Oil Spills In Brazil on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Brazil is the 10th largest energy consumer in the world and the largest in South America. At the same time, it is an important oil and gas producer in the region and the world's second largest ethanol fuel producer. The government agencies responsible for energy policy are the Ministry of Mines and Energy (MME), the National Council for Energy Policy (CNPE), the National Agency of Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuels (ANP) and the National Agency of Electricity (ANEEL).
OECD/ IEA. World Energy Outlook 2006.
State-owned companies
Brazil is the 10th largest energy consumer in the world and the largest in South America. At the same time, it is an important oil and gas producer in the region and the world's second largest ethanol fuel producer. The government agencies responsible for energy policy are the Ministry of Mines and Energy (MME), the National Council for Energy Policy (CNPE), the National Agency of Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuels (ANP) and the National Agency of Electricity (ANEEL).
OECD/ IEA. World Energy Outlook 2006.
State-owned companies
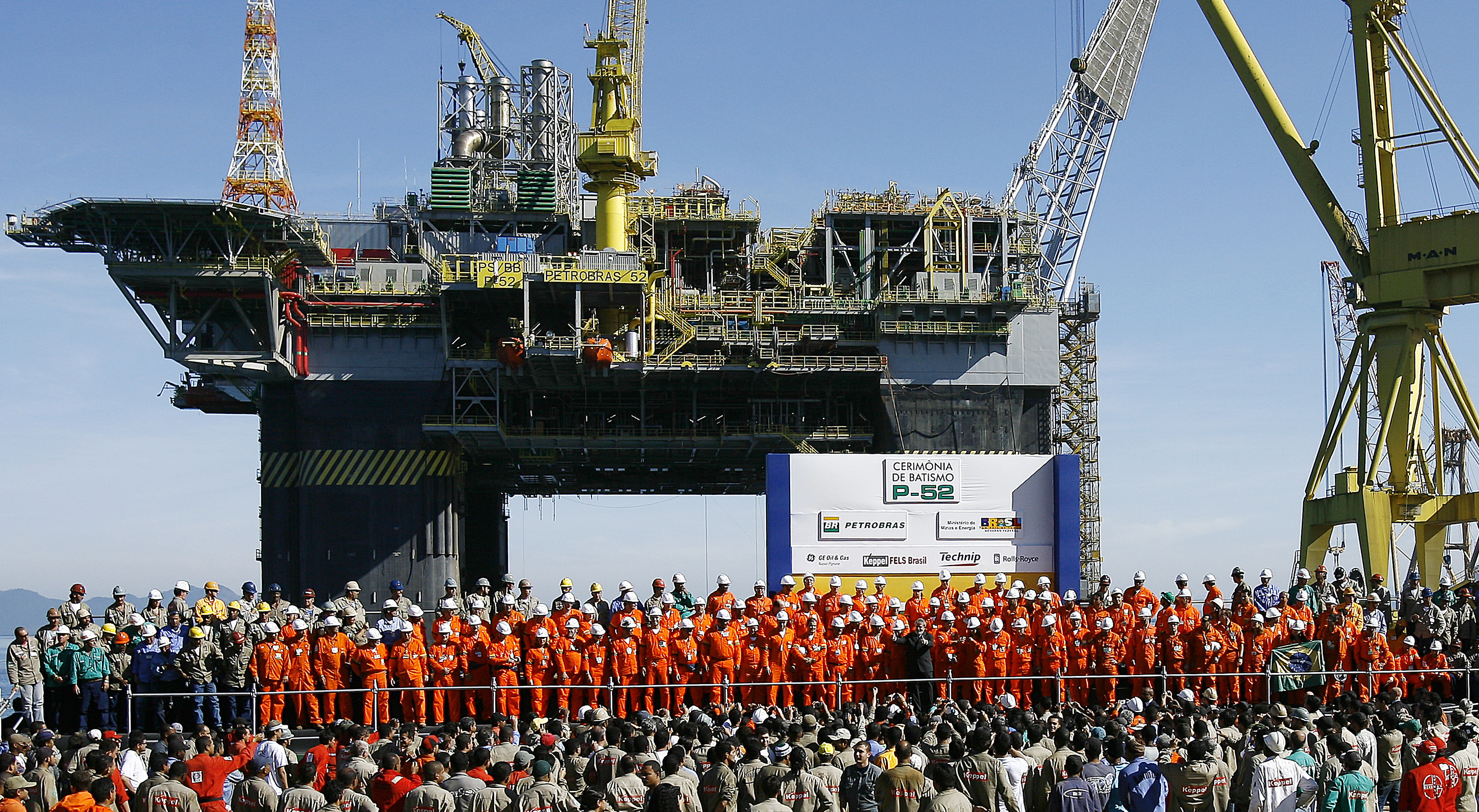



 Brazil is the world's 8th-largest oil producer. Up to 1997, the government-owned Petróleo Brasileiro S.A. (Petrobras) had a monopoly on oil. More than 50 oil companies now are engaged in oil exploration. The only global oil producer is Petrobras, with an output of more than of oil equivalent per day. It is also a major distributor of oil products, and owns oil refineries and oil tankers.
