Octopus Ink on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Cephalopod ink is a dark-coloured or luminous
Cephalopod ink is a dark-coloured or luminous
 Cephalopod ink has, as its name suggests, been used in the past as
Cephalopod ink has, as its name suggests, been used in the past as  Modern use of cephalopod ink is generally limited to cooking, primarily in Japan and the
Modern use of cephalopod ink is generally limited to cooking, primarily in Japan and the
An article on harvesting squid ink
{{Cephalopod anatomy Antipredator adaptations
 Cephalopod ink is a dark-coloured or luminous
Cephalopod ink is a dark-coloured or luminous ink
Ink is a gel, sol, or solution that contains at least one colorant, such as a dye or pigment, and is used to color a surface to produce an image, text, or design. Ink is used for drawing or writing with a pen, brush, reed pen, or quill. Thicker ...
released into water by most species of cephalopod, usually as an escape mechanism. All cephalopods, with the exception of the Nautilidae
The nautilus (, ) is a pelagic marine mollusc of the cephalopod family Nautilidae. The nautilus is the sole extant family of the superfamily Nautilaceae and of its smaller but near equal suborder, Nautilina.
It comprises six living species ...
and the Cirrina
Cirrina or Cirrata is a suborder and one of the two main divisions of octopuses. Cirrate octopuses have a small, internal shell and two fins on their head, while their sister suborder Incirrina has neither. The fins of cirrate octopods are asso ...
(deep-sea octopuses), are able to release ink to confuse predators
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill th ...
.
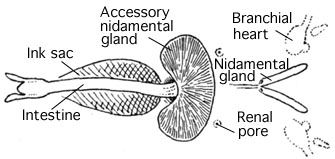
The ink is released from the ink sac
An ink sac is an anatomical feature that is found in many cephalopod mollusks used to produce the defensive cephalopod ink. With the exception of nocturnal and very deep water cephalopods, all Coleoidea (squid, octopus and cuttlefish) which dwell ...
s (located between the gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are ...
s) and is dispersed more widely when its release is accompanied by a jet of water from the siphon. Its dark color is caused by its main constituent, melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
. Each species of cephalopod produces slightly differently coloured inks; generally, octopuses produce black ink, squid ink is blue-black, and cuttlefish ink is a shade of brown.
A number of other aquatic molluscs have similar responses to attack, including the gastropod clade known as sea hare
The clade Anaspidea, commonly known as sea hares ('' Aplysia'' species and related genera), are medium-sized to very large opisthobranch gastropod molluscs with a soft internal shell made of protein. These are marine gastropod molluscs in the ...
s.
Types of ink shapes
The shapes taken by ink releases are classified as six types: * pseudomorphs; * pseudomorph series; * ink ropes; * clouds/smokescreens; * diffuse puffs; * mantle fills.Inking behaviors
Escape strategies
Two distinct behaviors have been observed in inking cephalopods. The first is the release of large amounts of ink into the water by the cephalopod in order to create a dark, diffuse cloud (much like asmoke screen
A smoke screen is smoke released to mask the movement or location of military units such as infantry, tanks, aircraft, or ships.
Smoke screens are commonly deployed either by a canister (such as a grenade) or generated by a vehicle (such as ...
) that can obscure the predator's view, allowing the cephalopod to make a rapid retreat by jetting away.
The second response to a predator is to release pseudomorphs ("false bodies"), smaller clouds of ink with a greater mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
content, which allows them to hold their shape for longer. These are expelled slightly away from the cephalopod in question, which will often release several pseudomorphs and change colour ( blanch) in conjunction with these releases. The pseudomorphs are roughly the same volume as and look similar to the cephalopod that released them, and many predators have been observed attacking them mistakenly, allowing the cephalopod to escape (this behaviour is often referred to as the "blanch-ink-jet manoeuvre"). Thus, such capture avoidance method is analogous to fighter jet dogfights where the followed pilot releases countermeasures (such as flares) to misdirect the sensors in some guided missiles.
