Nord-Noreg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Northern Norway ( nb, Nord-Norge, , nn, Nord-Noreg; se, Davvi-Norga) is a geographical
 Northern Norway covers about a third of Norway. The southernmost part, roughly the part south of the Arctic Circle, is called Helgeland. Here there is a multitude of islands and skerries on the outside of the coastal range, some flat, some with impressive shapes, like Mount Torghatten, which has a hole through it, and the Seven Sisters near Sandnessjøen. The inland is covered with dense spruce forests and mountains near the Swedish border; some of the biggest rivers in the region are the
Northern Norway covers about a third of Norway. The southernmost part, roughly the part south of the Arctic Circle, is called Helgeland. Here there is a multitude of islands and skerries on the outside of the coastal range, some flat, some with impressive shapes, like Mount Torghatten, which has a hole through it, and the Seven Sisters near Sandnessjøen. The inland is covered with dense spruce forests and mountains near the Swedish border; some of the biggest rivers in the region are the 

 Finnmark county has fjords and glaciers in the far southwest, and the northwestern coasts are characterized by big islands, like Sørøya and Seiland. The inland is covered by
Finnmark county has fjords and glaciers in the far southwest, and the northwestern coasts are characterized by big islands, like Sørøya and Seiland. The inland is covered by
 The oldest known historical culture in the region is called Komsa, named after a mountain in Alta. The first people possibly arrived 12,000–13,000 years ago, but it is uncertain whether they came from southern Norway or from the
The oldest known historical culture in the region is called Komsa, named after a mountain in Alta. The first people possibly arrived 12,000–13,000 years ago, but it is uncertain whether they came from southern Norway or from the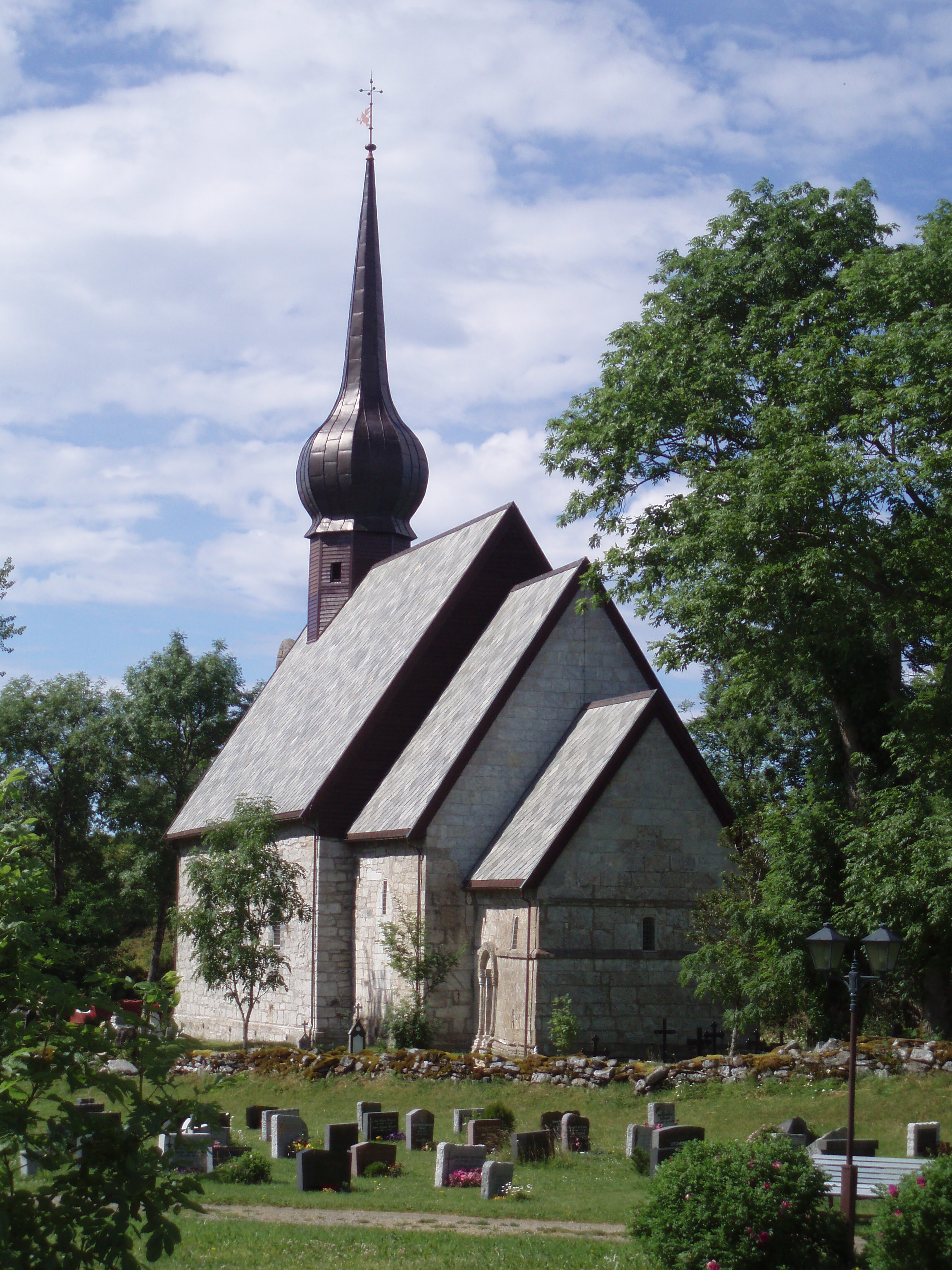  In the
In the  In the
In the  At the same time, the ethnic diversity of the area came under threat. Particularly after Norwegian independence (from the United Kingdoms of Sweden and Norway) in 1905, the Norwegian authorities were insistent that all should speak Norwegian only and schools became active tools of assimilation. The Sami language was banned in schools, churches and in public administration. Concerns about possible Finnish irredentism also led to increasing pressure on Kvens to assimilate. People who wanted to buy state-owned land in Finnmark had to prove they could speak Norwegian before they were allowed to settle.
This region of Norway was the area most affected by
At the same time, the ethnic diversity of the area came under threat. Particularly after Norwegian independence (from the United Kingdoms of Sweden and Norway) in 1905, the Norwegian authorities were insistent that all should speak Norwegian only and schools became active tools of assimilation. The Sami language was banned in schools, churches and in public administration. Concerns about possible Finnish irredentism also led to increasing pressure on Kvens to assimilate. People who wanted to buy state-owned land in Finnmark had to prove they could speak Norwegian before they were allowed to settle.
This region of Norway was the area most affected by  After World War II, Norway made a huge effort to rebuild the destroyed towns and villages. Modernizing fishing and agriculture was important, as Northern Norway was considerably poorer and less developed than the south. In 1946, the huge steel works of
After World War II, Norway made a huge effort to rebuild the destroyed towns and villages. Modernizing fishing and agriculture was important, as Northern Norway was considerably poorer and less developed than the south. In 1946, the huge steel works of 

 The Northern Norwegian dialects share a common, musical intonation, different from the southern dialects of Norway. Apart from this, there is great variation in sound system, grammar and vocabulary. In general, one can say that the southernmost of the northern dialects, particularly in Helgeland and Salten, are the most distinct. Notably they cut grammar endings (like French relative to Italian). In areas of Finnmark, the dialects are somewhat more in line with standard written Norwegian (
The Northern Norwegian dialects share a common, musical intonation, different from the southern dialects of Norway. Apart from this, there is great variation in sound system, grammar and vocabulary. In general, one can say that the southernmost of the northern dialects, particularly in Helgeland and Salten, are the most distinct. Notably they cut grammar endings (like French relative to Italian). In areas of Finnmark, the dialects are somewhat more in line with standard written Norwegian (


 Northern Norway is surrounded by some of the richest seas in the world, and seafood is the main source for traditional cuisine. However, agricultural produce has existed for at least 3,000 years in parts of the area ( Helgeland,
Northern Norway is surrounded by some of the richest seas in the world, and seafood is the main source for traditional cuisine. However, agricultural produce has existed for at least 3,000 years in parts of the area ( Helgeland,  Foods with dairy as an important ingredient include waffles, pancakes and rømmegrøt (sour-cream porridge), the latter always served with sugar and cinnamon. None of the aforementioned are distinctly Northern Norwegian foods, however, but are popular throughout Norway. There are a number of local traditions in this long region, including goat cheese from
Foods with dairy as an important ingredient include waffles, pancakes and rømmegrøt (sour-cream porridge), the latter always served with sugar and cinnamon. None of the aforementioned are distinctly Northern Norwegian foods, however, but are popular throughout Norway. There are a number of local traditions in this long region, including goat cheese from  Wild berries have long traditions in the local cuisine, and the most sought after is the cloudberry, used in marmalade, desserts and cakes. Other popular wild berries are
Wild berries have long traditions in the local cuisine, and the most sought after is the cloudberry, used in marmalade, desserts and cakes. Other popular wild berries are
 There are large climatic differences from southwest to northeast in this region.
There are large climatic differences from southwest to northeast in this region.
