Olorotitan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Olorotitan'' was a
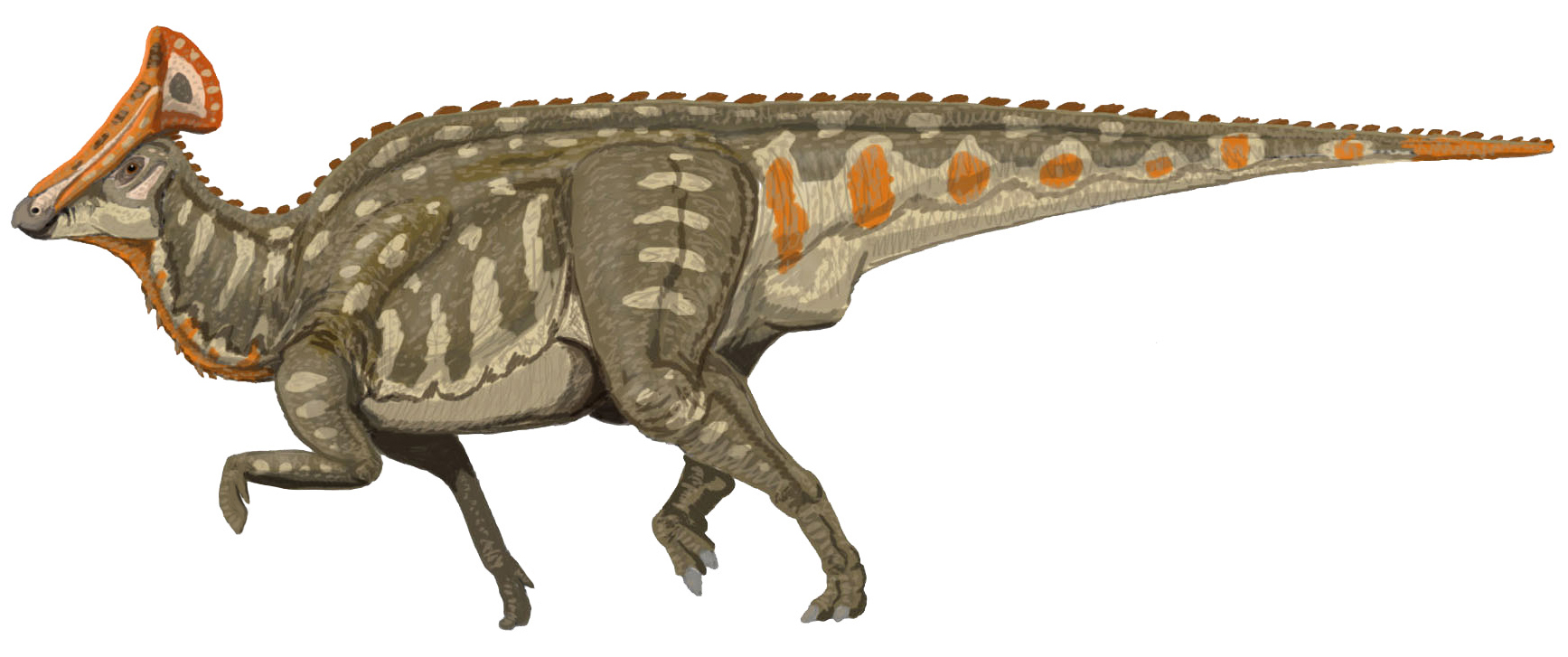 It is characterized by the large hatchet-like hollow crest adorning its skull, very distinct from the crests of all of its North American relatives. The skull itself was supported by a rather elongated neck, having eighteen
It is characterized by the large hatchet-like hollow crest adorning its skull, very distinct from the crests of all of its North American relatives. The skull itself was supported by a rather elongated neck, having eighteen
 ''O. arharensis'' shared its time and place with several other types of animal, including two other lambeosaurines: the ''
''O. arharensis'' shared its time and place with several other types of animal, including two other lambeosaurines: the ''
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
of lambeosaurine
Lambeosaurinae is a group of crested hadrosaurid dinosaurs.
Classification
Lambeosaurines have been traditionally split into the tribes or clades Parasaurolophini ('' Parasaurolophus'', ''Charonosaurus'', others (?).) and Lambeosaurini (''Cor ...
duckbilled dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
from the middle or latest Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval from ...
