Old Fort Erie on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Old Fort Erie, also known as Fort Erie, or the Fort Erie National Historic Site of Canada, was the first
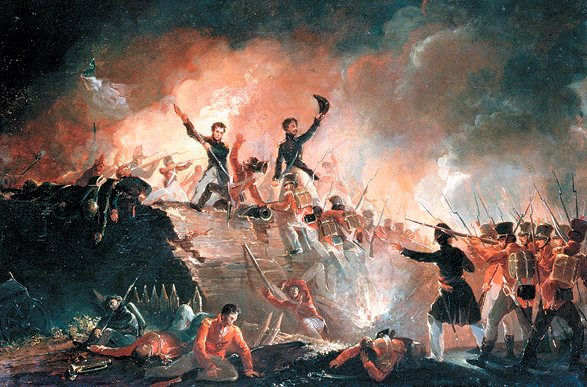 Fort Erie was the site of the bloodiest battles during the
Fort Erie was the site of the bloodiest battles during the
 The Fenians, Irish-American veterans of the
The Fenians, Irish-American veterans of the
 The reconstruction of the fort was started in 1937 (featuring only the walls and two barracks). The reconstruction was jointly sponsored by the Provincial and Federal governments and the
The reconstruction of the fort was started in 1937 (featuring only the walls and two barracks). The reconstruction was jointly sponsored by the Provincial and Federal governments and the
Old Fort Erie - Niagara Parks
Town of Fort Erie
Images from the Historic Niagara Digital Collections at the Niagara Falls Public Library
We Are Fort Erie
{{DEFAULTSORT:Erie History museums in Ontario Forts in Ontario War of 1812 forts Fort Erie, Ontario National Historic Sites in Ontario
British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
fort to be constructed as part of a network developed after the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754†...
(known as "the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
" in the colonies) was concluded by the Treaty of Paris (1763)
The Treaty of Paris, also known as the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763 by the kingdoms of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, Kingdom of France, France and Spanish Empire, Spain, with Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal in agree ...
, at which time France ceded its territories east of the Mississippi River (all of New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spai ...
) to Great Britain. The installation is located on the southern edge of what is now the Town of Fort Erie
Fort Erie is a town on the Niagara River in the Niagara Region, Ontario, Canada. It is directly across the river from Buffalo, New York, and is the site of Old Fort Erie which played a prominent role in the War of 1812.
Fort Erie is one of Ni ...
, Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
, directly across the Niagara River
The Niagara River () is a river that flows north from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario. It forms part of the border between the province of Ontario in Canada (on the west) and the state of New York (state), New York in the United States (on the east) ...
from Buffalo, New York
Buffalo is the second-largest city in the U.S. state of New York (behind only New York City) and the seat of Erie County. It is at the eastern end of Lake Erie, at the head of the Niagara River, and is across the Canadian border from South ...
, United States.
The fort and surrounding battlefield are owned and operated by the Niagara Parks Commission
The Niagara Parks Commission, commonly shortened to Niagara Parks, is an agency of the Government of Ontario which maintains the Ontario shoreline of the Niagara River.
History
The Commission was founded in 1885 and charged with preserving and ...
, a self-funded agency of the Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
provincial government.
History
The British established control of their new territory by occupying the French forts and by constructing a line of communications along the Niagara River and UpperGreat Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
. The original fort, built in 1764, was located on the Niagara River's edge below the present fort (parking lot on Lakeshore Road). It served as a supply depot and a port for ships transporting merchandise, troops and passengers via Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
to the Upper Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
. In 1795, the fort consisted of some wooden blockhouse
A blockhouse is a small fortification, usually consisting of one or more rooms with loopholes, allowing its defenders to fire in various directions. It is usually an isolated fort in the form of a single building, serving as a defensive stro ...
s surrounded by a wooden palisade
A palisade, sometimes called a stakewall or a paling, is typically a fence or defensive wall made from iron or wooden stakes, or tree trunks, and used as a defensive structure or enclosure. Palisades can form a stockade.
Etymology
''Palisade' ...
