Oran District on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Oran ( ar, ظˆظژظ‡ط±ط§ظ†, Wahrؤپn) is a major coastal city located in the north-west of
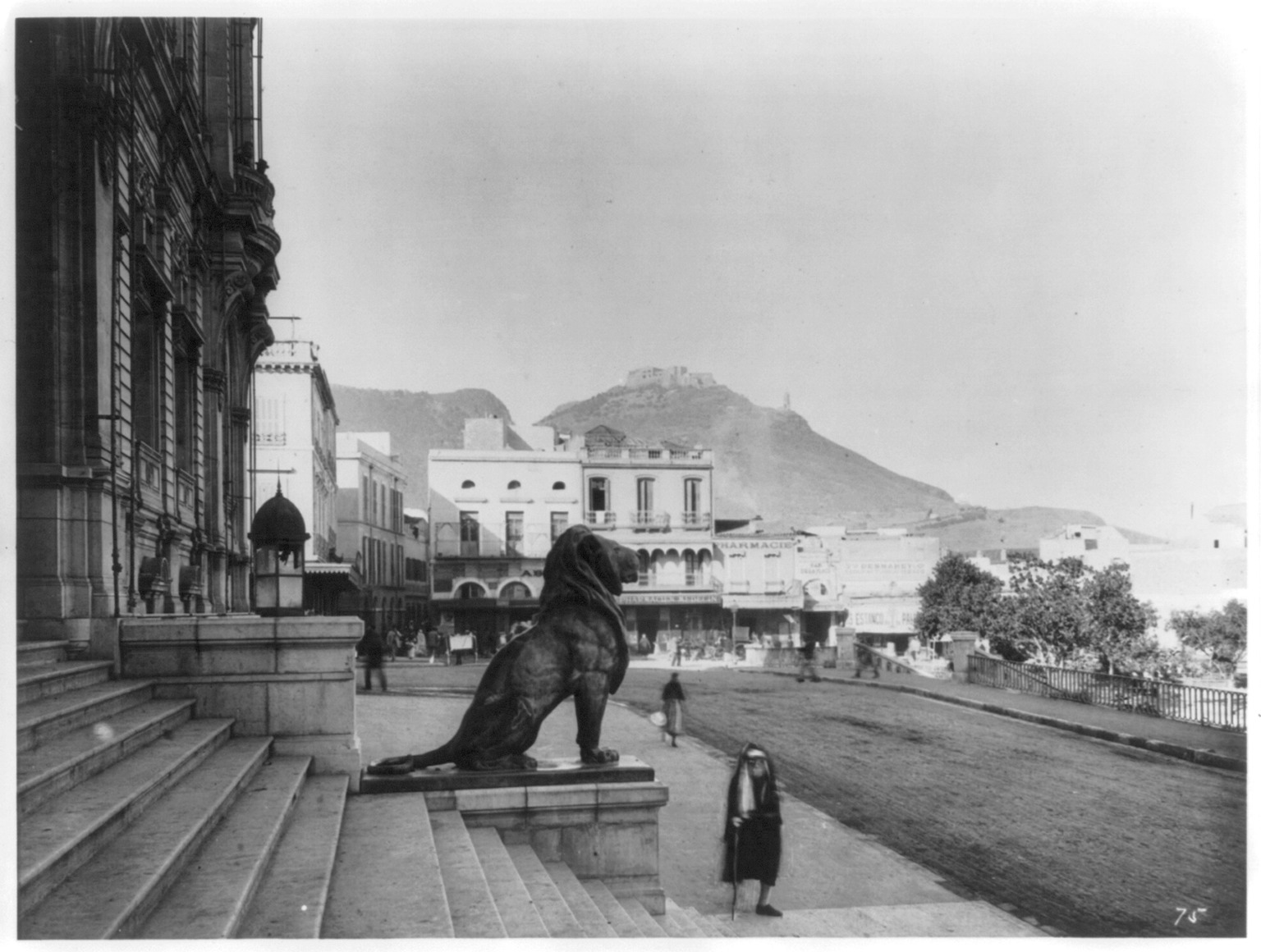
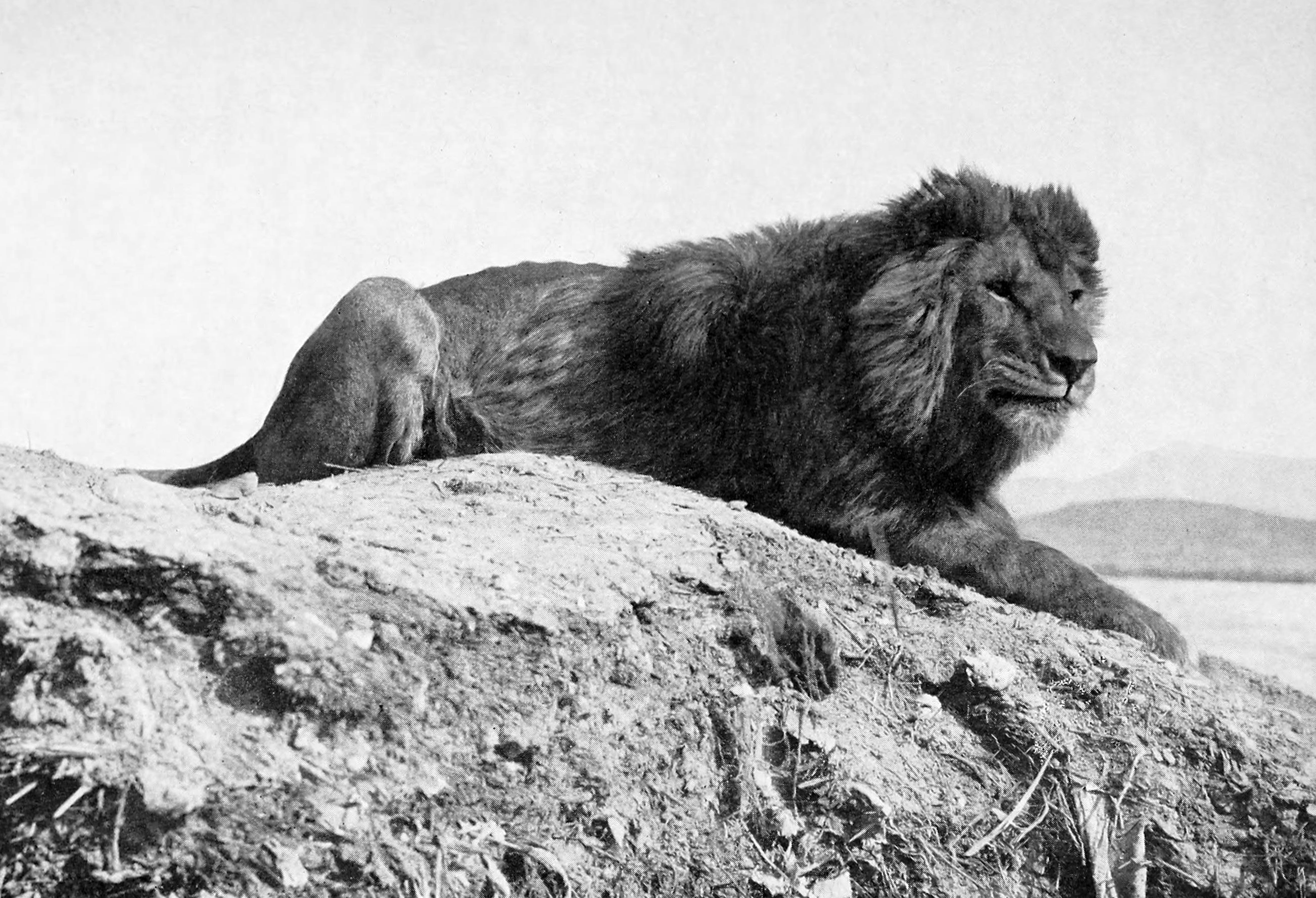 The word ''Wahran'' comes from the Berber expression ''wa - iharan'' (place of lions). A locally popular legend tells that in the period around AD 900, there were sightings of Barbary lions in the area. The last two lions were killed on a mountain near Oran, and it became known as ''la montagne des lions'' ("The Mountain of Lions"). Two giant lion statues stand in front of Oran's city hall, symbolizing the city.
The word ''Wahran'' comes from the Berber expression ''wa - iharan'' (place of lions). A locally popular legend tells that in the period around AD 900, there were sightings of Barbary lions in the area. The last two lions were killed on a mountain near Oran, and it became known as ''la montagne des lions'' ("The Mountain of Lions"). Two giant lion statues stand in front of Oran's city hall, symbolizing the city.