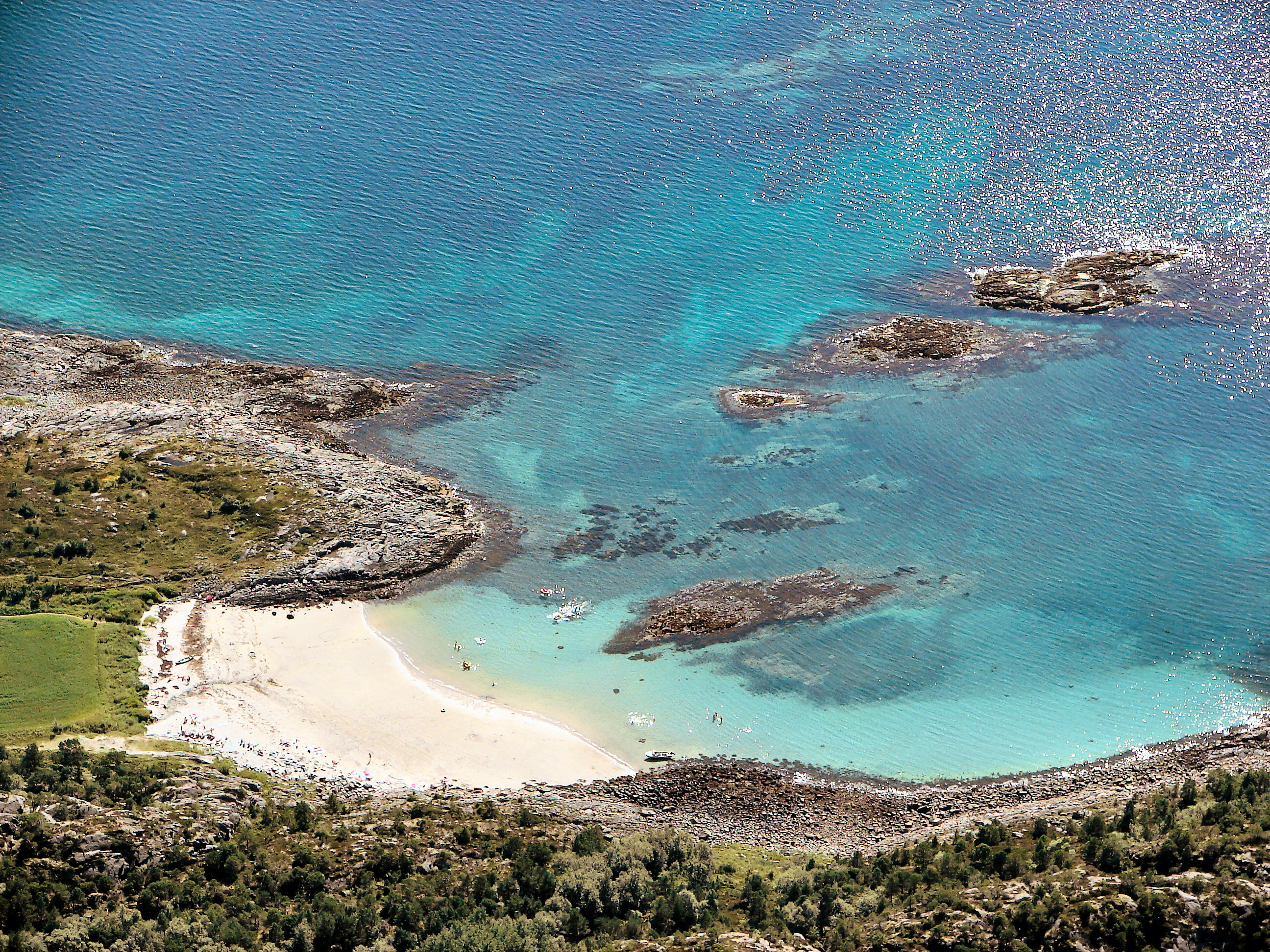 The coast of Helgeland in southern Nordland and some islands further north to Skrova in Lofoten have a temperate oceanic climate ( Cfb) with monthly mean temperatures above in winter, and four months with mean at or above . This includes the towns
The coast of Helgeland in southern Nordland and some islands further north to Skrova in Lofoten have a temperate oceanic climate ( Cfb) with monthly mean temperatures above in winter, and four months with mean at or above . This includes the towns
MADRID/RETIRO, SPAIN Weather History and Climate Data
. The warm climate in coastal areas, relative to other locations at the same latitude, is by many attributed to the relatively warm
Fruholmen fyr
in Måsøy not far from the North Cape. The most windy city in Northern Norway is Bodø with on average 153 days/year with strong breeze or more and 24 days with gale-force winds, while Vardø, also lacking shelter, sees 136 days of strong breeze or more and 18 days with gale. Inland valleys and sheltered fjord areas—particularly if sheltered by mountains—are much less windy. Tromsø, partly sheltered by large islands, experiences on average 27 days/year with strong breeze, and 1 day with gale, and
 Along the coast of Nordland north to southern Vesterålen, average winter temperatures hover just above freezing, getting gradually colder winters into the fjords, and the coldest are inland. Inland Finnmark, as in Karasjok, average temperatures remain below freezing for 7 months (October–April). In Tromsø, average temperatures stays below freezing for 4–5 months.
Along the coast of Nordland north to southern Vesterålen, average winter temperatures hover just above freezing, getting gradually colder winters into the fjords, and the coldest are inland. Inland Finnmark, as in Karasjok, average temperatures remain below freezing for 7 months (October–April). In Tromsø, average temperatures stays below freezing for 4–5 months.
 Precipitation occur in all seasons, usually as snow in winter, although often as rain on the Nordland coast. Snow accumulation in the mountains can exceed , and this abundance of snow is the reason for the numerous glaciers – more than 500, mostly in Nordland and Troms.
Autumn, and some places along the coast winter, tend to be the wettest season, often receiving more than twice as much precipitation as does spring and early summer. Only the interior areas of Finnmark tend to be wettest in summer. The areas with the least precipitation are some inland valleys, like Dividalen in
Precipitation occur in all seasons, usually as snow in winter, although often as rain on the Nordland coast. Snow accumulation in the mountains can exceed , and this abundance of snow is the reason for the numerous glaciers – more than 500, mostly in Nordland and Troms.
Autumn, and some places along the coast winter, tend to be the wettest season, often receiving more than twice as much precipitation as does spring and early summer. Only the interior areas of Finnmark tend to be wettest in summer. The areas with the least precipitation are some inland valleys, like Dividalen in
Lakselv in Porsanger at 70 degrees north latitude has a continental boreal climate with cold winters and sparse precipitation.

 Ranked by population in the town itself (not the municipality) as of 1. January 2008:
*
Ranked by population in the town itself (not the municipality) as of 1. January 2008:
*

 Northern Norway, located at the very northern periphery of Europe, has seen great improvements in transportation infrastructure in recent decades. The road network connects virtually all villages and towns, the most important roads are the E6, E10, E8. Seven road sections in the region are National Tourist Routes in Norway due to their scenic surroundings, from Helgeland in the south to the
Northern Norway, located at the very northern periphery of Europe, has seen great improvements in transportation infrastructure in recent decades. The road network connects virtually all villages and towns, the most important roads are the E6, E10, E8. Seven road sections in the region are National Tourist Routes in Norway due to their scenic surroundings, from Helgeland in the south to the
 * Harald "Dutte" Berg (1941–), football player.
*
* Harald "Dutte" Berg (1941–), football player.
*
NACC MA: North Norway
NorwayOnline: North Norway
Spildra – a small isolated Island in the middle of Northern Norway, known for its 8,000 years of continuous settlement
Image:Ice fishing on a fjord (Ramfjord)
Northern Norway's official tourism board
{{coord, 69, 40, N, 19, 0, E, source:ptwiki, display=title Regions of Norway
region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics ( physical geography), human impact characteristics ( human geography), and the interaction of humanity an ...
of Norway, consisting of the two northernmost counties Nordland and Troms og Finnmark, in total about 35% of the Norwegian mainland. Some of the largest towns in Northern Norway (from south to north) are Mo i Rana
Mo i Rana () is a city, and the administrative centre of the municipality of Rana, in Nordland county, Norway. It is located in the Helgeland region of Nordland, just south of the Arctic Circle. Some of the city's suburbs include Båsmoen and Yt ...
, Bodø, Narvik, Harstad
( se, Hárstták) is the second-most populated municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. It is mostly located on the large island of Hinnøya. The municipal center is the town of Harstad, the most populous town in Central Hålogalan ...
, Tromsø
Tromsø (, , ; se, Romsa ; fkv, Tromssa; sv, Tromsö) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the city of Tromsø.
Tromsø lies in Northern Norway. The municipality is the ...
and Alta. Northern Norway is often described as the land of the midnight sun
The midnight sun is a natural phenomenon that occurs in the summer months in places north of the Arctic Circle or south of the Antarctic Circle, when the Sun remains visible at the local midnight. When the midnight sun is seen in the Arctic, ...
and the land of the northern lights. Further north, halfway to the North Pole, is the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard, traditionally not regarded as part of Northern Norway.
The region is multi-cultural, housing not just Norwegians
Norwegians ( no, nordmenn) are a North Germanic ethnic group and nation native to Norway, where they form the vast majority of the population. They share a common culture and speak the Norwegian language. Norwegians are descended from the N ...
but also the indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
Sami people, Norwegian Finns
Finns or Finnish people ( fi, suomalaiset, ) are a Baltic Finnic ethnic group native to Finland.
Finns are traditionally divided into smaller regional groups that span several countries adjacent to Finland, both those who are native to these ...
(known as Kvens, distinct from the "Forest Finns
Forest Finns ( fi, Metsäsuomalaiset, Norwegian bokmål: ''Skogfinner'', Norwegian nynorsk: ''Skogfinnar'', sv, Skogsfinnar) were Finnish migrants from Savonia and Northern Tavastia in Finland who settled in forest areas of Sweden proper and N ...
