Oklahoma State Cowgirls Basketball Seasons on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Oklahoma (;

 Major land runs, including the Land Run of 1889, were held for settlers where certain territories were opened to settlement starting at a precise time. Usually land was open to settlers on a first come first served basis. Those who broke the rules by crossing the border into the territory before the official opening time were said to have been crossing the border ''sooner'', leading to the term '' sooners'', which eventually became the state's official nickname. Deliberations to make the territory into a state began near the end of the 19th century, when the Curtis Act continued the allotment of Indian tribal land.
Major land runs, including the Land Run of 1889, were held for settlers where certain territories were opened to settlement starting at a precise time. Usually land was open to settlers on a first come first served basis. Those who broke the rules by crossing the border into the territory before the official opening time were said to have been crossing the border ''sooner'', leading to the term '' sooners'', which eventually became the state's official nickname. Deliberations to make the territory into a state began near the end of the 19th century, when the Curtis Act continued the allotment of Indian tribal land.
 Attempts to create an all-Indian state named ''Oklahoma'' and a later attempt to create an all-Indian state named ''
Attempts to create an all-Indian state named ''Oklahoma'' and a later attempt to create an all-Indian state named '' The new state became a focal point for the emerging oil industry, as discoveries of oil pools prompted towns to grow rapidly in population and wealth. Tulsa eventually became known as the "
The new state became a focal point for the emerging oil industry, as discoveries of oil pools prompted towns to grow rapidly in population and wealth. Tulsa eventually became known as the " In 1995, Oklahoma City was the site of the most destructive act of domestic terrorism in American history. The Oklahoma City bombing of April 19, 1995, in which Timothy McVeigh detonated a large, crude explosive device outside the Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building, killed 168 people, including 19 children. For his crime, McVeigh was executed by the federal government on June 11, 2001. His accomplice, Terry Nichols, is serving life in prison without parole for helping plan the attack and prepare the explosive.
On May 31, 2016, several cities experienced record setting flooding.
On July 9, 2020, the
In 1995, Oklahoma City was the site of the most destructive act of domestic terrorism in American history. The Oklahoma City bombing of April 19, 1995, in which Timothy McVeigh detonated a large, crude explosive device outside the Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building, killed 168 people, including 19 children. For his crime, McVeigh was executed by the federal government on June 11, 2001. His accomplice, Terry Nichols, is serving life in prison without parole for helping plan the attack and prepare the explosive.
On May 31, 2016, several cities experienced record setting flooding.
On July 9, 2020, the
 Oklahoma is the 20th-largest state in the United States, covering an area of , with of land and of water. It lies partly in the
Oklahoma is the 20th-largest state in the United States, covering an area of , with of land and of water. It lies partly in the
File:turner falls ok.jpg, Turner Falls
File:Rose rocks.jpg, State rock (Desert rose (crystal), rose rock) specimens from Cleveland County
File:Illinois River Oklahoma.jpg, alt=, Illinois River in northeastern Oklahoma
File:Elk Mountain, OK.jpg, Elk Mountain, in the eastern Wichita Mountains, southwestern Oklahoma
File:Wichita Mountains Narrows.jpg, Wichita Mountains Narrows
File:Talimenavista1.jpg, The Ouachita Mountains cover much of Kiamichi Country, southeastern Oklahoma.
File:McIntosh County (Oklahoma).jpg, Grave Creek in McIntosh County, Oklahoma, McIntosh County
File:Gloss Mountains.jpg, Glass Mountains, Mesas rise above one of Oklahoma's state parks
 Due to Oklahoma's location at the confluence of many geographic regions, the state's climatic regions have a high rate of biodiversity. Forests cover 24 percent of Oklahoma and prairie, prairie grasslands composed of shortgrass, mixed-grass, and tallgrass prairie, harbor expansive ecosystems in the state's central and western portions, although Agricultural land, cropland has largely replaced native grasses. Where rainfall is sparse in the state's western regions, shortgrass prairie and shrublands are the most prominent ecosystems, though pinyon pines, red cedar (junipers), and Pinus ponderosa, ponderosa pines grow near rivers and creek beds in the panhandle's far western reaches. Southwestern Oklahoma contains many rare, Disjunct distribution, disjunct species including Acer saccharum, sugar maple, Acer grandidentatum, bigtooth maple, nolina and Quercus fusiformis, Texas live oak.
Marshlands, cypress forests and mixtures of Pinus echinata, shortleaf pine, Pinus taeda, loblolly pine, sabal minor, blue palmetto, and deciduous forests dominate the state's Kiamichi Country, southeastern quarter, while mixtures of largely Quercus stellata, post oak, elm, red cedar (''Juniperus virginiana'') and pine forests cover Green Country, northeastern Oklahoma.
The state holds populations of white-tailed deer, mule deer, Pronghorn, antelope, coyotes, Cougar, mountain lions, bobcats, elk, and birds such as quail, Columbidae, doves, Cardinal (bird), cardinals, bald eagles, red-tailed hawks, and pheasants. In prairie ecosystems, American bison, greater prairie chickens, badgers, and armadillo are common, and some of the nation's largest prairie dog towns inhabit shortgrass prairie in the state's panhandle. The Cross Timbers, a region transitioning from prairie to woodlands in Central Oklahoma, harbors 351 Vertebrate, vertebrate species. The Ouachita Mountains are home to American black bear, black bear, red fox, gray fox, and North American river otter, river otter populations, which coexist with 328 vertebrate species in southeastern Oklahoma. Also, in southeastern Oklahoma lives the American alligator.
Due to Oklahoma's location at the confluence of many geographic regions, the state's climatic regions have a high rate of biodiversity. Forests cover 24 percent of Oklahoma and prairie, prairie grasslands composed of shortgrass, mixed-grass, and tallgrass prairie, harbor expansive ecosystems in the state's central and western portions, although Agricultural land, cropland has largely replaced native grasses. Where rainfall is sparse in the state's western regions, shortgrass prairie and shrublands are the most prominent ecosystems, though pinyon pines, red cedar (junipers), and Pinus ponderosa, ponderosa pines grow near rivers and creek beds in the panhandle's far western reaches. Southwestern Oklahoma contains many rare, Disjunct distribution, disjunct species including Acer saccharum, sugar maple, Acer grandidentatum, bigtooth maple, nolina and Quercus fusiformis, Texas live oak.
Marshlands, cypress forests and mixtures of Pinus echinata, shortleaf pine, Pinus taeda, loblolly pine, sabal minor, blue palmetto, and deciduous forests dominate the state's Kiamichi Country, southeastern quarter, while mixtures of largely Quercus stellata, post oak, elm, red cedar (''Juniperus virginiana'') and pine forests cover Green Country, northeastern Oklahoma.
The state holds populations of white-tailed deer, mule deer, Pronghorn, antelope, coyotes, Cougar, mountain lions, bobcats, elk, and birds such as quail, Columbidae, doves, Cardinal (bird), cardinals, bald eagles, red-tailed hawks, and pheasants. In prairie ecosystems, American bison, greater prairie chickens, badgers, and armadillo are common, and some of the nation's largest prairie dog towns inhabit shortgrass prairie in the state's panhandle. The Cross Timbers, a region transitioning from prairie to woodlands in Central Oklahoma, harbors 351 Vertebrate, vertebrate species. The Ouachita Mountains are home to American black bear, black bear, red fox, gray fox, and North American river otter, river otter populations, which coexist with 328 vertebrate species in southeastern Oklahoma. Also, in southeastern Oklahoma lives the American alligator.

 Oklahoma is in a humid subtropical region which lies in a transition zone between semi-arid further to the west, humid continental to the north, and humid subtropical to the east and southeast. Most of the state lies in an area known as Tornado Alley characterized by frequent interaction between cold, dry air from Canada, warm to hot, dry air from Mexico and the Southwestern U.S., and warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico. The interactions between these three contrasting air currents produces severe weather (severe thunderstorms, damaging thunderstorm winds, large hail and tornadoes) with a frequency virtually unseen anywhere else on planet Earth. An average 62 tornadoes strike the state per year—one of the highest rates in the world.
Because of Oklahoma's position between zones of differing prevailing temperature and winds, weather patterns within the state can vary widely over relatively short distances, and they can change drastically in a short time. On November 11, 1911, the temperature at Oklahoma City reached (the record high for that date), then Great Blue Norther of November 11, 1911, a cold front of unprecedented intensity slammed across the state, causing the temperature to reach (the record low for that date) by midnight. This type of phenomenon is also responsible for many of the tornadoes in the area, such as the Tornado outbreak of April 27–29, 1912, 1912 Oklahoma tornado outbreak when a warm front traveled along a stalled cold front, resulting in an average of about one tornado per hour.
The humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') of central, southern and eastern Oklahoma is influenced heavily by southerly winds bringing moisture from the Gulf of Mexico. Traveling westward, the climate transitions progressively toward a semi-arid zone (Köppen ''BSk'') in the high plains of the Panhandle and other western areas from about Lawton, Oklahoma, Lawton westward, less frequently touched by southern moisture. Precipitation and temperatures decline from east to west accordingly, with areas in the southeast averaging an annual temperature of and an annual rainfall of generally over and up to , while areas of the (higher-elevation) panhandle average , with an annual rainfall under .
Over almost all of Oklahoma, winter is the driest season. Average monthly precipitation increases dramatically in the spring to a peak in May, the wettest month over most of the state, with its frequent and not uncommonly severe thunderstorm activity. Early June can still be wet, but most years see a marked decrease in rainfall during June and early July. Mid-summer (July and August) represents a secondary dry season over much of Oklahoma, with long stretches of hot weather with only sporadic thunderstorm activity not uncommon many years. Severe drought is common in the hottest summers, such as those of 1934, 1954, 1980 and 2011, all of which featured weeks on end of virtual rainlessness and highs well over . Average precipitation rises again from September to mid-October, representing a secondary wetter season, then declines from late October through December.
The entire state frequently experiences temperatures above or below , though below-zero temperatures are rare in south-central and southeastern Oklahoma. Snowfall ranges from an average of less than in the south to just over on the border of Colorado in the panhandle. The state is home to the Storm Prediction Center, the National Severe Storms Laboratory, and the Warning Decision Training Division, all part of the National Weather Service and in Norman, Oklahoma, Norman.
Oklahoma is in a humid subtropical region which lies in a transition zone between semi-arid further to the west, humid continental to the north, and humid subtropical to the east and southeast. Most of the state lies in an area known as Tornado Alley characterized by frequent interaction between cold, dry air from Canada, warm to hot, dry air from Mexico and the Southwestern U.S., and warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico. The interactions between these three contrasting air currents produces severe weather (severe thunderstorms, damaging thunderstorm winds, large hail and tornadoes) with a frequency virtually unseen anywhere else on planet Earth. An average 62 tornadoes strike the state per year—one of the highest rates in the world.
Because of Oklahoma's position between zones of differing prevailing temperature and winds, weather patterns within the state can vary widely over relatively short distances, and they can change drastically in a short time. On November 11, 1911, the temperature at Oklahoma City reached (the record high for that date), then Great Blue Norther of November 11, 1911, a cold front of unprecedented intensity slammed across the state, causing the temperature to reach (the record low for that date) by midnight. This type of phenomenon is also responsible for many of the tornadoes in the area, such as the Tornado outbreak of April 27–29, 1912, 1912 Oklahoma tornado outbreak when a warm front traveled along a stalled cold front, resulting in an average of about one tornado per hour.
The humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') of central, southern and eastern Oklahoma is influenced heavily by southerly winds bringing moisture from the Gulf of Mexico. Traveling westward, the climate transitions progressively toward a semi-arid zone (Köppen ''BSk'') in the high plains of the Panhandle and other western areas from about Lawton, Oklahoma, Lawton westward, less frequently touched by southern moisture. Precipitation and temperatures decline from east to west accordingly, with areas in the southeast averaging an annual temperature of and an annual rainfall of generally over and up to , while areas of the (higher-elevation) panhandle average , with an annual rainfall under .
Over almost all of Oklahoma, winter is the driest season. Average monthly precipitation increases dramatically in the spring to a peak in May, the wettest month over most of the state, with its frequent and not uncommonly severe thunderstorm activity. Early June can still be wet, but most years see a marked decrease in rainfall during June and early July. Mid-summer (July and August) represents a secondary dry season over much of Oklahoma, with long stretches of hot weather with only sporadic thunderstorm activity not uncommon many years. Severe drought is common in the hottest summers, such as those of 1934, 1954, 1980 and 2011, all of which featured weeks on end of virtual rainlessness and highs well over . Average precipitation rises again from September to mid-October, representing a secondary wetter season, then declines from late October through December.
The entire state frequently experiences temperatures above or below , though below-zero temperatures are rare in south-central and southeastern Oklahoma. Snowfall ranges from an average of less than in the south to just over on the border of Colorado in the panhandle. The state is home to the Storm Prediction Center, the National Severe Storms Laboratory, and the Warning Decision Training Division, all part of the National Weather Service and in Norman, Oklahoma, Norman.
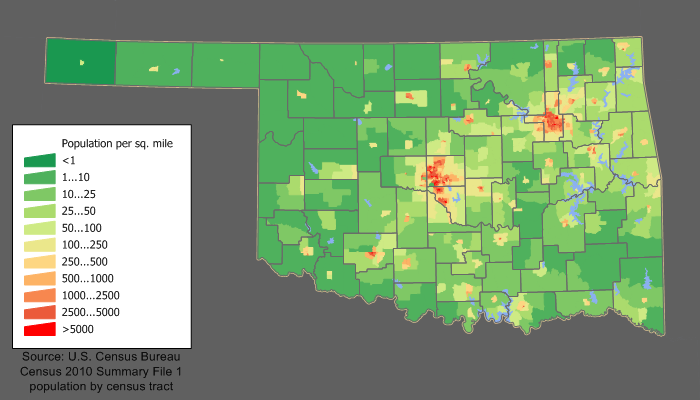
 The United States Census Bureau estimates Oklahoma's population was 3,963,516 during the 2020 United States census, a 5.66% increase since the 2010 United States census.
In 2010, the center of population of Oklahoma was in Lincoln County, Oklahoma, Lincoln County near the town of Sparks, Oklahoma, Sparks.
The state's 2006 Per capita personal income in the United States, per capita personal income ranked 37th at $32,210, though it has the third-fastest-growing per capita income in the U.S. Oklahoma ranks consistently among the lowest states in cost of living index.
In 2011, 7.0% of Oklahomans were under the age of 5, 24.7% under 18, and 13.7% were 65 or older. Females made up 50.5% of the population.
The United States Census Bureau estimates Oklahoma's population was 3,963,516 during the 2020 United States census, a 5.66% increase since the 2010 United States census.
In 2010, the center of population of Oklahoma was in Lincoln County, Oklahoma, Lincoln County near the town of Sparks, Oklahoma, Sparks.
The state's 2006 Per capita personal income in the United States, per capita personal income ranked 37th at $32,210, though it has the third-fastest-growing per capita income in the U.S. Oklahoma ranks consistently among the lowest states in cost of living index.
In 2011, 7.0% of Oklahomans were under the age of 5, 24.7% under 18, and 13.7% were 65 or older. Females made up 50.5% of the population.
 In 2011, 47.3% of Oklahoma's population younger than age1 were minorities, meaning they had at least one parent who was not non-Hispanic white.
In 2011, U.S. Census Bureau American Community Survey data from 2005 to 2009 indicated about 5% of Oklahoma's residents were born outside the United States. This is lower than the national figure (about 12.5% of U.S. residents were foreign-born).
In 2011, 47.3% of Oklahoma's population younger than age1 were minorities, meaning they had at least one parent who was not non-Hispanic white.
In 2011, U.S. Census Bureau American Community Survey data from 2005 to 2009 indicated about 5% of Oklahoma's residents were born outside the United States. This is lower than the national figure (about 12.5% of U.S. residents were foreign-born).
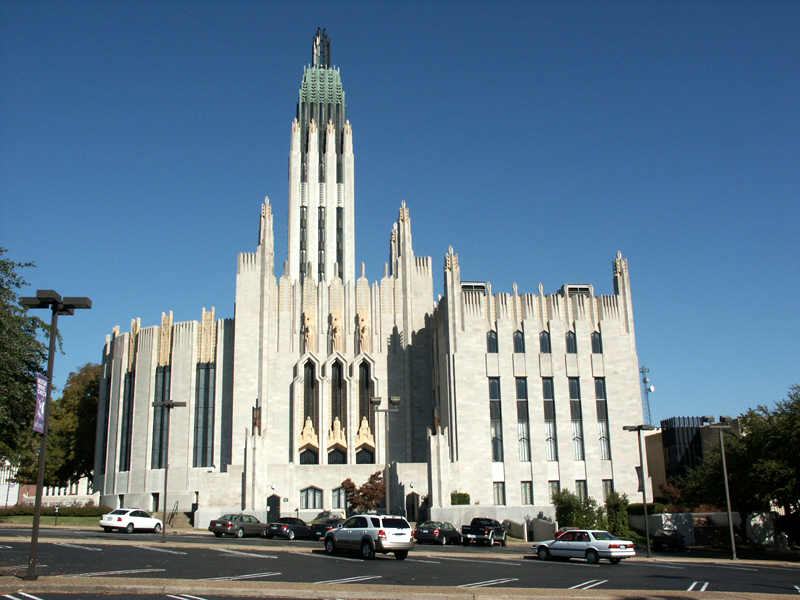 Oklahoma is part of a geographical region characterized by conservative and Evangelical Christianity known as the "Bible Belt". Spanning the southern and eastern parts of the United States, the area is known for Ideology, politically and socially conservative views, with the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party having the greater number of voters registered between the two parties. Tulsa, the state's second-largest city, home to Oral Roberts University, is sometimes called the "Bible Belt#Buckle, buckle of the Bible Belt".
In 2000, there were about 5,000 List of synagogues in Oklahoma, Jews and 6,000 Muslims, with ten congregations to each group.
According to the Pew Research Center in 2008, the majority of Oklahoma's religious adherents were Christian, accounting for about 80 percent of the population. The percentage of Catholics was half the national average, while the percentage of Evangelical Protestants was more than twice the national average (tied with Arkansas for the largest percentage of any state).
Oklahoma is part of a geographical region characterized by conservative and Evangelical Christianity known as the "Bible Belt". Spanning the southern and eastern parts of the United States, the area is known for Ideology, politically and socially conservative views, with the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party having the greater number of voters registered between the two parties. Tulsa, the state's second-largest city, home to Oral Roberts University, is sometimes called the "Bible Belt#Buckle, buckle of the Bible Belt".
In 2000, there were about 5,000 List of synagogues in Oklahoma, Jews and 6,000 Muslims, with ten congregations to each group.
According to the Pew Research Center in 2008, the majority of Oklahoma's religious adherents were Christian, accounting for about 80 percent of the population. The percentage of Catholics was half the national average, while the percentage of Evangelical Protestants was more than twice the national average (tied with Arkansas for the largest percentage of any state).
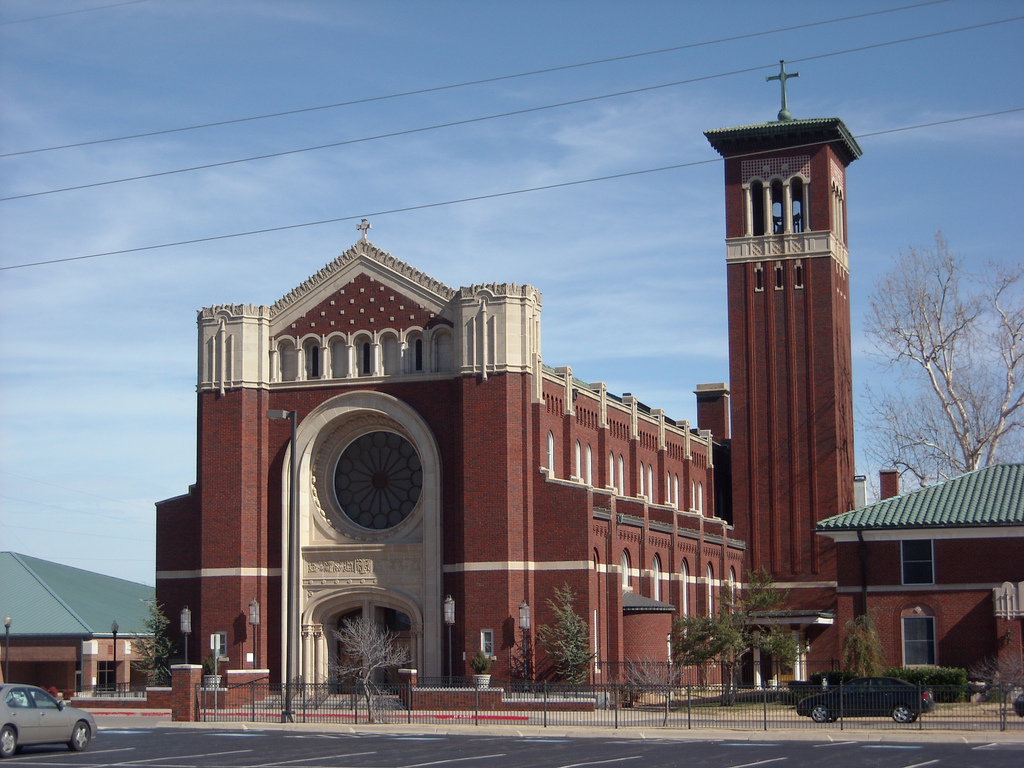 In 2010, the state's largest church memberships were in the Southern Baptist Convention (886,394 members), the United Methodist Church (282,347), the Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Church (178,430), and the Assemblies of God USA, Assemblies of God (85,926) and the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (Mormons) (47,349). Other religions represented in the state include Buddhism, Hinduism, and Islam.