 Before the Spaniards, the Portuguese launched a failed expedition to capture the city in July 1501. Four years later, the Spanish took Mers-el-Kأ©bir, located just west of Oran. Thus began the first organized incursions against the city which, at the time, numbered 25,000 inhabitants and counted 6,000 ''fueros''. Count
Before the Spaniards, the Portuguese launched a failed expedition to capture the city in July 1501. Four years later, the Spanish took Mers-el-Kأ©bir, located just west of Oran. Thus began the first organized incursions against the city which, at the time, numbered 25,000 inhabitants and counted 6,000 ''fueros''. Count 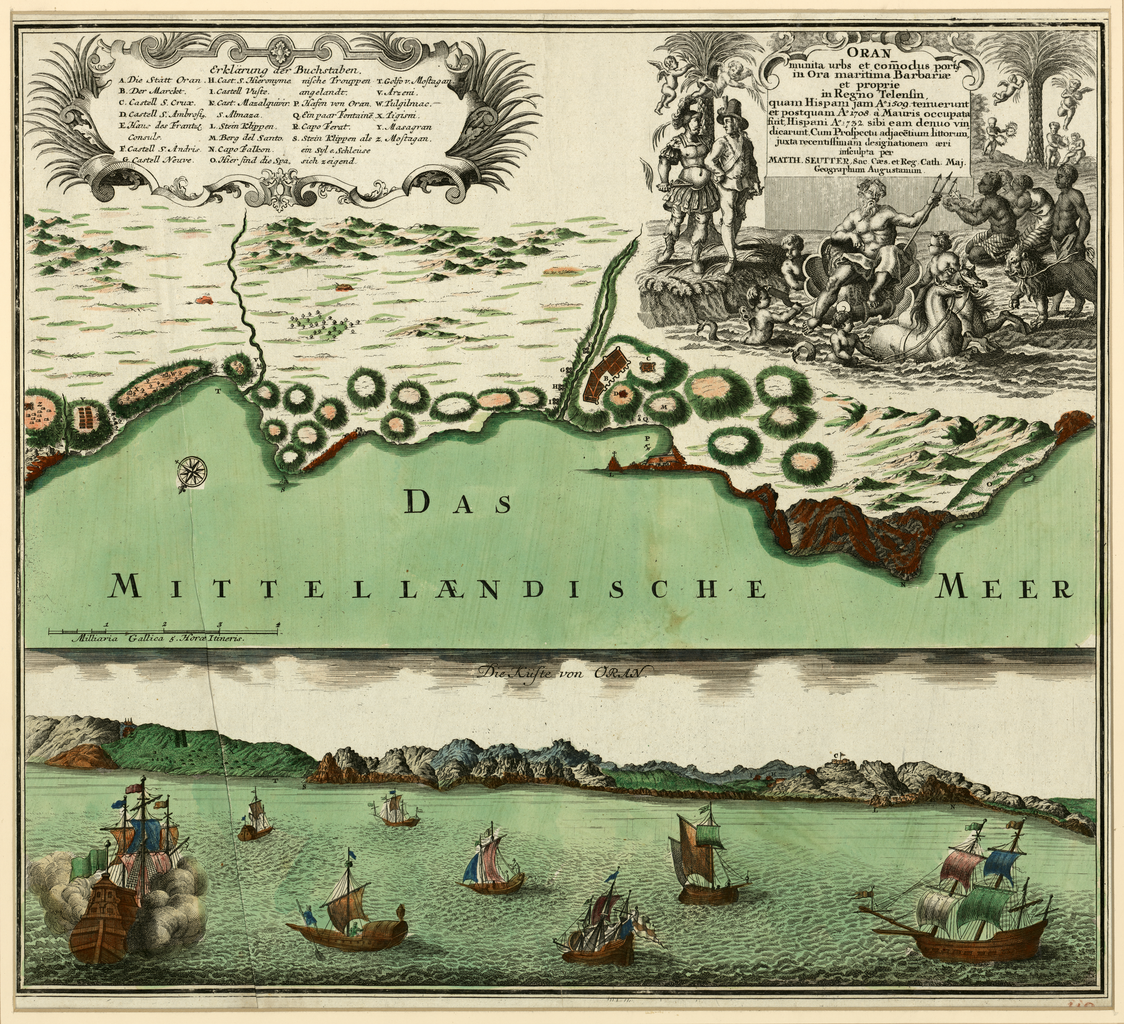 In April 1669 the Spanish governor, the 6th Marquess of Los Vأ©lez, expelled all the Jews who lived in Oran and
In April 1669 the Spanish governor, the 6th Marquess of Los Vأ©lez, expelled all the Jews who lived in Oran and
 The Spanish occupied the city until 1708, when the Bey of Mascara,
The Spanish occupied the city until 1708, when the Bey of Mascara,

 The town of 10,000 inhabitants was still in the possession of the
The town of 10,000 inhabitants was still in the possession of the
 Oran features a
Oran features a
 Since 2019, Oran have 18 communal dأ©lأ©gations (ex. districts) et les 83 quarters.
Since 2019, Oran have 18 communal dأ©lأ©gations (ex. districts) et les 83 quarters.
 El Hamri is a large and popular district in the center of Oran, known under French rule as Lamur. The football club Mouloudia d'Oran is found there.
Neighborhood streets
* Avenue of Lamur
* Street Captain-Rahou
* Sebbalet Ayada
* Place The Sahara
* Gahwat Ettoubi
* Street Staoueli
* Street Djemaa Gazouna
* Street Bougandoura
* Street Belhadri Smain
El Hamri is a large and popular district in the center of Oran, known under French rule as Lamur. The football club Mouloudia d'Oran is found there.
Neighborhood streets
* Avenue of Lamur
* Street Captain-Rahou
* Sebbalet Ayada
* Place The Sahara
* Gahwat Ettoubi
* Street Staoueli
* Street Djemaa Gazouna
* Street Bougandoura
* Street Belhadri Smain


 The Oranian metropolis comprises several
The Oranian metropolis comprises several 
 The city's public transportation is centered on the
The city's public transportation is centered on the
 The folk music Raأ¯ ("opinion" in Arabic), had its beginnings in Oran. This genre of music was formulated by shepherds in the 1930s through Arab and European influences. This music was surrounded by controversy due to women's key role in public performances of the music, as well as the hedonistic lyrics about love and alcohol. This led to strict governmental control in the area which led to arrests, injuries, and assassinations. Many notable Raأ¯ musicians (including Cheb Hasni, Khaled (musician), Cheb Khaled, and Rachid Taha) hail from Oran. The violinist Akim el Sikameya was also born in Oran. One of Oran's most famous emigrants is Yves Saint Laurent (designer), Yves Saint Laurent.
The folk music Raأ¯ ("opinion" in Arabic), had its beginnings in Oran. This genre of music was formulated by shepherds in the 1930s through Arab and European influences. This music was surrounded by controversy due to women's key role in public performances of the music, as well as the hedonistic lyrics about love and alcohol. This led to strict governmental control in the area which led to arrests, injuries, and assassinations. Many notable Raأ¯ musicians (including Cheb Hasni, Khaled (musician), Cheb Khaled, and Rachid Taha) hail from Oran. The violinist Akim el Sikameya was also born in Oran. One of Oran's most famous emigrants is Yves Saint Laurent (designer), Yves Saint Laurent.

 *Albert Camus' 1939 essay ''The Minotaur'' describes life in Oran.
*Albert Camus' 1947 novel ''The Plague (novel), The Plague'' presents a fictional tale of observations of a physician during the emergence and recession of bubonic plague in the 1940s in Oran.
*''El Gallardo Espaأ±ol'' (1615) by Miguel de Cervantes takes place in Oran.
*In the movie ''Casablanca (film), Casablanca'' (1942), the route for refugees fleeing to the Americas was Paris to Marseille, across the Mediterranean to Oran, then by train, auto or foot to Casablanca. If they acquired an exit visa, they went on to Lisbon from there.
*Paul Bowles' 1949 novel ''The Sheltering Sky'' mainly takes place in Oran.
*Part of Arturo Pأ©rez-Reverte's Capitأ،n Alatriste adventure novel, ''Corsarios de Levante'' (Pirates of the Levant, 2006), takes place in early 17th-century Oran. The action of the book occurs a few years after the forced expulsion of the last Moriscos (Spanish Christians of Muslim descent) from Valencia. Oran is featured as a sun-blasted North African military stronghold. Capitأ،n Diego Alatriste finds Oran to be manned by an impoverished garrison of Spanish Christians, living alongside Muslims (some fiercely loyal to Spain), and Sephardic Jews, descendants of refugees from the 1492 expulsions from Spain.
*In the ITV (TV network), ITV drama series ''Hornblower (TV series), Hornblower'', Lieutenant Hornblower is sent by Captain Pellew to Oran to obtain supplies, only to discover that the city was suffering from a bubonic plague epidemic.
*The heroine of Geraldine Brooks (writer), Geraldine Brooks' novel, ''Year of Wonders,'' emigrates to Oran after leaving her home village that was quarantined in 1666 due to the plague.
*Joann Sfar's graphic novel ''The Rabbi's Cat 2'' begins in Oran.
*Kamel Daoud's novel ''The Meursault Investigation'' is set in a bar in Oran.
*Albert Camus' 1939 essay ''The Minotaur'' describes life in Oran.
*Albert Camus' 1947 novel ''The Plague (novel), The Plague'' presents a fictional tale of observations of a physician during the emergence and recession of bubonic plague in the 1940s in Oran.
*''El Gallardo Espaأ±ol'' (1615) by Miguel de Cervantes takes place in Oran.
