Ov1-1 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Orbiting Vehicle 1-1 (COSPAR ID: 1965-F01, also known as OV1-1), was the first satellite in the OV1 series of the United States Air Force's
 The Orbiting Vehicle satellite program arose from a US Air Force initiative, begun in the early 1960s, to reduce the expense of space research. Through this initiative, satellites would be standardized to improve reliability and cost-efficiency, and where possible, they would fly on test vehicles or be piggybacked with other satellites. In 1961, the Air Force Office of Aerospace Research (OAR) created the Aerospace Research Support Program (ARSP) to request satellite research proposals and choose mission experiments. The USAF Space and Missiles Organization created their own analog of the ARSP called the Space Experiments Support Program (SESP), which sponsored a greater proportion of technological experiments than the ARSP. Five distinct OV series of standardized satellites were developed under the auspices of these agencies.
The OV1 series was an evolution of the 2.7 m "Scientific Passenger Pods" (SPP), which, starting on 2 October 1961, rode piggyback on suborbital Atlas missile tests and conducted scientific experiments during their short time in space. General Dynamics received a $2 million contract on 13 September 1963 to build a new version of the SPP (called the Atlas Retained Structure (ARS)) that would carry a self-orbiting satellite. Once the Atlas missile and ARS reached apogee, the satellite inside would be deployed and thrust itself into orbit. In addition to the orbital SPP, General Dynamics would create six of these satellites, each to be long with a diameter of , able to carry a payload into a circular orbit.
Dubbed "Satellite for Aerospace Research" (SATAR), the series of satellites was originally to be launched from the
The Orbiting Vehicle satellite program arose from a US Air Force initiative, begun in the early 1960s, to reduce the expense of space research. Through this initiative, satellites would be standardized to improve reliability and cost-efficiency, and where possible, they would fly on test vehicles or be piggybacked with other satellites. In 1961, the Air Force Office of Aerospace Research (OAR) created the Aerospace Research Support Program (ARSP) to request satellite research proposals and choose mission experiments. The USAF Space and Missiles Organization created their own analog of the ARSP called the Space Experiments Support Program (SESP), which sponsored a greater proportion of technological experiments than the ARSP. Five distinct OV series of standardized satellites were developed under the auspices of these agencies.
The OV1 series was an evolution of the 2.7 m "Scientific Passenger Pods" (SPP), which, starting on 2 October 1961, rode piggyback on suborbital Atlas missile tests and conducted scientific experiments during their short time in space. General Dynamics received a $2 million contract on 13 September 1963 to build a new version of the SPP (called the Atlas Retained Structure (ARS)) that would carry a self-orbiting satellite. Once the Atlas missile and ARS reached apogee, the satellite inside would be deployed and thrust itself into orbit. In addition to the orbital SPP, General Dynamics would create six of these satellites, each to be long with a diameter of , able to carry a payload into a circular orbit.
Dubbed "Satellite for Aerospace Research" (SATAR), the series of satellites was originally to be launched from the 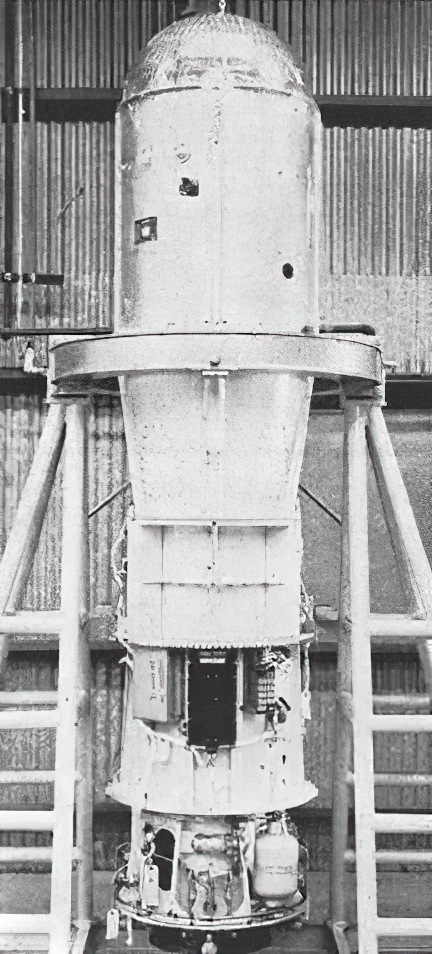
Orbiting Vehicle
Orbiting Vehicle or OV, originally designated SATAR (SATellite - Atmospheric Research), comprised five disparate series of standardized American satellites operated by the US Air Force, launched between 1965 and 1971. Forty seven satellite ...
program. OV1-1 was an American Earth science research satellite designed to measure radiation, micrometeoroid density, and magnetic fields in orbit. Launched 21 January 1965, the mission resulted in failure when, after a successful launch of its Atlas booster, OV1-1's onboard Altair motor failed to fire.
