Ninth Air Force (2009-2020) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Ninth Air Force (Air Forces Central) is a Numbered Air Force of the
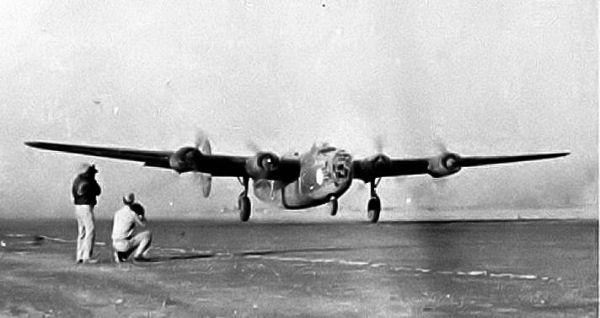 On 28 June 1942, Major General Lewis H. Brereton arrived at Cairo to command the U.S. Army Middle East Air Force (USAMEAF), which was activated immediately. USAMEAF comprised the
On 28 June 1942, Major General Lewis H. Brereton arrived at Cairo to command the U.S. Army Middle East Air Force (USAMEAF), which was activated immediately. USAMEAF comprised the



 On D-Day, IX Troop Carrier Command units flew over 2000 sorties conducting combat parachute jumps and glider landings as part of
On D-Day, IX Troop Carrier Command units flew over 2000 sorties conducting combat parachute jumps and glider landings as part of



 Following
Following

 * 380th Air Expeditionary Wing, Al Dhafra Air Base, United Arab Emirates, 25 January 2002 – present
: KC-10 Extender, RQ-4 Global Hawk, U-2 Dragon Lady
* 386th Air Expeditionary Wing, Ali Al Salem Air Base, Kuwait, 2002–present
: C-130 Hercules
Tenant Units assigned to the command are:
* 609th Air Operations Center, 609th Air and Space Operations Center, Al Udeid Air Base, Qatar, 1 January 1994 – present
* 1st Expeditionary Civil Engineer Group, Al Udeid Air Base, Qatar, October 2001 – present
** 557 Expeditionary Rapid Engineer Deployable Heavy Operational Repair Squadron Engineers, RED HORSE Squadron
** 577 Expeditionary PRIME BEEF Squadron
Note: The 432d Air Expeditionary Wing is an Air Combat Command unit headquartered at Creech AFB, Nevada. It operates RQ-1 Predator and MQ-9 Reaper UAV aircraft in the AFCENT AOR.
* 380th Air Expeditionary Wing, Al Dhafra Air Base, United Arab Emirates, 25 January 2002 – present
: KC-10 Extender, RQ-4 Global Hawk, U-2 Dragon Lady
* 386th Air Expeditionary Wing, Ali Al Salem Air Base, Kuwait, 2002–present
: C-130 Hercules
Tenant Units assigned to the command are:
* 609th Air Operations Center, 609th Air and Space Operations Center, Al Udeid Air Base, Qatar, 1 January 1994 – present
* 1st Expeditionary Civil Engineer Group, Al Udeid Air Base, Qatar, October 2001 – present
** 557 Expeditionary Rapid Engineer Deployable Heavy Operational Repair Squadron Engineers, RED HORSE Squadron
** 577 Expeditionary PRIME BEEF Squadron
Note: The 432d Air Expeditionary Wing is an Air Combat Command unit headquartered at Creech AFB, Nevada. It operates RQ-1 Predator and MQ-9 Reaper UAV aircraft in the AFCENT AOR.
IX Engineer Command
1 July 1944 – 2 December 1945 *
Official public website
Most current Factsheet (Apr 2013)
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20060322220454/http://www.psln.com/pete/pow_bomb_groups.htm PSLN.com], World War II Bomb Groups - European Theater of Operations (ETO)
Air Power in the Battle of the Bulge: A Theater Campaign Perspective
(World War II unit history published by Stars & Stripes) {{Authority control Air Forces of the United States Army Air Forces, 09 Cold War military history of the United States Military units and formations established in 1941 Military units and formations in South Carolina European theatre of World War II
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Aerial warfare, air military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part ...
headquartered at Shaw Air Force Base
Shaw Air Force Base (Shaw AFB) is a United States Air Force (USAF) base located approximately west-northwest of downtown Sumter, South Carolina. It is one of the largest military bases operated by the United States, and is under the jurisdict ...
, South Carolina. It is the Air Force Service Component of United States Central Command
The United States Central Command (USCENTCOM or CENTCOM) is one of the eleven unified combatant commands of the U.S. Department of Defense. It was established in 1983, taking over the previous responsibilities of the Rapid Deployment Joint Ta ...
(USCENTCOM), a joint Department of Defense combatant command
A unified combatant command (CCMD), also referred to as a combatant command, is a joint military command of the United States Department of Defense that is composed of units from two or more service branches of the United States Armed Forces, ...
responsible for U.S. security interests in 27 nations that stretch from the Horn of Africa through the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bod ...
region, into Central Asia.
Activated as 9th Air Force on 8 April 1942, the command fought in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
both in the Western Desert Campaign in Egypt and Libya and as the tactical fighter component of the United States Strategic Air Forces in Europe, engaging enemy forces in France, the Low Countries and in Nazi Germany. During the Cold War, it was one of two Numbered Air Forces of Tactical Air Command.
Co-designated as United States Central Command Air Forces (CENTAF) on 1 January 1983, on 2009 as part of a complicated transfer of lineage, the lineage and history of the Ninth Air Force was bestowed on USAFCENT, and a new Ninth Air Force, which technically had no previous history, was activated. On 20 August 2020, the 9 AF designation was returned to USAFCENT with the deactivation of the 2009 established 9 AF. It has fought in the 1991 Gulf War
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Iraq were carried out in two key phases ...
, War in Afghanistan
War in Afghanistan, Afghan war, or Afghan civil war may refer to:
*Conquest of Afghanistan by Alexander the Great (330 BC – 327 BC)
* Muslim conquests of Afghanistan (637–709)
*Conquest of Afghanistan by the Mongol Empire (13th century), see al ...
(OEF-A, 2001–present), the Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, حرب العراق (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, شەڕی عێراق ( Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict and the War on terror
, image ...
(OIF, 2003–2010), as well as various engagements within USCENTCOM.
History
United States Air Forces Central is the direct descendant organization of Ninth Air Force, established in 1941. AFCENT was formed as the United States Central Command Air Forces (CENTAF) under Tactical Air Command (TAC). CENTAF initially consisted of designated United States Air Force elements of theRapid Deployment Joint Task Force
The Rapid Deployment Joint Task Force (RDJTF) is an inactive United States Department of Defense Joint Task Force. It was first envisioned as a three-division force in 1979 as the Rapid Deployment Force, or RDF, a highly mobile force that could ...
(RDJTF) which was inactivated and reformed as USCENTCOM in 1983.
On 1 March 2008 USCENTAF was redesignated USAFCENT. It shared its commander with Ninth Air Force until August 2009. Ninth Air Force was redesignated USAFCENT on 5 August 2009. A new Ninth Air Force was established that date for command and control of CONUS-based Air Combat Command units formerly assigned to the previous Ninth Air Force.
World War II
Establishment
In the summer of 1941General Headquarters Air Force
The United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) was the aerial warfare service component of the United States Army between 1926 and 1941. After World War I, as early aviation became an increasingly important part of modern warfare, a philosophical ri ...
(GHQ AF) decided to establish commands to direct its air support
In military tactics, close air support (CAS) is defined as air action such as air strikes by fixed or rotary-winged aircraft against hostile targets near friendly forces and require detailed integration of each air mission with fire and movemen ...
mission in each of its numbered air forces, plus one additional command that would report directly to GHQ AF. These commands were manned from inactivating wings
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is expre ...
, and would initially control only observation squadrons, which would be transferred from the control of the corps and divisions, although they would remain attached to these ground units.Futrell, p 13 GHQ AF organized 5th Air Support Command at Bowman Field, Kentucky in September 1941, drawing its personnel and equipment from the 16th Bombardment Wing, which was simultaneously inactivated.Maurer, ''Combat Units'', pp. 464-465 New observation groups were formed, with a cadre drawn from National Guard
National Guard is the name used by a wide variety of current and historical uniformed organizations in different countries. The original National Guard was formed during the French Revolution around a cadre of defectors from the French Guards.
Nat ...
squadrons that had been mobilized in 1940 and 1941. 5th Air Support Command was redesignated as 9th Air Force in April 1942. It moved to Bolling Field The origins of the surname Bolling:
English: from a nickname for someone with close-cropped hair or a large head, Middle English bolling "pollard", or for a heavy drinker, from Middle English bolling "excessive drinking".
German (Bölling): from ...
, DC on 22 July and transferred without personnel or equipment to Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the Capital city, capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of ...
, Egypt on 12 November 1942.
