Okro on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Okra or Okro (, ), ''Abelmoschus esculentus'', known in many English-speaking countries as ladies' fingers or ochro, is a

 Okra is an
Okra is an  The plant was introduced to the
The plant was introduced to the
 The species is a
The species is a
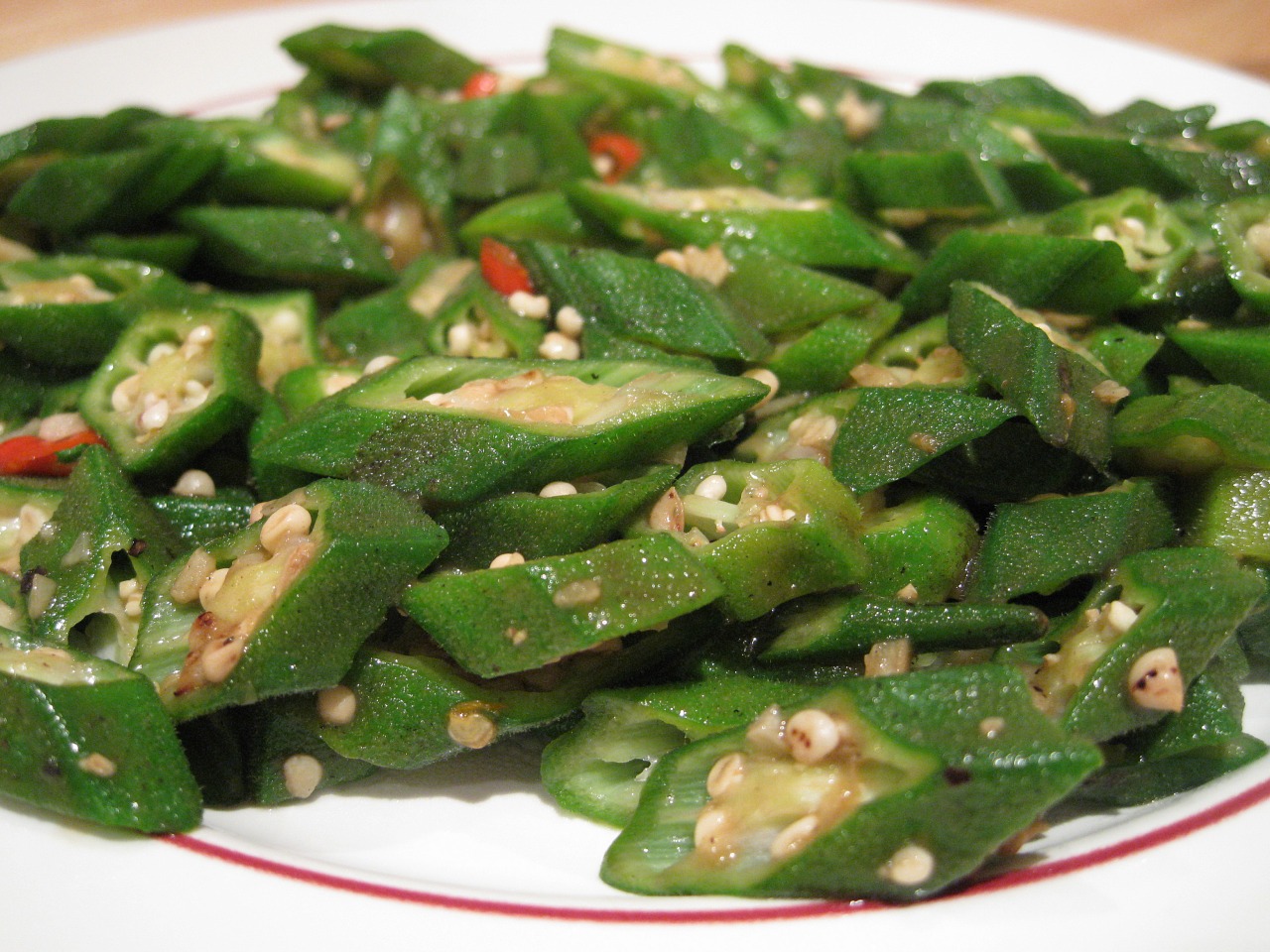 The pods of the plant are
The pods of the plant are
File:Giant okra plant.jpg, Large okra plants
File:Giant okra.jpg, A giant okra pod
File:Okra blossom with pollen.png, Flower close-up
File:Okra seedling, hydroponic, 7days.JPG, Young seedling showing
flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
in the mallow family
Malvaceae, or the mallows, is a family of flowering plants estimated to contain 244 genera with 4225 known species. Well-known members of economic importance include okra, cotton, cacao and durian. There are also some genera containing familiar o ...