In 2006, Brazil had the second-largest proven oil reserves in South America after Venezuela. The vast majority of proven reserves were located in the Campos and Santos offshore basins off the southeast coast of Brazil.Country Analysis Brief. Brazil
Brazil is the world's 8th-largest oil producer. Up to 1997, the government-owned Petróleo Brasileiro S.A. (Petrobras) had a monopoly on oil. More than 50 oil companies now are engaged in oil exploration. The only global oil producer is Petrobras, with an output of more than of oil equivalent per day. It is also a major distributor of oil products, and owns oil refineries and oil tankers.
In 2006, Brazil had the second-largest proven oil reserves in South America after Venezuela. The vast majority of proven reserves were located in the Campos and Santos offshore basins off the southeast coast of Brazil.Country Analysis Brief. Brazil
US Energy Information Agency, August 2006 In November 2007, Petrobras announced that it believed the offshore Tupi oil field had between 5 and of recoverable light oil and neighbouring fields may even contain more, which all in all could result in Brazil becoming one of the largest producers of oil in the world. Brazil has been a net exporter of oil since 2011. However, the country still
 At the end of 2017, the proven reserves of Brazil's natural gas were 369 x 109 m³, with possible reserves expected to be 2 times higher. Until recently natural gas was produced as a by-product of the oil industry. The main reserves in use are located at Campos and Santos Basins. Other natural gas basins include Foz do Amazonas, Ceara e Potiguar, Pernambuco e Paraíba,
Sergipe/Alagoas, Espírito Santo and Amazonas (onshore). Petrobras controls over 90 percent of Brazil’s natural gas reserves.
Brazil's inland gas pipeline systems are operated by
At the end of 2017, the proven reserves of Brazil's natural gas were 369 x 109 m³, with possible reserves expected to be 2 times higher. Until recently natural gas was produced as a by-product of the oil industry. The main reserves in use are located at Campos and Santos Basins. Other natural gas basins include Foz do Amazonas, Ceara e Potiguar, Pernambuco e Paraíba,
Sergipe/Alagoas, Espírito Santo and Amazonas (onshore). Petrobras controls over 90 percent of Brazil’s natural gas reserves.
Brazil's inland gas pipeline systems are operated by
, by Jean Laherrere, September 2005
 Brazil has the 6th largest uranium reserves in the world. Deposits of uranium are found in eight different states of Brazil. Proven reserves are 162,000 tonnes. Cumulative production at the end of 2002 was less than 1,400 tonnes. The
Brazil has the 6th largest uranium reserves in the world. Deposits of uranium are found in eight different states of Brazil. Proven reserves are 162,000 tonnes. Cumulative production at the end of 2002 was less than 1,400 tonnes. The
 Brazil is the third largest hydroelectricity producer in the world after China and Canada. The gross theoretical capability exceeds 3,000 TWh per annum, of which 800 TWh per annum is economically exploitable. In 2004, Brazil produced 321TWh of hydropower. In 2019, Brazil had 217 hydroelectric plants in operation, with an installed capacity of 98,581 MW, 60.16% of the country's energy generation.Quantas usinas geradoras de energia temos no Brasil?
Brazil is the third largest hydroelectricity producer in the world after China and Canada. The gross theoretical capability exceeds 3,000 TWh per annum, of which 800 TWh per annum is economically exploitable. In 2004, Brazil produced 321TWh of hydropower. In 2019, Brazil had 217 hydroelectric plants in operation, with an installed capacity of 98,581 MW, 60.16% of the country's energy generation.Quantas usinas geradoras de energia temos no Brasil?