*In the movie ''Casablanca (film), Casablanca'' (1942), the route for refugees fleeing to the Americas was Paris to Marseille, across the Mediterranean to Oran, then by train, auto or foot to Casablanca. If they acquired an exit visa, they went on to Lisbon from there.
*Paul Bowles' 1949 novel ''The Sheltering Sky'' mainly takes place in Oran.
*Part of Arturo Pأ©rez-Reverte's Capitأ،n Alatriste adventure novel, ''Corsarios de Levante'' (Pirates of the Levant, 2006), takes place in early 17th-century Oran. The action of the book occurs a few years after the forced expulsion of the last Moriscos (Spanish Christians of Muslim descent) from Valencia. Oran is featured as a sun-blasted North African military stronghold. Capitأ،n Diego Alatriste finds Oran to be manned by an impoverished garrison of Spanish Christians, living alongside Muslims (some fiercely loyal to Spain), and Sephardic Jews, descendants of refugees from the 1492 expulsions from Spain.
*In the ITV (TV network), ITV drama series ''Hornblower (TV series), Hornblower'', Lieutenant Hornblower is sent by Captain Pellew to Oran to obtain supplies, only to discover that the city was suffering from a bubonic plague epidemic.
*The heroine of Geraldine Brooks (writer), Geraldine Brooks' novel, ''Year of Wonders,'' emigrates to Oran after leaving her home village that was quarantined in 1666 due to the plague.
*Joann Sfar's graphic novel ''The Rabbi's Cat 2'' begins in Oran.
*Kamel Daoud's novel ''The Meursault Investigation'' is set in a bar in Oran.
EasyOran
€” The Oran electronic guide
Visit Oran
€”Voted in 2007 as "Oran's best website" by the ministry of culture and Panoramic Tours. Mostly dedicated to tourism. Features photo galleries, short films, news, city guides & information, hotel info & reservation forms, forum...
Le Souk d'Oran
€”Oran student's community
Oran's Community FORUM
€”The Community Discussion Forum for Oran and tourism. *
Oran MAPS
—Detailed maps of the Oran Region and City. *
Oran-dz
{{Authority control Oran, Cities in Algeria Province seats of Algeria Coastal cities in Algeria Communes of Oran Province Mediterranean port cities and towns in Algeria Populated coastal places in Algeria Port cities of the Mediterranean Sea Former Spanish colonies Spanish Africa Populated places established in the 1st century 903 establishments 10th-century establishments in Africa
Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
. It is considered the second most important city of Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
after the capital Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, ط§ظ„ط¬ط²ط§ط¦ط±, al-Jazؤپت¾ir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques ...
, due to its population and commercial, industrial, and cultural importance. It is west-south-west from Algiers. The total population of the city was 803,329 in 2008, while the metropolitan area has a population of approximately 1,500,000 making it the second-largest city in Algeria.
Etymology
 The word ''Wahran'' comes from the Berber expression ''wa - iharan'' (place of lions). A locally popular legend tells that in the period around AD 900, there were sightings of Barbary lions in the area. The last two lions were killed on a mountain near Oran, and it became known as ''la montagne des lions'' ("The Mountain of Lions"). Two giant lion statues stand in front of Oran's city hall, symbolizing the city.
The word ''Wahran'' comes from the Berber expression ''wa - iharan'' (place of lions). A locally popular legend tells that in the period around AD 900, there were sightings of Barbary lions in the area. The last two lions were killed on a mountain near Oran, and it became known as ''la montagne des lions'' ("The Mountain of Lions"). Two giant lion statues stand in front of Oran's city hall, symbolizing the city.
History
Overview
During theRoman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, خ’خ±دƒخ¹خ»خµخ¯خ± د„ل؟¶خ½ ل؟¬د‰خ¼خ±خ¯د‰خ½, Basileأa tأ´n Rhإچmaأإچn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
, a small settlement called ''Unica Colonia'' existed in the area of current Oran, but this settlement disappeared after the Arab conquest of the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, ط§ظ„ظ’ظ…ظژط؛ظ’ط±ظگط¨, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, ط§ظ„ظ…ط؛ط±ط¨ ط§ظ„ط¹ط±ط¨ظٹ) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
.
Present-day Oran was founded in 903 by the azdaja and ajissa berbers of the Maghrawa confederation who lived the area and eventually founded the modern city of Oran. the city enjoyed a period of prosperity under the Almohad
The Almohad Caliphate (; ar, ط®ظگظ„ظژط§ظپظژط©ظڈ ظ±ظ„ظ’ظ…ظڈظˆظژطظگظ‘ط¯ظگظٹظ†ظژ or or from ar, ظ±ظ„ظ’ظ…ظڈظˆظژطظگظ‘ط¯ظڈظˆظ†ظژ, translit=al-Muwaل¸¥ل¸¥idإ«n, lit=those who profess the Tawhid, unity of God) was a North African Berbers, Berber M ...
Caliph Abd al-Mu'min
Abd al Mu'min (c. 1094–1163) ( ar, ط¹ط¨ط¯ ط§ظ„ظ…ط¤ظ…ظ† ط¨ظ† ط¹ظ„ظٹ or ط¹ط¨ط¯ ط§ظ„ظ…ظˆظ…ظ† ط§ظ„ظ€ظ€ظƒظ€ظˆظ…ظٹ; full name: ت؟Abd al-Muت¾min ibn ت؟Alؤ« ibn ت؟Alwؤ« ibn Yaت؟lؤپ al-Kإ«mؤ« Abإ« Muل¸¥ammad) was a prominent member of the Almohad move ...
for a lengthy period of time where he built thirty vessels to connect it with Andalasia. It endured a long, prosperous reign under the zayyanid of tlemcen and used their ports as a key out outlet to spain in particular. It was captured by the Castilians
Castilians (Spanish: ''castellanos'') are those people who live in certain former areas of the historical Kingdom of Castile, but the region's exact limits are disputed. A broader definition is to consider as Castilians the population belonging ...
under Cardinal Cisneros
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**''Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**''Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, the ...
in 1509, and Spanish sovereignty lasted until 1708, when the city was conquered by the Algerians during the siege of Siege of Oran (1707–1708)
The siege of Oran was a battle between the Spanish Empire and the Regency of Algiers. It was started by Mustapha Bouchelaghem, the Bey of Mascara. The Algerian victory in the battle led to the city being reconquered by the Algerians for 24 years ...
. Spain recaptured the city in 1732. However, its value as a trading post had decreased greatly, so during the reign of King Charles IV the city was recaptured in 1790-1792 by a coalition of Algerian troops against Spain which resulted in victory for the bey of Oran despite the many attempts in 1563. The beylik lasted until 1831, when the city fell to the French.
Under French rule during the 19th and 20th centuries, Oran was the capital of a ''dأ©partement
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (french: dأ©partement, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level ("territorial collectivity, territorial collectivities"), between the regions of France, admin ...
'' of the same name (number 92). In July 1940, the British navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
shelled French warships in the port after they refused a British ultimatum to surrender; this action was taken to ensure the fleet would not fall into German hands, as the Nazis
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Na ...
had defeated France and occupied Paris. The action increased the hatred of the Vichy regime for Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
but convinced the world that the British would fight on alone against Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
and its allies. The Vichy government
Vichy France (french: Rأ©gime de Vichy; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was the fascist French state headed by Marshal Philippe Pأ©tain during World War II. Officially independent, but with half of its terr ...
held Oran during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
until its capture by the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
in late 1942, during Operation Torch
Operation Torch (8 November 1942 – Run for Tunis, 16 November 1942) was an Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of French North Africa during the Second World War. Torch was a compromise operation that met the British objective of secu ...
.
Also, during French rule, Jews were encouraged to modernize and take on jobs they had not before including agriculture, while Muslims were forced out of the city and their ancestral fertile lands were confiscated and given to Colons. Jews In the city were allowed to join the French Army starting October 24, 1870, while Muslims were forced to do military service
Military service is service by an individual or group in an army or other militia, air forces, and naval forces, whether as a chosen job (volunteer) or as a result of an involuntary draft (conscription).
Some nations (e.g., Mexico) require a ...
. Algerian Jews were granted citizenship Algerian Muslims were not. French Jews would soon be targeted after not choosing to side with the Algerian Muslims who fought for independence against France.
Before the Algerian War
The Algerian War, also known as the Algerian Revolution or the Algerian War of Independence,( ar, ط§ظ„ط«ظˆط±ط© ط§ظ„ط¬ط²ط§ط¦ط±ظٹط© '; '' ber, Tagrawla Tadzayrit''; french: Guerre d'Algأ©rie or ') and sometimes in Algeria as the War of 1 November ...