. It has edible green seed pods. The geographical origin of okra is disputed, with supporters of West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Maurit ...
n, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
n, Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
n, and South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;;;;; ...
n origins. Cultivated in tropical, subtropical, and warm temperate regions around the world, okra is used in the cuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, techniques and dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, customs, and ingredients combine to ...
s of many countries.
Etymology
''Abelmoschus'' isNew Latin
New Latin (also called Neo-Latin or Modern Latin) is the revival of Literary Latin used in original, scholarly, and scientific works since about 1500. Modern scholarly and technical nomenclature, such as in zoological and botanical taxonomy ...
from Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
أَبُو المِسْك (ʾabū l-misk, “father of musk”), while ''esculentus'' is Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
for being fit for human consumption.
The first use of the word ''okra'' (alternatively; ''okro'' or ''ochro'') appeared in 1679 in the Colony of Virginia
The Colony of Virginia, chartered in 1606 and settled in 1607, was the first enduring English colonial empire, English colony in North America, following failed attempts at settlement on Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland by Sir Humphrey GilbertG ...
, deriving from the Igbo
Igbo may refer to:
* Igbo people, an ethnic group of Nigeria
* Igbo language, their language
* anything related to Igboland, a cultural region in Nigeria
See also
* Ibo (disambiguation)
* Igbo mythology
* Igbo music
* Igbo art
*
* Igbo-Ukwu, a t ...
word . The word ''gumbo'' was first used in American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
vernacular around 1805, deriving from Louisiana Creole
Louisiana Creole ( lou, Kréyòl Lalwizyàn, links=no) is a French-based creole language spoken by fewer than 10,000 people, mostly in the state of Louisiana. It is spoken today by people who may racially identify as White, Black, mixed, and N ...
, but originates from either the Umbundu
Umbundu, or South Mbundu (autonym umb, úmbúndú), one of many Bantu languages, is the most widely-spoken autochthonous language of Angola. Its speakers are known as '' Ovimbundu'' and are an ethnic group constituting a third of Angola's popul ...
word ''ochinggômbo'' or the Kimbundu
Kimbundu, a Bantu language which has sometimes been called Mbundu
or 'North Mbundu' (see Umbundu), is the second-most-widely-spoken Bantu language in Angola.
Its speakers are concentrated in the north-west of the country, notably in the Lua ...
word ''ki-ngombo.'' Despite the fact that in most of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
the word ''gumbo'' often refers to the dish, gumbo
Gumbo (Louisiana Creole: Gombo) is a soup popular in the U.S. state of Louisiana, and is the official state cuisine. Gumbo consists primarily of a strongly-flavored stock, meat or shellfish (or sometimes both), a thickener, and the Creole ...
, many places in the Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion in the Southern United States. The term was first used to describe the states most dependent on plantations and slavery prior to the American Civil War. Following the war ...
may have used it to refer to the pods and plant as well as many other variants of the word found across the African diaspora in the Americas
The African diaspora in the Americas refers to the people born in the Americas with partial, predominantly, or completely African ancestry. Many are descendants of persons enslaved in Africa and transferred to the Americas by Europeans, then fo ...
.
Origin and distribution
 Okra is an
Okra is an allopolyploid
Polyploidy is a condition in which the cells of an organism have more than one pair of ( homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes, where each set contains ...
of uncertain parentage. However, proposed parents include ''Abelmoschus ficulneus
''Abelmoschus ficulneus'' is a species of flowering plant in the genus '' Abelmoschus'', family Malvaceae. Commonly known as white wild musk mallow or native rosella, it is fibrous perennial with a woody stem. Its flowers are about an inch in ...