/ref> At the end of 2021 Brazil was the 2nd country in the world in terms of installed hydroelectric power (109.4 GW). In total electricity generation, in 2019 Brazil reached 170,000 megawatts of installed capacity, more than 75% from renewable sources (the majority,

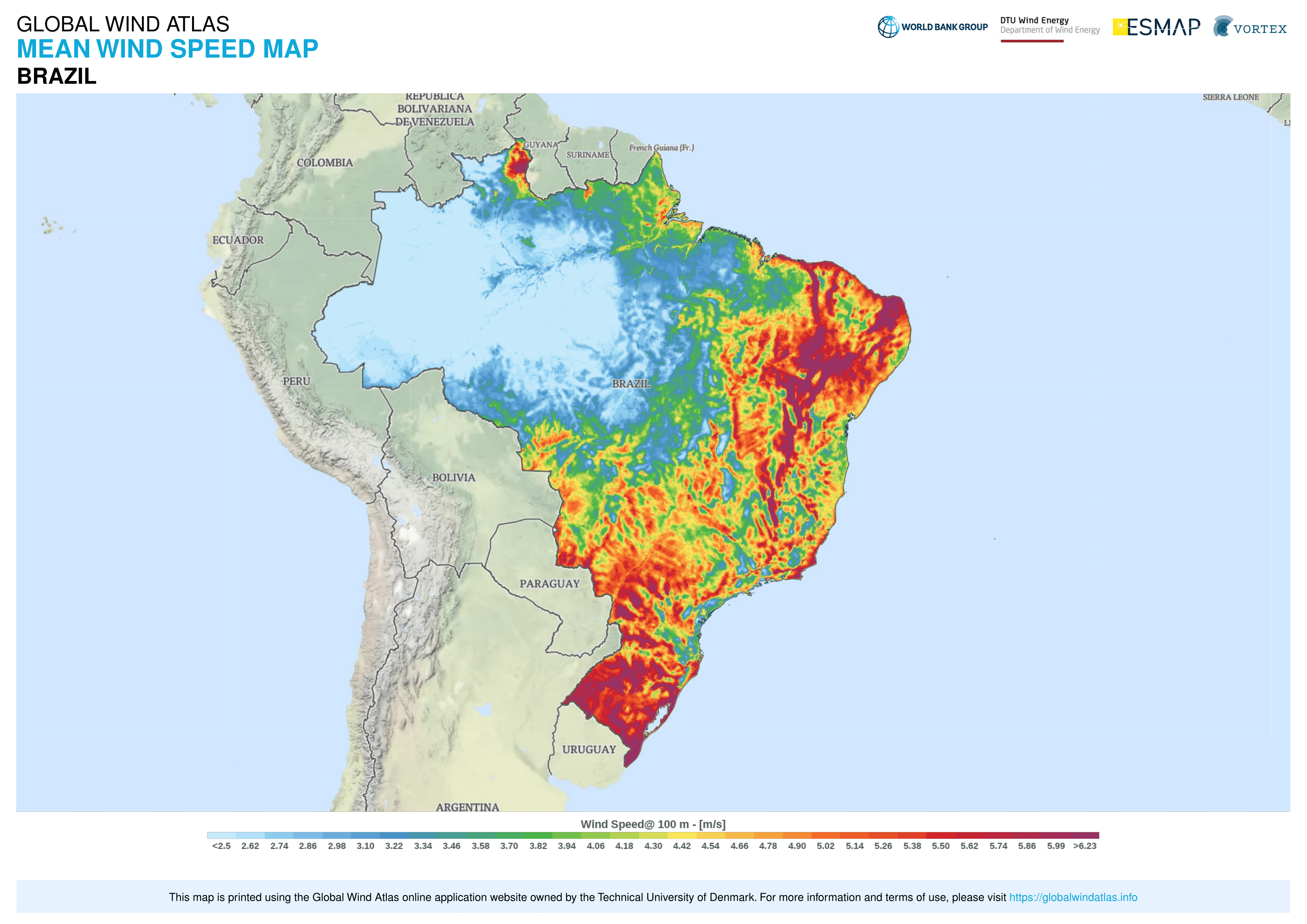 In July 2022 Brazil reached 22 GW of installed wind power. In 2021 Brazil was the 7th country in the world in terms of installed wind power (21 GW),RENEWABLE CAPACITY STATISTICS 2021
In July 2022 Brazil reached 22 GW of installed wind power. In 2021 Brazil was the 7th country in the world in terms of installed wind power (21 GW),RENEWABLE CAPACITY STATISTICS 2021
/ref> and the 4th largest producer of wind energy in the world (72 TWh), behind only China, USA and Germany. Brazil's gross wind resource potential was estimated, in 2019, to be about 522 GW (this, only onshore), enough energy to meet three times the country's current demand. according to ONS, total installed capacity was 18.9 GW, with average capacity factor of 58%. While the world average wind production capacity factors is 24.7%, there are areas in Northern Brazil, specially in Bahia State, where some wind farms record with average capacity factors over 60%; the average capacity factor in the Northeast Region is 45% in the coast and 49% in the interior. In 2019, wind energy represented 9% of the energy generated in the country. In 2020 Brazil was the 8th country in the world in terms of installed wind power (17.2 GW); in November 2021 Brazil reached 20 GW of installed wind power.