According to the Pew Research Center in 2014, the majority of Oklahoma's religious adherents were Christian accounting for 79 percent of the population, 9 percent higher than the national average. The percentage of Evangelical Protestants declined since the last study, but they remain the largest religious group in the state at 47 percent, over 20 percent higher than the national average. The largest growth over the six years between Pew's 2008 and 2014 survey was in the number of people who identify as irreligious, Unaffiliated in the state with an increase of 6 percent.
In 2010, the state's largest church memberships were in the Southern Baptist Convention (886,394 members), the United Methodist Church (282,347), the Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Church (178,430), and the Assemblies of God USA, Assemblies of God (85,926) and the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (Mormons) (47,349). Other religions represented in the state include Buddhism, Hinduism, and Islam.
According to the Pew Research Center in 2014, the majority of Oklahoma's religious adherents were Christian accounting for 79 percent of the population, 9 percent higher than the national average. The percentage of Evangelical Protestants declined since the last study, but they remain the largest religious group in the state at 47 percent, over 20 percent higher than the national average. The largest growth over the six years between Pew's 2008 and 2014 survey was in the number of people who identify as irreligious, Unaffiliated in the state with an increase of 6 percent.
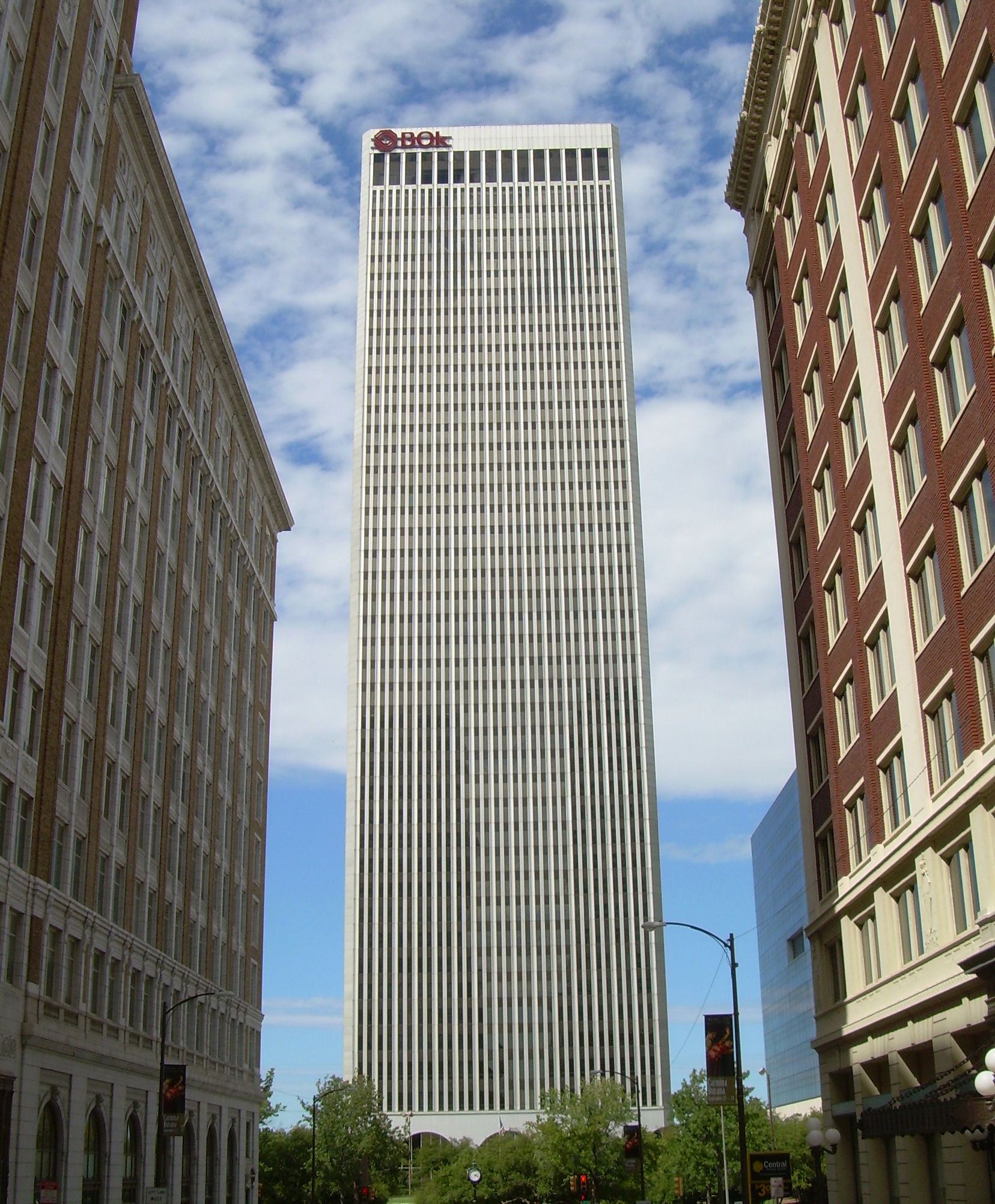 Oklahoma is host to a diverse range of sectors including aviation, energy, transportation equipment, food processing, electronics, and telecommunications. Oklahoma is an important producer of natural gas, aircraft, and agriculture, food. The state ranks third in the nation for production of natural gas, is the 27th-most agriculturally productive state, and also ranks 5th in production of wheat. Four Fortune 500 companies and six Fortune 1000 companies are headquartered in Oklahoma, and it has been rated one of the most business-friendly states in the nation, with the 7th-lowest tax burden in 2007.
* Total employment (2018): 1,385,228
* Number of employer establishments: 93,561
In 2010, Oklahoma City-based Love's Travel Stops & Country Stores ranked 18th on the Forbes list of largest private companies, Tulsa-based QuikTrip ranked 37th, and Oklahoma City-based Hobby Lobby ranked 198th in 2010 report. Oklahoma's gross domestic product grew from $131.9 billion in 2006 to $147.5 billion in 2010, a jump of 10.6 percent. Oklahoma's gross domestic product per capita was $35,480 in 2010, which was ranked 40th among the states.
Though oil has historically dominated the state's economy, a 1980s oil glut, collapse in the energy industry during the 1980s led to the loss of nearly 90,000 energy-related jobs between 1980 and 2000, severely damaging the local economy. Oil accounted for 35 billion dollars in Oklahoma's economy in 2007, and employment in the state's oil industry was outpaced by five other industries in 2007. , the state's unemployment rate is 5.3%.
Oklahoma is host to a diverse range of sectors including aviation, energy, transportation equipment, food processing, electronics, and telecommunications. Oklahoma is an important producer of natural gas, aircraft, and agriculture, food. The state ranks third in the nation for production of natural gas, is the 27th-most agriculturally productive state, and also ranks 5th in production of wheat. Four Fortune 500 companies and six Fortune 1000 companies are headquartered in Oklahoma, and it has been rated one of the most business-friendly states in the nation, with the 7th-lowest tax burden in 2007.
* Total employment (2018): 1,385,228
* Number of employer establishments: 93,561
In 2010, Oklahoma City-based Love's Travel Stops & Country Stores ranked 18th on the Forbes list of largest private companies, Tulsa-based QuikTrip ranked 37th, and Oklahoma City-based Hobby Lobby ranked 198th in 2010 report. Oklahoma's gross domestic product grew from $131.9 billion in 2006 to $147.5 billion in 2010, a jump of 10.6 percent. Oklahoma's gross domestic product per capita was $35,480 in 2010, which was ranked 40th among the states.
Though oil has historically dominated the state's economy, a 1980s oil glut, collapse in the energy industry during the 1980s led to the loss of nearly 90,000 energy-related jobs between 1980 and 2000, severely damaging the local economy. Oil accounted for 35 billion dollars in Oklahoma's economy in 2007, and employment in the state's oil industry was outpaced by five other industries in 2007. , the state's unemployment rate is 5.3%.
 Oklahoma is the nation's third-largest producer of natural gas, and its fifth-largest producer of crude oil. The state also has the second-greatest number of active drilling rigs, and it is even ranked fifth in crude oil reserves. While the state was ranked eighth for installed Wind power, wind energy capacity in 2011, it still was at the bottom of states in usage of renewable energy in 2009, with 94% of its electricity being generated by Non-renewable energy, non-renewable sources in 2009, including 25% from coal and 46% from natural gas.
Ten years later in 2019, 53.5% of electricity was produced from natural gas and 34.6% from wind power.
Oklahoma has no nuclear power plants. Ranking 13th for total energy consumption per capita in 2009, the state's energy costs were eighth-lowest in the nation.
As a whole, the oil energy industry contributes $35 billion to Oklahoma's gross domestic product (GDP), and employees of the state's oil-related companies earn an average of twice the state's typical yearly income. In 2009, the state had 83,700 commercial oil wells churning of crude oil. 8.5% of the nation's natural gas supply is held in Oklahoma, with being produced in 2009.
The Oklahoma Stack Play is a geographic referenced area in the Anadarko Basin. The oil field "Sooner Trend", Anadarko basin and the counties of Kingfisher and Canadian make up the basis for the "Oklahoma STACK". Other Plays such as the Eagle Ford are geological rather than geographical.
According to ''Forbes'' magazine, Oklahoma City-based Devon Energy, Devon Energy Corporation, Chesapeake Energy, Chesapeake Energy Corporation, and SandRidge Energy, SandRidge Energy Corporation are the largest private oil-related companies in the nation, and all Oklahoma's Fortune 500 companies are energy-related. Tulsa's ONEOK and Williams Companies are the state's largest and second-largest companies respectively, also ranking as the nation's second- and third-largest companies in the field of energy, according to Fortune (magazine), ''Fortune'' magazine. The magazine also placed Devon Energy as the second-largest company in the mining and crude oil-producing industry in the nation, while Chesapeake Energy ranks seventh respectively in that sector and Oklahoma Gas & Electric ranks as the 25th-largest gas and electric utility company.
Oklahoma Gas & Electric, commonly referred to as OG&E (NYSE: OGE) operates four base electric power plants in Oklahoma. Two of them are coal-fired power plants: one in Muskogee, Oklahoma, Muskogee, and the other in Red Rock, Oklahoma, Red Rock. Two are gas-fired power plants: one in Harrah, Oklahoma, Harrah and the other in Konawa, Oklahoma, Konawa. OG&E was the first electric company in Oklahoma to generate electricity from wind farms in 2003.
Oklahoma is the nation's third-largest producer of natural gas, and its fifth-largest producer of crude oil. The state also has the second-greatest number of active drilling rigs, and it is even ranked fifth in crude oil reserves. While the state was ranked eighth for installed Wind power, wind energy capacity in 2011, it still was at the bottom of states in usage of renewable energy in 2009, with 94% of its electricity being generated by Non-renewable energy, non-renewable sources in 2009, including 25% from coal and 46% from natural gas.
Ten years later in 2019, 53.5% of electricity was produced from natural gas and 34.6% from wind power.
Oklahoma has no nuclear power plants. Ranking 13th for total energy consumption per capita in 2009, the state's energy costs were eighth-lowest in the nation.
As a whole, the oil energy industry contributes $35 billion to Oklahoma's gross domestic product (GDP), and employees of the state's oil-related companies earn an average of twice the state's typical yearly income. In 2009, the state had 83,700 commercial oil wells churning of crude oil. 8.5% of the nation's natural gas supply is held in Oklahoma, with being produced in 2009.
The Oklahoma Stack Play is a geographic referenced area in the Anadarko Basin. The oil field "Sooner Trend", Anadarko basin and the counties of Kingfisher and Canadian make up the basis for the "Oklahoma STACK". Other Plays such as the Eagle Ford are geological rather than geographical.
According to ''Forbes'' magazine, Oklahoma City-based Devon Energy, Devon Energy Corporation, Chesapeake Energy, Chesapeake Energy Corporation, and SandRidge Energy, SandRidge Energy Corporation are the largest private oil-related companies in the nation, and all Oklahoma's Fortune 500 companies are energy-related. Tulsa's ONEOK and Williams Companies are the state's largest and second-largest companies respectively, also ranking as the nation's second- and third-largest companies in the field of energy, according to Fortune (magazine), ''Fortune'' magazine. The magazine also placed Devon Energy as the second-largest company in the mining and crude oil-producing industry in the nation, while Chesapeake Energy ranks seventh respectively in that sector and Oklahoma Gas & Electric ranks as the 25th-largest gas and electric utility company.
Oklahoma Gas & Electric, commonly referred to as OG&E (NYSE: OGE) operates four base electric power plants in Oklahoma. Two of them are coal-fired power plants: one in Muskogee, Oklahoma, Muskogee, and the other in Red Rock, Oklahoma, Red Rock. Two are gas-fired power plants: one in Harrah, Oklahoma, Harrah and the other in Konawa, Oklahoma, Konawa. OG&E was the first electric company in Oklahoma to generate electricity from wind farms in 2003.
 With an educational system made up of State school, public school districts and independent private school, private institutions, Oklahoma had 638,817 students enrolled in 1,845 public primary, secondary, and vocational education, vocational schools in 533 school districts . Oklahoma has the highest enrollment of Native American students in the nation with 126,078 students in the 2009–10 school year. Oklahoma spent $7,755 for each student in 2008, and was 47th in the nation in expenditures per student, though its growth of total education expenditures between 1992 and 2002 ranked 22nd.
The state is among the best in pre-kindergarten education, and the National Institute for Early Education Research rated it first in the United States with regard to standards, quality, and access to pre-kindergarten education in 2004, calling it "a model for early childhood education, early childhood schooling". High school dropout rate decreased from 3.1 to 2.5 percent between 2007 and 2008 with Oklahoma ranked among 18 other states with 3 percent or less dropout rate. In 2004, the state ranked 36th in the nation for the relative number of adults with high school diplomas, though at 85.2 percent, it had the highest rate among Southern states. According to a study conducted by the Pell Institute, Oklahoma ranks 48th in college-participation for low-income students.
The University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma State University, the University of Central Oklahoma, and Northeastern State University are the largest public institutions of higher education in Oklahoma, each operating through one primary campus and satellite campuses throughout the state. The two state universities, along with Oklahoma City University and the University of Tulsa, rank among the country's best in undergraduate business programs.
Oklahoma City University School of Law, University of Oklahoma College of Law, and University of Tulsa College of Law are the state's only ABA-accredited institutions. Both University of Oklahoma and University of Tulsa are Tier1 institutions, with the University of Oklahoma ranked 68th and the University of Tulsa ranked 86th in the nation.
Oklahoma holds eleven public regional universities, including Northeastern State University, the second-oldest institution of higher education west of the Mississippi River, also containing the only College of Optometry in Oklahoma and the largest enrollment of Indigenous peoples of the United States, Native American students in the nation by percentage and amount. Langston University is Oklahoma's only historically black college. Six of the state's universities were placed in the Princeton Review's list of best 122 regional colleges in 2007, and three made the list of top colleges for best value. The state has 55 post-secondary technical institutions operated by Oklahoma Department of Career and Technology Education, Oklahoma's CareerTech program for training in specific fields of industry or trade.
In the 2007–2008 school year, there were 181,973 undergraduate students, 20,014 graduate students, and 4,395 first-professional degree students enrolled in Oklahoma colleges. Of these students, 18,892 received a bachelor's degree, 5,386 received a master's degree, and 462 received a first professional degree. This means the state of Oklahoma produces an average of 38,278-degree-holders per completions component (i.e. July 1, 2007June 30, 2008). National average is 68,322 total degrees awarded per completions component.
Beginning on April 2, 2018, tens of thousands of K–12 public school teachers 2018 Oklahoma teachers' strike, went on strike due to lack of funding. According to the National Education Association, teachers in Oklahoma had ranked 49th out of the 50 states in terms of teacher pay in 2016. The Oklahoma Legislature had passed a measure a week earlier to raise teacher salaries by $6,100, but it fell short of the $10,000 raise for teachers, $5,000 raise for other school employees, and $200 million increase in extra education funding many had sought. A survey in 2019 found that the pay raise obtained by the strike lifted the State's teacher pay ranking to 34th in the nation.
With an educational system made up of State school, public school districts and independent private school, private institutions, Oklahoma had 638,817 students enrolled in 1,845 public primary, secondary, and vocational education, vocational schools in 533 school districts . Oklahoma has the highest enrollment of Native American students in the nation with 126,078 students in the 2009–10 school year. Oklahoma spent $7,755 for each student in 2008, and was 47th in the nation in expenditures per student, though its growth of total education expenditures between 1992 and 2002 ranked 22nd.
The state is among the best in pre-kindergarten education, and the National Institute for Early Education Research rated it first in the United States with regard to standards, quality, and access to pre-kindergarten education in 2004, calling it "a model for early childhood education, early childhood schooling". High school dropout rate decreased from 3.1 to 2.5 percent between 2007 and 2008 with Oklahoma ranked among 18 other states with 3 percent or less dropout rate. In 2004, the state ranked 36th in the nation for the relative number of adults with high school diplomas, though at 85.2 percent, it had the highest rate among Southern states. According to a study conducted by the Pell Institute, Oklahoma ranks 48th in college-participation for low-income students.
The University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma State University, the University of Central Oklahoma, and Northeastern State University are the largest public institutions of higher education in Oklahoma, each operating through one primary campus and satellite campuses throughout the state. The two state universities, along with Oklahoma City University and the University of Tulsa, rank among the country's best in undergraduate business programs.
Oklahoma City University School of Law, University of Oklahoma College of Law, and University of Tulsa College of Law are the state's only ABA-accredited institutions. Both University of Oklahoma and University of Tulsa are Tier1 institutions, with the University of Oklahoma ranked 68th and the University of Tulsa ranked 86th in the nation.
Oklahoma holds eleven public regional universities, including Northeastern State University, the second-oldest institution of higher education west of the Mississippi River, also containing the only College of Optometry in Oklahoma and the largest enrollment of Indigenous peoples of the United States, Native American students in the nation by percentage and amount. Langston University is Oklahoma's only historically black college. Six of the state's universities were placed in the Princeton Review's list of best 122 regional colleges in 2007, and three made the list of top colleges for best value. The state has 55 post-secondary technical institutions operated by Oklahoma Department of Career and Technology Education, Oklahoma's CareerTech program for training in specific fields of industry or trade.
In the 2007–2008 school year, there were 181,973 undergraduate students, 20,014 graduate students, and 4,395 first-professional degree students enrolled in Oklahoma colleges. Of these students, 18,892 received a bachelor's degree, 5,386 received a master's degree, and 462 received a first professional degree. This means the state of Oklahoma produces an average of 38,278-degree-holders per completions component (i.e. July 1, 2007June 30, 2008). National average is 68,322 total degrees awarded per completions component.
Beginning on April 2, 2018, tens of thousands of K–12 public school teachers 2018 Oklahoma teachers' strike, went on strike due to lack of funding. According to the National Education Association, teachers in Oklahoma had ranked 49th out of the 50 states in terms of teacher pay in 2016. The Oklahoma Legislature had passed a measure a week earlier to raise teacher salaries by $6,100, but it fell short of the $10,000 raise for teachers, $5,000 raise for other school employees, and $200 million increase in extra education funding many had sought. A survey in 2019 found that the pay raise obtained by the strike lifted the State's teacher pay ranking to 34th in the nation.