'', '' A. tuberculatus'' and a reported "diploid" form of okra. Truly wild (as opposed to naturalised
Naturalization (or naturalisation) is the legal act or process by which a non-citizen of a country may acquire citizenship or nationality of that country. It may be done automatically by a statute, i.e., without any effort on the part of the i ...
) populations are not known with certainty, and the West African variety has been described as a cultigen
A cultigen () or cultivated plant is a plant that has been deliberately altered or selected by humans; it is the result of artificial selection. These plants, for the most part, have commercial value in horticulture, agriculture or forestry. Beca ...
.
The geographical origin of okra is disputed, with supporters of Southeast Asian, South Asian, Ethiopian and West African origins. The Egyptians
Egyptians ( arz, المَصرِيُون, translit=al-Maṣriyyūn, ; arz, المَصرِيِين, translit=al-Maṣriyyīn, ; cop, ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, remenkhēmi) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian ...
and Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct or ...
of the 12th and 13th centuries used the Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
word for the plant, ''bamya'', suggesting it had come into Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
from Arabia, but earlier it was probably taken from Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
to Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
. The plant may have entered southwest Asia across the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
or the Bab-el-Mandeb
The Bab-el-Mandeb (Arabic: , , ) is a strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula, and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa. It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden.
Name
The strait derives its name from the dangers attendin ...
strait to the Arabian Peninsula, rather than north across the Sahara
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
, or from India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. One of the earliest European accounts is by a Spanish Moor who visited Egypt in 1216 and described the plant under cultivation by the locals who ate the tender, young pods with meal
A meal is an eating occasion that takes place at a certain time and includes consumption of food. The names used for specific meals in English vary, depending on the speaker's culture, the time of day, or the size of the meal.
Although they ca ...
. From Arabia, the plant spread around the shores of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
and eastward.
 The plant was introduced to the
The plant was introduced to the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
by ships plying the Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
by 1658, when its presence was recorded in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
. It was further documented in Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
in 1686. Okra may have been introduced to southeastern North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
from Africa in the early 18th century. By 1748, it was being grown as far north as Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
. Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
noted it was well established in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
by 1781. It was commonplace throughout the Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
by 1800, and the first mention of different cultivar
A cultivar is a type of cultivated plant that people have selected for desired traits and when propagated retain those traits. Methods used to propagate cultivars include: division, root and stem cuttings, offsets, grafting, tissue culture, ...
s was in 1806.
Botany and cultivation

 The species is a
The species is a perennial
A perennial plant or simply perennial is a plant that lives more than two years. The term ('' per-'' + '' -ennial'', "through the years") is often used to differentiate a plant from shorter-lived annuals and biennials. The term is also wide ...
, often cultivated as an annual
Annual may refer to:
* Annual publication, periodical publications appearing regularly once per year
**Yearbook
** Literary annual
* Annual plant
* Annual report
* Annual giving
* Annual, Morocco, a settlement in northeastern Morocco
* Annuals (b ...
in temperate climates, often growing to around tall. As a member of the Malvaceae, it is related to such species as cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor perce ...
, cocoa
Cocoa may refer to:
Chocolate
* Chocolate
* ''Theobroma cacao'', the cocoa tree
* Cocoa bean, seed of ''Theobroma cacao''
* Chocolate liquor, or cocoa liquor, pure, liquid chocolate extracted from the cocoa bean, including both cocoa butter and ...
, and hibiscus
''Hibiscus'' is a genus of flowering plants in the mallow family, Malvaceae. The genus is quite large, comprising several hundred species that are native to warm temperate, subtropical and tropical regions throughout the world. Member species ...
. The leaves
A leaf (plural, : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant plant stem, stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", wh ...
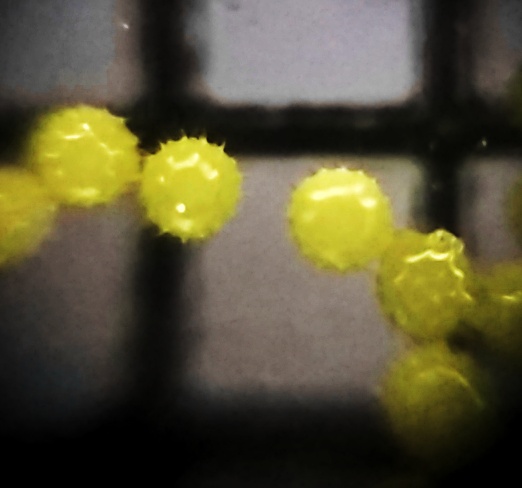
are long and broad, palmately lobed with 5–7 lobes. The flower
A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants (plants of the division Angiospermae). The biological function of a flower is to facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechani ...
s are in diameter, with five white to yellow petals, often with a red or purple spot at the base of each petal. The pollens are spherical and approximately 188 micron
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Unit ...
s in diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest chord of the circle. Both definitions are also valid for ...