" of Southern Norway) and Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
populations (mostly in Kirkenes). The Norwegian language
Norwegian ( no, norsk, links=no ) is a North Germanic language spoken mainly in Norway, where it is an official language. Along with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a dialect continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regio ...
dominates in most of the area; Sami speakers are mainly found inland and in some of the fjord areas of Nordland, Troms and particularly Finnmark – though ethnic Sámi who do not speak the language are found more or less everywhere in the region. Finnish is spoken in only a few communities in the east of Finnmark.
Geography
 Northern Norway covers about a third of Norway. The southernmost part, roughly the part south of the Arctic Circle, is called Helgeland. Here there is a multitude of islands and skerries on the outside of the coastal range, some flat, some with impressive shapes, like Mount Torghatten, which has a hole through it, and the Seven Sisters near Sandnessjøen. The inland is covered with dense spruce forests and mountains near the Swedish border; some of the biggest rivers in the region are the
Northern Norway covers about a third of Norway. The southernmost part, roughly the part south of the Arctic Circle, is called Helgeland. Here there is a multitude of islands and skerries on the outside of the coastal range, some flat, some with impressive shapes, like Mount Torghatten, which has a hole through it, and the Seven Sisters near Sandnessjøen. The inland is covered with dense spruce forests and mountains near the Swedish border; some of the biggest rivers in the region are the Vefsna
, also known as or , is the largest river in Nordland county, Norway. It is long and drains a watershed of . Its headwaters lie in the mountains of Børgefjell National Park at the lake Simskardvatnet. The river runs through the municipaliti ...
and the Ranelva
Ranelva is a long river in the municipality of Rana in Nordland county, Norway. It is one of the longest rivers in Nordland county. The catchment area of the river is . Before the power stations of ''Reinforsen'' (1925) and Langvatnet (1964) we ...
. The highest mountain in Northern Norway is found here in the Okstindan range south of Mo i Rana
Mo i Rana () is a city, and the administrative centre of the municipality of Rana, in Nordland county, Norway. It is located in the Helgeland region of Nordland, just south of the Arctic Circle. Some of the city's suburbs include Båsmoen and Yt ...
with Oksskolten reaching above sea level, and with the glacier Okstindbreen.
The Saltfjellet
Saltfjellet is a mountain area in Nordland county, Norway that separates the two regions of Helgeland and Salten. It is also a cultural border between the Southern and Central parts of Sápmi.
Geography and environment
The Saltfjell is one of the ...
range, with its Svartisen
Svartisen is a collective term for two glaciers located in Nordland county in northern Norway. It is part of Saltfjellet-Svartisen National Park, located in the Saltfjell mountain range. The glaciers are located in the municipalities of Beiarn, ...
glacier and intersecting Arctic Circle, divides Helgeland from the next region, called Salten
Salten is a traditional district in Nordland county, Norway. It includes the municipalities of Meløy, Gildeskål, Bodø, Beiarn, Saltdal, Fauske, Sørfold, Steigen, and Hamarøy. Salten covers an area of about and has a population (2016) ...
. Notable peaks in Salten are the Børvasstindan south of Bodø, Suliskongen near Fauske (, highest mountain north of the Arctic Circle), the Steigartindan and the phallic Hamarøytinden. Between Saltfjellet and eastern Finnmark, Norway spruce trees have originally been planted and are mostly privately owned. The older plantations are now producing lumber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, wi ...
, 80 years after planted.
Lofoten
Lofoten () is an archipelago and a traditional district in the county of Nordland, Norway. Lofoten has distinctive scenery with dramatic mountains and peaks, open sea and sheltered bays, beaches and untouched lands. There are two towns, Svolv� ...
is a chain of peaks that jut out of the ocean. From the mainland side it looks very barren, but behind the violet-black peaks there are also flatlands with good grazing for sheep, partially on soil made from seaweed. The Vesterålen islands consist of smaller and bigger islands with a huge variation in landscape. Ofoten, further inland, is a fjord landscape with high mountains, the highest is Storsteinfjellet in Narvik, 1,894 m above sea level, but the most well-known is Stetind, the national mountain of Norway. There are also glaciers, like Frostisen
or is a glacier in Narvik Municipality in Nordland county, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northern ...
and Blåisen.

Troms
Troms (; se, Romsa; fkv, Tromssa; fi, Tromssa) is a former county in northern Norway. On 1 January 2020 it was merged with the neighboring Finnmark county to create the new Troms og Finnmark county. This merger is expected to be reversed by t ...
county has surprising greenery for the latitude, and the inner waterways and fjords are lined with birch forests, and further inland there are extensive pine forests and highlands around the rivers Målselva
The Målselva is a river in Målselv Municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The long river flows through the Målselvdalen valley and then empties into the Målselvfjorden, an arm of the Malangen fjord. The municipality and the val ...
and Reisaelva. Big islands like Senja, Kvaløya and Ringvassøya have green, forested interiors and a barren, mountainous coastline, with smaller islands offshore. The Lyngen Alps
The Lyngen Alps ( no, Lyngsalpene) are a mountain range in northeastern Troms og Finnmark county in Norway, east of the city of Tromsø. The mountain range runs through the municipalities of Lyngen, Balsfjord, and Storfjord. The mountains follow ...
are the highest mountains of the area, rising to , an area of glaciers and waterfalls. The Mollisfossen waterfall in Nordreisa is the highest waterfall in the north, while Målselvfossen is Norway's national waterfall.
 Finnmark county has fjords and glaciers in the far southwest, and the northwestern coasts are characterized by big islands, like Sørøya and Seiland. The inland is covered by
Finnmark county has fjords and glaciers in the far southwest, and the northwestern coasts are characterized by big islands, like Sørøya and Seiland. The inland is covered by Finnmarksvidda
Finnmarksvidda ( sme, Finnmárkkoduottar; en, Finnmark plateau/highland) is Norway's largest plateau, with an area greater than . The plateau lies about above sea level. Approximately 36% of Finnmark lies on the Finnmarksvidda.
Geography
Fr ...
, a relatively barren plateau about high, with many lakes and rivers like Alta-Kautokeino and Tana/Deatnu. Even at this latitude, pine forests grow naturally in lowland areas inland. East of Honningsvåg
, other_name =
, native_name =
, nickname =
, settlement_type = Town
, image_skyline = Honningsvåg-01.jpg
, image_caption = View of the city
, pushpin_map = Finnmark#Nor ...
, there are no islands protecting the barren coasts that rise directly up from the sea. The landscape towards the Russian border is comparatively flat. Knivskjellodden on the island of Magerøya marks the northern end of Europe; tourism is directed to the much more accessible (and dramatic) North Cape, whereas Kinnarodden on the Nordkinn Peninsula is the northernmost point of Europe's mainland. Finnmark is situated north of northernmost Finland, and to the east Norway has a border with Russia.
History
 The oldest known historical culture in the region is called Komsa, named after a mountain in Alta. The first people possibly arrived 12,000–13,000 years ago, but it is uncertain whether they came from southern Norway or from the
The oldest known historical culture in the region is called Komsa, named after a mountain in Alta. The first people possibly arrived 12,000–13,000 years ago, but it is uncertain whether they came from southern Norway or from the Kola Peninsula
sjd, Куэлнэгк нёа̄ррк
, image_name= Kola peninsula.png
, image_caption= Kola Peninsula as a part of Murmansk Oblast
, image_size= 300px
, image_alt=
, map_image= Murmansk in Russia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Murmansk Oblas ...
. Today the rock carvings at Hjemmeluft in Alta or at Leknes in Nordland are among the remainders of the Stone Age cultures, showing reindeer swimming across the fjords. A significant find area is between the river Tana Tana may refer to:
Places
Africa
* Lake Tana, a lake in Ethiopia (and a source of the Nile River)
* Tana Qirqos, an island in the eastern part of Lake Tana in Ethiopia, near the mouth of the Gumara River
* Tana River County, a county of Coast P ...
and the fjord of Varanger, where the reindeer probably ran over the isthmus on the way between the winter and summer grazing. The question of the ethnic identity of the Stone Age cultures is politically charged, as many Sami feel the uncertainty surrounding the earliest settlers in Northern Norway is being used to question their status as an indigenous people. Metals were introduced around 500 BC.
The Sami culture can be traced back at least 2,000 years. There is also some archeological evidence of Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
agricultural settlements about 2,500 years old, as in Steigen
Steigen ('stejgen) is a municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the traditional district of Salten. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Leinesfjord. Other villages include Bogen, Leines, Nordfold, N ...
and Sømna
Sømna is a municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the Helgeland traditional region. The administrative center of Sømna is the village of Vik i Helgeland. Other villages in the municipality include Dalbotn, Sund, Vennesund, and ...
. In 2009, archeologist discovered evidence of barley grown in Kvæfjord near Harstad in the Bronze Age 1000 BC. A larger settlement by people of Germanic origin, with substantial archeological evidence, seem to have occurred 200–300 AD. These settled along the coasts roughly up to Tromsø. The two ethnic groups traded with each other, and there seems to have been quite a lot of intermarriage. The nature of the co-existence is hotly debated.
Viking Age
The Viking Age () was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonizing, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. It followed the Migration Period and the Germ ...
, several chieftains along the coast played a significant role in Norwegian history, usually resisting unification of Norway. The voyage and story of Ottar from Hålogaland was recorded by King Alfred the Great in Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons
, common_name = Wessex
, image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg
, map_caption = S ...
. Hårek from Tjøtta and Tore Hund
Modern and imaginary presentation of Tore Hund
Thorir Hund (Old Norse: Þórir hundr, Modern Norwegian: ''Tore Hund'', literally "''Thorir the Hound''") (born ca. 990) was one of the greatest chiefs in Hålogaland. Tore Hund was one of the le ...