(dropped from the plan was a magazine, officer's quarters, storehouses and guard house). Provisions were stored inside the fort, and just outside was a large wooden magazine (original plans were to have it built inside the fort), as well as houses for workmen. The fort was damaged by winter storms and in 1803, plans were made for a new fort on the higher ground behind the original. It was larger and made of flintstone but was not quite finished at the start of the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
.
The fort served as a supply base for British troops, United Empire Loyalists
United Empire Loyalists (or simply Loyalists) is an honorific title which was first given by the 1st Lord Dorchester, the Governor of Quebec, and Governor General of The Canadas, to American Loyalists who resettled in British North America duri ...
Rangers, and allied Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
warriors during the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
. The little fort at the water's edge suffered considerable damage due to continuous winter storms. In 1803, planning was authorized for a new Fort Erie on the heights behind the original post. The new fort was made more formidable as it was constructed of the Onondaga Onondaga may refer to:
Native American/First Nations
* Onondaga people, a Native American/First Nations people and one of the five founding nations of the Iroquois League
* Onondaga (village), Onondaga settlement and traditional Iroquois capita ...
flintstone that was readily available in the area.
War of 1812 (1812–1815)
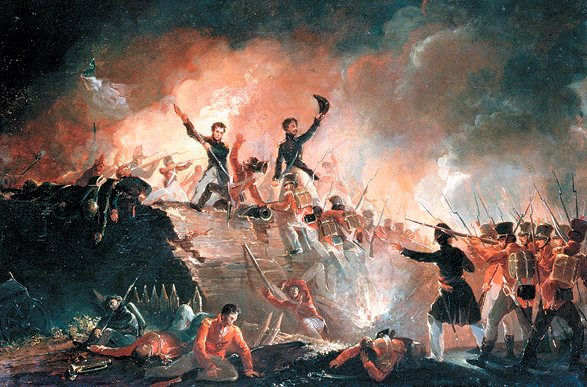 Fort Erie was the site of the bloodiest battles during the
Fort Erie was the site of the bloodiest battles during the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
. This new fort was unfinished when the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
declared war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
on June 18, 1812. Part of the garrison of Fort Erie fought at the Battle of Frenchman's Creek
The Battle of Frenchman's Creek took place during the War of 1812 between Great Britain and the United States in the early hours of November 28, 1812, in the Crown Colony of Upper Canada, near the Niagara River. The operation was conceived as a ...
against an American attack in November 1812. In 1813, Fort Erie was held for a period by U.S. forces and then abandoned on June 9, 1813. The fort had been partially dismantled by the small garrison of British troops and Canadian Militia as they withdrew.
British reoccupation followed American withdrawal from the area in December 1813. The British attempted to rebuild the fort. On July 3, 1814 another American force landed nearby and again captured Fort Erie. The U.S. Army used the fort as a supply base and expanded its size, adding to defensive fortifications. At the end of July, after the Battles of Chippawa and Lundy's Lane, the American army withdrew to Fort Erie. They were besieged by the British for an extended period. In the early hours of August 15, 1814, the British launched a four-pronged attack against the fortifications. A well-prepared American defence and an explosion in the North East Bastion destroyed the British chance for success, and they lost more than 1,000 of their men.
An American sortie on September 17 captured two of the British batteries and the American troops were able to spike
Spike, spikes, or spiking may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Books
* ''The Spike'' (novel), a novel by Arnaud de Borchgrave
* ''The Spike'' (book), a nonfiction book by Damien Broderick
* ''The Spike'', a starship in Peter F. Hamilto ...
the guns in one of them before being driven back to the fort. In the American sortie, NY Militia Brigadier General Davis died at the front of his column. Colonel Gibson was cut down as well. Brevet Lieutenant Colonel Eleazer D. Wood Eleazer Derby Wood (December 1783 – September 17, 1814) was a Colonel and American Army officer in the War of 1812. Fort Wood, which became the base of the Statue of Liberty, was named in his honor.