Operations in Western Desert Campaign, 1942–1943
In June 1942, the GermanAfrika Korps
The Afrika Korps or German Africa Corps (, }; DAK) was the German expeditionary force in Africa during the North African Campaign of World War II. First sent as a holding force to shore up the Italian defense of its African colonies, the ...
advance in North Africa forced the British Eighth Army to retreat towards Egypt putting British Middle East Command at risk. The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) had already planned for a buildup of American air power in the Middle East in January 1942 in response to a request from the British Chief of the Air Staff, but the first units arrived unexpectedly on 12 June 1942 as Col. Harry A. Halverson, commanding twenty-three B-24D Liberator heavy bombers and a hand-picked crews (a group called HALPRO – from "Halverson Project
The 376th Expeditionary Operations Group was a provisional United States Air Force Air Combat Command unit. It was stationed at the Transit Center at Manas International Airport, Kyrgyz Republic, up until 2014.
Originally activated in World ...
"), decided to move to Egypt. They had initially been assigned to the China Burma India Theater to attack Japan from airfields in China, but after the fall of Rangoon the Burma Road was cut, so the detachment could not be logistically supported in China. HALPRO was quickly diverted from its original mission to a new one—interdictory raids from airfields in Egypt against shipping and North African ports supporting Axis operations.
 On 28 June 1942, Major General Lewis H. Brereton arrived at Cairo to command the U.S. Army Middle East Air Force (USAMEAF), which was activated immediately. USAMEAF comprised the
On 28 June 1942, Major General Lewis H. Brereton arrived at Cairo to command the U.S. Army Middle East Air Force (USAMEAF), which was activated immediately. USAMEAF comprised the Halverson Project
The 376th Expeditionary Operations Group was a provisional United States Air Force Air Combat Command unit. It was stationed at the Transit Center at Manas International Airport, Kyrgyz Republic, up until 2014.
Originally activated in World ...
, Brereton's detachment ( 9th Bombardment Squadron (Heavy) and other personnel which Brereton brought from India), and the Air Section of the U.S. Military North African Mission. Several USAAF units were sent to join USAMEAF during next weeks in the destruction of Rommel's Afrika Korps by support to ground troops and secure sea and air communications in the Mediterranean.
In September 1942, RAF Middle East Command's Senior Air Staff Officer, Air CommodoreTemporary Air Vice Marshal from December 1942 H. E. P. Wigglesworth was authorized by Air Chief Marshal Sir Arthur Tedder to select targets for all U.S. heavy bombers.
On 1 November 1942, General Bernard Montgomery launched an attack on the ''Afrika Korps
The Afrika Korps or German Africa Corps (, }; DAK) was the German expeditionary force in Africa during the North African Campaign of World War II. First sent as a holding force to shore up the Italian defense of its African colonies, the ...
'' at Kidney Ridge. After initially resisting the attack, Field Marshal Erwin Rommel decided he no longer had the resources to hold his line and on 3 November he ordered his troops to withdraw. Allied victory in the Second Battle of Alamein was accomplished.
Ninth Air Force had been first constituted as V Air Support Command, part of Air Force Combat Command
Air Combat Command (ACC) is one of nine Major Commands (MAJCOMs) in the United States Air Force, reporting to Headquarters, United States Air Force (HAF) at the Pentagon. It is the primary provider of air combat forces for the Air Force, and ...
, at Bowman Field, Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia ...
on 11 September 1941. Its responsibility was to direct and coordinate the training activities of National Guard observation squadrons inducted into federal service with those of light bomber units training with the Army Ground Forces
The Army Ground Forces were one of the three autonomous components of the Army of the United States during World War II, the others being the Army Air Forces and Army Service Forces. Throughout their existence, Army Ground Forces were the large ...
. However a lack of unity of command in the organizational set-up led to an early discontinuation of the "air support commands" and V Air Support Command was redesignated as Ninth Air Force in April 1942.
It moved to Bolling Field The origins of the surname Bolling:
English: from a nickname for someone with close-cropped hair or a large head, Middle English bolling "pollard", or for a heavy drinker, from Middle English bolling "excessive drinking".
German (Bölling): from ...
, Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, on 22 July and transferred without personnel or equipment to Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the Capital city, capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
on 12 November 1942. The Ninth Air Force mission comprised: (1) Gain air superiority; (2) Deny the enemy the ability to replenish or replace losses, and (3) Offer ground forces close support in North-East Africa. On 12 November 1942, the US Army Middle East Air Force was dissolved and replaced by HQ Ninth Air Force, commanded by Lieutenant General Lewis H. Brereton. At that time, the Ninth Air Force consisted of:
* IX Bomber Command (Brigadier General Patrick W Timberlake
Patrick Weston Timberlake (December 25, 1901 – October 18, 1983) was a lieutenant general in the United States Air Force. During World War II, he served as member of the Army Air Forces in both the Mediterranean and Pacific theaters of operat ...
) at Ismailia, Egypt,
* IX Fighter Command
The IX Fighter Command was a United States Army Air Forces formation. Its last assignment was with the Ninth Air Force, based at Erlangen, Germany, wheret was inactivated on 16 November 1945.
IX Fighter Command was the primary tactical fighter ...
(Colonel John C Kilborn) en route to Egypt,
* IX Air Service Command (Brigadier General Elmer E Adler).
By the end of 1942 a total of 370 aircraft had been ferried to the Ninth Air Force. While the great majority were P-40s, Consolidated B-24 Liberators (The original Halverson Detachment (HALPRO), 98th Bombardment Group, 376th Bombardment Group, and RAF units), and B-25 Mitchells (12th) and 340th Bombardment Groups), there were also more than 50 twin-engine transports ( 316th Troop Carrier Group), which made it possible to build an effective local air transport service. Ninth Air Force P-40F fighters ( 57th, 79th, and 324th Fighter Groups) supported the British Eighth Army's drive across Egypt and Libya, escorting bombers and flying strafing and dive-bombing missions against airfields, communications, and troop concentrations. Other targets attacked were shipping and harbor installations in Libya, Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
, Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, Italy, Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, ...
, and Greece to cut enemy supply lines to Africa. The Palm Sunday Massacre was one noteworthy mission by the P-40 and Spitfire groups.
After an Allied air forces command reorganisation effective 18 February 1943, the Ninth Air Force began to report to RAF Middle East Command (RAFME) under Air Chief Marshal Sir Sholto Douglas. Additionally, the Ninth's 57th, 79th, and 324th Fighter Groups and its 12th and 340th Bombardment Groups were transferred to the operational control of the Northwest African Tactical Air Force (NATAF) under the command of Air Vice-Marshal Sir Arthur Coningham. The Ninth's 316th Troop Carrier Group flew its missions with the Northwest African Troop Carrier Command The Northwest African Troop Carrier Command (NATCC) was a combined British-U.S. air command of the Second World War.
It was a sub-command of the Northwest African Air Forces which itself was a sub-command of the Mediterranean Air Command (MAC). Th ...
(NATCC).
In February 1943, after the ''Afrika Korps'' had been driven into Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
, the Germans took the offensive and pushed through the Kasserine Pass before being stopped with the help of both Ninth and Twelfth Air Force units in the battle. The Allies drove the enemy back into a pocket around Bizerte and Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
, where Axis forces surrendered in May. Thus, Tunisia became available for launching attacks on Pantelleria (Operation Corkscrew
Operation Corkscrew was the codename for the Allied invasion of the Italian island of Pantelleria (between Sicily and Tunisia) on 11 June 1943, prior to the Allied invasion of Sicily, during the Second World War. There had been an early plan to ...
), Sicily (Operation Husky
Operation or Operations may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''Operation'' (game), a battery-operated board game that challenges dexterity
* Operation (music), a term used in musical set theory
* ''Operations'' (magazine), Multi-Ma ...
), and mainland Italy.
At the time of Operation Husky
Operation or Operations may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''Operation'' (game), a battery-operated board game that challenges dexterity
* Operation (music), a term used in musical set theory
* ''Operations'' (magazine), Multi-Ma ...
, the invasion of Sicily on 10 July 1943, Ninth Air Force Headquarters was still based at Cairo in Egypt while the Headquarters of Ninth Fighter Command and IX Bomber Command were stationed at Tripoli and Benghazi, Libya, respectively. During this critical period of World War II when the Allied forces finally left North Africa for Europe, the groups of the Ninth Air Force consisted of:
* 12th Bombardment Group at Sfax el Mau, Tunisia with B-25 Mitchells (81st, 82d, 83d, & 434th Bombardment Squadrons)
* 340th Bombardment Group at Sfax South, Tunisia with B-25 Mitchells (486th, 487th, 488th, & 489th Bombardment Squadrons)
* 57th Fighter Group at Hani Main, Tunisia with P-40F Warhawks (64th, 65th, & 66th Fighter Squadrons)
* 79th Fighter Group at Causeway Landing Ground, Tunisia with P-40F Warhawks (85th, 86th, & 87th Fighter Squadrons)
* 324th Fighter Group with P-40F Warhawks (314th Squadron at Hani Main, 315th Squadron at Kabrit, Egypt, & 316th Squadron at Causeway).
* 98th Bombardment Group with B-24D Liberators (343rd & 344th Squadrons at Lete, Libya; 345th & 415th Squadrons at Benina, Libya)
* 376th Bombardment Group at Berka, Tunisia with B-24D Liberators (512th, 513th, 514th, & 515th Bombardment Squadrons)
* 316th Troop Carrier Group at Deversoir, Egypt with C-47s, C-53s and DC3s (36th, 37th, & 44th Squadrons at Deversoir, Egypt; 45th Squadron at Castel Benito, Libya).