, who killed Saint Olav
Olaf II Haraldsson ( – 29 July 1030), later known as Saint Olaf (and traditionally as St. Olave), was King of Norway from 1015 to 1028. Son of Harald Grenske, a petty king in Vestfold, Norway, he was posthumously given the title '' Rex Per ...
at the Battle of Stiklestad
The Battle of Stiklestad ( no, Slaget på Stiklestad, non, Stiklarstaðir) in 1030 is one of the most famous battles in the history of Norway. In this battle, King Olaf II of Norway () was killed. During the pontificate of Pope Alexander III, ...
in 1030 were important leaders according to Heimskringla
''Heimskringla'' () is the best known of the Old Norse kings' sagas. It was written in Old Norse in Iceland by the poet and historian Snorre Sturlason (1178/79–1241) 1230. The name ''Heimskringla'' was first used in the 17th century, derive ...
. The chieftain and poet Øyvind Skaldespiller was the first to receive international acclaim, as his poems were rewarded when the Icelandic parliament organized a money collection to buy him a thick ring of gold. This flourishing period of resistance was followed by consolidation and centralization of the Norwegian state, which was (and is) dominated by southerners (in the relative sense of south of Northern Norway), reducing the power and wealth of the Northern Norwegian chieftains.
 In the
In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, churches and fortifications were built along the coast in an effort to stake a more firm claim for the kingdom of Norway along what was then the frontier of Norwegian settlement. By 1150, Lenvik Church was the northernmost church in Norway. In 1252 the first church, the Ecclesia Sanctae Mariae de Trums juxta paganos ("The Church of Saint Mary in Troms near the Heathens"), was built in Tromsø, along with a small rampart intended to serve as protection against Karelian raids. This was followed in 1307 by the consecration of Vardø Church in what is now eastern Finnmark. Finally, Vardøhus Fortress was constructed to mark and defend the border with the Karelian tributary lands of the Novgorod Republic
The Novgorod Republic was a medieval state that existed from the 12th to 15th centuries, stretching from the Gulf of Finland in the west to the northern Ural Mountains in the east, including the city of Novgorod and the Lake Ladoga regions of mod ...
. The traditional view has been that the fortress and church were constructed at roughly the same time, although recent research indicates that the fortress may have been constructed as late as the 1330s, after the border between Norway and Novgorod had become more fixed. At roughly the same time, the cod fishing gained momentum. Dried cod was exported through Bergen
Bergen (), historically Bjørgvin, is a city and municipality in Vestland county on the west coast of Norway. , its population is roughly 285,900. Bergen is the second-largest city in Norway. The municipality covers and is on the peninsula o ...
to the whole Hanseatic world, bringing prosperity to the north. This is reflected in the numerous pieces of imported church art from the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Renai ...
. There were numerous wars with the Novgorod Republic
The Novgorod Republic was a medieval state that existed from the 12th to 15th centuries, stretching from the Gulf of Finland in the west to the northern Ural Mountains in the east, including the city of Novgorod and the Lake Ladoga regions of mod ...
in Russia at the time, that stopped by the late 15th century.
Reduced fish prices in the 17th century and the exploitative trade practices of merchants from Bergen, who had been granted a royal monopoly on fish trading, led to a significant decline in the population and grinding poverty for those who remained. Large coastal areas were depopulated, and Sami culture made a comeback, as it was less dependent on fish exports. After 1700, Russian Pomors
Pomors or Pomory ( rus, помо́ры, p=pɐˈmorɨ, ''seasiders'') are an ethnographic group descended from Russian settlers, primarily from Veliky Novgorod, living on the White Sea coasts and the territory whose southern border lies on a ...
started to come every summer on trading expeditions, bringing rye in exchange for fish. Although this was in violation of Bergen's trade monopoly and the Danish–Norwegian monarchy made some attempts to curtail the Pomor trade, the trade was vital to the survival of many Northern Norwegian fishing communities. In the 1740s the first settlers started arriving in Northern Norway from Finland. The traditional view is that these were refugees escaping famine and warfare at home, although modern scholars have pointed out that many were simply looking for their own piece of land, which was getting scarce in Finland as a result of rapid population growth. In 1789, the trade monopoly of the city of Bergen
Bergen (), historically Bjørgvin, is a city and municipality in Vestland county on the west coast of Norway. , its population is roughly 285,900. Bergen is the second-largest city in Norway. The municipality covers and is on the peninsula o ...
was lifted, Hammerfest and Vardø were issued their city charters, and Tromsø followed suit in 1794. Interrupted by the British blockade of the Napoleonic wars, this introduced a period of unprecedented growth in the north as the trade monopoly had previously made cities nonviable in Northern Norway. Bodø was founded in 1816, and Vadsø
Vadsø (; sme, Čáhcesuolu; fkv, Vesisaari) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark County, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Vadsø, which was the administrative centre of the former Finnmark county. O ...
in 1833. The Hurtigruten
''Hurtigruten'' (), formally Kystruten Bergen-Kirkenes ("coastal route Bergen-Kirkenes"), is a Norwegian public coastal route transporting passengers that travel locally, regionally and between the ports of call, and also cargo between ports no ...
shipping line, introduced in 1893, gave quicker communications with the south. In 1906, the iron mines in Kirkenes opened.
 At the same time, the ethnic diversity of the area came under threat. Particularly after Norwegian independence (from the United Kingdoms of Sweden and Norway) in 1905, the Norwegian authorities were insistent that all should speak Norwegian only and schools became active tools of assimilation. The Sami language was banned in schools, churches and in public administration. Concerns about possible Finnish irredentism also led to increasing pressure on Kvens to assimilate. People who wanted to buy state-owned land in Finnmark had to prove they could speak Norwegian before they were allowed to settle.
This region of Norway was the area most affected by
At the same time, the ethnic diversity of the area came under threat. Particularly after Norwegian independence (from the United Kingdoms of Sweden and Norway) in 1905, the Norwegian authorities were insistent that all should speak Norwegian only and schools became active tools of assimilation. The Sami language was banned in schools, churches and in public administration. Concerns about possible Finnish irredentism also led to increasing pressure on Kvens to assimilate. People who wanted to buy state-owned land in Finnmark had to prove they could speak Norwegian before they were allowed to settle.
This region of Norway was the area most affected by World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. In 1940, the Norwegians and Allied forces fought the German Army to a standstill over the strategic port for iron exports of Narvik, until allied forces and equipment were withdrawn, leaving the remaining Norwegians with no option but surrender. King Haakon VII
Haakon VII (; born Prince Carl of Denmark; 3 August 187221 September 1957) was the King of Norway from November 1905 until his death in September 1957.
Originally a Danish prince, he was born in Copenhagen as the son of the future Frederick VI ...
and the government fled towards the north, and stayed in the Tromsø area for three weeks. On 27 May, Bodø was bombed by the Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...
, and on 7 June, the Allies retreated from the North, and the King and government fled to Britain from Tromsø. During the war, the area was used by the Kriegsmarine to stage U-boat attacks on Allied Arctic supply convoys resupplying the Eastern Front.
In 1944, the German Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
started to retreat from the Murmansk
Murmansk (Russian: ''Мурманск'' lit. "Norwegian coast"; Finnish: ''Murmansk'', sometimes ''Muurmanski'', previously ''Muurmanni''; Norwegian: ''Norskekysten;'' Northern Sámi: ''Murmánska;'' Kildin Sámi: ''Мурман ланнҍ'') ...
front. They burned everything after them in the area between the Russian border and the Lyngen fjord, as part of their tactics
Tactic(s) or Tactical may refer to:
* Tactic (method), a conceptual action implemented as one or more specific tasks
** Military tactics, the disposition and maneuver of units on a particular sea or battlefield
** Chess tactics
** Political tact ...
. The population was forcibly evacuated, although a third of them chose to hide in the wilderness instead. All who were found were shot.
 After World War II, Norway made a huge effort to rebuild the destroyed towns and villages. Modernizing fishing and agriculture was important, as Northern Norway was considerably poorer and less developed than the south. In 1946, the huge steel works of
After World War II, Norway made a huge effort to rebuild the destroyed towns and villages. Modernizing fishing and agriculture was important, as Northern Norway was considerably poorer and less developed than the south. In 1946, the huge steel works of Mo i Rana
Mo i Rana () is a city, and the administrative centre of the municipality of Rana, in Nordland county, Norway. It is located in the Helgeland region of Nordland, just south of the Arctic Circle. Some of the city's suburbs include Båsmoen and Yt ...
were founded, heralding industrialization of the north.
Transportation was also improved, as airports were built throughout the area, notably in Bodø in 1952 and Tromsø in 1964. The rail network was extended to reach Bodø in 1961. In 1972, the University of Tromsø opened, accompanied by a number of university colleges, notably in Bodø, Alta, Harstad and Narvik. In 1972 and 1994, the strong anti-EU movements of the north, largely based on concerns over EU mismanagement of its own fish stocks, were instrumental when Norway voted against EU membership in referendums.

Sami language
Acronyms
* SAMI, ''Synchronized Accessible Media Interchange'', a closed-captioning format developed by Microsoft
* Saudi Arabian Military Industries, a government-owned defence company
* South African Malaria Initiative, a virtual expertise ...
instruction was introduced in schools in the 1970s. In 1979, the building of a hydro-electric dam in Alta caused huge demonstrations, giving the Sami question national attention for virtually the first time. The result was a significant effort by the authorities to promote Sami language
Acronyms
* SAMI, ''Synchronized Accessible Media Interchange'', a closed-captioning format developed by Microsoft
* Saudi Arabian Military Industries, a government-owned defence company
* South African Malaria Initiative, a virtual expertise ...
and culture. In 1989, the Norwegian Sami parliament, Samediggi, opened, and the Law of Finnmark of 2005 was an attempt to deal with the question of land rights. A similar law is on the way for Nordland and Troms.