-age Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
, whose remains were found in the Udurchukan Formation
The Udurchukan Formation is a geological formation located in Amur Region, Far East Russia. Based on palynomorphs such as ''Wodehouseia spinata'' the Udurchukan is considered of Maastrichtian age of the Late Cretaceous, during the Cretaceous Perio ...
beds of Kundur, Amur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's List of longest rivers, tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China, Northeastern China (Inne ...
Region, Far Eastern Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
. The type, and only species is ''Olorotitan arharensis.'' It was one of the last non-avian dinosaurs and it went extinct during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event (also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction) was a sudden mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million years ago. With the ...
.
Discovery and naming
Theholotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several ...
specimen of ''Olorotitan'', consisting of a nearly complete skeleton, was discovered in field work in the Udurchukan Formation
The Udurchukan Formation is a geological formation located in Amur Region, Far East Russia. Based on palynomorphs such as ''Wodehouseia spinata'' the Udurchukan is considered of Maastrichtian age of the Late Cretaceous, during the Cretaceous Perio ...
of Kundur in the Amur region
Amur Oblast ( rus, Аму́рская о́бласть, r=Amurskaya oblast, p=ɐˈmurskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located on the banks of the Amur and Zeya Rivers in the Russian Far East. The administrativ ...
of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
between 1999 and 2001. Pascal Godefroit Pascal Godefroit is a Belgian paleontologist. He discovered dinosaurs like '' Olorotitan'' in 2003. Godefroit is the director of earth and life sciences
This list of life sciences comprises the branches of science that involve the scientific st ...
and colleagues described and named it as a new species in 2003. It was the first nearly complete dinosaur specimen to be described from Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, and is the most complete lambeosaurine
Lambeosaurinae is a group of crested hadrosaurid dinosaurs.
Classification
Lambeosaurines have been traditionally split into the tribes or clades Parasaurolophini ('' Parasaurolophus'', ''Charonosaurus'', others (?).) and Lambeosaurini (''Cor ...
skeleton discovered anywhere outside of western North America.
Large numbers of fragmentary dinosaur, turtle, and crocodilian specimens were found in the several hundred square metre area around the discovery site. Similarly aged localities in Blagoveschensk
Blagoveshchensk ( rus, Благове́щенск, p=bləgɐˈvʲeɕːɪnsk, meaning ''City of the Annunciation'') is a city and the administrative center of Amur Oblast, Russia. It is located at the confluence of the Amur and the Zeya Rivers, o ...
, also from the Udurchukan Formation and Jiayin, on the Chinese side of the Amur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's List of longest rivers, tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China, Northeastern China (Inne ...
, have yielded similarly high numbers of lambeosaurine fossils.
The generic name ''Olorotitan'' means "titanic swan
Swans are birds of the family (biology), family Anatidae within the genus ''Cygnus''. The swans' closest relatives include the goose, geese and ducks. Swans are grouped with the closely related geese in the subfamily Anserinae where they form t ...
" because its neck is longer when compared with other hadrosaurs, while the specific descriptor ''arharensis'' refers to Arhara County where the fossil was found.
Description
''Olorotitan arharensis'' is based on the most complete lambeosaurine skeleton found outsideNorth America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
to date. It was a large hadrosaurid, comparable with other large lambeosaurines such as ''Parasaurolophus cyrtocristatus
''Parasaurolophus'' (; meaning "near crested lizard" in reference to '' Saurolophus)'' is a genus of herbivorous hadrosaurid ornithopod dinosaur that lived in what is now North America and possibly Asia during the Late Cretaceous Period, ab ...
'', and may have grown up to in length, up to in height and within the range of in body mass.
 It is characterized by the large hatchet-like hollow crest adorning its skull, very distinct from the crests of all of its North American relatives. The skull itself was supported by a rather elongated neck, having eighteen
It is characterized by the large hatchet-like hollow crest adorning its skull, very distinct from the crests of all of its North American relatives. The skull itself was supported by a rather elongated neck, having eighteen vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic ...
e, exceeding the previous hadrosaurid maximum of fifteen. The sacrum
The sacrum (plural: ''sacra'' or ''sacrums''), in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part ...