, 1954–1962, Oran had one of the highest proportions of Europeans of any city in North Africa. In July 1962, after a ceasefire and accords with France, the FLN entered Oran and were shot at by a European. A mob attacked pied-noir
The ''Pieds-Noirs'' (; ; ''Pied-Noir''), are the people of French people, French and other White Africans of European ancestry, European descent who were born in Algeria during the French Algeria, period of French rule from 1830 to 1962; the v ...
neighborhoods in response to the attack and massacred
A massacre is the killing of a large number of people or animals, especially those who are not involved in any fighting or have no way of defending themselves. A massacre is generally considered to be morally unacceptable, especially when per ...
thousands of Europeans in Oran; 453 have been said to have "disappeared." This triggered a larger exodus of Europeans to France, which was already underway. Shortly after the end of the war, most of the European
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to:
In general
* ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe
** Ethnic groups in Europe
** Demographics of Europe
** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe ...
s and Algerian Jews
The History of the Jews in Algeria refers to the history of the Jewish community of Algeria, which dates to the 1st century CE. In the 15th century, many Spanish Jews fled to the Maghreb, including today's Algeria, following expulsion from Spai ...
living in Oran fled to France. In less than three months, Oran lost about half its population. This population loss is similar to the Jews as many fled after siding with France in the Algerian War for Independence. As the war progressed, those who supported independence in Algeria threatened those who sided with France causing these people to flee.
Religious history
With its location as the closest port to Spain and its prominence on the Mediterranean, Jewish refugees first immigrated to Oran to flee persecution and conversion to Christianity in Spain in 1391. This refuge brought other religious refugees that included both Jews again and Muslims in both 1492 and 1502. On October 24, 1870, with the French dominance, Algerian Jews were given French citizenship with theCrأ©mieux Decree
The Crأ©mieux Decree () was a law that granted French citizenship to the majority of the Jewish population in French Algeria (around 35,000), signed by the Government of National Defense on 24 October 1870 during the Franco-Prussian War. It was ...
. Later, despite a World War II sentiment that favored acceptance, Oran still had a history marked by intolerance. There was a decrease in the Jewish population as Muslims were the only group granted citizenship protection in 1963, one year after Algerian independence.
Islamic dynasties (910–1509)
Spanish period (1509–1708, 1732–1792)
 Before the Spaniards, the Portuguese launched a failed expedition to capture the city in July 1501. Four years later, the Spanish took Mers-el-Kأ©bir, located just west of Oran. Thus began the first organized incursions against the city which, at the time, numbered 25,000 inhabitants and counted 6,000 ''fueros''. Count
Before the Spaniards, the Portuguese launched a failed expedition to capture the city in July 1501. Four years later, the Spanish took Mers-el-Kأ©bir, located just west of Oran. Thus began the first organized incursions against the city which, at the time, numbered 25,000 inhabitants and counted 6,000 ''fueros''. Count Pedro Navarro
Pedro Navarro, Count of Oliveto (c. 1460 – 28 August 1528) was a Navarrese military engineer and general who participated in the War of the League of Cambrai. At the Battle of Ravenna in 1512 he commanded the Spanish and Papal infantry, but wa ...
, on the orders of Cardinal Francisco Jimأ©nez de Cisneros
Francisco Jimأ©nez de Cisneros, OFM (1436 – 8 November 1517), spelled Ximenes in his own lifetime, and commonly referred to today as simply Cisneros, was a Spanish cardinal, religious figure, and statesman. Starting from humble beginnings ...
, finally captured the city on May 17, 1509. The occupying forces set fire to the books and archives of the town.
By 1554, the Turks had reached Algiers. The governor of Oran, Count Alcaudete, allied himself with Moroccan Sultan Mohammed ash-Sheikh
''Mawlay'' Mohammed al-Shaykh al-Sharif al-Hassani ( ar, ظ…طظ…ط¯ ط§ظ„ط´ظٹط® ط§ظ„ط´ط±ظٹظپ ط§ظ„طط³ظ†ظٹ) known as Mohammed al-Shaykh ( ar, ظ…طظ…ط¯ ط§ظ„ط´ظٹط®) (b. 1490 – d. 23 October 1557) was the first sultan of the Saadian dynasty of Morocco ...
against them. Nine years later, in 1563, أپlvaro de Bazأ،n أپlvaro (, , ) is a Spanish, Galician and Portuguese male given name and surname (see Spanish naming customs) of Visigothic origin. Some claim it may be related to the Old Norse name Alfarr, formed of the elements ''alf'' "elf" and ''arr'' "warrio ...
, Marquis de Santa Cruz, built the fort of Santa-Cruz, strategically placed at the top of a mountain, l'Aأ¯dour, more than above the sea, directly to the west of the city. Pedro Garcerأ،n de Borja, Grand Master of the Order of Montesa
The Order of Montesa ( va, Ordre de Montesa, Aragonese and es, Orden de Montesa) is a Christian military order, territorially limited to the old Crown of Aragon. It was named after the castle of Montesa, its headquarters.
Templar background
T ...
, was captain of Oran when, on July 14, 1568, John of Austria
John of Austria ( es, Juan, link=no, german: Johann; 24 February 1547 – 1 October 1578) was the natural son born to Holy Roman Emperor Charles V late in life when he was a widower. Charles V met his son only once, recognizing him in a secret ...
(the illegitimate son of Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
and paternal half-brother of King Philip II Philip II may refer to:
* Philip II of Macedon (382–336 BC)
* Philip II (emperor) (238–249), Roman emperor
* Philip II, Prince of Taranto (1329–1374)
* Philip II, Duke of Burgundy (1342–1404)
* Philip II, Duke of Savoy (1438-1497)
* Philip ...
), led a flotilla
A flotilla (from Spanish, meaning a small ''flota'' (fleet) of ships), or naval flotilla, is a formation of small warships that may be part of a larger fleet.
Composition
A flotilla is usually composed of a homogeneous group of the same class ...
of 33 galleys against the Algerians.
 In April 1669 the Spanish governor, the 6th Marquess of Los Vأ©lez, expelled all the Jews who lived in Oran and
In April 1669 the Spanish governor, the 6th Marquess of Los Vأ©lez, expelled all the Jews who lived in Oran and Mers El Kأ©bir
Mers El Kأ©bir ( ar, ط§ظ„ظ…ط±ط³ظ‰ ط§ظ„ظƒط¨ظٹط±, translit=al-Marsؤپ al-Kabؤ«r, lit=The Great Harbor ) is a port on the Mediterranean Sea, near Oran in Oran Province, northwest Algeria. It is famous for the attack on the French fleet in 1940, in t ...
sending them to be resettled in either Nice
Nice ( , ; Niأ§ard: , classical norm, or , nonstandard, ; it, Nizza ; lij, Nissa; grc, خخ¯خ؛خ±خ¹خ±; la, Nicaea) is the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative c ...
, or Livorno
Livorno () is a port city on the Ligurian Sea on the western coast of Tuscany, Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Livorno, having a population of 158,493 residents in December 2017. It is traditionally known in English as Leghorn (pronou ...
.
The Spanish rebuilt Santa Cruz Fort to accommodate their city governors. "The fortifications of the place were composed of thick and continuous walls of over two and a half km in circumference, surmounted by strong towers spaced between them," with a central castle or ''kasbah
A kasbah (, also ; ar, ظ‚ظژظ€طµظژظ€ط¨ظژظ€ط©, qaل¹£aba, lit=fortress, , Maghrebi Arabic: ), also spelled qasba, qasaba, or casbah, is a fortress, most commonly the citadel or fortified quarter of a city. It is also equivalent to the term ''alca ...
'' where the Spanish governor had his headquarters. Under Spanish rule, the city continued to grow, requiring enlargement of the city walls. In spite of the improved fortifications, the city was the object of repeated attacks. Notable in this regard, Moroccan Sharif Moulay Ismail
Moulay Ismail Ibn Sharif ( ar, ظ…ظˆظ„ط§ظٹ ط¥ط³ظ…ط§ط¹ظٹظ„ ط¨ظ† ط§ظ„ط´ط±ظٹظپ), born around 1645 in Sijilmassa and died on 22 March 1727 at Meknes, was a Sultan of Morocco from 1672–1727, as the second ruler of the Alaouite dynasty. He was the se ...
tried to force his way past the defences in 1707, only to see his army decimated.
In 1739, trade with the surroundings was forbidden fop years due to the plague.
In 1744, king Philip V Philip V may refer to:
* Philip V of Macedon (221–179 BC)
* Philip V of France (1293–1322)
* Philip II of Spain, also Philip V, Duke of Burgundy (1526–1598)
* Philip V of Spain
Philip V ( es, Felipe; 19 December 1683 – 9 July 1746) was ...
asked the governor Tomأ،s du Rollet de la tour for dromedaries to replenish the stock at the Royal Palace of Aranjuez
The Royal Palace of Aranjuez ( es, Palacio Real de Aranjuez) is one of the official residences of the Spanish royal family. It is located in the town of Aranjuez (Madrid), Spain. Established in the 16th century as a royal hunting lodge, the pal ...
.
However, the former bey
Bey ( ota, ط¨ظƒ, beؤں, script=Arab, tr, bey, az, bة™y, tk, beg, uz, ذ±ذµذ؛, kz, ذ±ذ¸/ذ±ذµذ؛, tt-Cyrl, ذ±س™ذ؛, translit=bأ¤k, cjs, ذ؟ذ¸ذ¹/ذ؟ذµذ؛, sq, beu/bej, sh, beg, fa, ط¨غŒع¯, beyg/, tg, ذ±ذµذ؛, ar, ط¨ظƒ, bak, gr, خ¼د€خخ·د‚) is ...
of Oran had banned trade with the Spaniards and those dromedaries gradually sent to the king had been sold by thieving tribesmen.