Working against all this, emigration to the south has been strong after World War II. While there is a slight overall population growth in Northern Norway (as a result of surplus childbirths and immigration from abroad), this is significantly lower than in southern counties, although the regional centres of Bodø, Tromsø and Alta continue to grow at a relatively brisk pace. Lately, the off-shore gas field of Snøhvit, off Hammerfest, has brought hopes of new development in the north.
Languages

Bokmål
Bokmål () (, ; ) is an official written standard for the Norwegian language, alongside Nynorsk. Bokmål is the preferred written standard of Norwegian for 85% to 90% of the population in Norway. Unlike, for instance, the Italian language, there ...
, Nynorsk), particularly in those areas where Norwegian was primarily introduced by the school system as part of the assimilation process during the 20th century. In some inland valleys in the county of Troms, settlers from the inland of Southern Norway immigrated 200 years ago. Even today, these dialects have southern characteristics in intonation and vocabulary.
Earlier, northern dialects had a low status in Norway, but recently they have been used extensively in song lyrics, poetry, in TV and radio. Today, anyone can use their dialects. This is not to suggest that no prejudices remain, however.
Sami
Acronyms
* SAMI, ''Synchronized Accessible Media Interchange'', a closed-captioning format developed by Microsoft
* Saudi Arabian Military Industries, a government-owned defence company
* South African Malaria Initiative, a virtual expertise ...
is spoken in three main dialects (or languages, depending on the definition): Southern Sami south of the Arctic Circle, Lule Sami Lule may refer to:
* Lule people, an indigenous people of northern Argentina
* Lule language, a possibly extinct language of Argentina
* Lule Sami language, a language spoken in Sweden and Norway
* Luleå, also known as Lule, a town in Sweden
* ...
mainly between Bodø and Narvik, and Northern Sami
Northern may refer to the following:
Geography
* North, a point in direction
* Northern Europe, the northern part or region of Europe
* Northern Highland, a region of Wisconsin, United States
* Northern Province, Sri Lanka
* Northern Range, a ...
in the rest. Originally, Pite Sami and Ume Sami were spoken around Bodø, but these dialects are now extinct on the Norwegian side of the border. Eastern Sami was originally spoken in Neiden, close to Kirkenes, but it is more or less extinct. Overall, Northern Sami is by far the healthiest of the Sami languages today, primarily because it still has a relatively large number of first language speakers and maintains its dominance in core areas in Finnmark. Northern Sami is an official language (in addition to Norwegian) in the municipalities of Gáivuotna ( Kåfjord), Kautokeino, Karasjok
( se, Kárášjohka ; fkv, Kaarasjoki) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Karasjok. Other villages include Dorvonjárga, Šuoššjávri, and Váljohka.
Th ...
, Porsanger, Tana Tana may refer to:
Places
Africa
* Lake Tana, a lake in Ethiopia (and a source of the Nile River)
* Tana Qirqos, an island in the eastern part of Lake Tana in Ethiopia, near the mouth of the Gumara River
* Tana River County, a county of Coast P ...
and Nesseby
or (also unofficially ''Uuniemi'' in Kven) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Varangerbotn. Other villages in Nesseby include Gandvik, Karlebotn, Nesseby ...
.
The Finnish
Finnish may refer to:
* Something or someone from, or related to Finland
* Culture of Finland
* Finnish people or Finns, the primary ethnic group in Finland
* Finnish language, the national language of the Finnish people
* Finnish cuisine
See also ...
spoken in western regions, from Storfjord to Porsanger, is quite distinct, although comprehensible for people from Finland. Further east, around Vadsø and Kirkenes, the spoken Finnish resembles standard Finnish. People of Finnish descent in these eastern areas are also typically more likely to consider themselves as " Finnish Norwegians" rather than Kvens, arguing that the term Kven represents an attempt to cut them off from their Finnish roots. Finnish is official in addition to Sami and Norwegian in Porsanger municipality. Very few first language Finnish speakers remain in Northern Norway, and unlike Northern Sami, the Finnish language lacks a core region where it is still dominant in daily life.
Coastal and fjord areas of Northern Norway have much in common with Western Norway
Western Norway ( nb, Vestlandet, Vest-Norge; nn, Vest-Noreg) is the region along the Atlantic coast of southern Norway. It consists of the counties Rogaland, Vestland, and Møre og Romsdal. The region has no official or political-administrativ ...
, sometimes imagined in cultural terms as a shared "coastal identity". The topography and fjord landscape, the rich fisheries, the culture and even some aspects of the dialects (''Vestnorsk'') have clear similarities.
During the 18th and 19th centuries a Russian-Norwegian pidgin known as Russenorsk
Russenorsk (; russian: Руссено́рск, ; en, Russo-Norwegian) is an extinct dual-source "restricted pidgin" language formerly used in the Arctic, which combined elements of Russian and Norwegian. Russenorsk originated from Russian tr ...
developed for the communication of Russian traders and Norwegian fishermen in the Pomor trade.
Cuisine


Salten
Salten is a traditional district in Nordland county, Norway. It includes the municipalities of Meløy, Gildeskål, Bodø, Beiarn, Saltdal, Fauske, Sørfold, Steigen, and Hamarøy. Salten covers an area of about and has a population (2016) ...
, Lofoten, Harstad- Kvæfjord). In addition to fishing, each family traditionally had a small farm with a few cows (see Pietro Querinis shipwrecked at Røst in 1432), sheep or goats (goats being preferred in many places due to their superior adaptation to the rough and mountainous terrain found in much of Northern Norway) and had small grain fields (mostly barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley p ...
). After the introduction (and somewhat later acceptance) of potatoes from the Americas, these became a main staple in much of Northern Norway, as well as many other parts of Norway. Agriculture gradually becomes less important as a food source as one moves further north, and in the northern half (north of Balsfjord/Tromsø area) was usually of minor importance and certainly less important than fishing or Sami reindeer nomadic pastoralism
Nomadic pastoralism is a form of pastoralism in which livestock are herded in order to seek for fresh pastures on which to graze. True nomads follow an irregular pattern of movement, in contrast with transhumance, where seasonal pastures are fix ...
. Hunting has been important ever since the Stone Age, and the comparatively large areas of sparsely settled valleys, fells and mountains still hold wildlife.
In the winter, the codfish comes to the coastal waters to spawn, especially to the cod fisheries of Lofoten. Mølja, boiled codfish with liver and roe
Roe ( ) or hard roe is the fully ripe internal egg masses in the ovaries, or the released external egg masses, of fish and certain marine animals such as shrimp, scallop, sea urchins and squid. As a seafood, roe is used both as a cooked in ...
, is a delicacy that today is served in the best restaurants. In the summer, the coalfish, or saithe
The saithe ( or ) (''Pollachius virens'') is a species of marine fish in the Pollock genus '' Pollachius''. Together with '' P. pollachius'', it is generally referred to in the United States as pollock. Other names include the Boston blue (separ ...
, bites, and fresh saithe is often served on the beach, boiled in seawater over an open fire, or fried (typically the smaller coalfish). Halibut
Halibut is the common name for three flatfish in the genera '' Hippoglossus'' and '' Reinhardtius'' from the family of right-eye flounders and, in some regions, and less commonly, other species of large flatfish.
The word is derived from ''h ...
is traditional Christmas food. Most fish is served plainly poached, only accompanied by boiled potatoes, carrots and possibly fried bacon. A more particular kind of fish is "gammelsei", saithe
The saithe ( or ) (''Pollachius virens'') is a species of marine fish in the Pollock genus '' Pollachius''. Together with '' P. pollachius'', it is generally referred to in the United States as pollock. Other names include the Boston blue (separ ...
that has been conserved for a year or more. Other traditions are lutefisk
''Lutefisk'' ( Norwegian, in Northern and parts of Central Norway, in Southern Norway; sv, lutfisk ; fi, lipeäkala ; literally " lye fish") is dried whitefish (normally cod, but ling and burbot are also used). It is made from aged sto ...
and boknafisk, the latter made from stockfish, and in Nordland often from herring. Seawolf and rose fish
''Sebastes norvegicus'', the rose fish, ocean perch, Atlantic redfish, Norway haddock, golden redfish or pinkbelly rosefish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, the rockfishes, part of the family Scorpa ...
are regarded as good food, the latter often eaten salted and poached, with the brain (''krus'') highly regarded, sometimes fried with onions. In addition to cod, herring and potatoes were traditional staple foods (except in the most northern area). Salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family Salmonidae, which are native to tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus ''Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus '' Oncorhy ...
has long traditions as food along the rivers, and also trout
Trout are species of freshwater fish belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', '' Salmo'' and '' Salvelinus'', all of the subfamily Salmoninae of the family Salmonidae. The word ''trout'' is also used as part of the name of some non-salm ...
which are common also in the numerous lakes. In the latest decades consumption has increased in correspondence with increased salmon fish farming
upright=1.3, Salmon farming in the sea (mariculture) at Loch Ainort, Isle of Skye">mariculture.html" ;"title="Salmon farming in the sea (mariculture">Salmon farming in the sea (mariculture) at Loch Ainort, Isle of Skye, Scotland
Fish farming or ...
; smoked salmon
Smoked salmon is a preparation of salmon, typically a fillet that has been cured and hot or cold smoked.
Due to its moderately high price, smoked salmon is considered a delicacy. Although the term lox is sometimes applied to smoked salmon, t ...
is very popular, often on open sandwich
An open sandwich, also known as an open-face/open-faced sandwich, bread baser, bread platter or tartine, consists of a slice of bread or toast with one or more food items on top.