. The fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particu ...
is a capsule up to long with pentagon
In geometry, a pentagon (from the Greek πέντε ''pente'' meaning ''five'' and γωνία ''gonia'' meaning ''angle'') is any five-sided polygon or 5-gon. The sum of the internal angles in a simple pentagon is 540°.
A pentagon may be simpl ...
al cross-section, containing numerous seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiospe ...
s.
''Abelmoschus esculentus'' is cultivated throughout the tropical and warm temperate regions of the world for its fibrous fruits or pods containing round, white seeds. It is among the most heat- and drought-tolerant vegetable species in the world and will tolerate soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former te ...
s with heavy clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
and intermittent moisture, but frost can damage the pods. In cultivation, the seeds are soaked overnight prior to planting to a depth of . It prefers a soil temperature of at least for germination
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of fungi, fer ...
, which occurs between six days (soaked seeds) and three weeks. As a tropical plant, it also requires a lot of sunlight, and it should also be cultivated in soil that has a pH between 5.8 and 7, ideally on the acidic side. Seedlings require ample water. The seed pods rapidly become fibrous and woody and, to be edible as a vegetable
Vegetables are parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. The original meaning is still commonly used and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including the flowers, fruits, stems, ...
, must be harvested when immature, usually within a week after pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds, most often by an animal or by wind. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, birds ...
. The first harvest will typically be ready about 2 months after planting, and it will be approximately long.
The most common disease afflicting the okra plant is verticillium wilt
Verticillium wilt is a wilt disease affecting over 350 species of eudicot plants. It is caused by six species of ''Verticillium'' fungi: ''V. dahliae'', ''V. albo-atrum'', ''V. longisporum'', ''V. nubilum'', ''V. theobromae'' and ''V. tricorpu ...
, often causing a yellowing and wilting of the leaves. Other diseases include powdery mildew
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants. Powdery mildew diseases are caused by many different species of ascomycete fungi in the order Erysiphales. Powdery mildew is one of the easier plant diseases to identify, as ...
in dry tropical regions, leaf spot
A leaf spot is a limited, discoloured, diseased area of a leaf that is caused by fungal, bacterial or viral plant diseases, or by injuries from nematodes, insects, environmental factors, toxicity or herbicides. These discoloured spots or lesions ...
s, yellow mosaic and root-knot nematode
Root-knot nematodes are plant-parasitic nematodes from the genus ''Meloidogyne''. They exist in soil in areas with hot climates or short winters. About 2000 plants worldwide are susceptible to infection by root-knot nematodes and they cause appr ...
s. Resistance to yellow mosaic virus in ''A. esculentus'' was transferred through a cross with ''Abelmoschus manihot
''Abelmoschus manihot'', the aibika, is a flowering plant in the family Malvaceae. It was formerly considered a species of ''Hibiscus'', but is now classified in the genus ''Abelmoschus''. The plant is also known as the sunset muskmallow, sunset ...
'' and resulted in a new variety called ''Parbhani kranti''.
In the United States much of the supply is grown in Florida, especially around Dade in southern Florida. Okra is grown throughout the state to some degree, so okra is available ten months of the year. Yields range from less than to over . Wholesale
Wholesaling or distributing is the sale of goods or merchandise to retailers; to industrial, commercial, institutional or other professional business users; or to other wholesalers (wholesale businesses) and related subordinated services. In ...
prices can go as high as $18/bushel which is . The Regional IPM Centers provide integrated pest management
Integrated pest management (IPM), also known as integrated pest control (IPC) is a broad-based approach that integrates both chemical and non-chemical practices for economic control of pests. IPM aims to suppress pest populations below the econ ...
plans for use in the state.
