Ophthalmic Solution on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Eye drops or eyedrops are
Eye drops or eyedrops are
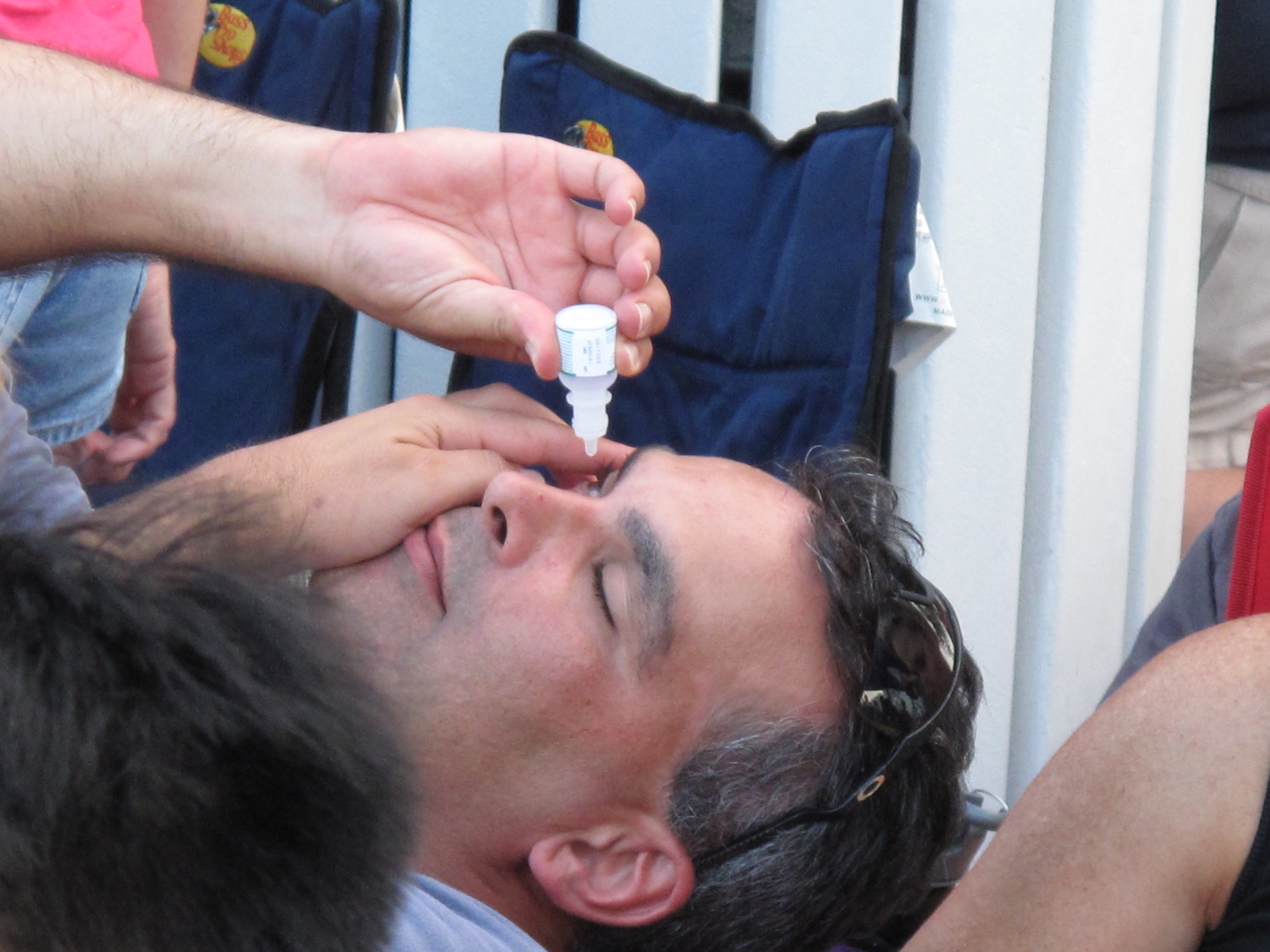 Steroid and antibiotic eye drops may cause stinging for one or two minutes when first used and if stinging continues, medical advice should be sought. Also, one should tell their doctor if vision changes occur or if they experience persistent sore throat, fever, easy bleeding or bruising when using drops with
Steroid and antibiotic eye drops may cause stinging for one or two minutes when first used and if stinging continues, medical advice should be sought. Also, one should tell their doctor if vision changes occur or if they experience persistent sore throat, fever, easy bleeding or bruising when using drops with

 Eye drops or eyedrops are
Eye drops or eyedrops are liquid drops
A drop or droplet is a small column of liquid, bounded completely or almost completely by free surfaces. A drop may form when liquid accumulates at the lower end of a tube or other surface boundary, producing a hanging drop called a pendant d ...