During most of 1943, the Ninth Air Force was officially assigned to RAF Middle East Command of the Mediterranean Air Command. However, the Ninth's 12th and 340th Bombardment Groups were assigned to the Tactical Bomber Force, the 57th and 79th Fighter Groups were assigned to the Desert Air Force
The Desert Air Force (DAF), also known chronologically as Air Headquarters Western Desert, Air Headquarters Libya, the Western Desert Air Force, and the First Tactical Air Force (1TAF), was an Allied tactical air force created from No. 204 ...
, and the 324th Fighter Group was surprisingly assigned to XII Air Support Command. The Tactical Bomber Force under Air Commodore Laurence Sinclair, the Desert Air Force under Air Vice Marshal Harry Broadhurst
:''See also Henry Broadhurst for the trade unionist and politician''
Air Chief Marshal Sir Harry Broadhurst, (28 October 1905 – 29 August 1995), commonly known as Broady, was a senior Royal Air Force commander and flying ace of the Second Wo ...
, and XII Air Support Command under Major General Edwin House were sub-commands of the Northwest African Tactical Air Force (NATAF) under Air Marshal Sir Arthur Coningham. NATAF was one of the three major sub-commands of the Northwest African Air Forces (NAAF) under Lieutenant General Carl Spaatz. NATAF, Northwest African Strategic Air Force (NASAF) and Northwest African Coastal Air Force The Northwest African Coastal Air Force (NACAF) was a specialized functional command of the combined Northwest African Air Forces. The Mediterranean Air Command (MAC) oversaw the combined air forces until superseded by the MAAF.
The NACAF had res ...
(NACAF), formed the classic ''tri-force'', the basis for the creation of NAAF in February 1943.
Ninth Air Force groups attacked airfields and rail facilities in Sicily and took part in Operation Husky, carried paratroopers, and flew reinforcements to ground units on the island. The heavy bombardment groups (B-24s) of the Ninth also participated in the low-level assault of the oil refineries at Ploesti, Romania on 1 August 1943.
On 22 August 1943 the following groups were transferred from the Ninth Air Force to the Twelfth Air Force:
* 12th Bombardment Group (Medium) at Gerbini, Sicily with B-25s
* 57th Fighter Group on Sicily with P-40s
* 79th Fighter Group on Sicily with P-40s
* 324th Fighter Group at El Haouaria, Tunisia with P-40s and
* 340th Bombardment Group (Medium) at Comiso, Sicily with B-25s
The 316th Troop Carrier Group was operating under Northwest African Troop Carrier Command The Northwest African Troop Carrier Command (NATCC) was a combined British-U.S. air command of the Second World War.
It was a sub-command of the Northwest African Air Forces which itself was a sub-command of the Mediterranean Air Command (MAC). Th ...
with C-47 Dakotas and CG4A Waco Gliders.
Ninth Air Force 1943 to June 1944
Concurrently with the amalgamation of Ninth Air Force formations in the Mediterranean with Twelfth Air Force, plans were afoot in Britain to devolve Eighth Air Force's medium bomber force to a separate command. This command was offered to Brereton, who accepted "with utmost eagerness", and the force was constituted, also as Ninth Air Force, on 16 October 1943. During the winter of 1943–1944 Ninth Air Force expanded at an extraordinary rate, so that by the end of May, its complement ran to 45 flying groups operating some 5,000 aircraft. With the necessary ground support units, the total number of personnel assigned to Ninth Air Force would be more than 200,000, a total greater than that of Eighth Air Force. HQ Ninth Air Force extended IX Bomber Command's choice of targets considerably, although first priority forOperation Pointblank
Point-blank range is any distance over which a certain firearm can hit a target without the need to compensate for bullet drop, and can be adjusted over a wide range of distances by sighting in the firearm. If the bullet leaves the barrel paral ...
he_Combined_Bomber_Offensive_(CBO)_of_US_and_RAF_air_forces_against_the_Luftwaffe_and_German_aircraft_industry.html" ;"title="Combined_Bomber_Offensive.html" ;"title="he Combined Bomber Offensive">he Combined Bomber Offensive (CBO) of US and RAF air forces against the Luftwaffe and German aircraft industry">Combined_Bomber_Offensive.html" ;"title="he Combined Bomber Offensive">he Combined Bomber Offensive (CBO) of US and RAF air forces against the Luftwaffe and German aircraft industryand next priority for Operation Crossbow (codename for operations against German V-weapon sites) targets was maintained. U.S. and British Air Forces aimed to defeat the German Luftwaffe in the air and on the ground, to bring about complete air supremacy prior to the invasion of Normandy. Operational missions involved attacks on rail marshaling yards, railroads, airfields, industrial plants, military installations, and other enemy targets in France, Belgium, and the Netherlands. Other targets were German Atlantic Wall defenses along the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
coast of France.
On 4 January 1944 XIX Air Support Command was activated at RAF Middle Wallop
Middle Wallop is a village in the civil parish of Nether Wallop in Hampshire, England, on the A343 road. At the 2011 Census the population was included in the civil parish of Over Wallop. The village has a public house, The George Inn, and a pe ...
to support Patton's Third Army in Europe. In February 1944 the Ninth Air Force underwent a reorganization and several troop carrier groups relocated headquarters. Major General Otto P. Weyland became commanding general of XIX Air Support Command, replacing Major General Elwood R Quesada. The latter assumed dual command of both IX Fighter Command and the IX Air Support Command, which took control of all its fighter and reconnaissance units. HQ IX Air Support Command changed from Aldermaston Court to Middle Wallop.
Major General Paul L. Williams, who had commanded the troop carrier operations in Sicily and Italy, replaced Giles in command of IX Troop Carrier Command. The IX TCC command and staff officers were an excellent mix of combat veterans from those earlier assaults, and a few key officers were held over for continuity. The groups assigned were a mixture of experience, but training would be needed to confront the expected massive movements of troops of the 82nd and 101st Airborne Divisions.
On 18 April 1944, the IX and XIX Air Support Commands were redesignated, respectively, as IX Tactical Air Command
The IX Tactical Air Command was a formation of the United States Army Air Forces. It fought in the European theater of World War II. Its last assignment was at Camp Shanks, New York, where it was inactivated on 25 October 1945.
History
Formed ...
and XIX Tactical Air Command
The XIX Tactical Air Command is an inactive United States Air Force unit. The unit's last assignment was with the Ninth Air Force based at Biggs Field, Texas, where it was inactivated on 31 March 1946.
During World War II, the mission of th ...
.
Between 1 May and the invasion on 6 June, the Ninth flew approximately 35,000 sorties, attacking targets such as airfields, railroad yards, and coastal gun positions. By the end of May 1944, the IX TCC had available 1,207 C-47 Skytrain troop carrier airplanes and was one-third overstrength, creating a strong reserve. Three-quarters of the aircraft were less than one year old on D-Day, and all were in excellent condition. Gliders were incorporated, Over 2,100 CG-4 Waco gliders had been sent to the UK, and after attrition during training operations, 1,118 were available for operations, along with 301 larger Airspeed Horsa gliders received from the British.
Order of battle, 6 June 1944
* IX Bomber Command ** 97th Bombardment Wing (Light) ***409th Bombardment Group
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures.
In mathematics
Four is the smallest c ...
( A-20)
**** 640th Bombardment Squadron (W5)
**** 641st Bombardment Squadron (7G)
**** 642d Bombardment Squadron (D6)
**** 643d Bombardment Squadron (5I)
*** 410th Bombardment Group (A-20)
**** 644th Bombardment Squadron (5Q)
**** 645th Bombardment Squadron (7X)
**** 646th Bombardment Squadron (8U)
**** 647th Bombardment Squadron (6Q)
*** 416th Bombardment Group (A-20)
**** 668th Bombardment Squadron (5H)
**** 669th Bombardment Squadron (2A)
**** 670th Bombardment Squadron (F6)
**** 671st Bombardment Squadron (5C)
** 98th Bombardment Wing (Medium)
*** 323d Bombardment Group
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many soci ...
( B-26)
**** 453d Bombardment Squadron (VT)
**** 454th Bombardment Squadron (RJ)
**** 455th Bombardment Squadron (YU)
**** 456th Bombardment Squadron (WT)
*** 387th Bombardment Group 387th may refer to:
*387th Air Expeditionary Group (387 AEG) is a provisional United States Air Force unit assigned to the 386th Air Expeditionary Wing at Ali Al Salem Air Base, Kuwait
*387th EOD (Explosive Ordnance Disposal) Company, part of the 7 ...