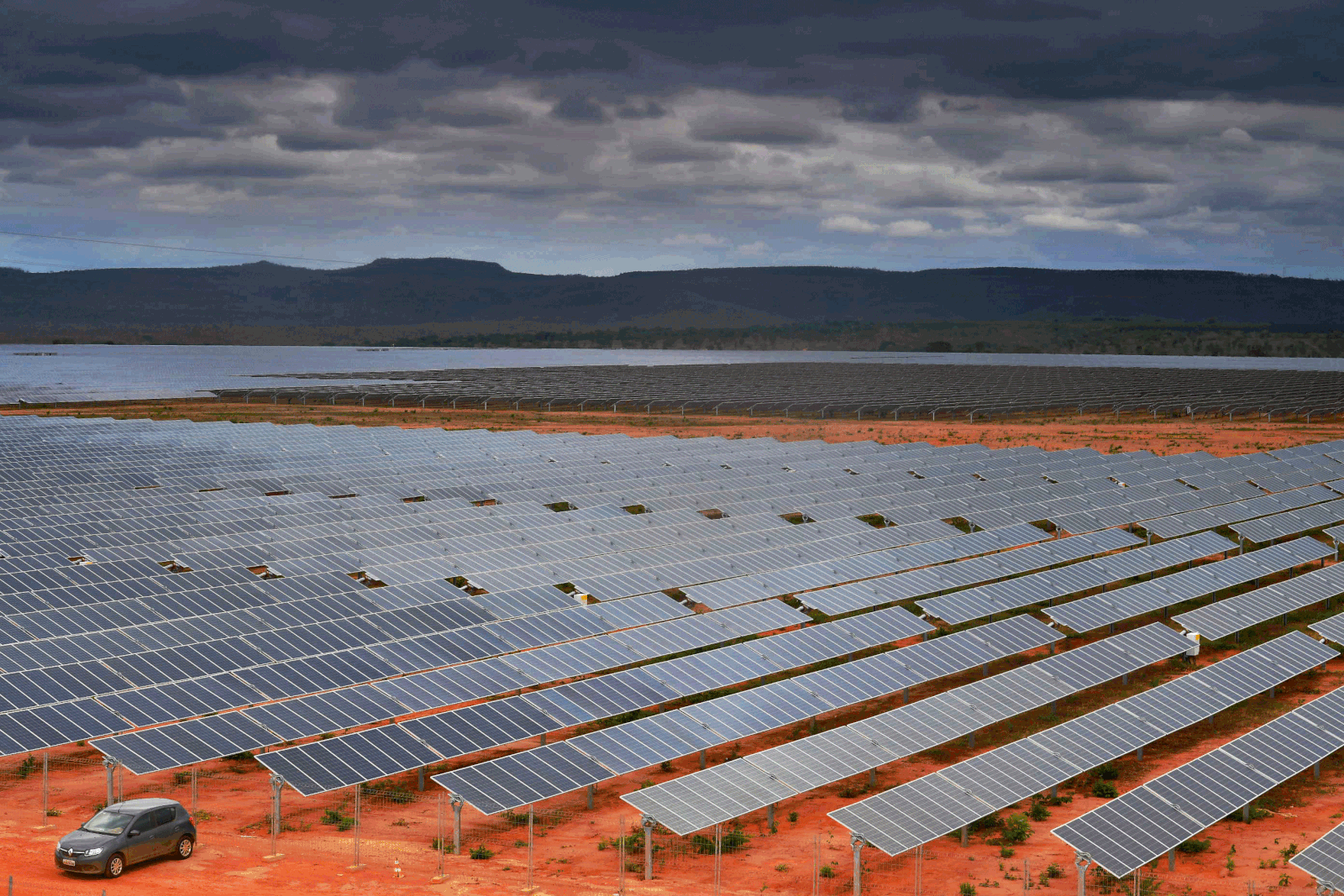 In October 2022 Brazil reached 21 GW of installed solar power. In 2021, Brazil was the 14th country in the world in terms of installed solar power (13 GW), and the 11th largest producer of solar energy in the world (16.8 TWh).
according to ONS, total installed capacity of
In October 2022 Brazil reached 21 GW of installed solar power. In 2021, Brazil was the 14th country in the world in terms of installed solar power (13 GW), and the 11th largest producer of solar energy in the world (16.8 TWh).
according to ONS, total installed capacity of
 Nuclear energy accounts for about 4% of Brazil's electricity. The nuclear power generation monopoly is owned by Eletronuclear (Eletrobrás Eletronuclear S/A), a wholly owned subsidiary of Eletrobrás. Nuclear energy is produced by two reactors at Angra. It is located at the Central Nuclear Almirante Álvaro Alberto (CNAAA) on the Praia de Itaorna in
Nuclear energy accounts for about 4% of Brazil's electricity. The nuclear power generation monopoly is owned by Eletronuclear (Eletrobrás Eletronuclear S/A), a wholly owned subsidiary of Eletrobrás. Nuclear energy is produced by two reactors at Angra. It is located at the Central Nuclear Almirante Álvaro Alberto (CNAAA) on the Praia de Itaorna in
 In 2020, Brazil was the 2nd largest country in the world in the production of energy through
In 2020, Brazil was the 2nd largest country in the world in the production of energy through Brazil - A Bio-Energy Superpower
, by Mario Osava, Tierramérica Ethanol fuel is produced from sugar cane. Brazil has the largest sugar cane crop in the world, and is the largest exporter of ethanol in the world. With the
 Brazil is the 10th largest energy consumer in the world and the largest in South America. At the same time, it is an important oil and gas producer in the region and the world's second largest ethanol fuel producer. The government agencies responsible for energy policy are the Ministry of Mines and Energy (MME), the National Council for Energy Policy (CNPE), the National Agency of Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuels (ANP) and the National Agency of Electricity (ANEEL).
