Nubuo Fujita on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
(1911 – 30 September 1997) was a Japanese
 Fujita was on board during the
Fujita was on board during the
 Fujita himself suggested the idea of a submarine-based seaplane to bomb military targets, including ships at sea, and attacks on the U.S. mainland, especially the strategic
Fujita himself suggested the idea of a submarine-based seaplane to bomb military targets, including ships at sea, and attacks on the U.S. mainland, especially the strategic
Samurai in the Oregon Sky
Produced by Ilana Sol {{DEFAULTSORT:Fujita, Nobuo Japanese military personnel of World War II Japanese naval aviators 1911 births Attack on Pearl Harbor 1997 deaths Oregon Coast Curry County, Oregon Japanese World War II pilots Imperial Japanese Navy officers
naval aviator
Naval aviation is the application of military air power by navies, whether from warships that embark aircraft, or land bases.
Naval aviation is typically projected to a position nearer the target by way of an aircraft carrier. Carrier-based a ...
and warrant flying officer of the Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrender ...
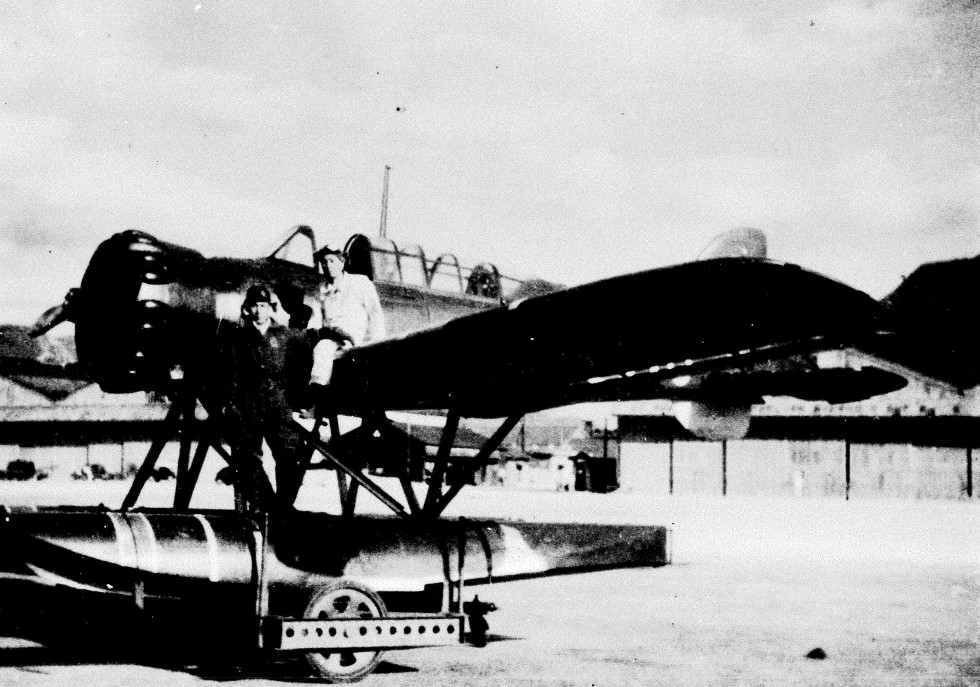
who flew a floatplane
A floatplane is a type of seaplane with one or more slender floats mounted under the fuselage to provide buoyancy. By contrast, a flying boat uses its fuselage for buoyancy. Either type of seaplane may also have landing gear suitable for land, ...
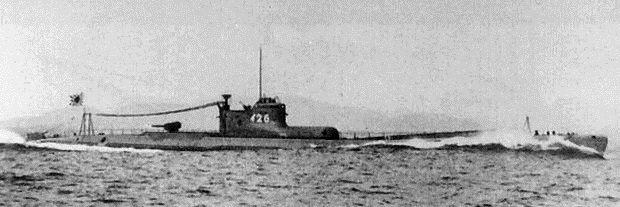
from the long-range submarine aircraft carrier
A submarine aircraft carrier is a submarine equipped with aircraft for observation or attack missions. These submarines saw their most extensive use during World War II, although their operational significance remained rather small. The most fam ...
and conducted the Lookout Air Raids
The Lookout Air Raids were minor but historic Japanese air raids that occurred in the mountains of Oregon, several miles outside Brookings during World War II.
On September 9, 1942, a Japanese Yokosuka E14Y ''Glen'' floatplane, launched fr ...
in southern Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
on September 9, 1942, making him the only Axis
An axis (plural ''axes'') is an imaginary line around which an object rotates or is symmetrical. Axis may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis
*Axis (mathematics), a designator for a Cartesian-coordinate ...
pilot during World War II to aerial bomb the contiguous United States
The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii ...