(B-26)
**** 556th Bombardment Squadron (FW)
**** 557th Bombardment Squadron (KS)
**** 558th Bombardment Squadron (KX)
**** 559th Bombardment Squadron (TQ)
*** 394th Bombardment Group (B-26)
**** 584th Bombardment Squadron (K5)
**** 585th Bombardment Squadron (4T)
**** 586th Bombardment Squadron (H9)
**** 587th Bombardment Squadron (5W)
*** 397th Bombardment Group (B-26)
**** 596th Bombardment Squadron (X2)
**** 597th Bombardment Squadron (9F)
**** 598th Bombardment Squadron (U2
**** 599th Bombardment Squadron (6B)
** 99th Bombardment Wing (Medium)
*** 322d Bombardment Group (B-26)
**** 449th Bombardment Squadron (PN)
**** 450th Bombardment Squadron (ER)
**** 451st Bombardment Squadron (SS)
**** 452nd Bombardment Squadron (DR)
*** 344th Bombardment Group (B-26)
**** 494th Bombardment Squadron (K9)
**** 495th Bombardment Squadron (Y5)
**** 496th Bombardment Squadron (N3)
**** 497th Bombardment Squadron (7L)
**** 1st Pathfinder Squadron (Provisional)
*** 386th Bombardment Group 386th may refer to:
*386th Air Expeditionary Wing, provisional United States Air Force unit assigned to United States Air Forces Central
*386th Fighter Squadron or 174th Air Refueling Squadron, unit of the Iowa Air National Guard 185th Air Refuelin ...
(B-26)
**** 552d Bombardment Squadron (RG)
**** 553d Bombardment Squadron (AN)
**** 554th Bombardment Squadron (RU)
**** 555th Bombardment Squadron (YA)
*** 391st Bombardment Group 391st may refer to:
* 391st Bombardment Group, non-flying unit of the Pennsylvania Air National Guard, stationed at Horsham Air National Guard Station
* 391st Bombardment Squadron, part of the 6th Air Mobility Wing at MacDill Air Force Base, Florid ...
(B-26)
**** 572d Bombardment Squadron (P2)
**** 573d Bombardment Squadron (T6)
**** 574th Bombardment Squadron (4L)
**** 575th Bombardment Squadron (O8)
* IX Fighter Command
The IX Fighter Command was a United States Army Air Forces formation. Its last assignment was with the Ninth Air Force, based at Erlangen, Germany, wheret was inactivated on 16 November 1945.
IX Fighter Command was the primary tactical fighter ...
**IX Tactical Air Command
The IX Tactical Air Command was a formation of the United States Army Air Forces. It fought in the European theater of World War II. Its last assignment was at Camp Shanks, New York, where it was inactivated on 25 October 1945.
History
Formed ...
*** 70th Fighter Wing
The 70th Fighter Wing (70th FW) is an inactive United States Air Force unit. Its last assignment was with the United States Air Forces in Europe, based at Neubiberg Air Base, Germany. It was inactivated on 25 September 1947.
History
Established ...
**** 48th Fighter Group (P-47
The Republic P-47 Thunderbolt is a World War II-era fighter aircraft produced by the American company Republic Aviation from 1941 through 1945. It was a successful high-altitude fighter and it also served as the foremost American fighter-bomber ...
)
***** 492d Fighter Squadron (F4)
***** 493d Fighter Squadron (I7)
***** 494th Fighter Squadron (6M)
**** 367th Fighter Group 367th may refer to:
* 367th Fighter Group, later the 133d Operations Group, the flying component of the Minnesota Air National Guard's 133d Airlift Wing
* 367th Fighter Squadron Inactivated in 1945, then reactivated at Homestead Air Reserve Base ...
(P-38
The Lockheed P-38 Lightning is an American single-seat, twin piston-engined fighter aircraft that was used during World War II. Developed for the United States Army Air Corps by the Lockheed Corporation, the P-38 incorporated a distinctive twi ...
)
***** 392d Fighter Squadron (H5)
***** 393d Fighter Squadron (8L)
***** 394th Fighter Squadron (4N)
**** 371st Fighter Group (P-47)
***** 404th Fighter Squadron (9Q)
***** 405th Fighter Squadron (8N)
***** 406th Fighter Squadron (4W)
**** 474th Fighter Group (P-38)
***** 428th Fighter Squadron (F5)
***** 429th Fighter Squadron (7Y)
***** 430th Fighter Squadron (K6)
*** 71st Fighter Wing
The 71st Fighter Wing (71 FW) is a disbanded unit of the United States Air Force, last stationed at Lambert Field, St. Louis, Missouri. It was withdrawn from the Missouri Air National Guard (MO ANG) and inactivated on 31 October 1950.
This win ...
**** 366th Fighter Group 366th may refer to:
*366th Bombardment Squadron, inactive United States Air Force unit
*366th Division (IDF), also known as the "Path of Fire" Division, a reserve armored division of the IDF
*366th Fighter Squadron, inactive United States Air Force ...
(P-47)
***** 389th Fighter Squadron (A6)
***** 390th Fighter Squadron (B2)
***** 391st Fighter Squadron (A8)
**** 368th Fighter Group 368th may refer to:
*368th Bombardment Squadron, inactive United States Air Force unit
*368th Expeditionary Air Support Operations Group (368 EASOG) is a support unit of the United States Air Force
*368th Fighter Group or 136th Airlift Wing, unit o ...
(P-47)
***** 359th Fighter Squadron (A7)
***** 396th Fighter Squadron (C2)
***** 397th Fighter Squadron (D3)
**** 370th Fighter Group
The 370th Fighter Group was a unit of the Ninth Air Force that was located in the European Theater of Operations during World War II.Maurer, Maurer. ''Air Force Combat Units Of World War II''. Maxwell AFB, Alabama: Office of Air Force History, 19 ...
(P-38)
***** 401st Fighter Squadron (9D)
***** 402nd Fighter Squadron (E6)
***** 485th Fighter Squadron (7F)
*** 84th Fighter Wing
**** 50th Fighter Group
5 (five) is a number, numeral (linguistics), numeral and numerical digit, digit. It is the natural number, and cardinal number, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number. It has attained significance throughout history in part because typ ...
(P-47)
***** 10th Fighter Squadron (T5)
***** 81st Fighter Squadron (2N)
***** 313th Fighter Squadron (W3)
**** 365th Fighter Group (P-47)
***** 386th Fighter Squadron (D5)
***** 387th Fighter Squadron (B4)
***** 388th Fighter Squadron (C4)
**** 404th Fighter Group
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures.
In mathematics
Four is the smalle ...
(P-47)
***** 506th Fighter Squadron (4K)
***** 507th Fighter Squadron (Y8)
***** 508th Fighter Squadron (7J)
**** 405th Fighter Group (P-47)
***** 509th Fighter Squadron (G9)
***** 510th Fighter Squadron (2Z)
***** 511th Fighter Squadron (K4)
** XIX Tactical Air Command
The XIX Tactical Air Command is an inactive United States Air Force unit. The unit's last assignment was with the Ninth Air Force based at Biggs Field, Texas, where it was inactivated on 31 March 1946.
During World War II, the mission of th ...
*** 100th Fighter Wing
**** 354th Fighter Group
The 354th Fighter Group was an element of the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) Ninth Air Force during World War II. The unit was known as the Pioneer Mustang Group and was the first to fly the P-51B Mustang in combat. The group served as bombe ...
(P-51
The North American Aviation P-51 Mustang is an American long-range, single-seat fighter and fighter-bomber used during World War II and the Korean War, among other conflicts. The Mustang was designed in April 1940 by a team headed by James ...
)
***** 353d Fighter Squadron (FT)
***** 354th Fighter Squadron (GQ)
***** 355th Fighter Squadron (AJ)
**** 358th Fighter Group 358th may refer to:
*358th Bombardment Squadron, inactive United States Air Force unit
* 358th Fighter Group, inactive United States Army Air Force unit
* 358th Fighter Squadron (358 FS), part of the 355th Fighter Wing at Davis-Monthan Air Force Ba ...
(P-47)
***** 365th Fighter Squadron (CH)
***** 366th Fighter Squadron (IA)
***** 367th Fighter Squadron (CP)
**** 362d Fighter Group (P-47)
***** 377th Fighter Squadron (E4)
***** 378th Fighter Squadron (G8)
***** 379th Fighter Squadron (B8)
**** 363d Fighter Group (P-51)
***** 380th Fighter Squadron (A9)
***** 381st Fighter Squadron (B3)
***** 382d Fighter Squadron (C3)
*** 303d Fighter Wing
**** 36th Fighter Group (P-47)
***** 22d Fighter Squadron (3T)
***** 23d Fighter Squadron (7U)
***** 53d Fighter Squadron (6V)
**** 373d Fighter Group (P-47)
***** 410th Fighter Squadron (R3)
***** 411th Fighter Squadron (U9)
***** 412th Fighter Squadron (V5)
**** 406th Fighter Group (P-47)
***** 512th Fighter Squadron (L3)
***** 513th Fighter Squadron (4P)
***** 514th Fighter Squadron (O7)
** 10th Photo Reconnaissance Group (F-3/F-5/F-6)
*** 30th Photographic Reconnaissance Squadron 030 may refer to:
* Motorola 68030
* BR-030
* Geographical telephone calling prefixes
** Greater Accra area code, Ghana
** Utrecht, Netherlands
** Berlin, Germany
** Bar Municipality and Ulcinj Municipality of Montenegro
** Province of Brescia ...
*** 31st Photographic Reconnaissance Squadron
*** 33d Photographic Reconnaissance Squadron
*** 34th Photographic Reconnaissance Squadron
*** 155th Photographic Reconnaissance Squadron
* IX Troop Carrier Command
The IX Troop Carrier Command was a United States Army Air Forces unit. Its last assignment was with the Ninth Air Force, based at Greenville Army Air Base, South Carolina. It was inactivated on 31 March 1946. As a component command of the Ninth ...