Food and uses
Pods
 The pods of the plant are
The pods of the plant are mucilaginous
Mucilage is a thick, gluey substance produced by nearly all plants and some microorganisms. These microorganisms include protists which use it for their locomotion. The direction of their movement is always opposite to that of the secretion of m ...
, resulting in the characteristic "goo" or slime
Slime may refer to:
Biology
* Slime mold, a broad term often referring to roughly six groups of Eukaryotes
* Biofilm, an aggregate of microorganisms in which cells adhere to each other and/or to a surface
* Slimy (fish), also known as the pony ...
when the seed pods are cooked; the mucilage contains soluble fiber
Dietary fiber (in British English fibre) or roughage is the portion of plant-derived food that cannot be completely broken down by human digestive enzymes. Dietary fibers are diverse in chemical composition, and can be grouped generally by the ...
. One possible way to de-slime okra is to cook it with an acidic food, such as tomatoes, to minimize the mucilage. Pods are cooked, pickled, eaten raw, or included in salads. Okra may be used in developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
to mitigate malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
and alleviate food insecurity
Food security speaks to the availability of food in a country (or geography) and the ability of individuals within that country (geography) to access, afford, and source adequate foodstuffs. According to the United Nations' Committee on World F ...
.
In cuisine
InCuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
and Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated ...
, the vegetable is referred to as ''quimbombó'', and is used in dishes such as ''quimbombó guisado'' (stewed okra), a dish very similar to Southern gumbo
Gumbo (Louisiana Creole: Gombo) is a soup popular in the U.S. state of Louisiana, and is the official state cuisine. Gumbo consists primarily of a strongly-flavored stock, meat or shellfish (or sometimes both), a thickener, and the Creole ...
. It is also used in traditional dishes in the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares wit ...
, where it is called ''molondrón''.
In the Brazilian state of Bahia
Bahia ( , , ; meaning "bay") is one of the 26 Federative units of Brazil, states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region, Brazil, Northeast Region of the country. It is the fourth-largest Brazilian state by population (after São Paulo (sta ...
, okra is known as ''quiabo'' and is used to prepare ''caruru'', a dish of cultural and religious importance - in addition to being a symbol of Afro-Brazilian
Afro-Brazilians ( pt, afro-brasileiros; ) are Brazilians who have predominantly African ancestry (see "Black people#Brazil, preto"). Most members of another group of people, Pardo Brazilians, multiracial Brazilians or ''pardos'', may also have a ...
cuisine.
In South Asia, the pods are used in many spicy vegetable preparations as well as cooked with beef, mutton, lamb and chicken.
Nutrition
Raw okra is 90% water, 2%protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
, 7% carbohydrates
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or may ...
and contains negligible fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers spec ...
. In a 100 gram reference amount, raw okra is a rich source (20% or more of the Daily Value
The Reference Daily Intake (RDI) used in nutrition labeling on food and dietary supplement products in the U.S. and Canada is the daily intake level of a nutrient that is considered to be sufficient to meet the requirements of 97–98% of health ...
, DV) of dietary fiber
Dietary fiber (in British English fibre) or roughage is the portion of plant-derived food that cannot be completely broken down by human digestive enzymes. Dietary fibers are diverse in chemical composition, and can be grouped generally by the ...
, vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical 'serum' ingredient to treat melasma (dark pigment spots) an ...
, and vitamin K
Vitamin K refers to structurally similar, fat-soluble vitamers found in foods and marketed as dietary supplements. The human body requires vitamin K for post-synthesis modification of certain proteins that are required for blood coagulation ...
, with moderate contents of thiamin
Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin, an essential micronutrient, that cannot be made in the body. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosphorylated forms of thia ...
, folate
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and ...
and magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
(table).
Leaves and seeds
Young okra leaves may be cooked similarly to the greens ofbeet
The beetroot is the taproot portion of a beet plant, usually known in North America as beets while the vegetable is referred to as beetroot in British English, and also known as the table beet, garden beet, red beet, dinner beet or golden beet ...
s, dandelion
''Taraxacum'' () is a large genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, which consists of species commonly known as dandelions. The scientific and hobby study of the genus is known as taraxacology. The genus is native to Eurasia and Nor ...
s, or used in salads. Okra seeds may be roasted and ground to form a caffeine-free substitute for coffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulant, stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world.