History
During the start of the middle ages, thin slabs of coa ...
es, alone or together with boiled or scrambled eggs
Scrambled eggs is a dish made from eggs (usually chicken eggs) stirred, whipped or beaten together while being gently heated, typically with salt, butter, oil and sometimes other ingredients.
Preparation
Only eggs are necessary to make scramble ...
or salad
A salad is a dish consisting of mixed, mostly natural ingredients with at least one raw ingredient. They are typically served at room temperature or chilled, though some can be served warm. Condiments and salad dressings, which exist in a va ...
.
Traditionally, northerners regarded shellfish and prawn
Prawn is a common name for small aquatic crustaceans with an exoskeleton and ten legs (which is a member of the order decapoda), some of which can be eaten.
The term "prawn"Mortenson, Philip B (2010''This is not a weasel: a close look at nature' ...
s as bait, but lately they have developed a taste for it, and the freshest and most succulent prawns and shellfish are easily obtainable all along the coast. Shark meat
Shark meat is a seafood consisting of the flesh of sharks. Several sharks are fished for human consumption, such as porbeagles, shortfin mako shark, requiem shark, and thresher shark, among others. Shark meat is popular in Asia, where it is ...
has traditionally not been used as food, even if some can grow nearly long. In later years, the large Red king crab
The red king crab (''Paralithodes camtschaticus''), also called Kamchatka crab or Alaskan king crab, is a species of king crab native to the Bering Sea and Gulf of Alaska. It was introduced to the Barents Sea. It grows to a leg span of , and is ...
has invaded Norwegian waters from the east and, having reached west to Hammerfest, are now served in the finest restaurants. The large sea bird colonies along the coast provided eggs for the local population, yet most of these are now protected by law. However, in Tromsø, sea gull eggs and beer from the local brewery is still a highly regarded dish to enjoy in the sun of late spring.
Tender whale meat is usually served as steaks, whereas seals are an acquired taste, due to the smell. However, when processed into "Barents ham", it gets more palatable. Fresh seal meat is served at the end of the hunting season in spring, and Tromsø is the place to look for it. Reindeer
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 sub ...
are often served as finnebiff, thin slices in a cream sauce. Reindeer filets have become more popular in high-end restaurants in recent years, but the price can be prohibitive as the reindeer industry is shielded from market forces by the Norwegian government (in essence, it is treated as a vital component of Sami culture, rather than a competitive industry, which means there is little pressure to actually sell the meat products). Lamb meat
Lamb, hogget, and mutton, generically sheep meat, are the meat of domestic sheep, ''Ovis aries''. A sheep in its first year is a lamb and its meat is also lamb. The meat from sheep in their second year is hogget. Older sheep meat is mutton. Gen ...
from sheep following the retreating snow line up the hills and mountains to get the most nutritious fresh vegetation throughout summer is highly regarded by the locals, and research seem to indicate that a varied diet does influence the taste of the meat. Game meat includes mountain hare, rock ptarmigan
The rock ptarmigan (''Lagopus muta'') is a medium-sized game bird in the grouse family. It is known simply as the ptarmigan in the UK. It is the official bird for the Canadian territory of Nunavut, where it is known as the ''aqiggiq'' (ᐊᕿ� ...
, willow grouse and moose
The moose (in North America) or elk (in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is a member of the New World deer subfamily and is the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is the largest and heaviest extant species in the deer family. Most adult ma ...
.
Balsfjord
Balsfjord ( sme, Báhccavuotna ; fkv, Paatsivuono) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Storsteinnes. Other villages include Mestervik, Mortenhals, and Nordkj ...
, ''Blanklefse'' and other variations of ''lefse
Lefse () is a traditional soft Norwegian flatbread. It is made with flour, can include riced potatoes, and includes butter, and milk, cream, or lard. It is cooked on a large, flat griddle. Special tools are used to prepare lefse, including a p ...
'' from Helgeland, and a number of variations of reindeer, an integral part of traditional Sami
Acronyms
* SAMI, ''Synchronized Accessible Media Interchange'', a closed-captioning format developed by Microsoft
* Saudi Arabian Military Industries, a government-owned defence company
* South African Malaria Initiative, a virtual expertise ...
culture.
bilberries
Bilberries (), or sometimes European blueberries, are a primarily Eurasian species of low-growing shrubs in the genus '' Vaccinium'' (family Ericaceae), bearing edible, dark blue berries. The species most often referred to is ''Vaccinium myrti ...
, lingonberry
''Vaccinium vitis-idaea'', the lingonberry, partridgeberry, mountain cranberry or cowberry, is a small evergreen shrub in the heath family Ericaceae, that bears edible fruit. It is native to boreal forest and Arctic tundra throughout the Norther ...
, raspberry (southern half of region, also cultivated in some private gardens), and there are also a number of less well known berries used for food. Mushroom
A mushroom or toadstool is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground, on soil, or on its food source. ''Toadstool'' generally denotes one poisonous to humans.
The standard for the name "mushroom" is ...
s are common in the forests from late July to September and also has seen some use in traditional food.
The use of kitchen gardens is limited by climatic factors, but still has a long history in the southern half of the region. Rhubarb and redcurrant has been used for more than 100 years; redcurrant also grows naturally in much of the region, blackcurrant is also common in gardens. In addition to potatoes and carrots, rutabaga
Rutabaga (; North American English) or swede (British English and some Commonwealth English) is a root vegetable, a form of ''Brassica napus'' (which also includes rapeseed). Other names include Swedish turnip, neep (Scots), and turnip (Scott ...
and sometimes cabbage have traditionally been grown (very little in Finnmark). Many wild plants were used for medical purposes or as spices, such as Garden Angelica
''Angelica archangelica'', commonly known as garden angelica, wild celery, and Norwegian angelica, is a biennial plant from the family Apiaceae, a subspecies of which is cultivated for its sweetly scented edible stems and roots. Like several oth ...
, but this has become rare in modern times. More lately is the imported strawberry which has become popular and are grown locally (mostly southern half of region). The unique growing conditions, with ripening in 24-hr daylight and modest warmth is sometimes claimed to enhance flavor.
Bioforsk, with research in terrestrial effects of climate and subarctic agriculture, has branches in four places in Northern Norway – Tromsø, Bodø, Tjøtta and Svanhovd in Sør-Varanger
Sør-Varanger ( sme, Máttá-Várjjat, fkv, Etelä-Varenki, fi, Etelä-Varanki, russian: Сёр-Вара́нгер/Syor-Varánger) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town ...
.
Climate
 There are large climatic differences from southwest to northeast in this region.
There are large climatic differences from southwest to northeast in this region. Finnmarksvidda
Finnmarksvidda ( sme, Finnmárkkoduottar; en, Finnmark plateau/highland) is Norway's largest plateau, with an area greater than . The plateau lies about above sea level. Approximately 36% of Finnmark lies on the Finnmarksvidda.
Geography
Fr ...
in the interior of Finnmark and some valleys in the interior of Troms, experience a more continental climate with much less precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
and much colder winters compared to the long coastal region.
Light
There are extreme variations in daylight between winter and summer. AtNordkapp
), North Cape, Norway, other uses, North Cape (disambiguation)
Nordkapp ( en, North Cape; sme, Davvinjárga or ; fkv, Kappa or ) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the tow ...
the midnight sun can be seen from 11 May to 31 July, and the sun does not rise above the horizon from 19 November to 22 January. For Tromsø, the dates are 17 May to 25 July, and 26 November to 15 January, respectively; and for Bodø from 30 May to 12 July (no polar night in Bodø). The mid-winter darkness is not totally dark on the mainland; there is twilight for about three hours around noon in Tromsø. Helgeland does not have true midnight sun, but the upper part of the sun disc never descends below the horizon as far south as Mosjøen in June. February is a transitional period when the sun rapidly returns, and March and April often feel like an explosion of light with long daylight hours and snow cover in most areas except the coastal strip of Nordland. The Aurora Borealis
An aurora (plural: auroras or aurorae), also commonly known as the polar lights, is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly seen in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). Auroras display dynamic patterns of bri ...
can be seen in the whole area from autumn to mid-April, after which it gets too bright to observe the Aurora. It is a natural phenomenon arising due to the collision between electrically charged particles from the sun that enter the atmosphere of the earth, and paint the sky all colors from the color palette.
Temperate oceanic climate to continental boreal climate
 The coast of Helgeland in southern Nordland and some islands further north to Skrova in Lofoten have a temperate oceanic climate ( Cfb) with monthly mean temperatures above in winter, and four months with mean at or above . This includes the towns
The coast of Helgeland in southern Nordland and some islands further north to Skrova in Lofoten have a temperate oceanic climate ( Cfb) with monthly mean temperatures above in winter, and four months with mean at or above . This includes the towns Brønnøysund
Brønnøysund () is a town and the administrative centre of Brønnøy Municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is also a former municipality within Nordland county. The village of Brønnøysund originally was declared a ladested in 1923 wh ...
and Sandnessjøen. In the same coastal area, but slightly into the fjords north to include Bodø, is a narrow area where winters are a little colder but summers still lasts four month, making this a humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
(Dfb).
A long area along the coast from Myken island in the south north along the outer coast north to Hasvik
Hasvik ( sme, Ákŋoluovtta gielda; fkv, Hasviikan komuuni) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Breivikbotn. Other villages in the municipality include Breivi ...
is the subpolar oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ...
(Cfc) with still not very cold winters (coldest month above ). This includes much of Lofoten and Vesterålen, the western coast of Troms north to Fruholmen in Måsøy in Finnmark. Towns in this area includes Leknes, Sortland
or is a municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the traditional region of Vesterålen. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Sortland. Other population centres in Sortland include Bø, Holand, Holmstad, ...