applied directly to the surface of the eye
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and conv ...
usually in small amounts such as a single drop or a few drops. Eye drops usually contain saline
Saline may refer to:
* Saline (medicine), a liquid with salt content to match the human body
* Saline water, non-medicinal salt water
* Saline, a historical term (especially US) for a salt works or saltern
Places
* Saline, Calvados, a commune in ...
to match the salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
of the eye. Drops containing only saline and sometimes a lubricant are often used as artificial tears to treat dry eyes or simple eye irritation
The human eye is a sensory organ, part of the sensory nervous system, that reacts to visible light and allows humans to use visual information for various purposes including seeing things, keeping balance, and maintaining circadian rhythm.
T ...
such as itching or redness
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a second ...
. Eye drops may also contain one or more medications to treat a wide variety of eye diseases. Depending on the condition being treated, they may contain steroids
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
, antihistamines, sympathomimetic
Sympathomimetic drugs (also known as adrenergic drugs and adrenergic amines) are stimulant compounds which mimic the effects of endogenous agonists of the sympathetic nervous system. Examples of sympathomimetic effects include increases in hea ...
s, beta receptor blockers, parasympathomimetics, parasympatholytic A parasympatholytic agent is a substance or activity that reduces the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system. (The parasympathetic nervous system is often colloquially described as the "Feed and Breed" or "Rest and Digest" portion of the aut ...
s, prostaglandin
The prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derive ...
s, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
s (NSAIDs), antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
s, antifungals, or topical anesthetics.
Eye drops have less of a risk of side effects than do oral medicines, and such risk can be minimized by occluding the lacrimal punctum (i.e. pressing on the inner corner of the eye) for a short while after instilling drops.
Prior to the development of single-use pre-loaded sterile plastic applicators, eye drops were administered using an eye dropper, a glass pipette with a rubber bulb.
Shelf life
Although most bottles of eye drops contain preservatives to inhibit contamination once opened, these will not prevent contamination indefinitely. Ophthalmologists recommend keeping bottles for no longer than three months after opening. Eye drops that contain no preservatives are usually packaged in single-use tubes. Dispensers typically oversize the drops; the human eye can only handle about 25 microlitres.Types and uses
Different pharmacological classes of eye drops can be recognized by patients by their different colored tops. For instance, the tops to dilating drops are a different color than anti-allergy drops.Dry eyes
Eyes drops sometimes do not have medications in them and are only lubricating and tear-replacing solutions. There is a wide variety of artificial tear eye drops that provide different surface healing strategies. One can find bicarbonate ions, hypotonicity, high viscosity gels and ointments, and non-preserved types. They all act differently and therefore, one may have to try different artificial tears to find the one that works the best.Steroid and antibiotic eye drops
Steroid and antibiotic eye drops are used to treat eye infections. They also have prophylactic properties and are used to prevent infections after eye surgeries. They should be used for the entire time prescribed without interruptions. The infection may relapse if the use of the medication is stopped.Pink eye
Antibiotic eye drops are prescribed when infection conjunctivitis is caused by bacteria but not when it is caused by a virus. In the case of allergic conjunctivitis, artificial tears can help dilute irritating allergens present in the tear film.Allergies
Some eye drops may contain histamine antagonists ornonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
(NSAIDs), which suppress the optical mast cell responses to allergens including (but not limited to) aerosolized dust particles.