S ...
. When importation of coffee was disrupted by the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
in 1861, the ''Austin State Gazette'' said, "An acre of okra will produce seed enough to furnish a plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. The ...
with coffee in every way equal to that imported from Rio
Rio or Río is the Portuguese, Spanish, Italian, and Maltese word for "river". When spoken on its own, the word often means Rio de Janeiro, a major city in Brazil.
Rio or Río may also refer to:
Geography Brazil
* Rio de Janeiro
* Rio do Sul, a ...
."
Greenish-yellow edible okra oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
is pressed from okra seeds; it has a pleasant taste and odor, and is high in unsaturated fat
An unsaturated fat is a fat or fatty acid in which there is at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain. A fatty acid chain is monounsaturated if it contains one double bond, and polyunsaturated if it contains more than one double bond.
...
s such as oleic acid
Oleic acid is a fatty acid that occurs naturally in various animal and vegetable fats and oils. It is an odorless, colorless oil, although commercial samples may be yellowish. In chemical terms, oleic acid is classified as a monounsaturated omega ...
and linoleic acid
Linoleic acid (LA) is an organic compound with the formula COOH(CH2)7CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)4CH3. Both alkene groups are cis-trans isomerism, ''cis''. It is a fatty acid sometimes denoted 18:2 (n-6) or 18:2 ''cis''-9,12. A linoleate is a salt (chem ...
. The oil content of some varieties of the seed is about 40%. At , the yield was exceeded only by that of sunflower oil
Sunflower oil is the non-volatile oil pressed from the seeds of the sunflower (''Helianthus annuus''). Sunflower oil is commonly used in food as a frying oil, and in cosmetic formulations as an emollient.
Sunflower oil is primarily composed ...
in one trial. A 1920 study found that a sample contained 15% oil.
Industrial uses
Bast fibre
Bast fibre (also called phloem fibre or skin fibre) is plant fibre collected from the phloem (the "inner bark", sometimes called "skin") or bast surrounding the stem of certain dicotyledonous plants. It supports the conductive cells of the phloe ...
from the stem of the plant has industrial uses such as the reinforcement of polymer composites. The mucilage produced by the okra plant can be used for the removal of turbidity
Turbidity is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. The measurement of turbidity is a key test of water quality.
Fluids can ...
from wastewater
Wastewater is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of domestic, industr ...
by virtue of its flocculant properties. Having composition similar to a thick polysaccharide film, okra mucilage is under development as a biodegradable
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradati ...
food packaging
Food packaging is a packaging system specifically designed for food and represents one of the most important aspects among the processes involved in the food industry, as it provides protection from chemical, biological and physical alterations ...
, as of 2018. A 2009 study found okra oil suitable for use as a biofuel
Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels, such as oil. According to the United States Energy Information Administration (E ...
.
Gallery
cotyledons
A cotyledon (; ; ; , gen. (), ) is a significant part of the embryo within the seed of a plant, and is defined as "the embryonic leaf in seed-bearing plants, one or more of which are the first to appear from a germinating seed." The numb ...
File:Okra with corriander.png, Sautéed fruits with coriander
Coriander (;
File:Манџа од бамји.jpg, Bamia
Bamia is a Middle Eastern, Assyrian, Armenian, Afghan, Kurdish, and Anatolian stew prepared using lamb, okra and tomatoes as primary ingredients.Claudia Roden, ''A New Book of Middle Eastern Food'', p. 248 Additional ingredients used include tom ...
, stewed okra with tomatoes
The tomato is the edible Berry (botany), berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to th ...
File:Ladies finger bharta.jpg, Bhindi bharta, a South Asian dish
File:Oklahoma-grown okra.jpg, Fresh-picked fruits (grown in Eastern Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
, USA)
File:Praline Connection New Orleans Sept 2018 Fried Okra.jpg, Deep-fried fruit pieces
References
External links
{{Authority control Igbo words and phrases Abelmoschus Asian vegetables Tropical agriculture Medicinal plants of Africa Fiber plants Pod vegetables Crops originating from Africa Cuisine of the Southern United States African cuisine