. Using incendiary bombs
Incendiary weapons, incendiary devices, incendiary munitions, or incendiary bombs are weapons designed to start fires or destroy sensitive equipment using fire (and sometimes used as anti-personnel weaponry), that use materials such as napalm, th ...
, his mission was to start massive forest fires in the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
near the city of Brookings, Oregon
Brookings is a city in Curry County, Oregon, United States. It was named after John E. Brookings, president of the Brookings Lumber and Box Company, which founded the city in 1908. As of the 2020 census, the population was 6,744.
History
F ...
with the objective of drawing the U.S. military's resources away from the Pacific Theater
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
. The strategy was also later used in the Japanese fire balloon
An incendiary balloon (or balloon bomb) is a balloon inflated with a lighter-than-air gas such as hot air, hydrogen, or helium, that has a bomb, incendiary device, or Molotov cocktail attached. The balloon is carried by the prevailing winds to ...
campaign.
Early life and military career
Nobuo Fujita joined theImperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrender ...
in 1932 and became a pilot in 1933. Fujita also had a younger brother who was killed in the war.
Pearl Harbor and U.S. West Coast
 Fujita was on board during the
Fujita was on board during the attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii, j ...
, where the ''I-25'' and three other submarines patrolled a line north of Oahu
Oahu () (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Oʻahu'' ()), also known as "The Gathering place#Island of Oʻahu as The Gathering Place, Gathering Place", is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million people—over t ...
. Fujita's plane, a Yokosuka E14Y
The Yokosuka E14Y ( Allied reporting name Glen) was an Imperial Japanese Navy reconnaissance seaplane transported aboard and launched from Japanese submarine aircraft carriers such as the during World War II. The Japanese Navy designation was " ...
"Glen" seaplane, did not function properly, and he was unable to participate in the reconnaissance mission planned before the attack.
After the attack on Pearl Harbor, ''I-25'' patrolled along the West Coast of the United States
The West Coast of the United States, also known as the Pacific Coast, Pacific states, and the western seaboard, is the coastline along which the Western United States meets the North Pacific Ocean. The term typically refers to the contiguous U.S ...
with eight other submarines. They attacked U.S. shipping before returning to their base in Kwajalein Atoll
Kwajalein Atoll (; Marshallese: ) is part of the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI). The southernmost and largest island in the atoll is named Kwajalein Island, which its majority English-speaking residents (about 1,000 mostly U.S. civilia ...
in the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Internati ...
. They arrived there on January 11, 1942 to be refuelled and refurbished.
South Pacific
''I-25''s next mission was to reconnoiter theAustralia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
n harbours of Sydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountain ...
, Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a met ...
and Hobart
Hobart ( ; Nuennonne/Palawa kani: ''nipaluna'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian island state of Tasmania. Home to almost half of all Tasmanians, it is the least-populated Australian state capital city, and second-small ...
, followed by the New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
harbours of Wellington
Wellington ( mi, Te Whanganui-a-Tara or ) is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the second-largest city in New Zealand by me ...
and Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The List of New Zealand urban areas by population, most populous urban area in the country and the List of cities in Oceania by po ...
. On 17 February 1942, Nobuo Fujita took off in the "Glen" for a reconnaissance flight over Sydney Harbour
Port Jackson, consisting of the waters of Sydney Harbour, Middle Harbour, North Harbour and the Lane Cove and Parramatta Rivers, is the ria or natural harbour of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. The harbour is an inlet of the Tasman Sea (p ...
to examine the city's airbase. By 07:30, he had returned to ''I-25'', disassembled the "Glen" and stowed it in the water-tight hangar.
The next mission was a similar flight over Melbourne, Australia
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a metropol ...
. Fujita took off from Cape Wickham on King Island King Island, Kings Island or King's Island may refer to:
Australia
* King Island (Queensland)
* King Island, at Wellington Point, Queensland
* King Island (Tasmania)
** King Island Council, the local government area that contains the Tasmanian is ...
at the western end of Bass Strait
Bass Strait () is a strait separating the island state of Tasmania from the Australian mainland (more specifically the coast of Victoria, with the exception of the land border across Boundary Islet). The strait provides the most direct waterwa ...
, about halfway between Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
and Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
. The floatplane was launched on 26 February for its flight to Melbourne over Port Phillip Bay
Port Phillip (Kulin: ''Narm-Narm'') or Port Phillip Bay is a horsehead-shaped enclosed bay on the central coast of southern Victoria, Australia. The bay opens into the Bass Strait via a short, narrow channel known as The Rip, and is completel ...
.
Fujita's next reconnaissance flight in Australia was over Hobart on 1 March. ''I-25'' then headed for New Zealand, where Fujita flew a reconnaissance flight over Wellington on 8 March. He flew over Auckland on 13 March, followed by Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
on 17 March. The submarine returned to its base at Kwajalein on 31 March.