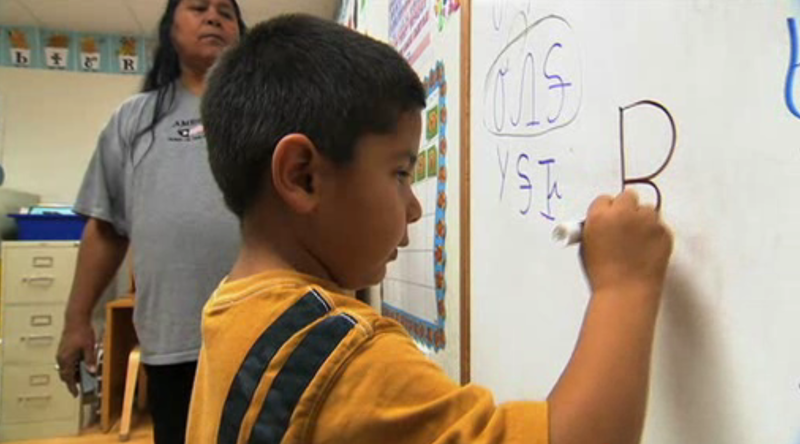 The Cherokee Nation instigated a ten-year plan in 2005 that involved growing new speakers of the Cherokee language from childhood as well as speaking it exclusively at home. The plan was part of an ambitious goal that in fifty years would have at least 80% of their people fluent. The Cherokee Preservation Foundation has invested $3 million into opening schools, training teachers, and developing curricula for language education, as well as initiating community gatherings where the language can be actively used.
A Cherokee language immersion school in Tahlequah, Oklahoma educates students from pre-school through eighth grade.
The Cherokee Nation instigated a ten-year plan in 2005 that involved growing new speakers of the Cherokee language from childhood as well as speaking it exclusively at home. The plan was part of an ambitious goal that in fifty years would have at least 80% of their people fluent. The Cherokee Preservation Foundation has invested $3 million into opening schools, training teachers, and developing curricula for language education, as well as initiating community gatherings where the language can be actively used.
A Cherokee language immersion school in Tahlequah, Oklahoma educates students from pre-school through eighth grade.
 Oklahoma is placed in the South by the United States Census Bureau, but other definitions place the state at least partly in the Southwestern United States, Southwest, Midwestern United States, Midwest, Upland South, and
Oklahoma is placed in the South by the United States Census Bureau, but other definitions place the state at least partly in the Southwestern United States, Southwest, Midwestern United States, Midwest, Upland South, and
 In the state's largest urban areas, pockets of jazz culture flourish, and Native American, Mexican Americans, Mexican American, and Asian American communities produce music and art of their respective cultures. The Oklahoma Mozart Festival in Bartlesville is one of the largest classical music festivals on the southern plains, and Oklahoma City's Festival of the Arts has been named one of the top fine arts festivals in the nation.
The state has a rich history in ballet with five Native American ballerinas attaining worldwide fame. These were Yvonne Chouteau, sisters Marjorie Tallchief, Marjorie and Maria Tallchief, Rosella Hightower and Moscelyne Larkin, known collectively as the Five Moons. ''The New York Times'' rates the Tulsa Ballet as one of the top ballet companies in the United States. The Oklahoma City Ballet and University of Oklahoma's dance program were formed by ballerina Yvonne Chouteau and husband Miguel Terekhov. The university program was founded in 1962 and was the first fully accredited program of its kind in the United States.
In Sand Springs, Oklahoma, Sand Springs, an outdoor amphitheater called "Discoveryland!" (since closed) is the official performance headquarters for the musical ''Oklahoma!'' Ridge Bond, native of McAlester, Oklahoma, starred in the Broadway theatre, Broadway and International touring productions of ''Oklahoma!'', playing the role of "Curly McClain" in more than 2,600 performances. In 1953 he was featured along with the ''Oklahoma!'' cast on a CBS Omnibus (U.S. TV series), Omnibus television broadcast. Bond was instrumental in the Oklahoma (Rodgers and Hammerstein song), Oklahoma! title song becoming the Oklahoma state song and is also featured on the U.S. postage stamp commemorating the musical's 50th anniversary. Historically, the state has produced musical styles such as The Tulsa Sound and western swing, which was popularized at Cain's Ballroom in Tulsa. The building, known as the "Carnegie Hall of Western Swing", served as the performance headquarters of Bob Wills and the Texas Playboys during the 1930s. Stillwater is known as the epicenter of Red Dirt (music), Red Dirt music, the best-known proponent of which is the late Bob Childers.
Prominent theatre companies in Oklahoma include, in the capital city, Lyric Theatre of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City Theatre Company, Carpenter Square Theatre, Oklahoma Shakespeare in the Park, and CityRep. CityRep is a professional company affording equity points to those performers and technical theatre professionals. In Tulsa, Oklahoma's oldest resident professional company is American Theatre Company, and Theatre Tulsa is the oldest community theatre company west of the Mississippi. Other companies in Tulsa include Heller Theatre and Tulsa Spotlight Theater. The cities of Norman, Lawton, and Stillwater, among others, also host well-reviewed community theatre companies.
Oklahoma is in the nation's middle percentile in per capita spending on the arts, ranking 17th, and contains more than 300 museums. The Philbrook Museum of Tulsa is considered one of the top 50 fine art museums in the United States, and the Sam Noble Oklahoma Museum of Natural History in Norman, one of the largest university-based art and history museums in the country, documents the natural history of the region. The collections of Thomas Gilcrease are housed in the Gilcrease Museum of Tulsa, which also holds the world's largest, most comprehensive collection of art and artifacts of the American West.
The Egyptian art collection at the Mabee-Gerrer Museum of Art in Shawnee is considered to be the finest Egyptian collection between Chicago and Los Angeles. The Oklahoma City Museum of Art contains the most comprehensive collection of glass sculptures by artist Dale Chihuly in the world, and Oklahoma City's National Cowboy & Western Heritage Museum documents the heritage of the American Western frontier. With remnants of the The Holocaust, Holocaust and artifacts relevant to Judaism, the Sherwin Miller Museum of Jewish Art of Tulsa preserves the largest collection of Jewish art in the Southwest United States.
In the state's largest urban areas, pockets of jazz culture flourish, and Native American, Mexican Americans, Mexican American, and Asian American communities produce music and art of their respective cultures. The Oklahoma Mozart Festival in Bartlesville is one of the largest classical music festivals on the southern plains, and Oklahoma City's Festival of the Arts has been named one of the top fine arts festivals in the nation.
The state has a rich history in ballet with five Native American ballerinas attaining worldwide fame. These were Yvonne Chouteau, sisters Marjorie Tallchief, Marjorie and Maria Tallchief, Rosella Hightower and Moscelyne Larkin, known collectively as the Five Moons. ''The New York Times'' rates the Tulsa Ballet as one of the top ballet companies in the United States. The Oklahoma City Ballet and University of Oklahoma's dance program were formed by ballerina Yvonne Chouteau and husband Miguel Terekhov. The university program was founded in 1962 and was the first fully accredited program of its kind in the United States.
In Sand Springs, Oklahoma, Sand Springs, an outdoor amphitheater called "Discoveryland!" (since closed) is the official performance headquarters for the musical ''Oklahoma!'' Ridge Bond, native of McAlester, Oklahoma, starred in the Broadway theatre, Broadway and International touring productions of ''Oklahoma!'', playing the role of "Curly McClain" in more than 2,600 performances. In 1953 he was featured along with the ''Oklahoma!'' cast on a CBS Omnibus (U.S. TV series), Omnibus television broadcast. Bond was instrumental in the Oklahoma (Rodgers and Hammerstein song), Oklahoma! title song becoming the Oklahoma state song and is also featured on the U.S. postage stamp commemorating the musical's 50th anniversary. Historically, the state has produced musical styles such as The Tulsa Sound and western swing, which was popularized at Cain's Ballroom in Tulsa. The building, known as the "Carnegie Hall of Western Swing", served as the performance headquarters of Bob Wills and the Texas Playboys during the 1930s. Stillwater is known as the epicenter of Red Dirt (music), Red Dirt music, the best-known proponent of which is the late Bob Childers.
Prominent theatre companies in Oklahoma include, in the capital city, Lyric Theatre of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City Theatre Company, Carpenter Square Theatre, Oklahoma Shakespeare in the Park, and CityRep. CityRep is a professional company affording equity points to those performers and technical theatre professionals. In Tulsa, Oklahoma's oldest resident professional company is American Theatre Company, and Theatre Tulsa is the oldest community theatre company west of the Mississippi. Other companies in Tulsa include Heller Theatre and Tulsa Spotlight Theater. The cities of Norman, Lawton, and Stillwater, among others, also host well-reviewed community theatre companies.
Oklahoma is in the nation's middle percentile in per capita spending on the arts, ranking 17th, and contains more than 300 museums. The Philbrook Museum of Tulsa is considered one of the top 50 fine art museums in the United States, and the Sam Noble Oklahoma Museum of Natural History in Norman, one of the largest university-based art and history museums in the country, documents the natural history of the region. The collections of Thomas Gilcrease are housed in the Gilcrease Museum of Tulsa, which also holds the world's largest, most comprehensive collection of art and artifacts of the American West.
The Egyptian art collection at the Mabee-Gerrer Museum of Art in Shawnee is considered to be the finest Egyptian collection between Chicago and Los Angeles. The Oklahoma City Museum of Art contains the most comprehensive collection of glass sculptures by artist Dale Chihuly in the world, and Oklahoma City's National Cowboy & Western Heritage Museum documents the heritage of the American Western frontier. With remnants of the The Holocaust, Holocaust and artifacts relevant to Judaism, the Sherwin Miller Museum of Jewish Art of Tulsa preserves the largest collection of Jewish art in the Southwest United States.
 Oklahoma's centennial celebration was named the top event in the United States for 2007 by the American Bus Association, and consisted of multiple celebrations saving with the 100th anniversary of U.S. state, statehood on November 16, 2007. Annual ethnic festivals and events take place throughout the state such as Native American powwows and ceremonial events, and include festivals (as examples) in Scottish Americans, Scottish, Irish Americans, Irish, German Americans, German, Italian Americans, Italian, Vietnamese Americans, Vietnamese, Chinese Americans, Chinese, Czech Americans, Czech, American Jews, Jewish, Arab Americans, Arab, Mexican Americans, Mexican and African-American communities depicting cultural heritage or traditions.
Oklahoma City is home to a few reoccurring events and festivals. During a ten-day run in Oklahoma City, the Oklahoma State Fair, State Fair of Oklahoma attracts roughly one million people along with the annual Festival of the Arts. Large national pow wows, various Latin and Culture of Asia, Asian heritage festivals, and cultural festivals such as the Juneteenth celebrations are held in Oklahoma City each year. The Oklahoma City Pride Parade has been held annually in late June since 1987 in the gay district of Oklahoma City on NW 39th Street Enclave, 39th and Penn. The First Friday Art Walk in the Paseo Arts District is an art appreciation festival held the first Friday of every month. Additionally, an annual art festival is held in the Paseo on Memorial Day Weekend.
The Tulsa State Fair attracts more than a million people each year during its ten-day run, and the city's Mayfest festival entertained more than 375,000 in four days during 2007. In 2006, Tulsa's Oktoberfest was named one of the top 10 in the world by ''USA Today''.
Norman plays host to the Norman Music Festival, a festival that highlights native Oklahoma bands and musicians. Norman is also host to the Medieval Fair of Norman, which has been held annually since 1976 and was Oklahoma's first medieval fair. The Fair was held first on the south oval of the University of Oklahoma campus and in the third year moved to the Duck Pond in Norman until the Fair became too big and moved to Reaves Park in 2003. The Medieval Fair of Norman is Oklahoma's "largest weekend event and the third-largest event in Oklahoma, and was selected by Events Media Network as one of the top 100 events in the nation".
Oklahoma's centennial celebration was named the top event in the United States for 2007 by the American Bus Association, and consisted of multiple celebrations saving with the 100th anniversary of U.S. state, statehood on November 16, 2007. Annual ethnic festivals and events take place throughout the state such as Native American powwows and ceremonial events, and include festivals (as examples) in Scottish Americans, Scottish, Irish Americans, Irish, German Americans, German, Italian Americans, Italian, Vietnamese Americans, Vietnamese, Chinese Americans, Chinese, Czech Americans, Czech, American Jews, Jewish, Arab Americans, Arab, Mexican Americans, Mexican and African-American communities depicting cultural heritage or traditions.
Oklahoma City is home to a few reoccurring events and festivals. During a ten-day run in Oklahoma City, the Oklahoma State Fair, State Fair of Oklahoma attracts roughly one million people along with the annual Festival of the Arts. Large national pow wows, various Latin and Culture of Asia, Asian heritage festivals, and cultural festivals such as the Juneteenth celebrations are held in Oklahoma City each year. The Oklahoma City Pride Parade has been held annually in late June since 1987 in the gay district of Oklahoma City on NW 39th Street Enclave, 39th and Penn. The First Friday Art Walk in the Paseo Arts District is an art appreciation festival held the first Friday of every month. Additionally, an annual art festival is held in the Paseo on Memorial Day Weekend.
The Tulsa State Fair attracts more than a million people each year during its ten-day run, and the city's Mayfest festival entertained more than 375,000 in four days during 2007. In 2006, Tulsa's Oktoberfest was named one of the top 10 in the world by ''USA Today''.
Norman plays host to the Norman Music Festival, a festival that highlights native Oklahoma bands and musicians. Norman is also host to the Medieval Fair of Norman, which has been held annually since 1976 and was Oklahoma's first medieval fair. The Fair was held first on the south oval of the University of Oklahoma campus and in the third year moved to the Duck Pond in Norman until the Fair became too big and moved to Reaves Park in 2003. The Medieval Fair of Norman is Oklahoma's "largest weekend event and the third-largest event in Oklahoma, and was selected by Events Media Network as one of the top 100 events in the nation".
 College athletics in the United States, Collegiate athletics are a popular draw in the state. The state has four schools that compete at the highest level of college sports, NCAA Division I. The most prominent are the state's two members of the Big 12 Conference, one of the so-called Power Five conferences of the top tier of college football, NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision, Division I FBS. The Oklahoma Sooners, University of Oklahoma and Oklahoma State Cowboys and Cowgirls, Oklahoma State University average well over 50,000 fans attending their football games, and Oklahoma's football program ranked 12th in attendance among American colleges in 2010, with an average of 84,738 people attending its home games. The two universities meet several times each year in rivalry matches known as the Bedlam Series, which are some of the greatest sporting draws to the state. ''Sports Illustrated'' magazine rates Oklahoma and Oklahoma State among the top colleges for athletics in the nation.
Two private institutions in Tulsa, the Tulsa Golden Hurricane, University of Tulsa and Oral Roberts Golden Eagles, Oral Roberts University; are also Division I members. Tulsa competes in FBS football and other sports in the American Athletic Conference, while Oral Roberts, which does not sponsor football, is a member of the Summit League. In addition, 12 of the state's smaller colleges and universities compete in NCAA Division II as members of three different conferences, and eight other Oklahoma institutions participate in the National Association of Intercollegiate Athletics, NAIA, mostly within the Sooner Athletic Conference.
Regular LPGA tournaments are held at Cedar Ridge Country Club in Tulsa, and Men's major golf championships, major championships for the Professional Golfers' Association of America, PGA or LPGA have been played at Southern Hills Country Club in Tulsa, Oak Tree Country Club in Oklahoma City, and Cedar Ridge Country Club in Tulsa. Rated one of the top golf courses in the nation, Southern Hills has hosted five PGA Championships, including one in 2022, and three U.S. Open (golf), U.S. Opens, the most recent in 2001. Rodeos are popular throughout the state, and Guymon, Oklahoma, Guymon, in the state's panhandle, hosts one of the largest in the nation.
ESPN called Oklahoma City "the center of the softball universe", specifically referring to the fast-pitch version, in a 2020 story. Oklahoma City is home to the governing body of the sport in the United States, USA Softball, which has its headquarters in a complex that also includes the USA Softball Hall of Fame Stadium. It annually hosts the Women's College World Series, the eight-team final round of the NCAA Division I softball tournament.
Wrestling is a sport with a strong tradition in Oklahoma. Oklahoma State Cowboys wrestling, Oklahoma State has the most NCAA Division I Wrestling Championships, NCAA national championships of any Collegiate wrestling, collegiate team with 34, with the Oklahoma Sooners having 7 NCAA wrestling titles. The National Wrestling Hall of Fame and Museum is headquartered in Stillwater, Oklahoma.
College athletics in the United States, Collegiate athletics are a popular draw in the state. The state has four schools that compete at the highest level of college sports, NCAA Division I. The most prominent are the state's two members of the Big 12 Conference, one of the so-called Power Five conferences of the top tier of college football, NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision, Division I FBS. The Oklahoma Sooners, University of Oklahoma and Oklahoma State Cowboys and Cowgirls, Oklahoma State University average well over 50,000 fans attending their football games, and Oklahoma's football program ranked 12th in attendance among American colleges in 2010, with an average of 84,738 people attending its home games. The two universities meet several times each year in rivalry matches known as the Bedlam Series, which are some of the greatest sporting draws to the state. ''Sports Illustrated'' magazine rates Oklahoma and Oklahoma State among the top colleges for athletics in the nation.
Two private institutions in Tulsa, the Tulsa Golden Hurricane, University of Tulsa and Oral Roberts Golden Eagles, Oral Roberts University; are also Division I members. Tulsa competes in FBS football and other sports in the American Athletic Conference, while Oral Roberts, which does not sponsor football, is a member of the Summit League. In addition, 12 of the state's smaller colleges and universities compete in NCAA Division II as members of three different conferences, and eight other Oklahoma institutions participate in the National Association of Intercollegiate Athletics, NAIA, mostly within the Sooner Athletic Conference.
Regular LPGA tournaments are held at Cedar Ridge Country Club in Tulsa, and Men's major golf championships, major championships for the Professional Golfers' Association of America, PGA or LPGA have been played at Southern Hills Country Club in Tulsa, Oak Tree Country Club in Oklahoma City, and Cedar Ridge Country Club in Tulsa. Rated one of the top golf courses in the nation, Southern Hills has hosted five PGA Championships, including one in 2022, and three U.S. Open (golf), U.S. Opens, the most recent in 2001. Rodeos are popular throughout the state, and Guymon, Oklahoma, Guymon, in the state's panhandle, hosts one of the largest in the nation.
ESPN called Oklahoma City "the center of the softball universe", specifically referring to the fast-pitch version, in a 2020 story. Oklahoma City is home to the governing body of the sport in the United States, USA Softball, which has its headquarters in a complex that also includes the USA Softball Hall of Fame Stadium. It annually hosts the Women's College World Series, the eight-team final round of the NCAA Division I softball tournament.
Wrestling is a sport with a strong tradition in Oklahoma. Oklahoma State Cowboys wrestling, Oklahoma State has the most NCAA Division I Wrestling Championships, NCAA national championships of any Collegiate wrestling, collegiate team with 34, with the Oklahoma Sooners having 7 NCAA wrestling titles. The National Wrestling Hall of Fame and Museum is headquartered in Stillwater, Oklahoma.
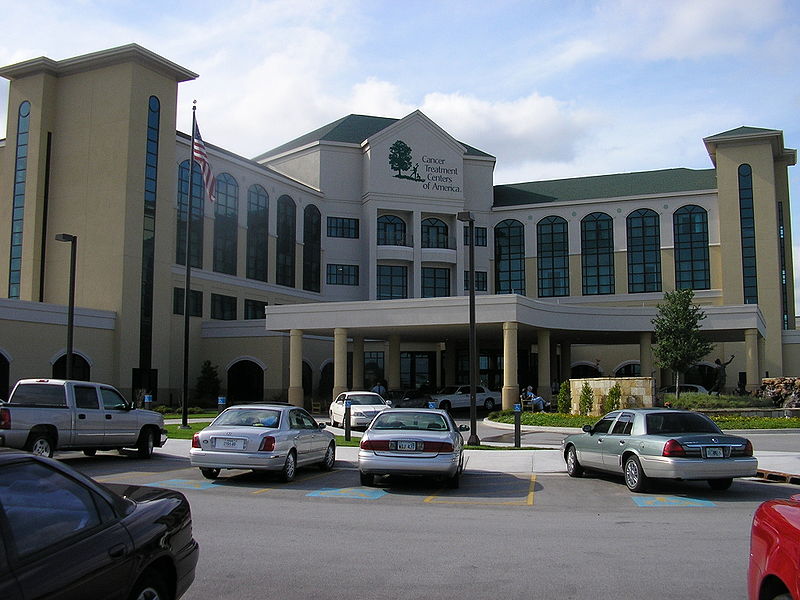 Oklahoma was the 21st-largest recipient of medical funding from the federal government in 2005, with health-related federal expenditures in the state totaling $75,801,364; immunizations, bioterrorism preparedness, and health education were the top three most funded medical items. Instances of major diseases are near the national average in Oklahoma, and the state ranks at or slightly above the rest of the country in percentage of people with asthma, Diabetes mellitus, diabetes, cancer, and hypertension.