Early career
Wood was born in Lunenburg, ...
was also killed leading this sortie. Shortly afterward, the British lifted the siege and retired to positions to the north at Chippawa. After an unsuccessful American attack at Cook's Mills, west of Chippawa, news reached the American forces that the eastern seaboard of the U.S. was under attack. On November 5, 1814, with winter approaching, the Americans destroyed the fort and withdrew to Buffalo.
Mid-19th century (1814–1866)
TheTreaty of Ghent
The Treaty of Ghent () was the peace treaty that ended the War of 1812 between the United States and the United Kingdom. It took effect in February 1815. Both sides signed it on December 24, 1814, in the city of Ghent, United Netherlands (now in ...
was signed December 24, 1814, ending the War of 1812. Fearing further American attacks, the British continued to occupy the ruined fort until 1823. Some of the stones from the fort were incorporated into the construction of St. Paul's Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
Church in 1824. It was rebuilt after fire and explosion in 1892. Today the church is adjacent to the later constructed Niagara Parkway north of the fort.
The town of Fort Erie began to develop north of the fort when a rail terminus and station were constructed to the area.
Fenian Raids (1866)
 The Fenians, Irish-American veterans of the
The Fenians, Irish-American veterans of the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
demanding independence from Britain for Ireland, mounted several raids on Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada (french: link=no, province du Haut-Canada) was a part of British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North America, formerly part of the ...
. One was quite large, attacking Fort Erie on June 1, 1866 after crossing the Niagara River with a large force of 1,000 to 1500 men (depending on the source of the report). The Fenians occupied the town and demanded food and horses. The only payment they could offer were Fenian bonds, which the townspeople would not accept. The Fenians cut the telegraph wires and tore up some railway tracks.
Afterwards, they marched to Chippewa and the next day to Ridgeway, where they fought the Battle of Ridgeway
The Battle of Ridgeway (sometimes the Battle of Lime Ridge or Limestone Ridge) was fought in the vicinity of the town of Fort Erie across the Niagara River from Buffalo, New York, near the village of Ridgeway, Canada West, currently Ontario, Ca ...
, a series of skirmishes with the Canadian militia. The Fenians returned to Fort Erie, where they defeated
Defeated may refer to:
* "Defeated" (Breaking Benjamin song)
* "Defeated" (Anastacia song)
*"Defeated", a song by Snoop Dogg from the album ''Bible of Love''
*Defeated, Tennessee, an unincorporated community
*''The Defeated
''The Defeated'', al ...
a small force of the Canadian militia.
Unable to get reinforcements from across the river, which was guarded by the Americans, and worried about the large force of British and militia that was approaching, the Fenian commander decided to retreat to the US. Some of his troops deserted. Approximately 850 surrendered to forces of the American navy. This was the last notable Fenian raid on Upper Canada.
Recent history (1866–present)
The fort lay vacant with old parts of the barracks, walls and mill still standing. It was eventually settled by military pensioners and others until it was sold to theNiagara Parks Commission
The Niagara Parks Commission, commonly shortened to Niagara Parks, is an agency of the Government of Ontario which maintains the Ontario shoreline of the Niagara River.
History
The Commission was founded in 1885 and charged with preserving and ...
in 1901.
 The reconstruction of the fort was started in 1937 (featuring only the walls and two barracks). The reconstruction was jointly sponsored by the Provincial and Federal governments and the
The reconstruction of the fort was started in 1937 (featuring only the walls and two barracks). The reconstruction was jointly sponsored by the Provincial and Federal governments and the Niagara Parks Commission
The Niagara Parks Commission, commonly shortened to Niagara Parks, is an agency of the Government of Ontario which maintains the Ontario shoreline of the Niagara River.
History
The Commission was founded in 1885 and charged with preserving and ...
, and was a way to invest in a long term project while providing employment during the Depression. The fort was restored to the 1812-1814 period and officially reopened on July 1, 1939. During the restoration, a mass grave of 150 British and 3 American soldiers was uncovered. A monument was erected at this site, in the ruins, in 1904.
The Niagara Parkway was constructed starting at Fort Erie and continues north to Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border sp ...