Pacific Northwest
On 28 May, Fujita performed a reconnaissance ofKodiak, Alaska
Kodiak (Alutiiq: , russian: Кадьяк), formerly Paul's Harbor, is the main city and one of seven communities on Kodiak Island in Kodiak Island Borough, Alaska. All commercial transportation between the island's communities and the outside wo ...
, in preparation for the invasion of the Aleutian Islands. On 21 June, ''I-25'' shelled the U.S. base of Fort Stevens, near Astoria, Oregon
Astoria is a port city and the seat of Clatsop County, Oregon, United States. Founded in 1811, Astoria is the oldest city in the state and was the first permanent American settlement west of the Rocky Mountains. The county is the northwest corne ...
. Fujita was on the deck of ''I-25'' during the attack.
Bombing Oregon
 Fujita himself suggested the idea of a submarine-based seaplane to bomb military targets, including ships at sea, and attacks on the U.S. mainland, especially the strategic
Fujita himself suggested the idea of a submarine-based seaplane to bomb military targets, including ships at sea, and attacks on the U.S. mainland, especially the strategic Panama Canal
The Panama Canal ( es, Canal de Panamá, link=no) is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a conduit ...
. The idea was approved, and the mission was given to . Submarine aircraft carriers such as the giant ''I-400''-class submarines would be developed specifically to bomb the Panama Canal.
At 06:00 on 9 September, ''I-25'' surfaced west of the Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
/California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
border where she launched the ''Glen'', flown by Fujita and Petty Officer
A petty officer (PO) is a non-commissioned officer in many navies and is given the NATO rank denotation OR-5 or OR-6. In many nations, they are typically equal to a sergeant in comparison to other military branches. Often they may be superior ...
Okuda Shoji, with a load of two incendiary bombs
Incendiary weapons, incendiary devices, incendiary munitions, or incendiary bombs are weapons designed to start fires or destroy sensitive equipment using fire (and sometimes used as anti-personnel weaponry), that use materials such as napalm, th ...
. Fujita dropped two bombs, one on Wheeler Ridge on Mount Emily
Mount Emily (Tolowa: en-may ) is a mountain in the Klamath Mountains of southwestern Oregon in the United States. It is located in southern Curry County in the extreme southwest corner of the state, near Brookings, approximately from the Pacifi ...
in Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
. The location of the other bomb is unknown. The Wheeler Ridge bomb started a small fire due east of Brookings Brookings may refer to:
Organizations
* Brookings Institution, a nonprofit, nonpartisan public policy organization based in Washington, D.C.
Places
* Brookings, Oregon, USA
* Brookings, South Dakota, USA
* Brookings County, South Dakota, USA ...
, which U.S. Forest Service
The United States Forest Service (USFS) is an agency of the U.S. Department of Agriculture that administers the nation's 154 national forests and 20 national grasslands. The Forest Service manages of land. Major divisions of the agency in ...
employees were able to extinguish. Rain the night before had made the forest very damp, and the bombs were rendered essentially ineffective. Fujita's plane had been spotted by two men, Howard Gardner and Bob Larson, at the Mount Emily fire lookout tower
A fire lookout tower, fire tower or lookout tower, provides housing and protection for a person known as a "fire lookout" whose duty it is to search for wildfires in the wilderness. It is a small building, usually on the summit of a mountain or ...
in the Siskiyou National Forest Siskiyou may refer to:
*Siskiyou Mountains, a mountain range in northern California and southern Oregon
*Siskiyou National Forest, in Oregon and California
*Siskiyou County, California
*Siskiyou Trail, an old Native American and pioneer trail connec ...
. Two other lookouts (the Chetco Point Lookout and the Long Ridge Lookout) reported the plane, but could not see it due to heavy fog. The plane was seen and heard by many people, especially when Fujita flew over Brookings in both directions. At about noon that day, Howard Gardner at the Mount Emily Lookout reported seeing smoke. The four U.S. Forest Service employees discovered that the fire was caused by a Japanese bomb. Approximately of fragments, including the nose of the bomb, were turned over to the United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cla ...
.
After the bombing, ''I-25'' came under attack by a USAAF
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
aircraft on patrol, forcing the submarine to dive and hide on the ocean floor off Port Orford
Port Orford (Tolowa: tr’ee-ghi~’- ’an’ ) is a city in Curry County on the southern coast of Oregon, United States. The population was 1,133 at the 2010 census.
The city takes its name from George Vancouver's original name for nearby Ca ...
. The American attacks caused only minor damage, and Fujita flew a second bombing sortie three weeks later on 29 September. Fujita used the Cape Blanco Light
Cape Blanco Light is a lighthouse located on Cape Blanco, Oregon, United States in Cape Blanco State Park.