In 2000, Oklahoma ranked 45th in physicians per capita and slightly below the national average in nurses per capita, but was slightly above the national average in hospital beds per 100,000 people and above the national average in net growth of health services over a twelve-year period. One of the worst states for percentage of insured people, nearly 25 percent of Oklahomans between the age of 18 and 64 did not have health insurance in 2005, the fifth-highest rate in the nation.
Oklahomans are in the upper half of Americans in terms of obesity prevalence, and the state is the 5th most obese in the nation, with 30.3 percent of its population at or near obesity. Oklahoma ranked last among the 50 states in a 2007 study by the Commonwealth Fund on health care performance.
The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, OU Medical Center, Oklahoma's largest collection of hospitals, is the only hospital in the state designated a LevelI trauma center by the American College of Surgeons. OU Medical Center is on the grounds of the Oklahoma Health Center in Oklahoma City, the state's largest concentration of medical research facilities.
The Cancer Treatment Centers of America at Southwestern Regional Medical Center in Tulsa is one of four such regional facilities nationwide, offering cancer treatment to the entire southwestern United States, and is one of the largest cancer treatment hospitals in the country. The largest Osteopathic medicine in the United States, osteopathic teaching facility in the nation, Oklahoma State University Medical Center at Tulsa, also rates as one of the largest facilities in the field of neuroscience.
On June 26, 2018, Oklahoma made Medical cannabis, marijuana legal for medical purposes, making it one of the most conservative states to approve medical marijuana.
Oklahoma was the 21st-largest recipient of medical funding from the federal government in 2005, with health-related federal expenditures in the state totaling $75,801,364; immunizations, bioterrorism preparedness, and health education were the top three most funded medical items. Instances of major diseases are near the national average in Oklahoma, and the state ranks at or slightly above the rest of the country in percentage of people with asthma, Diabetes mellitus, diabetes, cancer, and hypertension.
In 2000, Oklahoma ranked 45th in physicians per capita and slightly below the national average in nurses per capita, but was slightly above the national average in hospital beds per 100,000 people and above the national average in net growth of health services over a twelve-year period. One of the worst states for percentage of insured people, nearly 25 percent of Oklahomans between the age of 18 and 64 did not have health insurance in 2005, the fifth-highest rate in the nation.
Oklahomans are in the upper half of Americans in terms of obesity prevalence, and the state is the 5th most obese in the nation, with 30.3 percent of its population at or near obesity. Oklahoma ranked last among the 50 states in a 2007 study by the Commonwealth Fund on health care performance.
The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, OU Medical Center, Oklahoma's largest collection of hospitals, is the only hospital in the state designated a LevelI trauma center by the American College of Surgeons. OU Medical Center is on the grounds of the Oklahoma Health Center in Oklahoma City, the state's largest concentration of medical research facilities.
The Cancer Treatment Centers of America at Southwestern Regional Medical Center in Tulsa is one of four such regional facilities nationwide, offering cancer treatment to the entire southwestern United States, and is one of the largest cancer treatment hospitals in the country. The largest Osteopathic medicine in the United States, osteopathic teaching facility in the nation, Oklahoma State University Medical Center at Tulsa, also rates as one of the largest facilities in the field of neuroscience.
On June 26, 2018, Oklahoma made Medical cannabis, marijuana legal for medical purposes, making it one of the most conservative states to approve medical marijuana.
 Oklahoma City and Tulsa are the 45th- and 61st-largest media markets in the United States as ranked by Nielsen Media Research. The state's third-largest media market, Lawton-Wichita Falls, Texas, is ranked 149th nationally by the agency. Terrestrial television, Broadcast television in Oklahoma began in 1949 when KFOR-TV (then WKY-TV) in Oklahoma City and KOTV-TV in Tulsa began broadcasting a few months apart. Currently, all major American Television network, broadcast networks have affiliated television stations in the state.
The state has two primary newspapers. ''The Oklahoman'', based in Oklahoma City, is the largest newspaper in the state and 54th-largest in the nation by circulation, with a weekday readership of 138,493 and a Sunday readership of 202,690. The ''Tulsa World'', the second-most widely circulated newspaper in Oklahoma and 79th in the nation, holds a Sunday circulation of 132,969 and a weekday readership of 93,558. Oklahoma's first newspaper was established in 1844, called the ''Cherokee Advocate'', and was written in both Cherokee language, Cherokee and English. In 2006, there were more than 220 newspapers in the state, including 177 with weekly publications and 48 with daily publications.
The state's first radio station, WKY in Oklahoma City, began broadcasting in 1920. In 2006, there were more than 500 radio stations in Oklahoma broadcasting with various local or nationally owned networks. Five universities in Oklahoma operate non-commercial, public radio stations/networks.
Oklahoma has a few ethnic-oriented TV stations broadcasting in Spanish and Asian Americans, Asian languages, and there is some Native American programming. Trinity Broadcasting Network, TBN, a Christian religious television network, has a studio in Tulsa, and built its first entirely TBN-owned affiliate in Oklahoma City in 1980.
Oklahoma City and Tulsa are the 45th- and 61st-largest media markets in the United States as ranked by Nielsen Media Research. The state's third-largest media market, Lawton-Wichita Falls, Texas, is ranked 149th nationally by the agency. Terrestrial television, Broadcast television in Oklahoma began in 1949 when KFOR-TV (then WKY-TV) in Oklahoma City and KOTV-TV in Tulsa began broadcasting a few months apart. Currently, all major American Television network, broadcast networks have affiliated television stations in the state.
The state has two primary newspapers. ''The Oklahoman'', based in Oklahoma City, is the largest newspaper in the state and 54th-largest in the nation by circulation, with a weekday readership of 138,493 and a Sunday readership of 202,690. The ''Tulsa World'', the second-most widely circulated newspaper in Oklahoma and 79th in the nation, holds a Sunday circulation of 132,969 and a weekday readership of 93,558. Oklahoma's first newspaper was established in 1844, called the ''Cherokee Advocate'', and was written in both Cherokee language, Cherokee and English. In 2006, there were more than 220 newspapers in the state, including 177 with weekly publications and 48 with daily publications.
The state's first radio station, WKY in Oklahoma City, began broadcasting in 1920. In 2006, there were more than 500 radio stations in Oklahoma broadcasting with various local or nationally owned networks. Five universities in Oklahoma operate non-commercial, public radio stations/networks.
Oklahoma has a few ethnic-oriented TV stations broadcasting in Spanish and Asian Americans, Asian languages, and there is some Native American programming. Trinity Broadcasting Network, TBN, a Christian religious television network, has a studio in Tulsa, and built its first entirely TBN-owned affiliate in Oklahoma City in 1980.
 Transportation in Oklahoma is generated by an anchor system of Interstate Highway System, Interstate Highways, inter-city rail lines, airports, inland ports, and Public transport, mass transit networks. Situated along an integral point in the United States Interstate network, Oklahoma contains three List of Interstate Highways, primary Interstate highways and four List of auxiliary Interstate Highways, auxiliary Interstate Highways. In Oklahoma City, Interstate 35 intersects with Interstate 44 and Interstate 40, forming one of the most important intersections along the United States highway system.
More than of roads make up the state's major highway skeleton, including state-operated highways, ten Turnpikes of Oklahoma, turnpikes or major toll roads, and the longest drivable stretch of U.S. Route 66 in Oklahoma, Route 66 in the nation. In 2008, Interstate 44 in Oklahoma City was Oklahoma's busiest highway, with a daily traffic volume of 123,300 cars. In 2010, the state had the nation's third-highest number of bridges classified as structurally deficient, with nearly 5,212 bridges in disrepair, including 235 National Highway System Bridges.
Oklahoma's largest commercial airport is Will Rogers World Airport in Oklahoma City, averaging a yearly passenger count of more than 3.5 million (1.7 million boardings) in 2010. Tulsa International Airport, the state's second-largest commercial airport, served more than 1.3 million boardings in 2010. Between the two, six airlines operate in Oklahoma. In terms of traffic, Richard Lloyd Jones Jr. Airport, R. L. Jones Jr. (Riverside) Airport in Tulsa is the state's busiest airport, with 335,826 takeoffs and landings in 2008. Oklahoma has more than 150 public-use airports.
Oklahoma is connected to the nation's rail network via Amtrak's ''Heartland Flyer'', its only regional passenger rail line. It currently stretches from Oklahoma City to Fort Worth, Texas, though lawmakers began seeking funding in early 2007 to connect the ''Heartland Flyer'' to Tulsa.
Two inland ports on rivers serve Oklahoma: the Port of Muskogee and the Tulsa Port of Catoosa. The Tulsa Port of Catoosa is the one of the United States' most inland international ports, at head of navigation of the McClellan–Kerr Arkansas River Navigation System, which connects barge traffic from Tulsa and Muskogee to the Mississippi River. The port ships over two million tons of goods annually and is a designated Free-trade zone, foreign trade zone.
Transportation in Oklahoma is generated by an anchor system of Interstate Highway System, Interstate Highways, inter-city rail lines, airports, inland ports, and Public transport, mass transit networks. Situated along an integral point in the United States Interstate network, Oklahoma contains three List of Interstate Highways, primary Interstate highways and four List of auxiliary Interstate Highways, auxiliary Interstate Highways. In Oklahoma City, Interstate 35 intersects with Interstate 44 and Interstate 40, forming one of the most important intersections along the United States highway system.
More than of roads make up the state's major highway skeleton, including state-operated highways, ten Turnpikes of Oklahoma, turnpikes or major toll roads, and the longest drivable stretch of U.S. Route 66 in Oklahoma, Route 66 in the nation. In 2008, Interstate 44 in Oklahoma City was Oklahoma's busiest highway, with a daily traffic volume of 123,300 cars. In 2010, the state had the nation's third-highest number of bridges classified as structurally deficient, with nearly 5,212 bridges in disrepair, including 235 National Highway System Bridges.
Oklahoma's largest commercial airport is Will Rogers World Airport in Oklahoma City, averaging a yearly passenger count of more than 3.5 million (1.7 million boardings) in 2010. Tulsa International Airport, the state's second-largest commercial airport, served more than 1.3 million boardings in 2010. Between the two, six airlines operate in Oklahoma. In terms of traffic, Richard Lloyd Jones Jr. Airport, R. L. Jones Jr. (Riverside) Airport in Tulsa is the state's busiest airport, with 335,826 takeoffs and landings in 2008. Oklahoma has more than 150 public-use airports.
Oklahoma is connected to the nation's rail network via Amtrak's ''Heartland Flyer'', its only regional passenger rail line. It currently stretches from Oklahoma City to Fort Worth, Texas, though lawmakers began seeking funding in early 2007 to connect the ''Heartland Flyer'' to Tulsa.
Two inland ports on rivers serve Oklahoma: the Port of Muskogee and the Tulsa Port of Catoosa. The Tulsa Port of Catoosa is the one of the United States' most inland international ports, at head of navigation of the McClellan–Kerr Arkansas River Navigation System, which connects barge traffic from Tulsa and Muskogee to the Mississippi River. The port ships over two million tons of goods annually and is a designated Free-trade zone, foreign trade zone.
 Oklahoma is a constitutional republic with a government modeled after the federal government of the United States, with executive, legislative, and judicial branches. The state has List of counties in Oklahoma, 77 counties with jurisdiction over most local government functions within each respective domain, Oklahoma's congressional districts, five congressional districts, and a voting base with a plurality in the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party. State officials are elected by plurality voting in the state of Oklahoma.
Oklahoma has capital punishment in the United States, capital punishment as a legal sentence, and the state has had (between 1976 through mid-2011) the highest per capita execution rate in the nation.
In a 2020 study, Oklahoma was ranked as the 14th hardest state for citizens to vote in.
Oklahoma is a constitutional republic with a government modeled after the federal government of the United States, with executive, legislative, and judicial branches. The state has List of counties in Oklahoma, 77 counties with jurisdiction over most local government functions within each respective domain, Oklahoma's congressional districts, five congressional districts, and a voting base with a plurality in the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party. State officials are elected by plurality voting in the state of Oklahoma.
Oklahoma has capital punishment in the United States, capital punishment as a legal sentence, and the state has had (between 1976 through mid-2011) the highest per capita execution rate in the nation.
In a 2020 study, Oklahoma was ranked as the 14th hardest state for citizens to vote in.
 The executive branch consists of the Governor of Oklahoma, Governor, their staff, and other elected officials. The principal head of government, the Governor is the chief executive of the Oklahoma executive branch, serving as the List of Latin phrases (E), ex officio Commander-in-chief of the Oklahoma National Guard when not called into Federal government of the United States, Federal use and reserving the power to veto bills passed through the Legislature. The responsibilities of the Executive branch include submitting the budget, ensuring state laws are enforced, and ensuring peace within the state is preserved.
The executive branch consists of the Governor of Oklahoma, Governor, their staff, and other elected officials. The principal head of government, the Governor is the chief executive of the Oklahoma executive branch, serving as the List of Latin phrases (E), ex officio Commander-in-chief of the Oklahoma National Guard when not called into Federal government of the United States, Federal use and reserving the power to veto bills passed through the Legislature. The responsibilities of the Executive branch include submitting the budget, ensuring state laws are enforced, and ensuring peace within the state is preserved.

 During the first half-century of statehood, Oklahoma was considered a Democratic Party (United States), Democratic stronghold, being carried by the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party in only two presidential elections (1920 United States presidential election, 1920 and 1928 United States presidential election, 1928). After the 1948 United States presidential election, 1948 election, the state turned firmly Republican. Although registered Republicans were a minority in the state until 2015, Oklahoma has been carried by Republican presidential candidates in all but one election since 1952: Lyndon B. Johnson's 1964 United States presidential election, 1964 landslide victory. Every single county in the state has been won by the Republican candidate in each election since United States presidential election, 2004, 2004. Oklahoma City was the largest city in the United States carried by Republican Donald Trump in both the 2016 and 2020 elections.
Generally, Republicans are strongest in the suburbs of Oklahoma City and Tulsa, as well as the Panhandle. Democrats are strongest in the eastern part of the state and Little Dixie (Oklahoma), Little Dixie, as well as the most heavily African American and inner parts of Oklahoma City and Tulsa. With a population of 8.6% Native American in the state, it is also worth noting that most Native American precincts vote Democratic in margins exceeded only by African Americans.
Following the United States Census Bureau, 2000 census, the Oklahoma delegation to the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives was reduced from six to five representatives, each serving one congressional district. In the current Congress, Republicans comprise Oklahoma's entire delegation.
During the first half-century of statehood, Oklahoma was considered a Democratic Party (United States), Democratic stronghold, being carried by the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party in only two presidential elections (1920 United States presidential election, 1920 and 1928 United States presidential election, 1928). After the 1948 United States presidential election, 1948 election, the state turned firmly Republican. Although registered Republicans were a minority in the state until 2015, Oklahoma has been carried by Republican presidential candidates in all but one election since 1952: Lyndon B. Johnson's 1964 United States presidential election, 1964 landslide victory. Every single county in the state has been won by the Republican candidate in each election since United States presidential election, 2004, 2004. Oklahoma City was the largest city in the United States carried by Republican Donald Trump in both the 2016 and 2020 elections.
Generally, Republicans are strongest in the suburbs of Oklahoma City and Tulsa, as well as the Panhandle. Democrats are strongest in the eastern part of the state and Little Dixie (Oklahoma), Little Dixie, as well as the most heavily African American and inner parts of Oklahoma City and Tulsa. With a population of 8.6% Native American in the state, it is also worth noting that most Native American precincts vote Democratic in margins exceeded only by African Americans.
Following the United States Census Bureau, 2000 census, the Oklahoma delegation to the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives was reduced from six to five representatives, each serving one congressional district. In the current Congress, Republicans comprise Oklahoma's entire delegation.
 Oklahoma had 598 incorporated places in 2010, including four cities over 100,000 in population and 43 over 10,000. Two of the List of United States cities by population, fifty largest cities in the United States are in Oklahoma, Oklahoma City and Tulsa, and sixty-five percent of Oklahomans live within their metropolitan areas, or spheres of economic and social influence defined by the United States Census Bureau as a metropolitan statistical area. Oklahoma City, the state's capital and largest city, had the Oklahoma City Metroplex, largest metropolitan area in the state in 2020, with 1,425,695 people, and the Tulsa Metropolitan Area, metropolitan area of Tulsa had 1,015,331 residents. Between 2000 and 2010, the leading cities in population growth were Blanchard, Oklahoma, Blanchard (172.4%), Elgin, Oklahoma, Elgin (78.2%), Jenks, Oklahoma, Jenks (77.0%), Piedmont, Oklahoma, Piedmont (56.7%), Bixby, Oklahoma, Bixby (56.6%), and Owasso, Oklahoma, Owasso (56.3%).
Oklahoma had 598 incorporated places in 2010, including four cities over 100,000 in population and 43 over 10,000. Two of the List of United States cities by population, fifty largest cities in the United States are in Oklahoma, Oklahoma City and Tulsa, and sixty-five percent of Oklahomans live within their metropolitan areas, or spheres of economic and social influence defined by the United States Census Bureau as a metropolitan statistical area. Oklahoma City, the state's capital and largest city, had the Oklahoma City Metroplex, largest metropolitan area in the state in 2020, with 1,425,695 people, and the Tulsa Metropolitan Area, metropolitan area of Tulsa had 1,015,331 residents. Between 2000 and 2010, the leading cities in population growth were Blanchard, Oklahoma, Blanchard (172.4%), Elgin, Oklahoma, Elgin (78.2%), Jenks, Oklahoma, Jenks (77.0%), Piedmont, Oklahoma, Piedmont (56.7%), Bixby, Oklahoma, Bixby (56.6%), and Owasso, Oklahoma, Owasso (56.3%).
 In descending order of population, Oklahoma's largest cities in 2010 were: Oklahoma City (579,999, +14.6%), Tulsa (391,906, −0.3%), Norman (110,925, +15.9%), Broken Arrow, Oklahoma, Broken Arrow (98,850, +32.0%), Lawton (96,867, +4.4%), Edmond, Oklahoma, Edmond (81,405, +19.2%), Moore, Oklahoma, Moore (55,081, +33.9%), Midwest City, Oklahoma, Midwest City (54,371, +0.5%), Enid, Oklahoma, Enid (49,379, +5.0%), and Stillwater, Oklahoma, Stillwater (45,688, +17.0%). Of the state's ten largest cities, three are outside the metropolitan areas of Oklahoma City and Tulsa, and only Lawton has a metropolitan statistical area of its own as designated by the United States Census Bureau, though the metropolitan statistical area of Fort Smith, Arkansas extends into the state.
Under Oklahoma law, municipalities are divided into two categories: cities, defined as having more than 1,000 residents, and towns, with under 1,000 residents. Both have Legislature, legislative, Judiciary, judicial, and public power within their boundaries, but cities can choose between a Mayor–council government, mayor–council, Council–manager government, council–manager, or Mayor–council government, strong mayor form of government, while towns operate through an elected officer system.
In descending order of population, Oklahoma's largest cities in 2010 were: Oklahoma City (579,999, +14.6%), Tulsa (391,906, −0.3%), Norman (110,925, +15.9%), Broken Arrow, Oklahoma, Broken Arrow (98,850, +32.0%), Lawton (96,867, +4.4%), Edmond, Oklahoma, Edmond (81,405, +19.2%), Moore, Oklahoma, Moore (55,081, +33.9%), Midwest City, Oklahoma, Midwest City (54,371, +0.5%), Enid, Oklahoma, Enid (49,379, +5.0%), and Stillwater, Oklahoma, Stillwater (45,688, +17.0%). Of the state's ten largest cities, three are outside the metropolitan areas of Oklahoma City and Tulsa, and only Lawton has a metropolitan statistical area of its own as designated by the United States Census Bureau, though the metropolitan statistical area of Fort Smith, Arkansas extends into the state.