** 1st Pathfinder Group (Provisional)
** 50th Troop Carrier Wing
*** 439th Troop Carrier Group ( C-47/C-53)
**** 91st Troop Carrier Squadron (L4)
**** 92d Troop Carrier Squadron (J8)
**** 93d Troop Carrier Squadron (3B)
**** 94th Troop Carrier Squadron (D8)
*** 440th Troop Carrier Group 44 may refer to:
* 44 (number)
* one of the years 44 BC, AD 44, 1944, 2044
Military
*44M Tas, a Hungarian medium/heavy tank design of World War II
*44M Tas Rohamlöveg, a Hungarian tank destroyer design of World War II, derived from the 44M Tas ta ...
(C-47/C-53)
**** 95th Troop Carrier Squadron (9X)
**** 96th Troop Carrier Squadron (6Z)
**** 97th Troop Carrier Squadron (W6)
**** 98th Troop Carrier Squadron (8Y)
*** 441st Troop Carrier Group
The 441st Troop Carrier Group is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was to the 441st Troop Carrier Wing, stationed at Chicago O'Hare International Airport, Illinois, where it was inactivated on 14 March 1951.
...
(C-47/C-53)
**** 99th Troop Carrier Squadron (3J)
**** 100th Troop Carrier Squadron (8C)
**** 301st Troop Carrier Squadron (Z4)
**** 302d Troop Carrier Squadron (2L)
*** 442d Troop Carrier Group (C-47/C-53)
**** 303d Troop Carrier Squadron (J7)
**** 304th Troop Carrier Squadron (V4)
**** 305th Troop Carrier Squadron (4J)
**** 306th Troop Carrier Squadron (7H)
** 52d Troop Carrier Wing
*** 61st Troop Carrier Group (C-47/C-53)
****14th Troop Carrier Squadron (3I)
****15th Troop Carrier Squadron (Y9)
****53d Troop Carrier Squadron (3A)
****59th Troop Carrier Squadron (X5)
*** 313th Troop Carrier Group (C-47/C-53)
**** 29th Troop Carrier Squadron (5X)
**** 47th Troop Carrier Squadron (N3)
**** 48th Troop Carrier Squadron (Z7)
**** 49th Troop Carrier Squadron (H2)
*** 314th Troop Carrier Group (C-47/C-53)
**** 32nd Troop Carrier Squadron (S2)
**** 50th Troop Carrier Squadron (2R)
**** 61st Troop Carrier Squadron (Q9)
**** 62d Troop Carrier Squadron (E5)
*** 315th Troop Carrier Group (C-47/C-53)
**** 34th Troop Carrier Squadron (NM)
**** 43d Troop Carrier Squadron (UA)
**** 309th Troop Carrier Squadron (M6)
**** 310th Troop Carrier Squadron (4A)
*** 316th Troop Carrier Group (C-47/C-53)
**** 36th Troop Carrier Squadron (6E)
**** 37th Troop Carrier Squadron (W7)
**** 44th Troop Carrier Squadron (4C)
**** 45th Troop Carrier Squadron (T3)
** 53d Troop Carrier Wing
*** 434th Troop Carrier Group (C-47/C-53)
**** 71st Troop Carrier Squadron (CJ)
**** 72d Troop Carrier Squadron (CU)
**** 73d Troop Carrier Squadron (CN)
**** 74th Troop Carrier Squadron (ID)
*** 435th Troop Carrier Group 435th may refer to:
* 435th Air Ground Operations Wing, the first USAFE wing solely dedicated to supporting battlefield Airmen
*435th Bombardment Squadron, an inactive United States Air Force unit
*435th Fighter Training Squadron (435 FTS), part of ...
(C-47/C-53)
**** 75th Troop Carrier Squadron (SH)
**** 76th Troop Carrier Squadron (CW)
**** 77th Troop Carrier Squadron (IB)
**** 78th Troop Carrier Squadron (CM)
*** 436th Troop Carrier Group (C-47/C-53)
**** 79th Troop Carrier Squadron (S6)
**** 80th Troop Carrier Squadron (7D)
**** 81st Troop Carrier Squadron (U5)
**** 82d Troop Carrier Squadron (3D)
*** 437th Troop Carrier Group (C-47/C-53)
**** 83d Troop Carrier Squadron (T2)
**** 84th Troop Carrier Squadron (Z8)
**** 85th Troop Carrier Squadron (9O)
**** 86th Troop Carrier Squadron (5K)
*** 438th Troop Carrier Group 438th may refer to:
* 438th Air Expeditionary Advisory Group (438 AEAG), assigned to the 438th Air Expeditionary Wing of USAFCENT, stationed at Kabul Airport, Afghanistan
* 438th Air Expeditionary Group, provisional unit assigned to United States A ...
(C-47/C-53)
**** 87th Troop Carrier Squadron (3X)
**** 88th Troop Carrier Squadron (M2)
**** 89th Troop Carrier Squadron (4U)
**** 90th Troop Carrier Squadron (Q7)
* IX Air Force Service Command
** 1st Advanced Air Depot Area
*** 1st Tactical Air Depot
*** 2d Tactical Air Depot
*** 3d Tactical Air Depot
** 2d Advanced Air Depot Area
*** 4th Tactical Air Depot
*** 5th Tactical Air Depot
*** 6th Tactical Air Depot
** 1585th Quartermaster Truck Regiment
** 31st Transport Group
** IX Air Force Intransit Depot Group
** 13th Replacement Control Depot
** 20th Replacement Control Depot
** Signal Battalion (HC)
* IX Engineer Command
** 922d Engineer Aviation Regiment
** 924th Engineer Aviation Regiment
** 925th Engineer Aviation Regiment
** 926th Engineer Aviation Regiment
* IX Air Defense Command
** 1/8 Antiaircraft Group
** 51st Antiaircraft Artillery Brigade
** 52d Antiaircraft Artillery Brigade
Operations in Europe 1944–1945


 On D-Day, IX Troop Carrier Command units flew over 2000 sorties conducting combat parachute jumps and glider landings as part of
On D-Day, IX Troop Carrier Command units flew over 2000 sorties conducting combat parachute jumps and glider landings as part of American airborne landings in Normandy
The U.S. airborne landings in Normandy were the first U.S. combat operations during Operation Overlord, the invasion of Normandy by the Western Allies on June 6, 1944, during World War II. Around 13,100 American paratroopers of the 82nd and 1 ...
of Operation Neptune. Other Ninth Air Force units carried out massive air attacks with P-51 Mustang, P-47 Thunderbolt
The Republic P-47 Thunderbolt is a World War II-era fighter aircraft produced by the American company Republic Aviation from 1941 through 1945. It was a successful high-altitude fighter and it also served as the foremost American fighter-bom ...
fighter-bombers, North American B-25 Mitchell
The North American B-25 Mitchell is an American medium bomber that was introduced in 1941 and named in honor of Major General William "Billy" Mitchell, a pioneer of U.S. military aviation. Used by many Allied air forces, the B-25 served in ...
and Martin B-26 Marauder
The Martin B-26 Marauder is an American twin-engined medium bomber that saw extensive service during World War II. The B-26 was built at two locations: Baltimore, Maryland, and Omaha, Nebraska, by the Glenn L. Martin Company.
First used in t ...
medium bombers. Air cover during the morning amphibious assault by Allied forces on the beaches of France was flown by P-38 Lightning
The Lockheed P-38 Lightning is an American single-seat, twin piston-engined fighter aircraft that was used during World War II. Developed for the United States Army Air Corps by the Lockheed Corporation, the P-38 incorporated a distinctive tw ...
s.
With the beaches secure, its tactical air units then provided the air power for the Allied break-out from the Normandy beachhead in the summer of 1944 during the Battle of Cherbourg, Battle for Caen
The Battle for Caen (June to August 1944) is the name given to fighting between the British Second Army and the German in the Second World War for control of the city of Caen and its vicinity during the larger Battle of Normandy. The battle ...
, and the ultimate breakout from the beachhead, Operation Cobra
Operation Cobra was the codename for an offensive launched by the United States First Army under Lieutenant General Omar Bradley seven weeks after the D-Day landings, during the Normandy campaign of World War II. The intention was to take adv ...
.
Unlike Eighth Air Force, whose units stayed in the United Kingdom, Ninth Air Force units were very mobile, first deploying to France on 16 June 1944, ten days after the Normandy invasion by moving P-47 Thunderbolts to a beach-head landing strip.
Because of their short range, operational combat units would have to move to quickly prepared bases close to the front as soon as the Allied ground forces advanced. The bases were called " Advanced Landing Grounds" or "ALGs". On the continent, many ALGs were built either from scratch or from captured enemy airfields throughout France, the Low Countries and Germany. Ninth Air Force units moved frequently from one ALG to another.
By early August most Ninth Air Force operational fighter and bomber groups were transferred to bases in France and assigned to the U. S. Twelfth Army Group. These groups were then assigned to Tactical Air Command (TAC) organizations which supported Army ground units. XXIX Tactical Air Command (XXIX TAC) was activated in France on 15 September 1944, commanded by Brig. Gen. Richard E. Nugent, to support operations of the U.S. Ninth Army.