Construction of the light
In a deed recorded in 1867, John D. and Mary West sold the United States a tract of land. The Light-House ...
as a beacon. After 90 minutes flying east, he dropped his bombs and reported seeing flames, but the bombing remained unnoticed in the U.S.
The submarine torpedoed and sank the SS ''Camden'' and SS ''Larry Doheny'' and then sailed for home. On its way to Japan, ''I-25'' sank the Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
submarine '' L-16'', which was in transit between Dutch Harbor, Alaska
Dutch Harbor is a harbor on Amaknak Island in Unalaska, Alaska. It was the location of the Battle of Dutch Harbor in June 1942, and was one of the few sites in the United States to be subjected to aerial bombardment by a foreign power during Worl ...
, and San Francisco, California
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17th ...
, mistaking it for an American submarine (Japan and the USSR were not at war at the time).
The two attacks on Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
in September 1942 were the only enemy aircraft bombings on the contiguous United States
The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii ...
and were the second time the continental United States was attacked by such aircraft during World War II, following the bombing of Dutch Harbor in Unalaska, Alaska
Unalaska ( ale, Iluulux̂; russian: Уналашка) is the chief center of population in the Aleutian Islands. The city is in the Aleutians West Census Area, a regional component of the Unorganized Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. Unalaska ...
three months earlier.
Later life
Fujita continued as an Imperial Japanese Navy pilot, mainly in reconnaissance duties, until 1944, when he was transferred to the training of ''kamikaze
, officially , were a part of the Japanese Special Attack Units of military aviators who flew suicide attacks for the Empire of Japan against Allied naval vessels in the closing stages of the Pacific campaign of World War II, intending to d ...
'' pilots. After the war he opened a hardware store in Ibaraki Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region of Honshu. Ibaraki Prefecture has a population of 2,871,199 (1 June 2019) and has a geographic area of . Ibaraki Prefecture borders Fukushima Prefecture to the north, ...
, and later worked at a company making wire.
Fujita was invited to Brookings in 1962, after the Japanese government
The Government of Japan consists of legislative, executive and judiciary branches and is based on popular sovereignty. The Government runs under the framework established by the Constitution of Japan, adopted in 1947. It is a unitary state, c ...
was assured he would not be tried as a war criminal. He gave the City of Brookings his family's 400-year-old katana
A is a Japanese sword characterized by a curved, single-edged blade with a circular or squared guard and long grip to accommodate two hands. Developed later than the ''tachi'', it was used by samurai in feudal Japan and worn with the edge fa ...
in friendship. Ashamed of his actions during the war, Fujita had intended to use the sword to commit seppuku
, sometimes referred to as hara-kiri (, , a native Japanese kun reading), is a form of Japanese ritual suicide by disembowelment. It was originally reserved for samurai in their code of honour but was also practised by other Japanese people ...
if he were given a hostile reception. However, the town treated him with respect and affection, although his visit still raised some controversy.
Impressed by his welcome in the United States, during his visit, he promised to invite Brookings students to Japan. Despite the bankruptcy of his company, Fujita made good on his promise by co-sponsoring the visit of three female students from Brookings-Harbor High School
Brookings-Harbor High School (BHHS) is a public high school located in Brookings, Oregon, United States.
Attendance
Brookings-Harbor High School serves the city of Brookings and the surrounding area, including the community of Harbor. The school ...
to Japan in 1985. During the visit, Fujita received a dedicatory letter from an aide of President Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
"with admiration for your kindness and generosity."
Fujita returned to Brookings in 1990, 1992, and 1995. In 1992, he planted a tree at the bomb site as a gesture of peace. In 1995, he moved the samurai sword from the Brookings City Hall into the new library's display case. Fujita helped to gather money to build the library.
He was made an honorary citizen of Brookings several days before his death at a hospital in Tsuchiura
is a Cities of Japan, city located in Ibaraki Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 138,033 in 60,069 households and a population density of 1123 persons per km2. The percentage of the population aged over 65 was 29.7%. Th ...
, Ibaraki Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region of Honshu. Ibaraki Prefecture has a population of 2,871,199 (1 June 2019) and has a geographic area of . Ibaraki Prefecture borders Fukushima Prefecture to the north, ...
, on September 30, 1997, at the age of 85. In October 1998, his daughter, Yoriko Asakura, buried some of Fujita's ashes at the bomb site.
See also
*Attacks on North America during World War II
The American Theater was a theater of operations during World War II including all continental American territory, and extending into the ocean.
Owing to North and South America's geographical separation from the central theaters of ...
References
Further reading
*External links
Samurai in the Oregon Sky
Produced by Ilana Sol {{DEFAULTSORT:Fujita, Nobuo Japanese military personnel of World War II Japanese naval aviators 1911 births Attack on Pearl Harbor 1997 deaths Oregon Coast Curry County, Oregon Japanese World War II pilots Imperial Japanese Navy officers