Most of the maintenance of the place was paid by the bull of the Crusade
A crusade bull or crusading bull ( la, bulla cruciata) was a papal bull that granted privileges, including indulgences, to those who took part in the crusades against infidels.. A bull is an official document issued by a pope and sealed with a lea ...
, a contribution of the Spanish Catholic church.
Beylikal period (1708–1732, 1792–1831)
 The Spanish occupied the city until 1708, when the Bey of Mascara,
The Spanish occupied the city until 1708, when the Bey of Mascara, Mustapha Ben Youssef
Mustapha Bouchelaghem, also known as Bey Bouchelaghem was the Bey of the Western Beylik from 1686 to 1734/37.
Origins and early life
Mustapha, born as Mustapha ben Youcef was the son of an Algerian Arabic man called Youcef el-Mesrati, a noble ...
(''Bouchelaghem''), vassal of the Deylik of Algiers
The Regency of Algiers ( ar, ط¯ظˆظ„ط© ط§ظ„ط¬ط²ط§ط¦ط±, translit=Dawlat al-Jaza'ir) was a state in North Africa lasting from 1516 to 1830, until it was conquered by the French. Situated between the regency of Tunis in the east, the Sultanate o ...
, and who was an Arabized Berber
Arabized Berber denotes an inhabitant of the Maghreb region in western North Africa, whose native language is a local dialect of Arabic and whose ethnic origins are Berber.
Most populations in the Maghreb are of Berber heritage, including thos ...
from the Mascara region took advantage of the War of Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
to drive the Spanish out.
In 1732, Spanish forces returned under Josأ© Carrillo de Albornoz, capturing the city from Bouchelaghem. Spain maintained its hold over Oran for the next six decades.
In the night after October 8, 1790, a violent earthquake claimed more than 3,000 victims in less than seven minutes. Charles IV saw no advantage in continuing the occupation of the city, which had become increasingly expensive and perilous. He initiated discussions with the Dey of Algiers
Dey (Arabic: ط¯ط§ظٹ), from the Turkish honorific title ''dayؤ±'', literally meaning uncle, was the title given to the rulers of the Regency of Algiers (Algeria), Tripoli,Bertarelli (1929), p. 203. and Tunis under the Ottoman Empire from 1671 on ...
.
Siege of Oran and Mers el-Kأ©bir (1790-1792)
After another earthquake damaged the Spanish defences, the forces of the new Bey of Oran,Mohamed el-Kأ©bir
Muhammad was an Islamic prophet and a religious and political leader who preached and established Islam.
Muhammad and variations may also refer to:
*Muhammad (name), a given name and surname, and list of people with the name and its variations
...
besieged the city. By the end of 1790, there was a clear Algerian advantage. The Spanish, not wanting to risk their troops, signed an agreement with the Algerians on 12 September in Algiers, and on 12 December in Madrid
Madrid ( , ) is the capital and most populous city of Spain. The city has almost 3.4 million inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of approximately 6.7 million. It is the second-largest city in the European Union (EU), and ...
, which recognized Algerian control over the city. By February all Spanish troops evacuated. The capital was moved there the same year. In 1792, the Bey settled a Jewish community there. In 1796, the Pasha Mosque (in honour of Hassan Pasha, Beylerbey
''Beylerbey'' ( ota, ط¨ظƒظ„ط±ط¨ظƒغŒ, beylerbeyi, lit=bey of beys, meaning the 'commander of commanders' or 'lord of lords') was a high rank in the western Islamic world in the late Middle Ages and early modern period, from the Anatolian Seljuks ...
of Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, ط§ظ„ط¬ط²ط§ط¦ط±, al-Jazؤپت¾ir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques ...
) was built by the Bey with ransom money paid for the release of Spanish prisoners after Spain's final departure.
French period (1831–1962)

 The town of 10,000 inhabitants was still in the possession of the
The town of 10,000 inhabitants was still in the possession of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, ذخ¸د‰خ¼خ±خ½خ¹خ؛خ® خ‘د…د„خ؟خ؛دپخ±د„خ؟دپخ¯خ±, Othإچmanikؤ“ Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
when a squadron under the command of captain Bourmand seized el-Kأ©bir on December 14, 1830. The city was in a wretched state. On January 4, 1831, the French commanded by General Damrأ©mont occupied Oran.
In September 1831, General Berthezأ¨ne appointed Mr. Pujol as mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well a ...
of Oran; he had been captain of cavalry in retirement and was wounded in the right hand under the Empire.
In 1832, leading a force of five thousand men, the young Emir Abd al-Qadir
Abd al-Qadir or Abdulkadir ( ar, ط¹ط¨ط¯ ط§ظ„ظ‚ط§ط¯ط±) is a male Muslim given name. It is formed from the Arabic words '' Abd'', ''al-'' and '' Qadir''. The name means "servant of the powerful", ''Al-Qؤپdir'' being one of the names of God in the ...
attacked Oran. In April 1833, commander-in-chief, General Boyer, was replaced by the baron Louis Alexis Desmichels
Louis Alexis Desmichels, born in Digne March 15, 1779, died in Paris in 1845, was a French soldier, an ordinary soldier of the French Revolution became general under the July Monarchy, known for his role in the conquest of Algeria and relations w ...
. The city's defenders, under attack by Abd al Qadir, held their ground.
In World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, Oran was one of the landing points in Operation Torch
Operation Torch (8 November 1942 – Run for Tunis, 16 November 1942) was an Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of French North Africa during the Second World War. Torch was a compromise operation that met the British objective of secu ...
, the first American action in the Europe-North Africa theatre in November 1942. The Task Force suffered some damage to its fleet, trying to land in shallow water, but the enemy ships were sunk or driven off, and Oran surrendered after heavy fire from British battleships.Rohwer & Hummelchen 1992 p. 175.
Since independence (1962)
Due to the exodus ofPieds-Noirs
The ''Pieds-Noirs'' (; ; ''Pied-Noir''), are the people of French and other European descent who were born in Algeria during the period of French rule from 1830 to 1962; the vast majority of whom departed for mainland France as soon as Alger ...
, the Cathأ©drale du Sacrأ©-Cإ“ur d'Oran
Cathأ©drale du Sacrأ©-Cإ“ur d'Oran (''Sacred Heart Cathedral of Oran'') is a former Roman Catholic church located at Place de la Kahina, on Boulevard Hammou-boutlelis, in Oran, Algeria.
History
The church building was built between 1903 and 1913 ...
was converted into a public library in 1984. Further information: Aubert Library of Oran The Aubert Library is a library located in Oran, Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates ...
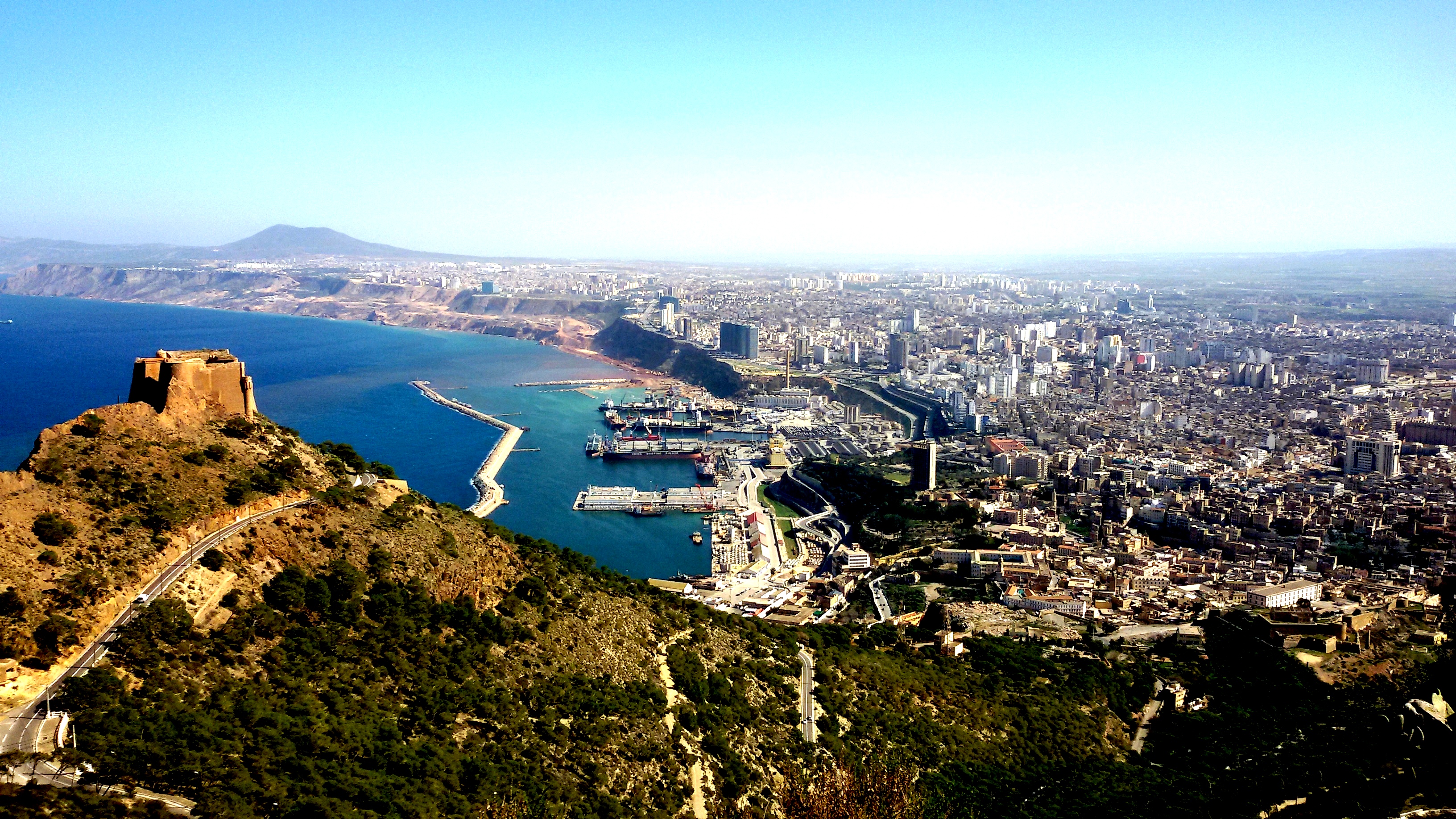
Today, Oran is a major port and a commercial centre, and has three universities. The old quarter of Oran has a casbah
A kasbah (, also ; ar, ظ‚ظژظ€طµظژظ€ط¨ظژظ€ط©, qaل¹£aba, lit=fortress, , Maghrebi Arabic: ), also spelled qasba, qasaba, or casbah, is a fortress
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territo ...