XXIX TAC supported the Ninth Army in the north; IX TAC supported the First Army in the center; and XIX TAC supported the Third Army in the south. Air cover over Allied-controlled areas on the continent was performed by the IX Air Defense Command. Ninth Air Force groups made numerous moves within France, the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
and western Germany to keep within range of the advancing battle front before the end of hostilities in May 1945.
During Operation Dragoon, the invasion of Southern France in August 1944, two Ninth fighter groups were transferred to the provisional United States/Free French 1st Tactical Air Force supporting the invasion force's drive north. As part of Operation Market-Garden
Operation Market Garden was an Allied military operation during the Second World War fought in the Netherlands from 17 to 27 September 1944. Its objective was to create a salient into German territory with a bridgehead over the River Rhine, ...
, the Ninth Air Force transferred its entire IX Troop Carrier Command with its fourteen C-47 groups to the 1st Allied Airborne Army in September 1944. Those troop carrier groups flew many of the C-47s and towed CG-4 Waco gliders for the Allied airborne unit drops— Operation Market Garden—to take the bridges northwest of Eindhoven at Son (mun. Son en Breugel), Veghel
Veghel () is a town and a former municipality in the southern Netherlands. On 1 January 2017 Veghel, together with Schijndel and Sint-Oedenrode, merged into a new municipality called Meierijstad creating the largest municipality of the provi ...
, Grave
A grave is a location where a dead body (typically that of a human, although sometimes that of an animal) is buried or interred after a funeral. Graves are usually located in special areas set aside for the purpose of burial, such as grav ...
, Nijmegen and Arnhem
Arnhem ( or ; german: Arnheim; South Guelderish: ''Èrnem'') is a city and municipality situated in the eastern part of the Netherlands about 55 km south east of Utrecht. It is the capital of the province of Gelderland, located on both ban ...
in the Netherlands.
In December 1944 through January 1945, Ninth Air Force fighters and bombers were critical in defeating the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
during the Battle of the Bulge
The Battle of the Bulge, also known as the Ardennes Offensive, was the last major German offensive campaign on the Western Front during World War II. The battle lasted from 16 December 1944 to 28 January 1945, towards the end of the war in ...
. Initially American, British, and Canadian air power was grounded by very bad winter weather, but then the bad weather broke, freeing the tactical air forces to help break the back of the Wehrmacht attack. The long smash across France, Belgium, and Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
was the highlight of the existence of the 9th Air Force.
In the spring of 1945, Ninth Air Force troop carrier units flew airborne parachute and glider units again during Operation Varsity
Operation Varsity (24 March 1945) was a successful airborne forces operation launched by Allied troops that took place toward the end of World War II. Involving more than 16,000 paratroopers and several thousand aircraft, it was the largest ai ...
, the Allied assault over the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
River on 24 March 1945. Operation Varsity was the single largest airborne drop in history. The operation saw the first use of the Curtiss-Wright C-46 Commando
The Curtiss C-46 Commando is a twin-engine transport aircraft derived from the Curtiss CW-20 pressurised high-altitude airliner design. Early press reports used the name "Condor III" but the Commando name was in use by early 1942 in company pub ...
transport in Europe, operating with the reliable C-47 Skytrain of previous airborne operations, an experiment which ended with the catastrophic loss of 28% of the C-46s participating.
Postwar demobilization
Ninth Air Force tactical air support operations were flown over western Germany until the end of hostilities on 7 May. However, once the victory had been gained, the United States plunged into demobilization, just as it had done at the end of theFirst World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
.
Most officers and men were sent back to the United States and their units inactivated. Others were assigned to the new United States Air Forces in Europe
United may refer to:
Places
* United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community
* United, West Virginia, an unincorporated community
Arts and entertainment Films
* ''United'' (2003 film), a Norwegian film
* ''United'' (2011 film), a BBC Two f ...
and were moved to captured Luftwaffe airfields to perform occupation duties. Some transport units relocated to France. Finally, with the mission completed, on 2 December 1945 the Ninth Air Force was inactivated at USAFE Headquarters at Wiesbaden
Wiesbaden () is a city in central western Germany and the capital of the state of Hesse. , it had 290,955 inhabitants, plus approximately 21,000 United States citizens (mostly associated with the United States Army). The Wiesbaden urban area ...
Germany.
Cold War
: ''see also:Nineteenth Air Force
The Nineteenth Air Force (19 AF) is an active Numbered Air Force of the United States Air Force. During the Cold War it was a component of Tactical Air Command, with a mission of command and control over deployed USAF forces in support of Unit ...
''



 Following
Following World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, Ninth Air Force was reactivated on 28 March 1946 at Biggs AAF, Texas. After several relocations, on 20 August 1954, Ninth Air Force Headquarters was assigned to Shaw Air Force Base
Shaw Air Force Base (Shaw AFB) is a United States Air Force (USAF) base located approximately west-northwest of downtown Sumter, South Carolina. It is one of the largest military bases operated by the United States, and is under the jurisdict ...
, South Carolina
)'' Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
, where it remains today. The postwar Numbered Air Forces were components of the new major command structure of the United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Aerial warfare, air military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part ...
, and Ninth Air Force became one of the tactical air forces of the new Tactical Air Command. Ninth Air Force commanded TAC Wings east of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
.
Initially being equipped with propeller-driven F-51, F-47 and F-82 aircraft during the postwar years, in the 1950s, Ninth Air Force units received the jet-powered F/RF-80 Shooting Star, F-84G/F Thunderjet, F-86D/H Sabre, and F-100 Super Sabre aircraft. Ninth Air Force squadrons and wings were frequently deployed to NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
during the 1950s and 1960s as "Dual-Based" USAFE units, and reinforcing NATO forces in West Germany and France during the Lebanon crisis of 1958 and the 1961 Berlin Wall Crisis.
During the 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis, Ninth Air Force units went on war alert, deploying to bases in Florida, being able to respond to the crisis on a moment's notice.
During the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam a ...
, detached Ninth Air Force units engaged in combat operations over Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
, Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailan ...
and Laos. The practice of stripping away squadrons and aircraft from their home Tactical Air Command Wings and attaching them indefinitely to a new wing under PACAF, Pacific Air Forces was the method used for long-term deployments to the South Vietnam and Thailand air bases engaged in combat operations. In addition to these operational deployments, Ninth Air Force units performed a "backfilling" role in Japan and South Korea for PACAF as well as in Italy and Spain for USAFE to replace units whose aircraft and personnel were deployed to Southeast Asia. With the end of American involvement during the early 1970s, these units were returned in large part to their home Ninth Air Force units in the United States.
During the remainder of the 1970s, NATO deployments resumed supporting the COMET, CORONET and CRESTED CAP exercises. These deployments were designed to exercise CONUS based Air Force squadrons long range deployment capabilities and to familiarize the personnel with the European theatre of operations. During these NATO deployments, exercises with Army infantry and armored units were conducted to enhance the Close Air Support role in Europe.
Ninth Air Force Wings in 1979 were:
* 1st Tactical Fighter Wing (F-15A/B) (FF) Langley Air Force Base, Virginia
* 4th Tactical Fighter Wing (F-4E) (SJ) Seymour Johnson Air Force Base, North Carolina
* 23d Tactical Fighter Wing (A-7D) (EL) England Air Force Base, Louisiana
* 31st Tactical Fighter Wing (F-4D) (ZE/HS) Homestead Air Force Base, Florida
* 33d Tactical Fighter Wing (F-15A/B) (EG) Eglin Air Force Base, Florida
* 56th Tactical Fighter Wing (F-4D/E) (MC) MacDill Air Force Base, Florida
* 347th Tactical Fighter Wing (F-4E) (MY) Moody Air Force Base, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia
* 354th Tactical Fighter Wing (A/OA-10A) (MB) Myrtle Beach Air Force Base, South Carolina
)'' Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
* 363d Tactical Reconnaissance Wing (RF-4C) (JO) Shaw Air Force Base
Shaw Air Force Base (Shaw AFB) is a United States Air Force (USAF) base located approximately west-northwest of downtown Sumter, South Carolina. It is one of the largest military bases operated by the United States, and is under the jurisdict ...
, South Carolina
During the 1980s, Ninth Air Force wings upgraded from the Vietnam-Era F-4s and A-7s to newer F-15s, F-16 and A-10 aircraft. First-generation F-15A/B models were later sent to Air National Guard fighter units while Regular Air Force units upgraded to the higher-capability F-15C/Ds and the new F-15E replaced the F-4E in the 4th TFW.
With the end of the Cold War in the early 1990s, the 1991 Base Realignment and Closure Commission (BRAC) reductions meant the closing of Myrtle Beach AFB and England AFB. MacDill AFB was realigned under Air Combat Command as the headquarters of United States Central Command
The United States Central Command (USCENTCOM or CENTCOM) is one of the eleven unified combatant commands of the U.S. Department of Defense. It was established in 1983, taking over the previous responsibilities of the Rapid Deployment Joint Ta ...
and United States Special Operations Command, but minus tactical aircraft operations with the reassignment of the 56th Fighter Wing to Air Education and Training Command and relocation to Luke AFB, Arizona.