History
 The Orbiting Vehicle satellite program arose from a US Air Force initiative, begun in the early 1960s, to reduce the expense of space research. Through this initiative, satellites would be standardized to improve reliability and cost-efficiency, and where possible, they would fly on test vehicles or be piggybacked with other satellites. In 1961, the Air Force Office of Aerospace Research (OAR) created the Aerospace Research Support Program (ARSP) to request satellite research proposals and choose mission experiments. The USAF Space and Missiles Organization created their own analog of the ARSP called the Space Experiments Support Program (SESP), which sponsored a greater proportion of technological experiments than the ARSP. Five distinct OV series of standardized satellites were developed under the auspices of these agencies.
The OV1 series was an evolution of the 2.7 m "Scientific Passenger Pods" (SPP), which, starting on 2 October 1961, rode piggyback on suborbital Atlas missile tests and conducted scientific experiments during their short time in space. General Dynamics received a $2 million contract on 13 September 1963 to build a new version of the SPP (called the Atlas Retained Structure (ARS)) that would carry a self-orbiting satellite. Once the Atlas missile and ARS reached apogee, the satellite inside would be deployed and thrust itself into orbit. In addition to the orbital SPP, General Dynamics would create six of these satellites, each to be long with a diameter of , able to carry a payload into a circular orbit.
Dubbed "Satellite for Aerospace Research" (SATAR), the series of satellites was originally to be launched from the
The Orbiting Vehicle satellite program arose from a US Air Force initiative, begun in the early 1960s, to reduce the expense of space research. Through this initiative, satellites would be standardized to improve reliability and cost-efficiency, and where possible, they would fly on test vehicles or be piggybacked with other satellites. In 1961, the Air Force Office of Aerospace Research (OAR) created the Aerospace Research Support Program (ARSP) to request satellite research proposals and choose mission experiments. The USAF Space and Missiles Organization created their own analog of the ARSP called the Space Experiments Support Program (SESP), which sponsored a greater proportion of technological experiments than the ARSP. Five distinct OV series of standardized satellites were developed under the auspices of these agencies.
The OV1 series was an evolution of the 2.7 m "Scientific Passenger Pods" (SPP), which, starting on 2 October 1961, rode piggyback on suborbital Atlas missile tests and conducted scientific experiments during their short time in space. General Dynamics received a $2 million contract on 13 September 1963 to build a new version of the SPP (called the Atlas Retained Structure (ARS)) that would carry a self-orbiting satellite. Once the Atlas missile and ARS reached apogee, the satellite inside would be deployed and thrust itself into orbit. In addition to the orbital SPP, General Dynamics would create six of these satellites, each to be long with a diameter of , able to carry a payload into a circular orbit.
Dubbed "Satellite for Aerospace Research" (SATAR), the series of satellites was originally to be launched from the Eastern Test Range
The Eastern Range (ER) is an American rocket range ( Spaceport) that supports missile and rocket launches from the two major launch heads located at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station and the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida. The range h ...
on Atlas missions testing experimental Advanced Ballistic Re-Entry System (ABRES) nosecones. However, in 1964, the Air Force transferred ABRES launches to the Western Test Range
The Western Range (WR) is the space launch range that supports the major launch head at Vandenberg Space Force Base. Managed by the Space Launch Delta 30, the WR extends from the West Coast of the United States to 90° East longitude in the ...
causing a year's delay for the program. Moreover, because WTR launches would be into polar orbit as opposed to the low-inclination orbits typical of ETR launches, less mass could be lofted into orbit using the same thrust, and the mass of the SATAR satellites had to be reduced. The OV1 program was managed by Lt. Col. Clyde Northcott, Jr.

Spacecraft design
OV1-1, like the other satellites in the OV1 series, was long and in diameter, and consisted of a cylindrical experiment housing capped with flattened cones on both ends containing 5000 solar cells (2500 on each end) producing 22watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James ...
s of power. Two antennas for transmitting telemetry and receiving commands extended from the sides of the spacecraft. 12 helium-pressurized hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%â ...
thrusters provided attitude control. Spacecraft systems, including telemetry, command systems, and data recording and playback were located in the satellite's end-caps. An onboard timer would shut down the satellite after 180 days of operation.
OV1-1 weighed , with its Altair booster.
Though the OV1 series was designed to be nose-launched from its carrying rocket, on OV1-1, the ARS was side-mounted.
Experiments
of space in the cylindrical portion of the spacecraft was allocated to a seven experiment package designed to measure micrometeoroid density, cosmic radio noise, electron density variations, magnetic fields, proton concentrations, and Earth-based infrared and ultraviolet emissions.Mission
Launched from Vandenberg's 576-B-3 launch pad at 21 January 1965 21:34:54 UTC, OV1-1 (then called Aerospace Research Vehicle (ARV)) was the first satellite launched into a western-facing orbit. Five minutes after launch, the ARS was designed to open so that the OV satellite could propel itself out at Atlas apogee. While the Atlas D carrying OV1-1 flew without incident, OV1-1's Altair booster did not fire at apogee, and the spacecraft remained stranded in its ARS, returning no data.Legacy and status
The OV1 program ultimately comprised 22 missions, the last flying on 19 September 1971.References
{{Orbital launches in 1965 Spacecraft launched in 1965 Military satellites Geospace monitoring satellites