Under Oklahoma law, municipalities are divided into two categories: cities, defined as having more than 1,000 residents, and towns, with under 1,000 residents. Both have Legislature, legislative, Judiciary, judicial, and public power within their boundaries, but cities can choose between a Mayor–council government, mayor–council, Council–manager government, council–manager, or Mayor–council government, strong mayor form of government, while towns operate through an elected officer system.

complete text online
900 pages of scholarly articles
Oklahoma Legislative Branch
Oklahoma Department of Commerce
Oklahoma Department of Human Services
Oklahoma Department of Transportation
Official Oklahoma Tourism Info
Oklahoma State Parks
Red Earth
Woody Guthrie Folk Festival
Oklahoma State Guide from the Library of Congress
Oklahoma Arts Council
Oklahoma Theatre Association
Oklahoma Oral History Research Program
Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture
Voices of Oklahoma Oral History Project
Oklahoma Genealogical Society
Realtime USGS geographic, weather, and geologic information
*
Oklahoma Digital Maps: Digital Collections of Oklahoma and Indian Territory
{{DEFAULTSORT:Oklahoma 1907 establishments in the United States Cherokee-speaking countries and territories Oklahoma, Southern United States States and territories established in 1907 States of the United States Contiguous United States List of place names of Choctaw origin in the United States
Choctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are ...
: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a state in the South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the north, Missouri on the northeast, Arkansas on the east, New Mexico on the west, and Colorado on the northwest. Partially in the western extreme of the Upland South, it is the 20th-most extensive and the 28th-most populous of the 50 United States. Its residents are known as Oklahomans and its capital and largest city is Oklahoma City.
The state's name is derived from the Choctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are ...
words , 'people' and , which translates as 'red'. Oklahoma is also known informally by its nickname, " The Sooner State", in reference to the settlers who staked their claims on land before the official opening date of lands in the western Oklahoma Territory or before the Indian Appropriations Act of 1889, which increased European-American settlement in the eastern Indian Territory. Oklahoma Territory
The Territory of Oklahoma was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 2, 1890, until November 16, 1907, when it was joined with the Indian Territory under a new constitution and admitted to the Union as th ...
and Indian Territory were merged into the State of Oklahoma when it became the 46th state to enter the union on November 16, 1907.
With ancient mountain ranges, prairie, mesas, and eastern forests, most of Oklahoma lies in the Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
, Cross Timbers, and the U.S. Interior Highlands
The U.S. Interior Highlands is a mountainous region in the Central United States spanning northern and western Arkansas, southern Missouri, eastern Oklahoma, and extreme southeastern Kansas. The name is designated by the United States Geologica ...
, all regions prone to severe weather. Oklahoma is at a confluence of three major American cultural regions. Historically it served as a government-sanctioned territory for Native Americans removed from east of the Mississippi River, a route for cattle drives from Texas and related regions, and a destination for Southern settlers. There are currently twenty-five Native American languages still spoken in Oklahoma.
A major producer of natural gas, oil, and agricultural products, Oklahoma relies on an economic base of aviation, energy, telecommunications, and biotechnology. Oklahoma City and Tulsa serve as Oklahoma's primary economic anchors, with nearly two-thirds of Oklahomans living within their metropolitan statistical areas.
Etymology
The name ''Oklahoma'' comes from the Choctaw language phrase , 'people', and , translated as 'red'. Choctaw Nation ChiefAllen Wright
Allen Wright ( cho, Kiliahote, italic=no) (born November 1826 – December 2, 1885) was Principal Chief of the Choctaw Republic from late 1866 to 1870. He had been ordained as a Presbyterian minister in 1852 after graduating from Union Theolog ...
suggested the name in 1866 during treaty negotiations with the federal government on the use of Indian Territory. He envisioned an all–American Indian state controlled by the United States Superintendent of Indian Affairs. ''Oklahoma'' later became the de facto name for Oklahoma Territory
The Territory of Oklahoma was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 2, 1890, until November 16, 1907, when it was joined with the Indian Territory under a new constitution and admitted to the Union as th ...
, and it was officially approved in 1890, two years after that area was opened to white settlers.
In the Chickasaw language, the state is known as , in Arapaho as (literally meaning 'red earth'), paw, Uukuhuúwa, and cay, Gahnawiyoˀgeh.
History


Settlements
Indigenous peoples were present in what is now Oklahoma by the last ice age. Ancestors of the Wichita and Affiliated Tribes (including Teyas andEscanjaques The Escanjaques were an American Indian tribe who lived in the Southern Plains.
Juan de Oñate encountered the Escanjaque in 1601 during an expedition to the Great Plains of Texas, Oklahoma, and Kansas. The Escanjaques may have been identical wit ...
and Tawakoni), Tonkawa, and Caddo
The Caddo people comprise the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma, a federally recognized tribe headquartered in Binger, Oklahoma. They speak the Caddo language.
The Caddo Confederacy was a network of Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, wh ...
(including Kichai) lived in what is now Oklahoma. Southern Plains villagers lived in the central and west of the state, with a subgroup, the Panhandle culture people living in the panhandle region. Caddoan Mississippian culture peoples lived in the eastern part of the state. Spiro Mounds, in what is now Spiro, Oklahoma, was a major Mississippian
Mississippian may refer to:
* Mississippian (geology), a subperiod of the Carboniferous period in the geologic timescale, roughly 360 to 325 million years ago
*Mississippian culture, a culture of Native American mound-builders from 900 to 1500 AD ...
mound complex that flourished between AD 850 and 1450. Plains Apache
The Plains Apache are a small Southern Athabaskan group who live on the Southern Plains of North America, in close association with the linguistically unrelated Kiowa Tribe. Today, they are centered in Southwestern Oklahoma and Northern Texas an ...
people settled in the Southern Plains and in Oklahoma between 1300 and 1500.
The Expedition of Spaniard Francisco Vázquez de Coronado
Francisco Vázquez de Coronado y Luján (; 1510 – 22 September 1554) was a Spanish conquistador and explorer who led a large expedition from what is now Mexico to present-day Kansas through parts of the southwestern United States between 15 ...
traveled through the state in 1541, but French explorers claimed the area in the early 18th century. By the 18th century, Comanche and Kiowa entered the region from the west and Quapaw and Osage peoples moved into what is now eastern Oklahoma. French colonists claimed the region until 1803, when all the French territory west of the Mississippi River was acquired by the United States in the Louisiana Purchase. The territory was a part of the Arkansas Territory from 1819 until 1828.
During the 19th century, the US federal government forcibly removed tens of thousands of Native Americans from their homelands from across North America and transported them to the area including and surrounding present-day Oklahoma. The Choctaw was the first of the Five Civilized Tribes to be removed from the Southeastern United States. The phrase " Trail of Tears" originated from a description of the removal of the Choctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are ...
Nation in 1831, although the term is usually used for the Cherokee removal.
Seventeen thousand Cherokees and 2,000 of their black slaves were deported. The area, already occupied by Osage The Osage Nation, a Native American tribe in the United States, is the source of most other terms containing the word "osage".
Osage can also refer to:
* Osage language, a Dhaegin language traditionally spoken by the Osage Nation
* Osage (Unicode b ...
and Quapaw tribes, was called for the Choctaw Nation until revised Native American and then later American policy redefined the boundaries to include other Native Americans. By 1890, more than 30 Native American nations and tribes had been concentrated on land within Indian Territory or "Indian Country".
All Five Civilized Tribes supported and signed treaties with the Confederate military during the American Civil War. The Cherokee Nation
The Cherokee Nation (Cherokee: ᏣᎳᎩᎯ ᎠᏰᎵ ''Tsalagihi Ayeli'' or ᏣᎳᎩᏰᎵ ''Tsalagiyehli''), also known as the Cherokee Nation of Oklahoma, is the largest of three Cherokee federally recognized tribes in the United States. It ...
had an internal civil war.
Slavery in Indian Territory was not abolished until 1866.
In the period between 1866 and 1899, cattle ranches in Texas strove to meet the demands for food in eastern cities and railroads in Kansas promised to deliver in a timely manner. Cattle trails and cattle ranches developed as cowboy
A cowboy is an animal herder who tends cattle on ranches in North America, traditionally on horseback, and often performs a multitude of other ranch-related tasks. The historic American cowboy of the late 19th century arose from the '' vaquer ...
s either drove their product north or settled illegally in Indian Territory. In 1881, four of five major cattle trails on the western frontier traveled through Indian Territory.
Increased presence of white settlers in Indian Territory prompted the United States Government to establish the Dawes Act in 1887, which divided the lands of individual tribes into allotments for individual families, encouraging farming and private land ownership among Native Americans but expropriating land to the federal government. In the process, railroad companies took nearly half of Indian-held land within the territory for outside settlers and for purchase.
 Major land runs, including the Land Run of 1889, were held for settlers where certain territories were opened to settlement starting at a precise time. Usually land was open to settlers on a first come first served basis. Those who broke the rules by crossing the border into the territory before the official opening time were said to have been crossing the border ''sooner'', leading to the term '' sooners'', which eventually became the state's official nickname. Deliberations to make the territory into a state began near the end of the 19th century, when the Curtis Act continued the allotment of Indian tribal land.
Major land runs, including the Land Run of 1889, were held for settlers where certain territories were opened to settlement starting at a precise time. Usually land was open to settlers on a first come first served basis. Those who broke the rules by crossing the border into the territory before the official opening time were said to have been crossing the border ''sooner'', leading to the term '' sooners'', which eventually became the state's official nickname. Deliberations to make the territory into a state began near the end of the 19th century, when the Curtis Act continued the allotment of Indian tribal land.
20th and 21st centuries
 Attempts to create an all-Indian state named ''Oklahoma'' and a later attempt to create an all-Indian state named ''
Attempts to create an all-Indian state named ''Oklahoma'' and a later attempt to create an all-Indian state named ''Sequoyah
Sequoyah (Cherokee language, Cherokee: ᏍᏏᏉᏯ, ''Ssiquoya'', or ᏎᏉᏯ, ''Se-quo-ya''; 1770 – August 1843), also known as George Gist or George Guess, was a Native Americans in the United States, Native American polymath of the Ch ...
'' failed but the Sequoyah Statehood Convention of 1905 eventually laid the groundwork for the Oklahoma Statehood Convention, which took place two years later. On June 16, 1906, Congress enacted a statute authorizing the people of the Oklahoma and Indian Territories (as well what would become the states of Arizona and New Mexico) to form a constitution and state government in order to be admitted as a state. On November 16, 1907, President Theodore Roosevelt issued Presidential Proclamation no. 780
__NOTOC__
Year 780 ( DCCLXXX) was a leap year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 780 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Euro ...
, establishing Oklahoma as the 46th state in the Union.
 The new state became a focal point for the emerging oil industry, as discoveries of oil pools prompted towns to grow rapidly in population and wealth. Tulsa eventually became known as the "
The new state became a focal point for the emerging oil industry, as discoveries of oil pools prompted towns to grow rapidly in population and wealth. Tulsa eventually became known as the "Oil Capital of the World The title of "Oil Capital of the World" is often used to refer to Tulsa, Oklahoma. Houston, Texas, the current center of the oil industry, more frequently uses the sobriquet “ The Energy Capital of the World.”
History
In mid-19th century, ...
" for most of the 20th century and oil investments fueled much of the state's early economy. In 1927, Oklahoman businessman Cyrus Avery
Cyrus Stevens Avery (1871–1963) was a businessperson, oilman, and highway commissioner. He created the U.S. Route 66 while being a member of the federal board appointed to create the Federal Highway System, then pushed for the establishment of ...
, known as the "Father of Route 66", began the campaign to create U.S. Route 66. Using a stretch of highway from Amarillo, Texas to Tulsa, Oklahoma to form the original portion of Highway 66, Avery spearheaded the creation of the U.S. Highway 66 Association
The U.S. Highway 66 Association was organized in Tulsa, Oklahoma in 1927. Its purpose was to get U.S. Highway 66 paved from end to end and to promote tourism on the highway.
The organization was similar to many that existed before the creation of ...
to oversee the planning of Route 66, based in his hometown of Tulsa.
Oklahoma also has a rich African-American history. Many Black towns, founded by the Freedmen of the Five Tribes during Reconstruction, thrived in the early 20th century with the arrival of Black Exodusters who migrated from neighboring states, especially Kansas. The politician Edward P. McCabe encouraged Black settlers to come to what was then Indian Territory. McCabe discussed with President Theodore Roosevelt the possibility of making Oklahoma a majority-Black state.
By the early 20th century, the Greenwood Green wood is unseasoned wood.
Greenwood or Green wood may also refer to:
People
* Greenwood (surname)
Settlements
Australia
* Greenwood, Queensland, a locality in the Toowoomba Region
* Greenwood, Western Australia, a suburb of Perth
C ...
district of Tulsa was one of the most prosperous African-American communities in the United States. Jim Crow laws had established racial segregation since before the start of the 20th century, but Tulsa's Black residents had created a thriving area.
Social tensions were exacerbated by the revival of the Ku Klux Klan
The Ku Klux Klan (), commonly shortened to the KKK or the Klan, is an American white supremacist, right-wing terrorist, and hate group whose primary targets are African Americans, Jews, Latinos, Asian Americans, Native Americans, and ...
after 1915. The Tulsa race massacre broke out in 1921, with White mobs attacking Black people and carrying out a pogrom in Greenwood. In one of the costliest episodes of racist violence in American history, sixteen hours of rioting resulted in 35 city blocks destroyed, $1.8 million in property damage, and a death toll estimated at between 75 and 300 people. By the late 1920s, the Ku Klux Klan had declined to negligible influence within the state.
During the 1930s, parts of the state began suffering the consequences of poor farming practices. This period was known as the Dust Bowl, throughout which areas of Kansas, Texas, New Mexico and northwestern Oklahoma were hampered by long periods of little rainfall, strong winds, abnormally high temperatures, and most notably, severe dust storms sending thousands of farmers into poverty and forcing them to relocate to more fertile areas of the western United States. Over a twenty-year period ending in 1950, the state saw its only historical decline in population, dropping 6.9 percent as impoverished families migrated out of the state after the Dust Bowl.
Soil and water conservation projects markedly changed practices in the state and led to the construction of massive flood control systems and dams; they built hundreds of reservoirs and man-made lakes to supply water for domestic needs and agricultural irrigation. By the 1960s, Oklahoma had created more than 200 lakes, the most in the nation.
Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
determined in ''McGirt v. Oklahoma
''McGirt v. Oklahoma'', 591 U.S. ___ (2020), was a landmark United States Supreme Court case which ruled that, as pertaining to the Major Crimes Act, much of the eastern portion of the state of Oklahoma remains as Native American lands of the pr ...
'' that the reservations of the Five Tribes, comprising much of Eastern Oklahoma, were never disestablished by Congress and thus are still "Indian Country" for the purposes of criminal law.
Geography
Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
near the geographical center of the 48 Contiguous United States, contiguous states. It is bordered on the east by Arkansas and Missouri, on the north by Kansas, on the northwest by Colorado, on the far west by New Mexico, and on the south and near-west by Texas.
Borders
Oklahoma's border with Kansas was defined as the 37th Parallel in the 1854 Kansas–Nebraska Act, Kansas-Nebraska Act. This was disputed with the Cherokee and Osage Nations which claimed their border extended North of this line and could not be part of the Kansas Territory. This was resolved in the 1870 with the Drum Creek Treaty that reestablished Kansas's Southern Border as the 37th Parallel. This also applied to the then No-Man's Land that became the Oklahoma Panhandle. The Oklahoma-Texas border consists of the Red River in the South and the 100th Meridian West as Western border between Oklahoma and the Texas Panhandle. These were first established in the 1819 Adams–Onís Treaty between the United States and Spain. The Oklahoma panhandle was originally part of the Panhandle of the Republic of Texas, but when Texas joined the Union as a slave state, it could not retain any lands north of 36 degrees 30 minutes, as specified in the Missouri Compromise. The Panhandle existed as a no-man's land until 1907 when Oklahoma acquired the territory upon gaining statehood. Oklahoma's Eastern border is divided between Missouri and Arkansas. The Missouri-Oklahoma border is defined as the Meridian passing through the Kawsmouth, where the Kansas River meets the Missouri River. This is the same Meridian as the Kansas-Missouri border. The Oklahoma-Arkansas border was originally defined by two lines: the borders between Arkansas and the Cherokee and Choctaw Reservations. This formed two diagonal lines meeting at the western edge of Fort Smith Arkansas, with one line running northeast from the Red River and the other running southeast from the Oklahoma-Arkansas-Missouri border. The Choctaw-Arkansas border was established in the 1820 Treaty of Doak's Stand, Treaty of Doak's Sand, and later refined in the 1830 Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek. These treaties left a 57-acre Enclave and exclave, exclave of the Choctaw reservation bounded by Arkansas, the Arkansas River and the Poteau River. This became the site of a smuggling camp called "Coke Hill", noted mostly for its importance in cocaine smuggling. After Petitioning congress to hand over jurisdiction, the 57 acres was given to Arkansas in 1905. The 1985 US Supreme Court Case Oklahoma v. Arkansas decided the land would remain Arkansas, even though the Choctaw had not been notified or asked about the territory being handed over. Therefore, the Poteau River serves as the Oklahoma-Arkansas boundary for approximately 1 mile, reducing the Choctaw Reservation and later Oklahoma by 57 acres as established in the treaties of the early 1800s.Topography
Oklahoma is between theGreat Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
and the Ozarks, Ozark Plateau in the Gulf of Mexico watershed, generally sloping from the high plains of its western boundary to the low wetlands of its southeastern boundary. Its highest and lowest points follow this trend, with its highest peak, Black Mesa (Oklahoma), Black Mesa, at above sea level, situated near its far northwest corner in the Oklahoma Panhandle. The state's lowest point is on the Little River near its far southeastern boundary near the town of Idabel, Oklahoma, Idabel, which dips to above sea level.
Among the most geographically diverse states, Oklahoma is one of four to harbor more than 10 distinct ecoregion, ecological regions, with 11 in its borders—more per square mile than in any other state. Its western and eastern halves, however, are marked by extreme differences in geographical diversity: Eastern Oklahoma touches eight ecological regions and its western half contains three. Although having fewer ecological regions Western Oklahoma contains many rare, relic species.
Oklahoma has four primary mountain ranges: the Ouachita Mountains, the Arbuckle Mountains, the Wichita Mountains, and the Ozarks, Ozark Mountains. Contained within the U.S. Interior Highlands
The U.S. Interior Highlands is a mountainous region in the Central United States spanning northern and western Arkansas, southern Missouri, eastern Oklahoma, and extreme southeastern Kansas. The name is designated by the United States Geologica ...
region, the Ozark and Ouachita Mountains are the only major mountainous region between the Rocky Mountains and the Appalachian Mountains, Appalachians. A portion of the Flint Hills stretches into north-central Oklahoma, and near the state's eastern border, The Oklahoma Tourism & Recreation Department regards Cavanal Hill as the world's tallest hill; at , it fails their definition of a mountain by one foot.
The Semi-arid climate, semi-arid High Plains (United States), high plains in the state's northwestern Oklahoma, northwestern corner harbor few natural forests; the region has a rolling to flat landscape with intermittent canyons and mesa ranges like the Glass Mountains. Partial plains interrupted by small, sky island mountain ranges like the Antelope Hills, Oklahoma, Antelope Hills and the Wichita Mountains dot southwestern Oklahoma; transitional prairie and oak savannas cover the Central Oklahoma, central portion of the state. The Ozark and Ouachita Mountains rise from west to east over the state's eastern third, gradually increasing in elevation in an eastward direction.
More than 500 named creeks and rivers make up Oklahoma's waterways, and with 200 lakes created by dams, it holds the nation's highest number of artificial reservoirs. Most of the state lies in two primary drainage basins belonging to the Red River of the South, Red and Arkansas River, Arkansas rivers, though the Lee and Little rivers also contain significant drainage basins.