and an 18th-century mosque
A mosque (; from ar, ظ…ظژط³ظ’ط¬ظگط¯, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
. The modern section of Oran is referred to as La Ville Nouvelle and was built after 1831; this section contrasts with the older section, La Blanca.
Geography
Climate
 Oran features a
Oran features a semi-arid climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-ar ...
(Kأ¶ppen climate classification
The Kأ¶ppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Kأ¶ppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Kأ¶ppen, notabl ...
''BSk''/''BSh''). Oran's climate does show influences of a Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
; however, the combination of the city's relatively high average annual temperature and relatively low annual precipitation precludes it from falling under that climate category. Oran averages of precipitation annually, the bulk of which falls between November and May. Summers are the warmest times of the year, with average high temperatures in the warmest month (August) approaching 32 degrees Celsius. Winters are the coolest times of the year in Oran, with high temperatures in the coolest month (January) at around 17 degrees Celsius.
Earthquakes
As Oran is located in Northern Algeria, it faces the threat of earthquakes that can cause damage. However, the last major earthquake was in 1790; 3,000 people died as a result. Many of the existing older buildings in the city have been reinforced, and newer construction is designed to withstand earthquakes. While the city dates back to the 900s, the oldest remaining buildings are from the French period in the 1800s making it easier to reinforce these buildings.Government
City districts
List of districts of Oran
Medina Jedida
or, ''new city'' in English, is a large historical and popular district. It was one of the Muslim quarters during the French colonial period. In this district, there is one of the biggest markets in the country, called Le Marchأ© de Medina Jedida (Medina Jedida Market).El Hamri
 El Hamri is a large and popular district in the center of Oran, known under French rule as Lamur. The football club Mouloudia d'Oran is found there.
Neighborhood streets
* Avenue of Lamur
* Street Captain-Rahou
* Sebbalet Ayada
* Place The Sahara
* Gahwat Ettoubi
* Street Staoueli
* Street Djemaa Gazouna
* Street Bougandoura
* Street Belhadri Smain
El Hamri is a large and popular district in the center of Oran, known under French rule as Lamur. The football club Mouloudia d'Oran is found there.
Neighborhood streets
* Avenue of Lamur
* Street Captain-Rahou
* Sebbalet Ayada
* Place The Sahara
* Gahwat Ettoubi
* Street Staoueli
* Street Djemaa Gazouna
* Street Bougandoura
* Street Belhadri Smain
Sidi El Houari
The historical district is a suburb in the north of the d'Oran city. The Saint-Louis college is there, as well as the old mosque of the Pasha dating from the 17th century. In this district the skin of Saint-Patron of the city in the name of "Sidi El Houari
''Sidi'' or ''Sayidi'', also Sayyidi and Sayeedi, ( ar, ط³ظٹط¯ظٹ, Sayyؤ«dؤ«, Sؤ«dؤ« (dialectal) "milord") is an Arabic masculine title of respect. ''Sidi'' is used often to mean "saint" or "my master" in Maghrebi Arabic and Egyptian Arabic. Wi ...
" rests. Other tourist curiosities: one ancient prefecture of the data base Stalingrad, the Spanish vestiges dating from the 16th century, and especially the Palate of the Bey d'Oran.
Oranian agglomeration


 The Oranian metropolis comprises several
The Oranian metropolis comprises several communes
An intentional community is a voluntary residential community which is designed to have a high degree of social cohesion and teamwork from the start. The members of an intentional community typically hold a common social, political, religious, ...
.
Mers El-Kأ©bir
Mers El Kأ©bir
Mers El Kأ©bir ( ar, ط§ظ„ظ…ط±ط³ظ‰ ط§ظ„ظƒط¨ظٹط±, translit=al-Marsؤپ al-Kabؤ«r, lit=The Great Harbor ) is a port on the Mediterranean Sea, near Oran in Oran Province, northwest Algeria. It is famous for the attack on the French fleet in 1940, in t ...
("The Great Port") is a municipality northwest of Oran, about from the city centre. As its name indicates, it is a major port and has an important naval base, home to the Algerian Navy.
Aأ¯n El-Turk
Aأ¯n El Turk ("Fountain of the Turks") is also northwest of Oran, at a distance of . It is a seaside town which includes several hotels and other tourist attractions.Es-Sأ©nia
Es Sأ©nia
Es Sأ©nia ( ar, ط§ظ„ط³ط§ظ†ظٹط©) (formerly La Sأ©nia) is a municipality in Oran Province, Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital ...
, located in the south of Oran, is home to industrial parks, several university institutes (Oran-Es-Sأ©nia University, Institut of Communication, ENPO "National Polytechnic School of Oran", CRASC "Research center in social sciences" etc.) and the international airport.
Bir El-Djir
Bir El Djir
Bir El Djir is a town located close north-east of Oran in the Oran Province, Algeria. According to the 2009 census it has a population of 171,883.
University
Bir El Djir hosts the University of Oran 2 Mohamed Ben Ahmed
2022 Mediterranean Game ...
is a commune that represents the suburbs of Oran (apart from the districts). It is the future beating heart of the Oranian agglomeration. It has several buildings which are the seats of institutions as the headquarters of Sonatrach
Sonatrach ( ar, ط³ظˆظ†ط§ط·ط±ط§ظƒ; french: Sociأ©tأ© Nationale pour la Recherche, la Production, le Transport, la Transformation, et la Commercialisation des Hydrocarbures) is the national state-owned oil company of Algeria. Founded in 1963, it is ...
's downstream activity, the hospital ''أ‰tablissement Hospitalo-universitaire'' "November 1st, 1954", the convention center (Palais des Congrأ¨s), University of sciences and technology (conceived by the Japanese architect Kenzإچ Tange
was a Japanese architect, and winner of the 1987 Pritzker Prize for architecture. He was one of the most significant architects of the 20th century, combining traditional Japanese styles with modernism, and designed major buildings on five cont ...
), the Institute of medical sciences, the Court of Justice and the National Centre of Research in Social and Cultural Anthropology
The National Centre of Research in Social and Cultural Anthropology (french: Centre national de recherche en anthropologie sociale et culturelle, CRASC) is an Algerian governmental research organisation in social sciences created by the decree 92 ...
. There is as well a stadium with a capacity of 50000 places under construction.
Bir El Djir is an urban extension east of Oran, from the city center, with a population of 118,000 inhabitants.
Misserghin
Misserghin
Misserghin is a city in Boutlأ©lis District, Oran Province, Algeria. Its territory is mainly covered by a salt lake called the ''Sebkha of Oran''.
In city, the known fruit clementine were discovered by Father Clأ©ment Rodier in 1892.
Dr. Chأ©rif ...
is a small city located to the southwest of Oran.