OECD/ IEA. World Energy Outlook 2006.
State-owned companies
Brazil is the 10th largest energy consumer in the world and the largest in South America. At the same time, it is an important oil and gas producer in the region and the world's second largest ethanol fuel producer. The government agencies responsible for energy policy are the Ministry of Mines and Energy (MME), the National Council for Energy Policy (CNPE), the National Agency of Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuels (ANP) and the National Agency of Electricity (ANEEL).
OECD/ IEA. World Energy Outlook 2006.
State-owned companies Petrobras
Petróleo Brasileiro S.A., better known by the portmanteau Petrobras (), is a state owned enterprise, state-owned Brazilian multinational corporation in the petroleum industry headquartered in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The company's name transla ...
and Eletrobras are the major players in Brazil's energy sector, as well as Latin America's.
Overview

Total energy matrix and Electric energy matrix
The main characteristic of the Brazilian energy matrix is that it is much more renewable than that of the world. While in 2019 the world matrix was only 14% made up of renewable energy, Brazil's was at 45%. Petroleum and oil products made up 34.3% of the matrix; sugar cane derivatives, 18%; hydraulic energy, 12.4%; natural gas, 12.2%; firewood and charcoal, 8.8%; varied renewable energies, 7%; mineral coal, 5.3%; nuclear, 1.4%, and other non-renewable energies, 0.6%. In the electric energy matrix, the difference between Brazil and the world is even greater: while the world only had 25% of renewable electric energy in 2019, Brazil had 83%. The Brazilian electric matrix is composed of: hydraulic energy, 64.9%; biomass, 8.4%; wind energy, 8.6%; solar energy, 1%; natural gas, 9.3%; oil products, 2%; nuclear, 2.5%; coal and derivatives, 3.3%.Reforms of the energy sector
At the end of the 1990s and the beginning of the 2000s, Brazil's energy sector underwent market liberalization. In 1997, the Petroleum Investment Law was adopted, establishing a legal and regulatory framework, and liberalizing oil production. It created the CNPE and the ANP, increased use of natural gas, increased competition in the energy market, and increased investment inpower generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery ( transmission, distribution, etc.) to end users or its stor ...
. The state monopoly on oil and gas exploration ended, and energy subsidies were reduced. However, the government retained monopoly control of key energy complexes and regulated the price of certain energy products.
Current government policies concentrate mainly on improving energy efficiency in both residential and industrial sectors, as well as increasing use of renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
. Further restructuring of the energy sector will be one of the key issues for ensuring sufficient energy investments to meet the rising need for fuel and electricity.
Primary energy sources
Oil

 Brazil is the world's 8th-largest oil producer. Up to 1997, the government-owned Petróleo Brasileiro S.A. (Petrobras) had a monopoly on oil. More than 50 oil companies now are engaged in oil exploration. The only global oil producer is Petrobras, with an output of more than of oil equivalent per day. It is also a major distributor of oil products, and owns oil refineries and oil tankers.
In 2006, Brazil had the second-largest proven oil reserves in South America after Venezuela. The vast majority of proven reserves were located in the Campos and Santos offshore basins off the southeast coast of Brazil.Country Analysis Brief. Brazil
Brazil is the world's 8th-largest oil producer. Up to 1997, the government-owned Petróleo Brasileiro S.A. (Petrobras) had a monopoly on oil. More than 50 oil companies now are engaged in oil exploration. The only global oil producer is Petrobras, with an output of more than of oil equivalent per day. It is also a major distributor of oil products, and owns oil refineries and oil tankers.
In 2006, Brazil had the second-largest proven oil reserves in South America after Venezuela. The vast majority of proven reserves were located in the Campos and Santos offshore basins off the southeast coast of Brazil.Country Analysis Brief. BrazilUS Energy Information Agency, August 2006 In November 2007, Petrobras announced that it believed the offshore Tupi oil field had between 5 and of recoverable light oil and neighbouring fields may even contain more, which all in all could result in Brazil becoming one of the largest producers of oil in the world. Brazil has been a net exporter of oil since 2011. However, the country still
import
An import is the receiving country in an export from the sending country. Importation and exportation are the defining financial transactions of international trade.
In international trade, the importation and exportation of goods are limited ...
s some light oil from the Middle East, because several refineries, built in the 1960s and 1970s under the military government
A military government is generally any form of government that is administered by military forces, whether or not this government is legal under the laws of the jurisdiction at issue, and whether this government is formed by natives or by an occup ...
, are not suited to process the heavy oil in Brazilian reserves, discovered decades later.