Flora and fauna
 Due to Oklahoma's location at the confluence of many geographic regions, the state's climatic regions have a high rate of biodiversity. Forests cover 24 percent of Oklahoma and prairie, prairie grasslands composed of shortgrass, mixed-grass, and tallgrass prairie, harbor expansive ecosystems in the state's central and western portions, although Agricultural land, cropland has largely replaced native grasses. Where rainfall is sparse in the state's western regions, shortgrass prairie and shrublands are the most prominent ecosystems, though pinyon pines, red cedar (junipers), and Pinus ponderosa, ponderosa pines grow near rivers and creek beds in the panhandle's far western reaches. Southwestern Oklahoma contains many rare, Disjunct distribution, disjunct species including Acer saccharum, sugar maple, Acer grandidentatum, bigtooth maple, nolina and Quercus fusiformis, Texas live oak.
Marshlands, cypress forests and mixtures of Pinus echinata, shortleaf pine, Pinus taeda, loblolly pine, sabal minor, blue palmetto, and deciduous forests dominate the state's Kiamichi Country, southeastern quarter, while mixtures of largely Quercus stellata, post oak, elm, red cedar (''Juniperus virginiana'') and pine forests cover Green Country, northeastern Oklahoma.
The state holds populations of white-tailed deer, mule deer, Pronghorn, antelope, coyotes, Cougar, mountain lions, bobcats, elk, and birds such as quail, Columbidae, doves, Cardinal (bird), cardinals, bald eagles, red-tailed hawks, and pheasants. In prairie ecosystems, American bison, greater prairie chickens, badgers, and armadillo are common, and some of the nation's largest prairie dog towns inhabit shortgrass prairie in the state's panhandle. The Cross Timbers, a region transitioning from prairie to woodlands in Central Oklahoma, harbors 351 Vertebrate, vertebrate species. The Ouachita Mountains are home to American black bear, black bear, red fox, gray fox, and North American river otter, river otter populations, which coexist with 328 vertebrate species in southeastern Oklahoma. Also, in southeastern Oklahoma lives the American alligator.
Due to Oklahoma's location at the confluence of many geographic regions, the state's climatic regions have a high rate of biodiversity. Forests cover 24 percent of Oklahoma and prairie, prairie grasslands composed of shortgrass, mixed-grass, and tallgrass prairie, harbor expansive ecosystems in the state's central and western portions, although Agricultural land, cropland has largely replaced native grasses. Where rainfall is sparse in the state's western regions, shortgrass prairie and shrublands are the most prominent ecosystems, though pinyon pines, red cedar (junipers), and Pinus ponderosa, ponderosa pines grow near rivers and creek beds in the panhandle's far western reaches. Southwestern Oklahoma contains many rare, Disjunct distribution, disjunct species including Acer saccharum, sugar maple, Acer grandidentatum, bigtooth maple, nolina and Quercus fusiformis, Texas live oak.
Marshlands, cypress forests and mixtures of Pinus echinata, shortleaf pine, Pinus taeda, loblolly pine, sabal minor, blue palmetto, and deciduous forests dominate the state's Kiamichi Country, southeastern quarter, while mixtures of largely Quercus stellata, post oak, elm, red cedar (''Juniperus virginiana'') and pine forests cover Green Country, northeastern Oklahoma.
The state holds populations of white-tailed deer, mule deer, Pronghorn, antelope, coyotes, Cougar, mountain lions, bobcats, elk, and birds such as quail, Columbidae, doves, Cardinal (bird), cardinals, bald eagles, red-tailed hawks, and pheasants. In prairie ecosystems, American bison, greater prairie chickens, badgers, and armadillo are common, and some of the nation's largest prairie dog towns inhabit shortgrass prairie in the state's panhandle. The Cross Timbers, a region transitioning from prairie to woodlands in Central Oklahoma, harbors 351 Vertebrate, vertebrate species. The Ouachita Mountains are home to American black bear, black bear, red fox, gray fox, and North American river otter, river otter populations, which coexist with 328 vertebrate species in southeastern Oklahoma. Also, in southeastern Oklahoma lives the American alligator.
Protected lands
Oklahoma has fifty-one state parks, six national parks or protected regions, two United States National Forest, national protected forests or grasslands, and a network of wildlife preserves and conservation areas. Six percent of the state's 10 million acres (40,000 km2) of forest is public land, including the western portions of the Ouachita National Forest, the largest and oldest national forest in the Southern United States. With , the Tallgrass Prairie Preserve in north-central Oklahoma is the largest protected area of tallgrass prairie in the world and is part of an ecosystem that encompasses only ten percent of its former land area, once covering fourteen states. In addition, the Black Kettle National Grassland covers of prairie in southwestern Oklahoma. The Wichita Mountains Wildlife Refuge is the oldest and largest of nine National Wildlife Refuges in the state and was founded in 1901, encompassing . Of Oklahoma's federally protected parks or recreational sites, the Chickasaw National Recreation Area is the largest, with . Other sites include the Santa Fe Trail, Santa Fe and Trail of Tears national historic trails, the Fort Smith National Historic Site, Fort Smith and Washita Battlefield National Historic Site, Washita Battlefield national historic sites, and the Oklahoma City National Memorial.Climate

Demographics
The people of Oklahoma can be of any race or ethnicity. An Oklahoman is a resident, native, or cultural descendant of Oklahoma.Population

Race and ethnicity
As of the 2010 United States census, 2010 census, 72.2% of the population was white people, white, 8.6% American Indian and Alaska Native, 7.4% African Americans, black or African American, 1.7% Asian, 0.1% Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander, 4.1% from some other race and 5.9% of two or more races. 8.9% of Oklahoma's population were of Hispanic and Latino Americans, Hispanic, Latino, or Spanish origin (they may be of any race). In 2005, Oklahoma's estimated ancestral makeup was 14.5% German, 13.1% Southern United States#European colonization, American, 11.8% Irish American, Irish, 9.6% English American, English, 8.1% African Americans, African American, and 11.4% Native American (including 7.9% Cherokee) though the percentage of people claiming American Indian as their only race was 8.1%. Most people from Oklahoma who self-identify as having American ancestry are of overwhelmingly English American, English and Scots-Irish Americans, Scots-Irish ancestry with significant amounts of Scottish American, Scottish, Welsh American, Welsh and Irish American, Irish inflection as well.Cities and towns
The state is in the U.S. Census' Southern United States, Southern region. According to the 2020 United States census, Oklahoma is the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 28th-most populous state with inhabitants but the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 19th-largest by land area spanning of land. In 2010, Oklahoma was divided into 77 County (United States), counties and contains 597 Municipal corporation, incorporated municipalities consisting of cities and towns. In Oklahoma, cities are all those incorporated communities which are 1,000 or more in population and are incorporated as cities. Towns are limited to town board type of municipal government. Cities may choose among aldermanic, mayoral, council-manager, and home-rule charter types of government. Cities may also petition to incorporate as towns. The Oklahoma City suburb Nichols Hills, Oklahoma, Nichols Hills is first on List of Oklahoma locations by per capita income, Oklahoma locations by per capita income at $73,661, though Tulsa County, Oklahoma, Tulsa County holds the highest average.Language
English
The English language has been official in the state of Oklahoma since 2010. The variety of North American English spoken is called Oklahoma English, and this dialect is quite diverse with its uneven blending of features of North Midland, South Midland, and Southern American English, Southern dialects. In 2000, 2,977,187 Oklahomans—92.6% of the resident population, five years or older—spoke only English at home, a decrease from 95% in 1990. 238,732 Oklahoma residents reported speaking a language other than English at home in the 2000 census, about 7.4% of the state's population.Native American languages
The two most commonly spoken native North American languages are Cherokee language, Cherokee andChoctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are ...
with 10,000 Cherokee speakers living within the Cherokee Nation tribal jurisdiction area of eastern Oklahoma, and another 10,000 Choctaw speakers living in the Choctaw Nation directly south of the Cherokees. Cherokee is an official language in the Cherokee Nation tribal jurisdiction area and in the United Keetoowah Band of Cherokee Indians.
Twenty-five Indigenous languages of the Americas, Native American languages are spoken in Oklahoma, second only to California. However, only Cherokee, if any, exhibits some language vitality at present. ''Ethnologue'' sees Cherokee as Endangered language, moribund because the only remaining active users of the language are members of the grandparent generation and older.
Other languages
Spanish language in the United States, Spanish is the second-most commonly spoken language in the state, with 141,060 speakers counted in 2000. German has 13,444 speakers representing about 0.4% of the state's population, and Vietnamese is spoken by 11,330 people, or about 0.4% of the population, many of whom live in the Asia District, Oklahoma City, Asia District of Oklahoma City. Other languages include French with 8,258 speakers (0.3%), Chinese Americans, Chinese with 6,413 (0.2%), Korean with 3,948 (0.1%), Arabic with 3,265 (0.1%), other Asian languages with 3,134 (0.1%), Tagalog language, Tagalog with 2,888 (0.1%), Japanese with 2,546 (0.1%), and African languages with 2,546 (0.1%).Religion
 Oklahoma is part of a geographical region characterized by conservative and Evangelical Christianity known as the "Bible Belt". Spanning the southern and eastern parts of the United States, the area is known for Ideology, politically and socially conservative views, with the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party having the greater number of voters registered between the two parties. Tulsa, the state's second-largest city, home to Oral Roberts University, is sometimes called the "Bible Belt#Buckle, buckle of the Bible Belt".
In 2000, there were about 5,000 List of synagogues in Oklahoma, Jews and 6,000 Muslims, with ten congregations to each group.
According to the Pew Research Center in 2008, the majority of Oklahoma's religious adherents were Christian, accounting for about 80 percent of the population. The percentage of Catholics was half the national average, while the percentage of Evangelical Protestants was more than twice the national average (tied with Arkansas for the largest percentage of any state).
Oklahoma is part of a geographical region characterized by conservative and Evangelical Christianity known as the "Bible Belt". Spanning the southern and eastern parts of the United States, the area is known for Ideology, politically and socially conservative views, with the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party having the greater number of voters registered between the two parties. Tulsa, the state's second-largest city, home to Oral Roberts University, is sometimes called the "Bible Belt#Buckle, buckle of the Bible Belt".
In 2000, there were about 5,000 List of synagogues in Oklahoma, Jews and 6,000 Muslims, with ten congregations to each group.
According to the Pew Research Center in 2008, the majority of Oklahoma's religious adherents were Christian, accounting for about 80 percent of the population. The percentage of Catholics was half the national average, while the percentage of Evangelical Protestants was more than twice the national average (tied with Arkansas for the largest percentage of any state).
 In 2010, the state's largest church memberships were in the Southern Baptist Convention (886,394 members), the United Methodist Church (282,347), the Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Church (178,430), and the Assemblies of God USA, Assemblies of God (85,926) and the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (Mormons) (47,349). Other religions represented in the state include Buddhism, Hinduism, and Islam.
According to the Pew Research Center in 2014, the majority of Oklahoma's religious adherents were Christian accounting for 79 percent of the population, 9 percent higher than the national average. The percentage of Evangelical Protestants declined since the last study, but they remain the largest religious group in the state at 47 percent, over 20 percent higher than the national average. The largest growth over the six years between Pew's 2008 and 2014 survey was in the number of people who identify as irreligious, Unaffiliated in the state with an increase of 6 percent.
In 2010, the state's largest church memberships were in the Southern Baptist Convention (886,394 members), the United Methodist Church (282,347), the Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Church (178,430), and the Assemblies of God USA, Assemblies of God (85,926) and the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (Mormons) (47,349). Other religions represented in the state include Buddhism, Hinduism, and Islam.
According to the Pew Research Center in 2014, the majority of Oklahoma's religious adherents were Christian accounting for 79 percent of the population, 9 percent higher than the national average. The percentage of Evangelical Protestants declined since the last study, but they remain the largest religious group in the state at 47 percent, over 20 percent higher than the national average. The largest growth over the six years between Pew's 2008 and 2014 survey was in the number of people who identify as irreligious, Unaffiliated in the state with an increase of 6 percent.
Incarceration
Oklahoma has been described as "the world's prison capital", with 1,079 of every 100,000 residents imprisoned in 2018, the highest incarceration rate of any state, and by comparison, higher than the List of countries by incarceration rate, incarceration rates of any country in the world.Economy
 Oklahoma is host to a diverse range of sectors including aviation, energy, transportation equipment, food processing, electronics, and telecommunications. Oklahoma is an important producer of natural gas, aircraft, and agriculture, food. The state ranks third in the nation for production of natural gas, is the 27th-most agriculturally productive state, and also ranks 5th in production of wheat. Four Fortune 500 companies and six Fortune 1000 companies are headquartered in Oklahoma, and it has been rated one of the most business-friendly states in the nation, with the 7th-lowest tax burden in 2007.
* Total employment (2018): 1,385,228
* Number of employer establishments: 93,561
In 2010, Oklahoma City-based Love's Travel Stops & Country Stores ranked 18th on the Forbes list of largest private companies, Tulsa-based QuikTrip ranked 37th, and Oklahoma City-based Hobby Lobby ranked 198th in 2010 report. Oklahoma's gross domestic product grew from $131.9 billion in 2006 to $147.5 billion in 2010, a jump of 10.6 percent. Oklahoma's gross domestic product per capita was $35,480 in 2010, which was ranked 40th among the states.
Though oil has historically dominated the state's economy, a 1980s oil glut, collapse in the energy industry during the 1980s led to the loss of nearly 90,000 energy-related jobs between 1980 and 2000, severely damaging the local economy. Oil accounted for 35 billion dollars in Oklahoma's economy in 2007, and employment in the state's oil industry was outpaced by five other industries in 2007. , the state's unemployment rate is 5.3%.
Oklahoma is host to a diverse range of sectors including aviation, energy, transportation equipment, food processing, electronics, and telecommunications. Oklahoma is an important producer of natural gas, aircraft, and agriculture, food. The state ranks third in the nation for production of natural gas, is the 27th-most agriculturally productive state, and also ranks 5th in production of wheat. Four Fortune 500 companies and six Fortune 1000 companies are headquartered in Oklahoma, and it has been rated one of the most business-friendly states in the nation, with the 7th-lowest tax burden in 2007.
* Total employment (2018): 1,385,228
* Number of employer establishments: 93,561
In 2010, Oklahoma City-based Love's Travel Stops & Country Stores ranked 18th on the Forbes list of largest private companies, Tulsa-based QuikTrip ranked 37th, and Oklahoma City-based Hobby Lobby ranked 198th in 2010 report. Oklahoma's gross domestic product grew from $131.9 billion in 2006 to $147.5 billion in 2010, a jump of 10.6 percent. Oklahoma's gross domestic product per capita was $35,480 in 2010, which was ranked 40th among the states.
Though oil has historically dominated the state's economy, a 1980s oil glut, collapse in the energy industry during the 1980s led to the loss of nearly 90,000 energy-related jobs between 1980 and 2000, severely damaging the local economy. Oil accounted for 35 billion dollars in Oklahoma's economy in 2007, and employment in the state's oil industry was outpaced by five other industries in 2007. , the state's unemployment rate is 5.3%.
Industry
In mid-2011, Oklahoma had a civilian labor force of 1.7 million and non-farm employment fluctuated around 1.5 million. The government sector provides the most jobs, with 339,300 in 2011, followed by the transportation and utilities sector, providing 279,500 jobs, and the sectors of education, business, and manufacturing, providing 207,800, 177,400, and 132,700 jobs, respectively. Among the state's largest industries, the aerospace sector generates $11 billion annually. Tulsa is home to the largest airline maintenance base in the world, which serves as the global maintenance and engineering headquarters for American Airlines. In total, aerospace accounts for more than 10 percent of Oklahoma's industrial output, and it is one of the top 10 states in aerospace engine manufacturing. Because of its position in the center of the United States, Oklahoma is also among the top states for logistic centers, and a major contributor to weather-related research. The state is the top manufacturer of tires in North America and contains one of the fastest-growing biotechnology industries in the nation. In 2005, international exports from Oklahoma's manufacturing industry totaled $4.3 billion, accounting for 3.6 percent of its economic impact. Tire manufacturing, meat processing, oil and gas equipment manufacturing, and air conditioner manufacturing are the state's largest manufacturing industries.Energy
 Oklahoma is the nation's third-largest producer of natural gas, and its fifth-largest producer of crude oil. The state also has the second-greatest number of active drilling rigs, and it is even ranked fifth in crude oil reserves. While the state was ranked eighth for installed Wind power, wind energy capacity in 2011, it still was at the bottom of states in usage of renewable energy in 2009, with 94% of its electricity being generated by Non-renewable energy, non-renewable sources in 2009, including 25% from coal and 46% from natural gas.
Ten years later in 2019, 53.5% of electricity was produced from natural gas and 34.6% from wind power.
Oklahoma has no nuclear power plants. Ranking 13th for total energy consumption per capita in 2009, the state's energy costs were eighth-lowest in the nation.
As a whole, the oil energy industry contributes $35 billion to Oklahoma's gross domestic product (GDP), and employees of the state's oil-related companies earn an average of twice the state's typical yearly income. In 2009, the state had 83,700 commercial oil wells churning of crude oil. 8.5% of the nation's natural gas supply is held in Oklahoma, with being produced in 2009.
The Oklahoma Stack Play is a geographic referenced area in the Anadarko Basin. The oil field "Sooner Trend", Anadarko basin and the counties of Kingfisher and Canadian make up the basis for the "Oklahoma STACK". Other Plays such as the Eagle Ford are geological rather than geographical.
According to ''Forbes'' magazine, Oklahoma City-based Devon Energy, Devon Energy Corporation, Chesapeake Energy, Chesapeake Energy Corporation, and SandRidge Energy, SandRidge Energy Corporation are the largest private oil-related companies in the nation, and all Oklahoma's Fortune 500 companies are energy-related. Tulsa's ONEOK and Williams Companies are the state's largest and second-largest companies respectively, also ranking as the nation's second- and third-largest companies in the field of energy, according to Fortune (magazine), ''Fortune'' magazine. The magazine also placed Devon Energy as the second-largest company in the mining and crude oil-producing industry in the nation, while Chesapeake Energy ranks seventh respectively in that sector and Oklahoma Gas & Electric ranks as the 25th-largest gas and electric utility company.
Oklahoma Gas & Electric, commonly referred to as OG&E (NYSE: OGE) operates four base electric power plants in Oklahoma. Two of them are coal-fired power plants: one in Muskogee, Oklahoma, Muskogee, and the other in Red Rock, Oklahoma, Red Rock. Two are gas-fired power plants: one in Harrah, Oklahoma, Harrah and the other in Konawa, Oklahoma, Konawa. OG&E was the first electric company in Oklahoma to generate electricity from wind farms in 2003.
Oklahoma is the nation's third-largest producer of natural gas, and its fifth-largest producer of crude oil. The state also has the second-greatest number of active drilling rigs, and it is even ranked fifth in crude oil reserves. While the state was ranked eighth for installed Wind power, wind energy capacity in 2011, it still was at the bottom of states in usage of renewable energy in 2009, with 94% of its electricity being generated by Non-renewable energy, non-renewable sources in 2009, including 25% from coal and 46% from natural gas.
Ten years later in 2019, 53.5% of electricity was produced from natural gas and 34.6% from wind power.
Oklahoma has no nuclear power plants. Ranking 13th for total energy consumption per capita in 2009, the state's energy costs were eighth-lowest in the nation.
As a whole, the oil energy industry contributes $35 billion to Oklahoma's gross domestic product (GDP), and employees of the state's oil-related companies earn an average of twice the state's typical yearly income. In 2009, the state had 83,700 commercial oil wells churning of crude oil. 8.5% of the nation's natural gas supply is held in Oklahoma, with being produced in 2009.
The Oklahoma Stack Play is a geographic referenced area in the Anadarko Basin. The oil field "Sooner Trend", Anadarko basin and the counties of Kingfisher and Canadian make up the basis for the "Oklahoma STACK". Other Plays such as the Eagle Ford are geological rather than geographical.
According to ''Forbes'' magazine, Oklahoma City-based Devon Energy, Devon Energy Corporation, Chesapeake Energy, Chesapeake Energy Corporation, and SandRidge Energy, SandRidge Energy Corporation are the largest private oil-related companies in the nation, and all Oklahoma's Fortune 500 companies are energy-related. Tulsa's ONEOK and Williams Companies are the state's largest and second-largest companies respectively, also ranking as the nation's second- and third-largest companies in the field of energy, according to Fortune (magazine), ''Fortune'' magazine. The magazine also placed Devon Energy as the second-largest company in the mining and crude oil-producing industry in the nation, while Chesapeake Energy ranks seventh respectively in that sector and Oklahoma Gas & Electric ranks as the 25th-largest gas and electric utility company.