, with 15 or 16 vertebrae, has at least 3 more vertebrae than other hadrosaurids. Further along the vertebral series, in the proximal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
third of the tail, there are articulations between the tips of the neural spines
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic ...
, making that caudal area particularly rigid; the regularity of these connections suggests that they are not due to a pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in ...
, although more specimens are needed to be certain. Godefroit and his coauthors found through a phylogenetic analysis
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
that it was closest to ''Corythosaurus
''Corythosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of hadrosaurid "duck-billed" dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Period (geology), Period, about 77–75.7 million years ago. It lived in what is now North America. Its name means "helmet lizard", derived fr ...
'' and ''Hypacrosaurus
''Hypacrosaurus'' (meaning "near the highest lizard" reek υπο-, ''hypo-'' = less + ακρος, ''akros'', high because it was almost but not quite as large as ''Tyrannosaurus'') was a genus of duckbill dinosaur similar in appearance to ''Co ...
''.
Palaeobiology
As a hadrosaurid, ''Olorotitan'' would have been abipedal
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' ...
/quadruped
Quadrupedalism is a form of locomotion where four limbs are used to bear weight and move around. An animal or machine that usually maintains a four-legged posture and moves using all four limbs is said to be a quadruped (from Latin ''quattuor' ...
al herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
, eating plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclud ...
s with a sophisticated skull that permitted a grinding motion analogous to chewing
Chewing or mastication is the process by which food is crushed and ground by teeth. It is the first step of digestion, and it increases the surface area of foods to allow a more efficient break down by enzymes. During the mastication process, th ...
, and was furnished with hundreds of continually-replaced teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tear ...
. Its tall, broad hollow crest, formed out of expanded skull bones containing the nasal passages, probably functioned in identification by sight and sound.
Palaeoecology
 ''O. arharensis'' shared its time and place with several other types of animal, including two other lambeosaurines: the ''
''O. arharensis'' shared its time and place with several other types of animal, including two other lambeosaurines: the ''Parasaurolophus
''Parasaurolophus'' (; meaning "near crested lizard" in reference to '' Saurolophus)'' is a genus of herbivorous hadrosaurid ornithopod dinosaur that lived in what is now North America and possibly Asia during the Late Cretaceous Period, abou ...
''-like ''Charonosaurus
''Charonosaurus'' ( ; meaning " Charon's lizard") is a genus of dinosaur whose fossils were discovered by Godefroit, Zan & Jin in 2000 on the south bank of the Amur River, dividing China from Russia. It is monotypic, consisting of the species ...
'' and more basal ''Amurosaurus
''Amurosaurus'' (; "Amur lizard") is a genus of lambeosaurine hadrosaurid dinosaur found in the latest Cretaceous period (66 million years ago)Godefroit, P., Lauters, P., Van Itterbeeck, J., Bolotsky, Y. and Bolotsky, I.Y. (2011). "Recent advanc ...
''. Additionally, remains from turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked tu ...
s, crocodilian
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living ...
s, theropod
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally c ...
s, and nodosaurid
Nodosauridae is a family of ankylosaurian dinosaurs, from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous period in what is now North America, South America, Europe, and Asia.
Description
Nodosaurids, like their close relatives the ankylosaurids, wer ...
s were found at its discovery site, and the ''Saurolophus
''Saurolophus'' (; meaning "lizard crest") is a genus of large hadrosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period of Asia and North America, that lived in what is now the Horseshoe Canyon and Nemegt formations about 70 million to 68 million ...
''-like hadrosaurine '' Kerberosaurus'' is also known from roughly contemporaneous rocks in the area. Unlike the situation in North America, where lambeosaurines are virtually absent from Late Maastrichtian rocks, Asian lambeosaurines are diverse and common at the end of the Mesozoic, suggesting climatic
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologic ...
or ecological
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps wi ...
differences.
See also
*Timeline of hadrosaur research
A timeline is a display of a list of events in chronological order. It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labelled with dates paralleling it, and usually contemporaneous events.
Timelines can use any suitable scale represent ...
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q132470 Lambeosaurines Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of Asia Maastrichtian life Fossil taxa described in 2003 Taxa named by Pascal Godefroit Maastrichtian genus first appearances Maastrichtian genus extinctions Ornithischian genera