The restructuring of USAF CONUS forces by the inactivation of Tactical Air Command and subsequent creation of Air Combat Command realigned Ninth Air Force with new units and new missions. In addition, the effects of Hurricane Andrew at Homestead AFB on 24 August 1992 essentially destroyed the facility. Although both George H. W. Bush and Bill Clinton, President Clinton promised to rebuild Homestead, the BRAC designated the installation for realignment to the Air Force Reserve, and on 1 April 1994, Headquarters, ACC inactivated its base support units and transferred base support responsibility to the Air Force Reserve Command and AFRC's 482d Fighter Wing, effectively ending ACC ownership of the base.
Concurrently, ACC also transferred responsibility for MacDill AFB to Air Mobility Command following the arrival of an air refueling unit and redesignation of the host air base wing as an air refueling wing (later redesignated as an air mobility wing).
CENTAF and the 1991 Gulf War
In 1980, Ninth Air Force units were allocated to the newRapid Deployment Joint Task Force
The Rapid Deployment Joint Task Force (RDJTF) is an inactive United States Department of Defense Joint Task Force. It was first envisioned as a three-division force in 1979 as the Rapid Deployment Force, or RDF, a highly mobile force that could ...
(RDJTF). In 1983, the RDJTF became a separate unified command known as the United States Central Command
The United States Central Command (USCENTCOM or CENTCOM) is one of the eleven unified combatant commands of the U.S. Department of Defense. It was established in 1983, taking over the previous responsibilities of the Rapid Deployment Joint Ta ...
(USCENTCOM), focusing on the Middle East. Ninth Air Force provided the aircraft, personnel and materiel to form United States Central Command Air Forces (USCENTAF), the USAF air power of CENTCOM, which was also headquartered at Shaw AFB. Starting in 1981, Ninth Air Force aircraft and personnel were deployed to Egypt for Exercise Bright Star.
During Operation Desert Shield (Gulf War), Operation Desert Shield and Operation Desert Storm, Ninth Air Force units deployed to the Middle East, and flew combat missions over Kuwait and Iraq.
After the end of hostilities, units from the Ninth flew air missions over Iraq as part of Operation Deny Flight, Operation Northern Watch and Operation Southern Watch. From 1991, the 4404th Wing (Provisional), 4404th Composite Wing (Provisional) served as a forward force, for most of that period flying from King Abdul Aziz AB, Saudi Arabia. Despite the boring nature of the quasi-peacetime patrols over both the northern and southern "no-fly zones," the years after 1991 were not entirely without hostile action. Time and time again Iraqi air defense radars came on line and "illuminated" American aircraft. There were also numerous cases where Iraqi anti-aircraft guns and missiles engaged American aircraft. In each case, the U.S. military aircraft would retaliate and in most cases, eliminate the offending air defense site(s). Among the deployed units were the 4th Air Expeditionary Wing, Camp Doha, Qatar (June 1996 and February 1997 in Air Expeditionary Force (AEF) Rotations III and IV respectively), the 347th Air Expeditionary Wing, Shaikh Isa AB, Bahrain, and the 363d Air Expeditionary Wing at Prince Sultan AB, Saudi Arabia.
During this "phony war," American pilots gained invaluable experience in air-to-ground tactics that could not be duplicated in practice missions back at home. Combat missions briefly resumed in 1998 during Operation Desert Fox.

Iraq and Afghanistan
Ninth Air Force units, flying as USCENTAF, flew operational missions during the 2002 Operation Enduring Freedom—Afghanistan (OEF-A) and the 2003 invasion of Iraq, Operation Iraqi Freedom (OIF). Air Expeditionary Force units are engaged in combat operations on an ongoing basis. U.S. Airmen are increasingly on the ground in Iraq: "They drive in convoys and even work with detainees. The main aerial hub in Iraq has 1,500 airmen doing convoy operations in and 1,000 working with detainees. The USAF is also involved in training Iraqis and performing other activities not usually associated with the Air Force. The dangers of the Air Force's new role were highlighted when the expeditionary wing lost its first female member in the line of duty in Iraq. A1C Elizabeth Jacobson, 21, was killed in a roadside bombing while performing convoy security near the U.S. detention center at Camp Bucca in southern Iraq." "More and more Air Force are doing Army jobs," said Senior Master Sgt. Matt Rossoni, 46, of San Francisco. "It's nothing bad about the Army. They're just tapped out." "Air Force Security Forces are traditionally associated with base defense, however, now they provide security for patrols and to deliver supplies." The Air Force also is keeping up with its traditional duties. In November, the 386th Air Expeditionary Wing delivered its one millionth passenger to Iraq since October 2003. USAF missions included transporting troops, casualties and cargo flights. The Air Force, Navy and Marine Corps flew thousands of missions in support of U.S. ground troops in Iraq this fall, including attacks by unmanned Predator aircraft armed with Hellfire missiles, military records show. American and allied refueling, transport and surveillance planes also are in the air. Airstrikes have been largely in areas where the insurgency is strongest, like Balad, Ramadi and in the vicinity of Baghdad, according to the U.S. Central Command.Components
* 332nd Air Expeditionary Wing, undisclosed location, Southwest Asia, May 2016 – present * 378th Air Expeditionary Wing, Prince Sultan Air Base, Saudi Arabia, 24 October 2005 – present : E-3 Sentry * 379th Air Expeditionary Wing, Al Udeid Air Base, Qatar, 2002–present : B-1B Lancer, C-130 Hercules, C-17 Globemaster III, E-6B Mercury, E-8C Joint STARS, KC-135 Stratotanker, P-3 Orion, RC-135 Rivet Joint * 380th Air Expeditionary Wing, Al Dhafra Air Base, United Arab Emirates, 25 January 2002 – present
: KC-10 Extender, RQ-4 Global Hawk, U-2 Dragon Lady
* 386th Air Expeditionary Wing, Ali Al Salem Air Base, Kuwait, 2002–present
: C-130 Hercules
Tenant Units assigned to the command are:
* 609th Air Operations Center, 609th Air and Space Operations Center, Al Udeid Air Base, Qatar, 1 January 1994 – present
* 1st Expeditionary Civil Engineer Group, Al Udeid Air Base, Qatar, October 2001 – present
** 557 Expeditionary Rapid Engineer Deployable Heavy Operational Repair Squadron Engineers, RED HORSE Squadron
** 577 Expeditionary PRIME BEEF Squadron
Note: The 432d Air Expeditionary Wing is an Air Combat Command unit headquartered at Creech AFB, Nevada. It operates RQ-1 Predator and MQ-9 Reaper UAV aircraft in the AFCENT AOR.
* 380th Air Expeditionary Wing, Al Dhafra Air Base, United Arab Emirates, 25 January 2002 – present
: KC-10 Extender, RQ-4 Global Hawk, U-2 Dragon Lady
* 386th Air Expeditionary Wing, Ali Al Salem Air Base, Kuwait, 2002–present
: C-130 Hercules
Tenant Units assigned to the command are:
* 609th Air Operations Center, 609th Air and Space Operations Center, Al Udeid Air Base, Qatar, 1 January 1994 – present
* 1st Expeditionary Civil Engineer Group, Al Udeid Air Base, Qatar, October 2001 – present
** 557 Expeditionary Rapid Engineer Deployable Heavy Operational Repair Squadron Engineers, RED HORSE Squadron
** 577 Expeditionary PRIME BEEF Squadron
Note: The 432d Air Expeditionary Wing is an Air Combat Command unit headquartered at Creech AFB, Nevada. It operates RQ-1 Predator and MQ-9 Reaper UAV aircraft in the AFCENT AOR.
Lineage and assignments
* Established as the 5th Air Support Command on 21 August 1941 : Activated on 1 September 1941 : Redesignated 9th Air Force on 8 April 1942 : Redesignated as Ninth Air Force on 18 September 1942 : Inactivated on 2 December 1945 * Activated on 28 March 1946 : Redesignated: Ninth Air Force (Tactical) on 1 August 1950 : Redesignated: Ninth Air Force on 26 June 1951 : Co-designation United States Central Command Air Forces established, 1 January 1983 :: CENTAF designation used for Ninth Air Force assets assigned toUnited States Central Command
The United States Central Command (USCENTCOM or CENTCOM) is one of the eleven unified combatant commands of the U.S. Department of Defense. It was established in 1983, taking over the previous responsibilities of the Rapid Deployment Joint Ta ...
: Redesignated: Ninth Air Force (Air Forces Central), on 1 March 2008.
: Redesignated: United States Air Forces Central Command, on 5 August 2009.
: Redesignated: Ninth Air Force (Air Forces Central), on 20 August 2020.
Assignments
*Air Force Combat Command
Air Combat Command (ACC) is one of nine Major Commands (MAJCOMs) in the United States Air Force, reporting to Headquarters, United States Air Force (HAF) at the Pentagon. It is the primary provider of air combat forces for the Air Force, and ...