Oklahoma Gas & Electric, commonly referred to as OG&E (NYSE: OGE) operates four base electric power plants in Oklahoma. Two of them are coal-fired power plants: one in Muskogee, Oklahoma, Muskogee, and the other in Red Rock, Oklahoma, Red Rock. Two are gas-fired power plants: one in Harrah, Oklahoma, Harrah and the other in Konawa, Oklahoma, Konawa. OG&E was the first electric company in Oklahoma to generate electricity from wind farms in 2003.
Wind generation
Agriculture
The 27th-most agriculturally productive state, Oklahoma is fifth in cattle production and fifth in production of wheat. Approximately 5.5 percent of American beef comes from Oklahoma, while the state produces 6.1 percent of American wheat, 4.2 percent of American pig products, and 2.2 percent of dairy products. The state had 85,500 farms in 2012, collectively producing $4.3 billion in animal products and fewer than one billion dollars in crop output with more than $6.1 billion added to the state's gross domestic product. Poultry and swine are its second- and third-largest agricultural industries.Education
 With an educational system made up of State school, public school districts and independent private school, private institutions, Oklahoma had 638,817 students enrolled in 1,845 public primary, secondary, and vocational education, vocational schools in 533 school districts . Oklahoma has the highest enrollment of Native American students in the nation with 126,078 students in the 2009–10 school year. Oklahoma spent $7,755 for each student in 2008, and was 47th in the nation in expenditures per student, though its growth of total education expenditures between 1992 and 2002 ranked 22nd.
The state is among the best in pre-kindergarten education, and the National Institute for Early Education Research rated it first in the United States with regard to standards, quality, and access to pre-kindergarten education in 2004, calling it "a model for early childhood education, early childhood schooling". High school dropout rate decreased from 3.1 to 2.5 percent between 2007 and 2008 with Oklahoma ranked among 18 other states with 3 percent or less dropout rate. In 2004, the state ranked 36th in the nation for the relative number of adults with high school diplomas, though at 85.2 percent, it had the highest rate among Southern states. According to a study conducted by the Pell Institute, Oklahoma ranks 48th in college-participation for low-income students.
The University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma State University, the University of Central Oklahoma, and Northeastern State University are the largest public institutions of higher education in Oklahoma, each operating through one primary campus and satellite campuses throughout the state. The two state universities, along with Oklahoma City University and the University of Tulsa, rank among the country's best in undergraduate business programs.
Oklahoma City University School of Law, University of Oklahoma College of Law, and University of Tulsa College of Law are the state's only ABA-accredited institutions. Both University of Oklahoma and University of Tulsa are Tier1 institutions, with the University of Oklahoma ranked 68th and the University of Tulsa ranked 86th in the nation.
Oklahoma holds eleven public regional universities, including Northeastern State University, the second-oldest institution of higher education west of the Mississippi River, also containing the only College of Optometry in Oklahoma and the largest enrollment of Indigenous peoples of the United States, Native American students in the nation by percentage and amount. Langston University is Oklahoma's only historically black college. Six of the state's universities were placed in the Princeton Review's list of best 122 regional colleges in 2007, and three made the list of top colleges for best value. The state has 55 post-secondary technical institutions operated by Oklahoma Department of Career and Technology Education, Oklahoma's CareerTech program for training in specific fields of industry or trade.
In the 2007–2008 school year, there were 181,973 undergraduate students, 20,014 graduate students, and 4,395 first-professional degree students enrolled in Oklahoma colleges. Of these students, 18,892 received a bachelor's degree, 5,386 received a master's degree, and 462 received a first professional degree. This means the state of Oklahoma produces an average of 38,278-degree-holders per completions component (i.e. July 1, 2007June 30, 2008). National average is 68,322 total degrees awarded per completions component.
Beginning on April 2, 2018, tens of thousands of K–12 public school teachers 2018 Oklahoma teachers' strike, went on strike due to lack of funding. According to the National Education Association, teachers in Oklahoma had ranked 49th out of the 50 states in terms of teacher pay in 2016. The Oklahoma Legislature had passed a measure a week earlier to raise teacher salaries by $6,100, but it fell short of the $10,000 raise for teachers, $5,000 raise for other school employees, and $200 million increase in extra education funding many had sought. A survey in 2019 found that the pay raise obtained by the strike lifted the State's teacher pay ranking to 34th in the nation.
With an educational system made up of State school, public school districts and independent private school, private institutions, Oklahoma had 638,817 students enrolled in 1,845 public primary, secondary, and vocational education, vocational schools in 533 school districts . Oklahoma has the highest enrollment of Native American students in the nation with 126,078 students in the 2009–10 school year. Oklahoma spent $7,755 for each student in 2008, and was 47th in the nation in expenditures per student, though its growth of total education expenditures between 1992 and 2002 ranked 22nd.
The state is among the best in pre-kindergarten education, and the National Institute for Early Education Research rated it first in the United States with regard to standards, quality, and access to pre-kindergarten education in 2004, calling it "a model for early childhood education, early childhood schooling". High school dropout rate decreased from 3.1 to 2.5 percent between 2007 and 2008 with Oklahoma ranked among 18 other states with 3 percent or less dropout rate. In 2004, the state ranked 36th in the nation for the relative number of adults with high school diplomas, though at 85.2 percent, it had the highest rate among Southern states. According to a study conducted by the Pell Institute, Oklahoma ranks 48th in college-participation for low-income students.
The University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma State University, the University of Central Oklahoma, and Northeastern State University are the largest public institutions of higher education in Oklahoma, each operating through one primary campus and satellite campuses throughout the state. The two state universities, along with Oklahoma City University and the University of Tulsa, rank among the country's best in undergraduate business programs.
Oklahoma City University School of Law, University of Oklahoma College of Law, and University of Tulsa College of Law are the state's only ABA-accredited institutions. Both University of Oklahoma and University of Tulsa are Tier1 institutions, with the University of Oklahoma ranked 68th and the University of Tulsa ranked 86th in the nation.
Oklahoma holds eleven public regional universities, including Northeastern State University, the second-oldest institution of higher education west of the Mississippi River, also containing the only College of Optometry in Oklahoma and the largest enrollment of Indigenous peoples of the United States, Native American students in the nation by percentage and amount. Langston University is Oklahoma's only historically black college. Six of the state's universities were placed in the Princeton Review's list of best 122 regional colleges in 2007, and three made the list of top colleges for best value. The state has 55 post-secondary technical institutions operated by Oklahoma Department of Career and Technology Education, Oklahoma's CareerTech program for training in specific fields of industry or trade.
In the 2007–2008 school year, there were 181,973 undergraduate students, 20,014 graduate students, and 4,395 first-professional degree students enrolled in Oklahoma colleges. Of these students, 18,892 received a bachelor's degree, 5,386 received a master's degree, and 462 received a first professional degree. This means the state of Oklahoma produces an average of 38,278-degree-holders per completions component (i.e. July 1, 2007June 30, 2008). National average is 68,322 total degrees awarded per completions component.
Beginning on April 2, 2018, tens of thousands of K–12 public school teachers 2018 Oklahoma teachers' strike, went on strike due to lack of funding. According to the National Education Association, teachers in Oklahoma had ranked 49th out of the 50 states in terms of teacher pay in 2016. The Oklahoma Legislature had passed a measure a week earlier to raise teacher salaries by $6,100, but it fell short of the $10,000 raise for teachers, $5,000 raise for other school employees, and $200 million increase in extra education funding many had sought. A survey in 2019 found that the pay raise obtained by the strike lifted the State's teacher pay ranking to 34th in the nation.
Non-English education
 The Cherokee Nation instigated a ten-year plan in 2005 that involved growing new speakers of the Cherokee language from childhood as well as speaking it exclusively at home. The plan was part of an ambitious goal that in fifty years would have at least 80% of their people fluent. The Cherokee Preservation Foundation has invested $3 million into opening schools, training teachers, and developing curricula for language education, as well as initiating community gatherings where the language can be actively used.
A Cherokee language immersion school in Tahlequah, Oklahoma educates students from pre-school through eighth grade.
The Cherokee Nation instigated a ten-year plan in 2005 that involved growing new speakers of the Cherokee language from childhood as well as speaking it exclusively at home. The plan was part of an ambitious goal that in fifty years would have at least 80% of their people fluent. The Cherokee Preservation Foundation has invested $3 million into opening schools, training teachers, and developing curricula for language education, as well as initiating community gatherings where the language can be actively used.
A Cherokee language immersion school in Tahlequah, Oklahoma educates students from pre-school through eighth grade.
Culture
 Oklahoma is placed in the South by the United States Census Bureau, but other definitions place the state at least partly in the Southwestern United States, Southwest, Midwestern United States, Midwest, Upland South, and
Oklahoma is placed in the South by the United States Census Bureau, but other definitions place the state at least partly in the Southwestern United States, Southwest, Midwestern United States, Midwest, Upland South, and Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
. Oklahomans have a high rate of English Americans, English, Scotch-Irish Americans, Scotch-Irish, German Americans, German, and Native Americans in the United States, Native American ancestry, with 25 different native languages spoken.
Because many Native Americans were forced to move to Oklahoma when White settlement in North America increased, Oklahoma has much linguistic diversity. Mary Linn, an associate professor of anthropology at the University of Oklahoma and the associate curator of Native American languages at the Sam Noble Oklahoma Museum of Natural History, Sam Noble Museum, notes Oklahoma also has high levels of language endangerment.
Sixty-seven Native American tribes are represented in Oklahoma, including 39 federally recognized tribes, who are headquartered and have Oklahoma Tribal Statistical Area, tribal jurisdictional areas in the state. Western ranchers, Native American tribes, Southern settlers, and eastern oil barons have shaped the state's cultural predisposition, and its largest cities have been named among the most underrated cultural destinations in the United States.
Residents of Oklahoma are associated with traits of Southern hospitality—the 2006 Catalogue for Philanthropy (with data from 2004) ranks Oklahomans 7th in the nation for overall generosity. The state has also been associated with a negative cultural stereotype first popularized by John Steinbeck's 1939 novel ''The Grapes of Wrath'', which described the plight of uneducated, poverty-stricken Dust Bowl-era farmers deemed "Okies". While the term is often used in a positive manner by Oklahomans, it is still considered a derogatory term by many.
Arts
 In the state's largest urban areas, pockets of jazz culture flourish, and Native American, Mexican Americans, Mexican American, and Asian American communities produce music and art of their respective cultures. The Oklahoma Mozart Festival in Bartlesville is one of the largest classical music festivals on the southern plains, and Oklahoma City's Festival of the Arts has been named one of the top fine arts festivals in the nation.
The state has a rich history in ballet with five Native American ballerinas attaining worldwide fame. These were Yvonne Chouteau, sisters Marjorie Tallchief, Marjorie and Maria Tallchief, Rosella Hightower and Moscelyne Larkin, known collectively as the Five Moons. ''The New York Times'' rates the Tulsa Ballet as one of the top ballet companies in the United States. The Oklahoma City Ballet and University of Oklahoma's dance program were formed by ballerina Yvonne Chouteau and husband Miguel Terekhov. The university program was founded in 1962 and was the first fully accredited program of its kind in the United States.
In Sand Springs, Oklahoma, Sand Springs, an outdoor amphitheater called "Discoveryland!" (since closed) is the official performance headquarters for the musical ''Oklahoma!'' Ridge Bond, native of McAlester, Oklahoma, starred in the Broadway theatre, Broadway and International touring productions of ''Oklahoma!'', playing the role of "Curly McClain" in more than 2,600 performances. In 1953 he was featured along with the ''Oklahoma!'' cast on a CBS Omnibus (U.S. TV series), Omnibus television broadcast. Bond was instrumental in the Oklahoma (Rodgers and Hammerstein song), Oklahoma! title song becoming the Oklahoma state song and is also featured on the U.S. postage stamp commemorating the musical's 50th anniversary. Historically, the state has produced musical styles such as The Tulsa Sound and western swing, which was popularized at Cain's Ballroom in Tulsa. The building, known as the "Carnegie Hall of Western Swing", served as the performance headquarters of Bob Wills and the Texas Playboys during the 1930s. Stillwater is known as the epicenter of Red Dirt (music), Red Dirt music, the best-known proponent of which is the late Bob Childers.
Prominent theatre companies in Oklahoma include, in the capital city, Lyric Theatre of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City Theatre Company, Carpenter Square Theatre, Oklahoma Shakespeare in the Park, and CityRep. CityRep is a professional company affording equity points to those performers and technical theatre professionals. In Tulsa, Oklahoma's oldest resident professional company is American Theatre Company, and Theatre Tulsa is the oldest community theatre company west of the Mississippi. Other companies in Tulsa include Heller Theatre and Tulsa Spotlight Theater. The cities of Norman, Lawton, and Stillwater, among others, also host well-reviewed community theatre companies.
Oklahoma is in the nation's middle percentile in per capita spending on the arts, ranking 17th, and contains more than 300 museums. The Philbrook Museum of Tulsa is considered one of the top 50 fine art museums in the United States, and the Sam Noble Oklahoma Museum of Natural History in Norman, one of the largest university-based art and history museums in the country, documents the natural history of the region. The collections of Thomas Gilcrease are housed in the Gilcrease Museum of Tulsa, which also holds the world's largest, most comprehensive collection of art and artifacts of the American West.
The Egyptian art collection at the Mabee-Gerrer Museum of Art in Shawnee is considered to be the finest Egyptian collection between Chicago and Los Angeles. The Oklahoma City Museum of Art contains the most comprehensive collection of glass sculptures by artist Dale Chihuly in the world, and Oklahoma City's National Cowboy & Western Heritage Museum documents the heritage of the American Western frontier. With remnants of the The Holocaust, Holocaust and artifacts relevant to Judaism, the Sherwin Miller Museum of Jewish Art of Tulsa preserves the largest collection of Jewish art in the Southwest United States.
In the state's largest urban areas, pockets of jazz culture flourish, and Native American, Mexican Americans, Mexican American, and Asian American communities produce music and art of their respective cultures. The Oklahoma Mozart Festival in Bartlesville is one of the largest classical music festivals on the southern plains, and Oklahoma City's Festival of the Arts has been named one of the top fine arts festivals in the nation.
The state has a rich history in ballet with five Native American ballerinas attaining worldwide fame. These were Yvonne Chouteau, sisters Marjorie Tallchief, Marjorie and Maria Tallchief, Rosella Hightower and Moscelyne Larkin, known collectively as the Five Moons. ''The New York Times'' rates the Tulsa Ballet as one of the top ballet companies in the United States. The Oklahoma City Ballet and University of Oklahoma's dance program were formed by ballerina Yvonne Chouteau and husband Miguel Terekhov. The university program was founded in 1962 and was the first fully accredited program of its kind in the United States.
In Sand Springs, Oklahoma, Sand Springs, an outdoor amphitheater called "Discoveryland!" (since closed) is the official performance headquarters for the musical ''Oklahoma!'' Ridge Bond, native of McAlester, Oklahoma, starred in the Broadway theatre, Broadway and International touring productions of ''Oklahoma!'', playing the role of "Curly McClain" in more than 2,600 performances. In 1953 he was featured along with the ''Oklahoma!'' cast on a CBS Omnibus (U.S. TV series), Omnibus television broadcast. Bond was instrumental in the Oklahoma (Rodgers and Hammerstein song), Oklahoma! title song becoming the Oklahoma state song and is also featured on the U.S. postage stamp commemorating the musical's 50th anniversary. Historically, the state has produced musical styles such as The Tulsa Sound and western swing, which was popularized at Cain's Ballroom in Tulsa. The building, known as the "Carnegie Hall of Western Swing", served as the performance headquarters of Bob Wills and the Texas Playboys during the 1930s. Stillwater is known as the epicenter of Red Dirt (music), Red Dirt music, the best-known proponent of which is the late Bob Childers.
Prominent theatre companies in Oklahoma include, in the capital city, Lyric Theatre of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City Theatre Company, Carpenter Square Theatre, Oklahoma Shakespeare in the Park, and CityRep. CityRep is a professional company affording equity points to those performers and technical theatre professionals. In Tulsa, Oklahoma's oldest resident professional company is American Theatre Company, and Theatre Tulsa is the oldest community theatre company west of the Mississippi. Other companies in Tulsa include Heller Theatre and Tulsa Spotlight Theater. The cities of Norman, Lawton, and Stillwater, among others, also host well-reviewed community theatre companies.
Oklahoma is in the nation's middle percentile in per capita spending on the arts, ranking 17th, and contains more than 300 museums. The Philbrook Museum of Tulsa is considered one of the top 50 fine art museums in the United States, and the Sam Noble Oklahoma Museum of Natural History in Norman, one of the largest university-based art and history museums in the country, documents the natural history of the region. The collections of Thomas Gilcrease are housed in the Gilcrease Museum of Tulsa, which also holds the world's largest, most comprehensive collection of art and artifacts of the American West.
The Egyptian art collection at the Mabee-Gerrer Museum of Art in Shawnee is considered to be the finest Egyptian collection between Chicago and Los Angeles. The Oklahoma City Museum of Art contains the most comprehensive collection of glass sculptures by artist Dale Chihuly in the world, and Oklahoma City's National Cowboy & Western Heritage Museum documents the heritage of the American Western frontier. With remnants of the The Holocaust, Holocaust and artifacts relevant to Judaism, the Sherwin Miller Museum of Jewish Art of Tulsa preserves the largest collection of Jewish art in the Southwest United States.
Festivals and events
 Oklahoma's centennial celebration was named the top event in the United States for 2007 by the American Bus Association, and consisted of multiple celebrations saving with the 100th anniversary of U.S. state, statehood on November 16, 2007. Annual ethnic festivals and events take place throughout the state such as Native American powwows and ceremonial events, and include festivals (as examples) in Scottish Americans, Scottish, Irish Americans, Irish, German Americans, German, Italian Americans, Italian, Vietnamese Americans, Vietnamese, Chinese Americans, Chinese, Czech Americans, Czech, American Jews, Jewish, Arab Americans, Arab, Mexican Americans, Mexican and African-American communities depicting cultural heritage or traditions.
Oklahoma City is home to a few reoccurring events and festivals. During a ten-day run in Oklahoma City, the Oklahoma State Fair, State Fair of Oklahoma attracts roughly one million people along with the annual Festival of the Arts. Large national pow wows, various Latin and Culture of Asia, Asian heritage festivals, and cultural festivals such as the Juneteenth celebrations are held in Oklahoma City each year. The Oklahoma City Pride Parade has been held annually in late June since 1987 in the gay district of Oklahoma City on NW 39th Street Enclave, 39th and Penn. The First Friday Art Walk in the Paseo Arts District is an art appreciation festival held the first Friday of every month. Additionally, an annual art festival is held in the Paseo on Memorial Day Weekend.
The Tulsa State Fair attracts more than a million people each year during its ten-day run, and the city's Mayfest festival entertained more than 375,000 in four days during 2007. In 2006, Tulsa's Oktoberfest was named one of the top 10 in the world by ''USA Today''.
Norman plays host to the Norman Music Festival, a festival that highlights native Oklahoma bands and musicians. Norman is also host to the Medieval Fair of Norman, which has been held annually since 1976 and was Oklahoma's first medieval fair. The Fair was held first on the south oval of the University of Oklahoma campus and in the third year moved to the Duck Pond in Norman until the Fair became too big and moved to Reaves Park in 2003. The Medieval Fair of Norman is Oklahoma's "largest weekend event and the third-largest event in Oklahoma, and was selected by Events Media Network as one of the top 100 events in the nation".
Oklahoma's centennial celebration was named the top event in the United States for 2007 by the American Bus Association, and consisted of multiple celebrations saving with the 100th anniversary of U.S. state, statehood on November 16, 2007. Annual ethnic festivals and events take place throughout the state such as Native American powwows and ceremonial events, and include festivals (as examples) in Scottish Americans, Scottish, Irish Americans, Irish, German Americans, German, Italian Americans, Italian, Vietnamese Americans, Vietnamese, Chinese Americans, Chinese, Czech Americans, Czech, American Jews, Jewish, Arab Americans, Arab, Mexican Americans, Mexican and African-American communities depicting cultural heritage or traditions.