. Sir Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, dur ...
was quoted saying that the parkway was "the prettiest Sunday drive in the world." Each year, during the second weekend of August, hundreds of historical re-enactment
Historical reenactment (or re-enactment) is an educational entertainment, educational or entertainment activity in which mainly amateur hobbyists and history enthusiasts dress in historic uniforms or costumes and follow a plan to recreate aspect ...
enthusiasts come together to re-enact the siege of Fort Erie.
On June 28, 1985 Canada Post
Canada Post Corporation (french: Société canadienne des postes), trading as Canada Post (french: Postes Canada), is a Crown corporation that functions as the primary postal operator in Canada. Originally known as Royal Mail Canada (the opera ...
issued 'Fort Erie, Ont.' one of the 20 stamps in the "Forts Across Canada Series" (1983 & 1985). The stamps are perforated 12½ x 13 and were printed by Ashton-Potter Limited based on the designs by Rolf P. Harder.
Affiliations
The Museum is affiliated with: CMA, CHIN, andVirtual Museum of Canada
The Digital Museums Canada (DMC; , ''MNC'') is a funding program in Canada "dedicated to online projects by the museum and heritage community," helping organizations to build digital capacity.
Administered by the Canadian Museum of History (CMH) ...
.
See also
* Fort George *Fort Meigs
Fort Meigs was a United States fortification along the Maumee River in what is now Perrysburg, Ohio during the War of 1812. The British Army, supported by Tecumseh's Confederacy, failed to capture the fort during the siege of Fort Meigs. It is n ...
* Fort Mississauga
Fort Mississauga National Historic Site is a fort on the shore of Lake Ontario, at the mouth of the Niagara River in Niagara-on-the-Lake, Ontario, Canada. The fort today consists of a box–shaped brick tower and historic star–shaped ear ...
* List of forts
This is a list for articles on notable historic forts which may or may not be under
current active use by a military. There are also many towns named after a Fort, the largest being Fort Worth, Texas, United States.
Antigua and Barbuda
* Fort ...
References
Further reading
* Whitehorne, Joseph, W.A., ''While Washington Burned: The Battle for Fort Erie, 1814,'' 1992, reprint 2006, The Nautical and Aviation Publishing Company of America, Charleston, South Carolina. * "Historic Fort Erie" brochure, The Niagara Parks Commission, 1991.External links
Old Fort Erie - Niagara Parks
Town of Fort Erie
Images from the Historic Niagara Digital Collections at the Niagara Falls Public Library
We Are Fort Erie
{{DEFAULTSORT:Erie History museums in Ontario Forts in Ontario War of 1812 forts Fort Erie, Ontario National Historic Sites in Ontario
Fort Erie
Fort Erie is a town on the Niagara River in the Niagara Region, Ontario, Canada. It is directly across the river from Buffalo, New York, and is the site of Old Fort Erie which played a prominent role in the War of 1812.
Fort Erie is one of Ni ...
Fort Erie
Fort Erie is a town on the Niagara River in the Niagara Region, Ontario, Canada. It is directly across the river from Buffalo, New York, and is the site of Old Fort Erie which played a prominent role in the War of 1812.
Fort Erie is one of Ni ...
Fort Erie
Fort Erie is a town on the Niagara River in the Niagara Region, Ontario, Canada. It is directly across the river from Buffalo, New York, and is the site of Old Fort Erie which played a prominent role in the War of 1812.
Fort Erie is one of Ni ...
Fort Erie
Fort Erie is a town on the Niagara River in the Niagara Region, Ontario, Canada. It is directly across the river from Buffalo, New York, and is the site of Old Fort Erie which played a prominent role in the War of 1812.
Fort Erie is one of Ni ...
War of 1812 National Historic Sites of Canada
1764 establishments in the British Empire
Old Fort Erie
Old Fort Erie, also known as Fort Erie, or the Fort Erie National Historic Site of Canada, was the first Great Britain, British fort to be constructed as part of a network developed after the Seven Years' War (known as "the French and Indian War" ...
Military installations established in 1764
Military installations closed in 1901
Protected areas established in 1901
Installations of the British Army
Foreign military bases in Canada
Military history of the Great Lakes