(later, Army Air Forces), 1 September 1941
* United States Army Forces in the Middle East, 12 November 1942
* European Theater of Operations, United States Army, 3 November 1943
* United States Strategic Air Forces in Europe
: (later, United States Air Forces in Europe
United may refer to:
Places
* United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community
* United, West Virginia, an unincorporated community
Arts and entertainment Films
* ''United'' (2003 film), a Norwegian film
* ''United'' (2011 film), a BBC Two f ...
), 22 February 1944 – 2 December 1945
* Tactical Air Command, 28 March 1946
* Continental Air Command, 1 December 1948
* Tactical Air Command, 1 December 1950
* Air Combat Command, 1 June 1992 – present
Stations
* Bowman Field, Kentucky, 1 September 1941 * New Orleans Army Air Base, Louisiana, 24 January 1942 * Bolling Field, Washington, D.C., 22 July – October 1942 *Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the Capital city, capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of ...
, Egypt, 12 November 1942 – October 1943
* Sunninghill Park, Berkshire, England, November 1943 – September 1944
* Chantilly, Oise, Chantilly, France, 15 September 1944
* Bad Kissingen, Germany, 6 June – 2 December 1945
* Biggs Field, Texas, 28 March 1946
* Greenville Army Air Base (later Greenville Air Force Base), South Carolina, 31 October 1946
* Langley Air Force Base, Virginia, 14 February 1949
* Pope Air Force Base, North Carolina, 1 August 1950
* Shaw Air Force Base
Shaw Air Force Base (Shaw AFB) is a United States Air Force (USAF) base located approximately west-northwest of downtown Sumter, South Carolina. It is one of the largest military bases operated by the United States, and is under the jurisdict ...
, South Carolina, 20 August 1954 – 5 Aug 2009
* Al Udeid Air Base, Qatar, 5 August 2009 – 20 August 2020
* Shaw Air Force Base, South Carolina, 20 August 2020 – present
Major components
World War II Units
; Commands * IX Air Defense Command: 1 July 1944 – 28 November 1945 * IX Bomber Command: 24 July 1942 – 20 November 1943IX Engineer Command
1 July 1944 – 2 December 1945 *
IX Troop Carrier Command
The IX Troop Carrier Command was a United States Army Air Forces unit. Its last assignment was with the Ninth Air Force, based at Greenville Army Air Base, South Carolina. It was inactivated on 31 March 1946. As a component command of the Ninth ...
: 16 October 1943 – 1 November 1944
* IX Fighter Command
The IX Fighter Command was a United States Army Air Forces formation. Its last assignment was with the Ninth Air Force, based at Erlangen, Germany, wheret was inactivated on 16 November 1945.
IX Fighter Command was the primary tactical fighter ...
: 23 December 1942 – 16 November 1945
* IX Tactical Air Command, IX Air Support (later, IX Tactical Air) Command): 4 December 1943 – 17 August 1945
* XIX Tactical Air Command, XIX Air Support (later, XIX Tactical Air Command): 4 January 1944 – 20 November 1945
* XXIX Tactical Air Command, XXIX Air Support (later, XXIX Tactical Air) Command: 30 November 1943 – 3 October 1945
; Groups
* 12th Bombardment Group: 21 January 1941 – 18 April 1942, 16 August 1942 – 22 August 1943
* 36th Fighter Group: 4 April-1 October 1944
* 366th Fighter Group: 8 January-15 February 1944
* 67th Observation Group, 29 March 1942 – 15 May 1942
* 363d Tactical Reconnaissance Group: 20 November – 11 December 1945
; Squadrons
* 12th Observation Squadron: 21 January – 29 March 1942
* 915th Air Refueling Squadron, 15th Bombardment Squadron: 14 October 1941 – unknown
* 425th Night Fighter Squadron: 23 May – 10 June 1944; 7 July – 9 September 1945
USAF Air Divisions
* 12th Air Division: 23 February – 27 June 1949 * 19th Air Division : (formerly, 19 Bombardment Wing; IX Bomber Command; 9 Bombardment Division; 9 Air Division; 19 Bombardment Wing) : 24 July 1942 – 20 November 1945; 22 December 1948 – 1 February 1949. 21 Air: 22 December 1948 – 1 February 1949. * 42d Air Division: 1 July – 1 October 1957 * 49th Air Division: 22 December 1948 – 1 February 1949 * 69th Air Division: 23 February – 27 June 1949 * 302d Air Division: 22 December 1948 – 1 February 1949 * 833d Air Division: 1 October 1964 – 24 December 1969 * 834d Air Division: 25 September – 1 October 1957; 1 July 1964 – 15 October 1966 * 836th Air Division: 8 October 1957 – 1 July 1961; 1 July 1962 – 30 June 1971 * 837th Air Division: 8 February 1958 – 1 February 1963 * 838th Air Division: 25 September – 11 December 1957 * 839th Air Division: 8 October 1957 – 1 July 1963; 9 November 1964 – 1 December 1974 * 840th Air Division: 1 October 1964 – 24 December 1969Groups
* 46th Bombardment Group: 1 September 1941 – 18 April 1942Known Inactive Air Expeditionary units
: ''See Organization of United States Air Force Units in the Gulf War for units and deployment of CENTAF forces during Operation Desert Shield and Operation Desert Storm'' * 128th Air Expeditionary Group : Flights at several bases in AFCENT AOR * 368th Expeditionary Air Support Operations Group : Camp Victory, Baghdad, Iraq * 370th Air Expeditionary Advisory Group : Sather AB, Iraq * 376th Air Expeditionary Wing : Transit Center at Manas, Kyrgyzstan * 398th Air Expeditionary Group : Flights at several bases in AFCENT AOR * 384th Air Expeditionary Wing : Shaikh Isa Air Base, Bahrain * 406th Air Expeditionary Wing : RAFO Thumrait, Oman * 410th Air Expeditionary Wing : H-5 Air Base, Jordan : Shaheed Mwaffaq AB, Jordan * 416th Air Expeditionary Group : Karshi-Khanabad AB, Uzbekistan * 447th Air Expeditionary Group : Sather AB, Iraq * 506th Air Expeditionary Group : Kirkuk AB, Iraq * 732d Air Expeditionary Group : Balad AB, Iraq * 4417th Air Expeditionary Force : Shaheed Mwaffaq AB, JordanService and campaign streamers
* War in Southwest Asia ** Defense of Saudi Arabia (Desert Shield) 1990-1991 ** Liberation of Kuwait (Desert Storm) 1991Awards
List of commanders
AFCENT Commanders
9 AF/AFCENT Commanders
References
Notes
; Explanatory notes ; CitationsBibliography
* * : Further reading * Bozung, Jack H. (ed). ''The 9th Sees France and England''. Los Angeles, California: AAF Publications Company, 1947. * Coles, Harry C. ''Ninth Air Force Participation in the Western Desert Campaign to January 1943 (USAAF Historical Study, No. 30)''. Air Force Historical Research Agency, 1945. * Coles, Harry C. ''Participation of the Ninth and Twelfth Air Forces in the Sicilian Campaign (USAAF Historical Study, No. 37)''. Air Force Historical Research Agency, 1945. * Craven, Wesley F. and James L. Cate. ''The Army Air Forces in World war II, Vols. 1–7''. Chicago, Illinois: Chicago University Press, 1948/51 (Reprinted 1983, ). * Dorr, Robert F. and Thomas D. Jones. ''Hell Hawks!: The Untold Story of the American Fliers Who Savaged Hitler's Wehrmacht''. St Paul, MN: Zenith Press, 2008. . * * * Freeman, Roger A. ''The Ninth Air Force in Colour. UK and the Continent-World War II''. London: Arms and Armor Press, 1995. * Freeman, Roger A. ''UK Airfields of the Ninth, Then and Now''. London: Battle of Britain Publications, 1994. * George, Robert H. ''Ninth Air Force, April to November 1944 (USAAF Historical Study, No. 36)''. Air Force Historical Research Agency, 1945. * Hamlin, John F. ''Support and Strike!: A Concise History of the U.S. Ninth Air Force in Europe''. Bretton, Peterborough, UK: GMS Enterprises, 1991. . * Marx, Milton. ''Ninth Air Force, USAAF''. Paris, France: Desfosses-Neogravure, 1945. LCCN 49028944. Dewey 940.541273. OCLC 3784313. * * Ramsey, John F. ''Ninth Air Force in the ETO, 16 October 1943 to 16 April 1944 (USAAF Historical Study, No. 32)''. Air Force Historical Research Agency, 1945. * Rogers, Edith. ''The AAF in the Middle East: A Study of the Origins of the Ninth Air Force (USAAF Historical Study, No. 108)''. Air Force Historical Research Agency, 1945. * Rust, Kenn C. ''Ninth Air Force Story...in World War II''. Temple City, California: Historical Aviation Album, 1982. . *External links
Official public website
Most current Factsheet (Apr 2013)
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20060322220454/http://www.psln.com/pete/pow_bomb_groups.htm PSLN.com], World War II Bomb Groups - European Theater of Operations (ETO)
Air Power in the Battle of the Bulge: A Theater Campaign Perspective
(World War II unit history published by Stars & Stripes) {{Authority control Air Forces of the United States Army Air Forces, 09 Cold War military history of the United States Military units and formations established in 1941 Military units and formations in South Carolina European theatre of World War II