Furthermore, green turtle
The green sea turtle (''Chelonia mydas''), also known as the green turtle, black (sea) turtle or Pacific green turtle, is a species of large sea turtle of the family Cheloniidae. It is the only species in the genus ''Chelonia''. Its range exten ...
(''Chelonia mydas'') hatchlings that have been observed mistakenly attacking pseudomorphs released by '' Octopus bocki'' have subsequently ignored conspecific
Biological specificity is the tendency of a characteristic such as a behavior or a biochemical variation to occur in a particular species.
Biochemist Linus Pauling stated that "Biological specificity is the set of characteristics of living organis ...
octopuses.
Hiding strategy
The spotty bobtail squid releases ropes of ink longer than itself and hides among them, maybe to be confused with floatingseagrass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four families (Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and Cymodoceaceae), all in the or ...
leaves.
Behavior around eggs
Octopuses have also been observed squirting ink atsnail
A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class G ...
s or crabs approaching their eggs
Humans and human ancestors have scavenged and eaten animal eggs for millions of years. Humans in Southeast Asia had domesticated chickens and harvested their eggs for food by 1,500 BCE. The most widely consumed eggs are those of fowl, especial ...
.
Numerous cuttlefish species add a coat of ink to their eggs, presumably to camouflage them from potential predators.
Properties
Attack protection
Inking has been shown to protect species of squids against predatory fish attacks, as well during the capture phase as during the consummatory phase, due to visual and chemical effects of the ink releases.Chemical effects
Many cephalopod predators (for instancemoray eel
Moray eels, or Muraenidae (), are a family of eels whose members are found worldwide. There are approximately 200 species in 15 genera which are almost exclusively marine, but several species are regularly seen in brackish water, and a few are f ...
s) have advanced chemosensory systems, and some anecdotal evidenceMacGinitie, G.E. and MacGinitie, N. (1968) ''Natural History of Marine Animals'', pp. 395–397, 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill, New York. suggests that compounds (such as tyrosinase
Tyrosinase is an oxidase that is the rate-limiting enzyme for controlling the production of melanin. The enzyme is mainly involved in two distinct reactions of melanin synthesis otherwise known as the Raper Mason pathway. Firstly, the hydroxy ...
) found in cephalopod ink can irritate, numb or even deactivate such apparatus. Few controlled experiments have been conducted to substantiate this. Cephalopod ink is nonetheless generally thought to be more sophisticated than a simple "smoke screen"; the ink of a number of squid and cuttlefish has been shown to function as a conspecific chemical alarm.
Physical properties
'' Sepia officinalis'' ink forms a polydisperse suspension composed by spheric particles with a size between 80 and 150 nm (measured byTRPS
Tunable Resistive Pulse Sensing (TRPS) is a single-particle technique used to measure the size, concentration and zeta potential of particles as they pass through a size-tunable nanopore.
The technique adapts the principle of resistive pulse se ...
and SEM). The particles have a density of , which may be due to the amount of metals that the ink has in its composition (4.7% in weight).
''Heteroteuthis dispar
''Heteroteuthis dispar'', also known as the odd bobtail, is a small deep water squid found in the North Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
Taxonomy
''Heteroteuthis dispar'' is a deep sea species of squid and relatively little is known ab ...
'' is a cephalopod species known for releasing luminous ink. The light comes from a substance produced by a dedicated organ before being transferred into the ink sac.
Chemical composition
Cephalopod ink contains a number of chemicals in a variety of different concentrations, depending on the species. However, its main constituents aremelanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
and mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
. It can also contain, among others, tyrosinase
Tyrosinase is an oxidase that is the rate-limiting enzyme for controlling the production of melanin. The enzyme is mainly involved in two distinct reactions of melanin synthesis otherwise known as the Raper Mason pathway. Firstly, the hydroxy ...