Transpetro, a wholly owned subsidiary of Petrobras, operates a crude oil transport network. The system consists of of crude oil pipelines, coastal import terminals, and inland storage facilities.
Natural gas
 At the end of 2017, the proven reserves of Brazil's natural gas were 369 x 109 m³, with possible reserves expected to be 2 times higher. Until recently natural gas was produced as a by-product of the oil industry. The main reserves in use are located at Campos and Santos Basins. Other natural gas basins include Foz do Amazonas, Ceara e Potiguar, Pernambuco e Paraíba,
Sergipe/Alagoas, Espírito Santo and Amazonas (onshore). Petrobras controls over 90 percent of Brazil’s natural gas reserves.
Brazil's inland gas pipeline systems are operated by
At the end of 2017, the proven reserves of Brazil's natural gas were 369 x 109 m³, with possible reserves expected to be 2 times higher. Until recently natural gas was produced as a by-product of the oil industry. The main reserves in use are located at Campos and Santos Basins. Other natural gas basins include Foz do Amazonas, Ceara e Potiguar, Pernambuco e Paraíba,
Sergipe/Alagoas, Espírito Santo and Amazonas (onshore). Petrobras controls over 90 percent of Brazil’s natural gas reserves.
Brazil's inland gas pipeline systems are operated by Petrobras
Petróleo Brasileiro S.A., better known by the portmanteau Petrobras (), is a state owned enterprise, state-owned Brazilian multinational corporation in the petroleum industry headquartered in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The company's name transla ...
subsidiary Transpetro. In 2005, construction began on the Gas Unificação (Gasun pipeline) which will link Mato Grosso do Sul
Mato Grosso do Sul () is one of the Midwestern states of Brazil. Neighboring Brazilian states are (from north clockwise) Mato Grosso, Goiás, Minas Gerais, São Paulo and Paraná. It also borders the countries of Paraguay, to the southwest, and ...
in southwest Brazil, to Maranhão in the northeast. China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
’s Sinopec is a contractor for the Gasene pipeline, which will link the northeast and southeast networks. Petrobras is also constructing the Urucu-Manaus pipeline, which will link the Urucu gas reserves to power plants in the state of Amazonas.
In 2005, the gas production was 18.7 x 109 m³, which is less than the natural gas consumption of Brazil. Gas imports come mainly from Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg
, flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center
, flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ...
's Rio Grande basin through the Bolivia-Brazil gas pipeline (Gasbol pipeline), from Argentina through the Transportadora de Gas de Mercosur pipeline ( Paraná-Uruguaiana pipeline), and from LNG imports. Brazil has held talks with Venezuela and Argentina about building a new pipeline system Gran Gasoducto del Sur
The Gran Gasoducto del Sur (also known as Venezuela-Argentina Gas Line) was a proposed long natural gas pipeline to connect Venezuela, Brazil and Argentina. The overall project cost was expected to be around US$17-23 billion.
History ...
linking the three countries; however, the plan has not moved beyond the planning stages.
Coal
Brazil has total coal reserves of about 30 billion tonnes, but the deposits vary by the quality and quantity. The proved recoverable reserves are around 10 billion tonnes. In 2004 Brazil produced 5.4 million tonnes of coal, while coal consumption reached 21.9 million tonnes. Almost all of Brazil’s coal output is steam coal, of which about 85% is fired in power stations. Reserves ofsub-bituminous coal Sub-bituminous coal is a lower grade of coal that contains 35–45% carbon. The properties of this type are between those of lignite, the lowest grade of coal, and those of bituminous coal, the second-highest grade of coal. Sub-bituminous coal i ...
are located mostly in the states of Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul (, , ; "Great River of the South") is a Federative units of Brazil, state in the South Region, Brazil, southern region of Brazil. It is the Federative_units_of_Brazil#List, fifth-most-populous state and the List of Brazilian st ...
, Santa Catarina and Paraná.
Oil shale
Brazil has the world's second largest known oil shale (the Irati shale and lacustrine deposits) resources and has second largest shale oil production after Estonia. Oil shale resources lie inSão Mateus do Sul
São Mateus do Sul (St. Matthew of the South) is a municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which i ...
, Paraná, and in Vale do Paraíba. Brazil has developed the world’s largest surface oil shale pyrolysis retort Petrosix
Petrosix is the world's largest surface oil shale pyrolysis retort with an diameter vertical shaft kiln, operational since 1992. It is located in São Mateus do Sul, Brazil, and it is owned and operated by the Brazil energy company Petrobras. Pet ...