Transportation
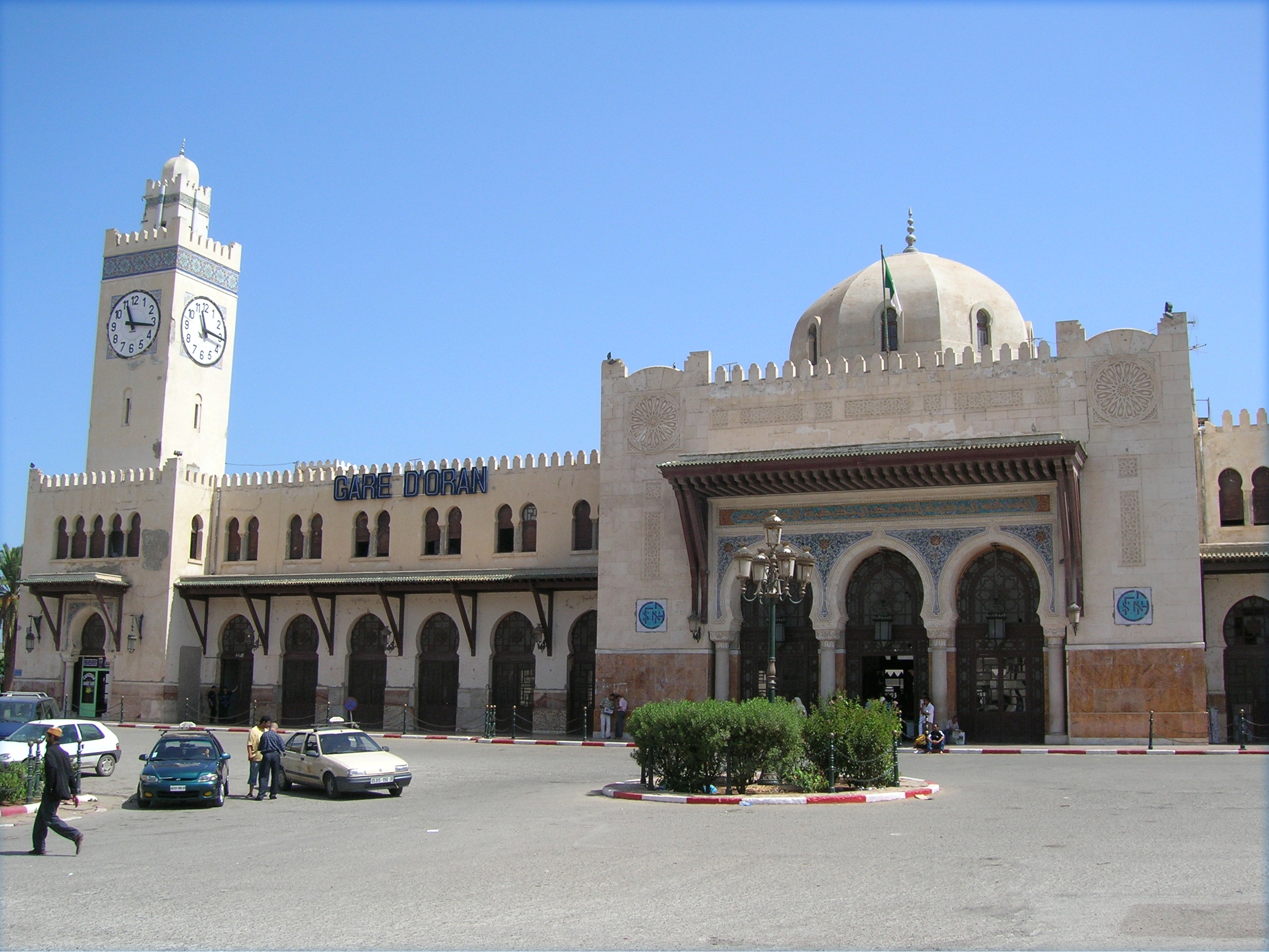
 The city's public transportation is centered on the
The city's public transportation is centered on the Oran Metro
The Oran Metro (Arab : ''ظ…طھط±ظˆ ظˆظ‡ط±ط§ظ†'') is planned to be an extensive network of rapid transit electrified railway lines that will run mostly underground in central Oran and into the city's suburbs. It will be part of the larger public ...
covering coastal neighborhoods with the connecting Oran tramway covering suburbs not yet served by the metro. There is an extensive network of "clandestine" taxis in the City. A project started in 2008/9 and lasted approximately two to three years, to deliver the first line of the tramway in 2010. It should comprise 31 stations over a distance of going to Es-Sأ©nia, in the South and Sidi Maarouf in the east side, while passing by the centre town The tramway should serve Haأ¯ Sabbah, University of Sciences and Technology (USTO), the Crossroads of the Three Private clinics, the Law courts, Dar El Baأ¯da, the Plate-Saint Michel, the Place of the 1st November, Saint-Anthony, Boulanger, Saint-Hubert, the 3rd Ring road and finally The University of Es-Sأ©nia. The Ahmed Ben Bella Airport
Ahmed Ben Bella Airport ( ar, ظ…ط·ط§ط± ط£طظ…ط¯ ط¨ظ† ط¨ظ„ط©), formally Es-Sأ©nia Airport is an airport located 4.7 nautical mile, nm (8.7 km) south of Oran (near Es Sأ©nia), in Algeria.
History
During World War II, La Sأ©nia Airport was f ...
, also known as Es-Senia Airport, serves both domestic and international flights, with frequent connections to the capital Algiers, served by the public airline company Air Algأ©rie, Air Algerie. The same company also has flights to many French cities (Marseille, Paris, Lyon, etc.) and other European and EMEA cities. The Es Senia Airport also serves passengers from most smaller towns in proximity to Oran (Sig, Mostaganem, Arzew, etc.). The airport building is a fairly limited construction and does not operate on a 24-h basis.
Sports
Oran held its first international marathon on November 10, 2005. The event, sponsored by Toyota of Algeria, attracted runners from Morocco, Libya, Spain, France and Kenya. The marathon served to publicize the health benefits of running and to provide a novel form of public entertainment for the city's residents. The Championnat d'Afrique d'Athlأ©tisme was scheduled to be held in Oran in June 2021. The 2021 Mediterranean Games, XIX Mediterranean Games was held in Oran in 2022.Culture
 The folk music Raأ¯ ("opinion" in Arabic), had its beginnings in Oran. This genre of music was formulated by shepherds in the 1930s through Arab and European influences. This music was surrounded by controversy due to women's key role in public performances of the music, as well as the hedonistic lyrics about love and alcohol. This led to strict governmental control in the area which led to arrests, injuries, and assassinations. Many notable Raأ¯ musicians (including Cheb Hasni, Khaled (musician), Cheb Khaled, and Rachid Taha) hail from Oran. The violinist Akim el Sikameya was also born in Oran. One of Oran's most famous emigrants is Yves Saint Laurent (designer), Yves Saint Laurent.
The folk music Raأ¯ ("opinion" in Arabic), had its beginnings in Oran. This genre of music was formulated by shepherds in the 1930s through Arab and European influences. This music was surrounded by controversy due to women's key role in public performances of the music, as well as the hedonistic lyrics about love and alcohol. This led to strict governmental control in the area which led to arrests, injuries, and assassinations. Many notable Raأ¯ musicians (including Cheb Hasni, Khaled (musician), Cheb Khaled, and Rachid Taha) hail from Oran. The violinist Akim el Sikameya was also born in Oran. One of Oran's most famous emigrants is Yves Saint Laurent (designer), Yves Saint Laurent.
Cuisine
The traditional Algerian lemon sorbet creponne originated in Oran.Representation in other media

 *Albert Camus' 1939 essay ''The Minotaur'' describes life in Oran.
*Albert Camus' 1947 novel ''The Plague (novel), The Plague'' presents a fictional tale of observations of a physician during the emergence and recession of bubonic plague in the 1940s in Oran.
*''El Gallardo Espaأ±ol'' (1615) by Miguel de Cervantes takes place in Oran.
*In the movie ''Casablanca (film), Casablanca'' (1942), the route for refugees fleeing to the Americas was Paris to Marseille, across the Mediterranean to Oran, then by train, auto or foot to Casablanca. If they acquired an exit visa, they went on to Lisbon from there.
*Paul Bowles' 1949 novel ''The Sheltering Sky'' mainly takes place in Oran.
*Part of Arturo Pأ©rez-Reverte's Capitأ،n Alatriste adventure novel, ''Corsarios de Levante'' (Pirates of the Levant, 2006), takes place in early 17th-century Oran. The action of the book occurs a few years after the forced expulsion of the last Moriscos (Spanish Christians of Muslim descent) from Valencia. Oran is featured as a sun-blasted North African military stronghold. Capitأ،n Diego Alatriste finds Oran to be manned by an impoverished garrison of Spanish Christians, living alongside Muslims (some fiercely loyal to Spain), and Sephardic Jews, descendants of refugees from the 1492 expulsions from Spain.
*In the ITV (TV network), ITV drama series ''Hornblower (TV series), Hornblower'', Lieutenant Hornblower is sent by Captain Pellew to Oran to obtain supplies, only to discover that the city was suffering from a bubonic plague epidemic.
*The heroine of Geraldine Brooks (writer), Geraldine Brooks' novel, ''Year of Wonders,'' emigrates to Oran after leaving her home village that was quarantined in 1666 due to the plague.
*Joann Sfar's graphic novel ''The Rabbi's Cat 2'' begins in Oran.
*Kamel Daoud's novel ''The Meursault Investigation'' is set in a bar in Oran.
*Albert Camus' 1939 essay ''The Minotaur'' describes life in Oran.
*Albert Camus' 1947 novel ''The Plague (novel), The Plague'' presents a fictional tale of observations of a physician during the emergence and recession of bubonic plague in the 1940s in Oran.