, Harstad, the mildest parts of Tromsø close to the sea and Hasvik
Hasvik ( sme, Ákŋoluovtta gielda; fkv, Hasviikan komuuni) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Breivikbotn. Other villages in the municipality include Breivi ...
.
The largest part of North Norway are within the boreal climate (also known as subarctic), but with large variation of temperatures and precipitation from south to northeast. Most towns along the fjords falling into this climate zone in North Norway have winters milder and wetter than the typical boreal climate, and a complete lack of permafrost; this includes Mosjøen, Mo i Rana, Narvik, Tromsø and Hammerfest. Colder winters are found in Bardufoss, Alta, Kirkenes and Vadsø. The really cold areas are inland in Finnmark where Karasjok
( se, Kárášjohka ; fkv, Kaarasjoki) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Karasjok. Other villages include Dorvonjárga, Šuoššjávri, and Váljohka.
Th ...
and Kautokeino have mean annual below and patchy permafrost. However, the inland towns seldom see strong winds, and Karasjok only experiences on average 1 day/year with strong breeze (22 knots) or more.
A substantial area of the region, especially towards the border with Sweden and north to the Lyngen alps east of Tromsø, are mountains and highlands with alpine tundra climate above the treeline.
The mean annual temperature difference between Brønnøysund () and Kautokeino () is 8 °C (13 °F), about the same as the difference between Brønnøysund and Madrid, SpainMADRID/RETIRO, SPAIN Weather History and Climate Data
. The warm climate in coastal areas, relative to other locations at the same latitude, is by many attributed to the relatively warm
North Atlantic Current
The North Atlantic Current (NAC), also known as North Atlantic Drift and North Atlantic Sea Movement, is a powerful warm western boundary current within the Atlantic Ocean that extends the Gulf Stream northeastward.
The NAC originates from where ...
, an extension of the Gulf Stream.
Wind
Wind strength is strongest in winter and late autumn, when the Lows are strongest. Summers and early autumn are much less windy and will rarely see the wind strength that can be experienced in winter. Every winter sees windstorms disrupting communications (ferries, air traffic), especially along the outer seaboard. However, many winter days are completely calm. The most windy location in continental Norway (apart from mountain summits) is Fruholmen LighthouseFruholmen fyr
in Måsøy not far from the North Cape. The most windy city in Northern Norway is Bodø with on average 153 days/year with strong breeze or more and 24 days with gale-force winds, while Vardø, also lacking shelter, sees 136 days of strong breeze or more and 18 days with gale. Inland valleys and sheltered fjord areas—particularly if sheltered by mountains—are much less windy. Tromsø, partly sheltered by large islands, experiences on average 27 days/year with strong breeze, and 1 day with gale, and
Bardufoss
Bardufoss is a town and commercial centre in Målselv Municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The three villages of Andselv, Andslimoen, and Heggelia together form the Bardufoss area. Bardufoss is located in the Målselvdalen val ...
sees on average only 11 days with strong breeze or more and scarcely ever experiences gale. In winter, there might sometimes blow cold winds from the freezing highlands out through the large fjords, and strong breeze will feel very cold on the skin. Mild westerlies are still much more common in most winters. Weather patterns are inherently unpredictable in this northern region—both low pressure and high pressure weather can occur at any time of year, although the strongest winds occur in winter.
Winter
 Along the coast of Nordland north to southern Vesterålen, average winter temperatures hover just above freezing, getting gradually colder winters into the fjords, and the coldest are inland. Inland Finnmark, as in Karasjok, average temperatures remain below freezing for 7 months (October–April). In Tromsø, average temperatures stays below freezing for 4–5 months.
Along the coast of Nordland north to southern Vesterålen, average winter temperatures hover just above freezing, getting gradually colder winters into the fjords, and the coldest are inland. Inland Finnmark, as in Karasjok, average temperatures remain below freezing for 7 months (October–April). In Tromsø, average temperatures stays below freezing for 4–5 months.
Summer
Even if winter temperatures depends largely on the distance to the sea, the length of the season varies mostly with latitude (and altitude). While the southern coast of Nordland have four months of summer, the northeasternmost areas just averages two months, such as Kirkenes and Vadsø. The warmest summer daily highs are in the inland valleys and sheltered fjords, in towns like Mosjøen, Rognan, Narvik, Bardufoss, Alta and Karasjok. A small strip of land along the extreme northeastern coast fromNordkapp
), North Cape, Norway, other uses, North Cape (disambiguation)
Nordkapp ( en, North Cape; sme, Davvinjárga or ; fkv, Kappa or ) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the tow ...
to Vardø was earlier partly tundra (Arctic climate) due to lack of summer warmth, however with the updated climate normals 1991–2020, summers have warmed and the tundra climate has changed to a boreal climate along this northernmost coast, but still with very modest summer warmth.
Precipitation
Målselv
Målselv ( sme, Málatvuomi suohkan) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Moen. The main commercial centre of the municipality is the Bardufoss area (including And ...
with only precip/year, and upper Saltdal and Skibotn with about the same. Inland Finnmark is the only large area with less than precipitation/year. The wettest areas are generally the Helgeland region; Lurøy
Lurøy is a municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the Helgeland traditional region. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Lurøy, located on the island of Lurøya. Other villages in Lurøy include Aldra ...
on the west coast of Saltfjell averages /year.
Record temperatures
The coldest temperature recorded is in Karasjok on 1.January 1886, and the warmest recorded is at Mosjøen Airport on 27 July 2019. Many locations in North Norway have recorded what Norwegians know as "tropical nights" when the overnight low does not fall below . The warmest night ever recorded in Norway was 29 July 2019 at Sømna-Kvaløyfjellet (302 m) inSømna
Sømna is a municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the Helgeland traditional region. The administrative center of Sømna is the village of Vik i Helgeland. Other villages in the municipality include Dalbotn, Sund, Vennesund, and ...
near Brønnøysund with overnight low . The third warmest night recorded in Norway was at Makkaur in Båtsfjord
Båtsfjord ( sme, Báhcavuotna) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Båtsfjord (which is the only settlement remaining in the municipality). Båtsfjord Airport ...
with overnight low on 19 July 2018.
Brønnøysund at 65 degrees north latitude has a temperate oceanic climate and few extremes even with 150 years of recording.
Lakselv in Porsanger at 70 degrees north latitude has a continental boreal climate with cold winters and sparse precipitation.
Towns

 Ranked by population in the town itself (not the municipality) as of 1. January 2008:
*
Ranked by population in the town itself (not the municipality) as of 1. January 2008:
* Tromsø
Tromsø (, , ; se, Romsa ; fkv, Tromssa; sv, Tromsö) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the city of Tromsø.
Tromsø lies in Northern Norway. The municipality is the ...
* Bodø
Towns with fewer than 30,000 inhabitants, ranked by population:
* Harstad
( se, Hárstták) is the second-most populated municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. It is mostly located on the large island of Hinnøya. The municipal center is the town of Harstad, the most populous town in Central Hålogalan ...
* Mo i Rana
Mo i Rana () is a city, and the administrative centre of the municipality of Rana, in Nordland county, Norway. It is located in the Helgeland region of Nordland, just south of the Arctic Circle. Some of the city's suburbs include Båsmoen and Yt ...
* Narvik
* Alta
* Mosjøen
Mosjøen (; sma, Mussere) is a town in Vefsn Municipality in Nordland county, Norway. Mosjøen is the oldest town in the Helgeland region, with only the town of Bodø being older within Nordland county. The town is also the administrative centre ...
* Hammerfest
* Fauske
* Sandnessjøen
* Vadsø
Vadsø (; sme, Čáhcesuolu; fkv, Vesisaari) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark County, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Vadsø, which was the administrative centre of the former Finnmark county. O ...
Towns with fewer than 5,000 inhabitants, ranked by population:
* Sortland
or is a municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the traditional region of Vesterålen. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Sortland. Other population centres in Sortland include Bø, Holand, Holmstad, ...
* Brønnøysund
Brønnøysund () is a town and the administrative centre of Brønnøy Municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is also a former municipality within Nordland county. The village of Brønnøysund originally was declared a ladested in 1923 wh ...
* Svolvær
Svolvær () is the administrative centre of Vågan Municipality in Nordland County, Norway. It is located on the island of Austvågøya in the Lofoten archipelago, along the Vestfjorden. The town has a population (2018) of 4,720 which gives t ...
* Finnsnes
Finnsnes () is a small town that is the administrative centre of Senja Municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The town is located on the mainland part of Norway, just across the Gisundet strait from the island of Senja. The Gisund ...
* Kirkenes
* Stokmarknes
is a town and the administrative centre of Hadsel Municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is located on the northern coast of the island of Hadseløya and on the small, neighboring island of Børøya. In 2000, Stokmarknes received "town stat ...
* Honningsvåg
, other_name =
, native_name =
, nickname =
, settlement_type = Town
, image_skyline = Honningsvåg-01.jpg
, image_caption = View of the city
, pushpin_map = Finnmark#Nor ...
* Leknes
* Vardø
There are settlements larger than Vardø which are not included in the list as they have not been granted or applied for township (such as Rognan, Løding
Løding is a village in the municipality of Bodø in Nordland county, Norway. It is located about east of the town of Bodø, and is connected to the town by the Tverlandet Bridge. The village is mostly referred to as ''Tverlandet'', which als ...
, Andenes
is the administrative centre of Andøy Municipality which is located in the Vesterålen district of Nordland county, Norway. The village of Andenes is the northernmost settlement of the island of Andøya (and in Nordland county). To the east ...