, operated by Petrobras. Production in 1999 was about 200,000 tonnes.Review on oil shale data, by Jean Laherrere, September 2005
Uranium
 Brazil has the 6th largest uranium reserves in the world. Deposits of uranium are found in eight different states of Brazil. Proven reserves are 162,000 tonnes. Cumulative production at the end of 2002 was less than 1,400 tonnes. The
Brazil has the 6th largest uranium reserves in the world. Deposits of uranium are found in eight different states of Brazil. Proven reserves are 162,000 tonnes. Cumulative production at the end of 2002 was less than 1,400 tonnes. The Poços de Caldas
Poços de Caldas is a municipality in the south of Minas Gerais state, Brazil, in the microregion of the same name. Its estimated population in 2020 was 168,641 inhabitants. The city is known for its hot springs.
History
Poços was founded in 1 ...
production centre in Minas Gerais state was shut down in 1997 and was replaced by a new plant at Lagoa Real
Lagoa Real is a municipality in the state of Bahia in the North-East region of Brazil.
See also
* List of municipalities in Bahia
References
Municipalities in Bahia
{{Bahia-geo-stub ...
in Bahia. There is a plan to build another production center at Itatiaia.
Electricity
Power sector reforms were launched in the mid-1990s and a new regulatory framework was applied in 2004. In 2004, Brazil had 86.5 GW of installed generating capacity and it produced 387 Twh of electricity. As of today 66% of distribution and 28% of power generation is owned by private companies. In 2004, 59 companies operated in power generation and 64 in electricity distribution. The major power company is Centrais Elétricas Brasileiras (Eletrobrás), which together with its subsidiaries generates and transmits approximately 60% of Brazil's electric supply. The largest private-owned power company isTractebel Energia
ENGIE Brasil formerly Tractebel Energia is a major Brazilian utility company, headquartered in Florianópolis, Santa Catarina. It is one of the largest private electricity producers in Brazil. Its 11 plants, six of them hydroelectric and the re ...
. An independent system operator ( - ((ONS)), responsible for the technical coordination of electricity dispatching and the management of transmission services, and a wholesale market were created in 1998.
During the electricity crisis in 2001, the government launched a program to build 55 gas-fired power stations with a total capacity of 22 GW, but only 19 power stations were built, with a total capacity of 4,012 MW.
Hydropower
 Brazil is the third largest hydroelectricity producer in the world after China and Canada. The gross theoretical capability exceeds 3,000 TWh per annum, of which 800 TWh per annum is economically exploitable. In 2004, Brazil produced 321TWh of hydropower. In 2019, Brazil had 217 hydroelectric plants in operation, with an installed capacity of 98,581 MW, 60.16% of the country's energy generation.Quantas usinas geradoras de energia temos no Brasil?
Brazil is the third largest hydroelectricity producer in the world after China and Canada. The gross theoretical capability exceeds 3,000 TWh per annum, of which 800 TWh per annum is economically exploitable. In 2004, Brazil produced 321TWh of hydropower. In 2019, Brazil had 217 hydroelectric plants in operation, with an installed capacity of 98,581 MW, 60.16% of the country's energy generation.Quantas usinas geradoras de energia temos no Brasil?/ref> At the end of 2021 Brazil was the 2nd country in the world in terms of installed hydroelectric power (109.4 GW). In total electricity generation, in 2019 Brazil reached 170,000 megawatts of installed capacity, more than 75% from renewable sources (the majority,
hydroelectric plants
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
).
In 2013, the Southeast used about 50% of the load of the National Integrated System (SIN), being the main energy consuming region in the country. The region's installed electricity generation capacity totaled almost 42,500 MW, which represented about a third of Brazil's generation capacity. The hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
generation represented 58% of the installed capacity in the region, with the remaining 42% basically corresponding to the thermoelectric generation. São Paulo accounted for 40% of this capacity; Minas Gerais by about 25%; Rio de Janeiro by 13.3%; and Espírito Santo for the rest.
The South Region has the Itaipu Dam, which was the largest hydroelectric plant in the world for several years, until the inauguration of the Three Gorges Dam in China. Remains the world's second largest operational hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
power plant. Brazil co-owns the Itaipu Dam with Paraguay: the dam is on the Paraná River
The Paraná River ( es, Río Paraná, links=no , pt, Rio Paraná, gn, Ysyry Parana) is a river in south-central South America, running through Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina for some ."Parana River". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Br ...
, located on the border between the countries. It has an installed generation capacity of 14 GW by 20 generating units of 700 MW each.
Northern Brazil has large hydroelectric plants such as Belo Monte
Belo Monte is a municipality located in the western of the Brazilian state of Alagoas. Its population is 6,710 (2020) and its area is 334 km².
The municipality was designated a priority area for conservation and sustainable use when the ...
and Tucuruí, which produce much of the national energy.
Brazil's hydroelectric potential has not yet been fully explored, so the country still has the capacity to build several renewable energy plants in its territory.