Glaucoma
Eye drops used in managing glaucoma help the eye'sfluid
In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that continuously deforms (''flows'') under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are substances which cannot resist any shear ...
to drain better and decrease the amount of fluid made by the eye which decreases eye pressure. They are classified by their active ingredient and they include: prostaglandin analogs
Prostaglandin analogues are a class of drugs that bind to a prostaglandin receptor.
Wider use of prostaglandin analogues is limited by unwanted side effects and their abortive potential.
Uses
Prostaglandin analogues such as misoprostol are used ...
, beta blockers, alpha agonists, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. There are also combination drugs available for those patients who require more than one type of medication.
Mydriatic eye drops
These make the eye's pupil widen to maximum, to let anoptometrist
Optometry is a specialized health care profession that involves examining the eyes and related structures for defects or abnormalities. Optometrists are health care professionals who typically provide comprehensive primary eye care.
In the Uni ...
have the best view inside the eyeball behind the iris. Afterwards in sunny weather they can cause dazzling and photophobia until the effect of the mydriatic has worn off.
In some countries including Russia and Italy, Tropicamide, a mydriatic eye drop, is used to some degree as an inexpensive recreational drug. Like other anticholinergics, when taken recreationally, tropicamide acts as a deliriant. When injected intravenously, as is most often the case, the tropicamide may cause problems such as slurred speech, unconsciousness, unresponsiveness, hallucinations, kidney pain, dysphoria, hyperthermia, tremors, suicidal tendency, convulsions, psychomotor agitation, tachycardia and headache.
Injectable medication
Syringe designed saline drops (e.g. Wallace Cameron Ultra Saline Minipod) are distributed in modern needle-exchange programmes as they can be used efficiently either by injection or ophthalmic (if the drug is potent in small doses) route of administer which is compared to intravenous use; by demonstration, the elimination of latanoprost acid from plasma is rapid (half-life 17 minutes) after either ophthalmic or intravenous administration.Side effects
 Steroid and antibiotic eye drops may cause stinging for one or two minutes when first used and if stinging continues, medical advice should be sought. Also, one should tell their doctor if vision changes occur or if they experience persistent sore throat, fever, easy bleeding or bruising when using drops with
Steroid and antibiotic eye drops may cause stinging for one or two minutes when first used and if stinging continues, medical advice should be sought. Also, one should tell their doctor if vision changes occur or if they experience persistent sore throat, fever, easy bleeding or bruising when using drops with chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by injection into a vein, it is used to treat meningitis, plague, cholera, a ...
. Also, one should be aware of symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as: rash, itching, swelling, dizziness, and trouble breathing. Long term steroid use can cause many adverse effects including steroid-induced glaucoma and cataract.
Prostaglandin analogs may cause changes in iris color and eyelid skin, growth of eyelashes, stinging, blurred vision
Blurred vision is an ocular symptom where vision becomes less precise and there is added difficulty to resolve fine details.
Temporary blurred vision may involve dry eyes, eye infections, alcohol poisoning, hypoglycemia, or low blood pressure. ...
, eye redness, itching, and burning. Beta blockers' side effects include low blood pressure, reduced pulse rate
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the nec ...
, fatigue
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve ...
, shortness of breath, and in rare occasions, reduced libido and depression. Alpha agonists can cause burning or stinging, fatigue, headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
, drowsiness, dry mouth and nose, and also they have a higher likelihood of allergic reaction. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors may cause stinging, burning, and eye discomfort.
Lubricant eye drops may cause some side effects and one should consult a doctor if pain in the eye or changes in vision occur. Furthermore, when redness occurs but lasts more than 3 days, one should immediately consult a doctor.
See also
* Artificial tears * Carboxymethyl cellulose *Mydriasis
Mydriasis is the dilation of the pupil, usually having a non-physiological cause, or sometimes a physiological pupillary response. Non-physiological causes of mydriasis include disease, trauma, or the use of certain types of drugs.
Normally, as ...
* Refractive error
* Tetrahydrozoline hydrochloride
* Visine
References
External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Eye Drop Dosage forms Drug delivery devices Ophthalmology drugs Ophthalmic drug administration