, Setermoen
Setermoen is the administrative centre of Bardu Municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The village is located along the Barduelva river, about east of the village of Sjøvegan and about south of Bardufoss.
The local council procl ...
and Skjervøy).
Transportation

 Northern Norway, located at the very northern periphery of Europe, has seen great improvements in transportation infrastructure in recent decades. The road network connects virtually all villages and towns, the most important roads are the E6, E10, E8. Seven road sections in the region are National Tourist Routes in Norway due to their scenic surroundings, from Helgeland in the south to the
Northern Norway, located at the very northern periphery of Europe, has seen great improvements in transportation infrastructure in recent decades. The road network connects virtually all villages and towns, the most important roads are the E6, E10, E8. Seven road sections in the region are National Tourist Routes in Norway due to their scenic surroundings, from Helgeland in the south to the Varanger Peninsula
The Varanger Peninsula ( no, Varangerhalvøya; sme, Várnjárga; fkv, Varenkinniemi) is a peninsula in Finnmark county, Norway. It is located in the northeasternmost part of Norway, along the Barents Sea. The peninsula has the Tanafjorden to ...
in the northeast, including two sections of the Norwegian County Road 17
County Road 17 ( no, Fylkesvei 17), also known as the Coastal Highway ( no, Kystriksveien), is a Norwegian highway that runs from the town of Bodø in Nordland county (in the north) to the town of Steinkjer in Trøndelag county (in the south). I ...
. Airports with long runways and direct flights to Oslo airport are located in Tromsø
Tromsø (, , ; se, Romsa ; fkv, Tromssa; sv, Tromsö) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the city of Tromsø.
Tromsø lies in Northern Norway. The municipality is the ...
, Bodø, Evenes
Evenes ( sme, Evenášši) is a municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the traditional district of Ofoten. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Bogen. Other villages in Evenes include Liland, Tårst ...
(near Harstad), Alta, Kirkenes and Bardufoss
Bardufoss is a town and commercial centre in Målselv Municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The three villages of Andselv, Andslimoen, and Heggelia together form the Bardufoss area. Bardufoss is located in the Målselvdalen val ...
, and there are also directs flights connecting Brønnøysund
Brønnøysund () is a town and the administrative centre of Brønnøy Municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is also a former municipality within Nordland county. The village of Brønnøysund originally was declared a ladested in 1923 wh ...
and Sandnessjøen with Oslo. There are smaller airports with regional flights near most towns. For Bodø, Fauske, Mo i Rana and Mosjøen the Nordland Line
The Nordland Line ( no, Nordlandsbanen, ) is a railway line between Trondheim and Bodø, Norway. It is the longest in Norway and lacks electrification. The route runs through the counties of Trøndelag (formerly Sør-Trøndelag and Nord-Trøndel ...
provides railway connection south to Trondheim (and on to Oslo), while Narvik has railway connection east to Sweden (and on to Stockholm). The Hurtigruten
''Hurtigruten'' (), formally Kystruten Bergen-Kirkenes ("coastal route Bergen-Kirkenes"), is a Norwegian public coastal route transporting passengers that travel locally, regionally and between the ports of call, and also cargo between ports no ...
calls at many ports in the region. Goods that are needed in northern Norway are generally freighted by train to Bodø or Narvik, and there reloaded to trucks. The freight trains from Oslo to Narvik has the majority of the amount. Export of fish and other products use the same trains in the reverse direction.
Sport
The Northern Norwegian Cup was a football tournament played from 1929 to 1969. TheEliteserien
Eliteserien () is a Norwegian professional league for association football clubs. At the top of the Norwegian football league system, it is the country's primary football competition. Contested by 16 clubs, it operates on a system of promotio ...
, Norway's primary men's football league, will feature two Northern team in the upcoming 2019 season, FK Bodø/Glimt and Tromsø IL
Tromsø Idrettslag is a Norwegian professional football club founded in 1920, based in the city of Tromsø. They play their home games at Alfheim Stadion. Tromsø play in the Eliteserien.
Tromsø have won the Norwegian Cup twice, in 1986 and 19 ...
. In women's football, IK Grand Bodø and Medkila IL (from Harstad) will play in the 1. divisjon, the second tier of Norwegian football.
In ice hockey, the Narvik IK
Narvik Arctic Eagles is an ice hockey team in Narvik, Norway. They currently play in the 1.division, the 2. level of Norwegian ice hockey.
History
The club was founded in 1962. In the 2011–12 season, they participated in the Swedish Division ...
plays in the second-tier Norwegian First Division
The Norwegian First Division, also called 1. divisjon and OBOS-ligaen (named sponsor is property developer OBOS), is the second-highest level of the Norwegian football league system. Each year, the top finishing teams in the 1. divisjon are ...
. In basketball, the BLNO has featured the Tromsø Storm and Harstad Vikings.
The Arctic Race of Norway is a cycling road race of the UCI Europe Tour
The UCI Continental Circuits are a series of road bicycle racing competitions which were introduced in 2005 by the Union Cycliste Internationale (UCI) to expand cycling around the world. The five circuits (representing the continents of Africa, the ...
held since 2013.
The Tromsø Midnight Sun Marathon is a marathon race held under midnight sun.
Notable people
 * Harald "Dutte" Berg (1941–), football player.
*
* Harald "Dutte" Berg (1941–), football player.
* Mari Boine
Mari Boine (born Mari Brit Randi Boine, 8 November 1956) is a Norwegian Sámi singer. She combined traditional Sámi joik singing with rock. In 2008, she became a professor of musicology at Nesna University College.
Biography
Mari Boine was b ...
(1956–), jazz artist, from Karasjok
* Petter Dass (1647–1707), the foremost Norwegian baroque poet, from Alstahaug
* Ailo Gaup (1980–), FMX World Champion
A world championship is generally an international competition open to elite competitors from around the world, representing their nations, and winning such an event will be considered the highest or near highest achievement in the sport, game, ...
, from Tromsø
* Mads Gilbert
Mads Fredrik Gilbert (born 2 June 1947) is a Norwegian physician, humanitarian, activist, and politician for the Red Party. He is a specialist in anesthesiology and head of the emergency medicine department at the University Hospital of North ...
, professor of emergency medicine, from Tromsø.
* Knut Hamsun
Knut Hamsun (4 August 1859 – 19 February 1952) was a Norwegian writer who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1920. Hamsun's work spans more than 70 years and shows variation with regard to consciousness, subject, Point of view ...
(1859–1952), author and Nobel laureate, from Hamarøy
* Helmer Hanssen (1870–1956), with Amundsen's team to the South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole, Terrestrial South Pole or 90th Parallel South, is one of the two points where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on Earth and lies antipod ...
in 1911, from Bjørnskinn
Bjørnskinn is a village in Andøy Municipality in Nordland county, Norway. The village of Bjørnskinn lies along the southern part of the island of Andøya, about northwest of the larger village of Risøyhamn. The village is the site of Bjø ...
* Geir Lundestad (1945–), director of the Nobel Institute and professor of history, from Bodø
* Lene Marlin (1980–), singer and songwriter, from Tromsø
* Morten Gamst Pedersen
Morten Gamst Pedersen (born 8 September 1981) is a Norwegian professional footballer who last played as a midfielder for Åsane.
Pedersen began his career with Tromsø, then played for English side Blackburn Rovers between 2004 and 2013. He the ...
(1981–), football player, from Vadsø
Vadsø (; sme, Čáhcesuolu; fkv, Vesisaari) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark County, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Vadsø, which was the administrative centre of the former Finnmark county. O ...
.
* The Röyksopp
Röyksopp (), a Norwegian electronic music duo from Tromsø formed in 1998. The duo consists of Svein Berge and Torbjørn Brundtland.
Berge and Brundtland were introduced to each other through a mutual friend in Tromsø, Norway. They enjoy ...
band duo Torbjørn Brundtland (1975–) and Svein Berge Svein is a Norwegian masculine given name which may refer to:
Rulers
* Sweyn Haakonsson (died c. 1016), in Norwegian Svein Håkonsson, an earl and co-ruler of Norway from 1000 to c. 1015
* Svein Knutsson (c. 1016–1035), King of Norway as Sweyn I ...
, from Tromsø
Tromsø (, , ; se, Romsa ; fkv, Tromssa; sv, Tromsö) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the city of Tromsø.
Tromsø lies in Northern Norway. The municipality is the ...
* Trond Sollied
Trond Johan Sollied (born 29 April 1959) is a Norwegian football manager and former player. He last managed Lokeren.
During his playing career, Sollied was a defender who won the Norwegian top flight five times. He also played for Norway's nat ...
(1959–), Football manager. Ranked as the ninth best manager in 2006.
* Iselin Steiro (1985–), supermodel, from Harstad
* Otto Sverdrup
Otto Neumann Knoph Sverdrup (31 October 1854, in Bindal, Helgeland – 26 November 1930) was a Norwegian sailor and Arctic explorer.
Early and personal life
He was born in Bindal as a son of farmer Ulrik Frederik Suhm Sverdrup (1833–1914) ...
, Arctic explorer, from Bindal
* Hans Erik Dyvik Husby (" Hank Von Helvete") (1972–), Vocalist in the death-punk band Turbonegro.
See also
* Arctic policy of NorwayReferences
External links
*NACC MA: North Norway
NorwayOnline: North Norway
Spildra – a small isolated Island in the middle of Northern Norway, known for its 8,000 years of continuous settlement
Image:Ice fishing on a fjord (Ramfjord)
Northern Norway's official tourism board
{{coord, 69, 40, N, 19, 0, E, source:ptwiki, display=title Regions of Norway