Wind energy

 In July 2022 Brazil reached 22 GW of installed wind power. In 2021 Brazil was the 7th country in the world in terms of installed wind power (21 GW),RENEWABLE CAPACITY STATISTICS 2021
In July 2022 Brazil reached 22 GW of installed wind power. In 2021 Brazil was the 7th country in the world in terms of installed wind power (21 GW),RENEWABLE CAPACITY STATISTICS 2021/ref> and the 4th largest producer of wind energy in the world (72 TWh), behind only China, USA and Germany. Brazil's gross wind resource potential was estimated, in 2019, to be about 522 GW (this, only onshore), enough energy to meet three times the country's current demand. according to ONS, total installed capacity was 18.9 GW, with average capacity factor of 58%. While the world average wind production capacity factors is 24.7%, there are areas in Northern Brazil, specially in Bahia State, where some wind farms record with average capacity factors over 60%; the average capacity factor in the Northeast Region is 45% in the coast and 49% in the interior. In 2019, wind energy represented 9% of the energy generated in the country. In 2020 Brazil was the 8th country in the world in terms of installed wind power (17.2 GW); in November 2021 Brazil reached 20 GW of installed wind power.
Solar power
 In October 2022 Brazil reached 21 GW of installed solar power. In 2021, Brazil was the 14th country in the world in terms of installed solar power (13 GW), and the 11th largest producer of solar energy in the world (16.8 TWh).
according to ONS, total installed capacity of
In October 2022 Brazil reached 21 GW of installed solar power. In 2021, Brazil was the 14th country in the world in terms of installed solar power (13 GW), and the 11th largest producer of solar energy in the world (16.8 TWh).
according to ONS, total installed capacity of photovoltaic solar
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially us ...
was 10.5 GW, with average capacity factor of 21%. Some of the most irradiated Brazilian States are MG ("Minas Gerais"), BA ("Bahia") and GO (Goiás), which have indeed world irradiation level records. In 2019, solar power represented 1,27% of the energy generated in the country. In 2020, Brazil was the 14th country in the world in terms of installed solar power (7.8 GW).
Nuclear energy
 Nuclear energy accounts for about 4% of Brazil's electricity. The nuclear power generation monopoly is owned by Eletronuclear (Eletrobrás Eletronuclear S/A), a wholly owned subsidiary of Eletrobrás. Nuclear energy is produced by two reactors at Angra. It is located at the Central Nuclear Almirante Álvaro Alberto (CNAAA) on the Praia de Itaorna in
Nuclear energy accounts for about 4% of Brazil's electricity. The nuclear power generation monopoly is owned by Eletronuclear (Eletrobrás Eletronuclear S/A), a wholly owned subsidiary of Eletrobrás. Nuclear energy is produced by two reactors at Angra. It is located at the Central Nuclear Almirante Álvaro Alberto (CNAAA) on the Praia de Itaorna in Angra dos Reis
Angra dos Reis (; Portuguese for ''cove'' or ''bay of the Kings'') is a Brazilian municipality located in the southern part of the state of Rio de Janeiro. The city is located by the sea and includes in its territory many offshore islands, the l ...
, Rio de Janeiro. It consists of two pressurized water reactors, Angra I, with capacity of 657 MW, connected to the power grid in 1982, and Angra II, with capacity of 1,350 MW, connected in 2000. A third reactor, Angra III, with a projected output of 1,350 MW, is planned to be finished by 2014 and work has been paralyzed due to environmental concerns, but the licenses are being approved and the heavy construction work will start in 2009. By 2025 Brazil plans to build seven more reactors.
Brazil signed a nuclear cooperation agreement with Argentina since 1991.
Biofuels
 In 2020, Brazil was the 2nd largest country in the world in the production of energy through
In 2020, Brazil was the 2nd largest country in the world in the production of energy through biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
(energy production from solid biofuels and renewable waste), with 15,2 GW installed.
Due to its ethanol fuel production, Brazil has sometimes been described as a bio-energy superpower., by Mario Osava, Tierramérica
1973 oil crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supp ...
, the Brazilian government initiated in 1975 the Pró-Álcool program. The Pró-Álcool or ''Programa Nacional do Álcool'' (National Alcohol Program) was a nationwide program financed by the government to phase out all automobile fuels derived from fossil fuels
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels ...
in favour of ethanol. The program successfully reduced by 10 million the number of cars running on gasoline in Brazil, thereby reducing the country's dependence on oil imports.
The production and consumption of biodiesel is expected to reach to 2% of diesel fuel in 2008 and 5% in 2013.
Brazil's peat reserves are estimated at 25 billion tonnes, the highest in South America. However, no production of peat for fuel has yet been developed. Brazil produces 65 million tonnes of fuelwood per year. The annual production of charcoal is about 6 million tonnes, used in the steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
industry. The cogeneration potential of agricultural and livestock residues varies from 4 GW to 47 GW by 2025.
References
Further reading
* Silvestre, B. S., Dalcol, P. R. T. (2009) Geographical proximity and innovation: Evidences from the Campos Basin oil & gas industrial agglomeration — Brazil. ''Technovation'', Vol. 29 (8), pp. 546–561. {{Authority control