*''El Gallardo Espaأ±ol'' (1615) by Miguel de Cervantes takes place in Oran.
*In the movie ''Casablanca (film), Casablanca'' (1942), the route for refugees fleeing to the Americas was Paris to Marseille, across the Mediterranean to Oran, then by train, auto or foot to Casablanca. If they acquired an exit visa, they went on to Lisbon from there.
*Paul Bowles' 1949 novel ''The Sheltering Sky'' mainly takes place in Oran.
*Part of Arturo Pأ©rez-Reverte's Capitأ،n Alatriste adventure novel, ''Corsarios de Levante'' (Pirates of the Levant, 2006), takes place in early 17th-century Oran. The action of the book occurs a few years after the forced expulsion of the last Moriscos (Spanish Christians of Muslim descent) from Valencia. Oran is featured as a sun-blasted North African military stronghold. Capitأ،n Diego Alatriste finds Oran to be manned by an impoverished garrison of Spanish Christians, living alongside Muslims (some fiercely loyal to Spain), and Sephardic Jews, descendants of refugees from the 1492 expulsions from Spain.
*In the ITV (TV network), ITV drama series ''Hornblower (TV series), Hornblower'', Lieutenant Hornblower is sent by Captain Pellew to Oran to obtain supplies, only to discover that the city was suffering from a bubonic plague epidemic.
*The heroine of Geraldine Brooks (writer), Geraldine Brooks' novel, ''Year of Wonders,'' emigrates to Oran after leaving her home village that was quarantined in 1666 due to the plague.
*Joann Sfar's graphic novel ''The Rabbi's Cat 2'' begins in Oran.
*Kamel Daoud's novel ''The Meursault Investigation'' is set in a bar in Oran.
Economy and infrastructure
Oran has become a major trading centre for the wider area, serving Arzew, the area's oil/gas port as well as Sonatrach, the country's biggest oil and gas company. Sonelgaz has built a new congress centre in Oran and in 2010 the 16th International Conference & Exhibition on Liquefied natural gas, Liquefied Natural Gas was held in the city of Oran, which attracted around 3,000 visitors and major companies from around the world. To accommodate all visitors, new hotels are currently being constructed and floating hotels will be used in the future. With a growth in urbanization, water quality and management is being harmed in Oran; this change in water quality is affecting marine life and the state of beaches in this tourism driven city. The city and region participates in the R20 Regions of Climate Action, with goals focused on reduced waste valorization and energy efficiency.Tourism
Oran has numerous hotels in all categories, from luxury to basic, as well as many restaurants offering Algerian specialities and other foods. Tourists will also find a variety of cinemas, arts centres, the regional theatre, an open-air theatre, the Museum, the historic city centre of Oran, the district of Sidi El Houari, the municipal gardens, Mأ©dina Djedida with its artisanal products, the cathedral, Djebel Murdjadjo, and nearby seaside resorts.Ahmed Ben Bella Airport
Ahmed Ben Bella Airport ( ar, ظ…ط·ط§ط± ط£طظ…ط¯ ط¨ظ† ط¨ظ„ط©), formally Es-Sأ©nia Airport is an airport located 4.7 nautical mile, nm (8.7 km) south of Oran (near Es Sأ©nia), in Algeria.
History
During World War II, La Sأ©nia Airport was f ...
is from the town centre. One can also reach Oran by ferries from the ports of Marseilles, Sأ¨te, Alicante and Almerأa, via the national company Algأ©rie Ferries. The Great Mosque is another attraction for tourists. The Great Mosque was built in 1796 to celebrate the end of Spanish rule of the city.
Attractions
The main museum in Oran is called Ahmed Zabana National Museum, Musأ©e National Ahmend Zabana. Although often overlooked by tourists, it includes a natural history exhibit in addition to art pieces like mosaics and portraits. Bey's Palace is another favorite spot for tourists, situated in Sidi al-Houari in the city center. It is an Ottoman era palace built of Islamic architecture, consists of harem, guard towers and stucco-painted halls.Water
Water supply in Oran has historically been stressed because of the lack of consistent rainfall. The regional government invested in hydraulic projects in the 2010s to increase retention of water, and installing a desalination plant increased water security. Oran's region uses a mix of groundwater (11%), surface water (51%) and desalinization (38%). The wilaya of Oran is also equipped with five desalination plants, including the unit of Macta, with a maximum daily capacity of 500,000 mآ³.International relations
Twin towns – sister cities
Oran is twin towns and sister cities, twinned with 21 cities: * Alicante, Spain * Bizerte, Tunisia * Bordeaux, France (2003) * Cairo, Egypt * Casablanca, Morocco (1999) * Dakar, Senegal * Durban, South Africa eThekwini Online: The Official Site of the City of Durban * Elche, Spain * Gdaإ„sk, Poland * Havana, Cuba * Jeddah, Saudi Arabia * Leicester, England (2001) * Lyon, France * Metz, France * Oujda, Morocco * Rangpur, Bangladesh, Rangpur, Bangladesh * Seoul, South Korea * Sfax, Tunisia (1989) * Strasbourg, France (2013) * Toulon, France * Zarqa, JordanPartner cities
In addition, Oran has partnerships and cooperation with one city: * Strasbourg, France (2013)Notable residents
Below the list of some of many notable personalities of Oran: *Kaddour Bekhloufi (1934-2019), played international football for FLN football team *Miloud Mourad Benamara (born 1977), actor *Jean Benguigui 1944, French Actor *Pierre Bأ©nichou (1938-2020), French journalist *Sirat Boumediأ¨ne (1947-1995), actor *Hamou Boutlأ©lis (1920-1957), nationalist militant forAlgerian War
The Algerian War, also known as the Algerian Revolution or the Algerian War of Independence,( ar, ط§ظ„ط«ظˆط±ط© ط§ظ„ط¬ط²ط§ط¦ط±ظٹط© '; '' ber, Tagrawla Tadzayrit''; french: Guerre d'Algأ©rie or ') and sometimes in Algeria as the War of 1 November ...
*Albert Camus (1913-1960), French philosopher, author, and journalist
*Alain Chabat (born 1958), French actor, director, screenwriter, producer and TV presenter
*أ‰tienne Daho (born 1956), French singer
*Habib Draoua (1914-2008), co-founder of the ALN football team
*Sidi El Houari
''Sidi'' or ''Sayidi'', also Sayyidi and Sayeedi, ( ar, ط³ظٹط¯ظٹ, Sayyؤ«dؤ«, Sؤ«dؤ« (dialectal) "milord") is an Arabic masculine title of respect. ''Sidi'' is used often to mean "saint" or "my master" in Maghrebi Arabic and Egyptian Arabic. Wi ...
(1350-1439), imam and patron saint of the city of Oran
*Jean-Pierre Elkabbach (born 1937), French journalist
*Maurice El Mediouni (born 1928), pianist, composer and interpreter of Andalusian, Raأ¯, Sephardic and Arab music
*Miloud El Mehadj (1909-2001), imam, writer and ulama
*Tayeb El Mehadj (1881-1969), imam and ulama
*Kader Firoud (1919-2005), professional footballer and manager
*Henri Fouques-Duparc (1903-1976), French politician, deputy and mayor of Oran
*Miloud Hadefi (1949-1994), international footballer and manager
*Abderrahmane Hadj-Salah (1928-2017), linguist
*Caأ¯da Halima (1859-1944), great personality and business woman
*Cheb Hasni (1968-1994), Raأ¯ singer
*Blaoui Houari (1926-2017), singer-songwriter, composer and conductor
*Khaled (singer), Khaled (born 1960), prominent Raأ¯ singer and multi-instrumentalist
*Mustapha Moussa (born 1962), former boxer, first Algerian Olympic medalist
*Armand Mouyal (1925–88), French world champion أ©pأ©e fencer
*Ahmed Saber (1937-1969), singer-songwriter, composer, conductor and actor
*Yves Saint Laurent (designer), Yves Saint Laurent (1936–2008), French fashion designer
*Henri Stambouli (born 1961), former footballer and current manager
*Ahmed Wahby (1921-1993), singer-songwriter, composer and conductor
*Ahmed Zabana (1926-1956), nationalist militant who participated in the outbreak of the Algerian War
*Belkacem Zeddour Mohamed Brahim (1923-1954), nationalist activist for Algerian War
See also
* European enclaves in North Africa before 1830References
Bibliography
External links
EasyOran
€” The Oran electronic guide
Visit Oran
€”Voted in 2007 as "Oran's best website" by the ministry of culture and Panoramic Tours. Mostly dedicated to tourism. Features photo galleries, short films, news, city guides & information, hotel info & reservation forms, forum...
Le Souk d'Oran
€”Oran student's community
Oran's Community FORUM
€”The Community Discussion Forum for Oran and tourism. *
Oran MAPS
—Detailed maps of the Oran Region and City. *
Oran-dz
{{Authority control Oran, Cities in Algeria Province seats of Algeria Coastal cities in Algeria Communes of Oran Province Mediterranean port cities and towns in Algeria Populated coastal places in Algeria Port cities of the Mediterranean Sea Former Spanish colonies Spanish Africa Populated places established in the 1st century 903 establishments 10th-century establishments in Africa