as the omnitruncated order-5 cubic honeycomb.See also
*Convex uniform honeycombs in hyperbolic space
In hyperbolic geometry, a uniform honeycomb in hyperbolic space is a uniform tessellation of uniform polyhedral cells. In 3-dimensional hyperbolic space there are nine Coxeter group families of compact convex uniform honeycombs, generated as ...
* Regular tessellations of hyperbolic 3-space
* Poincaré homology sphere Poincaré dodecahedral space
* Seifert–Weber space Seifert–Weber dodecahedral space
References
*Coxeter
Harold Scott MacDonald "Donald" Coxeter, (9 February 1907 – 31 March 2003) was a British and later also Canadian geometer. He is regarded as one of the greatest geometers of the 20th century.
Biography
Coxeter was born in Kensington to ...
, '' Regular Polytopes'', 3rd. ed., Dover Publications, 1973. . (Tables I and II: Regular polytopes and honeycombs, pp. 294–296)
*Coxeter
Harold Scott MacDonald "Donald" Coxeter, (9 February 1907 – 31 March 2003) was a British and later also Canadian geometer. He is regarded as one of the greatest geometers of the 20th century.
Biography
Coxeter was born in Kensington to ...
, ''The Beauty of Geometry: Twelve Essays'', Dover Publications, 1999 (Chapter 10: Regular honeycombs in hyperbolic space, Summary tables II,III,IV,V, p212-213)
* Jeffrey R. Weeks ''The Shape of Space, 2nd edition'' (Chapter 16-17: Geometries on Three-manifolds I,II)
* Norman Johnson ''Uniform Polytopes'', Manuscript
** N.W. Johnson: ''The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs'', Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Toronto, 1966
** N.W. Johnson: ''Geometries and Transformations'', (2018) Chapter 13: Hyperbolic Coxeter groups
{{DEFAULTSORT:Order-4 Dodecahedral Honeycomb
Honeycombs (geometry)