, dopamine, and L-DOPA
-DOPA, also known as levodopa and -3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, is an amino acid that is made and used as part of the normal biology of some plants and animals, including humans. Humans, as well as a portion of the other animals that utilize -DOPA ...
, as well as small amounts of free amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha a ...
s, including taurine
Taurine (), or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is an organic compound that is widely distributed in animal tissues. It is a major constituent of bile and can be found in the large intestine, and accounts for up to 0.1% of total human body weight. I ...
, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group side ...
, and lysine.
Use by humans
 Cephalopod ink has, as its name suggests, been used in the past as
Cephalopod ink has, as its name suggests, been used in the past as ink
Ink is a gel, sol, or solution that contains at least one colorant, such as a dye or pigment, and is used to color a surface to produce an image, text, or design. Ink is used for drawing or writing with a pen, brush, reed pen, or quill. Thicker ...
for pens and quills; the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
name for cuttlefish, and the taxonomic name of a cuttlefish genus, ''Sepia
Sepia may refer to:
Biology
* ''Sepia'' (genus), a genus of cuttlefish
Color
* Sepia (color), a reddish-brown color
* Sepia tone, a photography technique
Music
* ''Sepia'', a 2001 album by Coco Mbassi
* ''Sepia'' (album) by Yu Takahashi
* " ...
'', is associated with the brown colour of cuttlefish ink (for more information, see sepia
Sepia may refer to:
Biology
* ''Sepia'' (genus), a genus of cuttlefish
Color
* Sepia (color), a reddish-brown color
* Sepia tone, a photography technique
Music
* ''Sepia'', a 2001 album by Coco Mbassi
* ''Sepia'' (album) by Yu Takahashi
* " ...
).
 Modern use of cephalopod ink is generally limited to cooking, primarily in Japan and the
Modern use of cephalopod ink is generally limited to cooking, primarily in Japan and the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
, where it is used as a food colouring
Food coloring, or color additive, is any dye, pigment, or substance that imparts color when it is added to food or drink. They come in many forms consisting of liquids, powders, gels, and pastes. Food coloring is used in both commercial food ...
and flavouring, for example in pasta
Pasta (, ; ) is a type of food typically made from an unleavened dough of wheat flour mixed with water or eggs, and formed into sheets or other shapes, then cooked by boiling or baking. Rice flour, or legumes such as beans or lentils, ar ...
and sauces
In cooking, a sauce is a liquid, cream, or semi-solid food, served on or used in preparing other foods. Most sauces are not normally consumed by themselves; they add flavor, moisture, and visual appeal to a dish. ''Sauce'' is a French wor ...
, and '' calamares en su tinta''. For this purpose it is generally obtainable from fishmonger
A fishmonger (historically fishwife for female practitioners) is someone who sells raw fish and seafood. Fishmongers can be wholesalers or retailers and are trained at selecting and purchasing, handling, gutting, boning, filleting, displaying, m ...
s, gourmet food suppliers, and is widely available in markets in Japan and Spain. The ink is extracted from the ink sacs during preparation of the dead cephalopod, usually cuttlefish, and therefore contains no mucus. While it is not commonly used in China, cephalopod ink is sometimes used to dye the dough of dumplings.
Studies have shown that cephalopod ink is toxic to some cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
s, including tumor cells
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
. It is being researched in mice for its antitumor activity against Meth-A fibrosarcoma. It currently remains unclear however if any of the antitumor activity of squid ink can be obtained from oral consumption, and this is indicated as an area for future investigation.
References
External links
An article on harvesting squid ink
{{Cephalopod anatomy Antipredator adaptations
Ink
Ink is a gel, sol, or solution that contains at least one colorant, such as a dye or pigment, and is used to color a surface to produce an image, text, or design. Ink is used for drawing or writing with a pen, brush, reed pen, or quill. Thicker ...
Mollusc products
Inks