Oklahoma City is home to a few reoccurring events and festivals. During a ten-day run in Oklahoma City, the Oklahoma State Fair, State Fair of Oklahoma attracts roughly one million people along with the annual Festival of the Arts. Large national pow wows, various Latin and Culture of Asia, Asian heritage festivals, and cultural festivals such as the Juneteenth celebrations are held in Oklahoma City each year. The Oklahoma City Pride Parade has been held annually in late June since 1987 in the gay district of Oklahoma City on NW 39th Street Enclave, 39th and Penn. The First Friday Art Walk in the Paseo Arts District is an art appreciation festival held the first Friday of every month. Additionally, an annual art festival is held in the Paseo on Memorial Day Weekend.
The Tulsa State Fair attracts more than a million people each year during its ten-day run, and the city's Mayfest festival entertained more than 375,000 in four days during 2007. In 2006, Tulsa's Oktoberfest was named one of the top 10 in the world by ''USA Today''.
Norman plays host to the Norman Music Festival, a festival that highlights native Oklahoma bands and musicians. Norman is also host to the Medieval Fair of Norman, which has been held annually since 1976 and was Oklahoma's first medieval fair. The Fair was held first on the south oval of the University of Oklahoma campus and in the third year moved to the Duck Pond in Norman until the Fair became too big and moved to Reaves Park in 2003. The Medieval Fair of Norman is Oklahoma's "largest weekend event and the third-largest event in Oklahoma, and was selected by Events Media Network as one of the top 100 events in the nation".
Sports
The Oklahoma City Thunder of the National Basketball Association (NBA) is the state's only Major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada, major league sports franchise. The state had a team in the Women's National Basketball Association, the Tulsa Shock, from 2010 through 2015, but the team relocated to Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, Dallas–Fort Worth after that season and became the Dallas Wings. Oklahoma has teams in several minor leagues, including Minor League Baseball at the Triple-A (baseball), Triple-A and Double-A (baseball), Double-A levels (the Oklahoma City Dodgers and Tulsa Drillers, respectively), hockey's ECHL with the Tulsa Oilers, and a number of indoor football leagues. In the last-named sport, the state's most notable team was the Tulsa Talons, which played in the Arena Football League until 2012, when the team was moved to San Antonio, Texas. The Oklahoma Defenders replaced the Talons as Tulsa's only professional arena football team, playing the CPIFL. The Oklahoma City Blue, of the NBA G League, relocated to Oklahoma City from Tulsa in 2014, where they were formerly known as the Tulsa 66ers. Tulsa is the base for the Tulsa Revolution, which plays in the American Indoor Soccer League. Enid and Lawton host professional basketball teams in the USBL and the Continental Basketball Association, CBA.Current professional teams
Health
 Oklahoma was the 21st-largest recipient of medical funding from the federal government in 2005, with health-related federal expenditures in the state totaling $75,801,364; immunizations, bioterrorism preparedness, and health education were the top three most funded medical items. Instances of major diseases are near the national average in Oklahoma, and the state ranks at or slightly above the rest of the country in percentage of people with asthma, Diabetes mellitus, diabetes, cancer, and hypertension.
In 2000, Oklahoma ranked 45th in physicians per capita and slightly below the national average in nurses per capita, but was slightly above the national average in hospital beds per 100,000 people and above the national average in net growth of health services over a twelve-year period. One of the worst states for percentage of insured people, nearly 25 percent of Oklahomans between the age of 18 and 64 did not have health insurance in 2005, the fifth-highest rate in the nation.
Oklahomans are in the upper half of Americans in terms of obesity prevalence, and the state is the 5th most obese in the nation, with 30.3 percent of its population at or near obesity. Oklahoma ranked last among the 50 states in a 2007 study by the Commonwealth Fund on health care performance.
The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, OU Medical Center, Oklahoma's largest collection of hospitals, is the only hospital in the state designated a LevelI trauma center by the American College of Surgeons. OU Medical Center is on the grounds of the Oklahoma Health Center in Oklahoma City, the state's largest concentration of medical research facilities.
The Cancer Treatment Centers of America at Southwestern Regional Medical Center in Tulsa is one of four such regional facilities nationwide, offering cancer treatment to the entire southwestern United States, and is one of the largest cancer treatment hospitals in the country. The largest Osteopathic medicine in the United States, osteopathic teaching facility in the nation, Oklahoma State University Medical Center at Tulsa, also rates as one of the largest facilities in the field of neuroscience.
On June 26, 2018, Oklahoma made Medical cannabis, marijuana legal for medical purposes, making it one of the most conservative states to approve medical marijuana.
Oklahoma was the 21st-largest recipient of medical funding from the federal government in 2005, with health-related federal expenditures in the state totaling $75,801,364; immunizations, bioterrorism preparedness, and health education were the top three most funded medical items. Instances of major diseases are near the national average in Oklahoma, and the state ranks at or slightly above the rest of the country in percentage of people with asthma, Diabetes mellitus, diabetes, cancer, and hypertension.
In 2000, Oklahoma ranked 45th in physicians per capita and slightly below the national average in nurses per capita, but was slightly above the national average in hospital beds per 100,000 people and above the national average in net growth of health services over a twelve-year period. One of the worst states for percentage of insured people, nearly 25 percent of Oklahomans between the age of 18 and 64 did not have health insurance in 2005, the fifth-highest rate in the nation.
Oklahomans are in the upper half of Americans in terms of obesity prevalence, and the state is the 5th most obese in the nation, with 30.3 percent of its population at or near obesity. Oklahoma ranked last among the 50 states in a 2007 study by the Commonwealth Fund on health care performance.
The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, OU Medical Center, Oklahoma's largest collection of hospitals, is the only hospital in the state designated a LevelI trauma center by the American College of Surgeons. OU Medical Center is on the grounds of the Oklahoma Health Center in Oklahoma City, the state's largest concentration of medical research facilities.
The Cancer Treatment Centers of America at Southwestern Regional Medical Center in Tulsa is one of four such regional facilities nationwide, offering cancer treatment to the entire southwestern United States, and is one of the largest cancer treatment hospitals in the country. The largest Osteopathic medicine in the United States, osteopathic teaching facility in the nation, Oklahoma State University Medical Center at Tulsa, also rates as one of the largest facilities in the field of neuroscience.
On June 26, 2018, Oklahoma made Medical cannabis, marijuana legal for medical purposes, making it one of the most conservative states to approve medical marijuana.
Life expectancy
The residents of Oklahoma have a lower life expectancy than the U.S. national average. In 2014, males in Oklahoma lived an average of 73.7 years compared to a male national average of 76.7 years and females lived an average of 78.5 years compared to a female national average of 81.5 years. Moreover, increases in life expectancy have been below the national average. Male life expectancy in Oklahoma between 1980 and 2014, increased by an average of 4.0 years, compared to a male national average of a 6.7 year increase. Life expectancy for females in Oklahoma between 1980 and 2014, increased by 1.0 years, compared to a female national average of a 4.0 year increase. Using 2016–2018 data, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation calculated that life expectancy (all sexes) for Oklahoma counties ranged from 71.2 years for Okfuskee County to 79.7 years for Cimarron County, Cimarron and Logan County, Oklahoma, Logan counties. Life expectancy for the state as a whole was 76.0 years.Impact of Covid
As of December 22, 2022, Oklahoma has been impacted more by Covid than the average U.S. State. Statistics for the U.S. as a whole are 331 deaths per 100,000 population with 68 percent of the population fully vaccinated. The comparable statistics for Oklahoma are 405 deaths per 100,000 population with 59 percent of the population fully vaccinated. 16,041 deaths from Covid have been recorded in Oklahoma. A wide variation in deaths from Covid exists between Oklahoma counties. Greer County, Oklahoma, Greer County recorded a death rate of .00753 (753 deaths per 100,000 residents). Payne County, Oklahoma, Payne County recorded a death rate of only .00231 (231 deaths per 100,000 residents.Media
 Oklahoma City and Tulsa are the 45th- and 61st-largest media markets in the United States as ranked by Nielsen Media Research. The state's third-largest media market, Lawton-Wichita Falls, Texas, is ranked 149th nationally by the agency. Terrestrial television, Broadcast television in Oklahoma began in 1949 when KFOR-TV (then WKY-TV) in Oklahoma City and KOTV-TV in Tulsa began broadcasting a few months apart. Currently, all major American Television network, broadcast networks have affiliated television stations in the state.
The state has two primary newspapers. ''The Oklahoman'', based in Oklahoma City, is the largest newspaper in the state and 54th-largest in the nation by circulation, with a weekday readership of 138,493 and a Sunday readership of 202,690. The ''Tulsa World'', the second-most widely circulated newspaper in Oklahoma and 79th in the nation, holds a Sunday circulation of 132,969 and a weekday readership of 93,558. Oklahoma's first newspaper was established in 1844, called the ''Cherokee Advocate'', and was written in both Cherokee language, Cherokee and English. In 2006, there were more than 220 newspapers in the state, including 177 with weekly publications and 48 with daily publications.
The state's first radio station, WKY in Oklahoma City, began broadcasting in 1920. In 2006, there were more than 500 radio stations in Oklahoma broadcasting with various local or nationally owned networks. Five universities in Oklahoma operate non-commercial, public radio stations/networks.
Oklahoma has a few ethnic-oriented TV stations broadcasting in Spanish and Asian Americans, Asian languages, and there is some Native American programming. Trinity Broadcasting Network, TBN, a Christian religious television network, has a studio in Tulsa, and built its first entirely TBN-owned affiliate in Oklahoma City in 1980.
Oklahoma City and Tulsa are the 45th- and 61st-largest media markets in the United States as ranked by Nielsen Media Research. The state's third-largest media market, Lawton-Wichita Falls, Texas, is ranked 149th nationally by the agency. Terrestrial television, Broadcast television in Oklahoma began in 1949 when KFOR-TV (then WKY-TV) in Oklahoma City and KOTV-TV in Tulsa began broadcasting a few months apart. Currently, all major American Television network, broadcast networks have affiliated television stations in the state.
The state has two primary newspapers. ''The Oklahoman'', based in Oklahoma City, is the largest newspaper in the state and 54th-largest in the nation by circulation, with a weekday readership of 138,493 and a Sunday readership of 202,690. The ''Tulsa World'', the second-most widely circulated newspaper in Oklahoma and 79th in the nation, holds a Sunday circulation of 132,969 and a weekday readership of 93,558. Oklahoma's first newspaper was established in 1844, called the ''Cherokee Advocate'', and was written in both Cherokee language, Cherokee and English. In 2006, there were more than 220 newspapers in the state, including 177 with weekly publications and 48 with daily publications.
The state's first radio station, WKY in Oklahoma City, began broadcasting in 1920. In 2006, there were more than 500 radio stations in Oklahoma broadcasting with various local or nationally owned networks. Five universities in Oklahoma operate non-commercial, public radio stations/networks.
Oklahoma has a few ethnic-oriented TV stations broadcasting in Spanish and Asian Americans, Asian languages, and there is some Native American programming. Trinity Broadcasting Network, TBN, a Christian religious television network, has a studio in Tulsa, and built its first entirely TBN-owned affiliate in Oklahoma City in 1980.
Transportation
Law and government
 Oklahoma is a constitutional republic with a government modeled after the federal government of the United States, with executive, legislative, and judicial branches. The state has List of counties in Oklahoma, 77 counties with jurisdiction over most local government functions within each respective domain, Oklahoma's congressional districts, five congressional districts, and a voting base with a plurality in the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party. State officials are elected by plurality voting in the state of Oklahoma.
Oklahoma has capital punishment in the United States, capital punishment as a legal sentence, and the state has had (between 1976 through mid-2011) the highest per capita execution rate in the nation.
In a 2020 study, Oklahoma was ranked as the 14th hardest state for citizens to vote in.
Oklahoma is a constitutional republic with a government modeled after the federal government of the United States, with executive, legislative, and judicial branches. The state has List of counties in Oklahoma, 77 counties with jurisdiction over most local government functions within each respective domain, Oklahoma's congressional districts, five congressional districts, and a voting base with a plurality in the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party. State officials are elected by plurality voting in the state of Oklahoma.
Oklahoma has capital punishment in the United States, capital punishment as a legal sentence, and the state has had (between 1976 through mid-2011) the highest per capita execution rate in the nation.
In a 2020 study, Oklahoma was ranked as the 14th hardest state for citizens to vote in.
State government
The Oklahoma Legislature, Legislature of Oklahoma consists of the Oklahoma Senate, Senate and the Oklahoma House of Representatives, House of Representatives. As the lawmaking branch of the state government, it is responsible for raising and distributing the money necessary to run the government. The Senate has 48 members serving four-year terms, while the House has 101 members with two-year terms. The state has a term limit for its legislature that restricts any one person to twelve cumulative years service between both legislative branches. Oklahoma's judicial branch consists of the Oklahoma Supreme Court, the Oklahoma Court of Criminal Appeals, and 77 District Courts that each serve one county. The Oklahoma judiciary also contains two independent courts: a Court of Impeachment and the Oklahoma Court on the Judiciary. Oklahoma has two courts of last resort: the state Supreme Court hears civil cases, and the state Court of Criminal Appeals hears criminal cases (this split system exists only in Oklahoma and neighboring Texas). Judges of those two courts, as well as the Court of Civil Appeals are appointed by the Governor upon the recommendation of the state Judicial Nominating Commission, and are subject to a non-partisan retention vote on a six-year rotating schedule.Local government
The state is divided into 77 County (United States), counties that govern locally, each headed by a three-member council of elected commissioners, a tax assessor, clerk, court clerk, treasurer, and Sheriffs in the United States, sheriff. While each municipality operates as a separate and independent local government with executive, legislative and judicial power, county governments maintain jurisdiction over both incorporated cities and non-incorporated areas within their boundaries, and have executive power but no legislative or judicial power. Both county and municipal governments collect taxes, employ a separate police force, hold elections, and operate emergency response services within their jurisdiction. Other local government units include school districts, technology center districts, community college districts, rural fire departments, rural water districts, and other special use districts. Thirty-nine Native American tribal governments are based in Oklahoma, each holding limited powers within designated areas. While Indian reservations are typical in most of the United States, they are not present in Oklahoma, tribal governments hold land granted during the Indian Territory era, but with limited jurisdiction and no control over state governing bodies such as municipalities and counties. Tribal governments are recognized by the United States as quasi-sovereign entities with executive, judicial, and legislative powers over tribal members and functions, but are subject to the authority of the United States Congress to revoke or withhold certain powers. The tribal governments are required to submit a constitution and any subsequent amendments to the United States Congress for approval. Oklahoma has 11 substate districts including the two large Councils of Governments, INCOG in Tulsa (Indian Nations Council of Governments) and ACOG (Association of Central Oklahoma Governments).National politics
Military
Cities and towns
Major cities
 Oklahoma had 598 incorporated places in 2010, including four cities over 100,000 in population and 43 over 10,000. Two of the List of United States cities by population, fifty largest cities in the United States are in Oklahoma, Oklahoma City and Tulsa, and sixty-five percent of Oklahomans live within their metropolitan areas, or spheres of economic and social influence defined by the United States Census Bureau as a metropolitan statistical area. Oklahoma City, the state's capital and largest city, had the Oklahoma City Metroplex, largest metropolitan area in the state in 2020, with 1,425,695 people, and the Tulsa Metropolitan Area, metropolitan area of Tulsa had 1,015,331 residents. Between 2000 and 2010, the leading cities in population growth were Blanchard, Oklahoma, Blanchard (172.4%), Elgin, Oklahoma, Elgin (78.2%), Jenks, Oklahoma, Jenks (77.0%), Piedmont, Oklahoma, Piedmont (56.7%), Bixby, Oklahoma, Bixby (56.6%), and Owasso, Oklahoma, Owasso (56.3%).
Oklahoma had 598 incorporated places in 2010, including four cities over 100,000 in population and 43 over 10,000. Two of the List of United States cities by population, fifty largest cities in the United States are in Oklahoma, Oklahoma City and Tulsa, and sixty-five percent of Oklahomans live within their metropolitan areas, or spheres of economic and social influence defined by the United States Census Bureau as a metropolitan statistical area. Oklahoma City, the state's capital and largest city, had the Oklahoma City Metroplex, largest metropolitan area in the state in 2020, with 1,425,695 people, and the Tulsa Metropolitan Area, metropolitan area of Tulsa had 1,015,331 residents. Between 2000 and 2010, the leading cities in population growth were Blanchard, Oklahoma, Blanchard (172.4%), Elgin, Oklahoma, Elgin (78.2%), Jenks, Oklahoma, Jenks (77.0%), Piedmont, Oklahoma, Piedmont (56.7%), Bixby, Oklahoma, Bixby (56.6%), and Owasso, Oklahoma, Owasso (56.3%).
 In descending order of population, Oklahoma's largest cities in 2010 were: Oklahoma City (579,999, +14.6%), Tulsa (391,906, −0.3%), Norman (110,925, +15.9%), Broken Arrow, Oklahoma, Broken Arrow (98,850, +32.0%), Lawton (96,867, +4.4%), Edmond, Oklahoma, Edmond (81,405, +19.2%), Moore, Oklahoma, Moore (55,081, +33.9%), Midwest City, Oklahoma, Midwest City (54,371, +0.5%), Enid, Oklahoma, Enid (49,379, +5.0%), and Stillwater, Oklahoma, Stillwater (45,688, +17.0%). Of the state's ten largest cities, three are outside the metropolitan areas of Oklahoma City and Tulsa, and only Lawton has a metropolitan statistical area of its own as designated by the United States Census Bureau, though the metropolitan statistical area of Fort Smith, Arkansas extends into the state.
Under Oklahoma law, municipalities are divided into two categories: cities, defined as having more than 1,000 residents, and towns, with under 1,000 residents. Both have Legislature, legislative, Judiciary, judicial, and public power within their boundaries, but cities can choose between a Mayor–council government, mayor–council, Council–manager government, council–manager, or Mayor–council government, strong mayor form of government, while towns operate through an elected officer system.
In descending order of population, Oklahoma's largest cities in 2010 were: Oklahoma City (579,999, +14.6%), Tulsa (391,906, −0.3%), Norman (110,925, +15.9%), Broken Arrow, Oklahoma, Broken Arrow (98,850, +32.0%), Lawton (96,867, +4.4%), Edmond, Oklahoma, Edmond (81,405, +19.2%), Moore, Oklahoma, Moore (55,081, +33.9%), Midwest City, Oklahoma, Midwest City (54,371, +0.5%), Enid, Oklahoma, Enid (49,379, +5.0%), and Stillwater, Oklahoma, Stillwater (45,688, +17.0%). Of the state's ten largest cities, three are outside the metropolitan areas of Oklahoma City and Tulsa, and only Lawton has a metropolitan statistical area of its own as designated by the United States Census Bureau, though the metropolitan statistical area of Fort Smith, Arkansas extends into the state.
Under Oklahoma law, municipalities are divided into two categories: cities, defined as having more than 1,000 residents, and towns, with under 1,000 residents. Both have Legislature, legislative, Judiciary, judicial, and public power within their boundaries, but cities can choose between a Mayor–council government, mayor–council, Council–manager government, council–manager, or Mayor–council government, strong mayor form of government, while towns operate through an elected officer system.

State symbols
State law codifies Oklahoma's state emblems and honorary positions; the Oklahoma Senate or House of Representatives may adopt resolutions designating others for special events and to benefit organizations. In 2012 the House passed HCR 1024, which would change the state motto from "Labor Omnia Vincit" to "Oklahoma—In God We Trust!" The author of the resolution stated a constituent researched the Oklahoma Constitution and found no "official" vote regarding "Labor Omnia Vincit", therefore opening the door for an entirely new motto.See also
* Index of Oklahoma-related articles * Outline of OklahomaNotes
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * *complete text online
900 pages of scholarly articles
External links
Government
*Oklahoma Legislative Branch
Oklahoma Department of Commerce
Oklahoma Department of Human Services
Oklahoma Department of Transportation
Tourism and recreation
Official Oklahoma Tourism Info
Oklahoma State Parks
Red Earth
Woody Guthrie Folk Festival
Culture and history
Oklahoma State Guide from the Library of Congress
Oklahoma Arts Council
Oklahoma Theatre Association
Oklahoma Oral History Research Program
Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture
Voices of Oklahoma Oral History Project
Maps and demographics
Oklahoma Genealogical Society
Realtime USGS geographic, weather, and geologic information
*
Oklahoma Digital Maps: Digital Collections of Oklahoma and Indian Territory
{{DEFAULTSORT:Oklahoma 1907 establishments in the United States Cherokee-speaking countries and territories Oklahoma, Southern United States States and territories established in 1907 States of the United States Contiguous United States List of place names of Choctaw origin in the United States